Paragon Care Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Paragon Care Bundle
Paragon Care's competitive landscape is shaped by several key forces, including the bargaining power of its buyers and the intensity of rivalry within the healthcare sector. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for strategic planning and identifying potential growth opportunities.
The threat of new entrants and the availability of substitute services also play a significant role in defining Paragon Care's market position. Each force presents unique challenges and opportunities that can impact profitability and market share.
The bargaining power of suppliers, particularly for specialized medical equipment and pharmaceuticals, can influence Paragon Care's cost structure and operational efficiency. This necessitates careful supplier relationship management.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Paragon Care’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Paragon Care's dependence on specialized medical equipment and consumables from a select group of manufacturers significantly amplifies supplier bargaining power. This is particularly true when these suppliers possess patents or exclusive distribution agreements for critical products, limiting Paragon Care's negotiation leverage on pricing and contract terms.
For instance, in the healthcare sector, highly specialized diagnostic equipment or unique surgical instruments often come with limited sourcing options. In 2024, the average lead time for critical medical devices in Australia saw an increase, reflecting potential supply chain constraints that further bolster supplier influence.
This dependency directly impacts Paragon Care's cost structure, potentially leading to elevated input expenses and a subsequent erosion of profit margins. The inability to secure alternative suppliers for essential, proprietary items means Paragon Care must often accept prevailing market prices, even if unfavorable.
Paragon Care faces substantial supplier power due to the high costs associated with switching providers for critical medical equipment. These expenses can encompass rigorous re-qualification processes, complex integration with existing IT and operational systems, and extensive staff training, making a change a significant undertaking.
These elevated switching costs inherently limit Paragon Care's negotiation leverage, effectively strengthening the position of current suppliers. Suppliers can leverage this situation to dictate pricing and terms, as the cost and disruption of finding and onboarding a new vendor are considerable deterrents.
The substantial investments made in established supplier relationships and their specialized equipment create a formidable barrier for Paragon Care to explore or transition to new vendors. This entrenches existing partnerships and further solidifies the bargaining power of these suppliers.
Supplier concentration significantly impacts bargaining power. When a few dominant suppliers control essential medical components or finished goods needed by Paragon Care, their collective leverage increases substantially. This can translate into less favorable pricing and supply terms for Paragon Care.
For example, in 2024, the global medical device market experienced supply chain challenges, particularly for specialized electronic components. Companies relying on a limited number of manufacturers for these critical inputs, like certain diagnostic imaging parts, found themselves facing price hikes and extended lead times. This scenario highlights how a concentrated supplier base can dictate terms.
Paragon Care must therefore proactively manage its relationships with these key suppliers. Ensuring strong partnerships and exploring alternative sourcing options where feasible are crucial strategies to mitigate the risks associated with a concentrated supplier market and maintain supply chain resilience.
Forward Integration Threat from Suppliers
Suppliers possessing robust brand recognition or substantial financial resources may threaten Paragon Care by integrating forward, meaning they could bypass distributors and sell directly to healthcare providers. This capability can pressure Paragon Care into accepting less favorable terms to secure its role in the supply chain.
This potential for direct sales by suppliers directly jeopardizes Paragon Care's revenue streams and could diminish its market share within the healthcare sector. For instance, a major medical device manufacturer with strong direct sales capabilities could capture a significant portion of the market previously served by distributors like Paragon Care.
- Forward Integration Threat: Suppliers with strong brands or deep pockets may bypass distributors like Paragon Care and sell directly to healthcare facilities.
- Impact on Terms: This threat can force Paragon Care to accept less favorable terms to maintain its position in the supply chain.
- Revenue and Market Share: Such a move would directly impact Paragon Care's revenue streams and market share.
Importance of Paragon Care to Suppliers
The relative importance of Paragon Care as a customer significantly shapes its bargaining power with suppliers. If Paragon Care constitutes a large percentage of a supplier's overall sales, that supplier will likely be more amenable to negotiating favorable pricing and terms to retain such a valuable client. This dynamic can lead to cost efficiencies for Paragon Care.
