Hearst Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Hearst Bundle
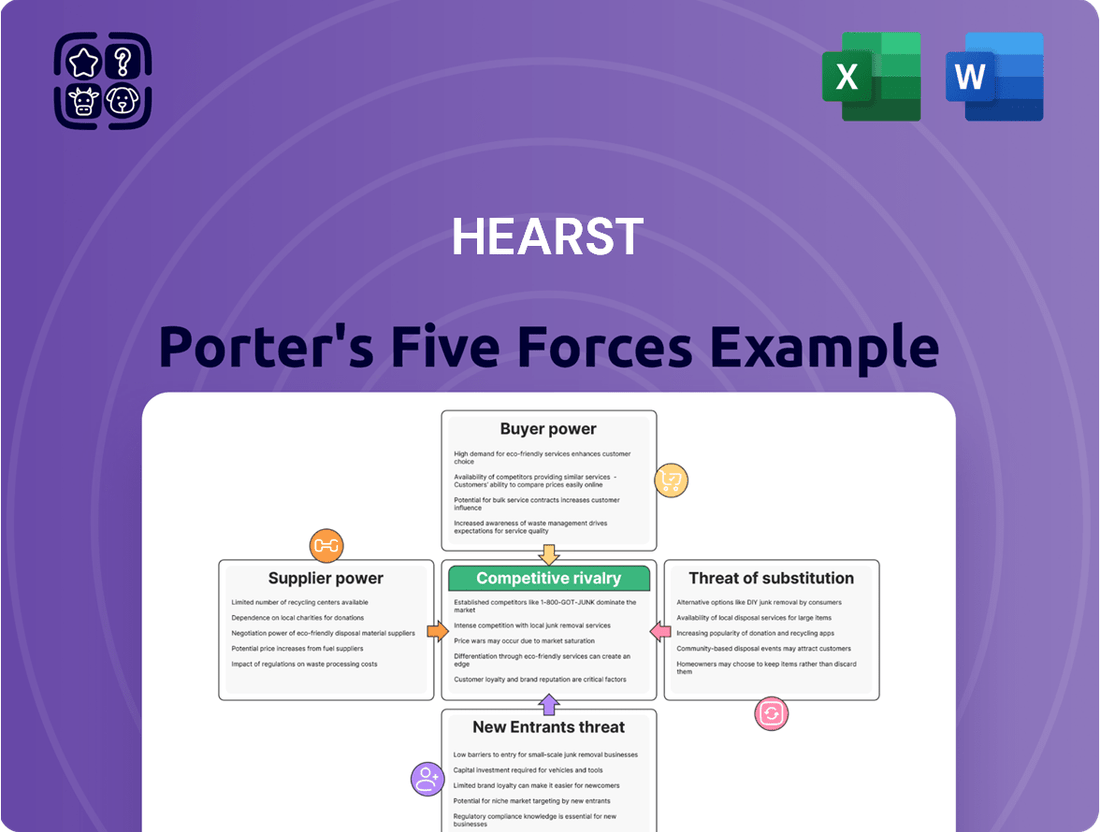
Understanding the competitive landscape is crucial for any business, and Hearst is no exception. Our Porter's Five Forces analysis delves into the intricate web of forces shaping Hearst's industry, from the bargaining power of buyers to the threat of new entrants.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Hearst’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Hearst's reliance on content creators, including journalists and writers, means these suppliers hold significant bargaining power. Highly sought-after individuals or those with specialized expertise can negotiate higher compensation, directly impacting Hearst's operational costs. For instance, in 2024, the demand for exclusive, high-quality investigative journalism continued to rise, giving top journalists more leverage.
The bargaining power of these content suppliers is amplified when their work is crucial for differentiating Hearst's publications in a crowded digital and print market. Unique perspectives and exclusive content are key differentiators, allowing creators to command better terms. This is particularly true in niche areas where specialized knowledge is scarce.
Hearst, a major media company, relies on technology and software suppliers for its digital operations, content management, and advertising. The bargaining power of these suppliers can be substantial if they offer unique, critical software that is hard to substitute, such as advanced AI tools or specialized data analytics platforms. For instance, in 2024, the global market for AI software was projected to reach over $200 billion, indicating the significant value and potential leverage of key AI providers.
