Frial Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Frial Bundle
Porter's Five Forces Analysis reveals the intense competitive landscape Frial operates within, highlighting the significant bargaining power of buyers and the constant threat of new entrants. Understanding these forces is crucial for Frial's strategic positioning and long-term success.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Frial’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of Frial's suppliers hinges on the concentration and specialization within the seafood market. When only a handful of suppliers can provide specific, high-demand seafood species, particularly those with specialized certifications or those that are challenging to harvest, their leverage naturally grows. For instance, in 2024, the global market for sustainably certified seafood, a key area for premium suppliers, saw continued growth, potentially increasing the power of those holding such certifications.
The quality and traceability of Frial's products are paramount to its brand, directly linking its reputation to the reliability and standards of its suppliers. For instance, in 2024, the seafood industry faced increased scrutiny regarding sourcing practices, with consumers increasingly demanding transparency. Suppliers offering high-quality, certified sustainable, or uniquely sourced seafood, such as those adhering to specific MSC (Marine Stewardship Council) standards, possess significant bargaining power due to Frial's commitment to these attributes.
The costs Frial incurs to switch suppliers are a significant factor in supplier bargaining power. These costs can include the expense of re-establishing quality control standards, setting up new logistical networks, and the potential for operational disruptions during the transition. For instance, in 2024, the global seafood industry saw increased volatility in raw material sourcing, with some companies reporting up to a 15% increase in transition costs when changing aquaculture partners due to the need for new certifications and supplier audits.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
Suppliers in the frozen seafood industry, particularly large fishing cooperatives or aquaculture operations, could significantly enhance their bargaining power by threatening forward integration. If these entities decide to establish their own processing facilities and distribution networks, they could effectively bypass intermediaries like Frial. This move would allow them to capture more of the value chain and exert greater control over pricing and market access.
For instance, a major shrimp farm in Southeast Asia with significant production volume might consider investing in its own freezing and packaging plants, directly supplying major retailers or food service companies. This capability directly challenges Frial's role as a processor and distributor, giving the supplier a stronger hand in contract negotiations. The threat is most potent for suppliers of high-volume commodities or unique, specialized seafood products where direct market access is a key differentiator.
- Forward Integration Threat: Suppliers can increase their leverage by integrating into processing and distribution, bypassing Frial.
- Impact on Leverage: This bypass allows suppliers to control more of the value chain, strengthening their negotiation position.
- Relevance: The threat is particularly strong for suppliers of high-volume or specialized frozen seafood.
Availability of Substitute Inputs
The availability of substitute inputs significantly influences the bargaining power of suppliers in the seafood industry. If Frial can readily switch between different types of fish or source from various geographical regions without compromising quality or incurring substantial cost increases, the power of any single supplier is reduced. For instance, if demand for cod rises and cod suppliers increase prices, Frial might pivot to sourcing haddock or pollock from a different region, thereby limiting the cod suppliers' leverage.
However, the scenario changes for specialized or premium seafood products. For highly specific species, unique preparation methods, or seafood with recognized brand names, substitution options are often limited. In such cases, suppliers of these niche products can exert greater bargaining power due to Frial's dependence on their offerings. For example, a supplier of sustainably farmed salmon with a strong reputation might command higher prices if Frial cannot easily find an equivalent alternative that meets its sustainability and quality standards.
- Impact of Substitutability: If Frial can easily switch sourcing for its primary seafood products, supplier power is weakened.
- Niche Product Power: Suppliers of specialized or branded seafood products often hold greater power due to limited substitution options.
- Regional Sourcing Flexibility: Access to diverse sourcing regions can mitigate the impact of localized supply disruptions or price hikes.
- Cost of Switching: The cost and complexity associated with changing suppliers or product types directly affect supplier leverage.
The bargaining power of Frial's suppliers is amplified when they are concentrated and possess unique, specialized products. For instance, in 2024, the global market for certain high-value seafood, like specific types of tuna or rare shellfish, saw suppliers with exclusive fishing rights or unique aquaculture techniques hold considerable sway. This concentration means fewer alternatives for Frial, allowing these suppliers to dictate terms more effectively.
Suppliers' ability to raise prices or reduce quality is also a significant factor. If Frial faces high switching costs, such as the need for new certifications or logistical overhauls, suppliers can leverage this. In 2024, the seafood industry experienced increased regulatory compliance costs, with some suppliers passing these on, potentially raising transition expenses for buyers like Frial by 10-20% if new certifications were required.
