Incyte Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Incyte Bundle
Incyte faces significant competitive pressures, from the intense rivalry among existing players to the substantial threat of new entrants in the biopharmaceutical sector. Understanding the bargaining power of both buyers and suppliers is crucial for navigating this dynamic market.
The full analysis reveals the strength and intensity of each market force affecting Incyte, complete with visuals and summaries for fast, clear interpretation. Unlock key insights into Incyte’s industry forces—from buyer power to substitute threats—and use this knowledge to inform strategy or investment decisions.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Incyte's reliance on a select group of specialized suppliers for crucial raw materials and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) significantly amplifies supplier bargaining power. These suppliers often possess unique expertise or proprietary processes, making it difficult for Incyte to find readily available alternatives.
For instance, the biopharmaceutical industry generally sees a high degree of supplier concentration for highly regulated and specialized components. This concentration means that a disruption or price hike from even a single key supplier could have a substantial ripple effect on Incyte's manufacturing timelines and overall cost of goods sold.
Suppliers possessing patents or proprietary technologies crucial for Incyte's drug development and manufacturing processes wield significant bargaining power. This is especially true in sophisticated therapeutic fields requiring specialized reagents, cell lines, or unique equipment. For instance, if a key component for a novel gene therapy is only available from a single supplier with strong patent protection, Incyte's options become limited, potentially driving up costs.
The biopharmaceutical industry presents significant switching costs for companies like Incyte. These costs involve rigorous validation of new raw materials, extensive re-qualification of manufacturing processes, and the complex, lengthy journey through regulatory approvals. This substantial investment in time and capital makes it difficult and expensive for Incyte to change suppliers.
These high switching costs directly empower Incyte's suppliers. When it's costly for Incyte to move to a different supplier, existing suppliers gain leverage, potentially leading to less favorable pricing or terms for Incyte. For instance, the development and approval of a new cell line or a specialized reagent can take years and millions of dollars, locking Incyte into existing relationships.
Availability of alternative suppliers
The availability of alternative suppliers significantly impacts Incyte's bargaining power. A scarcity of qualified and compliant suppliers, particularly for specialized components or services crucial in hematology/oncology and autoimmunity, inherently bolsters the negotiating position of those few existing suppliers.
If Incyte faces a limited or non-existent pool of viable alternative suppliers, its ability to negotiate favorable terms and pricing is considerably weakened. Conversely, a more robust and competitive supplier landscape would naturally dilute this power, offering Incyte greater leverage.
- Limited Supplier Pool: Incyte's reliance on a narrow set of specialized suppliers for critical raw materials or manufacturing processes in its niche therapeutic areas grants those suppliers increased bargaining power.
- Impact on Costs: A lack of readily available alternatives can lead to higher input costs for Incyte, directly affecting its cost of goods sold and overall profitability.
- Supply Chain Risk: Dependence on a few suppliers also introduces supply chain risks, as disruptions from a single source can have a significant impact on Incyte's production schedules.
- Strategic Sourcing: Incyte's strategy to mitigate supplier power often involves identifying and qualifying new suppliers, fostering long-term relationships, and potentially developing in-house capabilities for critical inputs.
Supplier's ability to forward integrate
The bargaining power of suppliers is influenced by their ability to forward integrate, meaning they could potentially enter Incyte's market. If key suppliers, such as contract manufacturing organizations (CMOs) or specialized research partners, possess the expertise and resources to develop their own therapeutics, they gain leverage. This threat of competition from suppliers can significantly impact Incyte's negotiation power.
For instance, a CMO that has developed proprietary drug delivery technology could decide to leverage this to create its own generic or biosimilar versions of Incyte's products, directly competing. This capability would naturally elevate their position in any negotiation for manufacturing services.
- Supplier Forward Integration Threat: If suppliers can move into Incyte's market, their bargaining power increases.
- Potential Competitors: CMOs and research organizations with significant expertise are key potential forward integrators.
- Impact on Negotiations: The credible threat of a supplier becoming a competitor enhances their negotiating position.