Conversely, if Paragon Care represents only a small fraction of a supplier's business, its influence over pricing and terms is considerably weaker. In such scenarios, suppliers may have less incentive to offer concessions, potentially increasing the cost of goods and services for Paragon Care. Understanding these supplier dependencies is crucial for managing procurement costs effectively.
- Supplier Dependence: The degree to which suppliers rely on Paragon Care for revenue directly impacts Paragon Care's leverage.
- Pricing Power: A significant customer like Paragon Care can negotiate better prices if it represents a substantial portion of a supplier's sales volume.
- Terms Negotiation: Favorable payment terms or delivery schedules are more achievable when Paragon Care is a key client for its suppliers.
Paragon Care's bargaining power with suppliers is significantly influenced by the concentration of the supplier market. When a few key suppliers dominate the provision of critical medical equipment or consumables, their collective leverage increases, potentially leading to less favorable pricing and terms for Paragon Care. For example, in 2024, the Australian healthcare sector experienced shortages of certain specialized medical components, with a notable increase in lead times from dominant suppliers, impacting procurement costs for entities like Paragon Care.
| Factor | Impact on Paragon Care | 2024 Data/Observation |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Limited choice enhances supplier leverage, potentially increasing costs. | Increased lead times for specialized medical components observed in the Australian market. |
| Switching Costs | High costs associated with changing suppliers limit Paragon Care's negotiation flexibility. | Re-qualification and system integration costs remain significant barriers. |
| Forward Integration | Suppliers may bypass distributors, directly impacting Paragon Care's revenue. | Major medical device manufacturers possess growing direct sales capabilities. |
| Customer Importance | Paragon Care's significance as a client influences supplier willingness to negotiate. | Smaller clients often face higher prices and less favorable terms compared to key accounts. |
What is included in the product
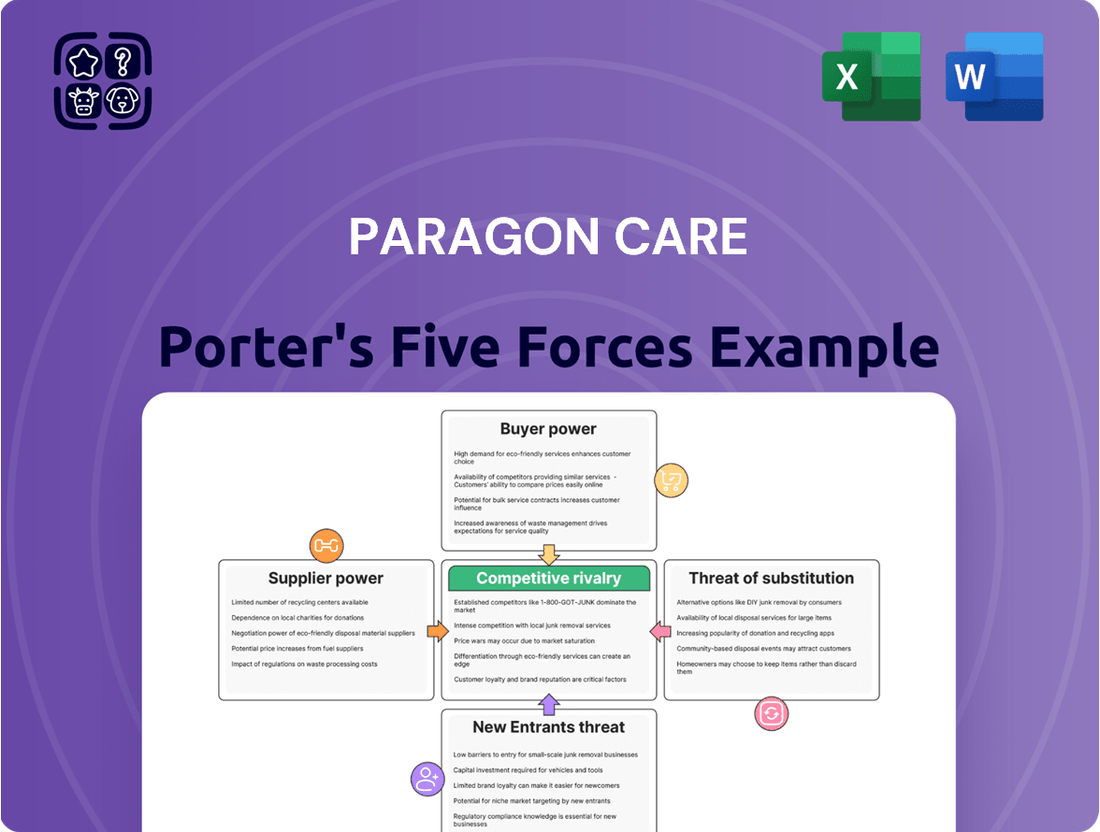
This analysis dissects Paragon Care's competitive environment, examining the bargaining power of suppliers and buyers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the healthcare sector.