The threat of suppliers integrating forward, meaning they might start their own processing or distribution, also strengthens their hand. If a key supplier of premium salmon, for example, decided to bypass Frial and sell directly to retailers, it would diminish Frial's market position and increase the supplier's bargaining power. This is especially true for suppliers of high-volume, differentiated seafood products.
| Factor | Impact on Supplier Power | 2024 Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High concentration increases power | Continued consolidation in some wild-caught fisheries |
| Switching Costs for Frial | High costs empower suppliers | Increased regulatory compliance driving up transition expenses |
| Forward Integration Threat | Potential for suppliers to bypass Frial | Growing interest in direct-to-consumer models in premium seafood |
| Availability of Substitutes | Limited substitutes empower suppliers | Niche, certified seafood products have fewer alternatives |
What is included in the product
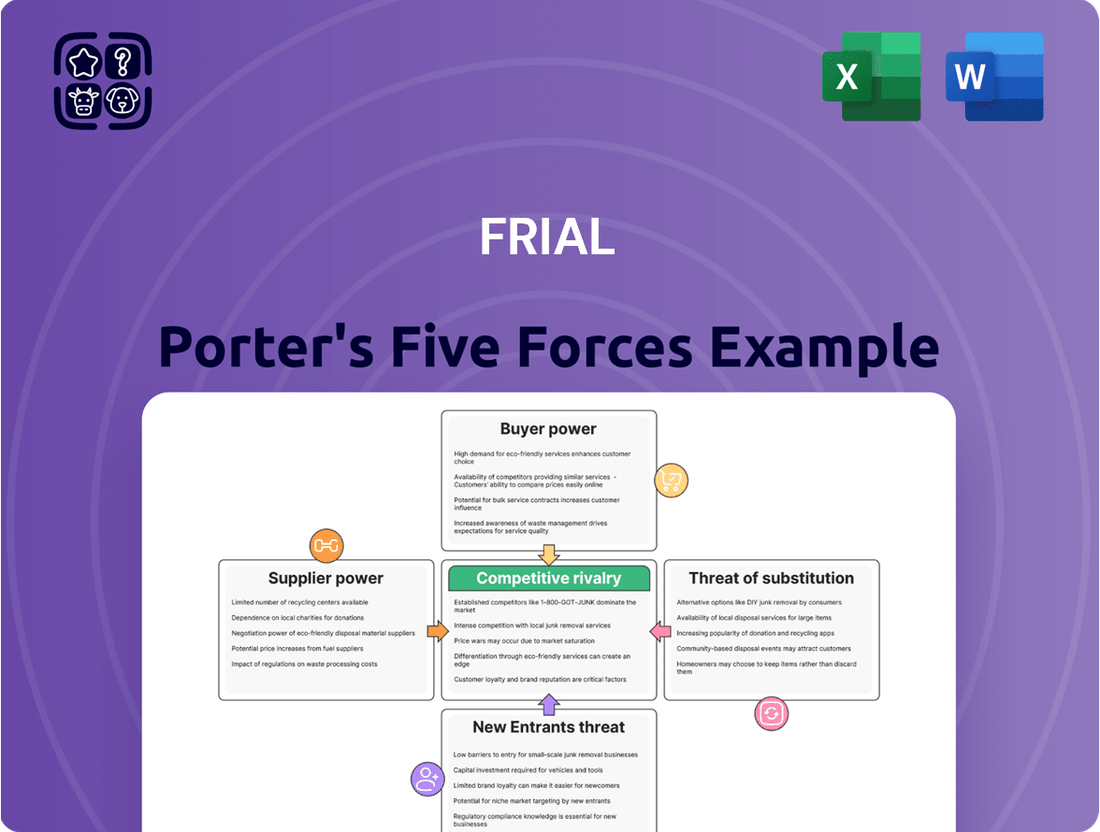
The Frial Porter's Five Forces Analysis dissects the competitive intensity of Frial's industry by examining the power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the rivalry among existing competitors.
Pinpoint and neutralize competitive threats by understanding the intensity of each of the five forces.
Customers Bargaining Power
Frial's customer base is diverse, spanning both high-volume retail giants like major supermarket chains and significant players in the foodservice industry, such as large restaurant groups. These substantial buyers wield considerable influence, often leveraging the sheer volume of their purchases to negotiate favorable pricing and terms, a key aspect of their bargaining power.
