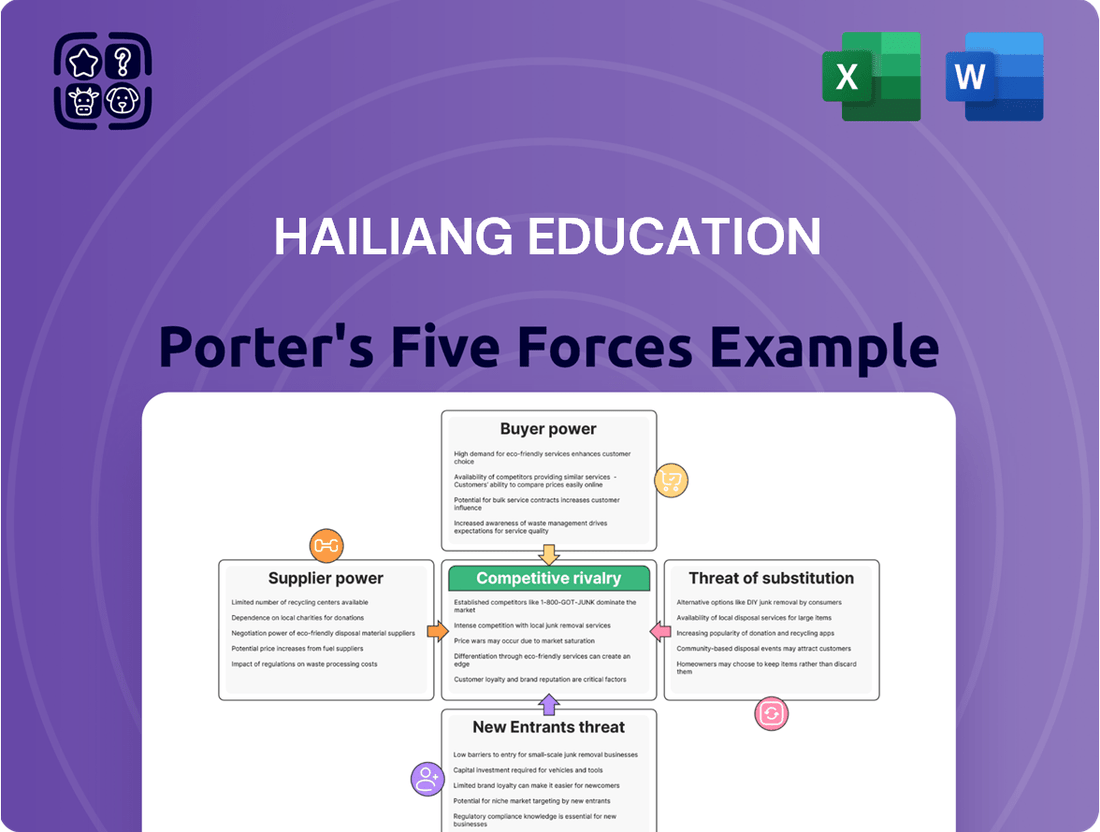
Hailiang Education Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Hailiang Education Bundle
Hailiang Education faces significant competitive pressures, with moderate buyer power and a growing threat from substitute educational models. Understanding the intensity of these forces is crucial for any stakeholder.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Hailiang Education’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The availability of skilled educators, particularly for specialized subjects or international curricula, directly influences Hailiang Education's operational capacity. A scarcity of qualified teachers, or superior offerings from rival educational institutions, empowers these educators as suppliers, potentially escalating personnel expenses for Hailiang. This dynamic is crucial as the company prioritizes high-quality instruction and global program integration.
Suppliers of curriculum content, textbooks, and digital learning platforms exert moderate bargaining power over Hailiang Education. The availability of diverse educational materials and platforms means Hailiang can often switch providers, limiting individual supplier leverage. However, for highly specialized or proprietary content, such as specific international curricula like A-levels or advanced STEM resources, where alternatives are scarce, these suppliers can command higher prices and more favorable terms.
As Hailiang Education integrates more technology, the suppliers of educational tech, IT infrastructure, and digital solutions hold significant sway. Their power hinges on how unique and vital their products are, and how difficult it would be for Hailiang to switch to another provider. For instance, a specialized AI-driven learning platform provider might command higher prices if its technology is proprietary and difficult to replicate.
