Good Times Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Good Times Bundle
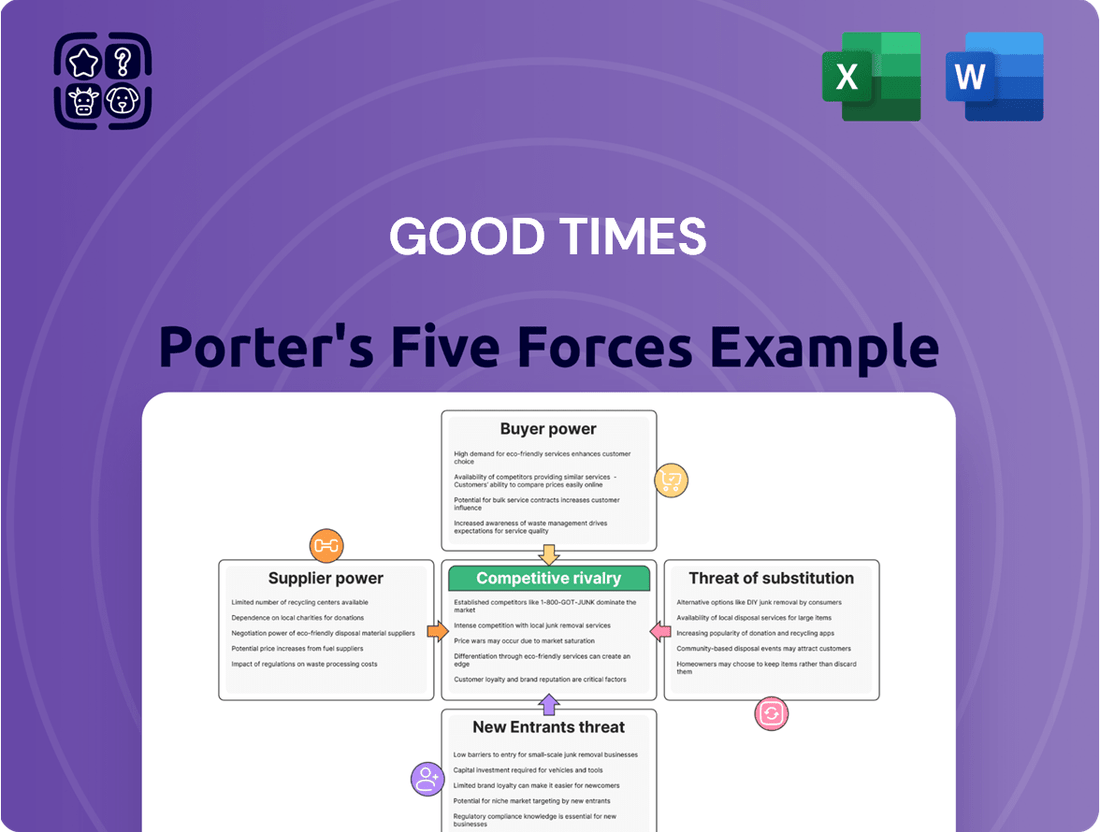
Good Times's Porter's Five Forces Analysis reveals a competitive landscape shaped by moderate buyer power and intense rivalry within the fast-food sector. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating the challenges and opportunities ahead.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Good Times’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Good Times Restaurants Inc.'s focus on high-quality, all-natural ingredients means they might depend on a limited number of suppliers who can consistently provide these specific components. If these suppliers are few and concentrated, they gain considerable leverage in setting prices and dictating terms. For instance, if a key supplier for a unique, all-natural beef blend or a specialized dairy source has few other customers of similar scale, they can command higher prices, impacting Good Times' cost structure.
The restaurant industry, including Good Times, is grappling with persistent increases in food costs, especially for essential ingredients like beef. This inflationary pressure enhances supplier leverage, allowing them to dictate higher prices, which directly squeezes restaurant profit margins. For instance, the rising cost of ground beef has a tangible effect on Good Times' operational expenses.