Quickly identify and address the most impactful competitive pressures with a visual, easy-to-understand summary of each Porter's Five Forces element.
Customers Bargaining Power
Consolidated healthcare procurement, particularly by large hospital groups and aged care chains, significantly amplifies customer bargaining power. These entities, by pooling their purchasing needs, can negotiate from a position of considerable strength. For example, in 2024, major hospital networks often represent a substantial portion of a medical supplier's revenue, allowing them to demand favorable terms.
This consolidated buying power translates into tangible demands for suppliers like Paragon Care. Customers can push for significant bulk discounts, which directly impact supplier margins. Furthermore, they often dictate extended payment terms, affecting cash flow for the supplier. Specialized service level agreements are also common, adding complexity and cost to the supplier's operations.
The sheer scale of these consolidated buyers allows them to exert considerable pressure during pricing and contract negotiations. A single large customer's decision can represent a material change in a supplier's sales volume and profitability. This dynamic forces suppliers to be highly competitive on price and service to secure and retain these key accounts.
When basic medical consumables become standardized, customers, such as hospitals and clinics, gain significant bargaining power. This is because they can easily find multiple suppliers offering similar products. For instance, in 2024, many general-purpose items like gauze or saline solutions are readily available from numerous manufacturers, making it simple for purchasers to compare prices and terms.
This lack of product differentiation means that switching between suppliers is usually straightforward and low-cost for the customer. If a particular supplier's pricing or delivery schedule is unfavorable, a customer can readily shift their business to another provider without a substantial disruption. This ease of switching directly enhances the customer's leverage in negotiations.
The commoditization of these essential items naturally leads to a highly competitive market among suppliers. Companies often find themselves competing primarily on price for these common products. This intense price pressure can squeeze profit margins for manufacturers who don't have unique selling propositions for their standardized offerings.
Large healthcare providers, a key customer segment for Paragon Care, possess a significant bargaining power through their ability to self-service or backward integrate. This means they could potentially bring certain functions in-house, such as equipment maintenance or even direct procurement of medical supplies, thereby diminishing their dependence on external suppliers like Paragon Care. For instance, a major hospital network might invest in its own biomedical engineering department capable of handling complex equipment repairs, a service Paragon Care offers.
While complete backward integration, like a hospital manufacturing its own specialized medical devices, is often prohibitively complex and costly, the mere credible threat of such an action can be a potent bargaining tool. This leverage allows these large customers to negotiate more favorable terms, pricing, and service level agreements with Paragon Care. The potential for a large client to reduce its reliance on Paragon Care's offerings can compel the company to be more competitive.
Consider the scenario where a large hospital group, accounting for a substantial portion of Paragon Care's revenue, begins exploring direct import channels for high-volume consumables or even certain types of diagnostic equipment. This action directly challenges Paragon Care's role as an intermediary. In 2024, the trend towards greater operational efficiency and cost control in healthcare sectors globally has amplified the leverage of such large customers.
Price Sensitivity of Healthcare Budgets
Public and private healthcare providers in Australia, like Paragon Care's customers, operate under considerable budget pressures. This means they are very focused on the price of medical equipment and supplies. For instance, in 2024, Australian government healthcare spending was projected to exceed $100 billion, with significant portions allocated to procurement.
This high price sensitivity gives healthcare providers substantial bargaining power. They can, and do, negotiate hard for lower prices and demand more cost-effective solutions from suppliers like Paragon Care. This forces suppliers to be competitive and innovative in their pricing strategies.
