Sagentia Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Sagentia Group Bundle
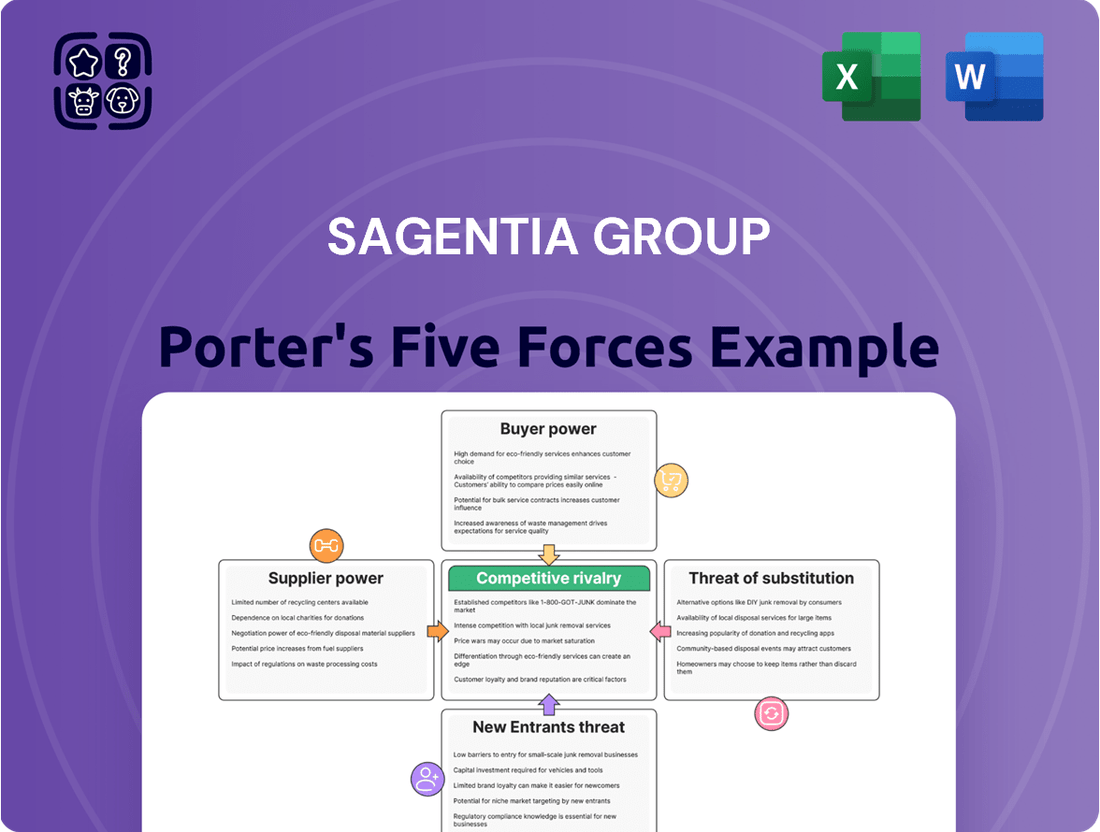
The Sagentia Group operates in a dynamic market shaped by several key competitive forces. Understanding the intensity of rivalry, the power of buyers and suppliers, and the threats of substitutes and new entrants is crucial for strategic planning.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Sagentia Group’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Sagentia Innovation's dependence on highly specialized talent, such as advanced engineers and unique technology providers, significantly impacts supplier power. The scarcity of top-tier expertise in niche scientific and design fields empowers these individuals and specialized recruitment firms. For instance, in 2024, the demand for AI and machine learning engineers continued to outstrip supply, with average salaries for senior roles in these fields reaching well over $150,000 annually in key tech hubs, reflecting this scarcity.
Furthermore, suppliers offering cutting-edge research and development equipment or proprietary simulation software often possess a unique value proposition. When Sagentia lacks readily available substitutes for these specialized tools or technologies, these suppliers gain considerable leverage. The high cost and long development cycles for specialized R&D hardware, often costing millions of dollars, mean that switching suppliers is not a trivial undertaking, thus reinforcing their bargaining power.