Advertising technology providers wield considerable influence over Hearst's revenue streams, which are deeply intertwined with advertising across digital, print, and television. These suppliers, encompassing ad exchanges, programmatic platforms, and data management solutions, are crucial for Hearst's ability to reach specific audiences and measure campaign success.
The power of these tech suppliers stems from their control over the infrastructure that enables targeted advertising and provides essential analytics. Their efficiency in ad placement and data utilization directly affects Hearst's advertising revenue and its overall market competitiveness. For instance, in 2024, the digital advertising market continued its growth, with programmatic advertising accounting for a significant portion, underscoring the dependence on these technology providers.
Print and Distribution Services
For Hearst's traditional print media, the bargaining power of suppliers in printing, paper, and distribution is a key consideration. Fluctuations in paper prices, a critical input, directly impact costs. For instance, global paper prices saw significant volatility in recent years, with some grades experiencing substantial increases due to supply chain disruptions and demand shifts.
The number of printing presses available and the efficiency of distribution networks also play a role. A limited number of specialized printing facilities or a consolidated distribution landscape can grant suppliers greater leverage. For example, if a major printing company or a key logistics provider experiences operational challenges or increases its rates, Hearst's costs could rise.
- Paper Costs: Global paper prices can fluctuate significantly, impacting Hearst's production expenses for magazines and newspapers.
- Printing Capacity: The availability and cost of printing services depend on the capacity and pricing power of printing press operators.
- Distribution Networks: The efficiency and consolidation of physical distribution channels can influence the bargaining power of logistics providers.
- Supplier Consolidation: Increased consolidation among paper manufacturers, printers, or distributors can lead to higher supplier bargaining power.
Talent and Production Houses (Television/Entertainment)
Hearst's engagement with cable television networks and local broadcast stations places it directly in the path of powerful suppliers: talent and production houses. When highly sought-after actors, charismatic hosts, or innovative producers are involved, their leverage increases significantly. This is especially true for content that is unique or commands a premium audience, such as exclusive sports broadcasts or critically acclaimed dramatic series.
The bargaining power of these suppliers is amplified by factors like their specialized skills, the strong brand recognition they've built, and the exclusive rights they hold to their creative output. For instance, a production house that has perfected a unique visual effects technique or a talent agency representing a globally recognized star can demand higher fees and more favorable terms.
- Talent Scarcity: In 2023, the average salary for a lead actor in a major television production could range from $100,000 to over $1 million per episode, reflecting the high demand for established stars.
- Production House Expertise: Specialized production companies, particularly those with a proven track record in high-demand genres like live sports or unscripted reality television, can command significant project fees, often in the millions of dollars for major productions.
- Content Exclusivity: Proprietary content, such as exclusive rights to a popular franchise or a unique documentary series, gives production houses substantial leverage in negotiations with broadcasters like Hearst.
- Reputation and Demand: A production house or talent that consistently delivers high ratings and critical acclaim will naturally have greater bargaining power when negotiating new contracts.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Hearst is a critical factor, influencing costs and profitability across its diverse media operations. From content creators to technology providers and traditional print inputs, understanding this power is key to strategic planning.
For content creators, the demand for exclusive, high-quality journalism in 2024 means top journalists can negotiate higher compensation, impacting Hearst's operational expenses. Similarly, in the technology sector, providers of critical AI or data analytics tools hold significant leverage, especially given the projected over $200 billion global AI software market in 2024.
The media industry's dependence on advertising technology also grants these suppliers considerable influence. Their ability to facilitate targeted advertising and provide essential analytics directly affects Hearst's revenue. The continued growth of programmatic advertising in 2024 further highlights this reliance.
Traditional print operations face supplier power from paper manufacturers, printers, and distributors. Fluctuations in paper prices, driven by supply chain issues, can significantly raise costs. The consolidation within these sectors further amplifies supplier leverage.
