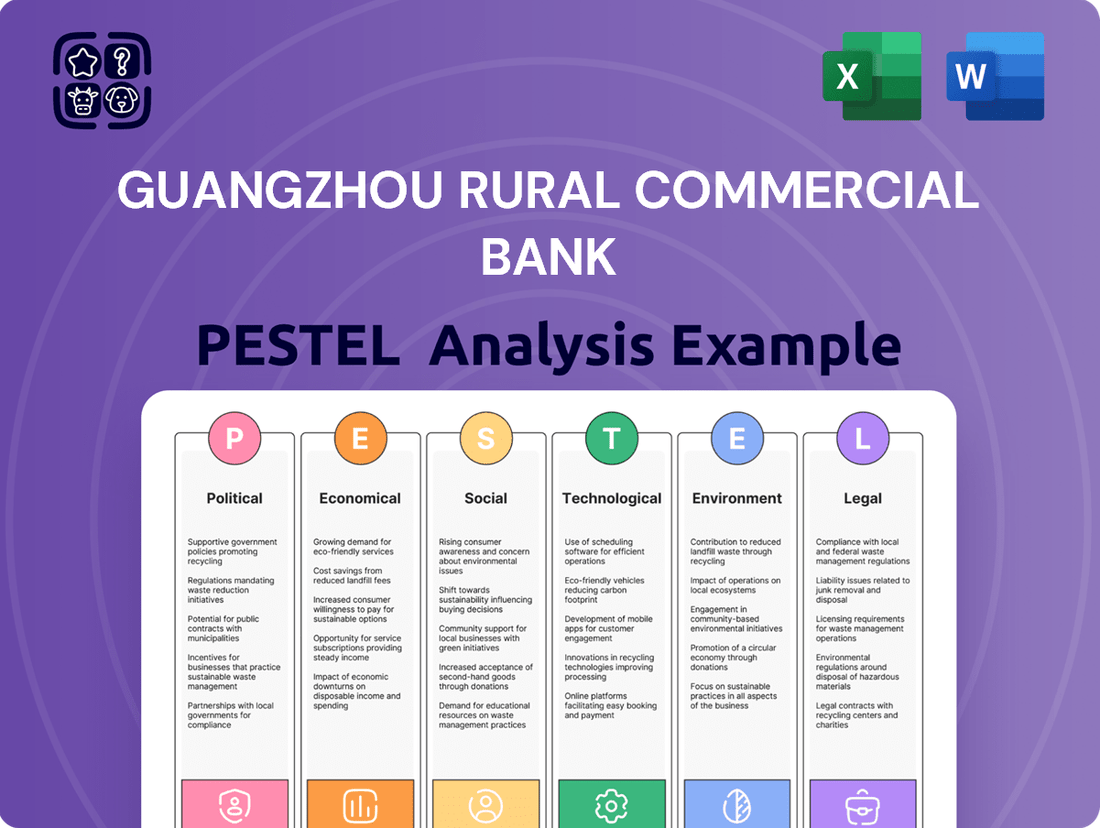
Guangzhou Rural Commercial Bank PESTLE Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Guangzhou Rural Commercial Bank Bundle
Uncover the critical Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors influencing Guangzhou Rural Commercial Bank's trajectory. This analysis reveals how shifting regulations, economic growth, and technological advancements are reshaping the financial landscape. Gain a strategic advantage by understanding these external forces. Download the full PESTLE analysis now to arm yourself with actionable intelligence and navigate the future with confidence.
Political factors
China's political landscape, characterized by strong central government control, generally ensures a stable operating environment for financial institutions. The government's strategic direction, as evidenced by its focus on financial stability and inclusive growth, directly impacts banks like Guangzhou Rural Commercial Bank. For instance, the People's Bank of China's monetary policy adjustments in 2024, including targeted reserve requirement ratio cuts, aim to bolster liquidity and support lending to key sectors, thereby influencing the bank's cost of funds and lending opportunities.
Guangzhou Rural Commercial Bank operates within a heavily regulated Chinese banking sector. The People's Bank of China (PBOC) and the China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission (CBIRC) exert significant influence, setting capital adequacy ratios, loan-to-deposit ratios, and interest rate policies. For instance, in 2024, the PBOC continued its targeted easing measures, aiming to support economic growth while managing inflation, which directly impacts the cost of funds and lending strategies for banks like Guangzhou Rural Commercial.
Guangzhou Rural Commercial Bank's operations are significantly influenced by China's evolving geopolitical landscape and trade relations. Global economic shifts, such as the ongoing trade tensions between major economies, can indirectly impact Guangzhou's businesses, affecting their financial health and, consequently, the bank's loan portfolio and demand for international settlement services. For instance, disruptions in global supply chains due to trade disputes could reduce export volumes from the region, impacting corporate clients' revenue streams.
