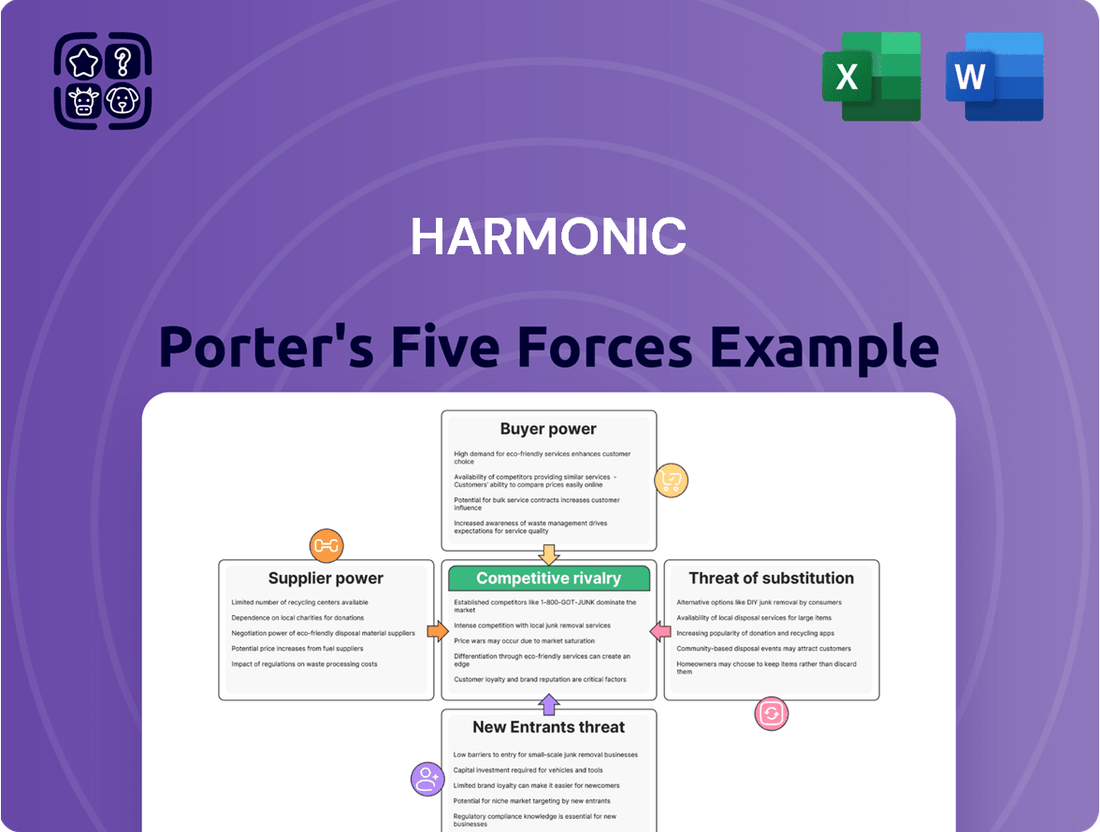
Harmonic Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Harmonic Bundle
Harmonic's Porter's Five Forces Analysis reveals the intense competitive landscape it navigates, highlighting the power buyers hold and the constant threat of new entrants. Understanding these forces is crucial for any stakeholder looking to grasp Harmonic's strategic positioning.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Harmonic’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The concentration of Harmonic Inc.'s suppliers is a key factor in their bargaining power. When a small number of suppliers provide essential components or software, those suppliers gain considerable leverage regarding pricing and contract terms. For instance, if Harmonic relies heavily on a single provider for a specialized chip, that provider can dictate terms more effectively.
A more diversified supplier base for Harmonic would naturally dilute supplier bargaining power. Having multiple options for critical inputs allows Harmonic to switch suppliers if terms become unfavorable, thereby maintaining greater control over costs and supply chain stability. This diversification is crucial for mitigating the risk associated with supplier concentration.
The uniqueness of inputs significantly bolsters supplier bargaining power. When suppliers provide highly specialized technologies or proprietary components that are hard to substitute or find elsewhere, their leverage grows. For Harmonic, this could manifest in reliance on specific vendors for advanced video processing chips or unique broadband networking technologies that are not readily available from multiple sources.
