Pure Storage Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Pure Storage Bundle
Pure Storage navigates a competitive landscape shaped by significant buyer power, especially from large enterprises seeking cost-effective, high-performance storage solutions. The threat of new entrants, while somewhat mitigated by high initial capital requirements, remains a consideration due to evolving technology and cloud-based offerings.
The threat of substitute products, particularly the ongoing evolution of cloud storage and software-defined storage, presents a continuous challenge to Pure Storage's hardware-centric model. Existing rivalry within the storage industry is intense, with established players and emerging innovators constantly vying for market share.
Supplier power, though generally moderate, can fluctuate based on the availability of critical components and the consolidation of semiconductor manufacturers. Understanding these forces is crucial for strategic planning.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Pure Storage’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Pure Storage's reliance on a concentrated group of suppliers for essential components, particularly NAND flash memory, significantly amplifies supplier bargaining power. This limited supplier base means that these entities can exert considerable influence over pricing and availability.
The impact of this concentration is evident in cost fluctuations. For instance, during Q4 FY2025, fluctuations in NAND flash memory costs directly affected Pure Storage's gross margins, highlighting the vulnerability stemming from supplier dependence.
Should a key supplier encounter production disruptions or decide to increase prices, Pure Storage faces a direct hit to its cost of goods sold. This situation can consequently erode its overall profitability, underscoring the strategic importance of managing these supplier relationships.
While Pure Storage develops proprietary software, its reliance on external hardware suppliers means switching costs for these suppliers can be high. Qualifying new hardware vendors or redesigning products to integrate different components requires significant time and financial investment. This can grant suppliers leverage, especially if Pure Storage relies on specialized or niche components.
The uniqueness of certain high-performance components, particularly cutting-edge flash memory technologies, can significantly influence Pure Storage's bargaining power with its suppliers. If these specialized components are only available from a limited number of manufacturers, Pure Storage faces a higher risk of its suppliers dictating terms. This reliance on few, highly specialized suppliers can limit Pure Storage's ability to negotiate favorable pricing or secure alternative sourcing options, directly impacting its cost structure and profitability.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into the all-flash array market themselves is generally low for Pure Storage. While suppliers of core components like flash memory chips theoretically could enter the market, the significant complexity involved in designing, manufacturing, and supporting enterprise-grade storage solutions makes this a less common strategy. Pure Storage's proprietary software and integrated system design create a barrier, reducing the likelihood of component suppliers directly competing.
However, suppliers' strategic partnerships with other storage vendors can still indirectly exert pressure. By aligning with competitors, suppliers can influence pricing or component availability, impacting the competitive landscape. Despite this, the specialized nature of Pure Storage's technology and its deep integration of hardware and software mean that a direct forward integration by a component supplier is unlikely to pose a significant threat.
For instance, in 2024, major flash memory suppliers like Samsung and Micron remained focused on their core semiconductor manufacturing business rather than directly entering the enterprise storage system market. Their revenue streams are predominantly tied to chip sales, not the more complex integration and support services required for all-flash arrays. Micron's reported revenue for fiscal year 2024 reached $16.4 billion, highlighting their scale in component production.
The bargaining power of suppliers, specifically concerning forward integration, is thus mitigated by several factors:
- High Complexity of Enterprise Storage: Developing and marketing complete enterprise storage solutions requires extensive R&D, software development, and customer support infrastructure, which is beyond the typical scope of component manufacturers.
- Pure Storage's Proprietary Technology: Pure Storage's unique software stack and system architecture create a distinct offering that is not easily replicated by component suppliers.
- Supplier Focus on Core Competencies: Major flash memory suppliers primarily focus on maximizing volume and innovation within the semiconductor industry, rather than diversifying into a highly competitive and specialized hardware market.
- Strategic Partnerships as Indirect Influence: While direct integration is unlikely, suppliers' relationships with other storage vendors can still influence market dynamics, though this is a less potent threat than direct competition.
Importance of Pure Storage to Suppliers
Pure Storage is a substantial buyer within the enterprise flash storage sector. This scale grants it a degree of bargaining power over its suppliers, influencing pricing and terms based on the volume of its procurement. For instance, in 2023, Pure Storage reported revenue growth, indicating an increased demand for components from its supply chain.
