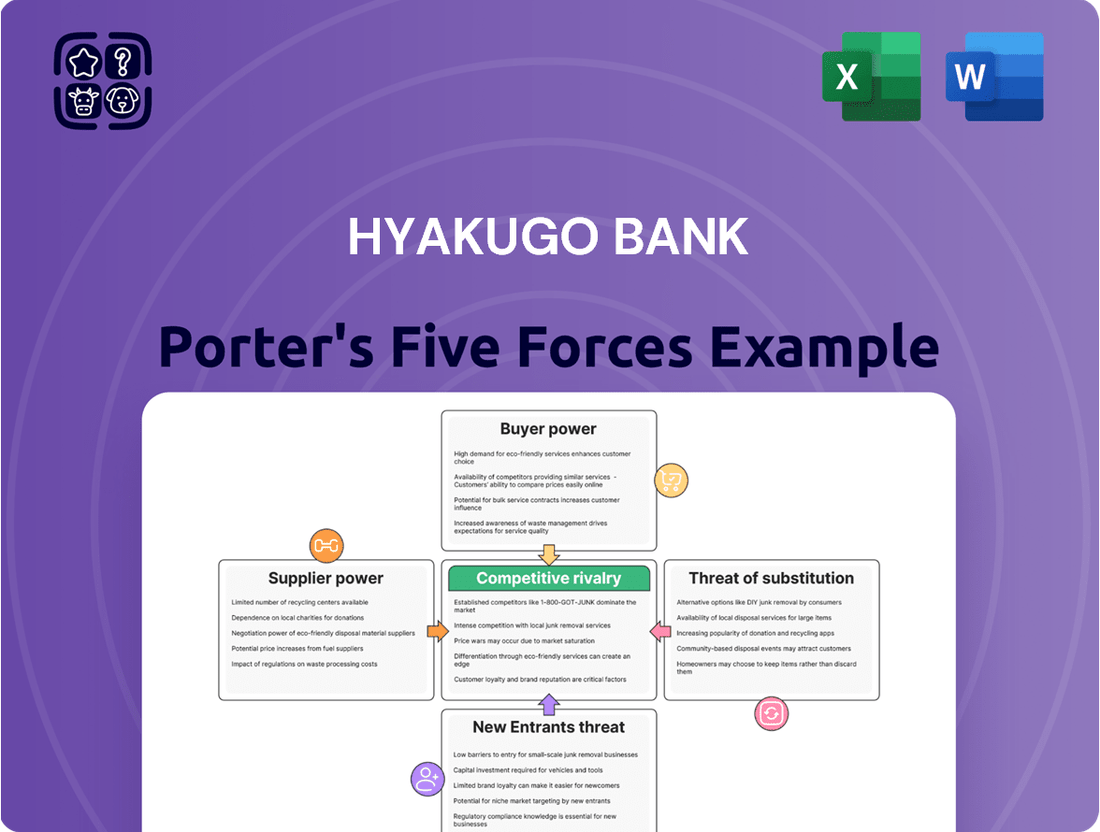
Hyakugo Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Hyakugo Bank Bundle
Hyakugo Bank operates within a dynamic financial landscape, facing pressures from rivals and the constant threat of new entrants. Understanding the bargaining power of its customers and the availability of substitute financial products is crucial for its strategic positioning.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Hyakugo Bank’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of suppliers for Hyakugo Bank is relatively low. This is primarily because the core financial infrastructure and technology Hyakugo Bank relies on are largely commoditized. For instance, many core banking systems and IT services are offered by multiple providers, preventing any single supplier from dictating terms. Furthermore, the stringent regulatory landscape in Japan's banking sector often standardizes many operational requirements, further reducing supplier leverage.
While specialized fintech solutions or advanced cybersecurity platforms might offer some suppliers more influence, Hyakugo Bank, like many Japanese financial institutions, can typically find alternative vendors. In 2024, the banking sector continued to see a competitive market for IT services, with cloud adoption and digital transformation driving demand for flexible and cost-effective solutions, which limits the power of individual technology suppliers.
