HP Hood Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
HP Hood Bundle
HP Hood navigates a dynamic dairy market, where buyer power from large retailers and intense rivalry significantly shape its strategy.
Understanding the threat of new entrants and the bargaining power of suppliers is crucial to grasping HP Hood's operational landscape.
The presence of readily available substitute products, like plant-based alternatives, adds another layer of complexity to its competitive environment.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore HP Hood’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping HP Hood’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
HP Hood sources a substantial amount of its raw milk from dairy farmer cooperatives. While numerous individual dairy farms exist, the consolidation of these farms into large entities like the Dairy Farmers of America (DFA) centralizes significant power. DFA, for instance, reported revenues of approximately $24.5 billion in 2023, highlighting its scale. This concentration grants cooperatives considerable leverage in negotiating milk prices and supply terms, often impacting costs for processors like HP Hood. Their collective bargaining strength means they can command better terms than individual farmers might achieve.
Suppliers of raw milk and other essential inputs like feed, energy, and labor face significant cost volatility. For instance, dairy feed prices, a major component, saw an increase of over 10% in early 2024 compared to the previous year, driven by grain market fluctuations. This instability in input costs allows suppliers to potentially pass higher raw material prices directly to processors such as HP Hood. Such price increases can notably impact HP Hood’s operational profitability and overall financial margins. Effectively, this elevates the bargaining power of suppliers.
The U.S. dairy market, vital for HP Hood, is significantly shaped by government regulations, including Federal Milk Marketing Orders (FMMOs). These FMMOs establish minimum milk prices, effectively providing a price floor for suppliers and bolstering their bargaining power. For instance, in 2024, these orders continue to dictate prices across different regions. Anticipated reforms to FMMOs in 2025, currently under discussion, are expected to further impact milk prices, introducing a layer of uncertainty for both producers and buyers.
Importance of Milk Quality and Consistency
HP Hood's emphasis on extended-shelf-life (ESL) and other premium dairy products necessitates a consistent supply of high-quality milk. This specific requirement amplifies the bargaining power of dairy farmers and cooperatives capable of reliably meeting stringent quality standards. The company's ongoing commitment to product innovation and quality reinforces its dependency on dependable, top-tier raw milk inputs, which can influence procurement costs. In 2024, milk quality remains a critical factor for processors like HP Hood, with supply chain resilience being key.
- HP Hood's ESL products demand consistent, high-quality milk.
- Suppliers meeting these standards gain increased bargaining leverage.
- Innovation focus reinforces the need for reliable, premium inputs.
- Milk quality and supply chain stability are paramount in 2024.
Limited Differentiation of Raw Milk
Raw milk, while quality-dependent, functions largely as a commodity, offering limited differentiation among suppliers. This characteristic generally diminishes the bargaining power of individual milk producers or cooperatives, as processors like HP Hood possess some flexibility to source from various networks. However, the intricate logistics of milk collection and deep-rooted relationships with established local dairy cooperatives introduce practical switching costs. In 2024, US milk production continues to be robust, with the USDA forecasting stable output, which further supports the commodity nature of raw milk.
- Limited differentiation in raw milk reduces individual supplier leverage over processors.
- Logistical complexities and existing cooperative relationships create practical switching costs for HP Hood.
- The USDA projected US milk production for 2024 around 227 billion pounds, highlighting ample supply.
- Consolidated milk collection routes can make changing suppliers less straightforward despite commodity pricing.
