Ipsos Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Ipsos Bundle
Understand the core dynamics shaping Ipsos's competitive landscape with this Porter's Five Forces Analysis. We've outlined the key pressures, from the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers to the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the industry. This foundational understanding is crucial for any strategic planning or investment decision related to Ipsos.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Ipsos’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of suppliers for Ipsos is a key factor in its operational costs and profitability. Primary suppliers include data collection service providers, crucial technology vendors for survey platforms and analytics software, and panel providers who grant access to specific demographic groups. The influence these suppliers wield can differ substantially, largely depending on their unique specialization and the ease with which Ipsos can find alternative sources.
For example, specialized panel providers who possess exclusive access to hard-to-reach or niche audiences often command greater bargaining power. This is because Ipsos may have fewer options for obtaining that specific data, making these suppliers more indispensable. In 2024, the market for specialized data panels remained competitive, but providers with unique methodologies or deep access to certain consumer segments continued to hold leverage.
Technology vendors for Ipsos's survey platforms and analytics software also represent a significant supplier group. The power of these vendors is influenced by the proprietary nature of their technology and the cost and complexity of switching to a different provider. As of mid-2025, many of these technology solutions are deeply integrated into Ipsos's workflows, potentially increasing switching costs and thus supplier leverage.
Suppliers of advanced technology, particularly in AI and machine learning, are increasingly influential for companies like Ipsos. The demand for sophisticated data analysis tools, such as specialized qualitative software, amplifies this trend. Leading providers of these cutting-edge solutions are finding themselves in a stronger negotiating position.
Ipsos's strategic investment in generative AI and similar platforms highlights a growing dependence on these advanced technologies. This reliance means that the bargaining power of top AI solution providers is likely to grow. For instance, the global AI market was projected to reach over $500 billion in 2024, showcasing the significant economic clout of these technology vendors.
Human capital, especially skilled researchers, data scientists, and strategists, acts as a crucial supplier of expertise for Ipsos. The intense demand for specialized talent in fields such as advanced analytics, neuromarketing, and digital ethnography significantly boosts the bargaining power of these individuals. This can directly influence Ipsos's operational costs and its ability to maintain cutting-edge capabilities.
Supplier Power 4
While the market for general consumer data providers appears fragmented, certain entities can still exert significant bargaining power. This is particularly true if they possess unique, high-quality, or real-time datasets that are challenging for competitors to replicate. Ipsos, as a research and insights firm, heavily relies on the availability of comprehensive and compliant consumer data to deliver its services, making supplier relationships critical.
For instance, in 2024, the global market for data analytics and business intelligence solutions was projected to reach over $35 billion, highlighting the immense value placed on data. Companies like Ipsos need reliable data sources to maintain their competitive edge. The ability of a data provider to offer specialized demographic segments, behavioral patterns, or predictive analytics can elevate their standing and influence pricing or contract terms.
- Data Uniqueness: Providers with proprietary or difficult-to-acquire data sets hold more sway.
- Data Quality and Compliance: High-quality, accurate, and GDPR-compliant data is essential and commands premium.
- Supplier Concentration: Even with many providers, if a few dominate niche data areas, their power increases.
- Switching Costs: The effort and expense involved in changing data providers can make existing suppliers more powerful.
Supplier Power 5
The bargaining power of suppliers in the market research industry is facing a notable shift, particularly with the rise of automation and synthetic data. As companies like Ipsos increasingly leverage AI and machine learning for data collection and analysis, the demand for traditional human-powered fieldwork may diminish. This trend suggests a potential recalibration of power, moving from established data collection agencies to the technology providers enabling these new methods. For instance, investments in AI for data analysis are projected to grow significantly; Grand View Research estimated the global AI in market research market size at USD 3.4 billion in 2023, with expectations of substantial expansion.