The Bank of Japan (BOJ) and regulatory bodies are key 'suppliers' for Hyakugo Bank, providing monetary policy and regulatory frameworks. Changes in these, like the BOJ's interest rate adjustments, directly affect the bank's funding costs and profitability. Following the BOJ's rate hikes initiated in March 2024, deposit interest rates have seen an upward trend, impacting Hyakugo Bank's financial performance.
Technology providers for core banking systems and digital transformation initiatives wield considerable influence, particularly when their solutions are proprietary. This leverage is somewhat tempered by the expanding market for these services driven by Japan's banking sector's embrace of digital transformation and cloud adoption, which fosters greater supplier competition.
Supplier Power 4
The bargaining power of suppliers for Hyakugo Bank is moderately influenced by the demand for specialized human capital. Skilled professionals in areas like IT, cybersecurity, and financial consulting hold leverage due to the intense competition for their expertise in the rapidly digitizing financial sector. For instance, in 2024, the global shortage of cybersecurity professionals meant that companies, including banks, faced bidding wars for talent, driving up compensation packages.
This reliance on a limited pool of highly skilled individuals gives these suppliers a degree of influence. The need for Hyakugo Bank to stay competitive in digital offerings and security measures means they must attract and retain top talent, which can translate to higher costs for these essential services.
- Talent Acquisition Costs: Banks are experiencing increased recruitment and retention expenses for IT and cybersecurity roles.
- Industry Demand: High demand for financial consultants specializing in digital transformation impacts supplier negotiation power.
- Skill Specialization: Niche skills, such as AI implementation in finance, further concentrate supplier power.
- Competitive Landscape: The need to match competitor compensation packages for critical roles strengthens supplier positions.
Supplier Power 5
The bargaining power of suppliers for Hyakugo Bank is generally low. This is primarily because essential services like utilities and office supplies are provided by numerous vendors, offering ample substitution possibilities. Furthermore, these costs typically represent a small fraction of the bank's total operating expenses, diminishing their leverage.
For instance, in 2024, the cost of office supplies and utilities for many financial institutions remained a relatively minor component of their budget, often below 5% of total administrative expenses. This low dependency means suppliers have little room to dictate terms or significantly impact Hyakugo Bank's profitability.
- Numerous Alternatives: The market for utilities and office supplies is highly competitive, with many providers available.
- Low Cost Concentration: These expenses are a small percentage of Hyakugo Bank's overall operational costs.
- Limited Supplier Leverage: Consequently, individual suppliers have minimal power to influence pricing or terms.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Hyakugo Bank is generally low, particularly for commoditized services like utilities and office supplies, where numerous vendors offer ample substitution. These costs represent a small fraction of the bank's total operating expenses, limiting supplier leverage.
However, specialized technology providers and highly skilled human capital do possess more significant influence. The demand for niche IT skills, such as AI implementation in finance, and cybersecurity expertise, intensified in 2024 due to a global talent shortage, driving up acquisition costs for banks like Hyakugo.
Regulatory bodies and the Bank of Japan are unique 'suppliers' whose policy changes, like interest rate adjustments in March 2024, directly impact Hyakugo Bank's funding costs and profitability, demonstrating a distinct form of supplier power.
| Supplier Category | Leverage Factor | Impact on Hyakugo Bank | 2024 Data Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| Utilities & Office Supplies | High availability, low cost concentration | Minimal | Costs < 5% of administrative expenses for many banks |
| Core Banking IT Services | Commoditization, multiple vendors | Low to Moderate | Continued competitive IT service market |
| Specialized IT/Cybersecurity Talent | Skill scarcity, high demand | Moderate to High | Increased recruitment and retention expenses |
| Regulatory/Monetary Policy (BOJ) | Mandatory compliance, direct financial impact | High | BOJ rate hikes from March 2024 influenced deposit rates |
What is included in the product
Tailored exclusively for Hyakugo Bank, analyzing its position within its competitive landscape and identifying key drivers of competition and customer influence.
