Health Catalyst Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Health Catalyst Bundle
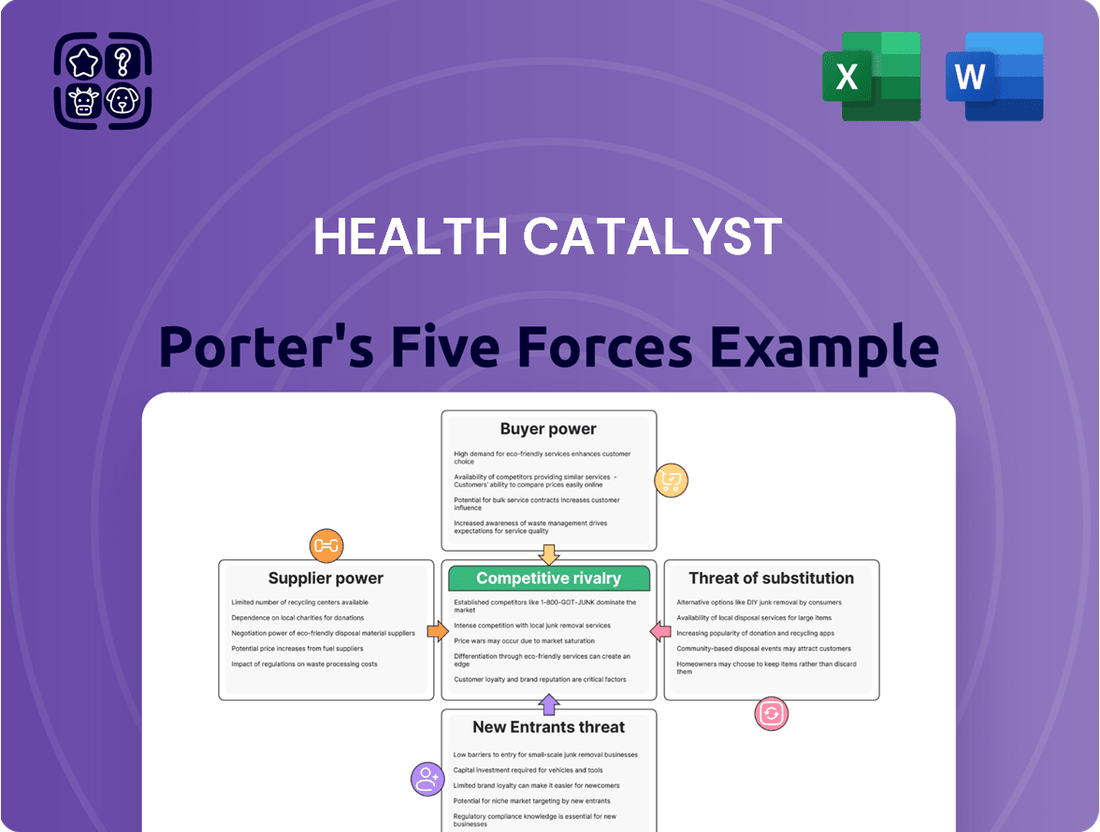
Health Catalyst operates in a dynamic healthcare technology landscape shaped by intense competition and evolving client needs. Understanding the forces of buyer power, supplier leverage, threat of new entrants, substitute products, and industry rivalry is crucial for strategic planning.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Health Catalyst’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Health Catalyst's reliance on data integration and software providers introduces a significant factor in its supplier bargaining power. The uniqueness and criticality of the data or software these suppliers offer, coupled with the costs and difficulties associated with switching, directly influence their leverage. For instance, if Health Catalyst depends on a highly specialized data set or a proprietary software component that is difficult to replicate, the supplier's bargaining power increases substantially.
Health Catalyst, as a cloud-based data platform provider, faces significant reliance on major cloud infrastructure players like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud. In 2024, these providers continue to wield substantial bargaining power, a trend driven by their massive infrastructure investments and unparalleled economies of scale.