This technological evolution can impact supplier power in several ways. Suppliers who can offer advanced automated data solutions, such as sophisticated synthetic data generation platforms or AI-driven analytics tools, are likely to gain leverage. Conversely, traditional suppliers of human enumerators or focus group moderators might see their power wane if they cannot adapt or integrate technological solutions. The increasing efficiency and cost-effectiveness of automated processes could put pressure on pricing for traditional services.
- Automation's Impact: The increasing adoption of AI and automation in market research is reducing reliance on traditional human data collection methods.
- Shift in Power: Bargaining power is likely to shift from traditional field service suppliers to technology providers offering automated solutions.
- Data Generation: Synthetic data generation, powered by AI, offers a scalable and potentially cost-effective alternative to human-collected data.
- Market Growth: The global AI in market research market was valued at approximately USD 3.4 billion in 2023, indicating a strong trend toward technological integration.
The bargaining power of Ipsos's suppliers is significantly influenced by data uniqueness, quality, and concentration within niche areas. High-quality, compliant data is essential, and providers offering proprietary or hard-to-acquire datasets, especially those with specialized demographic access, hold considerable leverage. Switching costs associated with integrating new data sources also strengthen the position of incumbent suppliers.
Technology vendors, particularly those providing advanced AI and analytics solutions, are increasingly powerful due to the integral role their proprietary technologies play in Ipsos's operations. The significant global market for AI solutions, projected to exceed $500 billion in 2024, underscores the economic influence of these specialized tech suppliers.
| Supplier Type | Key Influencing Factors | Impact on Ipsos |
|---|---|---|
| Specialized Panel Providers | Exclusive access to niche demographics, unique methodologies | Higher costs, potential for essential data acquisition |
| Technology Vendors (AI/Analytics) | Proprietary technology, integration complexity, market growth | Increased reliance, potential for price increases |
| Data Scientists/Researchers | Demand for specialized skills (AI, neuromarketing) | Higher labor costs, talent acquisition challenges |
What is included in the product
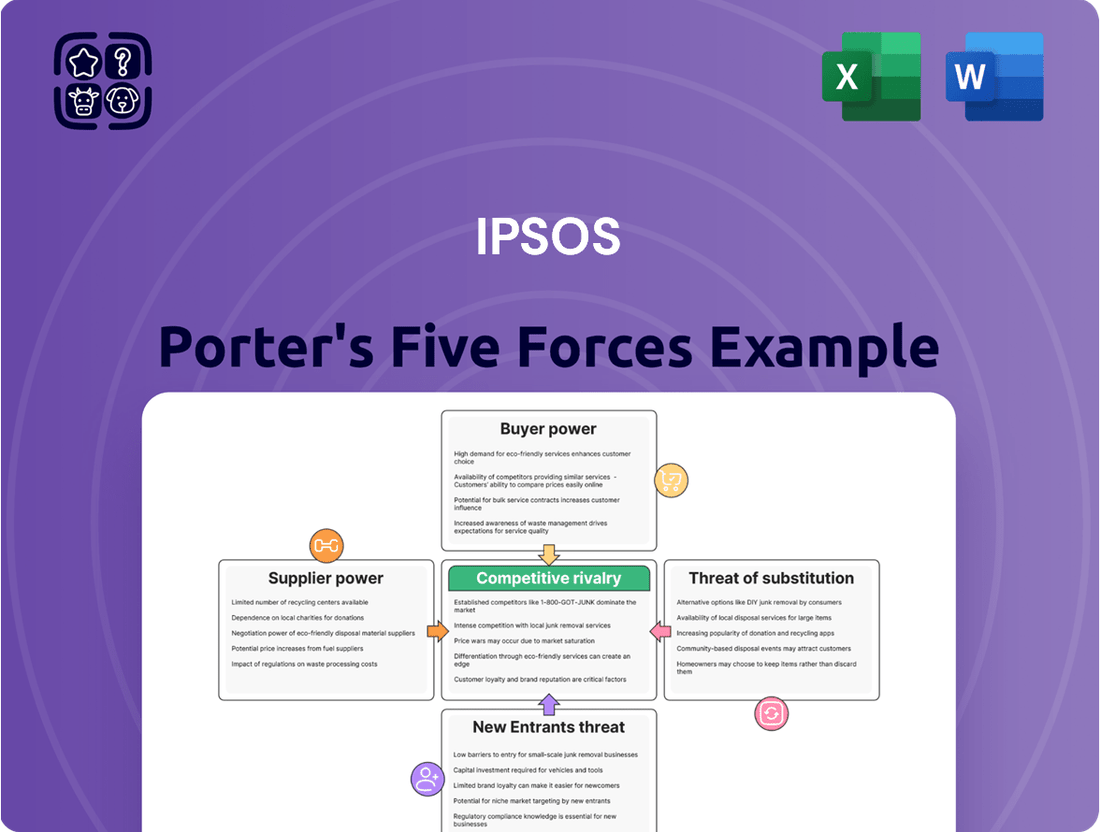
This analysis dissects the competitive forces impacting Ipsos, examining industry rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threats from new entrants and substitutes to inform strategic decision-making.