Real Estate and Facilities
The bargaining power of suppliers in real estate and facilities for Hailiang Education is considerable. Given their extensive network of schools, particularly in China's dynamic real estate market, suppliers of land, construction, and maintenance services can exert significant influence. The quality and location of these facilities are crucial differentiators in the competitive educational landscape.
The cost of land and construction services in China has seen fluctuations. For instance, the average price of commercial land in major Chinese cities experienced a notable increase in early 2024, impacting the upfront investment for new school campuses. This trend suggests that suppliers in these sectors hold a strong hand.
- Land Acquisition Costs: Rising land prices in key development areas directly increase the cost of establishing new educational facilities.
- Construction Service Demand: High demand for construction services, especially in infrastructure and development projects, can lead to increased pricing power for construction firms.
- Specialized Maintenance Needs: Schools often require specialized maintenance for their facilities, giving suppliers of these services more leverage.
- Location Sensitivity: The strategic importance of school location means that suppliers of prime real estate can command premium prices.
Specialized Service Providers (e.g., Study Tour Operators)
For educational support services like study-tour programs, specialized tour operators and international exchange program providers act as suppliers. Their bargaining power hinges on factors such as their established reputation, exclusive access to specific destinations or unique programs, and the overall demand for these specialized educational experiences from Hailiang's student population. For instance, in 2024, the global inbound tourism market, which includes educational travel, saw a significant rebound, with many specialized operators reporting increased bookings for unique cultural immersion programs.
- Reputation and Specialization: Highly reputable operators with niche offerings command greater influence.
- Access to Unique Programs: Exclusive partnerships or curated experiences strengthen supplier leverage.
- Student Demand: High student interest in specific study tour destinations or themes increases supplier power.
- Market Trends: In 2024, there was a notable surge in demand for sustainable and culturally immersive educational travel, benefiting operators specializing in these areas.
Suppliers of specialized educational technology and digital learning platforms hold considerable bargaining power due to the unique nature of their offerings and the difficulty Hailiang Education might face in finding comparable alternatives. This is particularly true for proprietary AI-driven learning systems, which can command premium pricing. For example, the global EdTech market was projected to reach over $400 billion by 2025, indicating significant investment and reliance on specialized tech providers.
| Supplier Type | Bargaining Power Level | Key Factors Influencing Power | 2024 Market Context |
|---|---|---|---|
| Educational Technology & Digital Platforms | High | Proprietary technology, difficulty in switching, specialization | Strong demand for AI-integrated learning tools; market growth exceeding 15% annually. |
| Real Estate & Construction Services | High | Location sensitivity, rising land/construction costs, demand for quality facilities | Commercial land prices in Tier 1 Chinese cities increased by an average of 8-10% in early 2024. |
| Skilled Educators | Moderate to High | Scarcity of specialized skills, competitive offers from rivals | Teacher shortages reported in STEM and international curriculum areas, leading to salary pressures. |
| Curriculum Content & Textbooks | Moderate | Availability of alternatives, standardization of materials | Shift towards digital and interactive content, but some specialized international curricula remain concentrated. |
| Study Tour & Exchange Program Providers | Moderate | Reputation, exclusivity of programs, student demand | Educational tourism rebound in 2024, with a 20% increase in demand for culturally immersive experiences. |
What is included in the product
Tailored exclusively for Hailiang Education, this analysis dissects the competitive forces shaping its market, including buyer and supplier power, new entrant threats, substitute offerings, and existing rivalry.
Instantly identify and address competitive threats with a comprehensive overview of industry rivalry, buyer power, supplier power, threat of new entrants, and threat of substitutes.
Gain actionable insights into market dynamics, enabling proactive strategies to mitigate risks and capitalize on opportunities within the education sector.
Customers Bargaining Power
Parents and students in China wield significant bargaining power in the private education sector. The growing number of private schools, international programs, and overseas study options means they have more choices than ever before. This competition forces institutions to focus on delivering quality education and demonstrating a clear return on investment to attract and retain students.
Government policies, such as China's 2021 'Double Reduction Policy,' significantly reshaped the private education landscape. This policy aimed to reduce homework and off-campus tutoring, directly impacting customer demand for services like those offered by Hailiang Education. The market saw a substantial contraction in the for-profit tutoring sector, forcing companies to pivot their offerings.
