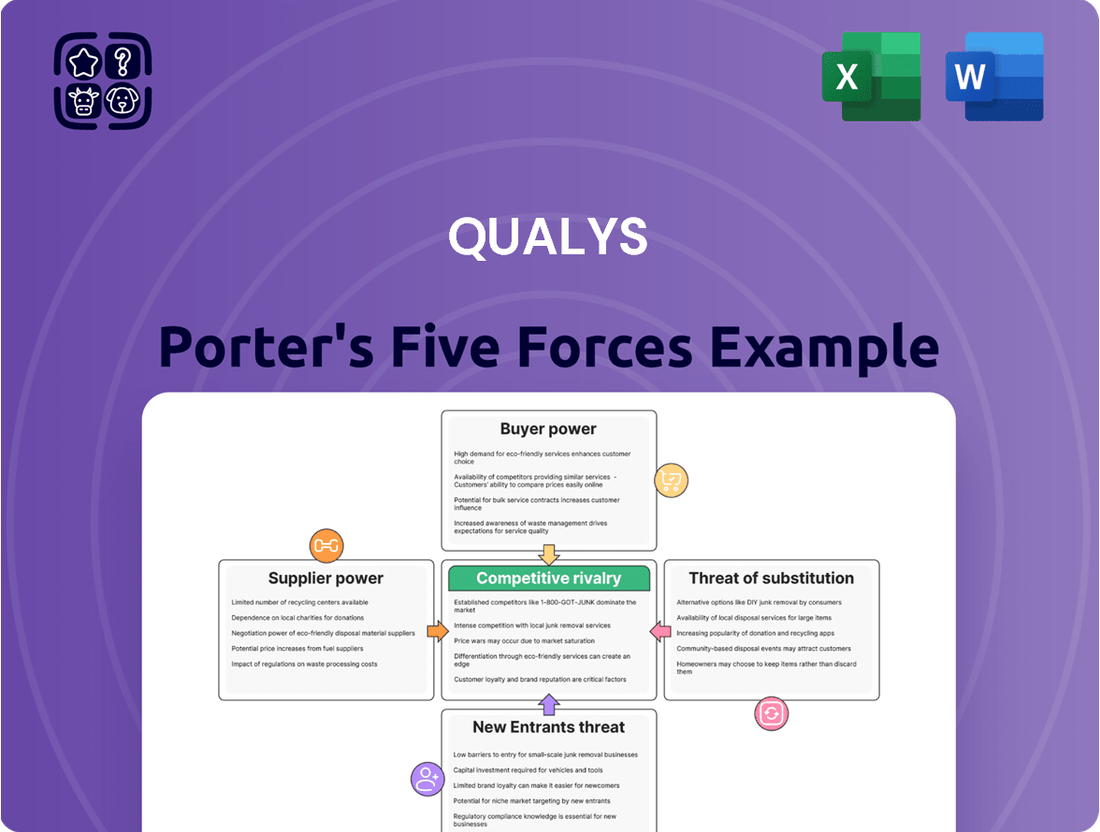
Qualys Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Qualys Bundle
Qualys operates in a dynamic cybersecurity landscape, heavily influenced by the forces outlined in Porter's Five Forces analysis. Understanding these pressures is crucial for grasping Qualys's market position and strategic outlook. This brief snapshot only scratches the surface of these intricate competitive dynamics. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Qualys’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Qualys, operating as a cloud-based security and compliance solutions provider, is inherently dependent on a small group of major cloud infrastructure providers. Companies like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and Microsoft Azure dominate this essential market segment. This concentration of power among a few key players significantly amplifies their bargaining leverage over companies like Qualys.
The strategic alliances Qualys maintains with these cloud giants are not merely beneficial; they are foundational to its ability to deliver its services effectively and scale its operations. In 2024, the global cloud computing market continued its robust expansion, with AWS, Azure, and GCP holding substantial market shares, underscoring their critical role and influence in the ecosystem.
Qualys's platform relies on specialized software components that are crucial for its comprehensive cybersecurity offerings. While the specifics of these suppliers are confidential, the company's reliance on advanced technology means that providers of unique or leading-edge software modules can hold significant bargaining power. This dependency is further underscored by Qualys's own emphasis on securing its software supply chain, indicating the importance of these external technology providers.
