Instacart Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Instacart Bundle
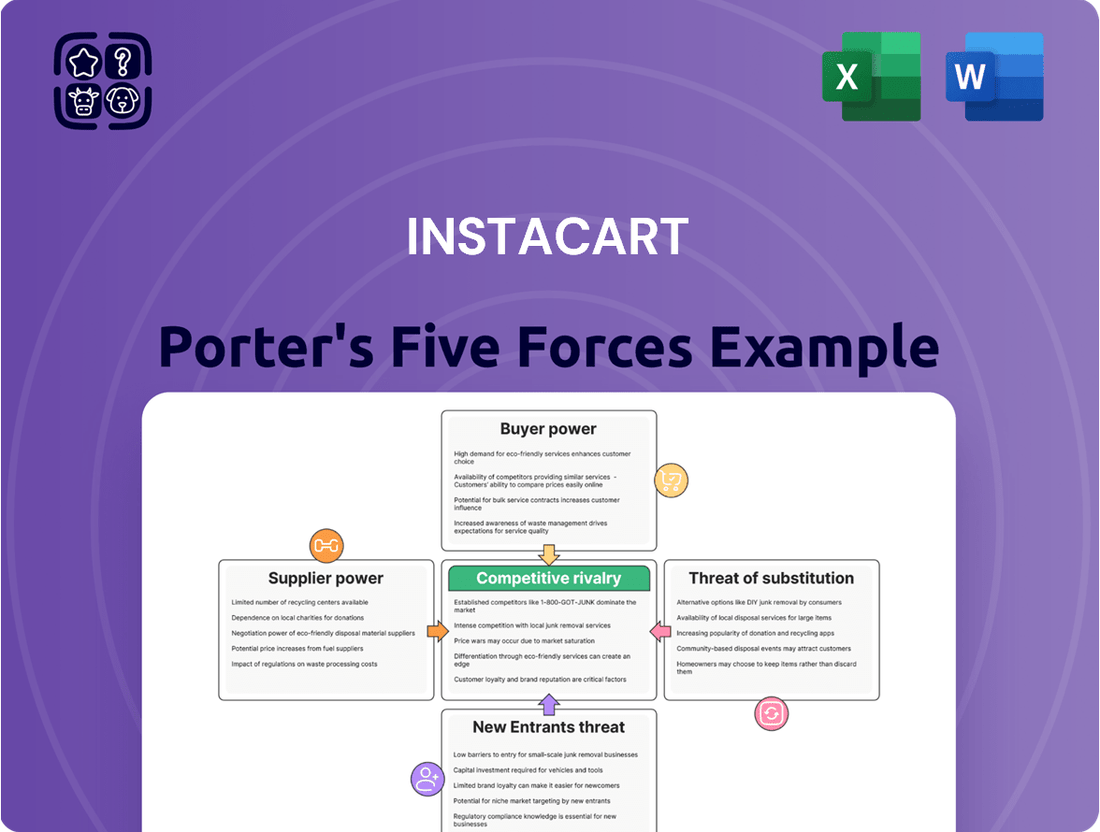
Instacart operates in a dynamic grocery delivery landscape shaped by intense rivalry among existing players and the constant threat of new entrants. Buyer bargaining power is significant due to the availability of alternatives, while supplier power is moderate, influenced by Instacart's scale. The threat of substitutes, though currently low, could rise with evolving consumer habits.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Instacart’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Instacart's model hinges on its vast pool of independent shoppers, meaning the power of any single shopper is minimal. However, the sheer number of available gig workers does create a potential for collective influence if labor market conditions shift dramatically or if shoppers organize.
Instacart has seen fluctuations in shopper earnings. For instance, in early 2024, reports indicated ongoing discussions and adjustments to Instacart's payment system, reflecting the company's efforts to manage costs while retaining its shopper base.