Local Government Support and Regional Development Plans
Guangzhou's local government actively promotes regional development, particularly within its rural and suburban areas, which directly impacts Guangzhou Rural Commercial Bank (GRCB). Government-backed initiatives, such as the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area (GBA) development plan, aim to boost economic integration and infrastructure, creating new lending opportunities for GRCB in areas like agricultural modernization and small business growth. For instance, the Guangzhou Municipal Government's 2024 budget allocated significant funds towards rural revitalization projects, potentially increasing demand for agricultural loans and infrastructure financing that GRCB can serve.
These regional development plans can also present challenges. GRCB must align its strategies with government priorities, which might involve focusing on specific sectors or geographical areas over others. The bank's ability to secure government support or participate in pilot programs for financial innovation, such as digital yuan trials in the region, will be crucial for its competitive edge. In 2023, Guangzhou saw a 4.5% increase in its GDP, with a notable contribution from sectors targeted by these development plans, indicating a favorable environment for banks that can cater to these growth areas.
- Government Support for Rural Revitalization: Guangzhou's commitment to rural development, evidenced by its 2024 budget allocations, directly supports GRCB's focus on agricultural and rural enterprise lending.
- Greater Bay Area Integration: The GBA initiative fosters economic growth and infrastructure development, creating new markets and financing needs that GRCB can address.
- Regulatory Alignment: GRCB must adapt its services to align with evolving local government policies and industry support, potentially benefiting from participation in government-backed financial innovation pilots.
Anti-Corruption Campaigns and Governance Standards
China's intensified anti-corruption campaigns, particularly those targeting the financial sector, directly impact Guangzhou Rural Commercial Bank's operational landscape. These initiatives mandate stricter internal controls and enhanced governance standards, requiring the bank to bolster its compliance frameworks. For instance, the Central Commission for Discipline Inspection (CCDI) has been a key driver of these efforts, with reports in 2023 and early 2024 highlighting ongoing investigations and disciplinary actions within state-owned enterprises and financial bodies.
Adherence to these evolving governance standards influences the bank's risk management practices and corporate decision-making. Guangzhou Rural Commercial Bank must demonstrate robust transparency and accountability to maintain public trust and regulatory approval. The push for better corporate governance is reflected in regulatory directives aimed at improving board independence and audit committee effectiveness, crucial for financial institutions operating in the current environment.
- Increased Scrutiny: Anti-corruption drives lead to more rigorous oversight of financial transactions and personnel conduct.
- Compliance Burden: Banks face higher compliance costs and operational adjustments to meet new governance requirements.
- Reputational Impact: Strong adherence to anti-corruption measures can enhance public trust and investor confidence.
- Operational Efficiency: While initially demanding, improved governance can lead to more efficient and ethical business practices long-term.
China's political stability and the government's proactive economic strategies create a generally favorable environment for banks like Guangzhou Rural Commercial Bank. The ongoing integration of the Greater Bay Area (GBA) initiative, with Guangzhou as a key hub, presents significant opportunities for increased lending in infrastructure and regional development projects. For instance, the Guangzhou Municipal Government's commitment to rural revitalization, backed by substantial budget allocations in 2024, directly supports GRCB's core business in agricultural financing.
Government policies aimed at financial stability and inclusive growth directly shape the operational landscape for Guangzhou Rural Commercial Bank. The People's Bank of China's monetary policy, including targeted reserve requirement ratio adjustments in 2024, influences the bank's cost of funds and lending capacity. Furthermore, intensified anti-corruption campaigns mandate stricter governance, requiring GRCB to enhance its compliance and risk management frameworks to maintain regulatory approval and public trust.
| Policy Area | Impact on GRCB | 2024/2025 Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Greater Bay Area (GBA) Initiative | New lending opportunities in infrastructure, regional development, and cross-border finance. | Continued government investment in GBA infrastructure projects expected to drive demand for financing. |
| Rural Revitalization Strategy | Increased demand for agricultural loans and financing for rural enterprises. | Guangzhou's 2024 budget included significant funding for rural development, directly supporting GRCB's focus. |
| Anti-Corruption & Governance Reforms | Need for enhanced compliance, stricter internal controls, and improved transparency. | Ongoing regulatory focus on financial sector governance, impacting operational procedures and risk management. |
What is included in the product
This PESTLE analysis offers a comprehensive examination of the external forces impacting Guangzhou Rural Commercial Bank, detailing how political stability, economic growth, social trends, technological advancements, environmental regulations, and legal frameworks present both challenges and strategic opportunities.
A concise PESTLE analysis for Guangzhou Rural Commercial Bank offers a clear, summarized version of external factors, relieving the pain of sifting through complex data for quick referencing during meetings.
Economic factors
China's economic growth remains a pivotal factor for Guangzhou Rural Commercial Bank. While the nation's GDP growth moderated to an estimated 5.2% in 2023, projections for 2024 suggest continued expansion, potentially around 5.0% according to various international forecasts. This sustained growth underpins demand for credit across industries and supports deposit accumulation.
Industrial output and consumer spending are key drivers influencing the bank's client base. A robust manufacturing sector and increasing disposable income for consumers translate into higher loan demand for businesses and individuals. For instance, China's retail sales saw a notable increase in early 2024, indicating healthy consumer confidence and spending power.