Supplier bargaining power for HP Hood is significant due to large dairy cooperatives like DFA, which reported $24.5 billion in 2023 revenue, dictating terms. Volatile input costs, like dairy feed up over 10% in early 2024, allow suppliers to pass on increases. Federal Milk Marketing Orders continue to set minimum prices in 2024, further bolstering supplier leverage. HP Hood's need for high-quality milk for ESL products also enhances the power of compliant suppliers.
| Factor | Impact on Power | 2024 Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Consolidation | High | DFA 2023 Revenue: $24.5B |
| Input Cost Volatility | High | Dairy Feed Prices: Up >10% early 2024 |
| Regulatory Support | High | FMMOs set 2024 minimum milk prices |
What is included in the product
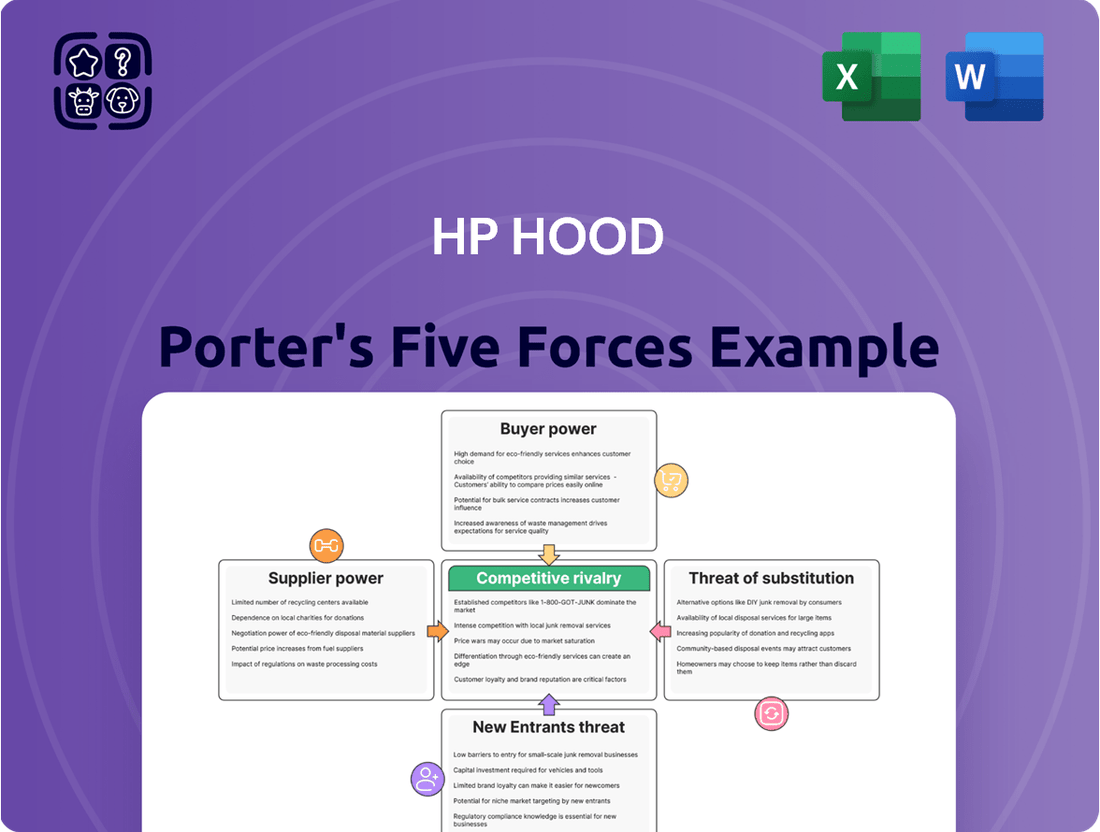
HP Hood's Porter's Five Forces analysis delves into the intensity of rivalry within the dairy industry, assessing the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitutes on HP Hood's profitability and strategic positioning.
Visualize competitive intensity with a dynamic Porter's Five Forces chart, simplifying complex market pressures for HP Hood's strategic planning.
Customers Bargaining Power
HP Hood's customer base, including major supermarket chains like Kroger and Ahold Delhaize, along with club stores and convenience outlets, wields substantial bargaining power. This power stems from their large order volumes and the ability to influence shelf space and promotional activities. Retail consolidation, an ongoing trend in 2024, further intensifies this leverage, as fewer, larger entities control a greater share of the market. This concentration allows them to demand more favorable pricing and terms from suppliers like HP Hood, impacting profitability. For instance, the top 10 US grocery retailers account for over 50% of sales, giving them considerable sway.