Harmonic's bargaining power of suppliers is influenced by switching costs. If Harmonic faces substantial expenses to change suppliers, perhaps due to specialized equipment integration or extensive employee retraining, its reliance on current suppliers increases. This dependence grants suppliers greater leverage.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
Suppliers in the telecommunications equipment sector, including those providing components or services to Harmonic, possess a significant threat if they can integrate forward into Harmonic's core business of video delivery and broadband solutions. This means a supplier could potentially become a direct competitor, offering their own integrated services to Harmonic's customer base. For instance, a component manufacturer could develop its own software platform for video streaming, directly challenging Harmonic's offerings.
This capability for forward integration significantly bolsters a supplier's bargaining power. Knowing that a supplier could potentially enter their market and capture a portion of their revenue stream gives that supplier leverage in price negotiations and contract terms. This is particularly relevant in industries where specialized components are critical, and switching suppliers can be costly and time-consuming for Harmonic.
- Threat of Forward Integration: Suppliers could leverage their expertise to offer Harmonic's video delivery or broadband solutions directly to customers.
- Increased Bargaining Power: This potential for direct competition enhances suppliers' ability to dictate terms and prices.
- Industry Dynamics: For example, a network infrastructure provider could expand into offering managed broadband services, competing with Harmonic's existing customer base.
Importance of Harmonic to Suppliers
The significance of Harmonic as a customer directly influences its suppliers' bargaining power. If Harmonic accounts for a significant percentage of a supplier's overall sales, that supplier is likely more inclined to offer competitive pricing and favorable contract terms to retain such a valuable client. This dependency can shift leverage towards Harmonic.
Conversely, if Harmonic represents only a minor portion of a supplier's revenue, the supplier holds considerably more power. In such scenarios, suppliers are less motivated to concede on terms, as losing Harmonic's business would have a minimal impact on their financial performance. This dynamic strengthens the supplier's position.
For example, if a key component supplier's revenue is heavily reliant on Harmonic, perhaps generating over 15% of their annual income, they'll likely be more accommodating. However, if Harmonic's purchases constitute less than 2% of a supplier's total revenue, that supplier has little incentive to negotiate aggressively.
- Supplier Dependency: Harmonic's revenue contribution to its suppliers is a critical factor.
- Negotiating Leverage: Higher revenue contribution by Harmonic grants it more negotiating power.
- Supplier's Market Share: If Harmonic is a small client, suppliers' power increases significantly.
- Impact on Terms: Supplier dependency directly impacts the terms Harmonic can secure.
The bargaining power of Harmonic's suppliers is a critical element of its competitive landscape. When suppliers provide unique or highly specialized inputs, their leverage increases significantly, as seen with specialized video processing chips not readily available elsewhere. High switching costs for Harmonic, stemming from integration complexities or retraining needs, further empower these suppliers by making it difficult and expensive to change providers. For instance, if a supplier accounts for a substantial portion of a vendor's revenue, that vendor is more likely to offer favorable terms to retain Harmonic as a key client.
| Factor | Impact on Supplier Bargaining Power | Example for Harmonic (Hypothetical) |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High if few suppliers exist | Reliance on a single provider for advanced broadband modulators |
| Uniqueness of Input | High if inputs are specialized and hard to substitute | Proprietary software for video compression |
| Switching Costs | High if integration is complex or costly | Significant investment in specialized network hardware |
| Threat of Forward Integration | High if suppliers can enter Harmonic's market | A component manufacturer offering its own cloud-based video platform |
| Harmonic's Importance to Supplier | Low if Harmonic is a small customer | Supplier has little incentive to offer discounts if Harmonic represents < 1% of their sales |
What is included in the product
Harmonic's Porter's Five Forces Analysis provides a comprehensive framework for understanding the competitive intensity and attractiveness of the markets it operates in, by examining threats of new entrants, bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry.
Effortlessly identify and quantify competitive pressures, transforming complex market dynamics into actionable insights for strategic advantage.