Instacart's bargaining power with grocery retailers and brands is moderate. While Instacart partners with over 1,500 retail banners, providing them with crucial e-commerce and delivery capabilities, some retailers are sensitive to the high commissions charged, which can impact their already thin profit margins. This creates a dynamic where both parties rely on the partnership, limiting the leverage of either side.
Instacart's reliance on specialized technology, such as AI-powered smart carts like Caper Carts and point-of-sale (POS) integrations, can empower its technology and software providers. These suppliers, especially those offering proprietary or highly integrated solutions crucial for Instacart's operational efficiency and innovation, may possess significant bargaining leverage.
Payment Processors
Payment processors are crucial for Instacart, handling millions of daily transactions. While the presence of multiple established providers typically dilutes the bargaining power of any single processor, the demand for secure and efficient payment infrastructure remains high.
Instacart's reliance on these services means processors hold some sway, especially concerning transaction fees and integration capabilities. For instance, in 2024, the global digital payment market was projected to reach over $10 trillion, highlighting the scale and importance of these services.
- High Transaction Volume: Instacart's operational scale necessitates robust payment processing, making processors indispensable.
- Market Competition: The availability of several major payment processors generally limits the power of any one provider over Instacart.
- Critical Infrastructure: Secure, fast, and cost-effective payment solutions are vital for Instacart's customer experience and operational efficiency.
Advertising Partners
Instacart's advertising partners, particularly major brands, can wield significant bargaining power. As Instacart's advertising revenue continues to grow, reaching a 14% year-over-year increase in Q1 2025 and supported by thousands of brand partnerships, these large advertisers may leverage their substantial ad spend. This is especially true if they represent a disproportionately large segment of Instacart's advertising income or if they demand highly specific, performance-based metrics that Instacart must meet to retain their business.
The expansion of Instacart's retail media network and its push into off-platform advertising also influences this dynamic. As more brands seek to reach Instacart's user base through various channels, their collective importance can amplify their negotiating leverage. This is particularly relevant for brands that can easily shift their advertising budgets to competing platforms if Instacart's offerings do not meet their evolving needs or cost-effectiveness expectations.
- Instacart's advertising revenue saw a 14% year-over-year increase in Q1 2025.
- Thousands of brands partner with Instacart for advertising.
- Major advertisers may gain leverage as Instacart expands its ad network.
- Demand for specific performance metrics can increase advertiser bargaining power.
Instacart's suppliers, particularly those providing specialized technology and payment processing, hold moderate bargaining power. While Instacart's scale means it works with multiple providers, the critical nature of these services, especially for payment processing which handled billions in transactions in 2024, gives suppliers some leverage. For instance, proprietary AI solutions or integrated POS systems are essential for Instacart's efficiency, meaning providers of such tech can command favorable terms.
| Supplier Type | Bargaining Power Assessment | Key Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Technology Providers (AI, POS Integration) | Moderate to High | Proprietary solutions, integration complexity, reliance on innovation |
| Payment Processors | Moderate | High transaction volume, multiple provider options, critical infrastructure need |
| Grocery Retailers | Moderate | Mutual reliance, commission sensitivity, large network of partners |
What is included in the product
This analysis unpacks the competitive forces shaping Instacart's market, examining supplier power, buyer bargaining, new entrant threats, substitute services, and the intensity of rivalry.
Instacart's Porter's Five Forces analysis acts as a pain point reliever by providing a clear, one-sheet summary of all competitive pressures, perfect for quick strategic decision-making.
Customers Bargaining Power
Individual consumers hold moderate bargaining power. The existence of numerous online grocery delivery services and the enduring option of traditional in-store shopping means customers can easily switch if they find better value elsewhere. This makes them sensitive to pricing, including delivery fees, service charges, and any product markups.
For instance, in 2024, reports indicated that delivery and service fees were significant factors influencing customer choice in the online grocery market. Instacart counters this by emphasizing convenience, a wide product selection, and loyalty programs like Instacart+ which aims to reduce perceived costs for frequent users by offering benefits such as waived delivery fees on eligible orders.