As Pure Storage continues to grow its customer base, including significant recent design wins with hyperscale clients, its purchasing power is likely to strengthen further. This expansion means Pure Storage can negotiate more favorable terms, potentially leading to cost reductions or improved supply chain reliability from its vendors. This trend is evident as the demand for high-performance flash storage continues to rise across major cloud providers.
- Significant Buyer: Pure Storage's substantial purchase volumes in the enterprise flash market provide leverage over suppliers.
- Growing Influence: Expansion into hyperscale markets enhances Pure Storage's ability to negotiate better terms.
- Market Demand: The increasing need for advanced flash storage solidifies Pure Storage's position as a key customer.
Pure Storage faces considerable supplier bargaining power due to its reliance on a concentrated number of suppliers for critical components like NAND flash memory. This concentration allows suppliers to influence pricing and availability, as demonstrated by cost fluctuations impacting Pure Storage's gross margins in Q4 FY2025.
While Pure Storage's proprietary software is a differentiator, the high switching costs for hardware components mean suppliers can wield significant leverage. The uniqueness of certain high-performance components, especially cutting-edge flash memory, further limits Pure Storage's ability to negotiate favorable terms or find alternative sources.
Major flash memory suppliers like Micron, which reported $16.4 billion in revenue for fiscal year 2024, generally focus on semiconductor manufacturing rather than directly entering the complex enterprise storage system market, mitigating the threat of direct forward integration.
However, suppliers' strategic partnerships with competitors can indirectly exert pressure on Pure Storage by influencing pricing or component availability within the broader market.
| Supplier Characteristic | Impact on Pure Storage | Example/Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Concentrated Supplier Base (NAND Flash) | High Bargaining Power | Fluctuations in NAND flash costs affected gross margins (Q4 FY2025). |
| High Switching Costs for Hardware | Supplier Leverage | Redesigning for new components is time-consuming and costly. |
| Uniqueness of High-Performance Components | Supplier Leverage | Limited availability of cutting-edge flash memory restricts sourcing options. |
| Supplier Forward Integration Threat | Low (Direct) | Component suppliers focus on chip sales; Micron FY2024 revenue: $16.4B. |
| Supplier Strategic Partnerships | Indirect Pressure | Can influence pricing or availability through alliances with competitors. |
What is included in the product
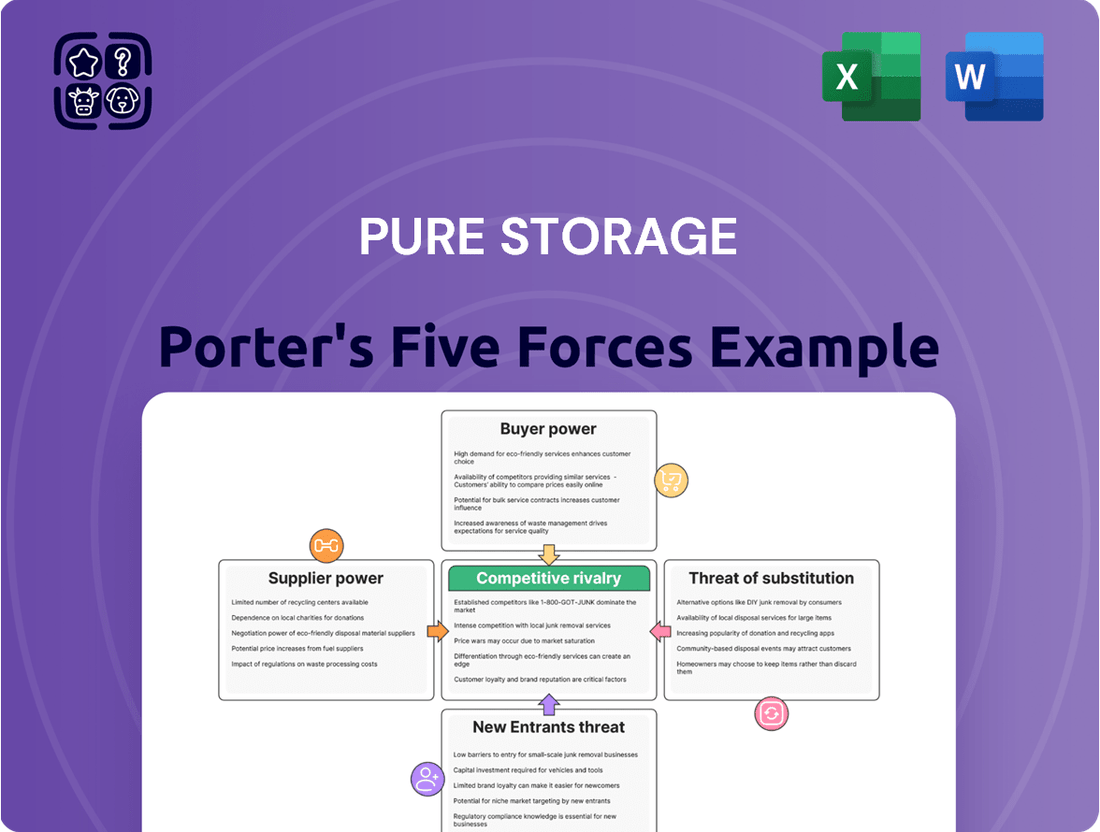
This analysis unpacks the competitive forces shaping Pure Storage's market, examining buyer and supplier power, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the enterprise storage industry.