The high switching costs and technical complexities involved in migrating vast datasets and critical operations between cloud platforms further solidify the leverage of AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud. This dependency means Health Catalyst must navigate pricing structures and service agreements carefully, as changes can directly impact operational expenses and service delivery.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Health Catalyst, particularly concerning talent and expertise, is substantial. Highly specialized professionals in healthcare data science, analytics, artificial intelligence, and cybersecurity are crucial for the company's success and ongoing innovation.
The scarcity of individuals possessing this niche expertise in the current market significantly amplifies their leverage. This scarcity directly influences Health Catalyst's recruitment expenses, necessitates robust retention programs, and ultimately impacts overall operational costs, as evidenced by the competitive salary trends in these fields observed through 2024.
Cybersecurity Solution Providers
Health Catalyst's acquisition of Intraprise Health in November 2024 underscores the critical role of cybersecurity in healthcare. This move signals a strategic effort to bolster internal security, yet the continued need for specialized external cybersecurity solutions, threat intelligence feeds, and compliance expertise means these providers retain a degree of bargaining power. Their influence is amplified when their services are unique or proprietary, making switching costs for Health Catalyst potentially significant.
The bargaining power of cybersecurity solution providers for Health Catalyst is moderate. While Health Catalyst is a significant player, the cybersecurity market is competitive, offering multiple vendors for many standard solutions. However, specialized threat intelligence or compliance tools, especially those tailored to healthcare regulations like HIPAA, can command higher prices and influence due to limited alternatives.
- Specialized Offerings: Providers with unique or highly specialized cybersecurity solutions, such as advanced threat detection tailored for healthcare data, can exert greater influence.
- Switching Costs: The integration of cybersecurity solutions into Health Catalyst's existing infrastructure can create high switching costs, giving established providers more leverage.
- Market Concentration: While the overall cybersecurity market is vast, specific niches relevant to healthcare data security may have fewer dominant players, increasing their bargaining power.
- Regulatory Compliance: Providers offering expertise in navigating complex healthcare regulations, like HIPAA compliance, hold significant sway due to the critical nature of these requirements.
Consulting and Professional Services Partners
Health Catalyst engages with consulting and professional services partners for data strategy and implementation. The bargaining power of these partners is influenced by their industry standing, unique expertise, and the general demand for their skills in the dynamic healthcare IT sector. For instance, specialized data analytics consulting firms with proven track records in healthcare can command higher fees, increasing their bargaining power.
Factors influencing this power include the concentration of specialized consultants, the availability of alternative service providers, and the switching costs for Health Catalyst. If a particular consulting firm possesses proprietary methodologies or deep insights into healthcare data regulations, its leverage grows. In 2024, the demand for specialized healthcare data consulting remained robust, driven by the ongoing digital transformation in the industry.
- Reputation and Specialization: Consulting firms with a strong reputation and niche expertise in areas like clinical data integration or population health analytics often hold significant bargaining power.
- Demand in Healthcare IT: The high demand for skilled professionals in healthcare IT, particularly those adept at navigating complex data environments, strengthens the position of these service providers.
- Availability of Alternatives: The presence of numerous consulting firms and independent experts in the market can moderate the bargaining power of any single partner.
Health Catalyst's reliance on major cloud infrastructure providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud in 2024 gives these suppliers significant bargaining power. Their massive scale and ongoing infrastructure investments create high switching costs for Health Catalyst, impacting operational expenses.
The bargaining power of talent suppliers for Health Catalyst is substantial due to the scarcity of specialized professionals in healthcare data science and AI. This drives up recruitment and retention costs, as seen in competitive salary trends throughout 2024.
Specialized cybersecurity and consulting firms also hold considerable leverage, particularly those with unique healthcare data solutions or deep regulatory expertise. The integration of these services into Health Catalyst's platform can lead to high switching costs, further strengthening supplier influence.