Instacart+ members, paying an annual fee for perks like free delivery, form a more committed customer base. While their subscription reduces their immediate bargaining power, they still demand high service quality, fast delivery, and good value. Instacart leverages this program to encourage more frequent orders and larger purchases.
Consumers are definitely feeling the pinch with rising prices, and this makes them more aware of every dollar spent. For Instacart, this means customers might look for cheaper options, perhaps even going back to shopping in physical stores to avoid delivery fees and service charges. This growing price sensitivity directly boosts the bargaining power of Instacart's customers.
Because customers are more likely to shop around, Instacart is compelled to keep its pricing competitive. They're also pushed to offer deals, discounts, and loyalty programs to keep people coming back. In 2024, for example, many grocery delivery services, including Instacart, have been observed to ramp up promotional offers to combat customer churn due to cost concerns.
Convenience and Time Savings Demand
Customers highly value the convenience and time savings Instacart provides. This core benefit, however, can be eroded if competing services offer comparable or better ease of use, or if Instacart’s platform becomes difficult to navigate. For instance, in 2024, the demand for quick and effortless shopping experiences remains a primary driver for online grocery adoption.
- Customer Convenience: The ability to order groceries from home saves significant time compared to traditional in-store shopping.
- Time Savings: Reduced travel, browsing, and checkout times are key attractions for Instacart users.
- Competitive Landscape: If competitors match or exceed Instacart’s convenience, customer loyalty may falter.
- User Experience: A clunky or inefficient app interface can directly impact customer satisfaction and retention.
Broad Selection and Accessibility
Instacart's extensive network of retail partners across North America, offering a vast array of products, significantly enhances customer choice. This broad selection, available through a single platform, dilutes the bargaining power of any single customer by presenting numerous alternatives for their grocery needs. Customers, in turn, come to expect this wide accessibility as a standard feature.
- Vast Product Assortment: Instacart partners with over 1,400 retailers, including major chains and local grocers, providing millions of unique SKUs to consumers.
- Customer Expectation: The platform's ability to aggregate diverse offerings means customers anticipate finding virtually any grocery item they desire.
- Reduced Individual Leverage: With so many options readily available on Instacart, individual customers have less power to negotiate prices or terms with the platform itself.
Customers' bargaining power remains significant due to the ease of switching between grocery delivery services and the continued availability of traditional in-store shopping. This price sensitivity, amplified by economic conditions in 2024, pushes Instacart to maintain competitive pricing and offer promotions. While Instacart+ aims to foster loyalty, customers still expect high service quality and value, directly influencing their purchasing decisions.
Instacart's broad retail partnerships, offering millions of products, dilute individual customer leverage by providing extensive choice. Customers expect this wide accessibility as a standard, making them less inclined to negotiate with the platform itself. The convenience and time savings offered by Instacart are key differentiators, but they can be challenged by competitors offering similar or superior user experiences.
| Factor | Impact on Bargaining Power | Instacart's Response |
|---|---|---|
| Price Sensitivity (2024) | High; customers seek value, scrutinize fees. | Promotional offers, loyalty programs (Instacart+). |
| Availability of Alternatives | Moderate to High; easy switching to competitors or in-store. | Emphasis on convenience, wide selection, and user experience. |
| Customer Loyalty Programs | Reduced for members, but expectations remain high. | Waived delivery fees, exclusive perks for Instacart+ members. |
| Product Variety | Diluted; vast selection reduces individual customer leverage. | Partnerships with over 1,400 retailers, offering millions of SKUs. |
What You See Is What You Get
Instacart Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. It details Instacart's competitive landscape through a Porter's Five Forces analysis, examining threats from new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry within the online grocery delivery market.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Instacart contends with fierce rivalry from giants like DoorDash and Uber Eats, both actively broadening their grocery delivery offerings. These platforms benefit from established, vast networks of delivery personnel and loyal customer bases cultivated through their restaurant delivery operations, enabling a swift incursion into the grocery sector.