In broadcast media, talent and production houses with unique content or highly sought-after individuals can command premium fees. For instance, lead actors in major TV productions in 2023 could earn upwards of $1 million per episode, showcasing the significant bargaining power of top talent.
| Supplier Type | Key Factors Influencing Bargaining Power | Illustrative 2024 Data/Trends |
|---|---|---|
| Content Creators | Scarcity of specialized skills, demand for exclusive content | Rising demand for investigative journalism, increased leverage for top journalists. |
| Technology Providers (AI, Data Analytics) | Uniqueness of solutions, criticality to operations | Global AI software market projected over $200 billion; critical for Hearst's digital strategy. |
| Advertising Technology Providers | Control over ad delivery and analytics, market share | Programmatic advertising's significant share of the growing digital ad market. |
| Print Suppliers (Paper, Printing) | Price volatility, availability of capacity, industry consolidation | Significant paper price fluctuations due to supply chain disruptions. |
| Talent & Production Houses | Star power, exclusivity of content, production expertise | High fees for top talent (e.g., lead actors earning up to $1M+ per episode in 2023). |
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects the competitive forces impacting Hearst, providing strategic insights into industry rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threats of new entrants and substitutes.
Effortlessly identify and address competitive threats with a visual breakdown of Porter's Five Forces, simplifying complex market dynamics.
Customers Bargaining Power
Individual consumers wield significant bargaining power over Hearst's media outlets. The proliferation of content choices, from streaming services to social media feeds, allows consumers to easily shift their attention and spending. For instance, the trend of cord-cutting continues to impact traditional television viewership, with a significant portion of households opting for streaming alternatives.
This ease of switching is amplified by the availability of free digital content, forcing Hearst to continuously innovate. In 2024, the digital advertising market saw continued shifts, with publishers needing to demonstrate unique value propositions to capture audience attention amidst a crowded landscape. Hearst's strategy must focus on delivering exclusive, high-quality content and flexible subscription options to maintain customer loyalty.
Advertisers wield significant influence over Hearst's media operations. The advertising landscape is highly fragmented, offering businesses a vast array of choices beyond traditional media. In 2024, digital advertising spending continued its upward trajectory, projected to reach over $350 billion in the US alone, a testament to the competitive pressure advertisers can exert.
The proliferation of digital platforms, including social media giants and streaming services, provides advertisers with numerous alternatives for reaching consumers. This abundance of options allows advertisers to negotiate for more favorable terms, such as reduced ad rates and enhanced targeting precision, directly impacting Hearst's revenue streams.
Furthermore, advertisers increasingly demand demonstrable return on investment, pushing media companies like Hearst to provide sophisticated analytics and measurable campaign results. This focus on data-driven outcomes strengthens the advertisers' position, enabling them to dictate terms based on performance metrics and the perceived value of Hearst's audience reach.
For Hearst's business information services, including Fitch Group and Hearst Health, the bargaining power of their B2B customers is a significant factor. Customers' leverage hinges on how unique Hearst's data and insights truly are, as well as the costs and effort involved in switching to a different provider. If alternative data sources are readily available and comparable, customer power naturally increases.
The intensity of competition among business intelligence providers directly impacts customer bargaining power. A market with many comparable options empowers customers to demand better pricing and terms. For instance, if a business can easily find similar financial data from multiple sources, they are less reliant on any single provider like Fitch.
Cable and Satellite Operators
Cable and satellite operators hold substantial bargaining power over content providers like Hearst. These operators are crucial intermediaries, packaging and distributing content to millions of households. Their ability to bundle channels and control subscriber access makes them powerful negotiators regarding carriage fees and content licensing.
The concentration within the cable and satellite industry amplifies this power. For instance, as of early 2024, the top three U.S. cable operators, Charter Communications, Comcast, and Cox Communications, serve a significant majority of the pay-TV market. This consolidation means fewer entities are negotiating with content creators, giving them greater leverage to demand favorable terms for carrying networks like ESPN or A+E Networks.
- Significant Market Share: Major cable operators like Comcast and Charter control a large portion of the pay-TV subscriber base, giving them considerable sway in negotiations.
- Gatekeeper Role: Operators act as the primary conduit between content providers and consumers, controlling what content reaches the end viewer.
- Consolidation Impact: Industry consolidation has led to fewer, larger operators, increasing their collective bargaining strength when negotiating carriage agreements and fees with content owners.