The cybersecurity industry is experiencing a significant deficit in skilled professionals, a situation that directly amplifies the bargaining power of specialized talent. This scarcity means that companies like Qualys must actively compete to attract and retain top-tier cybersecurity engineers and experts, crucial for driving innovation and maintaining a competitive technological advantage.
The intense demand for cybersecurity expertise, coupled with a limited supply, inevitably leads to increased labor costs. This upward pressure on wages can directly impact a company's operating expenses and potentially extend product development timelines as they navigate the challenges of securing essential human capital. For instance, in 2024, cybersecurity roles continued to see substantial salary growth, with some specialized positions experiencing double-digit percentage increases year-over-year.
Proprietary Technology and Licensing
Suppliers offering unique security technologies, such as advanced threat intelligence feeds or specialized algorithms, can wield significant bargaining power. This uniqueness makes their offerings difficult to replicate, giving them leverage in negotiations with companies like Qualys. Qualys may be compelled to license these proprietary technologies, and the supplier's market standing directly impacts the terms of these licensing agreements, potentially influencing Qualys' operational costs and the capabilities of its product suite.
For instance, in 2024, the cybersecurity market saw continued innovation in areas like AI-driven threat detection. Companies specializing in these niche, high-demand technologies, particularly those with patented algorithms, often command premium licensing fees. This directly impacts the cost structure for SaaS providers like Qualys, as access to cutting-edge capabilities is crucial for maintaining a competitive edge.
- Proprietary Advantage: Suppliers with patented or highly specialized security algorithms possess a distinct advantage, making their offerings indispensable.
- Licensing Terms: The negotiation power of these suppliers allows them to dictate licensing terms, impacting a company's expenses.
- Product Differentiation: Qualys' ability to integrate unique supplier technologies can enhance its product features and market differentiation.
- Cost Implications: High licensing costs for proprietary technology can directly affect Qualys' profit margins and pricing strategies.
Infrastructure and Hardware Providers
Qualys, while predominantly a cloud-based platform, relies on a foundation of physical infrastructure and hardware. Companies providing servers, networking gear, and data center space are key suppliers. Their pricing and the quality of their offerings directly impact Qualys' operational costs and the reliability of its service delivery to customers worldwide. The demand for robust, secure, and high-performance hardware means these suppliers hold significant bargaining power.
For example, in the server market, major players like Dell Technologies and Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE) often command strong positions due to the specialized nature of the equipment needed for cloud operations. Similarly, providers of high-speed networking components, such as Cisco Systems, are critical. The need for continuous uptime and data security in Qualys' operations makes it imperative to partner with dependable, albeit potentially powerful, suppliers. This dependence can translate into higher costs if suppliers face capacity constraints or choose to increase prices, impacting Qualys' overall cost structure.
- Critical Infrastructure Dependency: Qualys' global data center operations necessitate reliable hardware and network infrastructure, giving suppliers leverage.
- Supplier Market Concentration: Key hardware and infrastructure providers often operate in concentrated markets, increasing their bargaining power.
- Service Reliability Impact: The performance and uptime of Qualys' services are directly tied to the quality of infrastructure supplied, making these relationships vital and potentially costly.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Qualys is significant, primarily due to the concentration of cloud infrastructure providers and the specialized nature of certain software components. These key suppliers, like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, hold substantial market shares, giving them considerable leverage in negotiations. Furthermore, providers of unique cybersecurity technologies and skilled talent also exert strong influence, impacting Qualys' costs and operational capabilities.
| Supplier Type | Key Players (Examples) | Impact on Qualys | 2024 Market Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cloud Infrastructure | AWS, Azure, Google Cloud | High dependency, significant pricing leverage | Continued market dominance, robust growth |
| Specialized Software | Providers of AI threat detection, unique algorithms | Potential for high licensing fees, impacts product features | Increased demand for patented technologies |
| Hardware & Networking | Dell Technologies, HPE, Cisco | Influences operational costs and service reliability | Strong market positions, potential for price increases |
| Skilled Talent | Cybersecurity Engineers, AI specialists | Drives up labor costs, impacts development timelines | Significant salary growth in specialized roles |
What is included in the product
Qualys' Porter's Five Forces analysis meticulously examines the competitive intensity within the cybersecurity market, detailing the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the rivalry among existing players to define Qualys' strategic positioning.