In 2024, DoorDash reported a significant increase in its grocery delivery volume, aiming to capture a larger share of Instacart's market. Uber Eats has also made substantial investments in expanding its grocery partnerships and delivery infrastructure, directly challenging Instacart's dominance.
Large retailers like Walmart, Amazon with Amazon Fresh, and Kroger are formidable rivals, having built their own sophisticated online grocery and delivery operations. These giants can seamlessly blend their online and physical store experiences, often undercutting prices and utilizing their extensive, well-established supply chains to their advantage.
The online grocery sector is experiencing robust expansion, yet it's also becoming a more competitive arena. Instacart, while holding a significant market share, particularly in outsourced delivery services, is feeling the pressure to sustain its growth and profitability. This is due to the escalating rivalry and evolving consumer spending patterns.
In 2024, the online grocery market continued its upward trajectory, with projections indicating further growth. However, this expansion has attracted numerous players, intensifying competition. Instacart's ability to navigate this crowded landscape and maintain its market leadership is crucial for its ongoing success and financial health.
Pricing and Fee Competition
Instacart faces intense rivalry through aggressive pricing tactics, including delivery fees, service charges, and product markups. Competitors frequently undercut Instacart by offering lower fees or innovative subscription plans designed to lure customers away. This forces Instacart to continually analyze and adjust its pricing to stay competitive in the crowded grocery delivery market.
- Delivery Fee Wars: Many services offer free or significantly reduced delivery fees, especially for new users or with minimum order values.
- Subscription Models: Competitors are experimenting with various subscription tiers that bundle benefits like free delivery, reduced service fees, and exclusive discounts, directly challenging Instacart's existing membership programs.
- Product Markup Differentiation: Some platforms may absorb costs or operate with thinner margins on certain popular grocery items to appear more attractive on price comparison, pressuring Instacart's overall price perception.
- Promotional Campaigns: Frequent discounts, BOGO offers, and loyalty rewards are standard competitive tools, requiring Instacart to invest heavily in marketing and promotions to retain its customer base.
Technological Innovation and Strategic Partnerships
Technological innovation is a major battleground in the grocery delivery space, with companies constantly seeking an edge. Instacart is actively investing in AI for better customer recommendations and optimizing delivery routes. For instance, their investment in Caper Carts, which are AI-powered, checkout-free grocery carts, signals a move towards in-store tech integration.
Strategic partnerships are also crucial for expanding services and reach. Instacart has formed alliances with companies like Uber Eats to broaden its delivery capabilities and with YouTube for content integration. These collaborations are vital for staying competitive in a market where differentiation through technology and service offerings is key.
- AI-Driven Enhancements Instacart is leveraging artificial intelligence for personalized shopping experiences and efficient logistics.
- Strategic Alliances Partnerships with entities like Uber Eats and YouTube expand Instacart's service ecosystem and customer engagement.
- In-Store Technology Investments Ventures like Caper Carts demonstrate Instacart's commitment to innovating the physical grocery shopping experience.
Instacart faces intense competition from established players like DoorDash and Uber Eats, who are rapidly expanding their grocery delivery services. These competitors leverage their existing vast delivery networks and large customer bases to gain market share. In 2024, DoorDash reported substantial growth in its grocery delivery volume, directly challenging Instacart's position.
Major retailers such as Walmart, Amazon (with Amazon Fresh), and Kroger are also significant rivals, possessing their own robust online grocery and delivery infrastructure. These companies can offer competitive pricing and integrate online and in-store experiences seamlessly, utilizing their extensive supply chains.
The competitive landscape is characterized by aggressive pricing strategies, including delivery fee wars and varied subscription models designed to attract and retain customers. Companies are frequently offering lower fees or bundled benefits, forcing Instacart to continually adapt its pricing and promotional efforts.