Visualize competitive pressures with an intuitive spider chart, instantly highlighting Hyakugo Bank's strategic position and potential vulnerabilities.
Customers Bargaining Power
Hyakugo Bank faces a moderate to high bargaining power from its customers. This is especially true for large corporate clients and high-net-worth individuals who can easily switch to other financial institutions, including larger city banks or international competitors. These sophisticated customers often have the leverage to negotiate for more favorable interest rates and demand highly customized banking solutions. For instance, in 2024, the average deposit rate offered by regional banks like Hyakugo Bank often remained competitive, but larger institutions with greater scale could offer even more attractive terms, putting pressure on Hyakugo Bank to match or provide added value.
For Hyakugo Bank, the bargaining power of retail customers in Mie Prefecture is generally moderate. While individual customers may have limited leverage, their collective demand for digital convenience and competitive pricing can exert pressure. For instance, a 2024 survey indicated that over 60% of Japanese consumers are increasingly comfortable with online banking, suggesting a growing expectation for robust digital offerings from regional banks.
The increasing availability of digital banking and fintech alternatives in Japan significantly bolsters customer bargaining power. With easier switching processes and a wider array of choices, customers can more readily move their business to competitors offering better terms or services.
The rapid adoption of mobile payments and digital wallets by Japanese consumers is a prime example of this trend. This surge in fintech innovation compels traditional institutions like Hyakugo Bank to continuously improve their digital platforms and customer value propositions to retain their client base.
Bargaining Power 4
The bargaining power of customers for Hyakugo Bank is influenced by several factors, particularly in the evolving Japanese financial landscape. As of mid-2024, with the Bank of Japan's tentative moves towards normalizing monetary policy and potentially higher interest rates, customers are becoming more attuned to deposit yields. This shift means they are more likely to shop around for better returns, increasing their sensitivity to Hyakugo Bank's pricing on loans and deposit products.
The availability of alternative financial institutions and fintech solutions further amplifies customer power. Customers can readily compare offerings from numerous banks, credit unions, and online financial platforms. For instance, in 2023, digital banking adoption continued its upward trend in Japan, with a significant portion of the population utilizing mobile banking services, providing them with easy access to competitive rates and product comparisons.
- Increased Sensitivity to Pricing: Higher potential deposit rates encourage customers to seek better returns, making them less loyal to a single institution based solely on convenience.
- Availability of Alternatives: The proliferation of digital banking and fintech options provides customers with a wider array of choices, intensifying competition for Hyakugo Bank.
- Information Accessibility: Online comparison tools and readily available financial news empower customers with the knowledge to negotiate better terms or switch providers.
Bargaining Power 5
Customers of Hyakugo Bank are demonstrating increased bargaining power, influenced by Japan's evolving economic landscape. A notable shift from a savings-first approach to a more investment-focused mindset is empowering consumers. This heightened financial literacy translates into a greater demand for superior investment products and sophisticated wealth management solutions.
This trend is reflected in the growing participation of individual investors in Japanese stock markets. For instance, in 2024, the number of retail investors actively trading on the Tokyo Stock Exchange continued its upward trajectory, driven by a desire for higher returns than traditional savings accounts offer. This growing segment of informed customers can more readily compare offerings and switch to competitors providing better value or higher yields, thereby pressuring Hyakugo Bank to enhance its product suite and service quality.
- Increased Customer Sophistication: Japanese consumers are increasingly seeking personalized wealth management and diverse investment options.
- Demand for Better Returns: A shift from savings to investment means customers are less tolerant of low-yield products.
- Competitive Landscape: The growing number of financially literate customers can easily switch to institutions offering more attractive investment products.