Quickly identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each of Porter's five forces in an intuitive, actionable format.
Customers Bargaining Power
Ipsos caters to a wide array of clients, from businesses and governments to various organizations. These clients often require highly customized research and practical advice, which can give them leverage.
Major corporate clients and government entities frequently wield considerable bargaining power. This is primarily due to the substantial volume of work they can offer and their capacity to select from numerous international research providers, potentially driving down service costs.
For instance, in 2024, the global market research industry saw continued consolidation, with larger clients having more options than ever. A significant portion of Ipsos's revenue can be tied to a relatively small number of key accounts, amplifying their influence.
This power is further enhanced when clients have the internal expertise or the ability to conduct some research themselves, or when they can easily switch to a competitor offering similar services at a lower price point.
Customers are gaining more power due to readily available DIY market research tools and the rise of in-house research capabilities. This trend, particularly for straightforward survey needs, can lessen their reliance on full-service agencies, thereby enhancing their bargaining leverage. For instance, the global market for survey software was projected to reach over $3.5 billion by 2024, indicating a significant shift towards self-service solutions.
Customers, especially those leveraging AI and automation, are demanding faster, more efficient, and clearly ROI-driven insights from market research firms like Ipsos. This trend places significant pressure on Ipsos to deliver quicker turnaround times and provide access to real-time data. For instance, in 2024, many clients across sectors are expecting predictive analytics capabilities to be standard, not an add-on. This directly impacts how Ipsos prices its services and structures its project delivery.
Customer Power 4
The bargaining power of customers in the market research industry is significant due to intense competition. With a multitude of global and niche firms competing for business, clients have ample choices and can readily switch providers if their needs aren't met or if better pricing is available. This dynamic directly empowers customers, allowing them to negotiate more favorable terms.
In 2024, the market research sector continued to showcase this customer leverage. For instance, major clients often command better pricing due to the volume of business they represent. A report from Statista in early 2024 indicated that the global market research industry was projected to reach over $115 billion, reflecting the scale of client spending and thus their inherent power.
- High Client Concentration: In many sectors, a few large clients may account for a substantial portion of a market research firm's revenue, giving them considerable negotiation leverage.
- Availability of Substitutes: The proliferation of DIY research tools and platforms, alongside traditional firms, offers clients alternatives, further strengthening their position.
- Price Sensitivity: Clients often prioritize cost-effectiveness, especially in budget-constrained environments, pushing firms to compete aggressively on price.
- Switching Costs: While sometimes a barrier, for many clients, the perceived low switching costs between research providers encourage them to seek better value.
Customer Power 5
Customers wield significant influence in the market, particularly when their satisfaction is at stake. Ipsos reported a high client satisfaction rate of 9 out of 10 in 2024, indicating a generally positive customer experience. However, this satisfaction is fragile; over half of negative customer experiences result in decreased spending, highlighting a strong propensity for clients to seek alternatives if their expectations are unmet.