Switching costs for Sagentia can be substantial, particularly with suppliers of specialized talent and integrated software. For instance, the cost and time required to retrain staff on a new R&D platform, or to onboard and integrate new expert consultants, can be significant. This reliance on existing, specialized suppliers grants them a measure of bargaining power.
While the tech landscape boasts numerous general providers, Sagentia Group faces a distinct challenge with the specific, high-tech inputs crucial for its advanced innovation projects. The availability of substitutes for these specialized components, such as unique laboratory equipment or patented research tools, is often limited to a select few suppliers.
This scarcity significantly amplifies the bargaining power of these niche suppliers. For instance, if a critical piece of custom-engineered testing apparatus is only manufactured by one or two firms globally, Sagentia has little leverage in price negotiations. In 2024, the semiconductor industry, a key area for innovation, continued to experience supply chain constraints for specialized fabrication equipment, further concentrating power among a handful of providers.
Threat of Forward Integration
The threat of forward integration from Sagentia Group's suppliers is generally considered low. Typically, Sagentia's suppliers are highly specialized individuals or small technology vendors. These entities often lack the substantial capital and the broad strategic vision required to establish a comprehensive consultancy business that mirrors Sagentia's service offerings.
However, there's a nuanced consideration with larger, well-resourced entities in adjacent sectors. Major software providers or established data analytics firms might possess the capacity to extend their services into more integrated research and development partnerships. While this is less common for the highly specific scientific and engineering challenges Sagentia tackles, these larger players could potentially offer more bundled R&D solutions.
- Low Likelihood for Niche Suppliers: Individual experts or small tech firms supplying Sagentia usually lack the financial muscle and business model complexity to integrate forward.
- Potential for Larger Tech Firms: Companies like major cloud service providers or large analytics software vendors (e.g., IBM, Accenture) could theoretically move into offering more end-to-end R&D support.
- Sagentia's Specialization as a Barrier: Sagentia's deep expertise in niche scientific and engineering domains creates a significant barrier to entry for potential integrators.
- Limited Historical Precedent: There is limited evidence of suppliers successfully integrating forward into Sagentia's core consulting market in recent years, indicating the difficulty of this strategic move.
Importance of Supplier Inputs to Sagentia's Business
The bargaining power of suppliers is a significant factor for Sagentia Innovation, particularly concerning specialized talent. In 2024, the demand for highly skilled engineers and scientists remained robust across the tech and innovation sectors, with average salaries for senior R&D roles often exceeding $150,000 annually. This scarcity of top-tier expertise grants individuals and specialized recruitment firms considerable leverage.
Sagentia's reliance on advanced technology and proprietary data further amplifies supplier power. For instance, access to cutting-edge simulation software or unique market intelligence databases can be controlled by a limited number of vendors. In 2024, the cost of specialized AI development tools and high-quality datasets for machine learning training could range from tens of thousands to hundreds of thousands of dollars per license or subscription, reflecting their critical nature and limited supply.
- Specialized Talent: Sagentia needs access to niche engineering and scientific expertise, making skilled individuals and recruitment agencies powerful.
- Advanced Technology: Dependence on proprietary software and hardware means vendors of these critical tools hold significant influence.
- Proprietary Data: Access to unique datasets for market analysis and R&D is crucial, and providers of such data have considerable bargaining power.
- Industry Dependence: Sagentia's innovation across diverse sectors means its need for specialized inputs is constant, reinforcing supplier leverage.