The ability of these large customers to commit to significant order volumes directly translates to increased bargaining power. For instance, a major supermarket chain might represent a substantial percentage of a particular product line's sales, giving them leverage in price discussions. This contrasts with smaller, independent customers who have less individual impact on Frial's overall sales volume.
Customer price sensitivity is a significant factor in the frozen food industry, impacting companies like Frial. Both individual shoppers and businesses like restaurants are keenly aware of pricing, easily comparing options from various brands. This means Frial must consistently offer competitive prices to attract and retain customers.
During economic slowdowns, this price sensitivity often intensifies. For instance, in 2024, consumer spending on non-essential food items saw fluctuations, with many households prioritizing value. This trend directly pressures frozen food manufacturers to manage their pricing strategies carefully to avoid losing market share.
Customers seeking frozen seafood have a vast selection of alternatives, ranging from fresh seafood counters to other frozen protein options like chicken or beef, and even plant-based meals. This abundance of choice directly translates into greater bargaining power for consumers.
If Frial's frozen seafood doesn't align with customer expectations regarding price, quality, or convenience, consumers can readily switch to a competitor or an entirely different food category. For instance, in 2024, the global frozen seafood market is projected to reach over $50 billion, indicating a highly competitive landscape with numerous players offering similar products.
The perceived value proposition between frozen and fresh seafood also plays a crucial role. While frozen seafood often offers convenience and longer shelf life, consumers may opt for fresh alternatives if they believe the quality or taste is superior, further amplifying their ability to negotiate or seek better deals.
Customer Information and Transparency
Customers, particularly large buyers in retail and foodservice, wield significant bargaining power due to enhanced access to market information. They are increasingly aware of pricing, sourcing methods, and quality standards across various suppliers, enabling them to negotiate more favorable terms. For instance, in 2024, major grocery chains leveraged detailed supply chain data to secure price reductions from produce suppliers, citing competitive market analysis.
This heightened transparency empowers customers to demand not only competitive pricing but also assurances regarding sustainable sourcing and ethical production practices. Online platforms and consumer review sites further amplify this power, allowing individual shoppers to compare products and prices easily, influencing purchasing decisions and supplier choices.
- Informed Negotiation: Customers can compare prices and quality across multiple suppliers, leading to more effective negotiation for better terms.
- Demand for Transparency: Buyers are increasingly asking for proof of sustainable sourcing and ethical practices.
- Impact of Online Reviews: Consumer feedback and online comparisons directly influence purchasing decisions and brand loyalty.
- Data-Driven Purchasing: In 2024, a significant percentage of large retail buyers used advanced analytics to benchmark supplier pricing and performance.
Low Switching Costs for Customers
For many standard frozen seafood items, the expense for customers to switch from Frial to a competing brand is minimal. This low barrier to entry means retailers can readily swap brands on their shelves, and restaurants can easily adjust their menus to feature different suppliers. In 2024, the global frozen seafood market saw continued price sensitivity, with consumers actively seeking value, further amplifying this customer bargaining power.
This ease of switching grants customers significant leverage. It necessitates that Frial consistently provides attractive pricing, superior product quality, and reliable service to maintain its customer loyalty. For instance, a 2024 industry report indicated that over 60% of foodservice buyers considered price the primary factor when selecting a frozen seafood supplier, highlighting the impact of low switching costs.
The implications for Frial are clear:
- Continuous Value Proposition: Frial must constantly demonstrate why it's the best choice, not just on price but also on quality and service.
- Market Responsiveness: The company needs to be agile in responding to competitor pricing and product innovations.
- Customer Retention Focus: Strategies should prioritize building strong relationships to reduce churn, rather than solely focusing on new customer acquisition.
Customers, especially large buyers like supermarket chains and restaurant groups, possess significant bargaining power due to their substantial order volumes. This leverage allows them to negotiate favorable pricing and terms, as seen in 2024 where major retailers used competitive analysis to secure price reductions. The frozen seafood market, projected to exceed $50 billion globally in 2024, is highly competitive, offering consumers numerous alternatives and amplifying their ability to switch suppliers if Frial's offerings don't meet their price, quality, or convenience expectations.
