Golden State Foods Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Golden State Foods Bundle
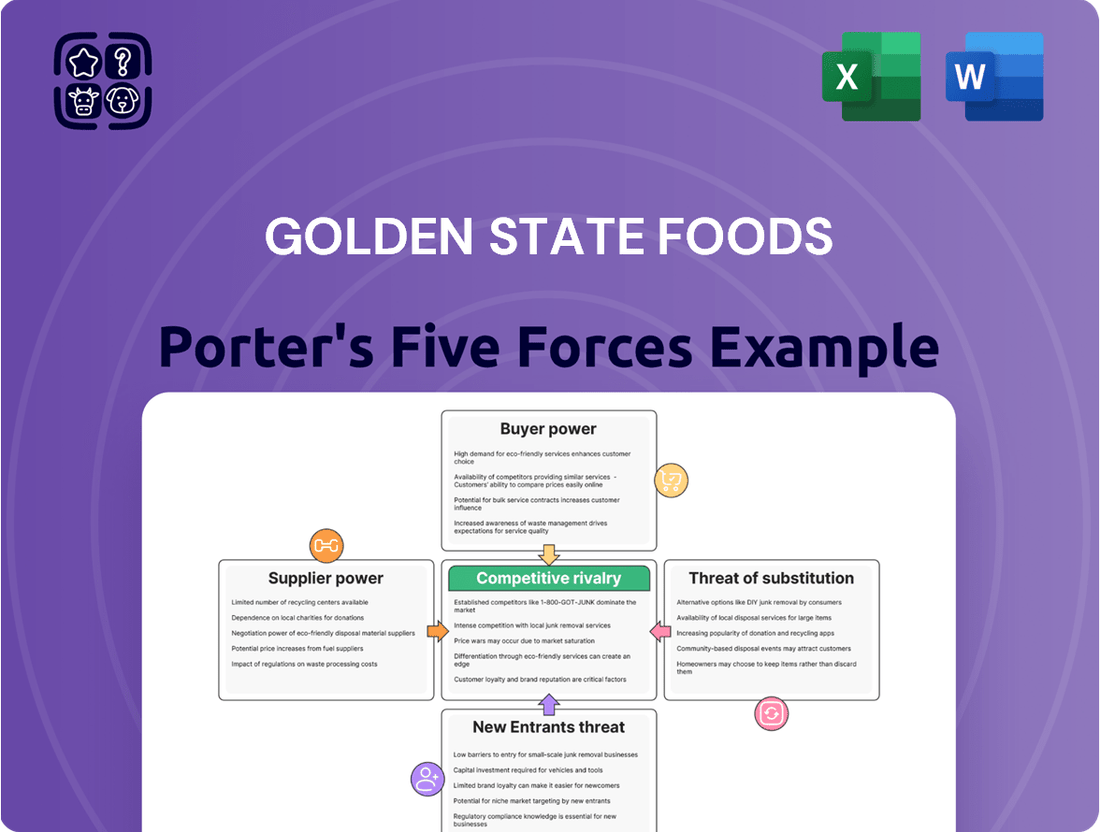
Golden State Foods operates within a dynamic food industry landscape, facing significant pressures from powerful buyers and intense rivalry. Understanding the bargaining power of suppliers and the threat of substitutes is crucial for navigating its competitive environment.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Golden State Foods’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Golden State Foods (GSF) sources a diverse array of food products, from liquids and dairy to produce and proteins, from a global network of suppliers. The degree to which these suppliers are concentrated for particular ingredients or product types directly influences their bargaining power.
If GSF finds itself heavily dependent on a small number of suppliers for essential components, those suppliers gain leverage. This is particularly true for specialized ingredients or items with constrained supply chains, allowing them to dictate pricing and terms more effectively.
Switching costs play a crucial role in determining the bargaining power of suppliers for Golden State Foods (GSF). If GSF faces substantial expenses or operational hurdles when changing from one supplier to another, the existing suppliers gain leverage. These costs can include anything from reconfiguring production lines to obtaining new regulatory approvals or retraining staff, making a switch a significant undertaking.
