Interpump Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Interpump Group Bundle
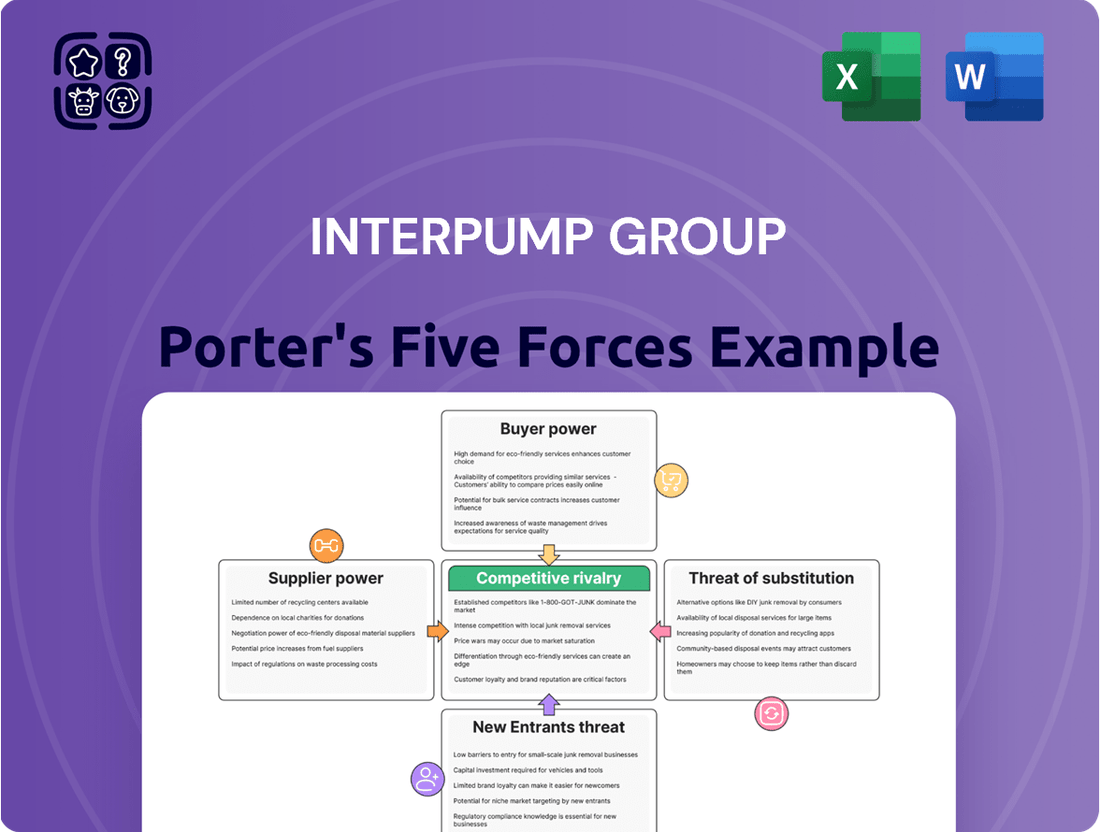
Interpump Group operates within a dynamic industrial landscape, influenced by several key competitive forces. Understanding the bargaining power of its buyers and suppliers is crucial for navigating pricing and supply chain stability. The threat of new entrants, while potentially moderate, requires constant innovation and brand loyalty to mitigate.
The intensity of rivalry among existing competitors significantly shapes Interpump Group's strategic decisions, demanding efficiency and differentiation. Furthermore, the availability of substitute products presents a persistent challenge, necessitating continuous product development and value proposition enhancement.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Interpump Group’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Interpump Group relies on suppliers for specialized components like high-grade metals and precision-engineered parts crucial for their high-pressure piston pumps, power take-offs, and hydraulic cylinders. The scarcity and proprietary nature of these components significantly influence supplier leverage. In 2024, the continued demand for advanced materials in hydraulic systems suggests that suppliers of these niche inputs would maintain a strong position, especially if few alternatives exist.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Interpump is significantly influenced by switching costs. For highly integrated or custom-designed components, the expense and complexity involved in changing suppliers can be considerable. This often necessitates re-tooling manufacturing processes, undergoing rigorous re-certification of products, and managing potential disruptions to ongoing production lines. These substantial switching costs can strengthen the leverage held by existing suppliers.