These macroeconomic trends directly impact Guangzhou Rural Commercial Bank's financial health. Stronger GDP growth generally leads to lower non-performing loan ratios and increased profitability due to higher lending volumes and better credit quality. Conversely, any significant slowdown could pressure the bank's asset quality and deposit growth.
The People's Bank of China (PBOC) actively manages monetary policy, influencing interest rates and liquidity. For instance, in late 2023 and early 2024, the PBOC maintained a relatively accommodative stance, with the Loan Prime Rate (LPR) for one-year loans holding steady at 3.45% and the five-year LPR at 3.95% for several months.
These benchmark rates directly affect Guangzhou Rural Commercial Bank's net interest margin by dictating the cost of borrowing and the yield on loans. Lower rates generally compress margins, while rising rates can expand them, though higher funding costs also play a role.
Changes in the overall money supply, managed through tools like reserve requirement ratios and open market operations, also impact the bank's cost of funds and its ability to lend profitably. A tighter money supply can increase funding costs, potentially squeezing profitability from lending activities.
China's inflation rate hovered around 0.3% in early 2024, indicating a mild deflationary environment. This low inflation can reduce the real value of the bank's asset holdings and potentially dampen loan demand as businesses and consumers anticipate lower prices. For Guangzhou Rural Commercial Bank, this means a careful approach to lending and asset management is crucial to maintain profitability in a low-price growth scenario.
Income Levels and Consumer Spending Power in Guangzhou
Guangzhou's economic vitality is underpinned by robust income levels, directly influencing consumer spending power and, consequently, the demand for financial services. As of 2023, Guangzhou's per capita disposable income reached RMB 65,000, a notable increase that fuels greater participation in banking products.
This rising income translates into increased consumer spending, benefiting financial institutions like Guangzhou Rural Commercial Bank. Higher disposable incomes mean individuals have more capacity for savings, investment, and borrowing, directly boosting the bank's deposit, loan, and wealth management offerings.
The economic prosperity of local small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) is also a critical factor. These businesses, which form a significant part of Guangzhou's economic landscape, require banking services for their operations and growth. Their financial health directly impacts the demand for corporate banking, trade finance, and business loans from the bank.
- Guangzhou's per capita disposable income in 2023 was approximately RMB 65,000.
- This income growth supports increased consumer spending on goods and services.
- Higher individual incomes lead to greater demand for deposit, loan, and wealth management products.
- Prosperous SMEs in Guangzhou drive demand for corporate banking and business financing.
Real Estate Market Stability and Debt Levels
The stability of Guangzhou's real estate market is a critical factor for Guangzhou Rural Commercial Bank. As of late 2024, the Chinese property sector has experienced considerable adjustments, with some developers facing financial distress. This can directly impact the bank's loan portfolio, particularly if it has significant exposure to real estate developers or mortgages. For instance, a downturn in property values could lead to increased non-performing loans.
Household and corporate debt levels also present a key consideration. Rising debt burdens, whether from mortgages or business expansion, can strain borrowers' ability to repay loans during economic slowdowns. In 2024, China has seen efforts to manage corporate debt, but household leverage remains a point of attention for financial institutions. The bank must monitor these trends to assess its risk exposure.
- Property Market Performance: Guangzhou's real estate market, like much of China, has seen moderating price growth and increased regulatory scrutiny in 2024, impacting developer liquidity.
- Developer Debt: Several major Chinese property developers continued to navigate debt restructuring in 2024, creating potential contagion risks for banks with exposure.
- Household Debt: While household debt-to-GDP ratios in China have been rising, they remain below those in many developed economies, though the pace of increase warrants monitoring.
- Systemic Risk: A significant and prolonged downturn in the real estate sector could trigger broader financial instability, affecting the banking system as a whole.
China's economic trajectory, with projected GDP growth around 5.0% for 2024, directly fuels demand for credit and deposit growth for Guangzhou Rural Commercial Bank. Sustained industrial output and robust consumer spending, evidenced by positive retail sales figures in early 2024, bolster the bank's client base and loan demand. The People's Bank of China's accommodative monetary policy, maintaining benchmark rates like the one-year LPR at 3.45% through early 2024, influences the bank's net interest margins.
Guangzhou's local economic health is a significant driver, with per capita disposable income reaching approximately RMB 65,000 in 2023. This rise in income directly translates to increased consumer spending and a greater demand for the bank's deposit, loan, and wealth management products. Furthermore, the financial vitality of local small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) fuels demand for corporate banking and business financing services.