Instantly identify and quantify competitive threats, allowing for proactive strategy adjustments and reduced market vulnerability.
Customers Bargaining Power
Qualys boasts a substantial and varied customer base, serving more than 10,000 subscription customers worldwide. This extensive reach includes a large number of Forbes Global 100 and Fortune 100 companies, highlighting the company's presence across numerous sectors.
The wide distribution of Qualys's customer base across industries like technology, finance, healthcare, government, and manufacturing helps to dilute the bargaining power of any single customer. This broad market penetration means that the loss of one or a few customers is less likely to have a catastrophic impact on Qualys's overall business.
Despite the diversity, very large enterprise clients, due to the sheer volume of their business and the strategic nature of Qualys's services to their operations, can still wield significant influence. These major clients might have greater leverage in negotiating terms or pricing based on their substantial contract values.
Customers integrating Qualys' cloud-based platform for vulnerability management, compliance, and threat detection often face significant switching costs. Migrating security solutions, reconfiguring IT environments, and retraining staff can be complex and expensive, making it difficult to move away from the established system.
This inherent stickiness significantly curtails the immediate bargaining power of individual customers, particularly once they are deeply embedded with Qualys' comprehensive suite of solutions. The effort and expense involved in a transition act as a powerful deterrent.
This reduced bargaining power is reflected in Qualys' strong customer retention. For instance, the company has consistently maintained a gross retention rate of approximately 90% in recent periods, underscoring the difficulty customers experience in leaving their platform.
Qualys' customer base comprises highly sophisticated IT and security professionals within large enterprises. These decision-makers are well-versed in cybersecurity solutions and conduct rigorous evaluations, scrutinizing every aspect of value and return on investment (ROI). This deep understanding means they are not easily swayed by marketing; they demand demonstrable efficacy and clear cost benefits.
The cybersecurity market in 2024 is characterized by intense budget scrutiny. Customers are actively seeking solutions that offer a strong value proposition, often prioritizing integrated platforms that can consolidate multiple security functions. This trend pressures vendors like Qualys to demonstrate not just product features but also tangible cost savings and operational efficiencies, limiting pricing flexibility.
For instance, many enterprises are consolidating their cybersecurity vendors to reduce complexity and leverage economies of scale. This means Qualys must continuously prove its competitive pricing and the comprehensive nature of its offerings against a backdrop of budget constraints and a desire for unified security management.
Demand for Integrated Platforms
Customers are increasingly seeking integrated security platforms to streamline operations and enhance efficiency. This consolidation trend can shift bargaining power towards buyers, as they can demand more comprehensive offerings from fewer vendors, potentially pressuring smaller, specialized providers.
Qualys’ strategic direction, particularly its Enterprise TruRisk Platform and TotalAppSec offerings, directly addresses this customer demand for unified solutions. By providing a holistic approach to risk management and application security, Qualys aims to become the go-to vendor for organizations looking to consolidate their security toolset.
The market is seeing a significant push towards platform consolidation. For instance, a 2024 industry survey indicated that over 60% of IT decision-makers are prioritizing vendors that offer integrated security solutions, up from 45% in 2022. This highlights a clear shift in customer preference that directly impacts vendor selection and negotiation leverage.
- Growing Demand for Unified Security: Customers prefer single-vendor solutions for better integration and management.
- Increased Bargaining Power: Consolidation allows customers to negotiate better terms by dealing with fewer, larger providers.
- Qualys' Platform Strategy: Qualys' Enterprise TruRisk Platform and TotalAppSec are designed to meet this need for integrated security.
- Market Shift: Over 60% of IT decision-makers in 2024 favored integrated security platforms, indicating a strong market trend.
Influence of Channel Partners
Qualys' reliance on channel partners for customer acquisition is a significant factor in the bargaining power of customers, as these partners act as crucial intermediaries. In 2024, a substantial portion of Qualys' revenue was driven by reseller and partner sales, indicating their influence. This expanded market reach, however, can empower partners who cultivate strong end-customer relationships, potentially allowing them to negotiate more favorable terms or demand higher margins.