Geopolitical instability, transportation issues, and extreme weather events are increasingly impacting global supply chains, leading to ingredient shortages and rising costs for businesses like Good Times. For instance, the ongoing conflicts and trade tensions in various regions can create significant bottlenecks. These disruptions can empower suppliers who demonstrate resilience and can guarantee a consistent flow of essential ingredients, potentially allowing them to command higher prices.
Switching Costs for Unique Inputs
Good Times' focus on 'all-natural' ingredients and specific quality benchmarks for its burgers and custard can significantly increase switching costs if it needs to change specialized suppliers. This is because finding, vetting, and ensuring the consistent quality of new suppliers can be a time-consuming and costly process, potentially requiring menu item reformulation.
For instance, a specialized supplier of a unique seasoning blend or a particular cut of beef might have proprietary processes. Good Times would need to invest in rigorous testing and potentially pilot programs to guarantee that any new supplier meets their exact specifications. This is particularly relevant as the fast-casual market, where Good Times operates, increasingly emphasizes ingredient transparency and quality to attract and retain customers.
- High Switching Costs: For specialized, high-quality ingredients like those Good Times uses, finding and qualifying new suppliers can be a lengthy and expensive undertaking.
- Quality Consistency: Maintaining the brand's reputation for 'all-natural' and premium quality necessitates ensuring new suppliers meet stringent standards, adding to the cost and complexity of a switch.
- Menu Reformulation: Changes in key ingredients might require Good Times to re-evaluate and potentially reformulate existing menu items, incurring research and development expenses.
Labor Costs in Supply Chain
Suppliers are increasingly passing on their own rising labor costs to businesses, including restaurants. This means the price of raw materials and finished goods can go up as suppliers try to protect their own profit margins. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics reported an average increase in hourly earnings for private industry workers. This ripple effect throughout the supply chain amplifies the bargaining power of suppliers.
These increased costs are a significant factor in the overall bargaining power of suppliers. When suppliers face higher expenses, from wages to raw materials, they are more likely to demand higher prices from their customers to maintain their own profitability. This is particularly relevant in sectors with tight margins, where even small cost increases can have a substantial impact.
- Rising Labor Expenses: Suppliers are experiencing higher wage demands and benefits costs for their workforce.
- Cost Pass-Through: These increased labor expenses are frequently passed on to buyers in the form of higher product prices.
- Supply Chain Inflation: This dynamic contributes to broader inflationary pressures across various industries.
- Supplier Profitability: Suppliers need to ensure their own financial health, leading them to adjust pricing in response to their own cost increases.
Good Times' reliance on specialized, high-quality ingredients means suppliers with unique offerings hold significant power. If these suppliers are few and their products are critical, they can dictate terms and prices, impacting Good Times' cost structure.
Rising food costs, particularly for beef, directly enhance supplier leverage in 2024, squeezing restaurant profit margins. Geopolitical events and supply chain disruptions further empower resilient suppliers who can guarantee consistent ingredient flow, allowing them to command higher prices.
The bargaining power of suppliers is amplified by their ability to pass on increased labor costs. As reported by the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, average hourly earnings for private industry workers saw increases in 2024, a trend that suppliers pass to buyers, contributing to overall supply chain inflation and impacting Good Times' operational expenses.
| Factor | Impact on Good Times | 2024 Data/Trend |
| Supplier Concentration | Limited suppliers for specialized ingredients increase their leverage. | Not directly quantifiable without specific supplier data for Good Times. |
| Ingredient Quality Standards | High standards for 'all-natural' items increase switching costs. | Fast-casual market emphasizes ingredient transparency, reinforcing this. |
| Rising Food Costs | Directly increases cost of goods sold. | Beef prices, a key ingredient, have seen significant inflationary pressure. |
| Labor Cost Pass-Through | Suppliers increase prices to cover their own rising labor expenses. | U.S. private industry hourly earnings increased in 2024. |
What is included in the product
Uncovers key drivers of competition, customer influence, and market entry risks tailored to Good Times, providing actionable insights into its competitive landscape.
