Prime Focus Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Prime Focus Bundle
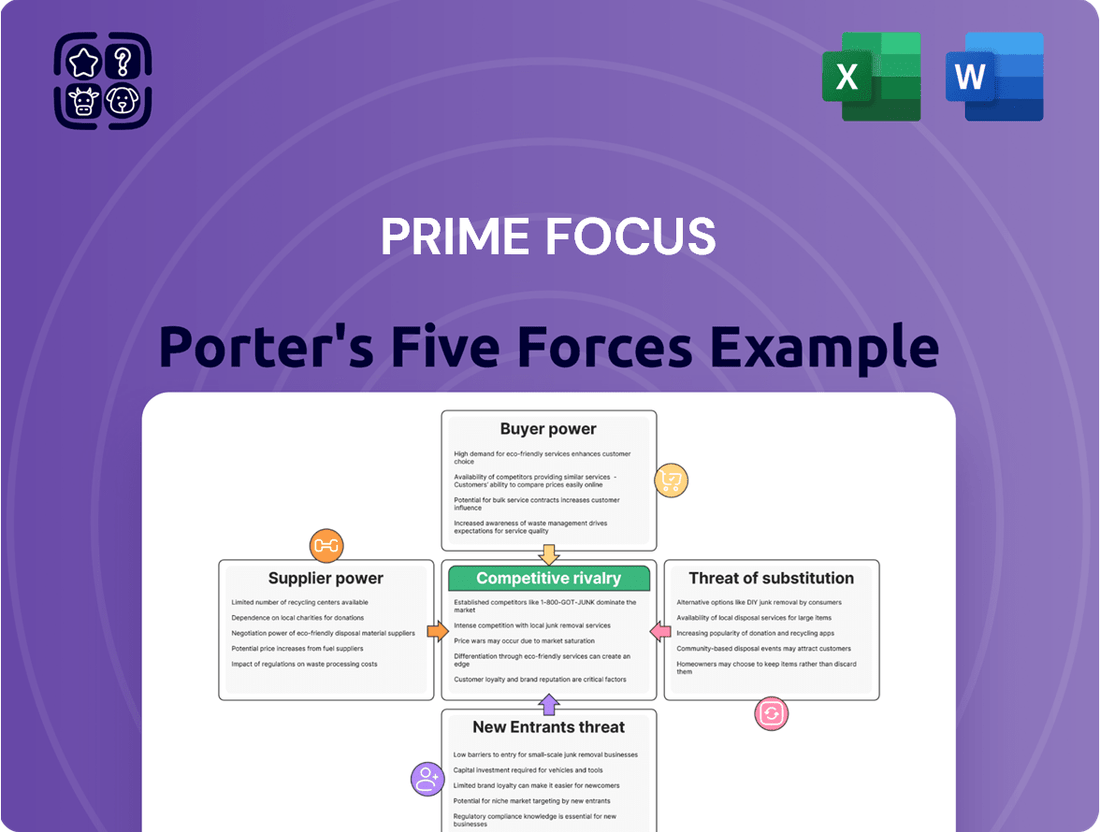
A Porter's Five Forces analysis offers a powerful lens to dissect the competitive landscape surrounding Prime Focus. Understanding the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the presence of substitutes is crucial for strategic planning.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Prime Focus’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Prime Focus's reliance on specialized talent, such as visual effects artists and animators, creates a vulnerability. The global scarcity of these highly skilled professionals, particularly those with expertise in complex, cutting-edge projects, empowers them to negotiate favorable terms. This can translate into increased salary demands and demands for enhanced working conditions, directly impacting Prime Focus's operational expenses.
In 2024, the demand for experienced VFX professionals outstripped supply in many key markets. For instance, reports indicated a shortage of over 10,000 skilled VFX artists globally, driving average salaries for senior roles up by an estimated 8-12% compared to 2023. This trend directly pressures companies like Prime Focus, as retaining and attracting top talent becomes a significant cost factor.
Companies heavily reliant on proprietary software like Autodesk or Adobe, and specialized hardware such as high-end render farms, face significant supplier bargaining power. These suppliers often hold strong market positions due to the critical nature of their offerings and the substantial costs involved in switching, granting them considerable leverage over pricing and licensing agreements.