Paragon Care needs to clearly show the value and efficiency of its offerings to win business in this cost-conscious market. Demonstrating how their products or services can lead to long-term savings or improved patient outcomes, beyond just the initial cost, is crucial for securing contracts.
- High Budget Constraints: Healthcare providers face ongoing pressure to manage costs, making price a primary factor in purchasing decisions.
- Negotiating Power: Customers leverage their budget sensitivity to demand lower prices and more competitive terms.
- Demand for Value: Suppliers must prove economic benefits and operational efficiencies to secure and retain business.
- Competitive Landscape: Paragon Care competes in an environment where demonstrating cost-effectiveness is key to market access.
Availability of Alternative Suppliers
The availability of numerous credible alternative suppliers for comparable healthcare equipment and services across Australia and New Zealand significantly bolsters customer bargaining power. This competitive landscape allows customers, such as hospitals and clinics, to readily solicit multiple bids and switch providers if they find Paragon Care's pricing or service offerings unsatisfactory. For instance, in 2024, the Australian medical equipment market saw continued growth with new entrants and established players vying for market share, creating a dynamic environment for purchasers.
This ease of switching puts pressure on Paragon Care to remain competitive in both its service delivery and pricing strategies. Customers can leverage the presence of competitors to negotiate better terms, potentially impacting Paragon Care's profit margins. The ability to compare offerings from various vendors means that customers are less reliant on any single supplier, thereby increasing their leverage in negotiations.
- Supplier Competition: A broad base of alternative suppliers in the ANZ healthcare sector limits customer lock-in.
- Price Sensitivity: Customers can easily compare prices, forcing suppliers like Paragon Care to offer competitive rates.
- Switching Costs: Low switching costs for customers further empower them to seek better value elsewhere.
- Market Dynamics: The increasing number of specialized healthcare technology providers in 2024 provides more options for sophisticated buyers.
The bargaining power of customers for Paragon Care is amplified by the trend towards consolidated procurement within the healthcare sector. Large hospital groups and aged care chains, by pooling their purchasing needs, can negotiate from a position of considerable strength in 2024. For instance, major hospital networks often represent a significant portion of a medical supplier's revenue, enabling them to demand favorable terms, including substantial bulk discounts and extended payment terms.
Preview Before You Purchase
Paragon Care Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Paragon Care Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of the competitive landscape within the healthcare sector. The document you see here is precisely what you will receive—a fully formatted and ready-to-use strategic tool. It delves into the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors, providing actionable insights for strategic decision-making. This is the exact, professionally crafted analysis you'll download immediately after purchase, ensuring no surprises and immediate utility for your business planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Australian and New Zealand healthcare equipment and services market features a diverse competitive landscape, encompassing both large multinational corporations and numerous smaller, specialized local providers. This broad spectrum of players, each with distinct capabilities and strategic approaches, significantly heightens the level of competition.
Paragon Care operates within this intensely competitive environment, facing rivals that range from global giants with extensive product portfolios to niche players offering highly specialized services. The sheer volume and variety of competitors mean that maintaining market share requires continuous adaptation and a strong focus on unique value propositions.
For instance, the medical device sector alone sees competition from companies like Cochlear, ResMed, and Fisher & Paykel Healthcare, alongside many smaller, focused distributors. This means Paragon Care must consistently innovate its offerings and service delivery to stay ahead and differentiate itself in a crowded marketplace.
The healthcare sector, including aged care and specialized medical services where Paragon Care is active, typically sees consistent growth. However, exceptionally high growth rates can indeed draw in new entrants, potentially amplifying competitive rivalry. In 2023, the Australian healthcare market was valued at approximately AUD 130 billion, with projections indicating continued expansion driven by an aging population and technological advancements.
Conversely, if industry growth slows, existing players often intensify their competition to capture a larger share of a more limited market. Paragon Care navigates a landscape characterized by steady demand, but this is increasingly met by a growing number of providers, leading to heightened competitive pressures as companies vie for customers and resources.