Maintaining robust relationships and attractive incentives with these channel partners is therefore paramount for Qualys to mitigate the increased bargaining power that can arise from their intermediary role. A well-incentivized partner ecosystem is more likely to prioritize Qualys' offerings and support its growth, thereby indirectly influencing customer purchasing decisions and bargaining leverage.
- Channel Partner Revenue Contribution: While specific 2024 figures are proprietary, industry trends suggest channel sales for SaaS companies like Qualys often represent 30-50% of total revenue, a significant lever for partner influence.
- Customer Relationship Leverage: Partners with deep-seated relationships with end-customers can leverage this trust to negotiate better pricing or terms for their clients, impacting Qualys' revenue and margins.
- Incentive Structures: The effectiveness of Qualys' partner incentive programs directly correlates with their ability to maintain favorable terms and limit partner-driven customer bargaining power.
Qualys' broad customer base, exceeding 10,000 subscription clients including many Fortune 100 companies, generally dilutes individual customer bargaining power. However, very large enterprise clients, due to their significant contract values and the strategic importance of Qualys' services, can still exert considerable influence on pricing and terms.
The high switching costs associated with migrating security platforms, estimated to involve complex IT reconfigurations and staff retraining, significantly limit customers' ability to change providers. This "stickiness" is reflected in Qualys' consistent gross customer retention rate of around 90%, demonstrating the difficulty customers face in leaving the platform.
In 2024, budget scrutiny and a strong preference for integrated security platforms empower customers. Over 60% of IT decision-makers prioritize vendors offering consolidated solutions, pressuring Qualys to demonstrate clear ROI and cost savings to maintain its competitive edge and pricing flexibility.
Channel partners, contributing significantly to Qualys' revenue in 2024, can also influence customer bargaining power. Partners with strong end-customer relationships may negotiate better terms for their clients, making effective partner incentive programs crucial for Qualys to manage this leverage.
| Factor | Impact on Bargaining Power | Qualys' Mitigation Strategy | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Customer Base Size & Diversity | Low for individual customers, High for very large enterprises | Broad market penetration | 10,000+ subscription customers |
| Switching Costs | Low | Platform integration, comprehensive suite | ~90% gross retention rate |
| Market Consolidation Trend | High | Enterprise TruRisk Platform, TotalAppSec | 60%+ IT decision-makers prefer integrated platforms |
| Channel Partner Influence | Moderate to High | Attractive partner incentives | Significant revenue through channel sales |
Preview Before You Purchase
Qualys Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Qualys Porter's Five Forces Analysis, which you will receive in its entirety and exact format immediately upon purchase. What you see here is the complete, professionally compiled document, offering an in-depth examination of the competitive landscape within the cybersecurity industry as analyzed through the Porter's Five Forces framework. You can be confident that the detailed insights and strategic evaluation presented are precisely what you will gain access to, ready for immediate use and application to your business objectives.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Qualys navigates a cybersecurity market characterized by intense rivalry and a fragmented vendor landscape. This environment features a mix of large, established cybersecurity providers and numerous agile startups, all vying for market share. The sheer number of players means that Qualys constantly faces competition across its various service offerings.
This crowded market dynamic directly impacts Qualys by fueling the need for continuous innovation and putting downward pressure on pricing strategies. Companies in this sector must consistently enhance their solutions to stay ahead, which can strain resources. For instance, the global cybersecurity market was projected to reach around $232 billion in 2024, indicating significant investment but also immense competition for a slice of that pie.
Qualys competes with a wide array of companies, from broad-spectrum security providers offering integrated platforms to niche players specializing in specific areas like vulnerability management or cloud security. This fragmentation means that customer needs are met by a diverse set of vendors, requiring Qualys to differentiate itself effectively.
Qualys faces significant competitive pressure from larger, well-funded platform vendors like Palo Alto Networks and CrowdStrike. These competitors are increasingly encroaching on Qualys' traditional strength in vulnerability management, often leveraging aggressive pricing strategies and bundling their offerings with broader security portfolios. For instance, Palo Alto Networks’ Cortex Xpanse, which includes attack surface management, directly competes with Qualys’ core offerings, aiming to capture customers seeking consolidated security solutions.