In 2024, Interpump's commitment to specialized, high-performance hydraulic components means that many of its key inputs are not off-the-shelf items. Developing and qualifying new suppliers for these critical parts can take many months, impacting production schedules and potentially leading to increased costs if a supplier faces issues. For instance, a lengthy qualification process for a new hydraulic seal manufacturer could delay the launch of a new product line, a risk that discourages frequent supplier changes.
For Interpump Group, the bargaining power of suppliers is significantly influenced by the critical nature of their inputs to Interpump's high-performance product lines. The quality and reliability of components are paramount, directly impacting the functionality and durability of Interpump's pumps and hydraulic systems. For instance, specialized seals or advanced materials that are integral to the core performance of their products can give these suppliers considerable leverage.
Suppliers of unique or patented components that are essential for Interpump's product differentiation hold a stronger position. If a particular supplier provides a component that is difficult to source elsewhere or is protected by intellectual property, Interpump's reliance on that supplier increases, thereby enhancing the supplier's bargaining power. This reliance is especially pronounced when these parts are vital for achieving Interpump's technological edge in the market.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into Interpump Group's business, essentially becoming competitors, is a key factor influencing supplier bargaining power. If suppliers could effectively produce the hydraulic components and systems that Interpump manufactures, they would gain leverage to dictate terms or even capture market share.
However, Interpump's established global presence and highly specialized, proprietary manufacturing processes create significant barriers to such forward integration. The capital investment required to replicate Interpump's sophisticated production capabilities, coupled with the need for extensive R&D and market access, makes this threat less probable for most suppliers.
For instance, Interpump's significant investment in advanced manufacturing technologies, including automated assembly lines and precision machining centers, represents a substantial hurdle. In 2023, Interpump Group reported capital expenditures of €172.6 million, a portion of which was allocated to enhancing these production efficiencies and capabilities, further solidifying its competitive edge.
- High Capital Requirements: Replicating Interpump's advanced manufacturing facilities requires substantial financial investment, deterring most suppliers.
- Proprietary Technologies: Interpump's specialized production techniques and intellectual property are difficult for suppliers to acquire or replicate.
- Economies of Scale: Interpump's large-scale operations provide cost advantages that smaller suppliers would struggle to match.
- Brand Recognition and Distribution: Interpump's established brand and extensive distribution network are crucial assets that suppliers would find challenging to build.
Volume of Purchases from Individual Suppliers
Interpump Group's significant scale of operations, spanning both its Hydraulics and Water Jetting divisions, translates into substantial purchasing volumes from its suppliers. This considerable demand grants Interpump considerable leverage, particularly for more standardized components, enabling the negotiation of favorable pricing and payment terms. For instance, in 2023, Interpump reported consolidated revenues of €2.18 billion, suggesting a vast procurement base. However, the bargaining power derived from volume may diminish for highly specialized or proprietary components where supplier options are limited.
- Interpump's substantial revenue base, reaching €2.18 billion in 2023, underscores its significant purchasing power.
- The diversified product portfolio across Hydraulics and Water Jetting allows for bulk purchasing across a wider range of inputs.
- Leverage is strongest for commoditized inputs where numerous suppliers exist.
- Conversely, reliance on specialized, single-source suppliers for critical components can reduce Interpump's bargaining strength.
Suppliers of specialized, high-performance components for Interpump Group, such as advanced metals and precision parts, hold considerable bargaining power due to the critical nature of these inputs and the limited availability of alternatives. In 2024, the ongoing demand for sophisticated hydraulic systems reinforces this supplier leverage, especially when switching costs for Interpump are high.
The bargaining power of suppliers is amplified when they provide unique or patented components essential for Interpump's product differentiation. If a supplier offers a difficult-to-source or proprietary part, Interpump's dependence increases, strengthening the supplier's negotiation position. This is particularly true for components integral to Interpump's technological advantage.
| Factor | Impact on Interpump | Data/Observation |
|---|---|---|
| Component Criticality | High | Suppliers of essential, high-performance hydraulic components have significant leverage. |
| Switching Costs | High | Re-tooling and re-certification for new suppliers of custom parts are costly and time-consuming. |
| Supplier Differentiation | High | Unique or patented components increase supplier power due to limited alternatives. |
| Forward Integration Threat | Low | Interpump's proprietary technology and scale create barriers for suppliers becoming competitors. |
What is included in the product
This analysis unpacks the competitive forces shaping Interpump Group's market, examining supplier and buyer power, new entrant threats, and the impact of substitutes on its profitability and strategic positioning.