The ability of competitors to make their offerings stand out is a key factor in how intense the rivalry is. When products and services are very alike, companies often compete mainly on price. Paragon Care attempts to differentiate itself by offering a full suite of services, from initial setup to ongoing upkeep and repairs.
This integrated approach aims to provide greater value and convenience to customers, setting Paragon Care apart from rivals who might only offer a piece of the solution. For instance, in the Australian healthcare sector in 2024, many providers are focusing on specialized equipment and associated support packages.
However, if rivals can easily copy these service components, the differentiation advantage diminishes, and competitive pressure, particularly on pricing, remains significant. The ease with which competitors can match or surpass these service offerings directly influences the level of rivalry within the market.
High Exit Barriers
High exit barriers significantly shape competitive rivalry in the healthcare equipment supply sector. The substantial capital outlay for specialized equipment, extensive inventory, and dedicated service infrastructure, coupled with the need for trained personnel, makes exiting the market a costly endeavor. This financial commitment discourages companies from leaving, even when market conditions are unfavorable, forcing them to remain and compete intensely.
Consequently, the industry often experiences sustained and vigorous competition as firms strive to maintain market share rather than incur the penalties of withdrawal. For instance, companies like GE Healthcare and Siemens Healthineers have invested billions in their imaging and diagnostic equipment portfolios, creating deep entrenchment. This significant investment acts as a powerful deterrent to exit, ensuring ongoing rivalry.
- Significant Capital Investment: Companies in healthcare equipment supply face substantial upfront costs for machinery, inventory, and specialized workforce training, creating a high financial threshold for exit.
- Discourages Withdrawal: The sunk costs associated with these investments make leaving the market economically unviable, leading firms to persevere through challenging periods.
- Intensified Rivalry: High exit barriers foster a competitive environment where companies are compelled to remain engaged and fight for market position, rather than cease operations.
- Example of Entrenchment: Major players like Philips, with its extensive medical device offerings, have long-term commitments that solidify their presence and contribute to persistent competitive pressures.
Intensity of Price Competition
The healthcare sector, where Paragon Care operates, often sees intense price competition, especially for commoditized services or products. When customers, like hospitals or aged care facilities, focus primarily on the lowest cost, it forces providers into aggressive pricing to win business. This can significantly squeeze profit margins for all players. For instance, in 2024, the Australian private hospital sector experienced heightened scrutiny on pricing for elective surgeries, with insurers pushing for greater cost efficiencies.
Paragon Care faces the challenge of navigating this price-sensitive environment. To remain competitive, the company must consider how its pricing strategies impact its ability to maintain healthy profit margins. This requires a careful balancing act. Simply lowering prices across the board could undermine profitability and limit the resources available for crucial investments.
- Price Sensitivity: Customers in the healthcare sector, particularly government bodies and large private insurers, often prioritize cost savings, leading to downward pressure on prices.
- Margin Erosion: A strong focus on price competition can lead to reduced profitability for all industry participants, including Paragon Care, as they are compelled to offer lower prices to secure contracts.
- Value-Added Services: Paragon Care needs to differentiate itself by offering value beyond just price, such as superior service quality, specialized equipment, or integrated solutions, to justify potentially higher costs.
- Strategic Pricing: The company must develop sophisticated pricing strategies that balance market competitiveness with the need to maintain healthy profit margins and fund future growth and innovation.
The competitive rivalry within the Australian healthcare equipment and services sector is significant, fueled by a market populated by both large global players and numerous specialized local firms. Paragon Care navigates this intense landscape where differentiation is key to market share, often involving a balance between price and value-added services.
The market's steady growth, projected to continue due to an aging population and technological advancements, attracts new entrants, further intensifying competition. For instance, the Australian healthcare market's value, exceeding AUD 130 billion in 2023, signals ongoing opportunities but also increased rivalry as more companies seek to capture market share.
Companies like Paragon Care must differentiate through comprehensive service offerings, such as end-to-end equipment management, to stand out. However, the ease with which competitors can replicate service components means that price remains a critical factor, potentially impacting profit margins if not managed strategically.
High exit barriers, stemming from substantial capital investments in specialized equipment and trained personnel, compel companies to remain in the market, leading to sustained and vigorous competition. This entrenchment, exemplified by major players like GE Healthcare and Siemens Healthineers, ensures that rivalry remains a constant challenge for all participants.