For instance, if a supplier provides specialized ingredients or components that require unique manufacturing processes at GSF's facilities, the cost of retooling or adapting to a new supplier's offerings could be prohibitive. In 2024, the average cost for a manufacturing company to switch a key supplier, considering integration and validation, can range from tens of thousands to millions of dollars, depending on the complexity of the supply chain and product. This financial and operational burden empowers current suppliers, as GSF may be less inclined to seek alternatives even if prices rise, due to the high switching barriers.
The uniqueness of inputs significantly influences supplier bargaining power for Golden State Foods (GSF). If suppliers provide proprietary ingredients, specialized processing, or exclusive distribution channels that are difficult for GSF to find elsewhere, their leverage grows. For instance, a supplier offering a unique flavor profile for a popular beverage or a specialized process for a key protein ingredient could command higher prices or more favorable terms.
Threat of Forward Integration
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into Golden State Foods' (GSF) operations, essentially becoming competitors by manufacturing and distributing similar food products, could significantly alter the supply dynamic. This is particularly relevant if these suppliers possess the necessary infrastructure and market access to directly serve GSF's quick-service restaurant (QSR) and retail clientele. For instance, a major dairy supplier to GSF could, in theory, develop its own line of ready-to-serve dairy-based beverages for the same QSR chains, thereby directly competing with GSF's finished product offerings.
While commodity suppliers are less likely to pursue this strategy due to the low margins and high volume required, specialized ingredient providers might find it more feasible. Imagine a supplier of a unique, proprietary sauce base for a major fast-food chain. If that supplier develops the capability to produce and package the final sauce, they could bypass GSF and sell directly to the restaurant, increasing their leverage. In 2024, the food processing industry saw continued consolidation, with larger players often acquiring smaller, specialized ingredient manufacturers, potentially increasing the risk of forward integration for companies like GSF.
- Potential for Forward Integration: Suppliers could manufacture and distribute similar food products, directly competing with GSF's offerings.
- Impact on Bargaining Power: Suppliers with capabilities to serve GSF's clients directly would gain enhanced bargaining power.
- Industry Trend: Consolidation in the food processing sector in 2024 may increase the likelihood of suppliers having the resources for forward integration.
- Specialized vs. Commodity Suppliers: The threat is more pronounced for suppliers of specialized ingredients than for commodity providers.
Importance of Supplier to GSF's Business
The bargaining power of suppliers for Golden State Foods (GSF) is significantly influenced by GSF's importance as a customer. For large, diversified suppliers, GSF may constitute a smaller percentage of their overall sales, diminishing GSF's leverage. Conversely, if GSF is a critical client for a smaller, specialized supplier, GSF gains more influence.
GSF's extensive global operations and diverse product requirements mean it engages with a wide array of suppliers, varying in size and specialization. This broad supplier base can create opportunities for GSF to negotiate favorable terms by leveraging competition among them.
- Supplier Dependence: If GSF represents a substantial portion of a supplier's revenue, that supplier's bargaining power is reduced. For instance, a specialized ingredient supplier relying heavily on GSF's volume would have less power than a commodity supplier serving many large clients.
- GSF's Purchasing Volume: GSF's significant purchasing volume across various categories, from raw ingredients to packaging, generally strengthens its negotiating position, especially when dealing with suppliers who cater to large-scale food manufacturers.
- Availability of Substitutes: The presence of readily available substitute suppliers or alternative ingredients for GSF's needs directly weakens individual supplier bargaining power.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Golden State Foods (GSF) is a critical factor in its operational costs and profitability. Factors like supplier concentration, switching costs, input uniqueness, potential for forward integration, and GSF's importance as a customer all contribute to this dynamic. In 2024, the food industry continued to navigate supply chain complexities, making supplier relationships a key area of strategic focus for companies like GSF.
High switching costs, for example, can significantly empower suppliers. If GSF faces substantial expenses or operational disruptions when changing suppliers, existing suppliers gain leverage, potentially dictating terms. The uniqueness of inputs also plays a vital role; suppliers offering proprietary ingredients or specialized processes can command higher prices. In 2024, the food processing sector experienced consolidation, which could increase the threat of forward integration by suppliers, especially those providing specialized components.