As Prime Focus leans more into cloud infrastructure for content management and workflows, major players like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) wield significant influence. The sheer scale and specialized nature of their services, coupled with the substantial investment required for data migration and platform integration, can create switching costs for Prime Focus. This makes it challenging to move away from an established provider, granting these suppliers a degree of pricing and service leverage. In 2024, the global cloud computing market reached an estimated $600 billion, highlighting the dominance and financial clout of these providers.
Specialized Equipment and Technology Vendors
Suppliers of specialized and advanced technologies, such as those involved in motion capture, 3D scanning, and virtual production, wield significant bargaining power. This is due to the high cost and unique nature of their proprietary equipment and software, which are crucial for staying competitive in the visual effects industry.
Prime Focus relies heavily on these cutting-edge tools to produce high-quality visual effects and maintain its industry standing. This dependency means they may face higher prices or less favorable terms from these specialized vendors, impacting their operational costs and project timelines.
- High R&D Investment: Vendors invest heavily in research and development for these niche technologies, justifying premium pricing.
- Limited Alternatives: Few companies can replicate or offer comparable specialized equipment, reducing supplier competition.
- Critical Functionality: The technology provided is often essential for delivering key project deliverables, making supplier switching difficult.
Content Libraries and Stock Media
Prime Focus may need to license specialized content, footage, or audio for certain projects from stock media libraries. If a limited number of suppliers control highly sought-after or unique assets, they gain significant leverage. This concentration of supply allows these providers to dictate pricing and terms, directly affecting Prime Focus's project budgets and the ability to execute creative visions efficiently. For instance, the global stock footage market was valued at approximately $3.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow, indicating a significant spend area where supplier power can be substantial.
The bargaining power of suppliers in the stock media sector is amplified when they offer exclusive or difficult-to-replicate assets. In such scenarios, Prime Focus has fewer alternatives, making it more susceptible to price increases or less favorable licensing agreements. This dependence can impact profitability, especially for projects with tight margins or those requiring a unique visual style that relies on specific licensed materials. The increasing demand for high-quality, diverse visual content across various media platforms further solidifies the position of key content providers.
- Concentrated Supply: Suppliers of niche or high-demand stock media can exert significant pricing power.
- Unique Assets: Proprietary or exclusive content grants suppliers greater control over licensing terms.
- Cost Impact: Supplier leverage can increase project costs for Prime Focus, affecting profitability.
- Creative Constraints: Limited access to specific assets due to supplier power may restrict creative options.
Suppliers of specialized technology, such as high-end render farms and motion capture equipment, possess considerable bargaining power. This is due to the high research and development costs these vendors incur, the limited number of alternative suppliers, and the critical nature of their offerings for visual effects production. In 2024, the global market for specialized VFX hardware and software saw significant investment, with key players reporting substantial revenue growth driven by demand for cutting-edge production tools.
| Supplier Type | Key Factors Influencing Bargaining Power | Impact on Prime Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Specialized Technology Providers | High R&D investment, limited alternatives, critical functionality | Increased costs for essential production tools, potential project delays if terms are unfavorable |
| Cloud Service Providers (AWS, Azure, GCP) | Dominant market share, high switching costs, specialized service offerings | Leverage in pricing and service level agreements, potential for increased operational expenses |
| Talent Agencies/Individual High-Skilled Artists | Global scarcity of specialized VFX talent, increasing demand | Higher salary demands, increased recruitment costs, potential retention challenges |
| Stock Media Libraries (Niche/Exclusive Content) | Concentrated supply of unique assets, proprietary content | Higher licensing fees for specific assets, potential creative limitations if desired content is unavailable or too expensive |
What is included in the product
Uncovers the competitive forces impacting Prime Focus, including the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry.
Identify and mitigate competitive threats with a comprehensive breakdown of each force, allowing for targeted strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Prime Focus's primary clients are major film studios, television broadcasters, and advertising agencies. These entities are typically large, well-established organizations with considerable financial clout, granting them substantial bargaining power. For instance, in 2024, major Hollywood studios continued to consolidate their post-production needs, meaning fewer but larger clients were engaging with service providers like Prime Focus.
The sheer volume of work these clients can commission allows them to negotiate highly favorable terms. They can leverage their scale to demand competitive pricing and expedited turnaround times, particularly when awarding contracts for multiple projects or entire production slates. This ability to bundle services provides a significant advantage in price discussions.