- Digitalization Impact: Online platforms and fintech innovations provide customers with more tools to research and compare financial services, amplifying their bargaining power.
Hyakugo Bank faces significant customer bargaining power, particularly from sophisticated clients and the general public increasingly empowered by digital tools and financial literacy. This pressure stems from the ease with which customers can compare rates and services across a growing number of financial providers, including fintech alternatives.
In 2024, the Japanese banking sector saw continued growth in digital service adoption, with over 70% of retail transactions occurring through online or mobile channels. This trend means customers expect seamless digital experiences and competitive pricing, forcing banks like Hyakugo to invest heavily in technology to remain competitive.
Customers are more sensitive to pricing, especially with potential shifts in monetary policy. For instance, if interest rates rise, customers will actively seek higher yields on deposits, readily switching to institutions offering better terms. This increased price sensitivity is a direct result of greater information accessibility and a wider choice of financial products available to consumers.
| Factor | Impact on Hyakugo Bank | 2024 Data/Trend |
| Digitalization | Increases customer ability to compare and switch | Over 70% of retail transactions online/mobile |
| Price Sensitivity | Customers demand competitive rates on deposits and loans | Growing customer focus on yield due to potential rate hikes |
| Fintech Alternatives | Offers convenient and often cheaper services | Continued rise in fintech app usage for banking and payments |
| Customer Sophistication | Demand for personalized services and better investment options | Increased retail investor participation in stock markets |
What You See Is What You Get
Hyakugo Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
The document you see is your deliverable. It’s ready for immediate use—no customization or setup required. This comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis of Hyakugo Bank details the competitive landscape, including the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers, the bargaining power of suppliers, the threat of substitute products or services, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. You are previewing the final version—precisely the same document that will be available to you instantly after buying.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Competitive rivalry in the Japanese banking sector is fierce, particularly among regional banks. Despite ongoing consolidation efforts, Japan still has a high density of banks, leading to intense competition for customers and market share. This overbanked environment means regional players like Hyakugo Bank must constantly innovate and differentiate themselves to stand out.
Hyakugo Bank contends with formidable rivals in the form of Japan's megabanks like MUFG, SMFG, and Mizuho. These giants wield significantly larger financial resources, enabling them to invest heavily in advanced digital transformation initiatives and offer a more extensive suite of financial products and services. For instance, in the fiscal year ending March 2024, MUFG reported total assets of ¥323.5 trillion, SMFG ¥213.7 trillion, and Mizuho ¥200.2 trillion, dwarfing Hyakugo Bank's scale and providing them with a distinct competitive advantage in market reach and technological innovation.
Digital banks and nimble fintech firms are increasingly challenging traditional players like Hyakugo Bank. These new entrants often boast lower overheads and a focus on user-friendly technology, attracting a growing customer base, particularly among younger, tech-savvy demographics. For instance, by the end of 2023, neobanks in several major markets had captured billions in deposits, demonstrating their rapid growth and ability to siphon market share from established institutions.
Competitive Rivalry 4
The Bank of Japan's shift towards monetary policy normalization and the subsequent rise in interest rates are creating a more competitive environment for Japanese banks. This tightening of monetary policy directly impacts profitability, particularly net interest margins, forcing institutions like Hyakugo Bank to actively seek ways to maintain or even expand their earnings in a changing landscape. As rates climb, the cost of funding increases, putting pressure on lending margins.
This environment is likely to intensify competition as banks vie for market share and strive to attract deposits to fund their lending activities. Banks may engage in more aggressive pricing strategies for loans and deposits, potentially leading to a more dynamic and challenging competitive landscape. For instance, in early 2024, many Japanese banks reported increased net interest income due to higher rates, but this also signals a greater sensitivity to funding costs.
- Rising Interest Rates: The Bank of Japan's policy normalization directly impacts the cost of funds for banks, influencing their lending rates and profitability.
- Net Interest Margin Pressure: As interest rates increase, banks face the challenge of balancing higher funding costs with the need to maintain competitive lending rates, impacting their core profitability.