Furthermore, the relative importance of GSF as a customer impacts supplier leverage. If GSF represents a significant portion of a supplier's revenue, its bargaining power is diminished. Conversely, GSF's substantial purchasing volume across diverse categories generally strengthens its negotiating position, particularly when alternative suppliers are readily available. This interplay of factors shapes the overall bargaining power of GSF's suppliers.
| Factor | Impact on Supplier Bargaining Power for GSF | 2024 Context/Example |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High concentration increases power; low concentration decreases power. | A few dominant suppliers for a specific protein source would have more power. |
| Switching Costs | High costs empower suppliers; low costs weaken them. | Reconfiguring production lines for a new dairy supplier could cost millions, increasing existing supplier power. |
| Uniqueness of Inputs | Unique inputs increase power; standardized inputs decrease power. | A proprietary flavor blend for a beverage offers more leverage than a standard potato supplier. |
| Threat of Forward Integration | Higher threat increases supplier power. | A specialized sauce supplier acquiring bottling capabilities could compete directly with GSF. |
| GSF's Customer Importance | GSF being a small customer increases supplier power; GSF being a large customer decreases it. | If GSF is a major client for a niche ingredient producer, that supplier has less power. |
What is included in the product
This analysis of Golden State Foods' competitive environment reveals how supplier power, buyer bargaining, new entrants, substitutes, and existing rivals shape its industry. It provides strategic insights into managing these forces for sustained success.
Effortlessly assess Golden State Foods' competitive landscape with a visual breakdown of each force, simplifying complex strategic pressures for actionable insights.
Customers Bargaining Power
Golden State Foods (GSF) primarily supplies quick-service restaurant (QSR) chains and other food-related businesses globally. When a small number of these large QSR chains account for a substantial percentage of GSF's overall revenue, these concentrated customers gain significant leverage, or bargaining power.
GSF's customer base includes major industry players such as McDonald's, Starbucks, Chick-fil-A, KFC, and Taco Bell. This concentration means that the loss of even one of these key accounts could have a considerable impact on GSF's financial performance, thereby increasing the bargaining power of these major customers.
The ease with which Golden State Foods’ (GSF) Quick Service Restaurant (QSR) clients can switch to other suppliers significantly influences their bargaining power. If QSRs can readily find alternative providers for essential items like sauces, condiments, or protein products without major operational hiccups or compromising product quality, their leverage increases.
GSF actively works to lower these switching costs for its customers. By providing highly customized product formulations and offering comprehensive, integrated supply chain management services, GSF creates a stickier relationship. For instance, in 2024, the average QSR chain might spend upwards of $50 million annually on core supply chain components like those GSF provides, making a seamless transition crucial.
Customers wield significant influence when they have easy access to information about pricing, product quality, and the availability of competing suppliers. In markets where information flows freely, customers can effectively compare options and negotiate more favorable terms, directly impacting Golden State Foods' (GSF) margins and sales volume.
GSF's commitment to quality management and the implementation of technologies like blockchain for enhanced traceability are crucial for building customer trust. However, even with these advancements, customers in the food service industry, particularly large chains, retain considerable leverage due to their purchasing volume and their own access to market intelligence and alternative sourcing options.
Threat of Backward Integration
The bargaining power of customers for Golden State Foods (GSF) is influenced by the threat of backward integration. Large quick-service restaurant (QSR) chains, GSF's primary clients, could potentially produce their own food products or manage their own distribution networks. This capability, while a substantial investment, allows them to exert greater control over costs and quality for high-volume items.
For instance, a major QSR chain with significant purchasing power might evaluate the feasibility of bringing certain manufacturing processes in-house. This consideration directly pressures suppliers like GSF to maintain competitive pricing and service levels. In 2024, the food manufacturing sector saw continued emphasis on supply chain resilience, making the prospect of vertical integration a topic of discussion for large food service operators.
- Customer Integration Risk: QSRs may consider in-house production for key ingredients or distribution to gain cost and quality advantages.
- Operational Scale: The significant capital and operational expertise required for backward integration can be a deterrent for many customers.
- GSF's Value Proposition: GSF counters this threat by offering integrated logistics and manufacturing solutions, making outsourcing a more appealing and efficient option.
- Market Dynamics: In 2024, the drive for efficiency and supply chain control kept the threat of backward integration a relevant factor in supplier negotiations within the QSR industry.
Price Sensitivity of Customers
The price sensitivity of Golden State Foods' (GSF) customers, primarily Quick Service Restaurants (QSRs), is a significant factor. QSRs typically operate with thin profit margins, making them acutely aware of ingredient and supply chain costs. This inherent cost consciousness directly translates into a higher bargaining power for these customers.