Customers Bargaining Power
Harmonic Inc.'s customer concentration is a significant factor in its bargaining power of customers. In 2024, the company's top ten customers were responsible for roughly 72% of its net revenue. This heavy reliance on a small group of clients, with Comcast alone making up 44% of net revenue in the same year, grants these major customers considerable leverage.
This substantial customer concentration directly translates into increased bargaining power for these key clients. They can exert pressure on Harmonic Inc. regarding pricing, contract terms, and service level agreements, potentially impacting the company's profitability and flexibility.
The bargaining power of Harmonic's customers is significantly influenced by the switching costs associated with their video delivery and broadband solutions. If it's relatively easy and inexpensive for media companies and service providers to transition to a competitor, their leverage increases.
For instance, if Harmonic's proprietary software or hardware requires substantial investment in new infrastructure or extensive retraining for staff, these high switching costs would diminish customer bargaining power. Conversely, if Harmonic's solutions are built on open standards or offer seamless integration with existing systems, switching costs are lower, empowering customers.
In 2024, the trend towards cloud-native and software-defined video solutions generally lowers switching costs compared to older, hardware-centric systems. This shift means customers can potentially migrate more readily to alternative vendors if they find better pricing or features, thereby enhancing their bargaining position against Harmonic.
Customer price sensitivity significantly impacts Harmonic's video and broadband markets. Consumers actively seek the most cost-effective ways to access high-quality streaming and broadcast services. This dynamic forces Harmonic to remain highly competitive on pricing to attract and retain subscribers.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
Customers' ability to integrate backward, meaning they could develop their own in-house video delivery or broadband infrastructure solutions, would significantly increase their bargaining power. This is particularly relevant for large media companies or service providers with substantial financial and technical resources.
For instance, a major cable provider might consider developing its own content streaming platform rather than relying on third-party solutions, thereby reducing its dependence on Harmonic's technology. This threat is amplified if customers possess the necessary technical expertise and capital to replicate the services provided by Harmonic. In 2024, the trend of vertical integration continued across various media sectors, with some large content creators exploring direct-to-consumer distribution models.
- Customer Integration Capability: Assess the financial and technical capacity of key customers to develop in-house solutions.
- Industry Trends: Monitor industry-wide movements towards vertical integration, especially among large media conglomerates.
- Customer Investment in R&D: Track customer investments in research and development for alternative delivery or infrastructure technologies.
- Strategic Partnerships: Observe if customers are forming alliances that could facilitate backward integration.
Customer Information and Market Knowledge
Customers who are well-informed about market prices, product features, and available alternatives wield significant power. In the fast-paced video and broadband sectors, this sophistication is particularly pronounced, as consumers readily compare offerings and switch providers based on value.
This heightened customer awareness directly translates to increased bargaining power. For instance, in 2024, the average broadband customer in the US had access to numerous providers, with many offering promotional pricing that encouraged switching. This competitive landscape means providers must constantly innovate and offer compelling value propositions to retain their customer base.
- Informed Customers: A significant portion of consumers actively research pricing and service quality before committing to a provider.
- Availability of Substitutes: The presence of multiple competing broadband and video service providers intensifies customer choice.
- Price Sensitivity: Many customers are highly sensitive to price changes, making them more likely to switch for better deals.
- Technological Awareness: Customers are increasingly aware of technological advancements, such as faster speeds and new streaming capabilities, and expect these to be reflected in their service.
Harmonic's customer concentration, with top ten clients accounting for 72% of net revenue in 2024, grants these major customers significant leverage. This concentrated customer base allows them to negotiate favorable pricing and contract terms, directly impacting Harmonic's profitability and operational flexibility.
The bargaining power of Harmonic's customers is further amplified by generally lower switching costs in the video and broadband sectors, especially with the 2024 trend towards cloud-native solutions. This ease of transition to competitors, driven by open standards and interoperability, empowers customers to demand better value.
Customers' ability to integrate backward, developing their own solutions, also enhances their bargaining power. This is a growing concern in 2024 as media companies explore vertical integration, potentially reducing reliance on third-party providers like Harmonic.
Additionally, informed customers, aware of market prices and alternatives, exert considerable influence. In 2024, the competitive U.S. broadband market, with numerous providers offering promotions, demonstrates this customer power, forcing companies to continuously offer competitive value.