This concentration of power among a few large customers means they can dictate terms and pricing more effectively. If Prime Focus were to refuse their demands, these studios and broadcasters have the capacity to shift their business to competitors, making it challenging for Prime Focus to resist significant price pressures or unfavorable contract clauses.
The media and entertainment sector's project-based procurement model significantly amplifies customer bargaining power. Clients, seeking visual effects (VFX) and post-production services, routinely solicit bids from numerous specialized studios for each new film or series. This practice directly fuels competition, allowing buyers to cherry-pick vendors based on cost-effectiveness and creative alignment.
This competitive bidding dynamic means customers can often negotiate favorable terms, pushing down prices for VFX and post-production work. For instance, in 2024, it's common for major studios to receive bids from a dozen or more VFX houses for a single blockbuster film, leading to intense price pressure on service providers.
Furthermore, the ability to switch vendors between projects without significant switching costs empowers customers. If a studio is dissatisfied with a particular vendor's pricing or quality on one project, they can easily opt for a different provider for the next, reinforcing their leverage in negotiations.
The visual effects and post-production industry, where companies like Prime Focus operate, is characterized by a significant number of established studios and an increasing number of new entrants. This robust vendor landscape directly empowers customers.
With numerous high-quality service providers available, clients possess substantial choice. This abundance of options diminishes their dependence on any single vendor, including Prime Focus, and makes it considerably easier for them to shift their business elsewhere if terms are not favorable.
For instance, the global VFX market was projected to reach approximately $60 billion by 2024, indicating a highly competitive environment with many firms vying for contracts. This competitive intensity naturally strengthens the bargaining power of the buyers.
In-house Production Capabilities
Some major clients, particularly large film studios, have the capability to develop or already possess their own in-house visual effects and post-production facilities. This potential for vertical integration directly diminishes their reliance on external service providers such as Prime Focus, thereby enhancing their bargaining leverage. For instance, major studios investing heavily in their own creative technology can shift significant portions of their workflow internally, reducing the volume of work outsourced to companies like Prime Focus.
This internal capability acts as a credible threat, forcing service providers to offer more competitive pricing and terms to retain business. It’s a strategic move that allows studios to control costs, timelines, and the creative direction of their projects more directly. The financial implications are substantial, as studios can potentially achieve cost savings and greater operational flexibility by managing these processes in-house.
- Reduced Dependency: Large customers can mitigate reliance on external VFX vendors.
- Vertical Integration: Studios investing in in-house capabilities gain more control.
- Negotiating Power: The threat of in-house production strengthens customer bargaining positions.
- Cost Control: Internal production can offer greater predictability in project expenses.
Demand for Cost-Effectiveness
Customers, especially those in budget-sensitive industries, are constantly seeking ways to reduce their operational expenses. This intense demand for cost-effectiveness directly influences their purchasing decisions, pressuring companies like Prime Focus to offer competitive pricing. For example, in 2024, many businesses across sectors like media and entertainment reported increased focus on optimizing their vendor spend to maintain profitability amidst economic uncertainties.
This drive for value means customers actively compare offerings and negotiate terms, seeking the best possible price for services. Prime Focus, therefore, must continuously innovate to deliver efficient solutions that meet these cost expectations. Failure to do so can lead to customers switching to competitors who can offer more budget-friendly alternatives.
The bargaining power of customers in this regard is magnified when:
- There are many alternative suppliers available.
- The cost of switching to a competitor is low for the customer.
- Customers are price-sensitive and have significant purchasing volume.
Prime Focus's customers, primarily major film studios and broadcasters, wield significant bargaining power due to their substantial size and purchasing volume. In 2024, industry consolidation meant fewer but larger clients, amplifying their ability to negotiate favorable terms and pricing. This concentration of demand allows them to leverage their scale, pushing down prices and demanding expedited services.
