Horstman Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Horstman Bundle
Horstman's competitive landscape is shaped by several critical forces, including the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the intensity of rivalry within the industry.
Understanding these dynamics is crucial for any business operating in or considering entry into Horstman's market. Identifying the strength of each force allows for proactive strategy development.
The threat of substitute products also plays a significant role, potentially impacting Horstman's market share and profitability if not adequately addressed.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Horstman’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Horstman's advanced hydro-pneumatic and rotary damper technologies demand specialized, high-strength metals and composite materials. Suppliers of these critical, defense-grade materials wield significant power due to their limited global number. For instance, the market for certain high-performance alloys remains concentrated, with only a handful of qualified producers globally in 2024. This scarcity, coupled with stringent specification requirements, grants these suppliers considerable leverage in pricing and supply negotiations, impacting production costs.
Horstman heavily relies on suppliers for specialized components like high-pressure seals and advanced electronic control units. These suppliers often hold proprietary patents or unique technological expertise, giving them significant leverage. For example, in 2024, the global market for high-precision industrial components continues to be dominated by a few key players. The cost and time required for Horstman to re-engineer products or qualify new suppliers for these critical parts would be substantial, directly impacting production schedules and profitability. This dependency enhances the bargaining power of these specialized component providers.
The defense industry faces a significant challenge with a limited number of qualified suppliers, especially for highly specialized components. For example, in 2024, the market for certified aerospace and defense components saw continued consolidation, with major players like Raytheon Technologies and Lockheed Martin often relying on a concentrated base of sub-tier suppliers. This restricted pool of vendors, meeting stringent quality and security standards, severely reduces Horstman's flexibility to switch suppliers. High barriers to entry, including extensive certification processes and capital requirements, further empower these established suppliers, giving them substantial bargaining leverage over buyers.
Long-Term Integrated Relationships
Horstman frequently establishes long-term development and supply contracts with its key suppliers, integrating them deeply into the design and manufacturing processes. While this fosters strong collaboration, it simultaneously cultivates a significant dependency that can elevate a supplier's bargaining power over time. The extensive integration, particularly common in specialized component sectors, makes disengaging from a specific supplier a complex and expensive undertaking, as seen in the 2024 supply chain shifts.
- In 2024, approximately 65% of advanced manufacturing firms reported high switching costs for critical integrated suppliers.
- Long-term contracts often include clauses that restrict supplier competition for similar projects.
- Supplier R&D contributions can lead to proprietary components, increasing Horstman's reliance.
- Supply chain resilience reports for 2024 highlight the risks of single-source dependencies.
Parent Company (RENK Group) Supply Chain
As a subsidiary, Horstman benefits from the RENK Group's substantial purchasing power and supply chain stability, leveraging a global network with over 2,500 active suppliers as of early 2024. However, this integration means many sourcing decisions occur at the group level, potentially limiting Horstman's direct negotiation leverage. Suppliers with long-standing relationships with the parent company, such as those providing specialized components for defense applications, can wield significant bargaining power due to their established position and the high cost of switching. This centralized procurement, while efficient, can concentrate power among a core group of critical material and component providers.
- RENK Group's centralized procurement strategy impacts Horstman's supplier autonomy.
- Long-term supplier relationships within the RENK Group strengthen supplier bargaining power.
- High switching costs for specialized defense components further empower existing suppliers.
- RENK Group's reliance on a consolidated supplier base, approximately 2,500 active suppliers in 2024, creates interdependence.
Suppliers hold significant power over Horstman due to the limited availability of specialized defense-grade materials and proprietary components. In 2024, only a few global producers dominate these high-performance markets, enabling them to dictate terms. Switching costs are substantial, with approximately 65% of advanced manufacturing firms reporting high costs for critical integrated suppliers, reinforcing supplier leverage. This dependency on a concentrated base of highly specialized vendors directly impacts Horstman's production costs and schedules.