What is included in the product
This analysis deeply examines the competitive landscape for Health Catalyst, detailing the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the availability of substitutes. It provides strategic insights into Health Catalyst's competitive positioning and potential vulnerabilities.
Gain immediate clarity on competitive pressures with a visual breakdown of each force, enabling faster, more informed strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Health Catalyst's customers, primarily hospitals and health systems, wield considerable bargaining power. These organizations are large, sophisticated buyers with substantial budgets, often spending millions on data analytics solutions. Their ability to negotiate favorable terms is amplified by the increasing availability of alternative data management and analytics tools, as well as their internal capacity to aggregate and analyze data, which can reduce reliance on a single vendor. For instance, in 2023, the average hospital operating margin was around 2.5%, meaning cost savings and demonstrable ROI are paramount, giving them leverage in price discussions.
The growing adoption of value-based care models significantly amplifies customer bargaining power. Healthcare systems are increasingly focused on demonstrating tangible improvements in patient outcomes and cost reductions, directly influencing their purchasing decisions.
This shift means customers, like hospitals and health networks, are more likely to demand solutions from Health Catalyst that clearly align with these value-based objectives. They may push for more flexible, performance-based contracts, tying payments to the achievement of specific quality metrics or cost savings, thereby increasing pressure on Health Catalyst to deliver measurable results.
While customers can exert pressure, the integration complexity of Health Catalyst's data operating system is a significant hurdle. The substantial upfront investment and the intricate process of embedding the system into existing healthcare IT infrastructure create high switching costs for clients.
These elevated switching costs, stemming from the deep integration and associated investments, effectively lock in customers. This makes it difficult and expensive for them to transition to a competitor once Health Catalyst's solution is in place, thereby diminishing their long-term bargaining power.
Consolidation of Healthcare Systems
The increasing consolidation of healthcare systems significantly amplifies customer bargaining power. As larger entities absorb smaller ones, their collective purchasing volume allows for more forceful negotiations on pricing and service terms with technology providers like Health Catalyst.
By 2024, the trend of hospital mergers and acquisitions continued, creating larger, more dominant healthcare networks. These consolidated systems, possessing greater market share, are better positioned to demand favorable contracts, potentially impacting Health Catalyst's revenue and profit margins.
- Increased Purchasing Power: Larger health systems can leverage their scale to negotiate lower prices for Health Catalyst's data and analytics solutions.
- Demand for Customization: Consolidated systems may demand more tailored solutions, increasing development costs for Health Catalyst.
- Vendor Consolidation: As customers consolidate, they may also seek to consolidate their vendor relationships, potentially reducing the number of partners like Health Catalyst.
Demand for Measurable ROI
Healthcare organizations are placing a significant emphasis on demonstrating a measurable return on investment (ROI) for their technology purchases. This trend is particularly pronounced in 2024, as budget constraints and a focus on value-based care intensify.
Customers are actively pressuring Health Catalyst to deliver concrete proof of cost savings, enhanced patient outcomes, and improved operational efficiencies. This demand translates into a need for sophisticated analytics and transparent reporting capabilities to validate the value proposition of Health Catalyst's solutions.
- Demand for Quantifiable Results: Healthcare providers are prioritizing technology that directly impacts their bottom line and patient care metrics.
- ROI Justification: Health Catalyst faces pressure to provide clear data showcasing cost reduction and outcome improvements from its platforms.
- Analytics and Reporting Needs: Robust analytics are crucial for customers to track and verify the effectiveness of Health Catalyst's offerings.
- Value-Based Care Alignment: The shift towards value-based reimbursement models amplifies the need for demonstrable ROI from healthcare IT investments.