This willingness to switch is amplified when core client needs are not addressed. Key areas where dissatisfaction can lead to customer departure include concerns about data accuracy, the clarity and frequency of communication, and the perceived actionability of the recommendations provided. These factors directly impact a client's ability to derive value from a service, making them critical determinants of customer loyalty.
- High Satisfaction, Yet Vulnerable: Ipsos' 2024 data shows a 9/10 satisfaction rate, but this masks a significant risk.
- Consequences of Poor Experience: More than 50% of negative customer interactions lead to reduced client spending.
- Drivers of Switching: Clients are quick to switch if they experience issues with data accuracy, communication, or the practical utility of recommendations.
- Customer Power: The ability of customers to readily switch providers based on unmet expectations grants them considerable bargaining power.
Customers possess considerable bargaining power due to the competitive landscape and the availability of substitutes. This leverage is amplified when clients can easily switch providers or conduct research in-house, especially with the rise of DIY tools. For instance, the global survey software market was projected to exceed $3.5 billion by 2024, indicating a strong shift towards self-service options that empower clients.
Major clients often command better pricing due to the sheer volume of business they represent. In 2024, the global market research industry, projected to reach over $115 billion, saw clients leveraging their spending power to negotiate favorable terms.
Ipsos's 2024 data shows a high client satisfaction rate of 9 out of 10, but over half of negative experiences lead to reduced spending, highlighting clients' willingness to switch for better value or if core needs like data accuracy and actionable insights are not met.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Competition Intensity | High; clients have many choices. | Global market research industry projected to exceed $115 billion. |
| Availability of Substitutes | Increases power; DIY tools and in-house capabilities. | Survey software market projected to exceed $3.5 billion. |
| Client Concentration | High for major clients, granting significant leverage. | Key accounts can represent substantial revenue portions. |
| Switching Costs | Perceived as low for many, enabling easier provider changes. | Clients switch if data accuracy, communication, or recommendations are poor. |
Full Version Awaits
Ipsos Porter's Five Forces Analysis
The document you see here is the complete Ipsos Porter's Five Forces Analysis you will receive. This preview accurately represents the final, professionally formatted document, ensuring you get exactly what you need to understand competitive pressures. What you are viewing is the actual deliverable, ready for immediate download and use upon purchase. There are no placeholders or sample sections; this is the full, unedited analysis.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The market research landscape is a crowded arena, with Ipsos facing robust competition from numerous global and regional players. Established giants like Nielsen, Kantar, and GfK command significant market share, offering comprehensive services that directly challenge Ipsos's offerings. This intense rivalry means constant pressure on pricing and innovation to retain and attract clients.
The competitive landscape for market research firms like Ipsos is becoming increasingly intense, largely due to the rapid advancement of digital, automated, and AI-driven research solutions. Companies such as Zappi and Qualtrics are making significant inroads by offering platforms that can generate insights much faster than traditional methods, putting pressure on established players.
This technological shift means that firms must adapt quickly to remain competitive. Ipsos is actively addressing this by investing heavily in its own AI capabilities, aiming to develop and integrate advanced solutions that can match or even surpass the speed and efficiency of its emerging rivals. This strategic focus on AI is crucial for maintaining market share and delivering value in a rapidly evolving industry.
Competitive rivalry within the market research industry, including players like Ipsos, is intense. Firms differentiate themselves through specialized expertise in sectors such as healthcare or consumer packaged goods, alongside innovation in methodologies like neuromarketing and digital ethnography. The ability to deliver profound, actionable insights is a critical battleground.
Ipsos itself highlights its extensive service portfolio and substantial global footprint as key competitive advantages, aiming to capture a broad spectrum of client needs. This comprehensive approach allows Ipsos to compete on both breadth and depth of service offerings.
In 2024, the market research sector continued to see significant investment in advanced analytics and AI-driven solutions. Companies that can effectively integrate these technologies to offer predictive insights and automated reporting are gaining a competitive edge. Ipsos, with its focus on innovation, is well-positioned to leverage these trends.