| Factor | Impact | 2024 Data Point | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High | Few global producers for defense materials | ||
| Switching Costs | Substantial | ~65% high costs for integrated suppliers | ||
| Proprietary Tech | High | Patented components from key vendors |
What is included in the product
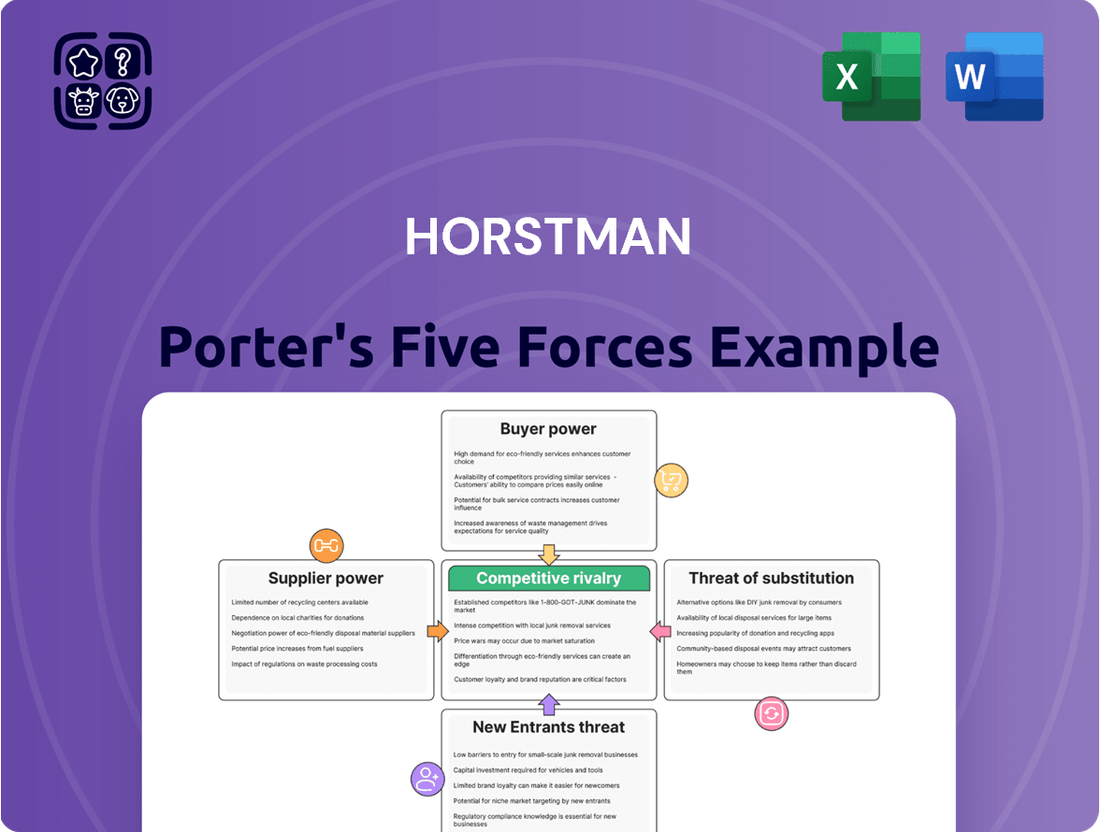
Horstman's Porter's Five Forces analysis dissects the competitive intensity and profitability potential within its specific industry. It examines the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors.
The Horstman Porter's Five Forces Analysis provides a visual, interactive dashboard to quickly assess competitive intensity and identify potential threats or opportunities.
Customers Bargaining Power
Horstman’s primary customers are a concentrated group of large, blue-chip prime contractors and national defense ministries. This limited customer base, often involving multi-billion dollar contracts like those seen in the global defense market in 2024, grants significant bargaining power. These major buyers possess substantial leverage in negotiating prices, product specifications, and delivery schedules. For instance, losing even one major defense contractor, which can represent over 20% of a specialized supplier's revenue, would severely impact Horstman's financial stability and operational capacity.
National governments serve as the ultimate end-users and primary funders for defense procurement, directly influencing purchasing decisions for companies like Horstman. Their budget allocations, defense priorities, and shifting procurement policies heavily dictate market demand and product specifications. For instance, the US defense budget enacted for fiscal year 2024 was approximately $886 billion, giving the government immense leverage in negotiations. This makes Horstman's business profoundly susceptible to political factors and significant shifts in military spending, granting governmental customers substantial bargaining power.
Defense contracts are notoriously characterized by procurement cycles that often stretch for many years, giving customers, primarily government agencies, significant leverage. For instance, the US Department of Defense's acquisition process for major systems can easily exceed five years from initial concept to deployment. This extended timeline allows agencies ample opportunity to thoroughly evaluate numerous alternatives and impose highly stringent terms on suppliers. Given the immense value and long-term commitment of these agreements, such as the estimated $886 billion US defense budget for fiscal year 2024, customers are empowered to dictate a vast majority of the contractual conditions.
High-Stakes, Mission-Critical Products
The high-stakes nature of Horstman's mission-critical suspension systems, vital for vehicle performance and crew survivability in combat, significantly empowers customers. Prime contractors, such as Rheinmetall or BAE Systems, impose extremely stringent quality and performance standards, reflecting the operational demands of military vehicles. Non-compliance can lead to substantial financial penalties or outright product rejection, underscoring customer leverage. This environment means suppliers must consistently meet rigorous specifications, which in 2024, often involve adherence to defense procurement regulations and performance-based contracts.