Identify and mitigate threats from new entrants and substitute products with a clear, actionable framework.
Strategically assess and navigate competitive pressures from rivals and buyer bargaining power to secure profitable market positions.
Customers Bargaining Power
Interpump Group's customer base is quite broad, spanning industrial, agricultural, and cleaning industries worldwide. This diversity typically spreads out customer demand, lessening the impact of any single buyer. However, within certain sectors, large original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) or major distributors can account for substantial purchase volumes, thereby increasing their bargaining leverage.
For example, in the hydraulic components market, Interpump is a supplier to significant industrial vehicle manufacturers. These large clients, due to their scale, can negotiate more favorable terms. In 2024, the industrial machinery sector, where many of these OEMs operate, continued to see robust demand, potentially giving these larger customers even more sway in price discussions.
Customers might find it moderately to highly costly to switch from Interpump's specialized high-pressure pumps and hydraulic components. These costs often involve significant efforts like redesigning entire systems, undertaking rigorous retesting procedures for new equipment, and ensuring seamless compatibility with products from alternative suppliers. This investment in integration and validation inherently limits the ease with which customers can move to competitors, thereby softening their bargaining leverage.
Interpump's reputation for reliability and the proven performance track record of its products further solidify customer loyalty, often referred to as customer stickiness. This established trust and the assurance of consistent operation make customers less inclined to risk disruption by switching to less proven alternatives, even if offered at a slightly lower price point. For instance, in industries where equipment failure can lead to substantial downtime and safety concerns, such as oil and gas or heavy manufacturing, the cost of switching extends beyond mere financial outlay to include potential operational risks.
In established industrial sectors, customers often show a keen awareness of pricing, particularly when dealing with more common or standardized parts. This can put pressure on suppliers to maintain competitive price points.
However, Interpump Group’s focus on high-performance and critical applications shifts this dynamic. For these specialized needs, factors like product reliability, advanced engineering, and robust after-sales support become far more important than a slight difference in price.
For instance, in the oil and gas sector, where Interpump products are crucial for demanding operations, the cost of equipment failure or downtime due to substandard parts far exceeds any initial savings from cheaper alternatives. This significantly lowers the bargaining power of customers based purely on price.
Interpump's ability to deliver superior performance and dependable service in these mission-critical areas means customers are often willing to pay a premium, thereby diminishing the direct impact of customer price sensitivity on the company’s profitability.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of customers integrating backward to produce their own high-pressure pumps or hydraulic components for Interpump Group is generally low. This is primarily because it demands highly specialized manufacturing expertise and substantial capital investment, barriers that most customers find difficult to overcome. Interpump's decades of experience and highly developed production processes further solidify its competitive advantage in this area.
Consider these factors:
- Specialized Expertise: Manufacturing advanced hydraulic components requires intricate knowledge of metallurgy, precision engineering, and complex assembly processes, which are core competencies of Interpump.
- Capital Investment: Establishing production facilities capable of meeting the quality and volume demands of the hydraulic industry necessitates significant upfront investment in machinery, tooling, and skilled labor.
- R&D Intensity: Continuous innovation and product development are crucial in this sector, demanding ongoing investment in research and development to stay competitive.
- Economies of Scale: Interpump benefits from economies of scale in its production, making it difficult for potential new entrants, including customers, to match its cost efficiency.
Customer Information and Product Standardization
Customers generally possess strong knowledge of product specifications and market pricing for standard components. However, for Interpump's specialized, engineered solutions, particularly those designed for unique applications, the inherent complexity and customization make direct product comparison difficult. This reduces the customers' ability to exert pressure based purely on readily available information.
Interpump Group's focus on highly engineered and differentiated solutions in niche markets significantly mitigates the bargaining power derived from customer information. For instance, in the high-pressure cleaning sector, where Interpump is a leading manufacturer, customers seeking specialized pump systems for industrial applications often rely on Interpump's technical expertise and tailored solutions rather than easily comparable off-the-shelf products. This specialization limits the commoditization of their offerings.