Preview Before You Purchase
Harmonic Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Harmonic Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a thorough examination of competitive intensity and industry attractiveness. The document you see here is precisely the same professionally crafted analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring full transparency and immediate usability.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Harmonic Inc. operates in a crowded marketplace, facing rivals that offer a range of video delivery and processing SaaS solutions. This includes established players providing SaaS video streaming platforms and major public cloud service providers who also offer related capabilities.
The competitive intensity is amplified by the presence of large, well-resourced companies. Giants such as Cisco (through its Arris acquisition), Broadcom, and MediaKind are significant competitors, boasting substantial market share and financial muscle. For instance, in 2023, Cisco reported revenues exceeding $57 billion, demonstrating the scale of resources available to its competitors.
The video streaming market is booming, with forecasts suggesting substantial growth. For instance, the global video streaming market was valued at approximately $57.2 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach over $247 billion by 2030, exhibiting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 23.3%. This rapid expansion naturally fuels intense competition as numerous players battle to capture a larger slice of this expanding pie.
Harmonic's competitive edge hinges on its ability to differentiate its video delivery software, products, and system solutions. Unique features, like their virtualised broadband solution, offer distinct advantages over competitors. This differentiation directly combats intense rivalry by providing specialized value propositions.
Superior performance and innovative offerings, such as AI-powered hybrid cloud solutions, further set Harmonic apart. These advanced capabilities reduce the likelihood of customers viewing competitors' offerings as direct substitutes. For instance, Harmonic's focus on cloud-native architectures in 2024 aims to deliver greater agility and scalability, a key differentiator in the evolving media landscape.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers in the video delivery and broadband solution markets can trap even struggling companies, leading to sustained, intense competition. These barriers often stem from significant investments in specialized infrastructure, such as fiber optic networks, which are difficult to repurpose or sell. For instance, the substantial capital expenditure required for 5G network deployment, estimated in the tens of billions of dollars globally, makes exiting the market exceptionally costly for telecom operators.
These costs can include:
- Specialized Assets: Infrastructure like cell towers and data centers are highly specific to the industry and have limited alternative uses, making them hard to divest.
- Long-Term Contracts: Commitments with customers or suppliers can obligate companies to continue operations even when unprofitable to avoid penalty clauses.
- High Fixed Costs: Ongoing maintenance, licensing fees, and operational overheads remain substantial, even if revenue declines, making it financially unviable to cease operations quickly.
Strategic Importance of the Industry
The strategic importance of delivering video content and maintaining robust broadband infrastructure creates a highly competitive landscape for service providers and media companies. This criticality drives significant investment and a fierce battle for market share.
Companies are actively pouring resources into technological advancements to solidify their standing. For instance, the development and rollout of DOCSIS 4.0 and advanced fiber optic solutions are key battlegrounds, with major players like Comcast and Charter Communications investing billions in network upgrades. In 2024, the global broadband market is projected to continue its growth, with significant capital expenditure focused on these next-generation technologies to meet escalating consumer demand for faster and more reliable internet services.
- Intense Rivalry: The core business of video delivery and broadband infrastructure is fundamental, making it a high-stakes arena for service providers.
- Innovation Investment: Companies are channeling substantial capital into new technologies like DOCSIS 4.0 and fiber to gain a competitive edge.
- Market Share Focus: The strategic importance of this sector compels businesses to aggressively defend and expand their market positions through innovation and service quality.
- Capital Expenditure: Billions are being invested globally in 2024 by leading companies in network upgrades to support advanced delivery methods.
Harmonic faces intense competition from large, well-funded companies like Cisco and Broadcom, which possess significant market share and financial resources. For example, Cisco’s 2023 revenue surpassed $57 billion, highlighting the scale of its competitive presence. The booming video streaming market, projected to grow from $57.2 billion in 2023 to over $247 billion by 2030, naturally attracts numerous players, intensifying rivalry as each seeks to capture market share.