Gain immediate clarity on competitive pressures with a visually intuitive spider chart, simplifying complex market dynamics for strategic planning.
Customers Bargaining Power
Pure Storage boasts an impressive customer roster, with over 60% of Fortune 500 companies and more than 13,500 clients globally as of early 2024. This broad customer base generally dilutes the bargaining power of any single customer.
However, the presence of large enterprise clients and hyperscalers presents a counterbalancing force. These major customers account for substantial purchase volumes, giving them significant leverage in negotiations.
The strategic importance of these large accounts to Pure Storage also amplifies customer bargaining power. Losing a key hyperscaler or a major Fortune 500 enterprise could have a notable impact on revenue and market perception.
Customers who adopt Pure Storage's all-flash storage solutions often find themselves deeply embedded within its ecosystem. This integration means that moving to a competitor isn't a simple swap; it involves significant hurdles.
These hurdles translate into tangible switching costs. For instance, migrating massive datasets from Pure Storage's platform to another vendor's can be a complex and time-consuming process, often requiring specialized tools and expertise. In 2023, the average cost for enterprise data migration projects often ranged from thousands to hundreds of thousands of dollars, depending on data volume and complexity, presenting a substantial barrier.
Beyond data migration, organizations must also account for the cost and effort of re-training their IT staff on new hardware and software. This retraining can involve direct training expenses, lost productivity during the learning curve, and potential integration challenges with existing workflows. Furthermore, the risk of operational disruption during a transition can be a major deterrent, impacting business continuity and revenue streams.
These combined factors create a strong lock-in effect. The investment in Pure Storage's technology, coupled with the operational complexities of switching, effectively raises the bargaining power of Pure Storage's customers, as they are less likely to switch providers due to these embedded costs.
Pure Storage emphasizes performance and simplicity, but customers are becoming more attuned to pricing, particularly with the availability of QLC storage and hybrid cloud options. This heightened price sensitivity grants them greater bargaining power.
The constant need for customers to weigh performance against the overall cost of ownership, or TCO, means they can negotiate more effectively with vendors like Pure Storage. For instance, while Pure Storage's all-flash arrays deliver speed, the upfront cost can be a significant factor for budget-conscious enterprises.
In 2024, the market saw continued pressure on storage pricing. IDC reported that while spending on flash storage solutions continued to grow, the average selling price per terabyte saw downward pressure due to increased competition and the adoption of more dense technologies like QLC NAND.
This dynamic allows customers to push for better terms, discounts, or more favorable service level agreements, as they have viable, lower-cost alternatives available, directly impacting Pure Storage's pricing power.
Availability of Substitutes and Alternatives
The bargaining power of customers in the storage market is significantly influenced by the availability of substitutes and alternatives, directly impacting Pure Storage's ability to command premium pricing. Customers can readily opt for traditional Hard Disk Drive (HDD) arrays, which offer a lower cost per gigabyte, or hybrid flash arrays that blend HDD and Solid State Drive (SSD) technologies for a balance of performance and price. Furthermore, the rise of hyperconverged infrastructure (HCI) solutions consolidates compute, storage, and networking, presenting an integrated alternative. Public cloud storage services from providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud also represent a substantial alternative, offering scalability and flexibility without the need for on-premises hardware investment.