- Limited Price Sensitivity for Specialized Products: Customers seeking Interpump's highly engineered solutions for critical applications exhibit lower price sensitivity due to the value derived from performance, reliability, and customization.
- Information Asymmetry in Niche Markets: For complex or proprietary pump technologies, customers may lack the deep technical understanding to fully assess product specifications and competitive pricing, thus reducing their informational leverage.
- Impact of Acquisitions on Product Portfolio: Interpump's strategic acquisitions, such as those in the fluid power and industrial sectors, have broadened its product portfolio. This comprehensive offering can make it harder for customers to source equivalent components from multiple suppliers, thereby consolidating their reliance on Interpump.
Interpump Group's customer bargaining power is generally moderate, influenced by customer concentration and switching costs. While a broad customer base dilutes individual power, large OEMs in sectors like industrial machinery, which saw robust demand in 2024, can negotiate more favorable terms due to their volume. High switching costs, stemming from system redesign and retesting, coupled with Interpump's reputation for reliability, create customer stickiness, especially in critical applications where failure is costly.
Customers' ability to exert pressure based on price is limited for Interpump's specialized, high-performance products. In mission-critical sectors like oil and gas, the cost of equipment failure far outweighs initial savings from cheaper alternatives, making customers less price-sensitive and more focused on reliability. This dynamic is further reinforced by Interpump's decades of specialized expertise, significant capital investment in advanced manufacturing, and ongoing R&D, which create high barriers to backward integration for customers.
Information asymmetry also plays a role, particularly for complex, engineered solutions where customers may not have the deep technical knowledge to fully assess competitive pricing. Interpump's strategic acquisitions have also broadened its portfolio, potentially increasing customer reliance and reducing their ability to source equivalent components elsewhere. This overall strategy positions Interpump to mitigate the direct impact of customer price sensitivity.
| Factor | Assessment | Impact on Interpump |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | Moderate; large OEMs in key sectors have significant leverage. | Potential for price pressure from major clients. |
| Switching Costs | High; involve system redesign, retesting, and compatibility efforts. | Reduces customer ability to switch easily, softening bargaining power. |
| Product Differentiation & Performance | High; focus on specialized, reliable, and high-performance solutions. | Lowers price sensitivity and increases customer loyalty. |
| Customer Information Availability | Low for specialized products; high for standard components. | Limits leverage based on price comparison for engineered solutions. |
| Threat of Backward Integration | Low; requires specialized expertise and substantial capital investment. | Customers are unlikely to produce components in-house. |
Same Document Delivered
Interpump Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Interpump Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of competitive forces within its industry. You'll gain insights into the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase, providing you with actionable intelligence without any surprises.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Interpump Group navigates a competitive arena populated by formidable global players like Parker Hannifin, Eaton Corporation, Danfoss, Flowserve Corporation, and Graco. These large multinationals offer a broad spectrum of products, often competing directly across multiple segments of Interpump's business.
Beyond these giants, the market also includes numerous specialized regional competitors. These smaller, focused companies can often offer niche expertise or more agile solutions, particularly in specific geographic markets or for particular applications, adding another layer of complexity to the competitive landscape.
For instance, in the hydraulic components sector, the sheer breadth of product offerings from companies like Eaton, which reported approximately $23.6 billion in revenue for 2023, demonstrates the scale of competition Interpump faces from diversified industrial conglomerates.
The high-pressure water jetting systems segment, while perhaps less dominated by a few massive entities, still sees significant competition from companies like Graco, which had revenues of around $2.2 billion in 2023, and various European manufacturers with strong regional presences.
The high-pressure pump market is poised for steady expansion, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 3.9% between 2025 and 2033. This indicates a healthy, albeit not explosive, market environment.
Simultaneously, the hydraulic cylinder market anticipates a more vigorous growth trajectory, forecasting a CAGR of 5.4% from 2024 to 2025. This segment's expansion suggests increasing demand for essential hydraulic components.
Further bolstering this positive outlook, the Power Take Off (PTO) market is experiencing robust growth. Valued at an estimated $2.5 billion in 2025, it is expected to exceed $4 billion by 2033, reflecting a significant CAGR of 6%. This strong growth in PTOs indicates a broader trend of increasing industrial mechanization and power transmission needs.