The bargaining power of Sagentia Group's suppliers is elevated due to the specialized nature of its inputs. For instance, in 2024, the demand for AI and machine learning talent continued to outpace supply, with average salaries for senior roles often exceeding $150,000 annually in key tech hubs, indicating strong leverage for these suppliers. Similarly, unique R&D equipment or proprietary software, often costing millions, presents limited substitution options, further empowering their providers.
| Supplier Type | Key Characteristics | Impact on Bargaining Power | Example Data (2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Specialized Talent | Niche engineering & scientific expertise | High | Senior AI Engineer Salary: $150,000+ |
| Advanced Technology | Proprietary R&D hardware/software | High | Specialized AI Development Tools Cost: $10,000s - $100,000s |
| Proprietary Data | Unique market intelligence, datasets | High | High-Quality ML Training Data Cost: Variable, often substantial |
What is included in the product
This analysis of Sagentia Group's competitive environment dissects the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, providing strategic insights into market dynamics.
Effortlessly visualize the intensity of each competitive force with a dynamic, interactive dashboard, allowing for immediate identification of strategic threats and opportunities.
Customers Bargaining Power
Sagentia Innovation's diverse client base across medical, consumer, industrial, and food & beverage sectors generally limits the bargaining power of any single customer. This fragmentation means no one client likely represents a dominant portion of their revenue, diffusing individual leverage.
While Sagentia works with large enterprise clients, and these can command some leverage due to the scale of projects, the overall lack of extreme customer concentration mitigates significant individual customer bargaining power. For instance, if Sagentia's top 10 clients in 2024 represented less than 30% of their total revenue, this would further underscore their limited individual bargaining power.
Clients working with Sagentia on intricate innovation initiatives face substantial costs if they decide to switch. These projects are deeply embedded within a client's research and development workflows, often involving the sharing of sensitive, proprietary data and requiring a long-term strategic partnership.
Ditching a current project or changing consultants midway through can lead to considerable setbacks, the forfeiture of valuable project-specific knowledge, and unexpected financial burdens for the client. For example, a client halting a complex R&D project with Sagentia might lose months of development progress and face significant costs to onboard a new firm.
This intricate integration and the potential for knowledge loss significantly reduce a client's inclination to explore alternative service providers. The investment in time, resources, and the unique understanding Sagentia builds makes switching a less appealing option, thereby strengthening Sagentia's bargaining position with its customers.
Many of Sagentia's clients, particularly large enterprises, have their own R&D divisions and innovation power. This means they could potentially develop their services in-house, a concept known as backward integration. For example, a large pharmaceutical company might have a robust internal drug discovery team, potentially reducing its need for external R&D support.
However, clients typically engage consultancies like Sagentia to tap into highly specialized knowledge, speed up new product development, or solve intricate problems that their internal teams struggle with. This reliance on external expertise often mitigates the threat of complete backward integration, as clients value the unique skills and perspectives brought by outside firms.
The growing integration of artificial intelligence (AI) within client organizations could indeed shift the landscape. By leveraging AI for tasks previously outsourced to consultancies, clients might decrease their dependence on external R&D services for certain projects, a trend observed across various industries as AI adoption accelerates.
Customer Price Sensitivity
Customer price sensitivity for Sagentia Group’s specialized innovation and R&D services is often tempered by the critical nature of their clients' needs. While cost-effectiveness is always a consideration, businesses engaging Sagentia are typically seeking solutions to complex technical challenges or aiming for rapid market entry, where the perceived value of successful innovation can significantly exceed the consultancy fees. For instance, in the competitive medtech sector, where Sagentia has a strong presence, the cost of a development delay due to suboptimal R&D can be far greater than the investment in expert consultancy.
Clients prioritize factors beyond mere price, such as the quality of the innovative outcome, the efficiency of the development process, and Sagentia’s capability to navigate intricate technical hurdles. Sagentia's approach, which emphasizes comprehensive lifecycle support from concept to market, directly addresses these priorities. This holistic support model aims to de-risk the innovation process, a factor that often commands a premium over transactional, price-focused engagements. For example, a successful product launch facilitated by Sagentia could generate millions in revenue, making the initial R&D investment a relatively minor component of the overall return.
- Innovation Value vs. Cost: Clients often see the value derived from breakthrough innovations as substantially outweighing the consultancy fees paid to specialized firms like Sagentia.