The industry's reliance on talent further fuels rivalry, as firms vie for skilled researchers and data scientists capable of translating complex data into strategic recommendations. This human capital component is as crucial as technological advancement in maintaining a competitive stance.
Competitive Rivalry 4
Competitive rivalry within the market research industry is indeed intense, driven significantly by pricing pressure. This is particularly true with the emergence of more affordable automated research tools and clients increasingly developing their own internal research capabilities. Ipsos, like its peers, faces the challenge of investing in cutting-edge technology while simultaneously offering competitive pricing to secure and grow its client base.
The need to balance technological investment with pricing strategies is critical for market share. For instance, in 2024, the global market research industry was valued at approximately $80 billion, and intense competition means that any company failing to offer value for money risks losing business to rivals or seeing clients bring functions in-house.
- Pricing Pressure: Increased competition from automated tools and in-house client capabilities exert downward pressure on service prices.
- Technological Investment: Companies like Ipsos must continually invest in advanced technologies to remain competitive, which adds to operational costs.
- Client Retention and Acquisition: Balancing these cost pressures with the need to offer attractive pricing is key to retaining existing clients and attracting new ones in a crowded market.
- Market Dynamics: The market research sector, valued at around $80 billion globally in 2024, is characterized by a significant number of players, further intensifying rivalry.
Competitive Rivalry 5
Competitive rivalry within the market research industry remains intense, driven by a constant push for enhanced capabilities and broader market reach. Larger entities, such as Ipsos, frequently engage in mergers and acquisitions to achieve these strategic objectives.
This consolidation trend is a clear indicator of the dynamic competitive landscape. For instance, Ipsos completed a significant acquisition in July 2025, underscoring the ongoing pursuit of market share and synergistic growth through strategic M&A activities.
- Ipsos' July 2025 acquisition: Expanded its data analytics and digital solutions portfolio.
- Industry M&A activity: Driven by the need to integrate new technologies and gain competitive advantages.
- Consolidation trend: Indicates a maturing market where scale and diversified offerings are crucial for success.
- Impact on rivalry: Intensifies competition as firms seek to differentiate through specialized services and global presence.
Competitive rivalry in the market research sector is fierce, with established giants and agile disruptors vying for dominance. Companies must constantly innovate and invest in technology, like AI, to stay ahead. The global market research industry, valued at approximately $80 billion in 2024, sees intense competition driven by pricing pressures and the rise of in-house research capabilities.
| Key Competitor | Primary Service Focus | Competitive Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Nielsen | Media measurement, audience insights | Established brand, extensive data |
| Kantar | Brand consulting, consumer insights | Global reach, deep sector expertise |
| GfK | Consumer goods analytics, retail data | Market penetration, data analytics |
| Zappi | Automated research platforms | Speed, cost-effectiveness |
| Qualtrics | Experience management, customer insights | Integrated platform, advanced analytics |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes is a significant concern for market research firms. Businesses increasingly possess internal capabilities, such as building in-house market research teams or leveraging readily available data analytics tools, which can fulfill similar needs without engaging external providers. This trend is amplified as many large multinational corporations establish their own in-house marketing agencies, thereby reducing their reliance on outside market research and consulting firms.
Big data analytics and business intelligence tools present a significant threat of substitutes for traditional market research and external data providers. Companies can now leverage their internal datasets, such as sales figures and customer relationship management (CRM) information, to gain valuable insights. For instance, in 2024, the global big data analytics market was projected to reach over $300 billion, highlighting the widespread adoption and capability of these internal solutions.
These advanced tools offer real-time, actionable intelligence without the need for lengthy and often costly external research engagements. This direct access to internal data allows for quicker decision-making and a more agile response to market dynamics. The efficiency gained by analyzing proprietary information directly can bypass the delays and costs associated with third-party data acquisition, making it a compelling alternative.