SSubstitutes Threaten
Healthcare facilities can opt for in-house maintenance and refurbishment of medical equipment, directly substituting Paragon Care's service offerings. This is especially true for simpler or older equipment where the cost-benefit analysis favors internal solutions. For instance, a hospital might invest in training its biomedical engineers to handle routine servicing, thereby reducing reliance on external providers like Paragon Care. This in-house capability directly eats into Paragon Care's potential service revenue streams.
Another significant substitute threat comes from third-party vendors specializing in refurbished medical equipment. These vendors often offer pre-owned, but fully functional, equipment at a lower price point than new units. This can be a compelling alternative for healthcare providers looking to manage capital expenditure, especially when acquiring equipment that doesn't require the absolute latest technology. For example, a diagnostic imaging center might find a refurbished MRI machine a viable and cost-effective substitute for a new one, impacting Paragon Care's new equipment sales.
Advances in medical technology frequently introduce alternative treatment methods that can diminish reliance on existing equipment. For instance, the rise of minimally invasive techniques or new drug therapies could potentially reduce the demand for certain surgical or diagnostic equipment that Paragon Care provides. The company's strategic imperative is to stay abreast of these technological shifts to ensure its product offerings remain relevant and competitive in the evolving healthcare landscape.
Large hospital networks and purchasing groups are increasingly exploring direct procurement of medical devices and consumables from manufacturers. This trend bypasses traditional distribution channels, presenting a significant substitute threat to companies like Paragon Care. For example, some major US hospital systems have begun negotiating directly with device makers, potentially reducing their reliance on distributors for a portion of their needs.
Telehealth and Remote Monitoring Solutions
The increasing adoption of telehealth and remote patient monitoring presents a significant threat of substitutes for Paragon Care. These digital solutions can directly replace the need for certain in-person diagnostic and monitoring equipment that Paragon Care traditionally supplies to healthcare facilities.
As healthcare delivery models evolve to embrace virtual consultations and at-home patient oversight, the demand for a portion of physical medical devices may diminish. For instance, a patient whose vital signs are continuously monitored via a wearable device at home might not require regular in-clinic check-ups involving standalone monitoring equipment.
This trend necessitates that Paragon Care actively adapts its product and service portfolio to integrate with or complement these burgeoning digital health solutions. Ignoring this shift could lead to a decline in market share as healthcare providers increasingly opt for integrated remote care platforms.
By mid-2024, the global telehealth market was projected to reach over $200 billion, highlighting the substantial and growing nature of this substitute threat. Paragon Care's strategic response will be crucial in navigating this evolving healthcare landscape.
- Telehealth adoption: Growing patient and provider comfort with virtual care.
- Remote monitoring devices: Wearables and home-based sensors reduce in-clinic visits.
- Market shift: Demand potentially moving from physical equipment to integrated digital platforms.
- Paragon Care's challenge: Need to offer solutions that align with or enhance remote care models.
Generic or Off-Patent Consumables
The threat of generic or off-patent consumables significantly impacts Paragon Care's market position. For many standard medical supplies, customers can easily find lower-cost alternatives once patents expire or when generic versions become available. This availability of substitutes directly pressures Paragon Care's pricing power and profit margins on these particular product lines.
To counter this, Paragon Care needs to focus on delivering value that extends beyond the basic functionality of the consumable itself. This could involve superior service, reliability, or integrated solutions that make switching to a generic option less attractive for healthcare providers. For instance, if Paragon Care offers efficient inventory management or specialized training alongside its consumables, these added benefits can justify a premium price, even in the face of cheaper alternatives.
Consider the market for basic surgical gloves. While many off-patent options exist at significantly lower price points, a provider might choose Paragon Care if they offer guaranteed stock availability, faster delivery times, or a bundled service package that streamlines their procurement process. This differentiation is crucial when the core product itself faces intense competition from generics.
- Generic Availability: Many medical consumables, particularly those used in high volumes, have expired patents or readily available generic equivalents.