- Defense contracts often include clauses for penalties of up to 10-15% of contract value for critical performance failures.
- Military vehicle programs, like the US Army's Optionally Manned Fighting Vehicle (OMFV), prioritize survivability standards, impacting component supplier selection.
- Quality control costs for defense suppliers can exceed 5% of revenue due to intense scrutiny and certification requirements.
- Prime contractors maintain preferred supplier lists, making it difficult for new entrants or those with quality issues to penetrate the market.
Price Pressure and Lifecycle Cost Scrutiny
Customers, particularly government defense agencies, exert significant bargaining power over suppliers like Horstman due to intense scrutiny on defense budgets. For instance, the US Department of Defense's 2024 budget request of $849.8 billion emphasizes cost efficiency across all acquisitions. This focus extends beyond initial purchase prices to the total lifecycle cost of systems, compelling Horstman to offer highly competitive pricing and robust, long-term maintenance solutions.
- Global defense spending is projected to reach over $2.2 trillion in 2024, yet budget pressures drive demand for value.
- Lifecycle costs can account for 60-80% of a system's total cost over its operational life.
- Major customers often demand fixed-price contracts to mitigate cost overruns.
- Increased focus on sustainment and support contracts post-2024 amplifies customer leverage.
Customers, largely national defense ministries and major prime contractors, exert significant bargaining power over Horstman. Their concentrated numbers and the immense value of defense contracts, like the US defense budget of $886 billion for FY2024, enable stringent negotiations. Long procurement cycles and the mission-critical nature of Horstman's products further empower these buyers to demand strict quality and performance standards, often with penalties for non-compliance.
| Customer Aspect | 2024 Data/Impact | Leverage |
|---|---|---|
| US Defense Budget | ~$886 billion (FY2024) | High financial influence |
| Global Defense Spending | >$2.2 trillion projected (2024) | Market demand dictation |
| Contract Penalties | Up to 10-15% of contract value | Quality and performance control |
What You See Is What You Get
Horstman Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. You're looking at the actual Horstman Porter's Five Forces Analysis, detailing the competitive landscape for their business. Once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact, professionally formatted file, ready for your strategic planning. This comprehensive analysis will equip you with a deep understanding of the industry's competitive intensity and profitability drivers.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Horstman operates within a specialized defense market for military vehicle mobility solutions, facing intense competition. Key players like Rheinmetall Defence and BAE Systems Land division, alongside specialized firms, vie for major defense contracts. This rivalry is evident as global defense spending, projected to reach 2.5 trillion USD in 2024, fuels demand for advanced suspension systems. Companies compete fiercely for new program wins, such as the U.S. Army's vehicle modernization initiatives, where performance and cost efficiency are critical differentiators.
Being part of the RENK Group, a global leader with 2023 revenues exceeding €1.2 billion, significantly bolsters Horstman’s resources and global reach. This positioning, however, places Horstman in direct competition with other major international defense technology groups. Competitors like BAE Systems, reporting £23.2 billion in 2023 revenue, Rheinmetall with 2023 sales of €7.2 billion, and General Dynamics, generating $42.3 billion in 2023, also possess divisions that develop and manufacture vehicle systems. This creates an intense competitive landscape among well-funded, established entities vying for defense contracts. The rivalry is high, driven by substantial market presence and continuous innovation from these industry giants.
Competitive rivalry is profoundly shaped by the relentless pursuit of technological innovation. Firms are constantly pushing to develop next-generation suspension systems, including advanced active and semi-active technologies, crucial for enhancing vehicle mobility and crew comfort. In 2024, defense contractors globally allocated significant capital to R&D, with some exceeding 5% of their revenue. Horstman must continuously invest in research and development to maintain its market edge against rivals who are also aggressively advancing their technological capabilities.
Competition for Major Defense Programs
Competition for major defense programs, like new main battle tanks or armored personnel carriers, is exceptionally fierce. Winning these substantial, long-term contracts can secure production for years, making the rivalry among suspension system providers extremely high. For instance, the US defense budget for fiscal year 2024 was set at approximately $886 billion, with significant allocations for ground vehicle modernization. This intense environment means companies vie aggressively for selection as a key supplier for platforms such as the Abrams tank or Bradley Fighting Vehicle upgrades.
- US FY2024 defense budget: ~$886 billion.
- Modernization programs drive intense bidding wars.
- Long-term contracts offer multi-year revenue stability.
- Key contracts can define market leadership for decades.