- Increased Competition for Deposits: To manage funding costs and support lending, banks are likely to compete more fiercely for customer deposits, potentially offering more attractive rates.
- Profitability Impact: The overall effect of these dynamics is a heightened competitive rivalry as banks adapt to a new monetary policy regime and its implications for their financial performance.
Competitive Rivalry 5
Hyakugo Bank's focus on regional economic development and local needs offers a degree of differentiation from larger national banks. However, it contends with intense rivalry from other regional financial institutions operating within Mie Prefecture and adjacent areas.
These regional competitors often share similar customer bases and product offerings, leading to price sensitivity and a constant need for service innovation. For instance, in 2023, the banking sector in Japan saw continued consolidation, with smaller regional banks actively seeking partnerships or mergers to enhance competitiveness against larger entities.
- Regional Focus: Hyakugo Bank's strategy targets specific local economic development, aiming to serve unique community needs.
- Direct Competition: It faces significant rivalry from other regional banks within Mie Prefecture and surrounding regions.
- Market Dynamics: The banking sector, particularly at the regional level, is characterized by price competition and the need for continuous service improvement.
- Industry Trends: Consolidation among regional banks, observed in 2023, highlights the pressure to achieve scale and efficiency in a competitive landscape.
The competitive rivalry for Hyakugo Bank is multifaceted, involving large national banks, agile fintechs, and other regional players. The Bank of Japan's monetary policy normalization in 2024 is intensifying this rivalry by increasing funding costs and creating pressure on net interest margins, forcing banks to compete more aggressively for deposits and lending opportunities.
While megabanks like MUFG, with ¥323.5 trillion in assets as of March 2024, possess significant advantages in scale and technology, digital disruptors are also capturing market share, particularly among younger demographics. This dynamic forces Hyakugo Bank to continually innovate and leverage its regional focus to maintain its competitive standing.
| Competitor Type | Key Characteristics | Example/Data Point (as of latest available, primarily 2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Megabanks | Vast financial resources, extensive product offerings, advanced digital capabilities | MUFG: ¥323.5 trillion in total assets (FY ending March 2024) |
| Digital Banks/Fintechs | Lower overheads, user-friendly technology, rapid growth | Billions in deposits captured by neobanks in key markets by end of 2023 |
| Regional Banks | Similar customer bases, price sensitivity, focus on local markets | Continued consolidation observed in 2023, indicating pressure for scale |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Hyakugo Bank's traditional services is considerable and growing, largely driven by rapid advancements in financial technology. Digital payment platforms and mobile wallets, for instance, offer increasingly convenient alternatives to traditional cash and card transactions, directly impacting Hyakugo's core business.
In 2024, the global digital payments market is projected to reach over $10 trillion, highlighting the significant shift away from traditional banking methods. This trend means customers can bypass banks for many everyday transactions, weakening Hyakugo's customer loyalty and transaction-based revenue streams.
Peer-to-peer (P2P) lending platforms and crowdfunding services present a growing threat by offering alternative financing avenues, especially for small businesses and individuals seeking to bypass traditional bank loans. These platforms connect borrowers directly with investors, often with more streamlined application processes and potentially different risk-return profiles than conventional banking. While their penetration in Japan has historically been lower than in some Western markets, the global trend indicates a significant and increasing adoption rate.
For instance, the global P2P lending market was valued at approximately $127.4 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow substantially in the coming years. This expansion means more potential customers for Hyakugo Bank might opt for these digital alternatives for personal loans, small business funding, or even real estate financing, thereby reducing the demand for traditional banking products.
The rise of investment apps and online brokerage platforms presents a significant threat by enabling individuals to manage their own portfolios, bypassing traditional bank investment services. This shift means customers can access a wider range of financial products and potentially lower fees than what banks typically offer. For instance, the increasing adoption of digital investment tools allows for direct investment in stocks, bonds, and ETFs, directly competing with bank-managed funds.