- Beyond Price: Key client drivers include the quality of innovation, speed to market, and the ability to solve complex technical problems, not just the lowest price.
- Lifecycle Support Premium: Sagentia's comprehensive support across the product lifecycle justifies higher fees by providing integrated solutions rather than fragmented services.
- Risk Mitigation: The ability of expert R&D services to reduce development risks and accelerate time-to-market is a significant factor in customer willingness to pay.
Product/Service Differentiation of Sagentia
Sagentia Innovation’s highly integrated approach to innovation, spanning concept development through commercialization, sets it apart. This comprehensive service offering across diverse, complex industries like medical technology and consumer electronics creates a unique value proposition. For instance, Sagentia's work in the medical device sector often involves intricate regulatory pathways and advanced engineering, areas where specialized knowledge is paramount.
The company's ability to provide end-to-end solutions means clients are less likely to piece together services from multiple, less specialized providers. This reduces the availability of direct substitutes, thereby diminishing the bargaining power of customers. In 2024, companies increasingly seek partners who can navigate the entire innovation lifecycle, a demand Sagentia is well-positioned to meet.
- Integrated Service Offering: Sagentia provides a full spectrum of innovation services, from initial strategy and R&D to product design, engineering, and commercialization support.
- Sector Specialization: The firm possesses deep expertise in complex and regulated sectors, including medical technology, industrial, and consumer products.
- Reduced Substitutability: This specialized, end-to-end capability limits the number of direct competitors capable of offering comparable solutions.
- Customer Dependence: Clients often rely on Sagentia for critical aspects of their product development, strengthening Sagentia's position and reducing customer leverage.
Sagentia Group's customers exhibit limited bargaining power due to the specialized and integrated nature of its innovation and R&D services. The high switching costs, stemming from embedded project knowledge and proprietary data, make clients hesitant to change providers. Furthermore, clients prioritize the value and expertise Sagentia brings, rather than solely focusing on price, especially for critical product development needs.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power | Supporting Data/Context (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | Low | Sagentia's diverse client base across multiple sectors limits the revenue contribution of any single customer, diffusing individual leverage. |
| Switching Costs | High | Projects are deeply integrated into client R&D, involving proprietary data and long-term partnerships, making switching costly and disruptive. |
| Price Sensitivity | Moderate | Clients prioritize innovation quality and speed to market over cost, as delays can be more expensive than consultancy fees. |
| Availability of Substitutes | Low | Sagentia's end-to-end innovation support across complex sectors limits the availability of direct, equally capable competitors. |
What You See Is What You Get
Sagentia Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
The document you see is your deliverable. It’s ready for immediate use—no customization or setup required. This comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis for the Sagentia Group details the intensity of competitive rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the threat of substitute products. Each force is meticulously examined to provide actionable insights into Sagentia's strategic positioning within its industry. You're previewing the final version—precisely the same document that will be available to you instantly after buying.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The competitive landscape for Sagentia Group, specifically within its innovation and R&D consulting arm, is quite varied. It's not a market dominated by just a few players; rather, it's fragmented. This means there are many different types of companies vying for business.
On one end, you have the really big, global consulting firms like Deloitte and Accenture. These giants have vast resources and broad service offerings. Then, you have specialized firms that focus on very specific areas of science, technology, or product development, much like Sagentia itself. These niche players often possess deep expertise in particular fields.
Beyond these, there are also numerous smaller, independent consultants or boutique firms. These can be very agile and offer highly personalized services. Sagentia Innovation's direct competitors are those firms that mirror its own focus on science, product, and technology innovation consulting, operating within similar industry sectors. This creates a dynamic and often intense competitive environment where differentiation through expertise and client relationships is key.
The innovation services market is booming, with projections indicating it will hit roughly $1.5 trillion by 2033, growing at a healthy 12% annual rate starting in 2025. This expansion provides a fertile ground for companies.
Furthermore, the engineering R&D services outsourcing sector is set to surpass $2.5 trillion by 2037, boasting an impressive CAGR of over 17.3% between 2025 and 2037. Such dynamic market expansion typically eases competitive pressures.