The competitive landscape further empowers buyers; with numerous VFX studios vying for contracts, clients can easily switch vendors, diminishing reliance on any single provider. The global VFX market, projected to reach approximately $60 billion by 2024, underscores this intense competition. Additionally, the growing trend of studios developing in-house capabilities creates a credible threat, enhancing customer leverage in negotiations and driving cost efficiencies for service providers.
| Factor | Impact on Prime Focus | 2024 Context |
|---|---|---|
| Client Size & Volume | High bargaining power due to large orders | Major studios consolidating post-production needs |
| Vendor Competition | Pressure to offer competitive pricing and terms | Global VFX market competition intensifying |
| Switching Costs | Low switching costs for clients increase leverage | Clients can easily shift to alternative VFX providers |
| In-house Capabilities | Threat of vertical integration by clients | Studios investing in internal VFX departments |
Full Version Awaits
Prime Focus Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces Analysis you will receive. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted report that will be available for immediate download upon purchase, ensuring no surprises and full usability. You're looking at the final, ready-to-use analysis, providing a thorough examination of competitive forces within an industry. What you're previewing is precisely what you'll get, enabling informed strategic decision-making.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The media and entertainment sector, especially in visual effects (VFX) and post-production, sees fierce competition among major global players. Companies like DNEG, Industrial Light & Magic (ILM), Framestore, and Weta Digital are constantly vying for prestigious projects and the industry's best creative minds. This intense rivalry means that studios must continually innovate and maintain high quality to secure lucrative contracts.
The industry grapples with substantial fixed costs, primarily driven by investments in cutting-edge technology, proprietary software licenses, and robust infrastructure. For instance, in the semiconductor manufacturing sector, the cost of a single advanced fabrication plant can exceed $20 billion.
Furthermore, the competitive landscape is shaped by the critical need to attract and retain highly skilled professionals, particularly in fields like AI development or specialized engineering. The average salary for a senior AI engineer in 2024, for example, can range from $180,000 to $250,000 annually, representing a significant operational expense.
These high fixed costs and talent acquisition expenses often compel companies to adopt aggressive pricing tactics. The objective is to secure contracts and ensure consistent utilization of their expensive assets, thereby spreading overheads and maintaining profitability.
This dynamic intensifies rivalry as firms compete fiercely for market share, often leading to price wars or innovative service bundling to capture demand and offset the burden of their substantial fixed investments.
Competitive rivalry in this sector is significantly fueled by the relentless pursuit of superior visual quality and groundbreaking innovative solutions. Companies, including Prime Focus, are locked in a battle to offer advancements like virtual production and real-time rendering, which redefine industry standards.
To stay ahead, continuous investment in research and development (R&D) is paramount for companies like Prime Focus. In 2024, the global market for visual effects (VFX) and post-production services was estimated to be worth over $60 billion, underscoring the high stakes and intense competition driven by technological advancement and creative excellence.
Talent development is equally critical; retaining and attracting skilled artists and technologists is a core differentiator. The ability to integrate efficient workflows also plays a crucial role in delivering value and maintaining a competitive edge in a rapidly evolving landscape.
Project-Based Nature and Bid Competition
The entertainment industry thrives on a project-by-project basis, making competitive rivalry a defining characteristic. Studios and production companies constantly engage in bidding wars for lucrative film, television, and advertising projects. This intense competition drives down prices and accelerates production schedules as companies strive to win contracts.
This dynamic leads to significant pressure on profit margins. For instance, in 2024, the average bid for a major streaming series often saw multiple studios offering highly competitive rates, sometimes sacrificing initial profitability for market share and talent acquisition. The constant need to secure new work means rivals are perpetually in a state of vying for opportunities, fostering an environment of aggressive pricing and demanding turnaround times.
- Project Bidding Intensifies Rivalry: Studios and production houses frequently compete through bidding for individual projects like films, TV series, and ad campaigns.
- Aggressive Pricing Strategies: The project-based nature leads to price wars, with companies offering lower bids to secure contracts.
- Compressed Timelines: Rivals often reduce production and delivery times to gain a competitive edge in the bidding process.
- Impact on Profitability: Constant bidding wars can squeeze profit margins as companies prioritize securing work over maximizing per-project earnings.
Market Growth and AI Integration
The visual effects market is poised for substantial growth, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate of 6.83% between 2025 and 2034. This expansion, however, is not without its competitive pressures.
The increasing adoption of artificial intelligence and machine learning is fundamentally altering the competitive landscape. Companies that successfully integrate AI into their content creation pipelines are better positioned to enhance efficiency and unlock novel creative avenues, thereby gaining a significant edge over rivals.