Incyte's suppliers hold considerable bargaining power due to the highly specialized nature of raw materials and APIs in the biopharmaceutical sector. This power is amplified by the significant switching costs and the limited availability of alternative qualified suppliers, particularly for niche therapeutic areas like hematology/oncology and autoimmunity.
The threat of suppliers forward integrating into Incyte's market, such as CMOs developing their own therapeutics, further strengthens their negotiating leverage. This dynamic can lead to increased input costs and supply chain risks for Incyte.
| Factor | Incyte's Vulnerability | Supplier Leverage |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High reliance on few specialized suppliers | Ability to dictate terms and pricing |
| Switching Costs | High costs for validation and regulatory approval | Difficulty for Incyte to change suppliers |
| Proprietary Technology | Dependence on patented materials/processes | Control over essential inputs |
| Forward Integration Threat | Potential competition from CMOs/partners | Increased negotiating power |
What is included in the product
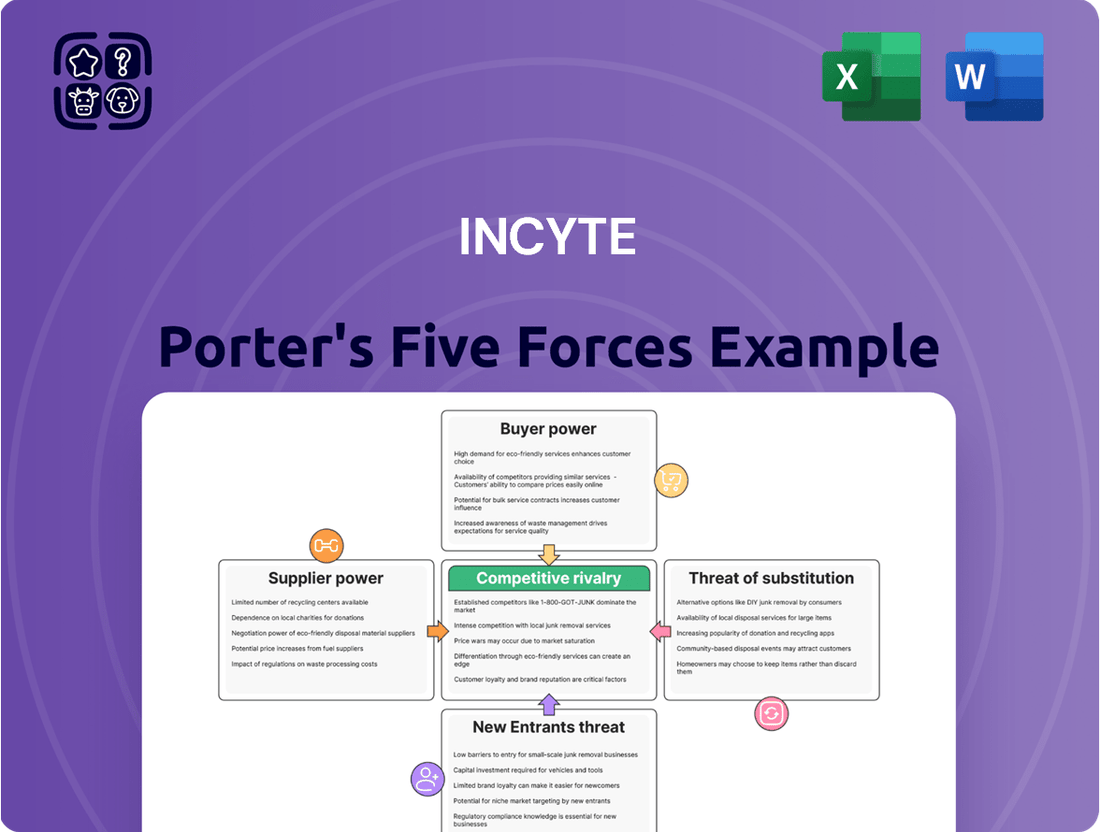
This Incyte Porter's Five Forces analysis dissects the competitive intensity within its operating environment, examining the power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the rivalry among existing players.