When markets are growing this rapidly, there's usually enough demand to go around, meaning companies aren't constantly fighting over a shrinking pie. This creates more room for new entrants and existing players to thrive.
Sagentia Innovation stands out by offering specialized technical expertise across the entire innovation journey, from concept to commercialization, particularly in demanding fields such as medical devices and agricultural technology. This deep specialization means clients aren't just buying a service; they're investing in a partner with niche knowledge critical to their product's success.
The cost and effort involved in switching to a competitor are substantial. Clients often integrate Sagentia's proprietary processes and extensive project-specific knowledge into their own operations, creating significant embedded value. This knowledge transfer and integration make it complex and time-consuming to onboard a new innovation partner, effectively raising switching costs and reinforcing client loyalty.
Exit Barriers
Exit barriers for companies like Sagentia Group within the innovation consulting sector are generally considered moderate to high. This is largely due to the highly specialized knowledge and expertise that consultants cultivate, often in niche areas of research and development. These skills can be difficult to redeploy in different industries, making a complete exit a complex undertaking. For instance, a consultant deeply embedded in advanced materials science for a specific client may find their skillset less applicable elsewhere, increasing the cost of exiting the market.
Furthermore, the nature of innovation consulting often involves long-term, intricate projects with significant client commitments. Unwinding these ongoing research and development initiatives can be both time-consuming and financially burdensome, acting as a significant deterrent to a swift departure. This can mean that even during economic downturns, competitors might persist in the market, contributing to sustained competitive rivalry as they try to recoup investments or fulfill existing contracts.
- Specialized Talent: High degree of specific technical and scientific skills required, limiting transferability to other sectors.
- Long-Term Projects: Commitment to ongoing R&D contracts makes immediate cessation of operations costly and complex.
- Client Relationships: Deeply entrenched relationships can make it difficult to disengage without significant reputational or financial repercussions.
- Asset Specificity: Investments in specialized equipment or intellectual property for specific client projects may have limited resale value.
Fixed Costs and Capacity
Innovation consultancies like Sagentia Group often face substantial fixed costs. These include the ongoing expense of employing highly specialized talent, maintaining cutting-edge research and development facilities, and investing in sophisticated software and equipment necessary for their work. For instance, in 2024, the average salary for a senior innovation consultant in the UK could easily exceed £90,000, representing a significant fixed personnel cost.
These high fixed costs create pressure for firms to operate at or near full capacity. When demand softens, there's a strong incentive to secure any available revenue to cover these persistent expenses. This can lead to intensified price competition as companies vie to keep their resources utilized, potentially driving down profit margins across the industry.
- High Fixed Costs: Retaining top-tier talent and maintaining advanced R&D infrastructure are significant ongoing expenses.
- Capacity Utilization Pressure: The need to cover fixed costs encourages firms to maximize their operational capacity.
- Price Competition Risk: During downturns, firms may lower prices to fill capacity, increasing rivalry.
- Impact on Profitability: Intense price competition can erode profit margins, especially for firms with high fixed cost structures.
The competitive rivalry within Sagentia Group's innovation consulting niche is characterized by a diverse mix of players, from global behemoths to specialized boutiques. This fragmentation means that while markets are expanding significantly—with the innovation services market projected to reach $1.5 trillion by 2033 and engineering R&D outsourcing nearing $2.5 trillion by 2037—competition remains robust.
Sagentia's differentiation lies in its deep, specialized technical expertise across the innovation lifecycle, particularly in high-stakes sectors. This focus, coupled with high switching costs for clients due to embedded knowledge and integrated processes, helps mitigate intense rivalry. However, the sector's reliance on highly skilled talent and long-term projects contributes to moderate to high exit barriers.