Chinese families are increasingly prioritizing a well-rounded education, moving away from a sole focus on test scores. They are actively looking for programs that incorporate international curricula, science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM), as well as arts and sports. This shift empowers customers, as they can exert pressure on institutions like Hailiang if they believe other schools are better equipped to provide this comprehensive educational experience.
Sensitivity to Tuition Fees and Value Proposition
Customers are increasingly sensitive to tuition fees, especially with rising education costs and economic uncertainties. This heightened cost-consciousness means they are more carefully evaluating the value proposition offered by private education providers like Hailiang Education.
Hailiang's pricing strategy is a direct determinant of customer decisions. The perceived quality of education and the tangible outcomes, such as graduate employment rates or further study success, significantly impact a customer's willingness to pay the charged tuition.
- Cost Sensitivity: A significant portion of parents, particularly those in middle-income brackets, are carefully budgeting for education expenses, making tuition fee increases a critical factor in their enrollment decisions.
- Value Perception: Parents are looking beyond just academic rankings, seeking evidence of strong career support, alumni networks, and demonstrable return on investment for their educational spending.
- Competitive Benchmarking: Families often compare Hailiang's tuition fees and program outcomes against those of other domestic and international institutions, influencing their perception of value.
Geographical Mobility and Online Alternatives
The increasing geographical mobility of students, allowing them to seek education in different cities or even internationally, significantly enhances their bargaining power. This mobility, combined with the proliferation of online learning platforms, presents a wider array of choices for prospective students.
If Hailiang Education's educational programs and services are not perceived as competitive in terms of accessibility, quality, or cost when compared to these readily available alternatives, students can easily opt for other institutions. For instance, in 2024, the global online education market was valued at over $300 billion, indicating a substantial and growing competitive landscape.
- Increased Choice: Students can compare Hailiang's offerings against numerous domestic and international institutions, as well as a vast selection of online courses.
- Price Sensitivity: The availability of affordable online programs puts pressure on traditional institutions like Hailiang to maintain competitive tuition fees.
- Quality Benchmarking: Students can easily research and compare faculty credentials, program outcomes, and student satisfaction rates across different educational providers.
- Accessibility Focus: Institutions that offer flexible learning formats, including hybrid or fully online options, cater to a broader student base and can leverage this to their advantage.
Customers in China's private education sector, primarily parents and students, possess substantial bargaining power. This is driven by a widening array of educational choices, including domestic private schools, international programs, and overseas study opportunities. Consequently, institutions must focus on delivering superior quality and demonstrating clear value to attract and retain students, especially with the global online education market exceeding $300 billion in 2024.
| Factor | Impact on Bargaining Power | Evidence/Data |
| Increased Choice | High | Proliferation of domestic and international institutions, plus online learning platforms. |
| Cost Sensitivity | High | Families are budget-conscious due to rising education costs and economic uncertainties. |
| Value Perception | High | Demand for well-rounded education, career support, and demonstrable ROI beyond academic scores. |
| Government Policies | Moderate | The 2021 'Double Reduction Policy' significantly impacted demand for certain private education services. |
Full Version Awaits
Hailiang Education Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Hailiang Education Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering an in-depth examination of the competitive landscape. The document you see here is precisely what you'll receive instantly after purchase, ensuring no surprises and immediate access to this professionally formatted report.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The competitive landscape for Hailiang Education is incredibly crowded, reflecting the sheer size and diversity of China's education sector. This market encompasses a wide array of institutions, from government-funded schools to a multitude of private K-12 operators and specialized tutoring services. As a significant private K-12 provider, Hailiang contends with both long-standing, well-regarded institutions and agile new entrants, especially in localized markets or specialized educational segments.
Government regulations and policy shifts represent a significant competitive force in the education sector. China's educational landscape, in particular, has seen substantial upheaval. For instance, the 2021 'Double Reduction Policy' aimed to ease the burden of homework and after-school tutoring for students, fundamentally altering the business models of many private education providers.
These policy changes create considerable uncertainty and can abruptly reshape the competitive environment. Stricter regulations on for-profit activities within education, as implemented by the Chinese government, directly impact how companies can operate and generate revenue. This necessitates rapid adaptation and strategic pivots, as seen with companies needing to diversify services or focus on different educational segments.
Competitors actively seek to attract students by developing distinct programs and specialized curricula, such as those focusing on Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (STEM) or international educational pathways. This intense rivalry means that educational institutions must continuously innovate their teaching methods and course offerings to stand out.