- Price Pressure: The presence of these low-cost substitutes forces companies like Paragon Care to compete on price for these specific items, potentially eroding margins.
- Value Beyond Product: Paragon Care must highlight and deliver added value through services, reliability, or integrated solutions to differentiate from generic offerings.
- Customer Loyalty: Building loyalty through superior customer experience and support can mitigate the impact of price-driven decisions by customers opting for cheaper substitutes.
The threat of substitutes for Paragon Care is multifaceted, encompassing in-house capabilities, refurbished equipment, technological advancements, direct procurement, and the burgeoning telehealth sector. Each of these substitutes directly challenges Paragon Care's traditional revenue streams by offering alternative solutions that can be more cost-effective or better aligned with evolving healthcare delivery models.
For instance, the global telehealth market's projected growth to over $200 billion by mid-2024 underscores the significant shift towards digital health solutions, potentially reducing demand for certain physical medical equipment. Similarly, the availability of generic consumables after patent expiry introduces intense price pressure on Paragon Care's product lines, necessitating a focus on service and added value to retain customers.
| Substitute Area | Description | Impact on Paragon Care | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| In-house Maintenance | Healthcare facilities servicing their own equipment. | Reduces demand for Paragon Care's service revenue. | Hospitals training biomedical engineers for routine servicing. |
| Refurbished Equipment | Third-party vendors offering pre-owned equipment. | Offers lower-cost alternatives for capital expenditure. | Diagnostic centers purchasing refurbished MRI machines. |
| Telehealth & Remote Monitoring | Digital solutions replacing in-person care. | Diminishes demand for certain physical monitoring devices. | Wearable devices reducing need for in-clinic vital sign checks. |
| Generic Consumables | Off-patent or generic versions of medical supplies. | Creates price pressure and erodes margins on specific products. | Lower-cost surgical gloves compared to branded options. |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the healthcare equipment supply market, the domain of companies like Paragon Care, demands a considerable financial outlay. This isn't just about buying stock; it involves significant investment in warehousing facilities, specialized transportation that can handle sensitive medical equipment, and building a reliable service network to support these products. For instance, setting up a national distribution network for medical devices can easily run into tens of millions of dollars.
Beyond the physical infrastructure, new players must also allocate substantial funds towards navigating the complex regulatory landscape. Obtaining necessary certifications, adhering to quality assurance standards, and ensuring product traceability are all costly but essential steps. These high upfront capital requirements act as a formidable barrier, effectively discouraging many potential new entrants from challenging established companies.
The healthcare industry, particularly in Australia and New Zealand, presents a formidable challenge for new companies due to rigorous regulatory hurdles. Navigating the complex web of product approvals, licensing, and adherence to stringent health and safety standards demands substantial investment in time and resources. This intricate regulatory landscape significantly deters potential new entrants, creating a robust barrier.
Failure to comply with these regulations can result in severe penalties, including hefty fines and outright exclusion from the market, further amplifying the threat of new entrants. For instance, therapeutic goods must undergo rigorous evaluation by the Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) in Australia, a process that can take many months or even years, depending on the product's complexity and novelty.
In 2024, the TGA continued to emphasize patient safety, leading to ongoing scrutiny of medical devices and pharmaceuticals. Companies seeking to enter the market must demonstrate a deep understanding of these evolving compliance requirements, which often necessitate specialized legal and regulatory expertise, adding to the upfront cost and complexity of market entry.
Paragon Care benefits significantly from deeply entrenched customer relationships, particularly with hospitals and aged care facilities. These long-standing ties, forged through consistent reliability and high-quality service, present a formidable barrier to new entrants. Building comparable trust and a strong reputation in the healthcare sector is a time-consuming and capital-intensive endeavor.
The loyalty of healthcare providers is a crucial factor; switching costs for essential medical supplies and services are often substantial, encompassing not only financial outlays but also the disruption of established operational workflows and patient care protocols. This inherent stickiness in customer relationships makes it challenging for newcomers to gain immediate traction and market share.
For instance, in 2023, Paragon Care reported that a significant portion of its revenue was derived from repeat business and long-term contracts, underscoring the strength of these existing relationships. New competitors would need to offer demonstrably superior value or a unique proposition to entice clients away from proven, trusted suppliers.