Consumers of dairy products, particularly commodity items like fluid milk, exhibit significant price sensitivity. This sensitivity is directly passed on to HP Hood by its retail customers, who fiercely compete for the end consumer's business. Private label products, which directly challenge branded offerings, held an estimated 19% share of the US food and beverage market in 2024, intensifying price competition for HP Hood. This forces Hood to maintain competitive pricing, impacting its margins within the dairy sector.
For both retailers and end consumers, the costs of switching between different dairy brands are remarkably low. Retailers can easily substitute one brand for another on their shelves, as seen with milk sales in 2024 where private labels continue to gain traction, representing a significant portion of the market. Consumers face minimal cost or inconvenience in choosing a different brand of milk, ice cream, or cottage cheese, often driven by price promotions or availability. This ease of substitution significantly reduces HP Hood's pricing power, as consumers can readily opt for alternatives if prices increase. The highly competitive dairy market, with numerous regional and national players, further reinforces this low switching cost environment.
Brand Loyalty and Differentiation
HP Hood effectively mitigates some customer bargaining power through its well-established brand name, Hood, complemented by licensed brands such as Lactaid and Almond Breeze. Strong brand recognition and a reputation for quality foster significant consumer preference and loyalty, which in turn encourages retailers to stock Hood products. The company's marketing efforts, including the memorable Always Good. Always Hood. slogan and the innovative LightBlock Bottle, are designed to strengthen this crucial brand differentiation. In 2024, brand strength remains a key competitive advantage for dairy and plant-based beverage producers.
- Hood's core brand maintains high household penetration in key regions as of 2024.
- Licensed brands like Lactaid continue to dominate specific market segments, showcasing strong consumer trust.
- Marketing investments in 2024 emphasize product quality and innovation, further cementing brand loyalty.
- Retailers prioritize stocking brands with proven consumer demand, directly benefiting Hood's distribution power.
Power of Foodservice Customers
HP Hood serves a robust foodservice sector, including schools, universities, and healthcare facilities. These large-volume purchasers, often representing significant aggregated demand, possess considerable bargaining power. For instance, the US foodservice market size was projected to reach over $1.1 trillion in 2024, highlighting the scale of these buyers. While their bulk orders can pressure pricing, their specific needs for customized product formulations, specialized packaging, and reliable, on-time delivery also foster a degree of interdependence, limiting their ability to easily switch suppliers without incurring costs.
- Bulk purchasing power influences pricing.
- Custom product needs create supplier lock-in.
- Reliable delivery is a critical service requirement.
- Foodservice market size underscores buyer influence.
HP Hood faces substantial customer bargaining power from large retailers like Kroger and Ahold Delhaize, which control significant market share, with the top 10 US grocery retailers accounting for over 50% of sales in 2024. Consumers exhibit high price sensitivity, exacerbated by private label products holding 19% of the US food and beverage market in 2024, and low switching costs. While Hood's strong brand mitigates some pressure, the foodservice sector also presents powerful bulk purchasers influencing terms.
| Customer Segment | Key Factor | 2024 Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Retailers | Market Concentration | Top 10 US Grocery Retailers: >50% Sales |
| Consumers | Private Label Share | US Food/Beverage Private Label: 19% |
| Foodservice | Market Size | US Foodservice Market: >$1.1 Trillion |
What You See Is What You Get
HP Hood Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This is the complete, ready-to-use HP Hood Porter's Five Forces Analysis. What you're previewing is what you get—professionally formatted and ready for your needs, detailing the competitive landscape of the dairy industry. You'll gain a comprehensive understanding of the forces shaping HP Hood's market, including the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. This analysis is designed to provide actionable insights into HP Hood's strategic positioning and potential challenges.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The U.S. dairy industry is notably fragmented and highly competitive, featuring numerous players from large national corporations to smaller regional processors. HP Hood faces significant rivalry from major entities like Prairie Farms Dairy, which reported over $4 billion in 2023 sales, Darigold, Land O'Lakes, and Dairy Farmers of America, a cooperative with 2023 net sales exceeding $24.5 billion. This extensive competitor landscape, with many firms vying for consumer attention and shelf space, naturally intensifies the competition for market share across various dairy product categories.