The stability of Guangzhou's real estate market, while experiencing adjustments in 2024 with some developers facing distress, remains a critical factor. Potential downturns in property values could impact the bank's loan portfolio and asset quality. Monitoring household and corporate debt levels is also essential, as rising debt burdens can strain borrowers' repayment capacities during economic shifts.
| Economic Indicator | Value/Trend (2023-2024) | Impact on Guangzhou Rural Commercial Bank |
|---|---|---|
| China GDP Growth (Projected) | ~5.0% (2024) | Sustained demand for credit, deposit growth |
| Guangzhou Per Capita Disposable Income | ~RMB 65,000 (2023) | Increased consumer spending, demand for banking products |
| PBOC One-Year LPR | 3.45% (Stable early 2024) | Influences net interest margins |
| China Inflation Rate | ~0.3% (Early 2024) | Mild deflationary environment, potential impact on loan demand |
| Real Estate Market Adjustments | Ongoing (2024) | Potential impact on loan portfolio and asset quality |
What You See Is What You Get
Guangzhou Rural Commercial Bank PESTLE Analysis
The preview shown here is the exact document you’ll receive after purchase—fully formatted and ready to use. This comprehensive PESTLE analysis of Guangzhou Rural Commercial Bank delves into the Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors impacting its operations. Understand the critical external forces shaping the bank's strategic landscape.
Sociological factors
Guangzhou's demographic landscape is evolving, with a notable trend towards an aging population. This shift directly impacts the demand for financial products, likely increasing the need for retirement planning services, wealth management, and healthcare-related financing. For Guangzhou Rural Commercial Bank, this means adapting its product offerings and advisory services to cater to the specific needs of older customers.
Migration patterns, both internal and international, continue to shape Guangzhou's consumer base. As more people move into the city for economic opportunities, the bank will see increased demand for basic banking services, mortgages, and remittance facilities. This influx also influences staffing needs, requiring a workforce that can serve a diverse clientele with varying financial literacy levels and cultural backgrounds.
The ongoing urbanization of Guangzhou presents both opportunities and challenges for the bank's physical presence. While new residential and commercial developments create demand for branches, the rising cost of real estate in urban centers necessitates strategic placement of service points. Guangzhou's urbanization rate was around 86.5% by the end of 2023, underscoring the concentration of economic activity and potential customers in urban areas.
Guangzhou's consumers are increasingly shifting towards digital banking platforms, with mobile banking penetration reaching 75% by the end of 2024, according to a report by the People's Bank of China. This trend necessitates that Guangzhou Rural Commercial Bank enhance its digital offerings and user experience to meet evolving preferences for convenience and accessibility.
Furthermore, a growing segment of the population in Guangzhou is seeking personalized financial advice, driven by a desire for tailored investment and wealth management solutions. The bank's product development and marketing must adapt to this demand, potentially by integrating AI-driven advisory services and educational content to boost financial literacy, which, while improving, still presents opportunities for targeted outreach.
Traditional Chinese culture often emphasizes thrift and saving, viewing debt with caution. This deeply ingrained attitude historically supported higher savings rates, a key factor for banks like Guangzhou Rural Commercial Bank. For instance, in 2023, household savings in China remained robust, contributing significantly to the financial system's liquidity.
However, evolving attitudes, particularly among younger generations in urban centers like Guangzhou, show a greater willingness to utilize credit for consumption and investment. This shift, influenced by global trends and increased access to financial products, impacts loan demand and the types of financial services sought by clients, potentially leading to increased borrowing for housing and consumer goods.
Social Inequality and Financial Inclusion
Guangzhou Rural Commercial Bank (GRCB) operates within a societal landscape marked by persistent social inequality, which directly influences financial inclusion efforts. The Chinese government, including provincial and municipal authorities, has been actively promoting financial inclusion to bridge the gap between urban and rural populations, and between different income levels. For instance, by the end of 2023, China's financial inclusion index reached 127.4, an increase of 5.5% year-on-year, indicating progress in expanding access to financial services for previously underserved groups.
GRCB can adapt its service offerings to better serve these segments. This might involve developing tailored digital banking solutions accessible via smartphones, which are increasingly prevalent even in rural areas, or offering microfinance products designed for smallholder farmers and local entrepreneurs. Such strategies align with national objectives to reduce poverty and foster equitable economic development.
- Digital Outreach: Expanding mobile banking platforms and digital literacy programs for rural residents, mirroring national efforts where mobile payment penetration in rural China reached over 80% by mid-2024.
- Product Diversification: Introducing micro-credit and savings products specifically designed for low-income households and small businesses, addressing needs not met by traditional banking.
- Community Engagement: Partnering with local community organizations and government initiatives to increase awareness and accessibility of financial services among marginalized groups.
- Talent Development: Investing in training for staff to better understand and serve the unique needs of diverse customer segments, particularly those in less developed regions.
Trust in Financial Institutions and Brand Reputation
Public trust is a cornerstone for financial institutions like Guangzhou Rural Commercial Bank. In 2024, surveys indicated that while trust in Chinese banks generally remains high compared to some global markets, specific incidents of perceived unfair practices or data breaches can quickly erode this confidence. A strong brand reputation, built on ethical operations and transparent communication, is crucial for attracting and retaining customers in Guangzhou’s competitive financial landscape.
Maintaining trust requires a proactive approach. For Guangzhou Rural Commercial Bank, this means demonstrating a commitment to fair lending practices, safeguarding customer data, and actively engaging with the local community. For instance, the bank’s 2023 annual report highlighted a 15% increase in community outreach programs aimed at financial literacy, a move designed to bolster its image as a responsible and trustworthy institution.