Customers, particularly large hospital systems, possess substantial bargaining power due to their significant spending and the increasing availability of alternative solutions. By 2024, the average operating margin for US hospitals hovered around 2.5%, making cost-effectiveness a critical factor in their purchasing decisions, which Health Catalyst must address.
| Factor | Impact on Health Catalyst | Customer Action | 2024 Data Point |
| Customer Size & Sophistication | High bargaining power | Negotiate pricing, demand customization | Average hospital operating margin: ~2.5% |
| Availability of Alternatives | Reduces reliance on single vendor | Seek competitive bids, develop in-house capabilities | Growing market for healthcare analytics platforms |
| Switching Costs | Mitigates customer power | High initial investment and integration complexity | Significant upfront costs for data system implementation |
Preview Before You Purchase
Health Catalyst Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Health Catalyst Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of competitive and market forces within the healthcare technology sector. The document displayed here is the part of the full version you’ll get—ready for download and use the moment you buy. You'll gain strategic insights into the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry, all presented in a professionally formatted report. This is the complete, ready-to-use analysis file; what you're previewing is what you get—professionally formatted and ready for your needs.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The healthcare analytics market is a bustling arena, characterized by intense competition among a diverse array of companies. From established giants in enterprise software to nimble, specialized analytics firms, and even the homegrown solutions developed by healthcare providers themselves, the landscape is crowded. This fragmentation fuels fierce rivalry as each entity strives to capture a significant share in this rapidly expanding industry.
The healthcare analytics sector sees intense rivalry, particularly around AI and machine learning. Companies are locked in a race to develop more advanced predictive models and personalized patient insights. This innovation push means Health Catalyst must continually refine its AI capabilities to stay competitive and prove its value.
Competitors are actively investing in AI to deliver enhanced operational efficiencies and deeper analytical insights. For instance, in 2024, the global AI in healthcare market was projected to reach over $15 billion, highlighting the significant investment and competition in this space. Health Catalyst faces pressure to demonstrate clear ROI from its AI solutions amidst this dynamic landscape.
The push for healthcare data interoperability, exemplified by the widespread adoption of standards like FHIR, intensifies competitive rivalry. While this fosters easier data integration for all players, it shifts the competitive edge towards the sophistication and insight derived from analytics rather than exclusive data access. For instance, by mid-2024, over 90% of eligible hospitals in the US reported adopting FHIR for data exchange, a significant increase from previous years, creating a more level playing field.
Pricing Pressure and Value Proposition
The healthcare analytics market is characterized by intense competition, allowing customers, particularly large health systems, to exert significant pricing pressure. With numerous vendors offering solutions, buyers can readily compare features and costs, forcing companies like Health Catalyst to justify their pricing through demonstrable value.
To combat this, Health Catalyst must continually refine and articulate its unique value proposition. This involves clearly showcasing how its solutions deliver superior patient outcomes, achieve tangible cost savings, and offer a user-friendly experience compared to alternatives. For instance, in 2024, the demand for AI-driven predictive analytics in healthcare saw a surge, with companies demonstrating ROI through reduced readmission rates or improved operational efficiency gaining a competitive edge.
- Demonstrating ROI: Health Catalyst's success hinges on proving a clear return on investment for its clients, often measured in millions of dollars saved annually.
- Differentiating Technology: The ability to offer advanced AI and machine learning capabilities that provide actionable insights beyond basic reporting is crucial for standing out.
- Customer Success Stories: Highlighting successful implementations with measurable improvements in clinical quality and financial performance is key to building trust and commanding premium pricing.
- Integration Capabilities: Seamless integration with existing electronic health record (EHR) systems and other data sources reduces implementation friction and enhances value.
Strategic Partnerships and Acquisitions
Competitive rivalry in the healthcare technology sector is intense, and this is clearly demonstrated through strategic partnerships and acquisitions. Companies are actively seeking ways to broaden their service offerings and strengthen their market standing through these strategic moves.