The threat of substitutes is significant for traditional market research methods. Social media listening and sentiment analysis platforms, such as Sprinklr and Talkwalker, offer a faster and often more cost-effective way to gauge consumer opinions and trends compared to traditional surveys or focus groups.
These digital tools provide real-time insights into consumer conversations, allowing businesses to react swiftly to evolving market sentiment. For instance, by analyzing millions of online mentions, companies can identify emerging issues or preferences without the lengthy and expensive process of commissioning custom research.
The accessibility of these platforms means that even smaller businesses can gain valuable market intelligence. In 2024, the market for social listening tools was projected to reach billions, underscoring their widespread adoption and perceived value as a substitute for older research methodologies.
4
Consulting firms that leverage publicly available data, industry reports, or their own internal expertise, rather than conducting primary research, can serve as significant substitutes for traditional market research providers. These firms offer strategic guidance and insights, enabling clients to make informed decisions without the expense and time commitment of bespoke research projects. For instance, a company seeking market entry strategies might find value in a consultant's analysis of existing market reports and competitor data, bypassing the need for a custom study.
The availability of these alternative consulting services can lower the perceived value of primary research. In 2024, the global consulting market was valued at approximately $330 billion, indicating a substantial demand for strategic advisory services, many of which may not rely on primary data collection. This broad market size suggests that clients have numerous avenues for obtaining strategic insights, making the threat of substitution a tangible concern for firms whose core offering is primary research.
Key aspects of this threat include:
- Cost-Effectiveness: Consultants often present a more budget-friendly option by repackaging existing information.
- Speed to Insight: Utilizing readily available data allows for quicker delivery of strategic recommendations compared to lengthy primary research cycles.
- Breadth of Expertise: Many consulting firms offer a wide array of services beyond research, providing a one-stop shop for strategic needs.
- Accessibility: Industry reports and readily available data are often more accessible to a broader range of businesses, reducing reliance on specialized research firms.
5
The threat of substitutes for Ipsos is intensifying, particularly with advancements in technology. Emerging fields like synthetic data generation are creating new ways to simulate respondent behavior. This can potentially lessen the reliance on traditional human panels for specific research needs, impacting Ipsos's core business model.
Consider the implications of AI-driven analytics platforms that can process vast datasets to extract insights, often mimicking the outcomes of traditional qualitative and quantitative research. For instance, in 2024, the market for AI in market research was projected to grow significantly, indicating a substantial shift towards tech-enabled alternatives. These substitutes offer faster turnaround times and potentially lower costs for certain types of information gathering.
- Synthetic Data: AI can generate realistic, anonymized datasets mimicking human responses, reducing the need for actual survey participants in some scenarios.
- AI-Powered Analytics: Platforms can analyze existing unstructured data (social media, reviews) to glean consumer sentiment and behavior without direct surveying.
- Automated Insights: Tools are emerging that automate the interpretation of data, providing insights that previously required human analysts.
- Cost and Speed: Substitutes often promise quicker delivery and reduced operational expenses compared to traditional panel-based research.
The threat of substitutes for traditional market research firms like Ipsos is substantial, driven by readily available technologies and alternative service providers. Businesses can increasingly leverage internal data analytics, big data platforms, and AI-powered tools to generate insights, bypassing the need for external research engagements. For example, the global big data analytics market was projected to exceed $300 billion in 2024, reflecting the widespread adoption of these internal capabilities.
Entrants Threaten
The threat of new entrants in the market research industry is moderately high, particularly due to technological advancements. Startups equipped with AI and machine learning can bypass some traditional capital requirements for data collection and analysis, offering niche services efficiently. For instance, platforms utilizing AI for sentiment analysis can launch with lower overheads compared to firms requiring extensive human resources for manual coding.
The threat of new entrants in the market research industry remains moderate, influenced by evolving technological accessibility. Lower capital requirements for basic online survey platforms and qualitative research tools now allow smaller firms and even individual consultants to enter the market more readily.
User-friendly software has significantly democratized sophisticated research capabilities, making them accessible to organizations of all sizes, not just large corporations. This ease of entry lowers the barrier for new players to offer specialized services.