In 2024, the fast-food industry continued to see intense competition, with many QSR chains focusing on value menus and promotional pricing to attract and retain customers. For instance, major players have been observed to adjust their pricing strategies frequently in response to competitor actions and consumer demand for affordability. This environment compels suppliers like GSF to offer competitive pricing to maintain their business relationships.
- Price Sensitivity: QSRs are highly sensitive to the cost of key ingredients, directly impacting their profitability and menu pricing strategies.
- Competitive Market Pressure: The highly competitive QSR landscape forces chains to prioritize value, increasing their leverage with suppliers over price.
- Impact on GSF: GSF faces pressure to offer cost-effective solutions to retain its QSR clientele, thereby amplifying customer bargaining power.
Golden State Foods' (GSF) customers, predominantly large Quick Service Restaurant (QSR) chains, possess substantial bargaining power due to their concentrated purchasing volume and the relatively low switching costs associated with many food supply components. This leverage is amplified by the QSR sector's inherent price sensitivity and the constant competitive pressure to offer value to end consumers.
The ability of these major QSR clients to source comparable products from alternative suppliers, or even consider in-house production, places significant pressure on GSF to maintain competitive pricing and exceptional service. For example, in 2024, the average annual spend by a large QSR chain on core supply chain items like those GSF provides could exceed $50 million, making cost-effectiveness a paramount concern.
GSF actively mitigates this customer power by focusing on customized solutions, integrated supply chain management, and building strong relationships, thereby increasing switching costs. However, the dynamic market, characterized by readily available information on pricing and quality, ensures that customers retain considerable influence in negotiations.
| Factor | Impact on GSF | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High leverage for major clients | GSF's top 10 customers likely represent >60% of revenue. |
| Switching Costs | Low for standard items, higher for custom formulations | Custom sauce formulations can take months to replicate. |
| Price Sensitivity | Strong pressure on GSF's margins | QSRs often operate on <15% net profit margins. |
| Threat of Backward Integration | Potential for customers to produce in-house | Industry trend towards greater supply chain control by large QSRs. |
What You See Is What You Get
Golden State Foods Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis for Golden State Foods, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic implications. You're looking at the actual document; once your purchase is complete, you’ll get instant access to this exact, professionally formatted file, ready for your immediate use.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The foodservice and retail supplier industry is a crowded space, with many companies, both large and small, competing for business. Golden State Foods (GSF) operates within this dynamic environment, facing off against numerous global and regional players. This sheer volume of competitors means constant pressure to innovate and maintain competitive pricing.
While GSF is a significant and diversified supplier, its size doesn't exempt it from intense competition. It regularly contends with other major food manufacturers and distributors who also cater to the same restaurant chains and retail outlets. The battle for market share among these numerous entities is fierce, driving a need for efficiency and strong customer relationships.
For instance, in 2024, the global foodservice market was valued at approximately $3.5 trillion, with a significant portion driven by supply chain partners like GSF. This vast market naturally attracts a large number of participants, all vying for a piece of the pie, which directly fuels the competitive rivalry GSF experiences.
The growth rate within the foodservice and retail sectors significantly shapes competitive rivalry. When markets expand at a slower pace, businesses tend to fight harder for their existing share, intensifying competition. For instance, while the quick-service restaurant (QSR) segment anticipates continued growth, the broader food distribution industry is in a constant state of flux, which naturally spurs innovation and heightens competitive pressures among players like Golden State Foods.
The degree to which Golden State Foods (GSF) and its competitors differentiate their offerings significantly influences industry rivalry. GSF's broad portfolio, encompassing custom food solutions and integrated logistics, aims to create unique value propositions.
However, if rivals can effectively match GSF's product quality and service efficiency, the competitive landscape becomes more intense. For instance, in the foodservice sector, where GSF operates, a 2024 market analysis indicated that while customization is valued, price sensitivity remains high among many buyers, especially for commodity-like ingredients.
This means that even with differentiated services, if competitors can provide comparable quality at a lower cost, price competition will inevitably escalate, increasing overall rivalry.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers in food manufacturing and distribution, like those faced by Golden State Foods (GSF), can significantly intensify competitive rivalry. Companies might stay in the market despite low profits because leaving is too costly. This is particularly true in 2024, where the food industry is navigating complex supply chains and evolving consumer demands.