Health Catalyst, for instance, has been a notable player in this consolidation trend. In late 2024, the company acquired Intraprise Health, bolstering its cybersecurity capabilities. Following this, in early 2025, Health Catalyst further expanded its patient engagement solutions by acquiring Upfront Healthcare. These acquisitions highlight a clear strategy to enhance its technology portfolio and gain a competitive edge.
- Acquisition of Intraprise Health (late 2024): Strengthened Health Catalyst's cybersecurity offerings.
- Acquisition of Upfront Healthcare (early 2025): Expanded Health Catalyst's patient engagement solutions.
- Industry Trend: Strategic partnerships and acquisitions are key tactics to consolidate market position and expand capabilities in the healthcare tech sector.
The competitive landscape for healthcare analytics is exceptionally crowded, with numerous players vying for market share. This intense rivalry means companies like Health Catalyst must constantly innovate and prove their unique value proposition to stand out. The market's growth, projected to exceed $50 billion by 2027, fuels this competition, attracting new entrants and prompting existing ones to invest heavily in advanced technologies.
SSubstitutes Threaten
Large healthcare organizations increasingly possess the resources and expertise to build their own internal data analytics capabilities. This trend is fueled by the growing availability of open-source tools and skilled data scientists, making in-house solutions a more attainable substitute for external vendors.
For instance, a significant portion of large health systems in 2024 are investing heavily in their IT infrastructure and data science teams, aiming to control their data and analytics processes directly. This internal development can significantly reduce reliance on third-party providers like Health Catalyst, especially as these organizations mature in their data maturity.
Generic business intelligence (BI) tools present a threat to Health Catalyst, particularly for organizations with simpler analytics needs. Tools like Tableau or Power BI, while not healthcare-specific, can fulfill basic descriptive analytics and dashboarding requirements. In 2024, the widespread adoption of these platforms means many healthcare entities might find them a more cost-effective alternative if advanced clinical analytics aren't a priority.
Healthcare providers can bypass Health Catalyst's integrated platform by engaging pure consulting firms for data strategy and analytics. These consultants often leverage proprietary methodologies and existing tools, offering a distinct alternative to a comprehensive technology solution.
For instance, a hospital seeking to improve patient outcomes through data analysis might hire a specialized consulting group rather than investing in a new data operating system. This approach allows them to tap into external expertise without the commitment to a specific technology vendor, potentially reducing upfront costs and implementation complexity.
Manual Data Analysis and Traditional Methods
In certain healthcare environments, especially those with less advanced technology, manual data analysis using spreadsheets and traditional reporting remains a viable substitute. While these methods are less efficient and don't scale well, they offer a basic alternative for organizations facing budget constraints or lacking technological infrastructure.
These traditional methods, though rudimentary, can still serve as a substitute for sophisticated data analytics platforms. For instance, a small rural clinic might rely on manually compiled patient records and basic financial spreadsheets rather than investing in a comprehensive health data analytics solution.
- Manual data entry and analysis: Many smaller practices still rely on manual input into spreadsheets, which is time-consuming and prone to errors.
- Spreadsheet-based reporting: Traditional reporting can be done using tools like Microsoft Excel, offering a low-cost but limited analytical capability.
- Limited scalability: These methods struggle to handle large volumes of data, making them impractical for growing healthcare organizations.
- Cost-effectiveness for small organizations: For entities with very limited budgets, these basic tools can be the only feasible option, representing a significant substitute for more advanced systems.
Point Solutions for Specific Needs
The threat of substitutes for integrated healthcare data platforms like Health Catalyst is significant, primarily stemming from the availability of point solutions. Many healthcare organizations opt to purchase specialized software for distinct functions rather than a unified system.
For instance, a hospital might acquire a best-of-breed revenue cycle management system, a standalone electronic health record (EHR) with limited analytics capabilities, and a separate population health management tool. This fragmented strategy, while potentially addressing immediate needs, acts as a direct substitute for a comprehensive data operating system.