The increasing adoption of hybrid and multi-cloud strategies by businesses further amplifies customer choice. This allows organizations to leverage different storage solutions across various environments, reducing reliance on any single vendor. For example, a company might use Pure Storage for its on-premises high-performance needs while utilizing AWS S3 for archival data. This fragmentation of storage needs across different platforms means customers can always find a comparable or more cost-effective solution elsewhere if Pure Storage’s offerings do not meet their specific price or feature requirements.
- Substitutes: Traditional HDD arrays, hybrid flash arrays, hyperconverged infrastructure.
- Cloud Alternatives: Public cloud storage services (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud).
- Market Trend: Growing adoption of hybrid and multi-cloud environments.
- Impact: Increased customer choice and reduced vendor lock-in.
Customer Information and Transparency
Enterprise customers, especially those in large organizations, possess significant bargaining power due to their extensive knowledge. They are often well-versed in market prices, rival offerings, and industry standards, a result of readily accessible online data and specialized consulting firms. This heightened awareness empowers them to negotiate for better pricing and more favorable contract terms.
This transparency directly translates into increased leverage for customers. For instance, in the enterprise storage market where Pure Storage operates, major clients can easily compare specifications, performance metrics, and total cost of ownership across various vendors. This makes it difficult for any single provider to command premium pricing without a clear, demonstrable advantage.
- Informed Decision-Making: Enterprise clients leverage vast amounts of market data, including competitor pricing and product reviews, to make informed purchasing decisions.
- Price Sensitivity: Increased transparency often leads to greater price sensitivity among buyers, pushing vendors to offer more competitive rates.
- Demand for Value: Customers can articulate specific needs and compare solutions against industry benchmarks, demanding higher value for their investment.
- Negotiation Advantage: Armed with market intelligence, customers can effectively negotiate pricing, service level agreements, and other contractual terms.
Pure Storage's extensive customer base, with over 13,500 clients globally as of early 2024, generally disperses individual customer power. However, its significant number of large enterprise clients and hyperscalers, who represent substantial purchase volumes, grants them considerable leverage in negotiations.
The strategic importance of these major accounts to Pure Storage means that losing even one could impact revenue and market perception, further amplifying customer bargaining power.
Switching costs for customers deeply integrated with Pure Storage's all-flash solutions are significant, encompassing data migration, IT staff retraining, and the risk of operational disruption. These factors create substantial lock-in, increasing customer leverage.
Customers are increasingly price-sensitive, comparing performance against total cost of ownership. The IDC reported downward pressure on average selling prices per terabyte for flash storage in 2023 due to competition and denser technologies like QLC NAND, empowering customers to negotiate better terms.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Drivers | Impact on Pure Storage |
|---|---|---|
| Large Enterprises/Hyperscalers | High purchase volume, strategic importance | Significant negotiation leverage on pricing and terms |
| Price-Sensitive Customers | Availability of lower-cost alternatives (e.g., QLC, HDD, cloud) | Pressure on pricing and margins |
| Technologically Integrated Customers | High switching costs (data migration, retraining) | Reduced power to switch, but strong incentive to negotiate favorable ongoing terms |
What You See Is What You Get
Pure Storage Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact, comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis of Pure Storage you'll receive immediately after purchase, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic positioning within the storage industry. You're looking at the actual document; once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact file, complete with in-depth analysis of threat of new entrants, bargaining power of buyers, bargaining power of suppliers, threat of substitute products or services, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. No mockups, no samples—the document you see here is exactly what you’ll be able to download after payment, ready for your strategic planning needs. This is the complete, ready-to-use analysis file, professionally formatted and meticulously researched, giving you a clear understanding of Pure Storage's competitive environment.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The enterprise data storage market is a crowded arena, featuring a diverse cast of competitors. You have the long-standing giants like Dell Technologies, NetApp, Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE), and IBM, all with established reputations and broad product portfolios. Then there are the newer, agile players focusing specifically on all-flash technology, and of course, the major cloud providers who offer storage as a service, adding another layer of competition.
Pure Storage itself carves out a significant niche, particularly in the all-flash array segment. In fact, as of the fourth quarter of 2023, they commanded a respectable 22.4% of that specific market. However, this success doesn't mean they operate in a vacuum; the competition is fierce across all the different storage solutions they offer, pushing them to continually innovate and differentiate.
The all-flash array market is booming, expected to hit $69.69 billion by 2030, growing at a 23.29% compound annual growth rate from 2025. This rapid expansion generally tempers direct competition as companies chase new customer acquisition.