The combination of moderate to strong growth across these related sectors suggests that while opportunities exist, the competitive landscape is likely to intensify. Companies will need to strategically position themselves to capture market share in these expanding, yet not hyper-growth, segments.
Interpump Group stands out by offering a broad range of products and specialized, high-quality engineered solutions. Their dual expertise in hydraulics and water jetting technology creates opportunities for cross-selling and leveraging technological advancements across these segments, setting them apart from competitors.
These differentiating factors, combined with moderate customer switching costs, effectively reduce intense price competition. Customers might face some inconvenience or investment in retraining if they switch brands, which encourages loyalty to Interpump’s integrated offerings.
For instance, in 2024, Interpump reported strong performance in its Water Jetting division, which benefits from this differentiation strategy. The ability to bundle hydraulic components with advanced water jetting systems makes it less appealing for customers to source parts from multiple providers.
The company’s commitment to innovation, as seen in its continuous product development pipeline, further solidifies its market position. This focus on unique, high-performance solutions means rivalry is often based on technological superiority and service rather than just price.
Exit Barriers
The pump and hydraulics industry, where Interpump Group operates, presents substantial exit barriers due to high capital investments. Companies must invest heavily in advanced manufacturing facilities, specialized machinery, and proprietary intellectual property. These significant sunk costs make it economically unviable for firms to exit the market quickly, even during periods of reduced profitability, thereby sustaining competitive intensity.
Interpump Group's strategic focus on expanding its productive capacity, as evidenced by its ongoing investments in new plants and upgrades, further solidifies these exit barriers for the industry. This commitment to growth means that any competitor considering departure faces the challenge of recouping substantial, specialized assets. For instance, in 2023, Interpump Group reported capital expenditures of €325 million, a significant portion of which was allocated to capacity enhancements, signaling a long-term investment horizon that discourages rapid market exits.
- High Capital Investment: The pump and hydraulics sector demands substantial upfront investment in specialized manufacturing equipment and R&D.
- Specialized Assets: Assets are often industry-specific, limiting resale value and increasing exit costs.
- Interpump's Investment: Interpump's continuous investment in capacity expansion (€325 million CAPEX in 2023) reinforces these barriers.
- Sustained Competition: High exit barriers encourage companies to remain active even in challenging economic conditions, intensifying rivalry.
Strategic Acquisitions and Market Share
Interpump Group has actively engaged in strategic acquisitions to bolster its product offerings and expand its global manufacturing presence. This approach has solidified its standing, evidenced by its approximately 15-20% market share in the high-pressure plunger pump sector.
However, the company's hydraulics division experienced a period of stagnation. This downturn contributed to a reported organic sales decline for Interpump Group in 2024 and continued into the first quarter of 2025, highlighting a key challenge in maintaining consistent growth across all segments.
- Acquisition Strategy: Interpump has consistently used acquisitions to broaden its product range and manufacturing capabilities.
- Market Position: The company holds a significant 15-20% share in the high-pressure plunger pump market.
- Hydraulics Division Performance: This segment faced stagnant growth, impacting overall company performance.
- 2024/Q1 2025 Sales Trend: Interpump Group reported an overall organic sales decline during this period.
Interpump Group faces intense competition from global giants like Parker Hannifin and Eaton, which offer extensive product lines that directly challenge Interpump across various segments. Additionally, numerous specialized regional players provide niche solutions, particularly in specific markets or applications, further fragmenting the competitive landscape.
The company differentiates itself through a broad product portfolio and specialized, high-quality engineered solutions, particularly in hydraulics and water jetting. This dual expertise, coupled with moderate customer switching costs, allows Interpump to mitigate intense price-based rivalry, focusing instead on technological superiority and service.
High capital investment and specialized assets in the pump and hydraulics sector create substantial exit barriers. Companies are discouraged from leaving the market even during downturns, which sustains competitive intensity. Interpump's own significant capital expenditures, such as €325 million in 2023 for capacity expansion, reinforce these barriers for rivals.