Technological innovation and strategic partnerships are key differentiators. Instacart is investing in AI for better customer experiences and route optimization, exemplified by its involvement with Caper Carts. Partnerships, such as the one with Uber Eats, are crucial for expanding service reach and staying competitive.
| Competitor | 2024 Grocery Delivery Focus | Key Competitive Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| DoorDash | Significant increase in grocery delivery volume | Leveraging existing delivery network, aggressive expansion |
| Uber Eats | Substantial investment in grocery partnerships and infrastructure | Expanding service offerings, integrating with broader mobility platform |
| Walmart | Continued growth of Walmart+ and curbside pickup | Integrated online/offline experience, competitive pricing, large store footprint |
| Amazon Fresh | Enhancing delivery speed and selection | Utilizing Prime membership benefits, extensive logistics network |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Traditional in-store grocery shopping remains the most significant substitute for Instacart's service. Many consumers still value the ability to personally inspect and select items, particularly fresh produce, and to bypass delivery fees and potential price markups inherent in online platforms. This preference directly impacts the growth trajectory of online grocery services.
The post-pandemic period has seen a notable resurgence in in-store shopping, which has consequently moderated the rapid growth observed in online grocery services during the height of the pandemic. For instance, while online grocery sales saw substantial increases in 2020 and 2021, growth rates have since normalized. In 2023, the U.S. online grocery market experienced a slowdown, with some reports indicating a slight contraction in market share compared to the peak pandemic years, underscoring the persistent appeal of brick-and-mortar retail.
Meal kit delivery services like HelloFresh and specialty online food retailers present a significant threat by directly substituting a portion of Instacart's traditional grocery shopping. These services offer curated ingredients and recipes, appealing to consumers prioritizing convenience and unique culinary experiences, thereby capturing a segment of the market that might otherwise rely on broader grocery delivery.
While these DTC options may not replace a full grocery basket, their growing popularity, particularly among busy professionals and food enthusiasts, directly erodes the demand for a comprehensive grocery shopping trip facilitated by Instacart. For instance, HelloFresh reported serving 4.2 million customers globally in the first quarter of 2024, highlighting the scale of this alternative.
General food delivery platforms like DoorDash and Uber Eats are a significant threat. These services, initially focused on restaurant meals, are broadening their scope to include convenience items and even full grocery orders, directly competing with Instacart's core business. For instance, in 2024, Uber Eats continued its expansion into grocery and convenience delivery, aiming to capture a larger share of the at-home food consumption market.
While Instacart has formed partnerships, such as with Uber Eats for restaurant delivery, these broader platforms still represent a substantial substitution for consumers who might otherwise opt for home meal preparation or traditional grocery shopping. The convenience and expanding selection offered by these competitors can divert customers away from Instacart's grocery-centric model.
Other Retailers' Online Platforms with Pickup Options
Many traditional grocery retailers and mass merchandisers, such as Walmart and Kroger, provide their own online ordering with curbside pickup. This service acts as a significant substitute by allowing customers to avoid delivery fees, making it a more economical choice for those prioritizing convenience without the extra cost of home delivery.
Consumers increasingly value the flexibility of picking up their groceries at their convenience, directly from the retailer's location. This trend is evident as curbside pickup adoption continued to grow through 2024, with many major retailers reporting substantial increases in their pickup order volumes compared to pre-pandemic levels.
- Cost Savings: Eliminates delivery fees, a key driver for consumers.
- Convenience: Offers flexibility in pickup times without waiting for a delivery window.
- Retailer Control: Customers interact directly with the retailer, potentially building loyalty.
Consumers Opting for Cheaper Alternatives or Smaller Basket Sizes
Economic pressures and inflation are significantly impacting consumer behavior, pushing shoppers towards more budget-friendly options. This often translates to reduced discretionary spending, smaller order sizes, or a deliberate switch to cheaper product alternatives. While not a direct substitute for the convenience of grocery delivery itself, these shifts represent a substitution of premium or larger orders with more cost-conscious shopping habits.