Effortlessly identify and quantify competitive threats with a visual, interactive dashboard that simplifies complex market dynamics.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customers in quick-service and fast-casual dining are showing a heightened sensitivity to price. This is particularly evident as inflation continues to make eating out more expensive than preparing meals at home. For instance, the U.S. Consumer Price Index for Food Away From Home saw a notable increase in 2023, outpacing the rise in Food At Home costs.
This price consciousness directly translates into increased customer power. When prices climb too high, consumers readily switch to cheaper options or simply cut back on dining out altogether. This behavior forces businesses to carefully consider their pricing strategies to retain their customer base.
The burger and quick-service food market is incredibly crowded, with countless competitors vying for customer attention. This means if a customer isn't happy with Good Times, they can easily find another place to eat. For instance, in 2024, the quick-service restaurant sector in the US alone generated over $300 billion in revenue, highlighting the sheer volume of options available.
For a quick-service restaurant like Good Times, the bargaining power of customers is amplified by low switching costs. Consumers can easily move between Good Times and competitors like McDonald's or Burger King with no contractual obligations or substantial financial investment. This ease of transition means customers are not locked in, making loyalty a fleeting commodity. In 2024, the fast-food industry saw continued intense competition, with many chains offering value menus and loyalty programs, further reducing the perceived cost of switching for consumers.
Influence of Digital Platforms and Information
The proliferation of digital platforms significantly amplifies customer bargaining power in the restaurant industry. With the rise of digital ordering, mobile apps, and social media, customers now have unprecedented access to information. They can easily compare menus, pricing, read reviews, and discover promotions from a wide array of restaurants. This heightened transparency and the sheer convenience of accessing multiple options at their fingertips empower consumers to make more informed choices and demand better value.
This digital shift allows customers to quickly assess and switch between providers, thereby increasing their leverage. For instance, a 2024 report indicated that over 70% of diners use online reviews and ratings to decide where to eat. Furthermore, the ease of ordering through third-party delivery apps means customers can compare delivery times and fees alongside menu prices, creating a more competitive landscape for restaurants. This dynamic directly translates to increased bargaining power for consumers.
- Enhanced Information Access: Digital platforms provide customers with detailed insights into restaurant offerings, pricing, and quality through reviews and ratings.
- Convenience of Comparison: Mobile apps and online services enable swift comparison of multiple restaurants, facilitating informed decision-making.
- Increased Switching Likelihood: Greater transparency and ease of access to alternatives encourage customers to switch providers based on price, quality, or promotions.
- Data-Driven Consumerism: Customers leverage digital information to negotiate better deals or choose providers offering superior value, a trend amplified in 2024.
Demand for Customization and Healthier Options
Modern consumers, especially younger demographics like Gen Z, are increasingly vocal about their desire for diverse menu options, the ability to personalize their orders, and a greater emphasis on healthier or plant-based choices. Good Times' responsiveness to these evolving preferences, such as incorporating all-natural ingredients, directly impacts customer loyalty and purchasing decisions. For instance, a 2024 consumer survey indicated that 68% of respondents consider ingredient transparency when choosing a restaurant, and 55% actively seek out healthier or plant-based menu items.
Failure to adapt to these changing tastes can push customers toward competitors who more readily align with their dietary needs or personal values. This growing demand for customization and healthier alternatives significantly strengthens the bargaining power of customers, as they have more choices than ever before.
- Growing Demand for Customization: Consumers expect to tailor their meals to specific preferences.
- Rise of Health-Conscious Consumers: A significant portion of the market prioritizes healthier and plant-based options.
- Impact on Purchasing Decisions: Ingredient quality and menu variety are key drivers of customer choice.
- Competitive Landscape: Restaurants failing to adapt risk losing customers to more accommodating competitors.