The market's growth provides ample opportunity, yet high fixed costs associated with specialized talent and R&D infrastructure create pressure for capacity utilization. This can trigger price competition, especially during economic slowdowns, as firms strive to cover ongoing expenses, impacting overall profitability.
| Competitor Type | Key Characteristics | Sagentia's Position |
|---|---|---|
| Global Consulting Firms (e.g., Deloitte, Accenture) | Vast resources, broad service offerings | Differentiated through deep specialization |
| Specialized Niche Firms | Deep expertise in specific tech/science areas | Direct competitors, mirroring focus |
| Boutique/Independent Consultants | Agile, personalized services | Smaller scale, but can be highly competitive |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The most significant substitute for Sagentia Innovation's services is a client's capacity to manage innovation entirely in-house. Many large corporations possess robust R&D departments, and the growing accessibility of AI tools and advanced data analytics platforms allows them to derive insights and achieve efficiencies internally.
For example, in 2024, approximately 75% of Fortune 500 companies reported having dedicated innovation labs or R&D centers, indicating a strong internal capability to pursue new product development and process improvements without external assistance.
This internal development trend is further amplified by the democratization of technology, where readily available cloud-based AI services and open-source data science tools lower the barrier to entry for complex analytical tasks, directly challenging the need for specialized external innovation consultancies.
General management consulting firms, such as McKinsey & Company, Deloitte, and PwC, present a notable threat of substitutes for Sagentia Group, particularly concerning strategic concept development and market entry advice. These large firms often possess broader capabilities in areas like operational efficiency and digital transformation, which can overlap with the strategic elements of Sagentia's science and technology innovation services. By 2024, these major consulting players have significantly ramped up their investments in artificial intelligence, allowing them to offer more data-driven insights and sophisticated strategic planning tools, potentially reducing the perceived need for specialized innovation consulting in certain strategic contexts.
Clients may bypass Sagentia's services by acquiring innovative startups or licensing their technologies. This provides a quicker path to market and mitigates research and development risks, directly substituting Sagentia's product development and commercialization support. For instance, in 2024, venture capital funding for technology startups reached an estimated $200 billion globally, indicating a robust market for acquiring novel solutions.
Price-Performance Trade-off of Substitutes
The threat of substitutes for Sagentia Group's services is influenced by how customers perceive the price-performance trade-off. While alternatives like in-house R&D or off-the-shelf solutions might seem budget-friendly initially, they often fall short in delivering the specialized expertise and integrated approach that Sagentia provides.
Sagentia’s value proposition, centered on deep technical knowledge and comprehensive end-to-end support, frequently justifies its pricing compared to less specialized options. For instance, companies seeking cutting-edge innovation might find that the long-term benefits of Sagentia's tailored solutions outweigh the perceived cost savings of simpler alternatives.
- Perceived Value: Customers weigh the cost of Sagentia's services against the unique benefits of specialized expertise and integrated solutions.
- In-house Limitations: Internal development may lack the breadth of technical knowledge and speed that Sagentia offers, leading to higher long-term costs.
- Licensing Drawbacks: Off-the-shelf solutions often require significant customization and may not offer the same level of strategic advantage.
- Sagentia's Justification: The demonstrable return on investment from Sagentia's deep technical insight and project management often validates its premium pricing.
Emergence of AI-Powered Innovation Platforms
The growing sophistication of AI-powered innovation platforms presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional innovation consultancy services. These platforms can automate crucial stages of the innovation lifecycle, from initial market analysis to idea generation and even early-stage product design. For instance, companies like IdeaScale and Spigit are increasingly integrating AI capabilities to streamline idea management and foster internal innovation, potentially diminishing the reliance on external expertise for certain projects. This trend accelerated in 2024, with a notable increase in AI adoption across various sectors for R&D and product development.
These AI tools offer a more cost-effective and potentially faster alternative for tasks that previously required significant human input and specialized consultancy. By automating data analysis and pattern recognition, AI can accelerate the identification of market opportunities and the generation of novel concepts. This efficiency directly impacts the value proposition of human-led innovation consulting, creating a potent substitute.