Hailiang Education's strategy hinges on providing a distinguished, specialized, and internationalized educational experience. However, the ability to sustain this differentiation in the face of aggressive competition is paramount for its long-term success. For instance, in 2024, many private education providers in China reported increased investment in curriculum development and teacher training to enhance their specialized offerings.
Access to Talent and Resources
Competitive rivalry in the education sector, particularly for Hailiang Education, significantly involves the intense competition for top-tier talent. This includes attracting and retaining highly qualified teachers, experienced administrators, and essential educational resources. Schools that cultivate strong reputations, offer competitive compensation and benefits, and embrace innovative teaching approaches are better positioned to secure and keep the best educators, directly influencing the quality of education provided.
In 2024, the demand for skilled educators remained high, with many regions experiencing teacher shortages. For instance, reports from early 2024 indicated that the average teacher salary in many developed countries saw modest increases, but the gap between starting salaries and the cost of living continued to be a challenge for recruitment and retention in some areas. Schools like Hailiang Education must therefore invest in professional development and create supportive work environments to stand out.
- Talent Acquisition Challenges: Schools compete not only on salary but also on professional growth opportunities and school culture to attract educators.
- Resource Competition: Access to cutting-edge technology, updated curriculum materials, and well-equipped facilities is a key differentiator.
- Impact on Quality: The ability to secure and retain high-caliber staff directly correlates with the educational outcomes and overall student experience.
- Market Differentiation: Innovative teaching methods and a strong institutional reputation are crucial for attracting both students and faculty in a crowded market.
Brand Reputation and Student Outcomes
In the fiercely competitive education sector, Hailiang Education, like its peers, hinges its success on a robust brand reputation and demonstrable student outcomes. Schools that consistently achieve high university admission rates and foster strong career pathways for their graduates inherently build trust and attract more students. This creates a virtuous cycle, reinforcing their market position.
For instance, in 2024, the demand for quality education continues to surge, making institutions with proven track records particularly attractive. Parents and students are increasingly scrutinizing performance metrics, such as college acceptance rates and alumni success stories, when making enrollment decisions. A strong brand built on academic excellence and positive student futures is a significant differentiator.
- Brand Reputation: A strong brand signals quality and reliability, influencing parental choice in a crowded market.
- Student Outcomes: High university acceptance rates and successful career placements are key indicators of an institution's effectiveness.
- Competitive Advantage: Schools excelling in these areas gain a significant edge in attracting and retaining students.
- Market Perception: Positive word-of-mouth and demonstrable success stories are crucial for maintaining a competitive edge.
The competitive rivalry for Hailiang Education is intense, driven by a vast number of private K-12 institutions in China vying for students. Differentiation through specialized programs, like STEM or international curricula, is key, with many institutions increasing investment in curriculum development and teacher training in 2024 to enhance these offerings.
Attracting and retaining top talent, including educators and administrators, is another critical battleground. Schools that offer competitive compensation, professional development, and a positive culture stand out, especially as teacher shortages persist in many regions. For example, early 2024 reports showed modest salary increases for teachers in developed nations, but cost-of-living challenges remained for recruitment.
Furthermore, a strong brand reputation built on demonstrable student outcomes, such as high university acceptance rates and successful career placements, significantly influences enrollment decisions. In 2024, parents and students increasingly scrutinize these performance metrics, making proven academic excellence a crucial differentiator in a saturated market.
| Metric | 2023 (Est.) | 2024 (Est.) | Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Private K-12 Institutions in China | ~15,000 | ~15,500 | Slight Increase |
| Average Teacher Salary Growth (China) | ~3-5% | ~4-6% | Moderate Increase |
| Investment in EdTech by Private Schools | High | Very High | Increasing |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The extensive state-run public education system in China presents a substantial threat of substitution for private education providers like Hailiang Education. The government's ongoing commitment to enhancing the quality and accessibility of public schooling directly competes with the demand for private alternatives. For instance, the Ministry of Education's 'Year of Strengthening Regulation in Basic Education' in 2023 aimed to standardize curriculum and teacher qualifications, potentially diminishing the perceived value proposition of private institutions.
The rise of online learning platforms presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional private education. Platforms like Coursera, edX, and Khan Academy, along with countless specialized digital courses, offer flexible and often more affordable alternatives. By 2024, the global e-learning market was projected to reach over $400 billion, demonstrating the substantial appeal and reach of these digital substitutes.