Need for Specialized Technical Expertise and Service Networks
The medical equipment industry, including companies like Paragon Care, demands a high level of specialized technical expertise for installation, maintenance, and ongoing servicing. This isn't something easily replicated; it requires significant investment in training and development to build a skilled workforce capable of handling complex machinery.
Establishing a comprehensive service network is another substantial barrier. New entrants would face considerable challenges in creating the widespread infrastructure and logistical capabilities that established players, such as Paragon Care, have cultivated over time. For instance, Paragon Care’s extensive network ensures rapid response times, a critical factor for healthcare providers.
The sheer cost and time involved in replicating these specialized technical skills and service networks present a formidable hurdle for potential new competitors.
- Specialized Expertise: High-level technical knowledge is essential for servicing advanced medical devices.
- Service Networks: Widespread, efficient service infrastructure is a significant competitive advantage.
- Barriers to Entry: Building these capabilities from the ground up is both costly and time-consuming.
- Paragon Care's Advantage: Existing infrastructure and skilled workforce make it difficult for new entrants to compete directly.
Economies of Scale and Scope
Established players like Paragon Care leverage significant economies of scale, particularly in procurement and logistics, which drives down their per-unit operating costs. For instance, a large healthcare provider might negotiate bulk discounts on medical supplies, a feat difficult for a new, smaller entrant to replicate immediately.
Paragon Care also benefits from economies of scope, offering a diverse portfolio of healthcare services and products. This breadth allows them to cross-sell and bundle offerings, creating a more compelling value proposition for customers. A new entrant would struggle to match this comprehensive service suite from inception, facing higher initial investment costs to achieve similar market penetration.
- Economies of Scale: Lower unit costs for established firms through bulk purchasing and optimized operations.
- Economies of Scope: Reduced costs by offering a wider range of related products and services.
- Barriers to Entry: New entrants face challenges in matching the cost efficiencies and product breadth of incumbents like Paragon Care.
- Competitive Disadvantage: New companies must invest heavily to overcome the cost and service advantages held by established market participants.
The threat of new entrants for Paragon Care is generally low, primarily due to the significant capital investment required and the stringent regulatory environment in the healthcare sector. Established players benefit from strong customer loyalty and specialized technical expertise.
New companies entering the healthcare equipment supply market face substantial capital requirements for infrastructure, distribution, and regulatory compliance, as evidenced by the tens of millions of dollars needed for a national distribution network. In 2024, regulatory bodies like Australia's Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) continued to emphasize patient safety, requiring rigorous product approvals and adherence to evolving compliance standards, adding to the cost and complexity for newcomers.
Paragon Care's deeply entrenched customer relationships with hospitals and aged care facilities, built on years of reliability, present a formidable barrier. The switching costs for essential medical supplies are often high, involving not just financial outlays but also operational disruption. In 2023, a significant portion of Paragon Care's revenue came from repeat business, highlighting the strength of these existing ties.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Paragon Care's Position |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High upfront investment for infrastructure, distribution, and regulatory compliance. | Discourages market entry due to significant financial outlay. | Established infrastructure and operational scale. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex product approvals, licensing, and health/safety standards. | Requires substantial time, resources, and specialized expertise. | Proficient navigation of TGA and similar bodies. |
| Customer Loyalty & Switching Costs | Long-standing relationships and operational integration with clients. | Challenging to gain market share due to established trust and disruption aversion. | High percentage of revenue from repeat business and long-term contracts. |
| Specialized Technical Expertise & Service Networks | Need for skilled workforce and widespread service infrastructure. | Costly and time-consuming to replicate existing capabilities. | Extensive, cultivated service network and skilled personnel. |
| Economies of Scale & Scope | Cost advantages from bulk purchasing and a diverse product/service portfolio. | New entrants struggle to match cost efficiencies and comprehensive offerings. | Leverages procurement discounts and cross-selling opportunities. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Paragon Care is built upon comprehensive data from publicly available financial reports, industry-specific market research, and reputable healthcare sector publications. We also incorporate insights from regulatory filings and analyst reports to provide a robust understanding of the competitive landscape.