- Market Expansion: The global visual effects market is expected to see robust growth.
- AI Disruption: AI and machine learning are key disruptors, driving efficiency.
- Competitive Advantage: Early and effective AI adopters will likely outperform competitors.
- Innovation Focus: Companies prioritizing AI-driven innovation will be more competitive.
Competitive rivalry in the VFX and post-production sector is exceptionally high, driven by a concentrated group of global players vying for prestigious projects and top talent. This intense competition necessitates continuous innovation and quality to secure lucrative contracts. For instance, in 2024, the global visual effects market was valued at over $60 billion, highlighting the significant stakes involved.
Companies face pressure from aggressive pricing strategies and compressed timelines due to the project-based nature of the industry. Bidding wars for films and series can significantly impact profit margins, as seen in 2024 where major streaming series bids often involved highly competitive rates, sometimes prioritizing market share over immediate profitability.
The integration of advanced technologies like AI and machine learning is a key differentiator. Those who effectively adopt AI for enhanced efficiency and creative solutions gain a substantial competitive edge. The VFX market is projected to grow, with an estimated compound annual growth rate of 6.83% from 2025 to 2034, further intensifying the race for innovation.
| Key Competitors (VFX/Post-Production) | 2024 Market Estimate (USD) | Projected CAGR (2025-2034) | Talent Cost Factor (Senior AI Engineer 2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| DNEG, ILM, Framestore, Weta Digital | $60 Billion+ | 6.83% | $180,000 - $250,000 Annually |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Large film studios and broadcast networks are increasingly investing in and expanding their in-house production capabilities, particularly in areas like visual effects and post-production. This strategic shift allows them to maintain tighter control over their creative vision, safeguard valuable intellectual property, and manage production costs more effectively. By bringing these functions in-house, major players are reducing their dependence on external service providers, including companies like Prime Focus.
This trend is evident as major studios aim for greater vertical integration. For instance, in 2024, several leading studios announced significant investments in expanding their internal VFX pipelines and talent acquisition, signaling a move away from outsourcing for core production elements. This internal development directly challenges the market share of independent VFX houses by offering a more integrated and potentially cost-controlled solution for studios.
The rapid evolution of Artificial Intelligence, particularly generative AI, presents a significant threat of substitution for traditional VFX and animation services. These advanced AI tools can automate and streamline aspects of content creation that previously required extensive manual labor.
AI's capability in areas like image recognition, motion tracking, and automated rotoscoping directly substitutes for specialized human skills. For instance, AI can now perform complex rotoscoping tasks in a fraction of the time it would take a human artist, impacting demand for those specific roles.
By 2024, the market for AI in creative industries is projected to grow substantially. Some estimates suggest the AI content creation market could reach tens of billions of dollars, indicating a tangible shift in how visual content is produced.
This technological advancement means that companies can potentially achieve similar or even superior visual results with fewer human resources, thereby reducing the perceived value and necessity of certain outsourced VFX and animation workflows.
Clients often turn to freelance artists and boutique studios for smaller projects or specialized tasks, bypassing larger, integrated service providers. These alternatives can present a significant threat by offering more competitive pricing and highly personalized services, especially for unique or niche creative needs.
For instance, the freelance platform Upwork reported over 10 million active freelancers in 2023, indicating a vast pool of talent readily available to take on projects at potentially lower overhead costs than larger agencies. This accessibility means that for many creative needs, a fully integrated studio is not the only, or even the most cost-effective, option.
Boutique studios, by focusing on specific artistic styles or industry sectors, can also provide a level of expertise and tailored output that larger, more generalized firms might struggle to match. This specialization allows them to capture market segments looking for highly specific creative solutions, directly competing with the offerings of larger players.
Generic Software and Accessible Tools
The proliferation of sophisticated, yet accessible, software tools presents a significant threat of substitutes for specialized creative services. For instance, platforms like Adobe Creative Cloud, Canva, and even user-friendly video editors are increasingly empowering businesses and individuals to handle tasks such as graphic design, basic video editing, and social media content creation internally.
This trend lowers the barrier to entry for content production, allowing clients to bypass external agencies for simpler projects. Consider that in 2024, the global graphic design software market was valued at approximately $8.5 billion, with many of these solutions offering intuitive interfaces and pre-built templates that reduce the need for expert intervention.