Furthermore, Japan's new NISA system, which commenced in 2024, is actively encouraging investment in riskier assets. This government initiative is expected to channel substantial funds into the capital markets, drawing capital away from traditional bank savings accounts and fixed-income products. Reports indicate a surge in NISA account openings, with many individuals actively shifting their savings towards growth-oriented investments, thereby reducing their reliance on bank-provided investment solutions.
Threat of Substitutes 4
Cryptocurrencies and stablecoins are emerging as potential substitutes for traditional banking services, particularly in payment systems. While their regulatory landscape in Japan is still developing, their increasing adoption globally suggests a future impact on how transactions are conducted. For instance, by the end of 2024, the global cryptocurrency market capitalization reached approximately $2.5 trillion, indicating significant user engagement.
These digital assets offer alternative ways to store value and facilitate transactions, potentially bypassing traditional banking infrastructure. This could reduce reliance on established payment networks and currency exchange services offered by banks like Hyakugo Bank. The ongoing innovation in decentralized finance (DeFi) further expands the scope of these substitutes, offering yield-generating opportunities outside traditional deposit accounts.
The threat is currently moderate but has the potential to grow as regulatory clarity increases and user acceptance expands in Japan. Factors influencing this shift include:
- Technological advancements: Continued development in blockchain technology enhances the efficiency and security of digital currencies.
- Regulatory evolution: Clearer regulations in Japan could foster greater institutional and retail adoption of cryptocurrencies and stablecoins.
- Consumer demand: Growing interest in alternative financial tools and faster, cheaper cross-border transactions fuels the demand for digital assets.
Threat of Substitutes 5
The threat of substitutes for traditional banking services is intensifying as non-financial companies increasingly enter the financial services arena. These new entrants often leverage their extensive customer bases and advanced technological capabilities to offer competing products. For instance, e-commerce giants are expanding into payment processing and lending, directly challenging banks in these core areas.
These disruptive forces are not merely theoretical. In 2024, fintech companies, often backed by significant venture capital, continued to gain traction. Consider the growth in digital wallets and buy-now-pay-later services, which bypass traditional banking channels for many consumer transactions. This trend is expected to accelerate, with projections indicating continued market share gains for non-bank financial providers.
The implications for established institutions like Hyakugo Bank are significant. The ease with which customers can access alternative financial solutions means that customer loyalty can be eroded quickly if banks fail to adapt. This necessitates a strategic focus on innovation and customer experience to remain competitive.
- E-commerce Integration: Major online retailers are embedding payment and credit options directly into their platforms, offering seamless alternatives to bank-issued credit cards.
- Fintech Innovations: Peer-to-peer lending platforms and digital payment solutions continue to attract users seeking faster, often cheaper, financial transactions.
- Technological Leverage: Non-financial companies can deploy advanced data analytics and AI to offer personalized financial products, a capability that traditional banks are also developing.
- Customer Base Advantage: Companies with millions of existing users, such as social media or ride-sharing platforms, can cross-sell financial services with a built-in audience.
The threat of substitutes for Hyakugo Bank's traditional services is substantial, primarily from digital payment platforms, P2P lending, and investment apps. These alternatives offer convenience and often lower costs, directly impacting Hyakugo's revenue. The global digital payments market, projected to exceed $10 trillion in 2024, underscores this shift, with customers increasingly bypassing traditional banking for everyday transactions.
Furthermore, the rise of fintech and non-financial companies integrating financial services into their platforms, like e-commerce giants offering payment processing and lending, poses a significant challenge. The increasing adoption of digital wallets and buy-now-pay-later services in 2024 exemplifies this trend, with projections indicating continued market share gains for these non-bank providers.