Digital Platforms and Aggregators
Digital platforms and aggregators, such as OpenAI, are increasingly influencing how content is accessed and monetized. Hearst's partnerships with these entities, like its content integration with OpenAI's AI products, demonstrate this shift. While these collaborations can significantly broaden content distribution, they also concentrate power in the hands of platforms that command vast user bases.
This aggregation of users gives platforms considerable leverage. They can influence terms for content licensing, data usage, and revenue-sharing models. For Hearst, this dynamic means a constant negotiation to balance the benefits of expanded reach against the need to retain control over its valuable intellectual property and ensure fair compensation.
- Platform Power: Major digital platforms and AI companies are becoming central gatekeepers for content distribution, wielding significant influence over publishers.
- Revenue Sharing: The terms of revenue sharing with these aggregators are critical, directly impacting a publisher's profitability and ability to invest in content creation.
- Content Control: Publishers like Hearst must actively manage their digital presence to maintain control over their content and brand integrity in an increasingly platform-dependent ecosystem.
The bargaining power of customers for Hearst's media operations is substantial, driven by abundant content alternatives and the ease with which consumers can switch platforms. This forces Hearst to continually enhance its offerings and pricing strategies. In 2024, the ongoing shift towards digital content consumption and the availability of free alternatives underscore the need for Hearst to provide unique value and flexible subscription models to retain its audience.
For Hearst's business-to-business segments, customer leverage is directly tied to the uniqueness and cost of switching from Hearst's data and insights. A competitive market for business intelligence providers means customers can more easily negotiate favorable terms if comparable alternatives exist. This situation intensifies pressure on Hearst to differentiate its specialized services.
| Customer Segment | Key Drivers of Bargaining Power | Impact on Hearst |
|---|---|---|
| Individual Consumers | Abundant content choices, ease of switching, availability of free digital content | Pressure on subscription pricing, need for high-quality exclusive content |
| Advertisers | Fragmented advertising market, rise of digital platforms, demand for ROI | Negotiation leverage for ad rates, need for sophisticated analytics |
| B2B Customers (e.g., Fitch Group, Hearst Health) | Availability of comparable data, cost of switching providers, competitive market | Pressure on pricing and terms for data and insights |
| Cable & Satellite Operators | Market concentration, gatekeeper role, consolidation | Negotiation power over carriage fees and content licensing |
| Digital Platforms & Aggregators | Large user bases, control over content distribution | Influence on licensing terms, data usage, and revenue sharing |
What You See Is What You Get
Hearst Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview displays the complete Hearst Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a thorough examination of the competitive landscape within the media industry. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no discrepancies or missing information. You can trust that the insights and data presented in this preview are representative of the full, ready-to-use document available for download.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Hearst faces robust competition from other major diversified media conglomerates like News Corp and Gannett. These rivals often possess similar expansive portfolios, encompassing print, digital, and broadcast media, which intensifies the battle for audience engagement and advertising dollars.
The rivalry extends across various media segments, as these companies vie for top talent and market share in an increasingly fragmented media landscape. For instance, in 2023, News Corp reported total revenue of $9.7 billion, showcasing the scale of operations these competitors manage.
Digital-native media companies, online publishers, and content platforms are significantly increasing competitive rivalry. These agile entities, often with leaner operational structures, are purpose-built for digital distribution and can pivot rapidly to align with evolving consumer tastes. For example, in 2024, digital advertising spend is projected to reach over $375 billion in the US alone, a substantial portion of which is now captured by these newer players, directly challenging traditional media's revenue streams.
Major tech and social media companies like Google, Meta, and TikTok are fierce rivals for advertising revenue, directly competing with Hearst's traditional media outlets. These platforms command immense, engaged user bases and offer advanced targeting tools, often outperforming traditional media in reach and efficiency. In 2023, digital advertising spending in the US was projected to reach over $300 billion, a significant portion of which diverts from traditional channels.
Niche Content Providers and Creator Economy
The rise of niche content providers and the creator economy intensifies competitive rivalry for Hearst. Independent creators and specialized streaming services are capturing audience attention by offering highly personalized content, a direct challenge to traditional media’s broader approach. This fragmentation means Hearst must continually innovate to retain and engage viewers.
These new entrants often leverage lower overheads and direct audience relationships. For instance, the creator economy saw significant growth in 2024, with platforms like YouTube and TikTok continuing to empower individual creators. Many creators are now earning substantial incomes, with some top YouTubers reporting annual earnings in the tens of millions of dollars, demonstrating the economic viability of niche content.