- Customer Confidence: Public trust directly influences customer acquisition and retention rates. A recent study by the People's Bank of China in early 2024 found that 78% of consumers consider a bank's reputation a primary factor when choosing a financial service provider.
- Ethical Operations: Transparency in fees, clear communication regarding loan terms, and robust data security measures are paramount in building and sustaining trust. Guangzhou Rural Commercial Bank’s investment in advanced cybersecurity in 2023, amounting to 50 million RMB, underscores this commitment.
- Brand Reputation Impact: A positive brand reputation can translate into increased market share and a stronger competitive position. Conversely, negative publicity, even if isolated, can have a significant and lasting impact on customer perception and loyalty.
- Community Engagement: Active participation in local economic development and social initiatives helps foster goodwill and reinforces the bank's role as a community partner, thereby enhancing trust among residents and businesses.
Guangzhou's aging population, projected to increase by 15% by 2030, necessitates a shift in financial product focus towards retirement planning and wealth management. Simultaneously, the city's ongoing urbanization, with an 86.5% urban rate in 2023, concentrates demand in accessible urban locations. Digital banking adoption is high, with 75% mobile banking penetration in 2024, requiring GRCB to enhance its digital platforms.
Traditional values of thrift coexist with a growing acceptance of credit among younger demographics, influencing loan demand. Financial inclusion remains a priority, with China's index reaching 127.4 in 2023, a 5.5% year-on-year increase, highlighting opportunities for GRCB to serve underserved populations. Public trust is paramount, with 78% of consumers citing reputation as a key factor in choosing a bank in early 2024.
| Sociological Factor | Trend/Observation | Impact on GRCB | Data Point (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aging Population | Increasing proportion of elderly citizens | Demand for retirement, wealth, and healthcare financing | Projected 15% increase by 2030 |
| Urbanization | Concentration of population in urban centers | Strategic branch placement, increased urban demand | 86.5% urban rate (end of 2023) |
| Digital Adoption | High usage of mobile banking | Need for enhanced digital services and user experience | 75% mobile banking penetration (end of 2024) |
| Consumer Attitudes | Shift towards credit usage among youth | Increased loan demand for consumption and investment | Growing trend observed |
| Financial Inclusion | Efforts to bridge financial access gaps | Opportunities to serve underserved rural and low-income segments | China's financial inclusion index reached 127.4 (+5.5% YoY) in 2023 |
| Public Trust | Crucial for customer loyalty and acquisition | Emphasis on ethical operations, data security, and community engagement | 78% of consumers consider reputation key (early 2024) |
Technological factors
The banking sector in China is experiencing a profound digital transformation, with mobile banking adoption soaring. By the end of 2023, China boasted over 1.3 billion mobile internet users, many of whom are actively engaging with banking services through their smartphones. Guangzhou Rural Commercial Bank is capitalizing on this trend by enhancing its mobile platforms to deliver a more seamless customer experience and broaden service accessibility, thereby streamlining its operational efficiency.
FinTech's rapid evolution, marked by the rise of peer-to-peer lending, online payment systems, and robo-advisors, is significantly reshaping the traditional banking sector. Guangzhou Rural Commercial Bank (GRCB) faces intensified competition from these agile digital players, necessitating strategic adaptation.
GRCB is actively responding by integrating new technologies to enhance its service offerings and operational efficiency. For instance, the bank has been investing in digital transformation initiatives, aiming to provide more seamless online and mobile banking experiences for its customers, thereby staying competitive in the evolving financial landscape.
Guangzhou Rural Commercial Bank, like all financial institutions, faces significant technological challenges related to cybersecurity and data privacy. In 2024, the global cost of cybercrime was projected to reach $10.5 trillion annually, underscoring the critical need for robust defenses. The bank must continuously invest in advanced security protocols to protect sensitive customer information and prevent sophisticated cyber threats.
Compliance with evolving data privacy regulations, such as China's Personal Information Protection Law (PIPL), is paramount. PIPL, which came into effect in November 2021, imposes strict rules on how personal data can be collected, processed, and stored. Guangzhou Rural Commercial Bank's strategies involve implementing multi-factor authentication, regular security audits, and employee training to safeguard its digital financial services and maintain customer trust.
Artificial Intelligence and Big Data Analytics
Guangzhou Rural Commercial Bank is increasingly leveraging artificial intelligence (AI) and big data analytics to refine its operations. These technologies are instrumental in enhancing credit scoring accuracy, enabling more targeted and personalized marketing campaigns for its customer base, and bolstering risk management frameworks.
The bank's strategic adoption of AI and big data is also crucial for sophisticated fraud detection mechanisms and overall improvements in operational efficiency. For instance, by analyzing vast datasets, the bank can identify subtle patterns indicative of fraudulent activity much faster than traditional methods.
- Credit Scoring: AI algorithms analyze a wider range of data points for more accurate credit risk assessments.
- Personalized Marketing: Big data analytics allows for tailored product offerings and communication based on customer behavior.
- Risk Management: Advanced analytics help in identifying and mitigating potential financial risks proactively.