These larger rivals benefit from their extensive resources and ability to offer a more comprehensive suite of cybersecurity services, presenting a compelling value proposition for organizations aiming to consolidate their vendor relationships. This can make it challenging for customers to choose a specialized solution like Qualys when a single, larger provider offers a seemingly complete package.
Qualys differentiates itself by highlighting its specialized expertise in end-to-end risk prioritization, a critical component for effective cybersecurity resource allocation. The company also emphasizes its cloud-native architecture, designed for agility and scalability, which can appeal to organizations prioritizing modern, flexible security infrastructure over bundled, potentially less specialized solutions.
The cybersecurity industry is a hotbed of innovation, and this pace directly fuels competitive rivalry. New threats emerge daily, and the technologies designed to counter them must constantly evolve. This rapid evolution means companies like Qualys face a significant challenge to keep their solutions cutting-edge.
The technology obsolescence cycle in cybersecurity is remarkably short, often falling within an 18-to-24-month window. This forces Qualys into a perpetual cycle of substantial investment in research and development to avoid falling behind. For instance, the constant emergence of zero-day exploits and sophisticated malware necessitates rapid updates to threat intelligence and detection capabilities.
Failure to innovate at this breakneck speed or to adapt swiftly to new attack vectors can quickly erode a company's market position. Competitors who can more effectively anticipate and respond to emerging threats can capture market share. In 2024, we saw a surge in AI-powered attacks, demanding equally advanced AI-driven defenses, highlighting the critical need for continuous R&D investment.
Pricing Pressure and Value Proposition
The cybersecurity market is quite crowded, leading to significant pricing pressure. Analysts observed a year-over-year pricing pressure of 7-12% in this sector during 2024. This intense competition means Qualys must continuously prove its worth by highlighting its superior value, maintaining healthy gross profit margins, and showcasing a strong return on investment for customers.
Qualys's profitability, evidenced by a robust adjusted EBITDA margin of 47%, demonstrates its operational efficiency. However, even with such strong margins, the prevailing market conditions heavily influence its pricing strategies. The company must navigate these dynamics carefully to remain competitive while still reflecting the value it provides.
- Crowded Market Dynamics: The cybersecurity landscape is highly saturated, intensifying competition and consequently exerting downward pressure on pricing.
- Value Justification: Qualys needs to consistently articulate and deliver superior value, high gross profit margins, and a compelling return on investment to support its pricing structure.
- Profitability vs. Market Forces: While Qualys boasts an impressive 47% adjusted EBITDA margin, indicating strong internal efficiency, external market forces and competitor pricing remain critical determinants of its own pricing strategy.
- Competitive Pricing Pressure: The industry experienced an estimated 7-12% year-over-year pricing pressure in 2024, a key factor Qualys must address in its strategic planning.
Customer Retention and Expansion Challenges
Qualys faces intense competition for customer loyalty, as rivals frequently try to lure away its existing client base. While Qualys maintains a strong customer retention rate, its net dollar retention rate holding steady at 103% indicates difficulties in increasing revenue from current customers through expanded product usage or additional services. This flat growth highlights the need for strategic initiatives to deepen relationships and drive greater value from the installed base.
To combat this, Qualys is emphasizing cross-selling and introducing new product suites designed to appeal to its existing customers. The company's recent strategic push into new customer acquisitions and strengthening channel partnerships are key tactics aimed at broadening its market reach and diversifying revenue streams, thereby mitigating the risks associated with upselling challenges.
- Customer Retention: Qualys generally sees high retention, a positive sign in a competitive SaaS market.
- Net Dollar Retention (NDR): A 103% NDR suggests that while existing customers aren't leaving in large numbers, there's limited growth from upselling and cross-selling within that base.
- Competitive Pressure: Competitors are actively trying to capture market share by targeting Qualys' existing customers, putting pressure on Qualys to demonstrate ongoing value and innovation.
- Growth Strategy: Qualys' focus on new customer acquisition and channel development aims to offset slower growth from its current customer base.