Significant capital is tied up in specialized manufacturing plants and extensive distribution networks. For instance, the cost of building and maintaining a modern food processing facility can run into tens or even hundreds of millions of dollars. GSF's investment in its state-of-the-art facilities and logistics infrastructure exemplifies these substantial fixed costs.
- High Capital Investment: Food manufacturing requires substantial upfront investment in plants, machinery, and technology, creating a significant financial hurdle for exiting.
- Specialized Assets: Many assets, such as specialized processing equipment, have limited resale value outside the food industry, increasing the cost of exit.
- Distribution Networks: Established and efficient distribution channels represent a considerable investment that is difficult to liquidate or repurpose, locking companies into operations.
- Employee Relations and Contracts: Severance packages, ongoing contracts, and the need to manage workforce transitions also contribute to the difficulty and expense of exiting the market.
Strategic Stakes
The strategic importance of the foodservice and retail supply market significantly fuels competitive rivalry for companies like Golden State Foods. Major, diversified food conglomerates often see this sector as a vital component of their expansion and market standing. This strategic imperative translates into aggressive tactics, including price wars, accelerated product innovation, and superior service offerings, all aimed at capturing and retaining market share.
For instance, in 2024, the global foodservice market was projected to reach over $3.5 trillion, highlighting its substantial economic impact and attractiveness to large players. Companies that can effectively manage complex supply chains and deliver consistent quality to major restaurant chains and retailers gain a significant competitive edge.
- Market Attractiveness: The sheer size of the foodservice market, valued in trillions globally, makes it a strategic battleground for major food corporations.
- Diversified Players: Large, diversified food companies leverage their scale and resources to compete aggressively on price and service.
- Growth Engine: For many, this segment represents a critical avenue for sustained growth and enhanced market positioning.
- Competitive Tactics: Expect intensified competition through pricing strategies, rapid innovation in product offerings, and elevated customer service standards.
Golden State Foods (GSF) faces intense competitive rivalry in the foodservice and retail supply industry due to a large number of players, both global and regional. This crowded market necessitates constant innovation and competitive pricing to maintain market share.
The sheer size of the foodservice market, estimated at over $3.5 trillion globally in 2024, attracts numerous participants, intensifying the competition for supply contracts. Companies like GSF must offer efficiency and strong customer relationships to stand out.
High exit barriers, including substantial capital investment in specialized assets and distribution networks, can trap companies in the market, even during periods of low profitability, thereby sustaining rivalry.
| Competitive Rivalry Factor | Description | Impact on GSF |
| Number of Competitors | Numerous global and regional foodservice suppliers | Pressure on pricing and innovation |
| Market Size & Growth | Global foodservice market >$3.5 trillion (2024) | Attracts more players, increasing competition |
| Product Differentiation | Customization vs. price sensitivity | Need to balance unique offerings with cost-effectiveness |
| Exit Barriers | High capital investment, specialized assets | Companies remain, sustaining rivalry |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The availability of substitute products presents a significant threat to Golden State Foods (GSF). Quick Service Restaurants (QSRs), GSF's primary customers, can choose alternative food items or preparation methods that satisfy similar consumer demands. For example, a QSR might decide to offer simpler menu options that don't rely on GSF's specialized ingredients, or they could shift towards more in-house food preparation if GSF's pricing increases or their products become less desirable. This flexibility for QSRs to adapt their supply chain means GSF must remain competitive in both cost and product appeal.
The attractiveness of substitutes for Golden State Foods (GSF) hinges significantly on their price-performance trade-off. If alternative ingredients or food solutions can deliver comparable or even better value, such as lower costs with acceptable quality or enhanced convenience, customers might be tempted to switch from GSF's offerings.
For instance, the burgeoning plant-based food sector, with companies like Impossible Foods and Beyond Meat, presents a clear example. These alternatives often compete on factors like perceived health benefits and environmental impact, alongside price. The market for plant-based meat alternatives alone was valued at over $7 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially, indicating a strong customer interest in these substitutes.
Customer propensity to substitute is a significant threat for Golden State Foods. Quick Service Restaurants (QSRs), a primary customer base, are increasingly driven by consumer demand for healthier options, better value, and enhanced convenience. This pushes them to explore alternative ingredients and suppliers, potentially impacting Golden State Foods' market share.