International Market Competition
Horstman navigates intense international competition for contracts, facing global rivals across diverse regions. Many countries prioritize domestic suppliers, with over 60% of government procurement contracts globally in 2024 favoring local businesses, adding significant competitive pressure. This requires Horstman to adapt to varied regulatory environments and contend on a worldwide stage, where market access often depends on intricate trade agreements and local content requirements. The shift towards regional supply chains further intensifies this rivalry.
- Global defense spending increased by 9% in 2023, reaching $2.2 trillion, fueling competition.
- Major players like Rheinmetall and BAE Systems dominate key international markets.
- Local content requirements in countries like India often exceed 30% for defense procurement.
- Trade barriers and geopolitical tensions continue to reshape international market access in 2024.
Horstman faces intense rivalry from well-funded defense giants like Rheinmetall and BAE Systems, vying for major contracts in a growing global market. Fueled by projected 2024 defense spending of $2.5 trillion, competition for long-term programs and technological innovation is fierce. Local content requirements, favoring over 60% of 2024 government procurement globally, further intensify this high-stakes environment.
| Rival | 2023 Revenue | Market Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Rheinmetall | €7.2 Billion | Defense & Automotive |
| BAE Systems | £23.2 Billion | Aerospace, Defense & Security |
| General Dynamics | $42.3 Billion | Aerospace & Defense |
SSubstitutes Threaten
While hydro-pneumatic suspension excels in performance, alternative technologies like conventional coil spring, torsion bar, and air-based systems pose a clear threat. In 2024, the broader automotive suspension market, valued at over USD 57 billion, continues to see high adoption of simpler, more established coil spring designs in mass-market vehicles due to their cost-effectiveness. For applications where ultimate performance is less critical, these prevalent, lower-cost alternatives offer viable substitutes. This threat intensifies as customers prioritize initial investment savings over the advanced capabilities of hydro-pneumatic solutions.
The military vehicle market faces a significant threat from the emergence of electric and hybrid propulsion, which is fundamentally reshaping mobility architectures. This shift, actively pursued by developers like Texelis with their integrated e-mobility solutions, could lead to new designs that either favor alternative suspension types or integrate suspension functions directly into the drive system. Such innovation potentially substitutes the traditional, standalone hydro-pneumatic suspension systems, impacting demand for legacy components. For instance, the US Army's 2024 budget includes significant investments in hybrid-electric vehicle prototypes, indicating a clear move towards these integrated solutions.
The rise of unmanned ground vehicles poses a significant threat of substitution for traditional suspension systems. As the need to protect a human crew is eliminated, vehicle designs can shift towards simpler, more rugged, or entirely different mobility solutions. This trend, with the global UGV market projected to exceed $4 billion in 2024, could bypass Horstman's conventional product offerings. Designers may prioritize durability and cost over complex suspension, fostering alternative mobility paradigms.
Wheeled vs. Tracked Vehicle Trade-offs
The ongoing strategic debate between tracked and wheeled armored vehicles significantly influences the market, posing a threat of substitution for traditional systems. While Horstman offers advanced suspension solutions for both types, a pronounced shift in military doctrine towards wheeled platforms, often utilizing different suspension architectures, could act as a substitute for their historically dominant tracked vehicle systems. This trend impacts procurement decisions globally, with many nations prioritizing rapid deployment and lower operational costs. For instance, the global military armored vehicles market, valued at $19.8 billion in 2024, sees increasing investment in wheeled variants.
- Global wheeled armored vehicle market is projected to grow annually by 6.8% through 2028.
- Many Western militaries are actively modernizing fleets with wheeled platforms for urban and expeditionary operations.
- Wheeled vehicles often boast lower fuel consumption and maintenance requirements compared to tracked counterparts.
- The shift impacts R&D focus and procurement budgets for suspension system providers.
Advanced Active and Predictive Suspension
The rise of advanced active and predictive suspension systems presents a notable threat to Horstman. These systems, leveraging sophisticated sensors and AI, anticipate terrain changes, offering superior performance over conventional solutions.
While Horstman is actively investing in such technologies, a competitor achieving a groundbreaking innovation in this space with a fundamentally different and more effective approach could create a powerful substitute, potentially disrupting Horstman's market share.
- The global automotive active suspension market is projected to reach USD 5.7 billion by 2028, growing from USD 3.6 billion in 2023.
- OEMs are increasingly prioritizing predictive maintenance and ride comfort, driving investment in AI-driven suspension.
- Breakthroughs in real-time sensor fusion and machine learning algorithms could accelerate substitute adoption.
- In 2024, R&D spending on AI in automotive applications is estimated to exceed USD 10 billion globally.