Visualize the competitive landscape instantly with a dynamic, interactive Porter's Five Forces model, eliminating the guesswork in strategic planning.
Customers Bargaining Power
In the biopharmaceutical sector, the bargaining power of customers is substantial, largely due to the concentration of buyers. Entities like national healthcare systems, large hospital networks, and Pharmacy Benefit Managers (PBMs) are major purchasers of drugs, wielding significant influence over pricing and reimbursement terms. These consolidated buyers can negotiate favorable terms due to the sheer volume of their purchases.
The impact of these large buyers is amplified by regulatory actions. For example, the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) in the United States has empowered Medicare to negotiate drug prices directly. This legislative change, effective from 2026 for the first set of drugs, directly increases the leverage of government payers, putting further downward pressure on drug pricing and impacting companies like Incyte.
Incyte's customers, particularly patients and healthcare systems, exhibit significant price sensitivity. This is largely due to shifts in reimbursement models and the growing burden of out-of-pocket expenses for patients. For example, in 2024, many insurers are implementing stricter prior authorization requirements and exploring tiered formularies, directly influencing which drugs are covered and at what cost.
Payers, including major government programs like Medicare and a multitude of private insurance companies, are increasingly focused on managing pharmaceutical spending. They are employing strategies such as value-based agreements, where payment is tied to patient outcomes, and aggressive utilization management techniques. These measures put considerable pressure on Incyte's pricing power, especially for treatments that may not demonstrate a clear, substantial clinical superiority over existing alternatives.
As Incyte's flagship products, like Jakafi, near their patent expiration dates, the availability of generic or biosimilar alternatives significantly bolsters customer bargaining power. This increased competition from lower-cost options empowers payers and patients, compelling Incyte to differentiate its offerings through enhanced efficacy, safety profiles, or robust patient support. The looming 'patent cliff' for key drugs, with Jakafi's patent expected to expire around 2028, intensifies this pressure.
Customer's access to information and comparative effectiveness data
Customers, particularly healthcare providers and payers, are increasingly empowered by readily available data regarding drug efficacy, safety profiles, and overall cost-effectiveness. This heightened transparency enables them to make more informed purchasing decisions, directly translating into a stronger demand for superior value and enhanced bargaining power.
The influence of comparative effectiveness research is a significant factor, directly impacting formulary decisions made by insurance providers and shaping the prescribing habits of physicians. For instance, by 2024, a substantial portion of major US health insurers were actively incorporating comparative effectiveness data into their drug coverage policies, aiming to steer patients towards treatments offering the best outcomes relative to cost.
- Increased Data Accessibility: Patients and healthcare professionals can easily access data on drug performance and pricing through online databases and health technology assessments.
- Informed Decision-Making: Access to comparative effectiveness data allows payers and providers to negotiate better terms based on real-world evidence of a drug's value.
- Cost-Conscious Negotiations: This transparency fuels negotiations, pushing pharmaceutical companies to justify higher prices with demonstrable clinical advantages.
- Market Pressure: The ability for customers to compare options puts pressure on manufacturers to innovate and price competitively, especially in therapeutic areas with multiple treatment options.
Switching costs for customers (e.g., changing prescribed treatments)
Switching costs for patients, while present due to established treatment routines, can be less of a barrier than perceived. If a new therapy offers demonstrably better efficacy or a more favorable side-effect profile, patients may be motivated to switch, especially if their current treatment isn't optimal. For example, if a patient experiences significant side effects from an existing JAK inhibitor, the appeal of a new one with a cleaner safety profile could outweigh the inertia of changing their medication.
Healthcare providers and payers, however, often face lower switching costs when evaluating new pharmaceutical options. The decision to prescribe or cover a particular drug is heavily influenced by clinical data, formulary status, and cost-effectiveness. For instance, if Incyte's new oncology drug, despite its innovation, is priced significantly higher than a competitor with comparable efficacy, payers and physicians might readily opt for the more budget-friendly alternative, impacting Incyte's market penetration. In 2024, the pressure on healthcare systems to manage costs remains a significant factor in drug adoption decisions.