Harmonic differentiates itself through unique offerings such as its virtualised broadband solution and AI-powered hybrid cloud capabilities, aiming to prevent customers from viewing competitors' products as direct substitutes. Their 2024 focus on cloud-native architectures further enhances agility and scalability, key advantages in the dynamic media sector.
High exit barriers, including specialized assets and long-term contracts, keep even struggling companies in the market, perpetuating intense competition. The substantial investment in infrastructure, like the tens of billions required for global 5G deployment, makes exiting the sector exceptionally costly.
The critical nature of video delivery and broadband infrastructure drives significant investment and a fierce battle for market share, with companies like Comcast and Charter Communications investing billions in network upgrades. Advancements in DOCSIS 4.0 and fiber optics are key battlegrounds in 2024, reflecting the industry's commitment to meeting escalating consumer demand for faster internet.
| Competitor | Approximate 2023 Revenue (USD billions) | Key Offerings |
|---|---|---|
| Cisco | >57 | Video delivery solutions, broadband infrastructure |
| Broadcom | Data not readily available for direct comparison in this context | Semiconductors for networking and broadband |
| MediaKind | Data not readily available for direct comparison in this context | Video delivery and processing solutions |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Harmonic's video delivery and broadband solutions is significant, stemming from alternative technologies that can meet similar customer needs. For instance, the rise of increasingly capable open-source software in network management and video processing offers a lower-cost alternative to proprietary Harmonic solutions.
Furthermore, advancements in software-defined networking (SDN) and edge computing present new ways to distribute content and manage broadband, potentially bypassing traditional hardware-centric approaches. By 2024, the global SDN market was projected to reach over $20 billion, indicating a strong shift towards software-based network control, which could impact demand for Harmonic's more hardware-dependent offerings.
Customers constantly weigh the price against the performance of available alternatives. If a substitute offers similar features or quality for less money, it directly challenges Harmonic's pricing power and market position.
For instance, in the telecommunications sector, while Harmonic provides advanced video delivery solutions, lower-cost, less feature-rich alternatives might appeal to smaller operators or those in emerging markets, impacting Harmonic's potential customer base.
This trade-off is particularly critical as technology evolves; a substitute that offers a 15% cost reduction with only a 5% performance dip could be highly attractive, potentially eroding Harmonic's market share if its value proposition isn't clearly superior.
The ease with which customers can switch to a substitute technology significantly influences the threat of substitutes. For instance, if a business relies on a particular software, and a comparable, more affordable alternative emerges with a simple data import function, the switching costs are low. This low friction encourages customers to explore and adopt these substitutes, thereby increasing the competitive pressure on the original product or service. In 2024, the rapid advancement of AI-powered tools, many offering free or low-cost tiers, exemplifies this trend, making it easier for users to transition from established, paid solutions.
Customer Propensity to Substitute
Customer willingness to switch to alternatives is a key factor. In 2024, the increasing adoption of cloud-based streaming services, which often bundle video and broadband, demonstrates a strong customer propensity to substitute traditional cable TV packages. For instance, a significant portion of households are cutting the cord, with estimates suggesting over 15 million US households have ditched traditional pay TV by early 2024.
The rapid evolution of technology in the video and broadband sectors directly fuels this propensity. Consumers are actively seeking more integrated and flexible solutions. This trend is evident in the growing popularity of smart TVs and the increasing demand for high-speed internet capable of supporting multiple streaming devices simultaneously, a shift that could pressure incumbent providers to adapt or lose market share.
The threat of substitutes is amplified by the ease with which customers can switch providers or adopt new technologies.
- Technological Advancements: The proliferation of 5G technology and advancements in Wi-Fi standards are making high-quality streaming accessible over alternative networks, reducing reliance on traditional broadband infrastructure.
- Bundling Strategies: Many companies now offer bundled packages that include internet, mobile, and streaming services, making it more convenient and cost-effective for customers to switch from single-service providers.
- Content Accessibility: The availability of a vast array of content on streaming platforms, often at lower price points than traditional cable, further incentivizes customers to substitute. For example, the average monthly cost of a top-tier streaming bundle in 2024 can be significantly less than a comparable cable package.