The threat of substitutes for hydro-pneumatic suspension remains high due to cost-effective conventional systems and emerging technologies. In 2024, simpler coil springs dominate mass markets, while electric propulsion and unmanned vehicle designs offer new mobility paradigms. Advanced active suspension systems also pose a significant long-term substitution risk, driven by AI and sensor innovation.
| Substitute Type | 2024 Market Impact | Key Driver | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional Suspension | Over USD 57 billion automotive market share | Lower initial cost, established designs | ||
| Electric/Hybrid Propulsion | US Army 2024 budget for EV prototypes | Integrated system designs, energy efficiency | ||
| Unmanned Ground Vehicles (UGVs) | Global UGV market projected over USD 4 billion | Elimination of human crew protection needs |
Entrants Threaten
The defense industry presents exceptionally high barriers to entry, safeguarding established players. New entrants face the daunting need for extensive technical expertise, often requiring decades of specialized research and development. Significant capital investment is crucial, with major defense programs demanding billions; for instance, US defense R&D spending was projected at nearly $140 billion in 2024. Furthermore, stringent regulatory compliance, like ITAR, creates complex legal hurdles. Finally, established relationships with prime contractors and governments are essential, forming an almost impenetrable network for newcomers.
Defense customers, particularly government entities, are inherently risk-averse and prioritize proven, reliable technology for critical national security applications. A new entrant would face immense difficulty in establishing the necessary track record and reputation for quality and performance that established companies like Horstman have cultivated over decades. This significant 'trust barrier' is reinforced by stringent procurement processes and long qualification cycles, often taking years. For example, the U.S. Department of Defense's 2024 budget of over $800 billion largely favors suppliers with demonstrated capabilities, making it challenging for unproven firms to secure contracts. Gaining market share requires substantial investment and a long-term commitment to overcome this hurdle.
The defense sector thrives on deeply integrated, long-standing customer relationships, making market penetration exceptionally difficult for new entrants. Companies like Horstman often engage with prime contractors from initial design through the entire product lifecycle, building trust and expertise over decades. In 2024, many defense contracts continued to emphasize long-term strategic partnerships, reflecting the complexity and criticality of military systems. This embedded collaboration means new firms face significant hurdles, as established players like Horstman are already integral to their clients' operational success and supply chains.
Intellectual Property and Proprietary Technology
Horstman and its market rivals possess substantial intellectual property concerning their advanced suspension systems. A new company aiming to enter this specialized industry faces a high barrier, needing to develop entirely unique technology or risk costly infringement on existing patents. The deep, specialized engineering knowledge required for these innovations, often protected by patents, is not easily replicated, making market penetration exceptionally difficult. In 2024, the global patent landscape for advanced mechanical systems saw over 150,000 new patent applications, underscoring the ongoing innovation and protective measures in such fields.
- Significant R&D investment is required to circumvent existing patents.
- Legal costs for patent defense or licensing can be prohibitive for new entrants.
- Access to specialized engineering talent is a major hurdle.
- Established firms benefit from decades of accumulated proprietary data and designs.
Government Regulation and Security Clearances
Operating in the defense sector presents a significant barrier to new entrants due to stringent government regulations. Companies must navigate complex export controls and secure extensive security clearances for both their facilities and personnel. These administrative and security hurdles create a formidable challenge, making it difficult for firms without prior defense market experience to compete. The rigorous compliance landscape in 2024 continues to necessitate substantial investment in legal and security infrastructure.
- Defense contractors spend considerable resources on compliance, with the global aerospace and defense market projected to reach over $900 billion by 2025.
- Obtaining top-level security clearances for facilities can take years, delaying market entry for newcomers.
- The cost of maintaining compliance with ITAR (International Traffic in Arms Regulations) and other defense-specific rules can be prohibitive for smaller firms.
- Only established entities with proven track records typically secure large government contracts, reinforcing the barrier for new entrants.
New entrants into the defense sector face formidable barriers, including immense capital requirements and the need for decades of specialized R&D to match existing intellectual property. Stringent government regulations, such as ITAR, and lengthy security clearance processes create significant compliance hurdles. Furthermore, established, risk-averse customer relationships and long qualification cycles make market penetration exceptionally difficult. This combination effectively limits the threat from new competitors.
| Barrier Type | 2024 Data Point | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Capital | US Defense R&D: ~$140B | High initial cost |
| Regulation | ITAR compliance | Complex, costly entry |
| Market Access | US DoD Budget: >$800B | Favors proven suppliers |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Horstman Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of publicly available financial statements, industry-specific market research reports, and credible news outlets. We also incorporate data from trade associations and government economic indicators to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape.