Customers wield significant power when they have numerous alternatives and low costs to switch. In the quick-service restaurant sector, this is particularly true. In 2024, the U.S. fast-food market, valued at over $300 billion, offers a vast array of choices, making it simple for consumers to move between brands like Good Times and its competitors.
The ease of switching is further enhanced by digital platforms, which provide extensive price and quality comparisons. For example, a 2024 survey revealed that over 70% of diners use online reviews to guide their dining decisions, empowering them to demand better value and readily switch if unsatisfied.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power | 2024 Data/Context |
| Number of Competitors | High | U.S. fast-food market revenue > $300 billion |
| Switching Costs | Low | Minimal financial or contractual barriers to changing restaurants |
| Information Availability | High | >70% of diners use online reviews for decisions |
| Price Sensitivity | High | Inflation driving consumers to seek value and cheaper alternatives |
Same Document Delivered
Good Times Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Good Times Porter's Five Forces Analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, offering a detailed examination of competitive forces within the industry. You're looking at the actual document, meaning no surprises or placeholder content will be present in your downloaded file. Once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact, professionally formatted analysis, ready for your strategic planning needs.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The quick-service restaurant (QSR) and fast-casual burger markets are incredibly crowded, with a vast number of competitors. Think of global giants like McDonald's and Burger King alongside numerous regional players and local burger joints. This sheer volume of businesses all chasing the same customers means competition is fierce, making it tough for any single brand to truly capture attention and market share.
Consumers are highly sensitive to price, leading competitors in the fast-food industry to engage in aggressive pricing and value-driven promotions. This intense competition forces companies like Good Times to meticulously balance customer perception of value with their own profitability. For instance, in 2024, many quick-service restaurants continued to emphasize value menus and limited-time offers to capture market share.
Major industry players are heavily investing in national value platforms to solidify their competitive position. This strategy aims to attract a broad customer base by offering consistently low prices on popular items. In 2024, we saw significant marketing spend dedicated to promoting these value propositions, directly impacting the competitive landscape for all brands, including Good Times.
Competitive rivalry within the fast-casual burger segment is intense, fueled by a constant drive for menu innovation. Companies like Good Times are actively introducing new burger creations, limited-time offers, and catering to evolving consumer preferences with healthier and plant-based options. This dynamic environment demands continuous adaptation to capture and retain customer attention.
Good Times aims to stand out through its commitment to 'all-natural' ingredients and a 'chef-driven menu' for its Bad Daddy's brand. However, even with these differentiators, the need for ongoing innovation remains paramount. For instance, the fast-casual market saw significant growth in plant-based options in 2023, with sales of plant-based meat alternatives reaching an estimated $8 billion in the US, highlighting the pressure to innovate in this area.
Intense Digital and Marketing Investments
Competitors are pouring money into digital upgrades, like AI for ordering and better mobile delivery, plus loyalty programs. This is all about making customers happier and operations smoother. Good Times needs substantial capital to match rivals who are using technology to boost sales and tailor their services.
For instance, McDonald's, a major player, announced in 2024 plans to invest $2.5 billion in technology and digital initiatives through 2027, aiming to enhance its customer experience and operational efficiency. This level of investment underscores the intense pressure on all quick-service restaurants to innovate digitally.
- Digital Transformation Costs: Competitors are investing heavily in AI, mobile apps, and delivery infrastructure.
- Customer Experience Focus: Technology is being used to personalize offerings and improve service speed.
- Capital Outlay Necessity: Good Times must allocate significant funds to remain competitive in this tech-driven landscape.
- Sales and Personalization Drivers: Rivals are leveraging technology to directly impact sales and customer engagement.
Operational Efficiency and Labor Challenges
Restaurants are grappling with persistent labor cost increases and widespread staffing shortages, directly affecting how efficiently they operate and the quality of service they can provide. In 2024, the restaurant industry continued to see these pressures, with many businesses struggling to find and retain qualified staff, driving up wages and benefits offered.