Yet, the broader enterprise storage sector, where Pure Storage also operates, is more mature. This maturity in certain segments intensifies rivalry, as established players and newcomers alike fight for existing market share.
While rapid growth offers opportunities, the mature segments mean that competitive pressures remain a significant factor for Pure Storage.
Pure Storage stands out in a competitive landscape by offering all-flash, software-defined storage solutions characterized by exceptional performance and its unique Evergreen subscription model. This model provides customers with non-disruptive upgrades and a flexible storage-as-a-service experience, moving away from traditional hardware refresh cycles.
The company’s commitment to continuous innovation is a key driver of its competitive advantage. Pure Storage heavily invests in cutting-edge technologies, such as AI-driven storage management and the adoption of QLC flash technology, which promises higher density and potentially lower costs, ensuring they stay ahead of rivals.
Exit Barriers and Industry Consolidation
Pure Storage operates in an environment where high capital investments in research and development, along with deeply entrenched customer relationships and proprietary intellectual property, create substantial exit barriers. These factors make it difficult and costly for companies to leave the market, forcing them to remain and compete aggressively. For instance, in the data storage sector, the substantial ongoing investment in developing next-generation flash and software technologies, often running into hundreds of millions of dollars annually, exemplifies these high R&D costs. This sustained competition intensifies rivalry among existing players.
The consequence of these exit barriers is a market characterized by persistent and often fierce competition. Companies are incentivized to stay and fight for market share rather than absorb the losses associated with exiting. This dynamic is particularly evident in the enterprise storage market, where established vendors have built strong relationships with large corporations over many years, making it challenging for new entrants to gain traction and for existing players to disengage. This sustained rivalry contributes to ongoing price pressures and a continuous drive for innovation to maintain competitive advantage.
- High R&D Investment: Companies in the data storage industry, like Pure Storage, often invest a significant portion of their revenue back into R&D to stay ahead. For example, many leading storage vendors reported R&D expenses in the hundreds of millions of dollars in their 2023 fiscal year.
- Customer Lock-in: Established customer bases represent a significant barrier. Once a company integrates a particular vendor's storage solutions into its IT infrastructure, switching can be complex and costly, involving data migration, retraining staff, and potential compatibility issues.
- Specialized Intellectual Property: Patents and proprietary technologies in areas like data reduction, array management, and cloud integration are crucial. These specialized assets are difficult and expensive to replicate, further solidifying the position of incumbent firms.
- Industry Consolidation: The presence of high exit barriers can also lead to industry consolidation as larger, well-capitalized players acquire smaller, struggling competitors, further intensifying the competitive landscape for those remaining.
Competitive Strategies and Pricing
Competitive rivalry in the data storage industry is fierce, with players like Dell EMC, NetApp, and HPE constantly vying for market share. This rivalry often plays out through aggressive pricing strategies, rapid feature enhancements, and the expansion of service offerings to attract and retain customers. For instance, in 2024, the market saw continued pressure on average selling prices for flash storage solutions.
Competitors are also increasingly focusing on integrated solutions, such as hyperconverged infrastructure (HCI), which combines compute, storage, and networking. Furthermore, the push towards hybrid and multi-cloud capabilities necessitates that Pure Storage and its rivals continuously adapt their strategies to offer seamless integration and management across diverse environments. This dynamic environment forces constant innovation and strategic adjustments to maintain a competitive edge.
- Aggressive Pricing: Competitors frequently engage in price wars, particularly in the enterprise storage market, impacting profitability.
- Feature Innovation: Rapid development and introduction of new features, like enhanced data reduction technologies and AI-driven management, are key differentiators.
- Integrated Solutions: The rise of HCI and converged infrastructure presents a significant competitive front, requiring vendors to offer comprehensive platforms.
- Cloud Capabilities: Strong hybrid and multi-cloud support is no longer optional but a critical requirement for retaining enterprise clients.
Competitive rivalry in the enterprise data storage market is intense, driven by established giants like Dell EMC, NetApp, and HPE, alongside cloud providers and specialized all-flash vendors. This fierce competition is characterized by aggressive pricing, rapid feature innovation, and a push towards integrated solutions like hyperconverged infrastructure. For instance, in 2024, the market experienced continued pressure on average selling prices for flash storage, forcing vendors to constantly adapt and differentiate.