The competitive rivalry in the dairy market is significantly heightened by the dominance of private label products. A substantial portion of the market, particularly in fluid milk, is controlled by private label offerings from major retailers. For instance, in 2024, private label brands continued to hold a majority volume share in the New England dairy market. This intense pressure forces branded producers like HP Hood to compete aggressively on both price and quality to justify their premium positioning.
The U.S. dairy industry faces relatively slow overall growth, with fluid milk sales volume projected to continue declining in 2024 and 2025, intensifying competitive rivalry as companies fight for market share. This mature market environment means that to grow, businesses like HP Hood often need to capture sales from existing competitors. However, there is optimism for volume growth in specific dairy categories, with U.S. per capita cheese consumption projected to increase to over 40 pounds by 2024, and butter and yogurt also showing more favorable trends.
Product Differentiation and Innovation
Competition within the dairy and food beverage sector for HP Hood extends beyond just pricing, emphasizing product innovation, superior quality, and strong branding. HP Hood consistently invests in research and development to introduce new offerings and enhance existing ones, notably with its extended-shelf-life dairy and growing portfolio of non-dairy beverages. This strategic focus on innovation is crucial for distinguishing itself in a highly competitive market as of 2024, attracting diverse consumer preferences. Their ability to adapt to evolving dietary trends and consumer demands provides a significant competitive edge.
- HP Hood's 2024 market strategy emphasizes differentiation through novel products.
- Significant R&D investment targets extended-shelf-life products and plant-based alternatives.
- Innovation helps capture new market segments and maintain brand loyalty.
- The company leverages product quality and branding to compete effectively beyond price points.
Mergers and Acquisitions Activity
The dairy industry frequently sees mergers and acquisitions, a common growth strategy that reshapes the competitive landscape. This consolidation creates larger, more powerful rivals, intensifying competition. HP Hood itself has expanded significantly through such acquisitions, including assets from Dean Foods in 2020, strengthening its market position. The potential for further consolidation, as seen with ongoing activity in sectors like specialty dairy, remains a critical factor in competitive intensity. This trend highlights a dynamic environment where market share can shift rapidly.
- Dairy M&A activity continues, though slowing from peak 2021-2022 levels, still drives consolidation.
- HP Hood's 2020 acquisition of Dean Foods assets notably expanded its reach in the Northeast.
- Major players like Lactalis and Saputo also remain active, signaling ongoing industry restructuring.
- Smaller regional dairies are often targets, leading to fewer, larger competitors by 2024.
HP Hood faces intense rivalry within the fragmented U.S. dairy market, competing with major players like Dairy Farmers of America, which reported over $24.5 billion in 2023 net sales. The dominance of private label brands, holding a majority volume share in New England in 2024, further intensifies price and quality competition. Slow overall market growth for fluid milk in 2024-2025 compels firms to aggressively vie for existing share. HP Hood counters this by investing in product innovation, including extended-shelf-life and non-dairy options, to differentiate itself.
| Metric | Key Data (2023-2024) | Impact on Rivalry |
|---|---|---|
| DFA Net Sales | Over $24.5 Billion (2023) | Indicates significant competitor scale |
| Prairie Farms Sales | Over $4 Billion (2023) | Highlights another large rival |
| NE Private Label Share | Majority Volume (2024) | Pressure on branded product pricing |
| US Cheese Consumption | >40 lbs/capita (2024 proj.) | Area of potential growth amid slow fluid milk |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The most significant substitute threat for traditional dairy products like those from HP Hood comes from the burgeoning market for plant-based alternatives. These include almond, oat, soy, and coconut milk, which are rapidly gaining consumer favor. This shift is driven by increasing awareness of health benefits, a rise in lactose intolerance, and growing sustainability concerns among consumers. The plant-based milk sector is experiencing robust growth, with the global market projected to reach approximately 40 billion USD by 2024, directly challenging the market share of conventional dairy.