To counter these issues, competitors are heavily investing in ways to boost labor productivity and adopt technologies such as self-service kiosks. These innovations aim to reduce reliance on manual labor and streamline operations, creating a competitive imperative for all businesses in the sector to enhance their own operational models and staffing strategies.
- Rising Labor Costs: In 2024, average hourly wages for restaurant workers saw continued upward trends, with some regions experiencing increases of 5-10% year-over-year.
- Staffing Shortages: Many quick-service restaurants reported being understaffed by 15-20% throughout much of 2024, impacting operating hours and service speed.
- Technology Adoption: Investment in automation, including self-ordering kiosks and AI-powered kitchen management systems, increased significantly in 2024 as a direct response to labor challenges.
The competitive rivalry in the burger market, including for brands like Good Times, is intense due to numerous players, price sensitivity, and significant investment in digital and operational improvements. Competitors are pushing value menus and national platforms, forcing Good Times to balance cost with customer value perception.
Innovation in menu offerings, such as plant-based options, is crucial, as demonstrated by the estimated $8 billion market for plant-based meat alternatives in the US in 2023. Furthermore, substantial capital is required to match rivals' digital investments, like McDonald's $2.5 billion commitment to technology through 2027.
Labor challenges, including rising wages and shortages, are driving competitors to invest in technology like self-service kiosks to boost productivity. In 2024, average hourly wages for restaurant workers saw increases of 5-10%, with many businesses reporting 15-20% understaffing.
| Competitive Factor | 2024 Impact/Trend | Example Investment/Data |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Competitors | High | McDonald's, Burger King, numerous regional and local chains |
| Price Sensitivity | High | Emphasis on value menus and limited-time offers |
| Digital Investment | Significant | McDonald's $2.5B tech investment (2024-2027) |
| Menu Innovation | Continuous | Growth in plant-based options (US market ~$8B in 2023) |
| Labor Costs & Shortages | Increasing | 5-10% wage increase, 15-20% understaffing reported in 2024 |
SSubstitutes Threaten
As inflation continues to impact consumer spending, home cooking and grocery shopping present increasingly compelling alternatives to dining out. This trend is particularly noticeable when the cost difference between preparing meals at home and eating at restaurants widens significantly.
In 2024, the average US household spent approximately $5,700 on food annually, with roughly half of that amount allocated to groceries. This figure highlights the substantial portion of budgets dedicated to food, making cost-saving measures like home cooking a primary consideration for many consumers.
Beyond direct burger rivals, consumers have a vast array of fast-casual and casual dining choices. These include pizza parlors, sandwich shops, and salad bars, all offering quick and quality meal solutions. This broad spectrum of alternatives can easily divert customers from Good Times, even if they are seeking a convenient meal, by satisfying different culinary preferences.
The burgeoning consumer preference for health-conscious and plant-based food choices poses a substantial threat of substitutes for traditional QSR burger offerings. Many quick-service restaurants and fast-casual chains are actively broadening their menus to incorporate these healthier alternatives, potentially diverting customers who prioritize wellness over conventional fast food. For instance, by mid-2024, the plant-based food market in the US was projected to reach over $7 billion, demonstrating a clear shift in consumer spending habits.
Meal Kits and Ready-to-Eat Grocery Items
The convenience of meal kits and ready-to-eat grocery items poses a significant threat to restaurants. These alternatives cater to consumers seeking quick and easy meal solutions, often at a perceived lower cost or with a healthier image. For instance, the global meal kit delivery service market was valued at approximately $15 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially, indicating a strong consumer shift towards these convenient options.
This trend directly impacts restaurants by offering a viable substitute for dining out. Busy professionals and families are increasingly opting for these services, reducing their reliance on traditional restaurant meals. The market for pre-prepared and ready-to-eat meals in supermarkets also continues to expand, further intensifying this competitive pressure.
- Convenience Factor: Meal kits and ready-to-eat grocery items offer a time-saving alternative to cooking from scratch or dining out.