While Interpump has a strong market position, particularly a 15-20% share in high-pressure plunger pumps, its hydraulics division experienced stagnation, contributing to an organic sales decline in 2024 and early 2025. This highlights the ongoing challenge of maintaining growth across all business segments amidst fierce competition.
| Competitor | Approx. 2023 Revenue | Key Overlap Areas |
|---|---|---|
| Parker Hannifin | ~$15.4 billion | Hydraulics, Filtration |
| Eaton Corporation | ~$23.6 billion | Hydraulics, Electrical Components |
| Danfoss | ~$11.6 billion | Hydraulics, Power Solutions |
| Flowserve Corporation | ~$4.0 billion | Pumps, Sealing |
| Graco Inc. | ~$2.2 billion | High-Pressure Pumps, Fluid Handling |
SSubstitutes Threaten
While direct substitutes for Interpump Group's core high-pressure piston pumps and specialized hydraulic components are scarce, alternative technologies do present a threat in specific applications. For example, electric actuators and pneumatic systems are increasingly viable replacements for hydraulic systems in tasks requiring lower forces or more precise, controlled movements, potentially impacting demand in sectors like automation and light manufacturing. The global industrial automation market, which heavily utilizes these alternative technologies, was valued at approximately $150 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly in the coming years.
The superior force output, precision, and durability of hydraulic cylinders often present a significant performance advantage over potential substitutes, particularly in demanding industrial applications. For instance, Interpump Group's hydraulic systems are engineered for extreme environments where reliability is paramount.
While alternative technologies like electric actuators or pneumatic systems might boast lower upfront costs, they frequently lag in power density or the sustained robustness required for heavy-duty tasks that Interpump's core markets depend on. This performance gap means that even with a higher initial investment, hydraulic solutions often deliver a better total cost of ownership through longevity and reduced downtime.
In 2023, the global hydraulic systems market was valued at approximately $22.5 billion, demonstrating a strong demand for these high-performance solutions. Substitutes, while growing, still represent a smaller share, especially in sectors like construction and agriculture where Interpump holds a strong presence, underscoring the enduring value proposition of hydraulics.
Customer willingness to switch to substitutes hinges on whether the perceived benefits, like enhanced energy efficiency or reduced maintenance, outweigh the costs and risks associated with adopting new technologies. For instance, a new pump technology offering a 15% energy saving might entice a customer if the payback period is less than two years, despite the initial investment.
In sectors where Interpump Group is a major player, such as industrial hydraulics and water management, reliability and a track record of consistent performance are absolutely critical. Customers in these fields are often hesitant to switch to alternative solutions unless those substitutes present truly substantial and demonstrable advantages, perhaps a 20% increase in operational lifespan or a significant reduction in downtime.
This cautious approach means that substitutes must offer a clear and compelling value proposition to overcome customer inertia. For example, if a competitor's pump offers a 10% lower total cost of ownership over five years, including energy, maintenance, and potential downtime, it could attract a portion of Interpump's customer base.
The threat of substitutes is therefore moderated by the high switching costs and the inherent need for dependable equipment in Interpump's core markets. A substitute product would need to prove its mettle through rigorous testing and case studies, demonstrating not just cost savings but also equivalent or superior reliability to gain significant traction against established solutions.
Technological Advancements in Substitutes
Technological advancements are continuously shaping the landscape for hydraulic components, potentially introducing substitutes. For instance, the push towards electrification across various industries, from automotive to industrial machinery, presents a significant long-term threat. As electric powertrains become more efficient and cost-effective, they may directly replace hydraulic systems in certain applications, particularly where precise power delivery and control are needed.
The growing emphasis on energy efficiency is a key driver behind this trend. Consider the automotive sector; by 2024, we're seeing a notable increase in the adoption of electric vehicles, which inherently reduce the reliance on traditional hydraulic power steering and braking systems. This shift could translate into similar innovations in industrial hydraulics, where electrified actuators or advanced pneumatic systems might offer competitive alternatives. Interpump Group, as a major player in hydraulic systems, must monitor these evolving technologies closely.
Smart systems and IoT integration also contribute to the threat of substitutes. While these can enhance hydraulic system performance, they also open doors for entirely new control paradigms. For example, advanced robotics with integrated electric drives might bypass the need for complex hydraulic power units in some assembly line applications. The global market for industrial automation, projected to reach significant growth by 2025, underscores the pace of these technological changes.