The bargaining power of customers, particularly payers like insurance companies and government health programs, is amplified by the availability of therapeutic alternatives. These entities can leverage competition to negotiate lower prices or demand evidence of superior value. For example, if Incyte faces competition in the myelofibrosis market from drugs offering similar patient outcomes but at a lower price point, payers can exert considerable pressure on Incyte to adjust its pricing strategy or risk being excluded from preferred formularies.
- Patient Inertia vs. Clinical Benefit: While patients may resist changing treatments, compelling clinical advantages in efficacy or safety can overcome this inertia.
- Provider and Payer Cost Sensitivity: Healthcare providers and payers often have lower switching costs if a new drug offers a clear cost advantage or superior outcomes, influencing prescription and coverage decisions.
- Competitive Landscape Impact: The presence of alternative treatments with comparable or better value propositions significantly increases the bargaining power of customers, enabling them to negotiate pricing and access.
The bargaining power of customers in the biopharmaceutical sector, especially for companies like Incyte, is considerable. This strength stems from the concentrated nature of buyers, such as national healthcare systems and Pharmacy Benefit Managers (PBMs), who leverage their purchasing volume to negotiate favorable pricing and reimbursement terms. For instance, the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) in the US, effective from 2026 for initial drug selections, directly empowers Medicare to negotiate drug prices, thereby increasing payer leverage and potentially pressuring Incyte's pricing.
Price sensitivity among patients and healthcare systems is a significant factor, exacerbated by evolving reimbursement models and increasing patient out-of-pocket costs. In 2024, stricter prior authorization requirements and tiered formularies implemented by insurers directly influence drug coverage and affordability. Furthermore, payers are increasingly adopting value-based agreements and aggressive utilization management, which puts substantial pressure on Incyte's pricing power, particularly when new treatments do not offer a clear clinical advantage over existing options.
The looming patent expirations for Incyte's key products, such as Jakafi (expected around 2028), significantly bolster customer bargaining power by paving the way for generic or biosimilar competition. This competitive pressure compels Incyte to emphasize superior efficacy, safety, or patient support to differentiate its offerings. Additionally, increased transparency through readily accessible data on drug performance and cost-effectiveness empowers healthcare providers and payers to negotiate more effectively, demanding greater value and pushing for competitive pricing.
| Factor | Impact on Incyte | 2024 Context |
|---|---|---|
| Buyer Concentration | High bargaining power for large payers | Major payers (Medicare, large insurers) drive negotiations |
| Price Sensitivity | Pressure on drug pricing | Increased patient out-of-pocket costs, stricter formularies |
| Therapeutic Alternatives | Leverage for payers to negotiate | Competition in myelofibrosis market influences Incyte's pricing |
| Regulatory Actions | Increased government negotiation power | IRA empowers Medicare price negotiation from 2026 |
| Switching Costs (Payers) | Lower for payers based on data | Cost-effectiveness and clinical data drive payer decisions |
Same Document Delivered
Incyte Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Incyte Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of the competitive landscape within the pharmaceutical industry. The document you see here is precisely what you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring full transparency and no hidden content. This professionally formatted analysis is ready for immediate download and use, providing you with actionable insights into Incyte's market position.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The biopharmaceutical landscape, especially within hematology/oncology and inflammation/autoimmunity, is fiercely competitive. Incyte operates in arenas populated by a multitude of established pharmaceutical behemoths and nimble, innovative biotech firms, all striving to capture significant market share.
The oncology sector, a key area for Incyte, exemplifies this intense rivalry. For instance, the market for specific cancer treatments is crowded, with over 100 PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors reportedly in various stages of development as of early 2024, highlighting the sheer volume of players and pipeline assets.
The oncology market remains a prime area for revenue and innovation, attracting substantial research and development investment throughout the industry. This inherent attractiveness presents significant growth prospects for companies like Incyte, which reported a 15% rise in total revenues for 2024, primarily due to strong performance from Jakafi and Opzelura.
However, this lucrative landscape also intensifies competitive rivalry. As more companies enter or bolster their presence in these profitable segments, the pressure on existing players to differentiate and maintain market share increases significantly.