Technological Advancements in Related Industries
Technological advancements in adjacent sectors pose a significant threat of substitutes. For instance, the rapid evolution of general-purpose cloud computing offers new avenues for service delivery that can bypass established industry infrastructure. In 2024, global cloud computing spending was projected to reach over $600 billion, highlighting the scale and accessibility of these platforms.
Furthermore, enhanced capabilities in consumer devices can enable alternative solutions. Think about how smartphones have evolved; they now offer sophisticated content creation and consumption tools that weren't possible a decade ago. This trend directly impacts industries reliant on specialized hardware or traditional distribution channels.
A prime example of this threat is the rise of direct-to-consumer streaming services. These platforms circumvent traditional broadcast networks and cable providers, offering a compelling substitute for legacy media consumption. By 2024, subscription video-on-demand services accounted for a substantial portion of video consumption globally, demonstrating their disruptive potential.
- Cloud Computing Growth: Global cloud infrastructure spending is expected to continue its upward trajectory, providing a scalable foundation for new substitute services.
- Consumer Device Innovation: Advancements in mobile processing power and connectivity enable more sophisticated on-device applications, potentially replacing specialized industry solutions.
- Streaming Service Dominance: Direct-to-consumer models have captured significant market share, illustrating the viability of bypassing traditional intermediaries.
- Emerging Technologies: Innovations in areas like AI-powered content generation could further disrupt existing value chains by offering more efficient or personalized alternatives.
The threat of substitutes for Harmonic's offerings is substantial, driven by evolving technologies and changing consumer preferences. These substitutes can fulfill similar customer needs, often at a lower cost or with greater convenience, directly impacting Harmonic's market position and pricing power.
The increasing accessibility of alternative solutions, such as open-source software and advancements in software-defined networking, presents a significant challenge. By 2024, the global SDN market's projected value exceeding $20 billion underscores the shift towards software-centric network control, potentially diminishing reliance on traditional hardware.
Customers readily evaluate substitutes based on a price-performance trade-off. A 15% cost reduction with only a minor performance compromise can strongly influence adoption, eroding market share if Harmonic's value proposition isn't clearly superior. This is particularly evident in the telecommunications sector, where smaller operators might opt for less feature-rich but more affordable alternatives.
The ease of switching to alternatives, exemplified by AI-powered tools with low-cost tiers in 2024, further intensifies this threat. Similarly, the significant trend of cord-cutting, with over 15 million US households ditching traditional pay TV by early 2024, highlights a strong customer propensity for substitutes like bundled streaming services.
| Substitute Category | Key Drivers | Impact on Harmonic |
|---|---|---|
| Open-Source Software | Lower cost, community support | Reduced demand for proprietary solutions |
| Software-Defined Networking (SDN) | Network flexibility, cost efficiency | Potential bypass of traditional infrastructure |
| Cloud Computing | Scalability, accessibility | Enables new service delivery models |
| Direct-to-Consumer Streaming | Content variety, convenience | Erosion of traditional video delivery revenue |
Entrants Threaten
The capital required to enter the video delivery and broadband solutions market presents a formidable barrier. Companies need to invest heavily in developing advanced software, robust hardware, and extensive global infrastructure. For instance, building out a comprehensive 5G network, a key component of modern broadband, can cost billions. In 2024, major telecommunications companies continued to report significant capital expenditures, with some allocating over $10 billion annually to network upgrades and expansion, underscoring the immense financial commitment necessary.
Harmonic, as a well-established player in the broadcast and video technology sector, benefits significantly from economies of scale. This means they can spread their substantial research and development, manufacturing, and customer support costs across a large volume of products and services. For instance, their investment in advanced video processing technologies, which might cost hundreds of millions, becomes more manageable on a per-unit basis when amortized over a global customer base.
New entrants face a considerable hurdle in matching these cost efficiencies. To compete effectively on price against Harmonic, a newcomer would need to achieve a similar production volume, which is incredibly difficult and capital-intensive in the early stages. This cost disadvantage makes it challenging for new companies to gain market share without significant upfront investment or a highly differentiated, premium offering.
Harmonic's established reputation and existing customer relationships significantly deter new entrants. The company's differentiated solutions, such as its CableOS software-defined access architecture, have fostered strong brand loyalty, making it difficult for newcomers to gain traction. For instance, Harmonic reported a revenue of $525 million for the first quarter of 2024, showcasing its substantial market presence and the scale of investment required to compete.