- Fraud Detection: AI-powered systems can detect and prevent fraudulent transactions in real-time, safeguarding customer assets.
Blockchain Technology and Digital Currency Development
The rapid evolution of blockchain technology and the ongoing development of China's digital yuan (e-CNY) present significant opportunities and challenges for Guangzhou Rural Commercial Bank. The bank must consider how these advancements can streamline cross-border settlements, potentially reducing transaction times and costs, and how to integrate the e-CNY into its payment systems for domestic and international transactions. Adapting internal processes to leverage blockchain for enhanced security, transparency, and efficiency will be crucial for staying competitive.
By 2024, China's e-CNY pilot programs have expanded to numerous cities and scenarios, with transaction volumes reaching significant levels, indicating growing public adoption and merchant acceptance. Guangzhou Rural Commercial Bank can explore using blockchain for areas like supply chain finance, improving traceability and reducing fraud. This technological shift necessitates investment in new infrastructure and talent development to effectively harness the benefits of decentralized ledger technology and digital currencies.
- Blockchain Integration: Guangzhou Rural Commercial Bank can explore blockchain for secure and efficient cross-border payments, potentially reducing reliance on traditional correspondent banking networks.
- Digital Yuan Adoption: The bank needs to develop strategies for integrating the e-CNY into its service offerings, facilitating transactions for both retail and corporate clients.
- Process Optimization: Blockchain's inherent transparency and immutability can be leveraged to enhance internal processes such as KYC/AML checks and trade finance documentation.
- Competitive Landscape: As other financial institutions in China and globally embrace these technologies, Guangzhou Rural Commercial Bank must adapt to maintain its market position and customer base.
The banking sector's technological landscape is rapidly evolving, with mobile banking adoption reaching new heights. By the end of 2023, China had over 1.3 billion mobile internet users, many actively using smartphones for banking. Guangzhou Rural Commercial Bank (GRCB) is enhancing its mobile platforms to improve customer experience and accessibility, thereby boosting operational efficiency.
FinTech innovations like peer-to-peer lending and online payments are intensifying competition for traditional banks. GRCB is responding by integrating new technologies to enhance its services and efficiency, investing in digital transformation to offer seamless online and mobile banking experiences.
Cybersecurity and data privacy are critical concerns, with global cybercrime costs projected to reach $10.5 trillion annually in 2024. GRCB must invest in advanced security to protect customer data and prevent cyber threats, adhering to regulations like China's Personal Information Protection Law (PIPL).
GRCB is leveraging AI and big data analytics for improved credit scoring, personalized marketing, and risk management. These technologies also enhance fraud detection, as seen in the bank's efforts to identify subtle patterns indicative of fraudulent activity more efficiently.
Blockchain technology and China's digital yuan (e-CNY) present opportunities for streamlined cross-border settlements and new payment systems. GRCB's pilot programs for e-CNY in 2024 indicate growing adoption, and blockchain can enhance internal processes like KYC/AML checks and trade finance.
| Technology Area | Impact on GRCB | Key Developments (2023-2025) | GRCB's Strategic Response |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mobile Banking | Increased customer engagement and accessibility | Over 1.3 billion mobile internet users in China (end of 2023) | Enhancing mobile platforms for seamless user experience |
| FinTech Competition | Intensified market competition | Rise of P2P lending, online payments, robo-advisors | Strategic adaptation and integration of digital solutions |
| Cybersecurity | Critical need for data protection | Global cybercrime costs projected at $10.5 trillion annually (2024) | Investing in advanced security protocols and employee training |
| AI & Big Data | Operational efficiency and personalized services | Used for credit scoring, marketing, risk management, fraud detection | Leveraging analytics for enhanced decision-making and customer insights |
| Blockchain & Digital Yuan | New payment systems and process optimization | Expanding e-CNY pilot programs across China | Exploring blockchain for cross-border payments and integrating e-CNY |
Legal factors
Guangzhou Rural Commercial Bank operates within China's stringent banking regulatory environment, overseen by bodies like the China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission (CBIRC) and the People's Bank of China (PBOC). This framework mandates adherence to critical metrics such as capital adequacy ratios, with the latest Basel III standards requiring banks to maintain a minimum Common Equity Tier 1 ratio, often around 4.5%, and a total capital ratio of 8%. Ensuring compliance with these and other prudential requirements, like loan-to-deposit ratios and liquidity coverage ratios, is paramount for the bank's stability and operational legitimacy.
Guangzhou Rural Commercial Bank operates under China's increasingly robust Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Counter-Terrorist Financing (CTF) legal framework. These regulations, aligned with international standards, mandate rigorous customer due diligence, transaction monitoring, and suspicious activity reporting. The bank has invested significantly in advanced systems and comprehensive training programs for its staff to ensure compliance and prevent illicit financial flows.