Pure Storage's all-flash, software-defined approach, coupled with its Evergreen subscription model, allows it to carve out a distinct position. However, the broader market maturity in some segments intensifies rivalry, demanding continuous innovation and strategic adjustments from all players to secure and maintain market share.
The high R&D investments, customer lock-in due to complex integration, and specialized intellectual property create significant barriers to exit, further fueling sustained competition. This environment necessitates aggressive strategies to capture market share, as seen in the ongoing development of AI-driven storage management and adoption of new flash technologies like QLC.
The all-flash array market, a key area for Pure Storage, is projected to reach $69.69 billion by 2030, growing at a substantial 23.29% CAGR from 2025, indicating significant growth opportunities amidst the rivalry.
| Key Competitors | Market Focus | Competitive Tactics |
|---|---|---|
| Dell EMC | Broad enterprise solutions, converged/hyperconverged infrastructure | Aggressive pricing, integrated offerings, extensive service portfolio |
| NetApp | Hybrid cloud, data management, all-flash | Cloud integration, data fabric strategy, performance differentiation |
| HPE | Hybrid IT, edge computing, storage solutions | Solution bundles, subscription services, focus on specific workloads |
| Cloud Providers (AWS, Azure, GCP) | Storage as a Service, cloud-native solutions | Scalability, pay-as-you-go, seamless integration with cloud ecosystems |
| Pure Storage | All-flash arrays, cloud-native storage, subscription model | Performance leadership, Evergreen subscription, AI-driven management |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Public cloud storage services from giants like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud present a significant threat of substitution for on-premise enterprise storage solutions. These providers offer highly scalable, flexible, and often cost-effective alternatives, particularly for workloads that don't require the absolute lowest latency or the highest levels of data sovereignty control. The appeal lies in their ability to rapidly provision and de-provision storage, aligning costs with actual usage.
While Pure Storage has achieved a notable design win with a hyperscaler, indicating some level of integration or partnership, the broader market trend toward cloud adoption remains a substantial substitution challenge. Enterprises are increasingly evaluating cloud storage for its agility and potential to reduce capital expenditure on hardware. For instance, the global cloud storage market was projected to reach over $100 billion in 2024, underscoring its growing dominance.
However, the threat isn't absolute. Businesses still weigh critical factors such as the cost predictability and potential for vendor lock-in associated with cloud storage against the perceived security and compliance benefits of maintaining data on-premise. Concerns about data egress fees and the ongoing operational costs of cloud services can temper the substitution effect for certain sensitive or high-volume data sets.
Traditional Hard Disk Drive (HDD) arrays and hybrid arrays remain viable substitutes for Pure Storage's all-flash solutions, particularly for organizations with less stringent performance requirements or tighter budgetary constraints. Hybrid arrays, which blend the speed of flash memory with the cost-effectiveness of HDDs, offer a compelling middle ground. For instance, IDC reported in early 2024 that while all-flash arrays continue to grow, hybrid solutions still command a significant market share, especially in sectors where the absolute highest IOPS are not critical.
Hyperconverged Infrastructure (HCI) presents a significant threat of substitution for traditional storage arrays. HCI solutions consolidate compute, storage, and networking into a unified, software-defined platform, often leveraging commodity hardware. This integration simplifies management and enhances scalability, appealing to businesses seeking operational efficiency.
The market for HCI is experiencing robust growth, directly impacting the demand for standalone storage solutions. For instance, the global HCI market was valued at approximately $15 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach over $40 billion by 2028, demonstrating a compound annual growth rate exceeding 20%. This expansion signifies HCI's increasing adoption and its capability to replace discrete storage infrastructure.
Software-Defined Storage (SDS) on Commodity Hardware
The threat of substitutes for traditional storage solutions, particularly proprietary all-flash arrays, is amplified by the rise of Software-Defined Storage (SDS) deployed on commodity hardware. Organizations can leverage off-the-shelf servers and drives, effectively creating their own flexible and potentially more cost-effective storage infrastructure.
This shift allows businesses to avoid vendor lock-in associated with specialized hardware. For instance, by 2024, the global SDS market was projected to reach over $30 billion, indicating a significant adoption trend driven by the desire for agility and reduced capital expenditure.
- Flexibility: Organizations can scale storage capacity and performance by adding commodity hardware, rather than being limited by proprietary array configurations.