Incyte's competitive edge hinges on differentiating its novel therapeutics, focusing on superior efficacy, safety, and unique mechanisms of action. This differentiation is vital in a biopharma sector where innovation constantly reshapes the competitive landscape. For instance, Incyte's JAK inhibitor, Jakafi (ruxolitinib), has established a strong market position due to its proven benefits in myelofibrosis and polycythemia vera.
The strength of Incyte's intellectual property, including patents and orphan drug designations, provides a significant barrier to entry. However, the rapid pace of research and development means that even established market leaders face continuous challenges from emerging therapies. Incyte's pipeline, featuring candidates like povorcitinib and mutCALR, aims to bolster its portfolio of differentiated products and maintain its competitive standing.
Exit barriers for competitors
The biopharmaceutical industry, including companies like Incyte, faces substantial exit barriers. These are largely driven by the immense capital required for research and development (R&D), specialized manufacturing facilities, and navigating stringent regulatory approval processes. For instance, the average cost to develop a new drug from discovery to market approval was estimated to be around $2.6 billion by the Tufts Center for the Study of Drug Development in recent analyses, a figure that underscores the significant financial commitment.
These high fixed costs mean that biopharma companies are often reluctant to exit the market, even when facing challenging economic conditions or competitive pressures. Instead, they tend to persevere, continuing to invest in their existing pipelines and fight for market share. This persistence intensifies the competitive rivalry as players are less likely to divest or shut down operations easily.
The long-term nature of drug development further cements these exit barriers. Companies commit years, often decades, and billions of dollars to bringing a single drug to market. This creates a strong incentive to continue supporting and commercializing their products, rather than abandoning them prematurely.
- High R&D Investment: Biopharmaceutical companies invest heavily in drug discovery and clinical trials, with R&D spending for major pharmaceutical firms often exceeding 15-20% of their revenue.
- Specialized Manufacturing: Building and maintaining cGMP (current Good Manufacturing Practice) compliant facilities requires massive capital outlay and specialized expertise, making them difficult to repurpose or sell.
- Regulatory Hurdles: The extensive and costly process of gaining approval from bodies like the FDA means significant sunk costs that are only recouped upon successful market entry.
- Pipeline Commitment: Companies are committed to their drug pipelines, having already invested substantial resources, making divestment a difficult strategic choice.
Strategic alliances, mergers, and acquisitions among competitors
Strategic alliances, mergers, and acquisitions are a constant feature in the biopharmaceutical sector. Companies actively pursue these moves to bolster their drug pipelines, secure broader market reach, or consolidate valuable intellectual property. This dynamic reshuffling significantly reshapes the competitive environment, often leading to the emergence of more formidable rivals or the swift introduction of groundbreaking treatments.
For Incyte, this means a continuous need for agility and strategic foresight. The industry witnessed substantial M&A activity in 2024, with major deals impacting therapeutic areas relevant to Incyte's focus. For instance, the acquisition of Seagen by Pfizer for approximately $43 billion, completed in late 2023 and impacting 2024 competitive dynamics, underscored the trend of consolidation in oncology. Similarly, the ongoing partnerships and licensing agreements in areas like gene therapy and precision medicine highlight the importance of strategic collaboration for pipeline expansion and market access.
- Increased Consolidation: Biopharma M&A activity remained robust in early 2024, with companies seeking scale and diversification.
- Pipeline Augmentation: Alliances and acquisitions are critical for biotechs to access novel drug candidates and technologies.
- Market Access: Mergers can provide immediate access to established markets and distribution networks.
- Competitive Response: Incyte must continually assess its strategic positioning in light of competitor consolidation and innovation.
Competitive rivalry is a defining characteristic of the biopharmaceutical industry, particularly in Incyte's core areas of hematology/oncology and inflammation/autoimmunity. The market is populated by numerous established pharmaceutical giants and agile biotech firms, all vying for market share and innovation leadership. This intense competition is fueled by the high attractiveness of these therapeutic sectors, drawing significant R&D investment and leading to crowded pipelines, especially in oncology where over 100 PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors were in development by early 2024.