In 2024, the market for healthcare IT point solutions remained robust, with continued investment in niche areas. For example, the global market for revenue cycle management software was projected to reach over $5 billion, demonstrating the widespread adoption of these specialized tools.
These point solutions can be seen as substitutes because they offer a piecemeal approach to data management, allowing organizations to address specific pain points without committing to a full-scale integrated platform. This can be particularly appealing to smaller or less technologically mature organizations.
- Fragmented Adoption: Healthcare organizations often adopt multiple point solutions instead of a single integrated data platform.
- Specialized Functionality: Point solutions excel in specific areas like revenue cycle management or basic EHR analytics.
- Cost and Implementation Considerations: A piecemeal approach can sometimes appear more manageable or cost-effective in the short term.
- Market Size of Point Solutions: The continued growth in specialized healthcare software markets indicates a strong substitute offering.
The threat of substitutes for Health Catalyst is substantial, driven by healthcare organizations' increasing ability to develop in-house analytics capabilities. Many large health systems in 2024 are investing in IT infrastructure and data science teams, making internal solutions a viable alternative to third-party vendors.
Generic business intelligence tools like Tableau and Power BI also pose a threat, especially for organizations with simpler analytics needs, offering a more cost-effective option for basic reporting and dashboards. Furthermore, specialized consulting firms can provide data strategy and analytics services, acting as a substitute by offering external expertise without requiring a commitment to a specific technology platform.
The market for point solutions remains a significant substitute, with organizations opting for specialized software for specific functions rather than a unified system. For instance, the revenue cycle management software market alone was projected to exceed $5 billion in 2024, highlighting the widespread adoption of these niche tools.
| Substitute Type | Description | 2024 Market Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| In-House Analytics | Organizations building their own data capabilities. | Growing investment in IT and data science teams. |
| Generic BI Tools | Platforms like Tableau, Power BI for basic analytics. | Widespread adoption for cost-effective reporting. |
| Consulting Services | Firms offering data strategy and analytics expertise. | Alternative to technology investment for specific needs. |
| Point Solutions | Specialized software for distinct healthcare functions. | Robust market for niche solutions like RCM software. |
Entrants Threaten
The threat of new entrants for companies like Health Catalyst is significantly dampened by the substantial capital investment and extensive data requirements inherent in the healthcare data analytics sector. Building a robust healthcare data operating system demands millions in upfront costs for technology, data integration, and skilled personnel. For instance, in 2024, the average cost for implementing a comprehensive healthcare data platform can easily exceed $5 million, a figure that can be prohibitive for startups.
The healthcare sector presents formidable regulatory barriers for any new company looking to enter. Strict data privacy laws like HIPAA, for instance, demand robust security measures and extensive compliance protocols.
Meeting these stringent requirements, including ongoing audits and certifications, demands substantial upfront investment in legal expertise, advanced technology, and dedicated operational teams.
For example, in 2024, the average cost for a healthcare organization to achieve and maintain HIPAA compliance can range from tens of thousands to hundreds of thousands of dollars annually, a significant deterrent for potential new entrants.
The healthcare analytics sector demands profound domain knowledge, encompassing clinical workflows, financial intricacies, and operational hurdles unique to healthcare. New competitors must invest heavily in acquiring or developing this specialized expertise, a process that is both time-consuming and expensive.
For instance, understanding the nuances of revenue cycle management or clinical decision support systems requires years of experience, making it difficult for newcomers to replicate the deep insights of established players like Health Catalyst, which has built its reputation on this very foundation.
Customer Trust and Relationship Building
The healthcare sector, particularly in technology solutions, thrives on deeply ingrained customer trust. Healthcare organizations often forge enduring partnerships with their technology providers, a necessity driven by the highly sensitive nature of patient data and the critical reliance on these systems for delivering quality care. This makes it challenging for new entrants to penetrate the market.