- Lowered Skill Requirement: Many generic software packages now incorporate AI-powered features and drag-and-drop interfaces, significantly reducing the technical expertise previously needed for tasks like video editing or logo design.
- Cost Efficiency for Clients: Businesses can save on outsourcing costs by utilizing affordable or even free software for their in-house content creation needs, a particularly attractive option for small to medium-sized enterprises.
- Increased Self-Sufficiency: The availability of online tutorials and communities around these accessible tools further enhances clients' ability to perform tasks independently, directly substituting for external creative services.
Emerging Technologies (e.g., Virtual Production)
Emerging technologies, particularly in virtual production and real-time rendering, pose a significant threat of substitution for traditional post-production services. These new methodologies can streamline workflows, reducing the reliance on complex and time-consuming VFX processes that Prime Focus traditionally offers. For example, advancements in Unreal Engine and other real-time rendering platforms allow for the creation of sophisticated visual effects directly within the production pipeline, potentially bypassing the need for extensive post-production work.
This shift impacts Prime Focus by offering an alternative way to achieve similar visual outcomes. While virtual production often requires specialized vendors and initial investment, its ability to integrate visual effects seamlessly into live-action shooting can lead to cost and time savings for clients in the long run. This represents a direct substitute for certain aspects of Prime Focus's service offerings, particularly in areas where real-time integration is feasible.
The market is already seeing adoption of these technologies. For instance, the 2023 film *Avatar: The Way of Water* extensively utilized advanced virtual production techniques, showcasing the potential of these substitutes to deliver high-quality visuals. As these technologies mature and become more accessible, their ability to substitute for traditional VFX services will likely increase, putting pressure on existing service providers like Prime Focus.
The key concern for Prime Focus lies in the potential for these technological shifts to fundamentally alter client expectations and operational demands. A company that can offer integrated virtual production solutions might be perceived as a more efficient and cost-effective alternative to a studio that relies heavily on separate post-production phases. This necessitates Prime Focus to continually adapt and potentially integrate these new technologies into its own service portfolio to remain competitive.
The threat of substitutes in the media and entertainment industry is significant, impacting companies like Prime Focus by offering alternative ways to achieve similar creative outputs. This can range from in-house production capabilities by major studios to the burgeoning impact of AI and accessible software.
Major film studios are increasingly bringing VFX and post-production in-house, reducing reliance on external providers. For example, in 2024, several studios announced substantial investments in expanding their internal VFX pipelines, a direct challenge to independent VFX houses. This vertical integration allows for greater control over creative vision and costs.
AI technologies are rapidly developing, automating tasks previously done by human artists. Generative AI can now perform complex rotoscoping, for instance, in a fraction of the time, significantly reducing the need for specialized human skills. The AI content creation market is projected to reach tens of billions of dollars by 2024, highlighting this shift.
The accessibility of sophisticated software like Adobe Creative Cloud and Canva empowers clients to handle tasks like graphic design and basic video editing internally. The global graphic design software market, valued around $8.5 billion in 2024, offers intuitive interfaces and templates that lower the barrier to entry for content production, directly substituting for external creative services.
Entrants Threaten
Establishing a competitive visual effects and post-production studio requires a significant upfront capital investment. This includes acquiring high-end computing infrastructure, such as powerful render farms and workstations, which can easily run into millions of dollars. For instance, a mid-sized studio might invest upwards of $5 million in hardware alone.
Beyond hardware, the cost of specialized software licenses for industry-standard programs like Maya, Houdini, and Nuke adds considerably to the entry barrier. Annual licenses for these can amount to hundreds of thousands of dollars. Furthermore, equipping a facility with state-of-the-art motion capture stages, sound mixing suites, and screening rooms represents another substantial financial commitment, often costing millions more.
This high capital requirement significantly deters potential new entrants, as securing such extensive funding is a major hurdle. For example, in 2024, many aspiring VFX startups struggled to secure seed funding in the tens of millions, highlighting the difficulty of meeting these initial financial demands. This barrier effectively limits the number of new players entering the market.
The animation industry's demand for a highly specialized talent pool presents a significant barrier to new entrants. This includes artists with expertise in 2D and 3D animation, rigging, texturing, lighting, and compositing, alongside technical roles like software developers and pipeline TDs. For instance, a report in late 2024 highlighted a growing deficit in experienced VFX supervisors, a critical role for managing complex animation projects.