The cybersecurity sector is exceptionally crowded, leading to intense rivalry. Qualys faces competition from both large, established players and nimble startups, all vying for market share. This dynamic forces continuous innovation and puts pressure on pricing, with an estimated 7-12% year-over-year pricing pressure observed in 2024. Despite a strong adjusted EBITDA margin of 47%, Qualys must carefully balance its pricing to remain competitive.
| Competitor | Key Offerings | Competitive Overlap with Qualys |
|---|---|---|
| Palo Alto Networks | Integrated security platforms, Cortex Xpanse (attack surface management) | Directly competes with Qualys' vulnerability management and cloud security solutions. |
| CrowdStrike | Endpoint security, cloud workload protection | Competes for broader security spend, potentially displacing specialized solutions like Qualys'. |
| Microsoft | Comprehensive cloud and security suite (Azure Sentinel, Microsoft Defender) | Leverages its dominant cloud position to bundle security services, challenging specialized vendors. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Internal IT security teams and manual processes represent a significant threat of substitutes for cloud-based vulnerability management solutions. Organizations, particularly smaller ones or those with specialized in-house skills, might choose to handle their IT security and vulnerability assessments internally, relying on manual efforts or open-source tools. This approach, while often less efficient and harder to scale, can present a more budget-friendly option compared to subscribing to a comprehensive platform like Qualys, especially for entities with constrained financial resources or very specific security needs.
For instance, a 2024 survey indicated that approximately 30% of small to medium-sized businesses (SMBs) still rely on a combination of manual checks and basic open-source scanners for their cybersecurity. This preference stems from a perceived lower upfront cost and a desire for greater control over the process. However, the scalability limitations and potential for human error in manual methods mean that as an organization's IT infrastructure grows, these internal solutions can become increasingly costly and less effective than a managed service.
Businesses might opt for specialized, single-purpose security tools from various niche providers instead of a comprehensive platform. This allows them to pick the best solution for each specific security task, like vulnerability scanning or patch management. For instance, a company might use a leading vulnerability scanner from Vendor A and a separate, highly-rated patch management tool from Vendor B. This fragmented approach, while creating tool complexity, directly substitutes the all-in-one offering of a provider like Qualys.
Broader IT management and network monitoring tools can act as indirect substitutes for Qualys' specialized security solutions. While these tools, like SolarWinds or Datadog, primarily focus on operational performance and uptime, they often include basic security monitoring or vulnerability scanning features. For instance, many offer network traffic analysis and log management, which can flag suspicious activities. In 2024, the IT infrastructure monitoring market was valued at approximately $5.5 billion, indicating a significant number of organizations already utilize such platforms.
These general IT tools may appeal to businesses prioritizing IT operations and seeking a consolidated platform, even if their security capabilities are less robust than dedicated cybersecurity suites. Organizations might opt for these if their perceived security needs are minimal or if they wish to avoid the complexity and cost of multiple specialized vendors. This approach fulfills a basic security requirement without investing in advanced, purpose-built security solutions, especially for smaller enterprises or those with less stringent compliance demands.
Managed Security Service Providers (MSSPs)
Managed Security Service Providers (MSSPs) present a significant threat of substitution for companies like Qualys. Organizations can offload their entire cybersecurity functions to MSSPs, who then deploy their own security tools and managed services. This means a business might opt for a comprehensive MSSP solution rather than directly licensing and managing Qualys' platform. For instance, the global MSSP market was valued at approximately $30 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially, indicating a strong demand for these outsourced security services.
While Qualys collaborates with MSSPs, the MSSP itself functions as a direct substitute. Instead of a company investing in and operating Qualys' technology stack, they entrust an MSSP to handle their security posture. This effectively bypasses a direct relationship with Qualys for the core security management functionality. This trend is fueled by the increasing complexity of cybersecurity and a shortage of skilled in-house security professionals. Reports from 2024 indicate that over 60% of organizations are considering or actively engaging MSSPs to address these challenges.
The decision to outsource to an MSSP shifts the procurement and implementation of security solutions to a third party. This third party may choose to integrate various security tools, potentially including those from competitors, or offer a proprietary integrated platform.
- MSSPs offer a holistic, outsourced approach to cybersecurity.
- They can act as a substitute for direct platform subscription and in-house management.
- The decision-making for security tools shifts to the MSSP.
- Market growth in MSSPs highlights their role as a viable alternative.