The sheer volume of players and the rapid pace of innovation mean that companies like Incyte must constantly differentiate their offerings through superior efficacy, safety profiles, and unique mechanisms of action. Incyte's JAK inhibitor, Jakafi, exemplifies successful differentiation, having secured a strong market position in myelofibrosis and polycythemia vera. However, the industry's high exit barriers, stemming from massive R&D costs (estimated at $2.6 billion per drug) and specialized manufacturing, encourage companies to persevere, intensifying rivalry.
Strategic alliances and mergers, such as the $43 billion acquisition of Seagen by Pfizer in late 2023, further reshape the competitive landscape. These moves aim to bolster drug pipelines, expand market reach, and consolidate intellectual property, forcing companies like Incyte to remain agile and strategically positioned to navigate this dynamic environment.
| Metric | Value | Source/Context |
| Incyte Revenue Growth (2024) | 15% | Incyte Financial Reports |
| PD-1/PD-L1 Inhibitors in Development (Early 2024) | Over 100 | Industry Analysis |
| Average Drug Development Cost | ~$2.6 billion | Tufts Center for the Study of Drug Development |
| Seagen Acquisition by Pfizer | ~$43 billion | Late 2023 / Early 2024 Market Data |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Incyte's products is significant, stemming from a broad range of alternative treatments. These include other drug classes targeting similar diseases, as well as non-pharmacological interventions like surgery, radiation therapy, and lifestyle modifications. For instance, in the realm of autoimmune diseases, patients can often choose between established immunosuppressants and advanced biologic therapies, some of which might offer cost advantages or distinct safety profiles.
The threat of substitutes for Incyte's products is amplified by the increasing focus on cost-effectiveness within healthcare systems. When alternative treatments offer similar results for less money, or even better outcomes at a comparable price, they become highly attractive. For example, in 2024, the pharmaceutical industry continued to see heightened scrutiny from payers and governments on drug pricing, pushing for demonstrable value in return for investment.
While inertia exists for patients on stable chronic condition treatments, switching costs can be low if a substitute offers a significant advantage. For example, if a new therapy boasts fewer side effects or greater convenience, providers may readily switch patients, overcoming minor administrative hurdles.
Innovation in competing therapeutic areas or technologies
Innovation in competing therapeutic areas or technologies presents a significant threat. For instance, advancements in gene editing technologies like CRISPR, which saw substantial research funding and clinical trial progress throughout 2024, could offer curative solutions for diseases currently managed by Incyte’s small molecule drugs. This emergence of entirely new treatment modalities can quickly shift market demand away from established therapies.
The development of novel small molecules or biologics targeting different pathways for Incyte's core indications, such as myelofibrosis or polycythemia vera, also poses a threat. Companies investing heavily in next-generation therapies, with R&D pipelines focused on overcoming resistance or improving patient outcomes, could introduce superior alternatives. For example, by mid-2024, several biotech firms announced promising early-stage data for novel kinase inhibitors with potentially improved safety profiles, directly challenging existing treatment paradigms.
- Emergence of Gene Therapies: Advancements in gene editing technologies could offer curative alternatives, impacting demand for Incyte's current treatments.
- Novel Small Molecules & Biologics: Competitors developing next-generation therapies with improved efficacy or safety profiles pose a direct threat.
- R&D Investment Trends: Significant R&D funding in competing therapeutic areas, as observed throughout 2024, indicates a strong pipeline of potential substitutes.
- Clinical Trial Progress: Positive early-stage data for alternative treatments can rapidly alter the competitive landscape and patient/physician preferences.
Regulatory and reimbursement policies favoring certain types of treatments
Government policies and reimbursement decisions heavily influence the appeal of substitute treatments. For instance, in 2024, many healthcare systems continue to prioritize cost-effectiveness, leading to favorable reimbursement for generic or biosimilar alternatives to branded pharmaceuticals. This can significantly increase the threat of substitution for innovative but more expensive therapies.