The rise of vocational training and skill-based learning presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional education providers like Hailiang Education. In 2024, the demand for skilled trades and immediate job readiness is intensifying, making these alternative learning paths highly attractive. For instance, reports indicate a growing enrollment in coding bootcamps and vocational programs, often with completion times and costs considerably lower than a four-year degree.
Overseas Education and International Study Programs
For affluent Chinese families, international study programs represent a significant substitute for domestic private education. The allure of global exposure, perceived higher quality of education, and enhanced future career prospects drives this trend. In 2024, the demand for overseas education continued to be robust, with millions of Chinese students pursuing studies abroad.
This external substitute directly impacts domestic private schools by offering an alternative pathway for students seeking a different educational experience. The increasing number of Chinese students enrolling in universities in countries like the United States, the United Kingdom, and Australia highlights the strength of this competitive force.
- Significant Demand: Millions of Chinese students sought international education in 2024, presenting a direct alternative to domestic private schooling.
- Perceived Quality and Opportunities: Factors like superior perceived educational quality and better long-term career opportunities abroad fuel this substitution.
- Global Exposure: The desire for international exposure and a broader worldview is a key driver for families choosing overseas programs.
- Competitive Pressure: The availability of these international options exerts considerable competitive pressure on domestic private education providers.
Self-Study and Informal Learning
The rise of self-study and informal learning presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional educational services. Vast amounts of free or low-cost educational content, tutorials, and online communities are readily accessible, allowing individuals to acquire knowledge independently.
While not a full replacement for formal education, this trend can diminish the perceived value of extensive private tutoring or certain supplementary educational support. For instance, platforms like Coursera and edX offer courses from top universities, often at a fraction of the cost of traditional enrollment. In 2023, the global e-learning market was valued at over $250 billion, indicating a substantial shift towards accessible learning resources.
- Accessibility of Online Resources: Platforms like YouTube host millions of educational videos, and online forums provide peer-to-peer learning opportunities.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Self-study often involves minimal or no direct financial outlay compared to formal educational programs.
- Flexibility: Learners can study at their own pace and on their own schedule, fitting education around other commitments.
- Growing Market: The demand for online courses and digital learning tools continues to expand, demonstrating a clear preference for alternative educational pathways.
The threat of substitutes for Hailiang Education is significant, stemming from both public education and alternative learning models. The robust Chinese public school system, continually improving in quality and accessibility, offers a compelling alternative to private schooling. Furthermore, the burgeoning e-learning market, projected to exceed $400 billion by 2024, provides flexible and cost-effective digital learning options that directly compete with traditional classroom settings.
Vocational training and international study programs also present strong substitutes. The increasing demand for skilled trades and immediate job readiness makes vocational paths attractive, while the allure of global exposure and perceived higher quality education drives millions of Chinese students to pursue studies abroad annually. These diverse alternatives collectively exert considerable pressure on domestic private education providers.
| Substitute Type | Key Characteristics | Impact on Private Education | Market Trend (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Public Education | Improved quality, accessibility, government investment | Reduces demand for private alternatives | Ongoing enhancement initiatives |
| E-Learning Platforms | Flexibility, affordability, vast content | Direct competition, lower perceived value for supplementary services | Global market > $400 billion projected for 2024 |
| Vocational Training | Skill-focused, job-ready, shorter duration | Appeals to students seeking immediate employment | Growing enrollment in coding bootcamps, trades |
| International Study | Global exposure, perceived higher quality, career prospects | Significant outflow of students, competitive pressure | Millions of Chinese students studying abroad |
Entrants Threaten
The Chinese government's increasingly strict oversight of the education sector, particularly for private and for-profit institutions, presents a substantial threat of new entrants. Policies like the 'Double Reduction Policy,' aimed at easing student homework and tutoring burdens, alongside controls on foreign capital in compulsory education, effectively erect high barriers. For instance, in 2021, this policy led to significant restructuring and closure of many after-school tutoring centers, demonstrating the government's power to reshape the market landscape.
Establishing a robust educational network, particularly one aiming for quality and international standards like Hailiang Education, demands significant upfront capital. This includes building and equipping numerous schools, investing in advanced learning technologies, and attracting highly qualified teaching staff. For instance, in 2023, the global education technology market was valued at over $120 billion, highlighting the substantial investment needed for modern educational infrastructure.