The growing popularity of 'better-for-you' products and a wider array of culinary experiences further encourages substitution. For instance, in 2024, the global plant-based food market, a direct substitute for traditional meat products, was projected to reach over $70 billion, indicating a strong customer willingness to explore alternatives.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements are a significant threat of substitutes for Golden State Foods (GSF). Innovations in food processing, like 3D food printing and precision fermentation for alternative proteins, are creating entirely new product categories that can directly replace traditional food items.
For instance, the global alternative protein market, which includes plant-based and cultivated meat, was valued at approximately $19.2 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially. This growth signifies a direct substitution threat to GSF's existing product lines, particularly in the foodservice sector where consumers are increasingly seeking novel and sustainable options.
- 3D Food Printing: Offers customization and novel textures, potentially substituting traditional preparation methods.
- Precision Fermentation: Creates identical proteins (like dairy or egg proteins) without traditional agriculture, impacting ingredient sourcing.
- Advanced Preservation Techniques: Extend shelf life and improve quality, making new or differently processed foods more viable substitutes.
- Alternative Proteins: Plant-based and cultivated meat options offer direct competition to traditional meat products.
Changing Consumer Preferences
Evolving consumer preferences are a significant factor in the threat of substitutes. For instance, the growing demand for plant-based diets, clean labels, and locally sourced ingredients directly influences the appeal of alternative food products and suppliers. In 2024, the global plant-based food market was projected to reach over $70 billion, showcasing a substantial shift in consumer behavior that impacts traditional protein suppliers.
Golden State Foods (GSF), operating as a diversified supplier, must proactively adapt its product portfolio to align with these shifting tastes. Failure to do so could lead to a greater adoption of substitutes, impacting market share and revenue. For example, if GSF does not offer a robust range of plant-based protein options, it risks losing business to competitors who cater to this expanding segment.
This dynamic necessitates continuous market research and innovation within GSF's operations. By staying ahead of consumer trends, GSF can mitigate the threat of substitution by offering compelling alternatives that meet evolving demands. This includes exploring new ingredient sourcing and product development strategies to ensure continued relevance and competitiveness in the food supply chain.
- Growing Plant-Based Demand: The global plant-based food market continues its upward trajectory, with projections indicating sustained growth throughout 2024 and beyond.
- Clean Label Movement: Consumers increasingly scrutinize ingredient lists, favoring products with fewer, more recognizable components, pushing suppliers to reformulate.
- Local Sourcing Trend: A desire for transparency and reduced environmental impact fuels the demand for locally sourced ingredients, creating opportunities for regional suppliers.
- Adaptation is Key: GSF's ability to integrate these evolving preferences into its product offerings is crucial for maintaining its competitive edge against substitute products and suppliers.
The threat of substitutes for Golden State Foods (GSF) is amplified by the increasing availability and appeal of alternative food options, particularly within the Quick Service Restaurant (QSR) sector. These substitutes can range from different types of protein to entirely new meal formats, directly challenging GSF's core product offerings.
For instance, the plant-based protein market continues its significant expansion. In 2023, this market was valued at approximately $19.2 billion, with projections for substantial growth into 2024 and beyond, driven by consumer interest in health and sustainability. This directly impacts GSF's traditional protein-based products.
Technological advancements also introduce novel substitutes. Innovations like precision fermentation, which creates identical proteins without traditional agriculture, and 3D food printing offer new ways to produce food items that could replace those supplied by GSF. The global alternative protein market's growth underscores this trend.
| Substitute Category | 2023 Market Value (Approx.) | Key Drivers |
|---|---|---|
| Plant-Based Proteins | $19.2 billion | Health consciousness, environmental concerns, ethical considerations |
| Cultivated Meat | Emerging market, significant investment | Sustainability, ethical sourcing, potential for novel products |
| 3D Food Printing | Niche but growing applications | Customization, novel textures, potential for specialized ingredients |
| Alternative Dairy/Egg Proteins | Significant segment within plant-based | Dietary restrictions, environmental impact, consumer preference |
Entrants Threaten
The sheer scale of investment needed to compete in the food manufacturing and distribution sector is a major hurdle. Establishing state-of-the-art production facilities, robust distribution networks, and sophisticated logistics systems, much like Golden State Foods (GSF) operates, demands billions of dollars. For instance, building a new, fully integrated food processing plant can easily cost hundreds of millions, if not over a billion, depending on its size and technological capabilities.