The increasing demand for electric and hybrid hydraulic systems is a direct response to these pressures. While this represents an evolution within the hydraulic sector, it also signifies a potential shift in the nature of competition. Companies that can effectively integrate electrification and digital control into their hydraulic offerings will be better positioned. For 2024, reports indicate a steady increase in R&D investment by major industrial component manufacturers into hybrid and electric solutions, highlighting the perceived threat and opportunity.
- Electrification: Growing adoption of electric vehicles and machinery may reduce demand for traditional hydraulic components in automotive and some industrial sectors.
- Energy Efficiency Drivers: Increased focus on energy conservation is spurring development of alternative, more efficient power transmission technologies.
- Smart Systems & IoT: Advancements in integrated electric drives and advanced control systems could offer new substitute solutions for power and motion control.
- Market Evolution: The threat isn't just substitution but also the evolution of hydraulics towards hybrid and electrified models, requiring adaptation from established players.
Indirect Substitution from Industry Trends
Broader industry trends can indirectly introduce substitute threats for Interpump Group's hydraulic systems. A significant trend is the increasing push towards automation and sustainability across various sectors. For example, if Interpump's hydraulic offerings are perceived as less energy-efficient compared to emerging electric or advanced pneumatic alternatives, particularly in sectors prioritizing reduced carbon footprints, this could drive substitution.
The emphasis on environmental sustainability is a key driver here. If hydraulic systems, which can sometimes be associated with fluid leaks or higher energy consumption in specific applications, are unable to adapt effectively to stringent environmental regulations or evolving customer demands for greener solutions, alternative power transmission methods could gain traction. By mid-2024, many industries reported significant investments in electrification, with some sectors seeing growth rates exceeding 15% year-over-year in electric-powered machinery, indicating a tangible shift.
Consider the following:
- Automation's Role: Increased automation may favor solutions that offer greater precision and control, potentially benefiting non-hydraulic systems if they can deliver these advantages more cost-effectively or efficiently.
- Sustainability Demands: Growing demand for energy-efficient and environmentally friendly solutions could lead to the adoption of electric or hybrid power systems, especially in mobile machinery and industrial applications where emissions are a concern.
- Technological Advancements: Breakthroughs in areas like advanced electric motors, high-density batteries, and innovative pneumatic technologies could present viable alternatives to hydraulic power in specific use cases.
- Regulatory Pressures: Stricter environmental regulations and mandates favoring lower emissions or reduced fluid usage could accelerate the adoption of substitute technologies.
While direct substitutes for Interpump Group's core hydraulic systems are limited in highly demanding applications, alternative technologies pose a threat in specific segments. Electric actuators and advanced pneumatic systems are becoming increasingly viable for tasks requiring less force or more precise control, impacting sectors like industrial automation. The global industrial automation market, valued at approximately $150 billion in 2023, saw continued growth in these alternative technologies.
The threat of substitutes is amplified by the drive for energy efficiency and sustainability. As electric power becomes more prevalent and cost-effective, particularly in sectors like automotive and mobile machinery, traditional hydraulic components may see reduced demand. For instance, by mid-2024, significant investments in electrification were noted across industries, with some electric-powered machinery sectors experiencing over 15% year-over-year growth.
| Substitute Technology | Key Advantage | Potential Impact on Interpump | Relevant Market Trend |
| Electric Actuators | Precise control, lower energy consumption in some applications | Threat in light automation, robotics | Growth in industrial automation market |
| Advanced Pneumatic Systems | Simplicity, speed in certain applications | Alternative for lower-force tasks | Focus on energy efficiency |
| Electrification (General) | Reduced emissions, potentially lower operating costs | Long-term threat across multiple sectors | Automotive electrification, hybrid machinery |
Customer adoption of substitutes is influenced by switching costs and the perceived value proposition. While hydraulic systems offer superior force density and durability, substitutes may gain traction if they demonstrate significant improvements in energy efficiency or a lower total cost of ownership, especially when facing increasing regulatory pressures for sustainability.
Entrants Threaten
Entering the high-pressure pump and hydraulic component manufacturing industry, like that in which Interpump Group operates, demands considerable capital. New entrants must invest heavily in research and development to create advanced, efficient products, and acquire specialized, often expensive, machinery for precision manufacturing. Furthermore, establishing state-of-the-art production facilities and robust global distribution networks requires significant upfront funding, presenting a formidable barrier to entry for potential competitors.