Building a strong brand reputation and earning parental trust in education is a lengthy, resource-intensive process. Newcomers must invest heavily in marketing and demonstrating consistent quality to even begin to rival established institutions like Hailiang Education, which has cultivated its reputation since 1995.
Talent Acquisition and Retention
Attracting and retaining top-tier educators, particularly those with specialized pedagogical skills or international teaching credentials, presents a significant hurdle for any new educational institution. This scarcity of qualified talent means new entrants must contend with established players for a limited pool, often necessitating higher salary offers and enhanced benefits packages. For instance, in 2024, the average teacher salary in the US continued its upward trend, with some states reporting significant increases to combat shortages, directly impacting the cost structure for new competitors.
This competition for talent can escalate operational expenses for newcomers. To lure experienced teachers away from established schools, new entrants might need to offer signing bonuses, relocation assistance, or more attractive professional development opportunities. These added costs directly increase the capital required to launch and sustain an educational service, thereby raising the barrier to entry.
The challenge is amplified by the demand for teachers proficient in specific curricula or advanced subjects.
- Teacher Shortages: Many regions face ongoing shortages in critical subject areas like STEM and special education.
- Competitive Compensation: To attract talent, new entrants may need to offer salaries 10-15% above the market average.
- International Hiring Costs: Recruiting and relocating international teachers involves significant visa processing and support expenses.
- Retention Incentives: High turnover rates necessitate ongoing investment in retention programs, further burdening new organizations.
Curriculum Development and Accreditation
Developing a robust curriculum that aligns with national standards and unique educational philosophies, such as international or specialized programs, presents a significant hurdle for new entrants. This process is inherently complex and requires substantial time investment.
Furthermore, securing the necessary accreditations is a critical step that demands considerable resources and expertise. New competitors must allocate significant capital to this area to ensure their offerings are competitive and recognized in the market.
- Curriculum Design Costs: Developing a comprehensive curriculum can cost tens of thousands of dollars, encompassing subject matter expert fees, content development software, and pedagogical research.
- Accreditation Fees: Obtaining accreditations from bodies like the Council for Higher Education Accreditation (CHEA) or regional accrediting agencies can involve application fees ranging from $1,000 to $5,000 or more, plus ongoing compliance costs.
- Time Investment: The accreditation process alone can take 18-24 months, requiring dedicated staff time for documentation, site visits, and program reviews.
The threat of new entrants into the education sector, particularly in China, is significantly mitigated by stringent government regulations and substantial capital requirements. Policies like the 2021 'Double Reduction Policy' have already demonstrated the government's capacity to reshape the market, making it challenging for newcomers to navigate. Furthermore, the immense upfront investment needed for infrastructure, technology, and quality staff creates a high barrier, as evidenced by the over $120 billion global education technology market valuation in 2023.
Building a trusted brand and attracting top-tier educators are also considerable challenges. New entrants must invest heavily in marketing and competitive compensation to lure talent from established institutions like Hailiang Education, which has been cultivating its reputation since 1995. For instance, in 2024, the rising teacher salaries in many regions, with some offering 10-15% above market average, increase operational expenses for new competitors.
The complexity of curriculum development and the lengthy accreditation process, often taking 18-24 months and costing tens of thousands of dollars, further deter new entrants. These factors, combined with the need for significant investment in curriculum design and accreditation fees, which can range from $1,000 to $5,000 or more, solidify the position of established players.
| Barrier | Description | Example Data |
|---|---|---|
| Government Regulation | Strict oversight and policy changes impacting private education. | 'Double Reduction Policy' (2021) led to widespread restructuring. |
| Capital Requirements | High upfront investment for infrastructure and technology. | Global EdTech market valued over $120 billion (2023). |
| Brand Reputation & Trust | Long-term effort to build credibility with parents. | Hailiang Education established in 1995. |
| Talent Acquisition | Competition for qualified educators, increasing salary demands. | New entrants may offer 10-15% above market average salaries (2024). |
| Curriculum & Accreditation | Complex development and lengthy approval processes. | Accreditation can cost $1,000-$5,000+ and take 18-24 months. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Hailiang Education is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including the company's annual reports, investor presentations, and publicly available financial statements. We also incorporate insights from reputable education industry research reports and market analysis firms to provide a robust understanding of the competitive landscape.