Newcomers face the significant hurdle of establishing credibility and overcoming the established trust that incumbent players have cultivated over time. This process is inherently slow in an industry that is inherently risk-averse, where the consequences of system failure or data breaches are severe.
For instance, in 2024, the average sales cycle for enterprise healthcare IT solutions can extend from 12 to 18 months, reflecting the extensive vetting and integration processes required. This lengthy period underscores the difficulty new entrants face in displacing established relationships and demonstrating reliability to potential clients.
- High Switching Costs: Implementing new health IT systems involves substantial costs, including data migration, staff training, and integration with existing workflows, creating a barrier for organizations considering a change.
- Regulatory Compliance: New entrants must navigate complex regulatory landscapes like HIPAA, demonstrating robust security and privacy protocols, which requires significant upfront investment and proven expertise.
- Data Integration Complexity: Healthcare data is often fragmented across various legacy systems. New entrants must prove their ability to seamlessly integrate and manage this complex data environment, a task that builds upon existing, trusted relationships.
- Proven Track Record: Healthcare providers prioritize vendors with a demonstrated history of reliability and successful implementation in similar environments, making it difficult for unproven entities to gain initial traction.
Technological Complexity and Integration Challenges
The technological complexity of integrating disparate healthcare data sources poses a significant barrier for new entrants. Developing robust integration capabilities and scalable platforms capable of handling diverse data formats and volumes requires substantial investment and expertise. For instance, in 2024, the average healthcare organization still grappled with data silos, with studies indicating that over 60% of patient data remained inaccessible or unusable due to interoperability issues.
New companies must overcome these hurdles to offer effective solutions. This involves building sophisticated data pipelines and ensuring compliance with stringent healthcare regulations like HIPAA. The sheer effort and capital required to establish these foundational technological elements act as a strong deterrent, limiting the number of credible new competitors.
- Data Integration Complexity: Healthcare systems often operate with a patchwork of legacy systems and modern applications, making seamless data aggregation a major challenge.
- Scalability Requirements: A new entrant's platform must scale efficiently to manage the ever-increasing volume and velocity of healthcare data generated daily.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to data privacy and security standards, such as HIPAA, adds another layer of technological and operational complexity.
- Interoperability Standards: The lack of universal interoperability standards in healthcare necessitates custom integration solutions for each client, increasing development costs and time.
The threat of new entrants in the healthcare data analytics space remains relatively low for companies like Health Catalyst. Significant capital investment, stringent regulatory compliance, and the need for deep domain expertise create substantial barriers to entry. Established players benefit from high switching costs and deeply ingrained customer trust, making it difficult for newcomers to gain a foothold.
New companies must demonstrate their ability to integrate complex, often fragmented healthcare data while adhering to strict privacy laws. The lengthy sales cycles in healthcare IT, often 12-18 months in 2024, further deter potential entrants who lack a proven track record and established credibility.
| Barrier to Entry | Description | Impact on New Entrants | 2024 Data Point/Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Investment | High costs for technology, data integration, and skilled personnel. | Prohibitive for startups. | Healthcare data platform implementation costs can exceed $5 million. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Strict data privacy laws (e.g., HIPAA) require robust security and compliance. | Demands significant upfront investment in legal and operational expertise. | Annual HIPAA compliance costs can range from tens of thousands to hundreds of thousands of dollars. |
| Domain Expertise | Deep understanding of clinical workflows, financial intricacies, and healthcare operations. | Difficult and time-consuming to acquire. | Replicating established players' insights into revenue cycle management or clinical decision support takes years. |
| Customer Trust | Healthcare organizations prioritize reliable, long-term partnerships. | Challenging for new entrants to displace established relationships. | Average enterprise healthcare IT sales cycles are 12-18 months, reflecting extensive vetting. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Health Catalyst Porter's Five Forces analysis leverages a comprehensive mix of data sources including industry-specific market research reports, public financial statements from key players, and regulatory filings to provide a robust understanding of the competitive landscape.