Interpump Group's established global presence allows it to leverage substantial economies of scale. This advantage is particularly evident in its manufacturing processes, where higher production volumes translate to lower per-unit costs. For instance, in 2023, Interpump reported revenues of €2.2 billion, demonstrating the scale of its operations.
Newcomers face a significant hurdle in matching Interpump's cost efficiencies. To achieve comparable economies of scale in manufacturing, procurement, and research and development, a new entrant would require a massive initial investment. Without this, they would likely be unable to compete effectively on price against a deeply entrenched player like Interpump.
Interpump Group benefits significantly from its strong product differentiation and deeply ingrained brand loyalty within its specialized hydraulic component markets. Its reputation for engineering excellence and reliable, high-performance solutions means customers often prioritize Interpump's offerings, making switching to a new supplier a considerable risk for many. This loyalty translates into a substantial barrier for potential new entrants who would face the daunting task of replicating Interpump's decades of accumulated trust and technical expertise.
Newcomers would need to commit substantial capital not only to manufacturing capabilities but also to extensive research and development to match Interpump's product sophistication. Furthermore, building a comparable brand reputation and marketing infrastructure to gain recognition and customer trust in these established niches represents a significant upfront investment, estimated to be in the tens of millions of dollars for a serious contender aiming to compete effectively in core segments like high-pressure pumps and hydraulic systems.
Access to Distribution Channels
Interpump Group benefits from deeply established global distribution networks that span a wide array of industrial sectors. These channels are critical for reaching customers efficiently and are a significant barrier for any new player attempting to enter the market.
For a new entrant, securing comparable access to these established distribution channels is a formidable challenge. It demands not only considerable financial investment but also a substantial commitment of time to build relationships and operational infrastructure from scratch.
- Global Reach: Interpump's distribution network is a key competitive advantage, facilitating sales and service across numerous international markets.
- High Investment Barrier: Replicating such an extensive network requires significant capital outlay, making it difficult for smaller or newer companies to compete.
- Established Relationships: Interpump's long-standing partnerships with distributors and clients create loyalty and preferential access that new entrants lack.
Intellectual Property and Regulatory Barriers
The pump and hydraulic systems industry, where Interpump Group operates, is characterized by significant intellectual property and regulatory hurdles that deter new entrants. Companies invest heavily in research and development, leading to patented technologies in areas like pump design and advanced hydraulic controls. For instance, patents related to efficiency improvements or novel sealing mechanisms can provide a competitive edge for established players.
Meeting stringent industry standards and regulatory compliance further raises the barrier to entry. These often include rigorous safety certifications, environmental regulations concerning emissions and material usage, and performance benchmarks. In 2024, the ongoing focus on sustainability and energy efficiency means that new entrants must demonstrate compliance with evolving standards, such as those mandated by the European Union's Ecodesign Directive, which impacts the energy consumption of pumps.
- Patented Technologies: Protection of proprietary pump designs and hydraulic system innovations limits direct replication by newcomers.
- R&D Investment: High costs associated with developing and securing intellectual property create a financial barrier.
- Industry Standards: Compliance with established quality and performance benchmarks requires significant upfront investment.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adherence to safety and environmental regulations, which are becoming increasingly stringent, necessitates substantial resources and expertise.
The threat of new entrants for Interpump Group remains moderate due to significant capital requirements for R&D, manufacturing, and distribution, coupled with strong brand loyalty and intellectual property protections. For example, Interpump's 2024 reported revenue growth, indicative of its market strength, further solidifies its position.
| Factor | Impact on Interpump Group | Evidence/Data (2024/Latest Available) |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High Barrier | Significant investment needed for advanced R&D and specialized machinery. Interpump's substantial asset base in 2024 reflects this. |
| Brand Loyalty & Differentiation | Strong Barrier | Decades of trust in engineering excellence and performance. Customer retention rates are key. |
| Distribution Networks | Strong Barrier | Established global channels require time and capital to replicate. Interpump's extensive network is a key asset. |
| Intellectual Property & Regulations | Moderate to High Barrier | Patented technologies and evolving standards like EU Ecodesign Directive (2024) necessitate investment and expertise. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Interpump Group Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of diverse data sources, including Interpump's annual reports, investor presentations, and financial statements. We also leverage industry-specific market research reports and publications from reputable sources like IHS Markit and Statista to capture competitive dynamics.