The quality and variety of dairy substitutes have significantly improved, with options like oat milk now offering taste profiles more palatable than earlier alternatives. Innovation in this space is continuous, with new flavors and formulations regularly entering the market, making alternatives increasingly viable. For instance, the plant-based milk market in the U.S. was projected to reach over $5 billion in 2024, reflecting strong consumer adoption. This shift empowers a broader range of consumers to choose substitutes, directly impacting traditional dairy sales for companies like HP Hood.
A significant threat to HP Hood stems from the growing health and wellness trends, as consumers increasingly seek plant-based alternatives. These substitutes, like oat or almond milk, are often perceived as healthier due to being lower in calories, fat, and cholesterol. This shift is amplified by the high prevalence of lactose intolerance, affecting an estimated 68% of the global population, driving demand for dairy-free options. Marketing efforts for these alternatives frequently highlight their nutritional advantages. The global plant-based milk market is projected to reach approximately $40.6 billion in 2024, showing strong consumer preference away from traditional dairy.
HP Hood's Participation in the Alternatives Market
HP Hood effectively mitigates the threat of substitutes by proactively entering the alternatives market. Through brands like Almond Breeze and Planet Oat, the company has diversified its portfolio, directly addressing the growing consumer demand for non-dairy options. This strategic move enables HP Hood to capture market share within the plant-based sector, which is projected to continue its robust growth through 2024 and beyond. Instead of solely competing against these alternatives, HP Hood transforms a potential threat into a significant opportunity for revenue expansion and market leadership.
- HP Hood's Almond Breeze and Planet Oat brands target the non-dairy segment.
- The plant-based milk market is estimated to reach over $35 billion globally by 2024.
- This strategy allows HP Hood to capitalize on evolving consumer preferences.
- Diversification turns a competitive threat into a growth driver for the company.
Price and Availability of Substitutes
The price gap between traditional dairy products and their plant-based substitutes, such as oat, almond, and soy milk, has significantly narrowed in 2024. This makes alternatives a more financially attractive option for consumers seeking non-dairy choices. Moreover, the availability of these substitutes in mainstream retail channels has surged, with supermarkets and online grocers offering a vast array of options, enhancing their competitive threat to HP Hood.
- US plant-based milk sales are projected to exceed $3 billion in 2024, demonstrating robust growth.
- Almond milk remains the top substitute, followed closely by oat milk, which saw a 2023 sales increase of 25% over the previous year.
- Over 70% of US households now purchase plant-based milk, reflecting widespread market penetration.
- The average retail price of plant-based milk has decreased by approximately 5-10% in recent years, making it more competitive.
The primary substitute threat for HP Hood's traditional dairy comes from the rapidly growing plant-based milk market. This sector, projected globally at $40.6 billion in 2024, benefits from increasing health awareness and lactose intolerance. HP Hood has strategically mitigated this by diversifying into non-dairy options like Almond Breeze and Planet Oat. This allows them to capitalize on the shift, turning a competitive challenge into a growth opportunity.
| Metric | 2024 Projection | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Global Plant-Based Milk Market | $40.6 Billion | Driven by health and sustainability trends. |
| US Plant-Based Milk Sales | Over $5 Billion | Reflects strong consumer adoption. |
| US Household Penetration | Over 70% | Widespread acceptance of alternatives. |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the dairy processing industry demands substantial capital outlay for manufacturing plants, specialized equipment, and extensive refrigerated distribution networks. For instance, companies like HP Hood have invested significantly, with one facility expansion alone exceeding $83 million in recent years. These high upfront costs represent a formidable financial barrier, effectively deterring many potential new competitors. Such capital intensity ensures that only well-funded entities can realistically consider market entry, maintaining a low threat from new entrants.