- Cost Savings: Utilizing standard server components and drives can lead to substantial cost reductions compared to purchasing high-end, specialized all-flash arrays.
- Increased IT Expertise: Implementing and managing SDS solutions often requires a higher level of in-house IT knowledge and skillsets for configuration and maintenance.
- Potential Performance Trade-offs: While cost-effective, SDS on commodity hardware might not always match the peak performance or specialized features of high-end proprietary solutions without significant tuning.
In-memory Computing and Data Processing
For demanding, high-performance applications, in-memory computing and databases can serve as a substitute for traditional persistent storage. This means that for certain workloads requiring extremely fast data access, the need for physical storage solutions might be reduced.
This is particularly relevant in niche but expanding areas like real-time analytics or high-frequency trading platforms where speed is paramount. For instance, by 2024, the global in-memory computing market was projected to reach significant figures, indicating a growing adoption of these technologies.
- In-memory databases process data directly in RAM, bypassing slower disk access.
- This offers orders of magnitude faster query responses compared to traditional disk-based systems.
- Examples include SAP HANA and Oracle TimesTen, which are increasingly used for critical business functions.
- The market for in-memory databases saw substantial growth through 2023 and into 2024, driven by big data and AI initiatives.
Public cloud storage services from AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud are significant substitutes, particularly for less latency-sensitive workloads. The global cloud storage market was projected to exceed $100 billion in 2024, highlighting its widespread adoption and competitive threat to on-premise solutions.
Traditional HDD arrays and hybrid storage solutions remain viable alternatives, especially for budget-conscious organizations or those without extreme performance demands. IDC data from early 2024 indicated that hybrid solutions still hold a considerable market share, offering a balance of cost and performance.
Hyperconverged Infrastructure (HCI) consolidates compute and storage, simplifying management and boosting scalability, posing a direct substitution threat. The HCI market's projected growth to over $40 billion by 2028, with a CAGR above 20%, underscores its increasing appeal over traditional storage architectures.
Software-Defined Storage (SDS) on commodity hardware allows businesses to build flexible, cost-effective storage, avoiding vendor lock-in. The SDS market, projected to surpass $30 billion by 2024, reflects a strong trend towards agility and reduced capital expenditure.
Entrants Threaten
Entering the enterprise data storage arena, especially with advanced all-flash technologies, demands significant upfront capital. Companies need to invest heavily in research and development to innovate, build robust manufacturing capabilities, and create extensive sales and customer support networks. For instance, in 2024, the average R&D spending for major storage vendors often exceeded hundreds of millions of dollars annually, a clear indication of the financial commitment required.
These substantial financial hurdles act as a formidable barrier, effectively deterring a large number of potential new competitors from even attempting to enter the market. The sheer scale of investment needed to compete with established players like Pure Storage is often prohibitive for smaller or less-funded entities, thus limiting the threat of new entrants.
Established players like Pure Storage leverage significant economies of scale in procurement, manufacturing, and distribution. For instance, in 2023, Pure Storage reported a gross profit margin of 73.5%, indicating strong cost efficiencies that new entrants would find challenging to replicate. This scale allows them to negotiate better terms with suppliers and spread fixed costs over a larger production volume, creating a substantial cost advantage.
Furthermore, the experience curve plays a crucial role, particularly in the development and refinement of complex storage software and hardware. Pure Storage has invested heavily over years in R&D, building deep expertise that translates into optimized product performance and reliability. This accumulated knowledge reduces the learning curve for new market entrants, making it difficult for them to match the innovation and operational efficiency of incumbents without considerable time and investment.
Pure Storage's extensive patent portfolio, exceeding 2,500 global patents and applications, presents a formidable barrier to new entrants. These patents, covering foundational technologies such as DirectFlash, make it exceptionally challenging and costly for newcomers to innovate and compete without risking infringement. This robust intellectual property shields Pure Storage’s market position by deterring direct replication of its core offerings.
Brand Loyalty and Customer Relationships
Pure Storage benefits from deeply ingrained brand loyalty and robust customer relationships. This is a significant barrier for new entrants aiming to disrupt the market. Their Net Promoter Score (NPS) consistently hovers around 81-82, indicating exceptionally high customer satisfaction and a strong propensity for advocacy. This level of loyalty makes it incredibly challenging for newcomers to win over existing Pure Storage clients.