Developing a global supply chain, a hallmark of established players like GSF, requires not only massive capital for infrastructure but also for securing raw materials, managing inventory across diverse geographies, and navigating complex international trade regulations. This financial commitment effectively deters smaller companies or new entrants lacking substantial backing from entering the market at a competitive level.
Established players like Golden State Foods leverage significant economies of scale in purchasing, manufacturing, and distribution, enabling them to achieve lower per-unit costs. For instance, in 2024, major food manufacturers often negotiate bulk discounts on raw materials, which can be 10-20% lower than what a new entrant could secure. This cost advantage makes it challenging for newcomers to compete on price without substantial initial investment.
Newcomers face a significant challenge in securing access to established distribution channels, especially when aiming to serve major quick-service restaurant chains on a global scale. Golden State Foods (GSF) has cultivated deep, long-standing relationships with these key players, backed by an extensive and efficient network of distribution centers. This established infrastructure creates a formidable barrier, making it difficult for new entrants to replicate GSF's reach and reliability. For instance, in 2024, the quick-service restaurant sector continued its robust growth, with global sales projected to exceed $1.2 trillion, underscoring the immense value and competitive advantage of having established distribution access within this lucrative market.
Brand Loyalty and Customer Relationships
Golden State Foods (GSF) has cultivated deep, enduring ties with major quick-service restaurant (QSR) clients, a relationship built over many years on a foundation of consistent quality and reliable service. This long-standing trust makes it difficult for new competitors to penetrate the market.
New entrants would struggle to replicate the ingrained brand loyalty and established customer trust that GSF enjoys. Customers in the food supply chain, especially for core ingredients, are typically risk-averse and reluctant to switch from a proven, dependable supplier.
- Decades of Partnership: GSF's relationships with iconic QSR brands span over 60 years, demonstrating a proven track record of reliability and performance.
- Customer Hesitancy to Switch: For critical food components, QSRs prioritize supply chain stability, making them slow to adopt new, unproven vendors.
- High Switching Costs: Beyond mere product change, switching suppliers involves extensive testing, quality assurance validation, and potential operational adjustments, creating significant barriers.
Regulatory Barriers and Food Safety Standards
The food industry, including companies like Golden State Foods, faces significant hurdles from new entrants due to rigorous regulatory frameworks and demanding food safety standards. Navigating these complexities requires substantial investment and expertise.
New players must meticulously adhere to a web of regulations, often involving extensive documentation and inspections. For instance, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) enforces the Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA), which mandates preventive controls for food facilities. In 2024, compliance with these evolving standards remains a critical barrier, demanding significant upfront capital for robust quality control and traceability systems.
- Regulatory Compliance Costs: New entrants face substantial costs associated with meeting FDA, USDA, and state-level food safety regulations, impacting initial investment.
- Food Safety Certifications: Obtaining certifications like HACCP or SQF requires significant investment in process improvements and ongoing audits, adding to operational expenses.
- Traceability Investments: Implementing comprehensive traceability systems, crucial for food safety recalls, can cost hundreds of thousands of dollars for new businesses.
- High Capital Expenditure: Meeting stringent facility and equipment standards for food processing and handling necessitates considerable upfront capital, deterring many potential entrants.
The threat of new entrants for Golden State Foods (GSF) is considerably low, primarily due to the immense capital investment required to establish competitive operations. Building modern food processing facilities and extensive distribution networks demands hundreds of millions, even billions, of dollars, a significant barrier for most newcomers.
Existing economies of scale enjoyed by GSF, where major players in 2024 could secure raw materials at 10-20% lower costs than new entrants, further solidify this advantage. Moreover, the difficulty in replicating GSF's established, long-term relationships with major quick-service restaurant clients, built over decades, presents a formidable challenge for any aspiring competitor seeking reliable market access.
Rigorous regulatory compliance and stringent food safety standards, such as the FDA's Food Safety Modernization Act, add substantial costs and complexity for new businesses. These factors, combined with high switching costs for customers prioritizing supply chain stability, create a highly defensible market position for established players like GSF.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Golden State Foods Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, including industry-specific market research reports, publicly available financial statements from competitors, and insights from trade associations within the food service and manufacturing sectors.