Cryptocurrencies and decentralized finance (DeFi) also represent emerging substitutes, particularly for payments and yield generation, though their impact in Japan is still developing. The global cryptocurrency market capitalization reaching approximately $2.5 trillion by the end of 2024 highlights the growing user engagement with these digital assets.
| Substitute Type | Key Characteristics | Impact on Hyakugo Bank | 2024 Market Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Digital Payments & Wallets | Convenience, speed, lower transaction fees | Reduced transaction revenue, customer disintermediation | Global market projected over $10 trillion |
| P2P Lending & Crowdfunding | Alternative financing, streamlined processes | Loss of loan origination and interest income | Global market valued at ~$127.4 billion (2022), with significant growth |
| Investment Apps & Online Brokerages | Direct access to markets, lower fees, self-management | Reduced demand for bank-managed investment products | Increased adoption driven by initiatives like Japan's new NISA (2024) |
| Cryptocurrencies & DeFi | Alternative payment systems, yield generation | Potential disintermediation of payment networks and deposit accounts | Global market cap ~$2.5 trillion (end of 2024) |
| Non-Financial Company Services | Integrated financial solutions within existing platforms | Erosion of customer loyalty, competition in core banking areas | Continued growth in fintech and e-commerce financial integrations |
Entrants Threaten
The threat of new entrants in Japan's banking sector is currently assessed as moderate. While the regulatory landscape, overseen by bodies like the Financial Services Agency (FSA), presents significant hurdles for establishing a full-fledged bank, there's a notable push towards fostering innovation.
The FSA, in particular, has been actively encouraging partnerships and collaborations between traditional financial institutions and burgeoning fintech firms. This strategic openness aims to inject new technologies and business models into the market, potentially lowering some traditional barriers over time.
For instance, as of early 2024, Japan has seen a growing number of specialized payment providers and digital-only financial service companies emerge, often operating under specific licenses rather than full banking charters. This indicates a pathway for new players to gain traction, even if broad market entry remains challenging.
The banking sector is experiencing a shift as regulators ease certain rules, making it easier for new players to enter. For instance, the opening of banking APIs allows fintech firms to connect with existing banking systems, reducing the need for extensive infrastructure development. This regulatory environment change is a significant factor in the threat of new entrants.
The introduction of a new brokerage category specifically for crypto asset transactions further lowers the barrier to entry for specialized financial services. This signals a broader trend where niche financial activities are becoming more accessible to startups. In 2024, the fintech sector continued to see substantial investment, with venture capital funding reaching billions globally, indicating a strong appetite for new financial service providers.
Digital-only banks and neobanks pose a significant threat, as they can launch with substantially lower overhead compared to traditional institutions like Hyakugo Bank. These agile competitors, unburdened by extensive branch networks and legacy systems, can offer highly competitive digital-first services. For example, by mid-2024, neobanks globally had attracted millions of customers, demonstrating their ability to quickly capture market share by focusing on user experience and lower fees, directly challenging established players.
Threat of New Entrants 4
Foreign financial institutions, especially those with advanced digital platforms, are increasingly eyeing the Japanese market. As Japan reviews its regulations to become more appealing to international investors, these new entrants could pose a significant threat to established players like Hyakugo Bank.
The digital transformation trend is a key driver here. For instance, in 2023, Japan saw a notable increase in fintech adoption, with over 60% of consumers reporting using at least one fintech service. This indicates a receptive market for innovative digital banking solutions that new foreign entrants can readily offer.
Consider these points regarding the threat of new entrants:
- Digital Prowess: Foreign banks often possess cutting-edge digital infrastructure and user-friendly interfaces, which can attract a significant customer base away from traditional institutions.
- Regulatory Easing: Ongoing efforts to liberalize Japan's financial sector could lower barriers to entry for foreign firms, making market penetration more feasible.
- Capital Inflow: Strong capital backing from international financial groups allows new entrants to invest heavily in marketing, technology, and competitive pricing, quickly gaining market share.
- Niche Market Focus: Some new entrants might target specific profitable segments, such as wealth management or SME lending, where Hyakugo Bank may have less dominance.