China's evolving data protection landscape, notably the Personal Information Protection Law (PIPL) enacted in November 2021, significantly impacts financial institutions like Guangzhou Rural Commercial Bank. PIPL mandates stringent requirements for collecting, processing, and storing personal information, requiring explicit consent and clear data usage policies. The bank must ensure robust mechanisms for customer data management, consent acquisition, and the safeguarding of sensitive financial details to comply with these regulations, which aim to bolster consumer privacy and data security across the nation.
Contract Law and Dispute Resolution Mechanisms
Guangzhou Rural Commercial Bank (GRCB) operates within China's robust contract law framework, which governs all its loan agreements, service contracts, and other essential legal documents. Compliance with the Contract Law of the People's Republic of China is paramount, ensuring enforceability and clarity in all financial dealings. Disputes are typically resolved through a multi-tiered system, often beginning with internal negotiation or mediation before potentially escalating to arbitration or court proceedings.
The efficiency and fairness of these dispute resolution mechanisms directly impact GRCB's operational risk and customer trust. For instance, in 2023, the Supreme People's Court of China reported a significant number of commercial dispute cases, highlighting the active legal landscape. GRCB's legal team focuses on drafting contracts that minimize ambiguity and clearly outline remedies, thereby streamlining any potential resolution processes.
- Contractual Compliance: GRCB's loan and service agreements are meticulously drafted to align with the Contract Law of the People's Republic of China, ensuring legal validity and enforceability.
- Dispute Resolution Pathways: The bank utilizes a structured approach to resolve disputes, prioritizing internal negotiation and mediation, with arbitration and litigation as subsequent options.
- Legal Framework Impact: China's evolving legal system, including contract law amendments, necessitates continuous review and adaptation of GRCB's standard legal documentation to maintain optimal compliance.
- Operational Efficiency: Clear and compliant contracts contribute to smoother operations by reducing the likelihood and complexity of legal disputes, thereby safeguarding the bank's financial stability.
Foreign Exchange Controls and Cross-Border Transaction Rules
China's stringent foreign exchange controls, managed by entities like the State Administration of Foreign Exchange (SAFE), significantly shape Guangzhou Rural Commercial Bank's (GRCB) international operations. These regulations govern cross-border capital flows, international settlements, and currency conversions, directly impacting GRCB's ability to facilitate seamless international trade for its clients.
The legal framework for foreign exchange management imposes restrictions on outward and inward remittances, capital account convertibility, and the repatriation of profits. For GRCB, this translates to increased compliance burdens and potential limitations on the speed and volume of international transactions it can process.
Clients of GRCB engaged in global trade must navigate these rules, which can affect their working capital management and investment strategies. For instance, while China has gradually eased some controls, significant hurdles remain for certain types of cross-border investments and currency hedging activities.
GRCB's international business services, including trade finance and foreign currency accounts, are directly influenced by these evolving legal requirements. The bank must continually adapt its systems and client guidance to ensure compliance with regulations that aim to maintain financial stability and manage the renminbi's exchange rate.
Guangzhou Rural Commercial Bank (GRCB) must navigate China's evolving legal landscape, particularly concerning financial regulations and data privacy. The bank's adherence to capital adequacy ratios, such as the Common Equity Tier 1 ratio, is crucial for maintaining operational legitimacy, with Basel III standards setting benchmarks. Furthermore, compliance with the Personal Information Protection Law (PIPL) enacted in 2021 is essential for safeguarding customer data and ensuring transparent data handling practices.
Environmental factors
China's commitment to green development is intensifying, with the government actively promoting green finance policies. In 2023, the outstanding balance of green loans in China reached 30.05 trillion yuan, marking a significant increase and signaling a strong regulatory push. Guangzhou Rural Commercial Bank is responding by integrating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors into its credit assessment and lending decisions.
This strategic shift means the bank is increasingly looking to support businesses and projects that align with sustainability goals. For instance, Guangzhou Rural Commercial Bank may offer preferential loan terms or dedicated financial products for renewable energy, energy efficiency, pollution control, and circular economy initiatives. This focus on sustainable lending not only addresses regulatory requirements but also taps into a growing market for environmentally conscious investments.
Guangzhou Rural Commercial Bank (GRCB) is navigating increasing global and domestic pressure for robust Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) reporting. This demand stems from investors, regulators, and the public seeking greater transparency on sustainability practices. For instance, by the end of 2024, many publicly listed Chinese companies, including financial institutions, are expected to align with evolving ESG disclosure standards, often referencing international benchmarks.
GRCB is responding by enhancing its ESG data collection and disclosure mechanisms. The bank is actively integrating sustainability considerations into its risk management frameworks and operational strategies. This includes assessing its carbon footprint and developing strategies to reduce its environmental impact, a trend mirrored across the banking sector as it aims to meet 2025 sustainability targets.
Guangzhou Rural Commercial Bank (GRCB) faces significant climate change risks that could impact its financial stability. Extreme weather events, such as intensified typhoons and flooding common in the Pearl River Delta region, pose direct threats to the bank's physical assets and its clients' businesses, potentially leading to increased non-performing loans. For instance, the Guangdong province experienced severe flooding in June 2024, impacting agricultural and industrial sectors that GRCB serves.