- Cost Perception: Consumers often perceive these options as more budget-friendly than restaurant meals, especially when factoring in the cost of ingredients and potential waste.
- Health Consciousness: Many meal kit services emphasize fresh ingredients and portion control, appealing to health-conscious consumers.
- Market Growth: The expanding market for meal kits and ready-to-eat foods signifies a growing consumer preference for these substitutes.
Alternative Food Service Channels
The rise of ghost kitchens, food trucks, and improved grab-and-go services at non-traditional locations like convenience stores presents a significant threat of substitutes for conventional quick-service restaurants. These alternatives offer comparable convenience and often a wider variety of culinary options, directly competing for consumer dining occasions.
For instance, the ghost kitchen sector has seen substantial growth, with some estimates suggesting it could reach over $1 trillion globally by 2030. In 2024, many established QSR brands are themselves investing in or partnering with ghost kitchen operations to expand their reach without the overhead of traditional brick-and-mortar stores, blurring the lines of substitution.
- Ghost Kitchens: These delivery-only kitchens operate without a storefront, reducing overhead and allowing for greater menu flexibility and faster expansion into new markets.
- Food Trucks: Offering mobility and lower startup costs, food trucks provide diverse and often gourmet options, catering to specific locations and events.
- Convenience Store Enhancements: Many convenience stores are upgrading their food offerings to include fresh meals and prepared foods, directly competing with QSRs for lunch and dinner traffic.
- Online Food Aggregators: Platforms like DoorDash and Uber Eats have made it easier than ever for consumers to access a wide array of dining options, including those from substitute channels, further intensifying competitive pressure.
The threat of substitutes for Good Times is significant, driven by evolving consumer habits and a widening array of convenient and cost-effective meal solutions. Home cooking, boosted by inflation, offers a direct cost advantage, with US households spending a substantial portion of their budget on groceries. Beyond burgers, consumers can choose from a vast range of fast-casual options like pizza and sandwich shops, satisfying diverse preferences.
The growing demand for healthier and plant-based options presents another major substitute threat, as many QSRs are adapting their menus. For instance, the US plant-based food market was projected to exceed $7 billion by mid-2024. Furthermore, meal kits and ready-to-eat grocery items are gaining traction, valued at approximately $15 billion globally in 2023, appealing to consumers seeking convenience and perceived health benefits.
| Substitute Category | Key Characteristics | Market Data (2023-2024 Estimates) |
|---|---|---|
| Home Cooking | Cost-effective, customizable | US Household Food Spending: ~$5,700 annually (approx. half on groceries) |
| Fast-Casual Dining | Variety, convenience, quality | Broad spectrum of choices (pizza, sandwiches, salads) |
| Health-Conscious/Plant-Based | Wellness focus, dietary preference | US Plant-Based Market: Projected >$7 billion (mid-2024) |
| Meal Kits & Ready-to-Eat | Convenience, perceived value, health focus | Global Meal Kit Market: ~$15 billion (2023) |
| Ghost Kitchens & Food Trucks | Flexibility, diverse offerings, mobility | Ghost Kitchen Sector: Potential to reach >$1 trillion globally by 2030 |
Entrants Threaten
Launching a new fast-casual restaurant like Bad Daddy's demands considerable upfront capital. This includes securing prime real estate, which can be a significant expense, especially in desirable locations. For instance, in 2024, the average cost for a suitable commercial lease in a high-traffic area could easily run into hundreds of thousands of dollars annually.
Beyond real estate, the costs extend to building out the space, purchasing essential kitchen equipment, and stocking initial inventory. Even for a 'small box' concept, these combined expenditures can easily reach several hundred thousand dollars, creating a substantial financial hurdle for aspiring new entrants looking to compete in the quick-service restaurant market.
Good Times and Bad Daddy's have cultivated strong brand recognition and fostered deep customer loyalty by consistently delivering on quality and unique dining experiences. This established presence makes it difficult for new competitors to gain a foothold.