- Niche Streaming Growth: The number of niche streaming services has expanded, offering specialized content from documentaries to esports, directly competing for viewer time.
- Creator Economy Earnings: In 2024, the top tier of content creators on platforms like Patreon and Substack reported significant revenue growth, indicating a strong financial incentive for creators to operate independently.
- Audience Engagement: Niche providers often foster highly engaged communities, providing personalized experiences that can be difficult for larger media conglomerates to replicate at scale.
B2B Information Service Providers
Hearst's B2B information services, including Fitch Group and Hearst Health, encounter significant competition from specialized data, analytics, and software firms. This intense rivalry stems from the consistent demand for precise, up-to-the-minute, and actionable business intelligence. Competitors actively vie for market share by prioritizing cutting-edge product development, maintaining superior data integrity, and cultivating robust client relationships.
The competitive landscape is characterized by a strong emphasis on differentiation through value-added services and specialized expertise. For instance, in the financial data sector, firms like S&P Global and Moody's Analytics offer comprehensive analytical tools and credit ratings, directly competing with Fitch Group. Similarly, in the health information segment, companies such as IQVIA and Clarivate provide extensive data and analytics for the life sciences industry, challenging Hearst Health's market position. The market for B2B information services is projected to continue its growth trajectory, with global spending on business intelligence and data analytics expected to reach over $30 billion in 2024, highlighting the high stakes and active competition.
- Intense Rivalry: Hearst competes with specialized data, analytics, and software providers in segments like Fitch Group and Hearst Health.
- Drivers of Competition: Demand for accurate, timely, and actionable insights fuels competition.
- Competitive Strategies: Competitors focus on product innovation, data quality, and client relationships to gain market share.
- Market Growth: Global spending on business intelligence and data analytics is a key indicator of competitive intensity.
Hearst's competitive rivalry is intense, driven by both established media giants and agile digital newcomers. Traditional rivals like News Corp, with its $9.7 billion revenue in 2023, compete across print, digital, and broadcast. However, the landscape is increasingly shaped by digital-native companies and tech giants like Google and Meta, which capture significant portions of the over $375 billion projected US digital ad spend for 2024. This fragmentation forces Hearst to continuously innovate to maintain audience engagement against specialized content providers and the burgeoning creator economy, where top YouTubers can earn tens of millions annually.
| Competitor Type | Key Competitors | 2023/2024 Data Point | Impact on Hearst |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diversified Media Conglomerates | News Corp, Gannett | News Corp revenue: $9.7 billion (2023) | Competition for audience and advertising revenue across traditional platforms. |
| Digital-Native Publishers | Various online news and content sites | US Digital Ad Spend: >$375 billion (2024 est.) | Capturing ad dollars and audience attention with agile digital strategies. |
| Tech & Social Media Platforms | Google, Meta, TikTok | US Digital Ad Spend: >$300 billion (2023) | Dominance in digital advertising due to reach and targeting capabilities. |
| Creator Economy | Individual content creators, niche platforms | Top YouTubers earn tens of millions annually. | Fragmenting audience attention with personalized and specialized content. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The rise of free online content, including user-generated material and ad-supported platforms, presents a substantial threat of substitutes for traditional paid media. Consumers can readily access news, entertainment, and information without incurring subscription fees, diminishing the perceived value of premium content. This shift is evident in the growing popularity of news aggregators, blogs, and social media feeds as primary information sources.
In 2024, the digital advertising market is projected to reach over $600 billion globally, underscoring the financial viability of ad-supported free content. Platforms like YouTube, TikTok, and various news websites leverage this model, offering vast libraries of content that directly compete with subscription services like cable television or paid news outlets. For instance, a significant portion of younger demographics, particularly Gen Z, increasingly relies on social media for news consumption, bypassing traditional channels.
The proliferation of streaming services like Netflix, Disney+, and Max presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional media. These platforms offer vast, on-demand content libraries, often at attractive subscription prices. In 2024, Netflix reported over 270 million paid subscribers globally, demonstrating the immense consumer shift towards these alternatives.