For instance, during 2024, many consumers actively sought out private label brands or promotional items to manage their grocery bills. This trend is evidenced by the continued growth of private label sales, which have been gaining market share across major retailers. Instacart's platform, while facilitating access to a wide range of products, is not immune to this underlying consumer demand for value.
- Consumer Spending Shifts: Inflationary pressures in 2024 have led to a noticeable decrease in the average basket size for many consumers.
- Preference for Value Brands: A growing number of shoppers are prioritizing lower-priced or store-brand alternatives over premium or national brands.
- Reduced Discretionary Purchases: Consumers are cutting back on non-essential items within their grocery orders to manage household budgets more effectively.
- Impact on Order Value: These combined factors can lead to a substitution of higher-value orders with more budget-focused shopping behaviors on platforms like Instacart.
The threat of substitutes for Instacart is substantial, encompassing traditional in-store shopping, meal kit services, and broader food delivery platforms. Consumers often prefer the tactile experience of selecting groceries themselves, especially for fresh items, and may bypass delivery fees and potential markups. In 2023, the U.S. online grocery market saw a normalization of growth rates after pandemic peaks, indicating the enduring appeal of brick-and-mortar retail.
Meal kit services like HelloFresh, which served 4.2 million global customers in Q1 2024, directly substitute a portion of Instacart's offering by providing curated ingredients for specific meals. Similarly, platforms like Uber Eats expanded their grocery delivery capabilities in 2024, competing for at-home food consumption. Retailers like Walmart and Kroger offer their own convenient curbside pickup options, allowing customers to avoid delivery fees and maintain direct relationships with the store.
| Substitute Type | Key Differentiator | Consumer Appeal | 2024 Relevance Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| In-Store Shopping | Personal item selection, no fees/markups | Tangible product inspection, cost savings | Resurgence in foot traffic post-pandemic |
| Meal Kit Services | Curated ingredients, recipes | Convenience, culinary exploration | HelloFresh: 4.2M global customers (Q1 2024) |
| Food Delivery Platforms | Broadened offerings (restaurants, convenience, groceries) | All-in-one delivery convenience | Uber Eats' continued grocery expansion |
| Retailer Curbside Pickup | Direct retailer fulfillment, no delivery fees | Cost-effectiveness, flexible pickup | Increased pickup order volumes reported by retailers |
Entrants Threaten
Launching a new online grocery delivery service demands a substantial financial commitment. This includes developing robust technology platforms, setting up efficient logistics and delivery networks, executing broad marketing campaigns, and recruiting a reliable base of shoppers and retail partners. For instance, building a competitive tech stack alone can cost millions, and establishing a national delivery infrastructure requires extensive investment in vehicles and warehousing.
This considerable upfront capital requirement acts as a significant hurdle for prospective competitors looking to enter the online grocery delivery market. Newcomers must secure substantial funding to even begin operations, making it difficult for smaller or less capitalized entities to challenge established players like Instacart. The sheer scale of investment needed creates a formidable barrier, protecting existing market participants from immediate new threats.
Instacart's established network effects present a significant barrier to new entrants. By mid-2024, the company boasted partnerships with over 1,500 retail banners, creating a vast selection for consumers.
Furthermore, a substantial base of active shoppers and customers across North America has been cultivated, making it difficult for newcomers to gain comparable traction. Replicating this intricate web of relationships and building equivalent trust with both retailers and consumers would be a formidable undertaking for any new player entering the grocery delivery market.
Instacart has cultivated strong brand recognition and a devoted customer base, significantly boosted by its Instacart+ subscription program which offers benefits like free delivery. This loyalty makes it challenging for new competitors to lure away shoppers.
To overcome Instacart's established presence, new entrants would require considerable investment in marketing and must present a highly attractive value proposition to entice customers to switch from their current, familiar service.