While established players benefit from brand recognition and extensive client networks, the digital shift means that innovative, agile newcomers can quickly gain traction. For instance, the global market for insights and analytics, which includes market research, was projected to grow by 6.7% in 2024, reaching approximately $121 billion, indicating ongoing expansion that new entrants can tap into.
The threat of new entrants in the consumer data insights sector is moderate. New players can leverage readily available consumer data from numerous data brokers and public sources, bypassing the costly need for extensive primary data collection. This accessibility allows them to quickly offer valuable insights, potentially disrupting established firms. For instance, the global data broker market was valued at approximately $2.4 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, indicating a dynamic landscape where new entrants can find opportunities.
4
The threat of new entrants in the market research industry, while present, is somewhat mitigated by substantial barriers to entry. New players would need to establish extensive global networks, cultivate deep industry-specific expertise, and build a strong brand reputation. Furthermore, the capacity to manage complex, large-scale projects is crucial, a feat that requires significant capital and proven operational capabilities.
Ipsos, for instance, benefits from its established global presence, with operations in numerous countries and a long history of client relationships that are difficult for newcomers to replicate. This entrenched position provides a significant competitive advantage, making it challenging for new firms to gain traction, especially in the full-service global market research segment.
- High Capital Requirements: Setting up a global research infrastructure is capital-intensive.
- Established Brand Reputation: Companies like Ipsos have spent years building trust and recognition.
- Proprietary Data and Technology: Access to and development of advanced research tools can be a barrier.
- Regulatory Compliance: Navigating diverse international data privacy laws requires specialized knowledge.
5
The threat of new entrants in the market research industry, particularly for a company like Ipsos, is significantly influenced by high barriers to entry. These barriers often involve substantial upfront capital requirements and specialized expertise.
Regulatory complexities, especially concerning data privacy like GDPR and CCPA, demand significant investment in robust data security infrastructure and legal compliance. Established players, such as Ipsos, already possess the necessary frameworks and experience to navigate these intricate regulations, making it a considerable hurdle for newcomers to match.
Furthermore, the need for advanced technological capabilities and a strong global presence, which Ipsos has cultivated over years, presents another challenge. Building the necessary data analytics platforms and establishing a worldwide network of operations requires considerable time and resources, acting as a deterrent for potential entrants.
Consider these factors impacting new entrants:
- High Capital Investment: Setting up advanced data analytics, technology infrastructure, and global operations requires millions in investment.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to data privacy laws like GDPR and CCPA necessitates significant legal and technical expertise, adding to costs.
- Brand Reputation and Trust: Established firms like Ipsos benefit from years of building client trust, a difficult attribute for new entrants to replicate quickly.
- Access to Talent: Attracting and retaining skilled data scientists and market researchers is competitive, favoring firms with strong employer branding.
The threat of new entrants into the market research space is moderate, largely due to significant barriers that favor established players like Ipsos. These hurdles include the substantial capital needed for global infrastructure, building a trusted brand reputation over time, and developing proprietary data and advanced technologies. Navigating complex international regulations, such as GDPR, also demands considerable investment and expertise.
| Barrier to Entry | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Establishing global operations and advanced analytics platforms requires significant investment, often in the millions. | High barrier, favoring firms with substantial financial backing. |
| Brand Reputation & Trust | Years of successful client relationships and proven track records are crucial for winning large contracts. | Difficult for newcomers to replicate quickly, delaying market penetration. |
| Proprietary Technology & Data | Access to unique data sources and advanced analytical tools provides a competitive edge. | New entrants may struggle to compete without comparable technological capabilities. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Adhering to diverse data privacy laws (e.g., GDPR, CCPA) requires robust legal and technical infrastructure. | Adds to the cost and complexity for new players, benefiting incumbents with established compliance frameworks. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, including company annual reports, industry-specific market research, and publicly available financial filings. This ensures a comprehensive understanding of competitive dynamics.