Podcasts and audiobooks present a significant threat to traditional media like radio and print. Their on-demand nature and diverse content allow consumers to engage with information while performing other tasks, a flexibility often lacking in older formats. This shift is evident in the growing listenership; by 2023, it was estimated that over 70% of the US population listened to podcasts, a figure projected to climb further.
The ease of entry for podcast creation has fueled an immense growth in content availability. This proliferation attracts listeners and advertising dollars, directly impacting revenue streams for established media. For instance, podcast advertising spend was anticipated to exceed $2 billion in 2023, diverting funds that might otherwise have gone to radio or print advertising.
Social Media as News and Information Source
Social media platforms increasingly serve as primary news conduits, particularly for younger audiences, directly substituting traditional media like newspapers and television. This shift means Hearst's content, while present, is often consumed within the social media environment, potentially diminishing direct website traffic and advertising revenue.
In 2024, a significant portion of the population, especially Gen Z and Millennials, relies heavily on social media for news. For instance, a Pew Research Center study indicated that a substantial percentage of U.S. adults get their news from social media. This trend directly challenges traditional media outlets like Hearst by diverting audience attention and advertising dollars to platforms where content is often aggregated and consumed passively.
- Audience Shift: Younger demographics are migrating to social media for news, bypassing traditional Hearst platforms.
- Revenue Impact: Direct traffic and associated advertising revenue for Hearst are likely suppressed as consumption moves to social media.
- Content Aggregation: Social media's model often aggregates news, potentially reducing brand recognition and loyalty for original publishers like Hearst.
AI-Generated Content and Personalized Feeds
The increasing sophistication of AI-generated content presents a growing substitute threat to traditional media and content creators. These AI tools can now produce articles, summaries, and even video content at a speed and scale that can rival human output, potentially lowering the perceived value of human-created content.
Furthermore, the hyper-personalization offered by major tech platforms curates content feeds for individual users. This can lead consumers to bypass traditional content sources altogether, opting for algorithmically selected information that directly matches their interests.
This trend is already impacting the content landscape. For instance, by early 2024, generative AI models like GPT-4 were demonstrating remarkable capabilities in producing coherent and informative text, raising questions about the future demand for human journalists and writers in certain capacities.
- AI Content Generation: Tools can now create articles, summaries, and videos, potentially reducing reliance on human creators.
- Personalized Feeds: Tech giants' algorithms curate content, bypassing traditional media outlets.
- Market Impact: By mid-2024, AI's ability to generate text was significantly advancing, impacting content creation industries.
The threat of substitutes for traditional media, including those produced by Hearst, is amplified by the growing prevalence of free, readily accessible digital content. Consumers increasingly turn to platforms offering news, entertainment, and information without direct payment, diminishing the perceived value of traditional subscription models. This shift is clearly demonstrated by the significant global growth in digital advertising, which funds many of these free alternatives.
In 2024, the digital advertising market is expected to exceed $600 billion worldwide. This substantial financial backing allows platforms like YouTube and various news aggregators to offer vast amounts of content, directly competing with established media. For instance, a significant portion of younger audiences now relies on social media feeds for their news consumption, a trend that bypasses traditional Hearst publications.
| Substitute Type | Impact on Traditional Media | Supporting Data (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Free Online Content (Aggregators, Blogs, Social Media) | Diverts audience attention and advertising revenue. | Global digital ad market projected over $600 billion in 2024. |
| Streaming Services (Netflix, Disney+) | Reduces demand for cable TV and traditional broadcast. | Netflix reported over 270 million paid subscribers globally in 2024. |
| Podcasts and Audiobooks | Challenges radio and print media with on-demand audio content. | Over 70% of the US population listened to podcasts by 2023; podcast ad spend exceeded $2 billion in 2023. |
| AI-Generated Content | Potentially lowers the value of human-created content and impacts creator demand. | Generative AI models showed significant advancements in text generation by early 2024. |
Entrants Threaten
The digital age has dramatically reduced the cost and complexity of creating and distributing content. Individuals and small businesses can now launch blogs, podcasts, or video channels with relatively little upfront investment, directly challenging established players for audience engagement. For instance, the global creator economy was valued at over $250 billion in 2023, demonstrating the scale of this shift.