New entrants must overcome the significant hurdle of building brand awareness and convincing consumers to switch from established, trusted brands. For instance, in the casual dining sector, a brand like Olive Garden, with decades of history, benefits from ingrained customer habits and positive associations that a newcomer struggles to replicate quickly.
The cost and time required to build comparable brand equity and loyalty are substantial, acting as a powerful deterrent. In 2024, marketing budgets for new restaurant chains often exceed millions of dollars just to achieve initial brand visibility.
Good Times' commitment to all-natural and fresh ingredients necessitates strong, established relationships with specific suppliers. New competitors entering the market would face significant hurdles in securing comparable access to these high-quality, consistent supply chains. This is particularly true for specialized ingredients that differentiate Good Times’ product offerings.
The cost and complexity of building these supplier relationships can act as a substantial barrier. For instance, the organic produce market, a likely source for Good Times, saw a 5.5% increase in sales in 2023, reaching $27.1 billion in the U.S., indicating a competitive landscape for sourcing. New entrants would need to invest considerable time and capital to replicate Good Times' ingredient sourcing capabilities, potentially facing higher initial costs for less established supplier networks.
Operational Expertise and Staffing Challenges
Operating a successful restaurant chain, particularly one with multiple brands and a presence across several states, demands considerable operational expertise. This includes mastery of kitchen management, consistent customer service delivery, and efficient supply chain logistics. Newcomers often struggle to replicate the established operational efficiencies of existing players.
Labor shortages and increasing wage demands present a significant hurdle for new entrants. For instance, the National Restaurant Association reported in early 2024 that 89% of restaurant operators were experiencing staffing challenges. This makes recruiting and retaining skilled employees, from line cooks to management, a costly and time-consuming endeavor.
- Staffing Shortages: Many restaurants, as of late 2023 and into 2024, are still grappling with finding enough qualified staff.
- Rising Labor Costs: The average hourly wage for restaurant workers has seen an upward trend, impacting profitability for new businesses.
- Training Investment: New entrants must invest heavily in training to ensure service quality and operational consistency, adding to initial costs.
Regulatory Compliance and Permitting
The restaurant sector faces significant regulatory hurdles that act as a barrier to new entrants. Navigating complex health, safety, and operational regulations, including obtaining necessary local permits and licenses, can be a time-consuming and costly process. For instance, in 2024, the average time to obtain all required food service permits in major US cities could extend from 3 to 9 months, significantly delaying market entry and increasing upfront investment.
These compliance requirements directly impact the initial capital needed and the ongoing operational expenses for any new restaurant. The need for adherence to food safety standards, building codes, and labor laws means that new businesses must allocate substantial resources to legal and administrative tasks before even opening their doors. This can range from investing in compliant kitchen equipment to hiring specialized staff for regulatory management, adding to the financial strain on emerging ventures.
- Increased Capital Requirements: New entrants must budget for legal fees, permit application costs, and potential upgrades to meet health and safety codes.
- Extended Time-to-Market: The permitting process can delay a restaurant's opening, impacting revenue projections and increasing the risk of market saturation by the time of launch.
- Ongoing Compliance Costs: Regular inspections, license renewals, and continuous staff training on updated regulations add to the operational expenses.
- Variability Across Jurisdictions: The complexity and cost of compliance can differ significantly between cities and states, creating an uneven playing field for national or regional expansion.
The threat of new entrants is moderate for the fast-casual restaurant sector. High startup costs, estimated to be several hundred thousand dollars for a basic setup in 2024, create a significant financial barrier. Furthermore, building brand loyalty and securing reliable, high-quality supply chains requires substantial investment and time, making it challenging for newcomers to compete with established players like Good Times and Bad Daddy's.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Good Times Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, incorporating information from industry-specific market research reports, company annual filings, and publicly available financial statements. This blend of sources allows for a comprehensive understanding of competitive intensity, supplier and buyer power, and the threat of new entrants and substitutes.