Changes in formulary guidelines by major payers, such as private insurers and government programs, directly impact prescribing patterns. If a formulary shifts to favor specific, often lower-cost, treatment pathways as a first-line option, it compels physicians to consider these alternatives, thereby amplifying the substitution threat for Incyte’s products.
The regulatory landscape also plays a crucial role. Policies that streamline the approval process for biosimilars, for example, can accelerate their market entry. By mid-2024, several key biologics are facing or are expected to face biosimilar competition, directly impacting the market share of originator products and highlighting the growing threat of substitution driven by regulatory enablement.
- Regulatory Favoritism: Policies favoring generics and biosimilars in 2024 increase substitution threats.
- Payer Influence: Formulary changes by insurers steer prescribers toward lower-cost alternatives.
- Biosimilar Approvals: Increased regulatory approvals for biosimilars in 2024 directly challenge established treatments.
The threat of substitutes for Incyte's products remains a significant concern, driven by a dynamic healthcare landscape and evolving treatment paradigms. In 2024, the market continued to see a rise in cost-effective alternatives, including other drug classes and non-pharmacological interventions, directly impacting patient and physician choices.
Innovation in competing therapeutic areas, such as gene editing technologies, presents a potent substitute threat, with substantial research and clinical trial advancements observed throughout 2024. Furthermore, regulatory policies favoring generics and biosimilars, alongside payer formulary shifts, actively encourage the adoption of lower-cost alternatives, thereby intensifying the substitution pressure on Incyte's portfolio.
| Therapeutic Area | Incyte's Key Products (Examples) | Potential Substitute Modalities | 2024 Market Trend Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Myelofibrosis | Jakafi (ruxolitinib) | Other JAK inhibitors, non-JAK targeted therapies, stem cell transplant | Increased competition from other JAK inhibitors with potentially different side effect profiles; ongoing research into novel pathways. |
| Polycythemia Vera | Jakafi (ruxolitinib) | Hydroxyurea, interferon alfa, phlebotomy | Continued availability of established, lower-cost treatments; focus on long-term management and quality of life. |
| Autoimmune Diseases | Baricitinib (in certain indications) | Established immunosuppressants (e.g., methotrexate), other biologics (e.g., TNF inhibitors), JAK inhibitors from competitors | Growing market for biologics with diverse mechanisms of action; price sensitivity driving preference for cost-effective options. |
Entrants Threaten
The biopharmaceutical sector demands massive upfront investment in research, clinical testing, and production facilities. This high capital intensity acts as a significant hurdle for any aspiring competitor looking to enter the market.
Bringing a new drug to market is a lengthy and costly endeavor, often exceeding $1 billion and spanning over a decade, effectively deterring potential new entrants.
Incyte's substantial commitment to R&D, with an estimated expenditure of $1.93 billion to $1.96 billion for 2025, underscores the substantial financial barriers inherent in this industry.
The threat of new entrants in the pharmaceutical industry, particularly for companies like Incyte, is significantly dampened by incredibly strict regulatory approval processes. Agencies like the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) impose lengthy and complex requirements that act as substantial barriers.
Developing a new drug involves years of rigorous preclinical research and multiple phases of clinical trials, often spanning over a decade. The sheer cost and expertise required to navigate these stages, including extensive data submission and review, make it exceptionally difficult for newcomers to enter the market.
For instance, the average cost to develop a new drug is estimated to be over $2 billion, with a success rate of less than 10% from initial discovery to market approval. This high financial and time investment deters many potential competitors from even attempting to enter the space.
Incyte's strong intellectual property portfolio, particularly its patents and exclusivity periods for approved drugs, acts as a significant barrier to new entrants. This protection makes it challenging for competitors to introduce directly comparable products, forcing them to innovate with novel approaches or different therapeutic areas.
Established brand loyalty and patient/physician relationships
Established brand loyalty and deep patient/physician relationships present a significant barrier for new entrants looking to compete with companies like Incyte. These relationships are cultivated over time through consistent clinical performance, targeted marketing, and robust patient support initiatives. For instance, Incyte’s work in myelofibrosis has fostered strong ties with key opinion leaders and patient advocacy groups.