Attracting and retaining these niche professionals is a substantial challenge, often requiring competitive salaries and attractive benefit packages that startups may struggle to offer. Many studios are actively investing in training programs to address skill gaps, but the immediate need for seasoned talent remains a hurdle. The cost of acquiring this expertise can be prohibitive, effectively limiting the number of new players who can realistically compete.
Prime Focus benefits significantly from its deeply entrenched client relationships with major Hollywood studios and a robust portfolio of acclaimed visual effects work. These long-standing partnerships, built over years of consistent delivery, create a formidable barrier for newcomers. Without a similar history of successful collaborations and a tangible portfolio demonstrating expertise, new entrants find it exceedingly difficult to earn the trust necessary to secure high-profile projects.
Technological Complexity and Rapid Evolution
The media and entertainment services sector is characterized by its high technological complexity and a pace of evolution that demands constant adaptation. New entrants face a significant hurdle in acquiring and mastering advanced VFX tools, sophisticated animation techniques, and cutting-edge content management systems. For instance, the global animation software market was projected to reach $1.2 billion in 2024, highlighting the substantial investment required.
The rapid advancement in these areas means that existing technologies can quickly become obsolete, necessitating continuous research and development. A new player must not only have the initial capital for these technologies but also the agility to integrate emerging innovations to stay competitive. Failing to do so can render a new entrant's offerings outdated, impacting their ability to attract talent and secure contracts.
- Significant upfront investment in advanced technology is crucial.
- Rapid technological evolution requires continuous R&D and adaptation.
- Expertise in VFX, animation, and content management is a key barrier.
- The need to integrate new tools quickly is vital for market relevance.
Brand Reputation and Intellectual Property Protection
A strong brand reputation is a significant barrier for new entrants, especially when vying for substantial contracts where reliability is paramount. Companies with established trust, built over years of consistent quality, often have a distinct advantage. For instance, in the tech sector, a company like Apple has cultivated a brand loyalty that makes it difficult for newcomers to displace its market share, even with competitive offerings.
Protecting intellectual property (IP) also presents a formidable challenge for new businesses. The legal complexities and costs associated with safeguarding patents, trademarks, and proprietary information can be substantial. In 2024, the increasing sophistication of cyber threats further complicates secure content handling, requiring significant investment in robust security measures. For example, the global cybersecurity market was projected to reach over $200 billion in 2024, highlighting the expense involved in protecting digital assets.
- Brand loyalty acts as a moat, making it harder for new players to capture market share, particularly in industries with high customer switching costs.
- Intellectual property, such as patents and proprietary algorithms, can be a critical differentiator and a barrier to imitation by new entrants.
- Navigating IP law is costly; litigation and enforcement can drain resources, deterring smaller or less capitalized new companies.
- Data security and content handling are increasingly complex and expensive due to evolving threats, adding another layer of operational cost for potential new entrants.
The threat of new entrants in the visual effects and animation industry is significantly mitigated by the immense capital required for cutting-edge technology and specialized talent. For example, in 2024, the demand for high-end render farms and advanced animation software continued to escalate, with costs often exceeding millions of dollars for even mid-sized operations. This financial hurdle, coupled with the scarcity of experienced VFX artists and supervisors, as highlighted by industry reports from late 2024, creates a formidable barrier.
Established client relationships and a proven track record are also critical deterrents. Newcomers struggle to gain the trust of major studios without a history of successful, high-profile projects. Furthermore, the rapid pace of technological advancement necessitates continuous investment in R&D and adaptation, a challenge that can be prohibitive for new businesses. The global animation software market's projected growth to $1.2 billion in 2024 underscores the substantial ongoing investment needed to remain competitive.
Brand reputation and robust intellectual property protection further solidify the positions of existing players. The increasing cost and complexity of cybersecurity measures in 2024, with the market exceeding $200 billion, add another layer of expense for potential entrants aiming to secure sensitive digital assets. Consequently, the combined effect of these factors significantly limits the likelihood of new, impactful competitors emerging.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Prime Focus Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, drawing from industry-specific market research reports, company annual filings, and reputable financial news outlets.