Transition risks associated with China's push towards a low-carbon economy also present challenges. As industries shift away from fossil fuels, GRCB's loan portfolio, which may include exposure to carbon-intensive sectors, could see asset valuations decline. The bank is enhancing its risk management frameworks to identify and quantify these climate-related exposures, aiming to stress-test its loan book against various climate scenarios and ensure operational resilience in the face of a changing environment.
Resource Scarcity and Operational Efficiency
Guangzhou Rural Commercial Bank is increasingly focused on its environmental footprint, recognizing the impact of its own operations. This includes managing energy consumption in its branches and offices, optimizing water usage, and minimizing waste generation. The bank is actively pursuing initiatives to enhance resource efficiency across its facilities, aiming to reduce its overall carbon emissions and embed sustainable practices throughout its business model.
In line with its sustainability goals, Guangzhou Rural Commercial Bank has been implementing measures to improve operational efficiency. For instance, as of 2024, the bank has reported a 15% reduction in paper consumption through digital transformation efforts, such as promoting e-statements and online transaction processing. Furthermore, the bank is investing in energy-efficient lighting and HVAC systems in its newly renovated branches, targeting a 10% decrease in electricity usage per square foot by the end of 2025.
- Digitalization Drive: Reduced paper usage by 15% through increased adoption of digital banking services and e-statements as of 2024.
- Energy Efficiency Upgrades: Ongoing investment in energy-efficient technologies for branches, with a target of 10% electricity reduction per square foot by end of 2025.
- Waste Management Programs: Implementation of enhanced recycling programs across all major office locations, aiming for a 20% increase in waste diversion from landfills by 2025.
- Sustainable Procurement: Prioritizing suppliers with strong environmental credentials for office supplies and equipment, contributing to a greener supply chain.
Public Awareness and Stakeholder Expectations for Sustainability
Public awareness of sustainability is rapidly growing, with consumers and investors increasingly scrutinizing companies' environmental and social impact. This heightened awareness directly influences brand perception and customer loyalty, making a strong commitment to environmental protection crucial for Guangzhou Rural Commercial Bank. For instance, a 2024 survey indicated that over 60% of retail investors consider ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) factors when making investment decisions.
Stakeholder expectations extend beyond mere compliance, demanding proactive engagement in sustainable development. This includes how the bank supports green initiatives and its own operational footprint. In 2024, the banking sector saw a 15% increase in demand for green financial products, signaling a clear market shift.
Guangzhou Rural Commercial Bank's dedication to environmental stewardship and sustainable development is therefore a key differentiator. It impacts not only its brand image and customer retention but also its attractiveness to socially responsible investors and its standing within the local community. The bank's 2024 sustainability report highlighted a 10% reduction in its carbon emissions compared to the previous year, a figure well-received by environmental advocacy groups.
- Growing ESG Investment: Global sustainable investment assets are projected to reach $50 trillion by 2025, underscoring the financial imperative for sustainability.
- Consumer Preference: A recent study found that 70% of consumers are willing to pay more for products from sustainable brands.
- Regulatory Scrutiny: Governments worldwide are implementing stricter environmental regulations, making proactive sustainability efforts essential for compliance and risk management.
- Reputational Risk: Negative publicity surrounding environmental negligence can significantly damage a bank's reputation, impacting its market share and access to capital.
China's strong commitment to green finance, evidenced by a 30.05 trillion yuan outstanding balance of green loans in 2023, directly influences Guangzhou Rural Commercial Bank's lending practices. The bank is actively integrating ESG factors, offering preferential terms for renewable energy and pollution control projects, aligning with national sustainability targets. This strategic focus on green finance is not just regulatory compliance but also a response to growing market demand for environmentally conscious investments.
| Factor | Description | Impact on GRCB | 2024/2025 Data/Trend |
| Green Finance Push | Government incentives and regulations promoting sustainable lending. | Opportunities for new loan products and client acquisition in green sectors. | China's green loan balance reached 30.05 trillion yuan in 2023; continued growth expected. |
| Climate Change Risks | Physical risks from extreme weather and transition risks from decarbonization. | Potential for increased non-performing loans and asset devaluation in carbon-intensive sectors. | Guangdong province experienced severe flooding in June 2024, impacting local businesses. |
| ESG Reporting Demand | Increasing pressure from investors and regulators for transparent ESG disclosures. | Need to enhance data collection and reporting mechanisms to meet evolving standards. | Many listed Chinese companies expected to align with enhanced ESG disclosure standards by end of 2024. |
| Operational Sustainability | Focus on reducing the bank's own environmental footprint. | Investment in energy efficiency and waste reduction initiatives. | GRCB reported a 15% reduction in paper consumption by 2024 and targets a 10% electricity reduction per square foot by end of 2025. |
PESTLE Analysis Data Sources
Our PESTLE analysis for Guangzhou Rural Commercial Bank is built on a comprehensive review of official Chinese government publications, financial regulatory bodies, and economic data from reputable institutions like the People's Bank of China and the National Bureau of Statistics of China. This ensures a robust understanding of the political, economic, and legal landscape impacting the bank.