Niche digital publishers and platforms are a growing threat. They can zero in on very specific audiences, often those overlooked by larger media companies. For instance, specialized online communities focused on niche hobbies or professional interests can cultivate highly engaged followings.
These new entrants often utilize cost-effective digital tools and social media marketing to scale quickly, bypassing the substantial infrastructure costs of traditional publishers. This agility allows them to capture audience attention and advertising revenue in segments that might not be profitable for giants like Hearst. In 2023, the digital advertising market continued to see growth in programmatic advertising, which benefits smaller, targeted publishers.
Tech startups are increasingly entering the media landscape with disruptive, innovative models. These new players often leverage cutting-edge technologies like artificial intelligence and big data analytics to create highly personalized content experiences. For instance, companies utilizing AI for content curation and recommendation engines can attract audiences away from traditional media outlets by offering more relevant and engaging material.
These startups can also disrupt established revenue streams through novel advertising approaches or subscription tiers that cater to niche audiences. For example, a startup focusing on interactive video advertising or a subscription service offering exclusive, AI-generated content could capture market share. The agility of these startups allows them to adapt quickly to changing consumer preferences and technological advancements, posing a significant threat to incumbent media companies.
Retailers and Brands as Media Owners
A significant threat emerges as major retailers and brands increasingly transform into media owners by launching their own retail media networks. This trend directly challenges traditional media companies by capturing advertising revenue.
Leveraging extensive first-party customer data, these new entrants offer highly targeted advertising solutions. For instance, Walmart Connect, a prominent retail media network, generated over $2.7 billion in advertising revenue in 2023, demonstrating the substantial financial backing and reach of these platforms.
- Retail Media Network Growth: The global retail media ad spend was projected to reach $125.7 billion in 2023, with significant growth expected to continue through 2025.
- Data Advantage: Retailers possess rich, transactional data that allows for precise audience segmentation, making their advertising offerings highly attractive to brands.
- Competitive Pressure: This shift diverts ad budgets from traditional publishers, increasing competition for marketing dollars and potentially impacting the revenue streams of established media entities.
Investment by Non-Media Companies in Content
Non-traditional media companies, especially tech giants, are significantly increasing their investment in content. For instance, in 2024, Amazon secured NFL Thursday Night Football rights for a reported $1 billion per year, and Apple TV+ continued its substantial spending on original series and film production, with estimates suggesting an annual content budget exceeding $3 billion.
These entrants, often possessing vast financial resources and diversified business models, can readily absorb initial content creation costs and potential losses. This allows them to aggressively scale their offerings, directly competing with established media companies like Hearst for audience attention and advertising revenue.
The threat is amplified by their ability to leverage existing technology platforms and user bases for content distribution. This integrated approach provides a competitive advantage that traditional media firms may find challenging to replicate.
- Tech giants like Amazon and Apple are investing billions in content rights and original productions.
- Their deep financial pockets enable them to absorb initial losses and scale rapidly.
- Leveraging existing platforms gives them a distribution advantage.
- This influx of capital and competition pressures traditional media players.
The threat of new entrants is significant for established media companies like Hearst. Digitalization has lowered barriers to entry, allowing individuals and small businesses to create and distribute content, directly competing for audience attention. For example, the global creator economy was valued at over $250 billion in 2023, highlighting this shift.
Tech giants and major retailers are increasingly entering the media space, leveraging vast financial resources and data advantages. Retail media networks, for instance, are projected to reach $125.7 billion in ad spend globally for 2023, diverting ad budgets. Companies like Amazon and Apple are also investing billions in content, creating substantial competitive pressure.
| New Entrant Type | Key Advantage | 2023/2024 Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Creator Economy Participants | Low cost, niche focus | Creator economy valued at >$250 billion (2023) |
| Retail Media Networks | First-party data, targeted ads | Global retail media ad spend projected at $125.7 billion (2023) |
| Tech Giants (e.g., Amazon, Apple) | Deep pockets, existing platforms | Amazon's NFL rights deal: ~$1 billion/year; Apple TV+ content budget: >$3 billion/year (estimated) |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, drawing from reputable sources such as industry-specific market research reports, company annual filings, and government economic data. This comprehensive approach ensures a thorough understanding of competitive dynamics.