The threat is amplified by the decreasing cost of AI development and deployment, making these platforms accessible to a broader range of businesses. As AI capabilities continue to advance, their ability to replicate and even surpass human performance in specific innovation-related tasks will only grow. For example, generative AI models are showing remarkable aptitude in creative content generation and problem-solving, directly challenging areas where consultancies traditionally excelled.
- AI Platforms Automate Key Innovation Stages: Tools now handle market analysis, idea generation, and initial design.
- Cost and Speed Advantages: AI offers a more economical and quicker alternative to human consultancy for certain tasks.
- Increasing AI Sophistication: Advanced AI models are demonstrating capabilities that rival human expertise in creative and analytical processes.
- Market Adoption in 2024: Significant uptake of AI in R&D and product development underscored this growing threat.
The threat of substitutes for Sagentia Group’s innovation services is significant, primarily stemming from clients’ ability to develop capabilities in-house, leveraging advancements in AI and data analytics. Furthermore, the acquisition of startups or licensing of their technologies offers a faster route to market, directly substituting Sagentia’s development support.
Generalist consulting firms are also a growing substitute, especially in strategic concept development, as they increasingly integrate AI into their offerings, making them more competitive in areas that overlap with Sagentia's services.
| Substitute Category | Key Characteristics | Impact on Sagentia |
|---|---|---|
| In-house R&D & AI Tools | Cost-effective for routine tasks, broad accessibility of AI platforms. | Reduces demand for specialized external innovation support. |
| Startup Acquisition/Licensing | Rapid market entry, reduced R&D risk. | Bypasses Sagentia’s product development and commercialization services. |
| General Management Consultancies | Broader capabilities, enhanced AI integration for strategic planning. | Competes on strategic elements and digital transformation, potentially overshadowing specialized innovation needs. |
Entrants Threaten
Establishing a presence as a respected innovation consultancy, akin to Sagentia Group, necessitates significant financial outlay. This includes investing in state-of-the-art R&D labs, sophisticated testing apparatus, and specialized software platforms. For instance, setting up a functional innovation lab can easily cost hundreds of thousands, if not millions, of dollars, depending on the required technological sophistication.
These substantial capital demands act as a formidable barrier, deterring potential newcomers from entering the market. The sheer scale of the upfront investment required to match the capabilities of established players like Sagentia Group makes it exceptionally challenging for new firms to gain a foothold, especially those lacking deep pockets or access to significant funding.
Sagentia Group's core strength is its access to a deep bench of highly specialized scientists, engineers, and innovation experts. This specialized talent is not easily replicated by new entrants, creating a significant barrier.
Attracting, retaining, and continuously developing this diverse and highly skilled workforce is a considerable challenge for any firm looking to enter the innovation consulting space. For example, the demand for AI and machine learning specialists, critical for many advanced R&D projects, continued to surge in 2024, with average salaries for senior roles often exceeding $200,000 annually in key tech hubs.
The high cost and difficulty in sourcing such niche expertise mean that new entrants would face substantial upfront investment and a prolonged period to build comparable capabilities. This talent gap directly impacts a new firm's ability to deliver the sophisticated solutions clients expect from established players like Sagentia.
In the consulting sphere, a solid reputation, a history of successful engagements, and deep-seated client connections are paramount for securing new projects. New entrants face a significant hurdle in replicating the decades of accumulated trust and expertise that established firms like Sagentia Group possess, making it difficult to compete for lucrative contracts.
For Sagentia Innovation, this translates into a considerable competitive advantage. Their established track record, evidenced by a consistent delivery of high-value solutions for numerous clients, acts as a strong barrier. For instance, in 2024, consulting firms with over 10 years of operation in niche sectors often reported a client retention rate upwards of 80%, a figure challenging for newcomers to match.
Intellectual Property and Proprietary Methodologies
Sagentia Group's development and application of proprietary methodologies and intellectual property (IP) create a significant barrier to entry for new competitors. These unique frameworks and accumulated IP are difficult for rivals to replicate, effectively deterring potential market entrants. For instance, companies heavily invested in R&D, like those in the tech consulting space, often see their IP as a core competitive asset. In 2023, the global R&D expenditure reached an estimated $2.5 trillion, highlighting the value placed on innovation and proprietary knowledge.