Threat of New Entrants 5
The threat of new entrants for Hyakugo Bank is moderate but growing, particularly from non-traditional players. Major technology companies, with their vast customer bases and advanced data analytics capabilities, are increasingly venturing into financial services. For instance, in 2024, companies like Apple and Google continued to expand their financial offerings, such as payment services and credit products, directly competing with traditional banks.
These tech giants possess significant advantages, including established brand loyalty and sophisticated digital infrastructure, allowing them to potentially offer more seamless and cost-effective financial solutions. Their ability to leverage existing ecosystems, like smartphone users or online marketplaces, presents a formidable challenge. By integrating financial services into their existing platforms, they can attract customers with convenience and competitive pricing, thereby lowering switching costs for consumers.
The barrier to entry in banking is traditionally high due to regulatory requirements and the need for substantial capital. However, the rise of fintech and the increasing digitization of financial services are lowering some of these barriers. For example, the global fintech market was projected to reach over $330 billion in 2024, indicating significant investment and innovation in this space. This trend suggests that while establishing a full-service bank remains difficult, niche financial service providers or technology-driven disruptors can emerge more readily.
- Technological Disruption: Major tech firms can leverage AI and big data to offer personalized financial products, potentially outmaneuvering traditional banks in customer acquisition and retention.
- Ecosystem Integration: Companies like Apple Pay and Google Pay have already captured significant market share in digital payments, demonstrating the power of integrating financial services into widely used consumer technologies.
- Regulatory Arbitrage: Some new entrants might initially operate under lighter regulatory frameworks, allowing them to innovate and scale more rapidly before facing the full weight of banking regulations.
- Customer Data Advantage: Tech companies possess extensive customer data from their core businesses, enabling them to better understand consumer behavior and tailor financial products accordingly.
The threat of new entrants for Hyakugo Bank is moderate but escalating, primarily driven by agile fintech firms and global tech giants. While stringent regulations and capital requirements remain high, the increasing digitization of financial services and the opening of banking APIs by regulators are lowering some traditional barriers. For instance, the global fintech market was projected to exceed $330 billion in 2024, showcasing substantial innovation and investment, making it easier for specialized players to emerge.
Digital-only banks and neobanks present a direct challenge due to their lower overhead and focus on user experience, as evidenced by their rapid customer acquisition globally by mid-2024. Furthermore, the growing interest of foreign financial institutions, equipped with advanced digital platforms, signals an increasing competitive landscape. The trend of fintech adoption in Japan, with over 60% of consumers using such services in 2023, indicates a receptive market for these new entrants.
Major technology companies are also expanding into financial services, leveraging their vast customer bases and data analytics capabilities. Companies like Apple and Google continued to broaden their financial offerings in 2024, utilizing their existing ecosystems to provide convenient and cost-effective solutions. This strategic integration into widely used consumer technologies, such as in digital payments, demonstrates a powerful pathway to market penetration.
| Factor | Impact on Hyakugo Bank | Key Data/Trends (2023-2024) |
| Regulatory Environment | Moderate barrier, but easing for fintech | FSA encouraging fintech partnerships; new crypto brokerage category |
| Fintech Innovation | High threat from specialized providers | Global fintech market projected >$330B in 2024; 60%+ Japanese consumers used fintech in 2023 |
| Digital-Only Banks (Neobanks) | Significant threat due to low overhead | Millions of global customers acquired by mid-2024 focusing on UX and lower fees |
| Tech Giants' Entry | Growing threat via ecosystem integration | Apple/Google expanding payment and credit services in 2024 |
| Foreign Financial Institutions | Potential threat with advanced digital platforms | Increased interest in Japanese market due to regulatory reviews |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Hyakugo Bank Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of reliable data, including the bank's annual reports, financial statements, and investor relations disclosures. We also incorporate insights from industry-specific publications and market research reports to capture the broader competitive landscape.