Adoption of Alternative Security Architectures
The adoption of alternative security architectures presents a significant threat of substitutes for Qualys. Emerging paradigms like Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) and the increasing sophistication of built-in security features from cloud service providers (CSPs) offer alternative ways for organizations to manage their security posture. For example, major CSPs like Amazon Web Services (AWS) with its Security Hub and Microsoft Azure with its Security Center are continuously enhancing their native vulnerability assessment and management capabilities. This trend, which gained considerable momentum through 2024, suggests that some organizations might find these integrated solutions sufficient, thereby reducing their reliance on specialized third-party vulnerability management platforms like Qualys for certain use cases.
While Qualys often integrates with these cloud environments, a strong organizational shift towards leveraging a CSP’s native security tools could diminish the perceived necessity for standalone vulnerability management solutions. This is particularly true for organizations with a primary cloud presence, where the convenience and cost-effectiveness of unified security management become more attractive. For instance, reports from 2024 indicated a growing preference among mid-sized businesses for consolidated security platforms, potentially impacting demand for best-of-breed solutions if native offerings mature sufficiently.
- Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA): A security model that requires strict identity verification for every person and device trying to access resources on a private network, regardless of location.
- Cloud-Native Security Tools: Security functionalities directly integrated into cloud platforms, such as vulnerability scanning, threat detection, and identity and access management.
- Market Trends: Increased adoption of ZTA and enhanced CSP security offerings observed throughout 2024.
- Impact: Potential reduction in demand for third-party vulnerability management solutions if native tools are perceived as adequate or superior.
Organizations may opt for specialized, single-purpose security tools from various niche providers instead of a comprehensive platform like Qualys. This allows them to cherry-pick the best solution for each specific security task, such as vulnerability scanning or patch management. For example, a company might utilize a leading vulnerability scanner from Vendor A and a separate, highly-rated patch management tool from Vendor B. This fragmented approach, while increasing tool complexity, directly substitutes the all-in-one offering of a provider like Qualys.
Broader IT management and network monitoring tools can serve as indirect substitutes for Qualys' specialized security solutions. While these tools primarily focus on operational performance, they often include basic security monitoring features. In 2024, the IT infrastructure monitoring market was valued at approximately $5.5 billion, highlighting the significant adoption of such platforms.
Managed Security Service Providers (MSSPs) represent a substantial threat of substitution. Businesses can outsource their entire cybersecurity functions to MSSPs, who then deploy their own security tools. This bypasses a direct relationship with Qualys for core security management. The global MSSP market was valued at around $30 billion in 2023, with strong projected growth.
Emerging security architectures like Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) and enhanced native security features from cloud service providers (CSPs) also pose a threat. CSPs like AWS and Azure are improving their integrated vulnerability assessment capabilities. Reports from 2024 showed a growing preference among mid-sized businesses for consolidated security platforms.
| Substitute Category | Description | Example | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Internal IT & Manual Processes | Handling security and vulnerability assessments in-house using manual efforts or open-source tools. | SMBs relying on manual checks and basic scanners. | Approximately 30% of SMBs used manual checks/basic scanners in 2024. |
| Niche Security Tools | Utilizing best-of-breed tools from different vendors for specific security tasks. | Vendor A for vulnerability scanning, Vendor B for patch management. | Diversification in security tool adoption continues. |
| IT Management & Monitoring Tools | Using broader IT tools with integrated basic security monitoring. | SolarWinds, Datadog. | IT infrastructure monitoring market valued at ~$5.5 billion in 2024. |
| Managed Security Service Providers (MSSPs) | Outsourcing all cybersecurity functions to a third-party provider. | Engaging an MSSP for comprehensive security management. | Global MSSP market valued at ~$30 billion in 2023; >60% of orgs considering MSSPs in 2024. |
| Cloud-Native Security | Leveraging security tools built directly into cloud platforms. | AWS Security Hub, Azure Security Center. | Growing preference for consolidated security platforms in mid-sized businesses. |
Entrants Threaten
Developing a truly comprehensive IT, security, and compliance platform akin to Qualys demands a colossal financial commitment. This includes building robust cloud infrastructure, investing heavily in ongoing research and development for cutting-edge solutions, and attracting top-tier cybersecurity and engineering talent. For instance, in 2024, major cybersecurity firms reported R&D expenditures in the hundreds of millions of dollars, highlighting the scale of investment required. This formidable capital barrier significantly discourages many smaller players from entering the market with a comparable offering.