New entrants would struggle immensely to gain access to established distribution channels, which are tightly controlled by major retailers and existing dairy companies. HP Hood, for instance, maintains deep, long-standing relationships with key supermarket chains like Kroger and Walmart, along with club stores and foodservice distributors, representing a significant portion of the US dairy market. Securing valuable shelf space in 2024, where competition for visibility is fierce, presents a substantial financial and logistical barrier for any new competitor. Building a reliable and extensive distribution network from scratch is a massive undertaking, making it difficult for newcomers to compete effectively on scale or reach.
The dairy market is dominated by well-established, trusted brands like HP Hood and its licensed products, which enjoy high consumer recognition and loyalty. New entrants face a significant hurdle in overcoming this entrenched brand equity. Competing with incumbents requires substantial investment in marketing and brand building; for instance, major food and beverage companies often allocate over 5% of their revenue to advertising and promotion, a significant barrier for startups. This long-standing reputation and consumer trust make it incredibly difficult for new companies to capture meaningful market share in 2024, as consumers tend to stick with familiar names.
Economies of Scale
Large, established dairy processors like HP Hood benefit significantly from economies of scale in 2024, spanning procurement, manufacturing, and distribution. Their ability to purchase raw milk and packaging materials in bulk, coupled with optimized production lines, allows them to achieve a lower cost per unit. This substantial cost advantage, where a new entrant might face unit costs 15-20% higher, makes it extremely difficult for smaller, new players to compete effectively on price and attain sustainable profitability in the highly competitive dairy market.
- HP Hood’s extensive distribution network reduces per-unit transportation costs.
- Bulk procurement of raw materials offers significant cost savings.
- Automated, high-volume processing plants lower labor and overhead per gallon.
- New entrants struggle to match established pricing due to higher initial operational costs.
Regulatory Hurdles
The dairy industry presents significant regulatory hurdles for new entrants, acting as a strong barrier. Companies like HP Hood operate under stringent food safety and labeling regulations from bodies such as the FDA, alongside complex state and federal milk marketing orders. For instance, the Pasteurized Milk Ordinance (PMO) sets strict standards for milk production and processing, a compliance cost that can deter new players. Navigating these requirements demands substantial expertise and financial resources, with compliance costs potentially reaching millions annually for large-scale operations in 2024. These regulations, while safeguarding consumers, effectively increase the difficulty and cost of market entry.
- FDA and state-specific regulations, like those for milk quality and labeling, create high compliance costs for new dairy businesses.
- Adhering to standards such as the Pasteurized Milk Ordinance requires significant capital investment in facilities and processes.
- The complexity of federal and state milk marketing orders adds an administrative burden, necessitating specialized legal and operational expertise.
- New entrants face substantial upfront and ongoing expenses to meet these regulatory demands, impacting profitability and scalability.
High capital requirements, including facility investments exceeding $83 million, and difficulty accessing entrenched distribution networks significantly deter new entrants. Established brand loyalty and substantial economies of scale, leading to 15-20% higher unit costs for newcomers, create formidable barriers. Furthermore, stringent 2024 regulatory compliance, with costs reaching millions annually, makes market entry prohibitively expensive, ensuring a low threat from new competition.
| Barrier Type | Impact on New Entrants | 2024 Data Point | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Intensity | High upfront investment required | Facility expansion example: $83M+ | ||
| Economies of Scale | Higher unit costs for smaller volumes | New entrant unit costs: 15-20% higher | ||
| Regulatory Compliance | Significant ongoing legal and operational costs | Annual compliance costs: Millions |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for HP Hood leverages data from industry-specific market research reports, financial filings of key competitors, and trade association publications to assess the competitive landscape.
We incorporate insights from consumer spending data, commodity price indices, and government agricultural reports to understand the forces influencing HP Hood's market position.