The complexity and originality of Sagentia's innovation processes, backed by its IP, make it challenging for newcomers to match its service offerings or achieve comparable efficiency. This requires substantial investment in research, development, and the acquisition of specialized talent, resources that nascent firms may lack. The threat of new entrants is therefore moderated by the high upfront costs and the time required to build a comparable knowledge base and patent portfolio.
- Proprietary Methodologies: Sagentia's unique innovation frameworks act as a competitive moat.
- Intellectual Property Accumulation: A strong IP portfolio is a significant barrier to replication by new firms.
- High Barrier to Entry: New entrants face substantial costs and time investments to match Sagentia's capabilities.
- R&D Investment: The high global R&D spend underscores the importance and cost of developing proprietary innovation.
Regulatory and Compliance Complexities
The threat of new entrants for Sagentia Group is significantly influenced by regulatory and compliance complexities. Operating in highly regulated sectors such as medical devices, food and beverage, and defense demands a deep understanding and adherence to stringent, often evolving, rules. For instance, the medical device sector alone saw the European Union's Medical Device Regulation (MDR) implementation create substantial compliance burdens, requiring extensive documentation and testing.
New companies looking to enter Sagentia's markets would face considerable upfront investment in developing the expertise and systems necessary to meet these demanding regulatory requirements. This includes navigating frameworks like the FDA's regulations in the US or similar bodies globally, which can take years and millions of dollars to master. The sheer cost and time involved in achieving compliance acts as a substantial barrier, limiting the number of potential new competitors capable of entering the market effectively.
- High Compliance Costs: New entrants must budget for significant legal, consulting, and operational expenses to ensure adherence to industry-specific regulations in sectors like medical and defense.
- Evolving Regulatory Landscape: Constant updates to regulations, such as changes in data privacy laws affecting connected medical devices, require continuous adaptation and investment.
- Specialized Knowledge Required: Understanding and implementing complex compliance protocols demands specialized technical and legal expertise not readily available to generalist firms.
- Long Lead Times for Approval: Gaining necessary certifications and approvals, like those from the FDA or EMA, can take years, delaying market entry and revenue generation for new players.
The threat of new entrants for Sagentia Group is considerably low due to the immense capital required to establish a competitive innovation consultancy. Significant investments in R&D labs, testing equipment, and specialized software, potentially costing millions, create a substantial financial hurdle. For example, setting up a cutting-edge innovation lab in 2024 could easily demand an initial outlay in the high hundreds of thousands to over a million dollars depending on the technological scope.
The need for highly specialized talent, such as AI and machine learning experts, further elevates the barrier to entry. In 2024, average salaries for senior specialists in these fields often surpassed $200,000 annually in major tech hubs, making talent acquisition a costly and time-consuming endeavor for newcomers. This talent gap directly impedes a new firm's ability to match the sophisticated solutions offered by established players like Sagentia.
Sagentia Group's accumulated intellectual property (IP) and proprietary methodologies also serve as robust defenses against new entrants. The development of unique frameworks and a strong IP portfolio, valued highly in sectors like tech consulting where global R&D expenditure reached an estimated $2.5 trillion in 2023, are difficult and costly to replicate. This makes it challenging for new firms to achieve comparable efficiency or service offerings, thus moderating the threat.
Furthermore, the complex regulatory landscape in sectors like medical devices and defense presents another significant barrier. Navigating stringent compliance requirements, such as the EU's MDR or FDA regulations, demands substantial upfront investment in specialized knowledge and systems, often taking years and millions of dollars. For instance, gaining necessary certifications can delay market entry, effectively limiting the number of viable new competitors.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis leverages a comprehensive mix of primary research, including customer surveys and expert interviews, alongside secondary data from industry association reports, market intelligence platforms, and financial disclosures.