Qualys benefits from a strong brand reputation and deep customer trust, a crucial asset in the cybersecurity sector. With over 10,000 global customers, including a significant portion of the Forbes Global 100, their established credibility is a formidable barrier.
Developing this level of trust and a proven track record in cybersecurity is a lengthy and resource-intensive process. New entrants would struggle to replicate the established reputation Qualys has cultivated over years of reliable service delivery.
The technological complexity inherent in developing advanced security solutions like vulnerability management and threat detection presents a significant barrier to new entrants. Companies like Qualys require substantial investment in specialized R&D to create platforms that can effectively address diverse IT landscapes, from traditional on-premise infrastructure to modern cloud, container, and API environments. This deep technical expertise and the need for continuous innovation mean newcomers face a steep learning curve, making it difficult to quickly establish a competitive offering.
Regulatory and Compliance Hurdles
The cybersecurity and compliance sector is heavily regulated, with mandates like PCI DSS, HIPAA, and SOC 2 demanding strict adherence. New companies entering this space must invest significant resources to understand and comply with these intricate requirements, a process that can delay market entry and increase initial operating costs.
Qualys benefits from its existing suite of compliance management solutions, which already meet many of these rigorous standards. This established presence and proven compliance track record offer a substantial barrier to entry for potential newcomers who lack similar certifications and expertise. For instance, Qualys' ability to support organizations in achieving and maintaining SOC 2 compliance, a framework that saw increasing adoption throughout 2024, directly addresses a critical need for many businesses seeking trusted cloud-based security and compliance partners.
- Regulatory Complexity: Navigating diverse and evolving regulations like GDPR, CCPA, and industry-specific standards presents a significant challenge for new entrants.
- Compliance Costs: Achieving and maintaining certifications (e.g., ISO 27001) requires substantial investment in technology, personnel, and ongoing audits.
- Established Player Advantage: Companies like Qualys, with pre-existing robust compliance offerings, have a distinct competitive edge, reducing the perceived risk for customers.
- Data Privacy Demands: Increasing global focus on data privacy, highlighted by ongoing enforcement actions in 2024 related to data breaches, necessitates sophisticated compliance capabilities from the outset.
Ecosystem and Partnership Development
Qualys’ established ecosystem, featuring key alliances with cloud giants like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, presents a significant barrier for newcomers. These integrations are complex and time-consuming to replicate, requiring substantial investment and industry trust. Furthermore, Qualys’ extensive network of channel partners, a cornerstone of its go-to-market strategy, deepens its market penetration and creates a formidable hurdle for any new entrant aiming to gain comparable reach and customer access.
The threat of new entrants is significantly mitigated by the difficulty in replicating Qualys' comprehensive partner network and deep cloud integrations. Building a comparable ecosystem requires not only financial resources but also a proven track record and established relationships within the IT security landscape. For instance, Qualys reported strong growth in its partner-led sales in 2023, indicating the effectiveness of this strategy in expanding its market footprint and making it harder for new players to gain traction.
- Ecosystem Integration Complexity: New entrants must invest heavily in developing and maintaining integrations with multiple cloud platforms, a process that is both technically demanding and resource-intensive.
- Channel Partner Network: Qualys leverages a robust channel-first strategy, making it difficult for new competitors to achieve similar market reach and customer engagement without extensive partner development.
- Industry Trust and Reputation: Establishing the credibility and trust necessary to form strategic partnerships and attract channel partners takes considerable time and a demonstrated history of reliable service delivery.
The threat of new entrants into the cybersecurity platform market, particularly for comprehensive solutions like Qualys, is considerably low due to substantial barriers. These include the immense capital required for R&D and infrastructure, the difficulty in building brand trust and customer loyalty, and the technical complexity of developing advanced security features. Furthermore, stringent regulatory compliance and the need for extensive partner ecosystems present significant hurdles that deter new players.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis utilizes data from industry-specific market research reports, financial statements of key players, and publicly available company filings to provide a comprehensive view of competitive dynamics.