Access to Distribution Channels
New entrants in the video delivery and content ecosystem face significant hurdles in securing access to established distribution channels. Major cable operators and media companies often have exclusive agreements or deeply entrenched relationships that are difficult for newcomers to penetrate. Harmonic, for instance, has cultivated long-standing partnerships with key players in the industry, providing them with a substantial competitive advantage that is not easily replicated by emerging companies.
The difficulty in accessing these critical channels means new entrants must either invest heavily in building their own infrastructure or find niche markets. For example, a startup attempting to offer a new streaming service would struggle to gain widespread carriage on traditional pay-TV platforms without significant leverage or a highly compelling offering that disrupts existing models. This barrier significantly limits the speed and scale at which new competitors can enter and gain traction.
Harmonic's existing distribution network is a critical asset, built over years of reliable service and integration with major service providers. As of early 2024, Harmonic's solutions are deployed by a significant portion of the top global service providers, underscoring the depth of their channel access. This established presence makes it challenging for new entrants to achieve comparable reach and customer penetration without substantial upfront investment and time.
- Existing relationships with major cable operators and media companies are a significant barrier.
- Harmonic's established infrastructure and integration provide a competitive moat.
- New entrants require substantial investment or niche strategies to bypass distribution channel challenges.
- As of early 2024, Harmonic's solutions are integral to the operations of numerous leading global service providers, demonstrating the strength of their channel access.
Regulatory Barriers and Intellectual Property
Regulatory hurdles and the significant investment required for intellectual property, particularly patents in video and broadband technology, act as a substantial deterrent for potential new entrants. Harmonic's proactive approach to research and development, evidenced by its robust patent portfolio, creates a formidable barrier to entry.
For instance, the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office reported over 300,000 utility patent grants in 2023 alone, highlighting the competitive landscape for technological innovation. Harmonic's strategic focus on securing and expanding its IP rights directly translates into a competitive advantage, making it more challenging for newcomers to replicate its offerings or operate without infringing existing patents.
- Regulatory Compliance: Navigating complex regulations in the telecommunications and media sectors requires significant upfront investment and expertise, acting as a barrier.
- Intellectual Property Protection: Harmonic's extensive patent portfolio, a result of consistent R&D spending, protects its core technologies and creates a competitive moat.
- High R&D Costs: The continuous need for innovation in video and broadband technology necessitates substantial and ongoing investment in research and development, which can be prohibitive for new players.
The threat of new entrants into the video delivery and broadband solutions market is significantly mitigated by substantial capital requirements. Developing cutting-edge software, hardware, and global infrastructure demands billions in investment, a scale few newcomers can match. For example, in 2024, major telecom players continued to invest heavily, with some exceeding $10 billion annually in network expansion, illustrating the immense financial commitment necessary.
Harmonic's established economies of scale further solidify this barrier. By spreading significant R&D and manufacturing costs across a vast customer base, they achieve cost efficiencies that new entrants struggle to replicate. A newcomer would need to achieve comparable production volumes, a capital-intensive feat in its initial stages, making it difficult to compete on price.
New entrants also face challenges in securing access to established distribution channels. Harmonic's long-standing partnerships with key industry players, including major cable operators and media companies, create a formidable moat. These entrenched relationships are difficult and time-consuming for new companies to penetrate, forcing them to either build their own infrastructure or target niche markets.
| Barrier Type | Harmonic's Advantage | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Established infrastructure and R&D capabilities | High upfront investment needed, limiting market entry |
| Economies of Scale | Large production volumes and cost efficiencies | New entrants face higher per-unit costs |
| Distribution Channels | Long-standing partnerships with key players | Difficult to gain access to established networks |
| Intellectual Property | Robust patent portfolio from ongoing R&D | Risk of patent infringement and replication challenges |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Harmonic Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of diverse data, including industry-specific market research reports, publicly available financial statements from key players, and expert commentary from leading trade publications. This comprehensive approach ensures a robust understanding of competitive intensity and strategic positioning.