The company's extensive customer base, which includes many Fortune 500 organizations, underscores the trust and reliance placed on Pure Storage solutions. Building comparable trust and displacing these established relationships in mission-critical enterprise environments would require substantial time, investment, and a proven track record that new entrants currently lack.
- Brand Recognition: Pure Storage has cultivated a strong reputation for innovation and reliability in the data storage industry.
- Customer Retention: High NPS scores (81-82) translate into strong customer loyalty and reduced churn, making it difficult for competitors to acquire market share.
- Enterprise Trust: The company's success with Fortune 500 clients demonstrates its ability to meet the stringent demands of large enterprises, a trust that is hard-earned and difficult for new entrants to replicate quickly.
- Switching Costs: Migrating complex enterprise data infrastructure involves significant technical challenges and potential disruptions, creating high switching costs for existing Pure Storage customers.
Regulatory and Compliance Hurdles
The enterprise storage market, particularly when dealing with sensitive data, faces significant regulatory and compliance mandates. For instance, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and similar data privacy laws globally require robust security and data handling capabilities. New entrants must dedicate substantial resources to ensure their storage solutions adhere to these complex and evolving standards.
These compliance requirements translate into considerable upfront investment for any new player looking to enter the market. Beyond product development, this includes legal expertise, auditing processes, and potentially obtaining certifications, all of which increase the barrier to entry. For example, achieving compliance with standards like ISO 27001 for information security management can take years and significant financial outlay, deterring smaller or less capitalized competitors.
- Regulatory Burden: New entrants must navigate a complex web of data privacy laws (e.g., GDPR, CCPA) and industry-specific regulations.
- Compliance Costs: Significant investment is required for legal counsel, auditing, and achieving necessary certifications to operate legally and credibly.
- Data Security Standards: Meeting stringent security protocols and data residency requirements adds technical complexity and operational overhead.
- Market Entry Barrier: The high cost and time associated with regulatory compliance act as a substantial deterrent for potential new competitors in the enterprise storage space.
The threat of new entrants into the enterprise data storage market, particularly for advanced solutions like those offered by Pure Storage, is considerably low. This is primarily due to the immense capital investment required for research, development, manufacturing, and establishing a global sales and support network. For instance, major storage vendors in 2024 routinely allocated hundreds of millions of dollars to R&D alone, a figure that presents a substantial barrier for any aspiring competitor.
Furthermore, established players like Pure Storage benefit from significant economies of scale, which translate into cost advantages that are difficult for newcomers to match. In 2023, Pure Storage demonstrated its efficiency with a gross profit margin of 73.5%, highlighting its ability to manage costs effectively. This scale also allows for better supplier negotiations and a more efficient spread of fixed costs, creating a pricing and operational hurdle for new market entrants.
Intellectual property and customer loyalty also play critical roles in limiting new entrants. Pure Storage holds over 2,500 patents, protecting its core technologies and making direct replication costly and legally risky for competitors. Coupled with exceptionally high customer retention, evidenced by a Net Promoter Score (NPS) consistently around 81-82, and deep trust built with Fortune 500 clients, the challenge for newcomers to gain traction is immense.
Navigating the complex regulatory landscape further elevates the barrier to entry. New companies must invest heavily in ensuring compliance with data privacy laws like GDPR and industry-specific security standards, which can take years and significant financial resources. Achieving certifications, such as ISO 27001, adds to the substantial upfront costs and operational complexity, effectively deterring many potential competitors.
| Factor | Impact on New Entrants | Pure Storage Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements (R&D, Manufacturing) | Extremely High | Established infrastructure and ongoing R&D investment (e.g., hundreds of millions annually) |
| Economies of Scale | Challenging to achieve | Cost efficiencies and strong supplier relationships (e.g., 73.5% gross margin in 2023) |
| Intellectual Property | Risk of infringement, high licensing costs | Extensive patent portfolio (over 2,500 patents) protecting core technologies |
| Customer Loyalty & Trust | Difficult to build | High NPS (81-82), strong relationships with Fortune 500 clients |
| Regulatory Compliance | Costly and time-consuming | Established processes and expertise in meeting data privacy and security standards |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Pure Storage leverages a combination of financial statements, industry analyst reports, and proprietary market intelligence databases. This approach ensures a comprehensive understanding of competitive intensity, supplier leverage, and customer power within the data storage market.