Newcomers must invest heavily in marketing and education to even begin chipping away at these entrenched connections. Building trust within the medical community is a slow and costly process, requiring demonstration of efficacy and safety that matches or exceeds existing treatments. In 2024, the pharmaceutical industry continued to see substantial R&D spending, with major players allocating billions to clinical trials and market penetration strategies, underscoring the investment needed to challenge established players.
- Brand Loyalty: Years of successful treatments and patient support build strong, lasting relationships.
- Physician Relationships: Trust and familiarity with existing therapies are hard for new entrants to overcome.
- Marketing & Education Costs: Significant investment is required to establish credibility and awareness for new products.
- Clinical Success: Proven track records in treating specific conditions are crucial for patient and physician adoption.
Access to distribution channels and payer formularies
New entrants in the pharmaceutical industry face significant hurdles in gaining access to crucial distribution channels and securing placement on payer formularies. This is a substantial barrier, as without these pathways, even innovative treatments struggle to reach patients and generate revenue.
For instance, in 2024, the landscape of pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs) and insurance companies remains highly consolidated, giving them immense power in negotiating formulary placement. Companies lacking established relationships or a substantial product pipeline find it exceptionally difficult to gain favorable terms. This often requires lengthy and complex negotiations, a process that can drain resources for smaller firms.
Emerging pharmaceutical companies may need to forge strategic alliances or partnerships to effectively navigate these intricate market access challenges. These collaborations can provide the necessary leverage and expertise to secure the desired distribution and formulary access, thereby mitigating the threat of new entrants in this critical area.
- Distribution Channel Access: New entrants must build or acquire robust networks to get their products to pharmacies and healthcare providers.
- Payer Formulary Placement: Gaining inclusion on insurance formularies is vital for patient affordability and market penetration.
- PBM Negotiations: Dealing with large PBMs for formulary inclusion is a complex and often costly process.
- Strategic Alliances: Partnerships can be essential for smaller companies to overcome market access barriers.
The threat of new entrants for Incyte is considerably low due to the immense capital required for research, development, and regulatory approval, often exceeding $2 billion per drug. The lengthy development cycle, frequently over a decade, and the low success rate of less than 10% from discovery to market further deter potential competitors. Incyte's substantial R&D investment, projected at $1.93 billion to $1.96 billion for 2025, highlights these significant financial barriers.
Navigating stringent regulatory pathways, such as those set by the FDA, presents another formidable obstacle. The complex and time-consuming approval process demands extensive clinical trials and data submission, making it exceptionally difficult for newcomers to enter the biopharmaceutical market. This regulatory landscape, combined with the high cost of clinical success, acts as a strong deterrent.
Furthermore, Incyte benefits from robust intellectual property protection through patents and exclusivity periods, which shields its products from direct competition. Established brand loyalty and strong relationships with physicians and patient advocacy groups, cultivated through years of successful treatments and support, are also difficult for new entrants to replicate. In 2024, the industry saw continued high R&D spending, reinforcing the investment needed to challenge established players.
Access to distribution channels and favorable formulary placement with consolidated payers like PBMs in 2024 pose significant market access challenges for new companies. These entities wield considerable negotiation power, making it difficult for firms without established relationships or strong product pipelines to secure market penetration. Strategic alliances are often necessary for smaller firms to overcome these barriers.
| Barrier | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High R&D, clinical trials, and manufacturing costs | Deters entry due to substantial financial investment needed |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Strict FDA approval processes and extensive data requirements | Lengthens time-to-market and increases development costs |
| Intellectual Property | Patents and exclusivity periods for approved drugs | Limits direct competition and forces innovation by new entrants |
| Market Access | Securing distribution and payer formulary placement | Challenging due to consolidated PBMs and payer negotiations |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Incyte Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of robust data, including Incyte's annual reports, SEC filings, and industry-specific market research from reputable firms like Evaluate Pharma and GlobalData. We also incorporate insights from clinical trial databases and patent filings to assess the threat of new entrants and the bargaining power of buyers.