Regulatory and Legal Hurdles
The gig economy model, central to Instacart's operations, faces increasing scrutiny and evolving labor laws concerning independent contractors. New entrants must grapple with a complex and often fragmented legal landscape, where regulations regarding worker classification and benefits can differ significantly by state or country, thereby increasing the cost and time to market.
Navigating these regulatory hurdles presents a substantial barrier. For instance, in 2023, several states continued to debate or implement new legislation impacting gig workers, potentially requiring businesses to reclassify contractors as employees. This could necessitate significant changes to operating models and cost structures for any new player attempting to enter the market.
- Evolving Labor Laws: Gig economy platforms are increasingly subject to legal challenges and legislative changes aimed at worker protections.
- Regional Variations: Compliance requirements for independent contractors vary widely across different jurisdictions, complicating nationwide or international expansion.
- Increased Operational Costs: Adhering to diverse and changing regulations can significantly raise the capital and ongoing expenses for new market entrants.
Technological Complexity and Operational Efficiency
The technological complexity inherent in Instacart's operations presents a substantial barrier to new entrants. Building and maintaining a robust platform capable of real-time inventory management, intricate order fulfillment, dynamic delivery routing, and comprehensive customer service demands significant technical expertise and ongoing investment. For instance, the sophisticated algorithms powering Instacart's logistics are a result of years of development and refinement, making it difficult for newcomers to replicate this level of efficiency quickly.
Achieving operational efficiency, especially in the demanding realm of last-mile delivery, is another critical hurdle. New entrants must not only develop the technology but also master the logistics of coordinating a large fleet of shoppers and drivers, optimizing delivery times, and ensuring customer satisfaction. This requires substantial capital for infrastructure, training, and continuous process improvement. In 2024, the average cost of last-mile delivery for e-commerce businesses can range significantly, but achieving profitability at scale, as Instacart aims to, necessitates overcoming these high operational costs.
- High Upfront Investment: New entrants face considerable costs in developing and scaling the necessary technology infrastructure.
- Technical Expertise Required: Sophisticated software for order management, routing, and customer service is crucial and difficult to replicate.
- Operational Complexity: Mastering last-mile logistics, including driver management and delivery optimization, is a significant challenge.
- Continuous Innovation: The need for ongoing platform improvements and efficiency gains requires sustained R&D and capital allocation.
The threat of new entrants into the online grocery delivery market, while present, is significantly mitigated by substantial barriers to entry. These include the immense capital required for technology, logistics, and marketing, alongside the complexities of navigating evolving labor laws and building established network effects. Instacart's existing scale, brand recognition, and customer loyalty further solidify its position, making it challenging for newcomers to gain substantial market share.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Developing robust tech platforms, logistics networks, and marketing campaigns demands millions in investment. | High hurdle, requiring significant funding for even basic operations. |
| Network Effects | Instacart's vast partnerships (over 1,500 retail banners by mid-2024) and large shopper/customer base create a strong ecosystem. | Difficult to replicate, making it hard for new players to offer comparable selection and convenience. |
| Brand Loyalty & Subscription Programs | Instacart+ offers benefits that foster customer retention, making switching costly for consumers. | Requires substantial marketing investment and a compelling value proposition to attract customers. |
| Regulatory Landscape | Evolving labor laws for gig workers, with regional variations, increase compliance costs and operational complexity. | Adds significant time and expense to market entry and ongoing operations. |
| Technological & Operational Complexity | Sophisticated platforms for real-time inventory, dynamic routing, and efficient last-mile delivery are difficult and costly to build and maintain. | Requires deep technical expertise and substantial ongoing investment for efficient operation. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Instacart Porter's Five Forces analysis is built on a foundation of diverse data, including Instacart's own investor relations disclosures, reports from major grocery retailers, and market research from firms specializing in e-commerce and food delivery.
We also incorporate data from industry publications, news articles detailing competitive moves, and consumer spending trend reports to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