The ease with which customers can switch brands in the frozen seafood sector, with minimal switching costs, further strengthens their negotiating position. This necessitates that Frial consistently deliver a strong value proposition through competitive pricing, high quality, and reliable service. For instance, a 2024 industry report highlighted that over 60% of foodservice buyers prioritize price when selecting suppliers, underscoring the impact of low switching costs.
| Factor | Impact on Frial | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Volume | High volume buyers command better pricing. | Major retailers leverage data for price concessions. |
| Price Sensitivity | Consumers actively seek value, especially during economic shifts. | Consumer spending on non-essentials fluctuated, prioritizing value. |
| Availability of Alternatives | Numerous competitors and substitute products increase customer choice. | Global frozen seafood market >$50 billion, indicating high competition. |
| Switching Costs | Low costs empower customers to easily change suppliers. | >60% of foodservice buyers cite price as primary selection factor. |
Same Document Delivered
Frial Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Porter's Five Forces analysis, detailing the competitive landscape of an industry by examining threat of new entrants, bargaining power of buyers, bargaining power of suppliers, threat of substitute products or services, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no surprises and full readiness for your strategic planning. You are looking at the actual document; once your purchase is complete, you’ll gain instant access to this comprehensive file.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The frozen seafood market is quite crowded, with a wide variety of companies competing. You'll find big global food companies alongside smaller, niche producers focusing on specific regions or types of seafood. This means Frial isn't just up against other frozen seafood specialists, but also against larger frozen food companies that might offer seafood as part of a broader product line.
This mix of competitors, from large-scale operators to specialized players, really heats up the competition. They're all trying to grab a bigger slice of the market, whether that's selling to grocery stores or to restaurants and food service providers. For example, in 2023, the global frozen seafood market was valued at approximately $48.2 billion, indicating a substantial market size that attracts many participants.
The growth rate of the frozen seafood market plays a crucial role in shaping competitive rivalry. When the market experiences slow growth or stagnation, companies tend to intensify their efforts to gain market share, often leading to price wars and increased promotional activities. This dynamic is particularly evident as organic expansion opportunities become scarce, pushing businesses to aggressively target each other's customer base.
Frial positions itself on quality and traceability, but many rivals echo these claims, making genuine differentiation a challenge. For instance, in 2024, the global food and beverage market saw numerous brands emphasizing sustainability and origin, a trend that intensified competitive pressures.
The ability to cultivate strong brand loyalty is crucial for Frial to stand out. When consumers perceive products as interchangeable, like many grocery staples, competition inevitably shifts to price. This price-driven rivalry can significantly escalate, impacting profit margins for all players.
Frial's sustained success hinges on its capacity to clearly articulate and deliver its unique value proposition to consumers. In 2023, brands that effectively communicated superior quality or unique sourcing often commanded premium pricing, demonstrating the power of differentiation.
Exit Barriers for Competitors
High exit barriers are a significant factor keeping competitors in the seafood processing market, even when they are struggling. These barriers include substantial investments in fixed assets like processing plants and cold storage facilities, which are difficult and costly to divest. For instance, the capital expenditure for a modern seafood processing plant can easily run into millions of dollars, making a quick exit unfeasible for many firms.
Specialized equipment, tailored for specific seafood types or processing methods, further complicates an exit. Selling such equipment often yields only a fraction of its original cost, especially if there's limited demand from other industries. Additionally, long-term contracts with suppliers or major buyers can lock companies into operations, preventing them from ceasing business without incurring penalties or significant losses.
These high exit barriers mean that even companies operating at a loss may continue to compete, contributing to market overcapacity. This situation intensifies price competition, as these less profitable players fight for market share to cover at least some of their fixed costs. The specialized nature of seafood processing, requiring specific knowledge and infrastructure, exacerbates this issue.
- Significant Fixed Assets: Seafood processors often have substantial investments in processing plants and cold storage, making them difficult to liquidate.
- Specialized Equipment: Machinery for tasks like filleting, freezing, or packaging seafood is often industry-specific, with low resale value outside the sector.
- Long-Term Contracts: Commitments to suppliers or buyers can obligate companies to continue operations, even in unfavorable market conditions.
- Market Overcapacity: The inability to exit easily perpetuates excess production capacity, leading to more aggressive pricing strategies among competitors.
Competitive Strategies and Innovation
Competitive rivalry within the frozen food sector, particularly for a company like Frial, is intense and multifaceted. Competitors frequently engage in strategic maneuvers such as introducing new product lines, intensifying advertising efforts, and even initiating price wars. Innovation in areas like packaging design and distribution efficiency also plays a crucial role in differentiating brands and capturing market share. For instance, in 2024, the frozen food market saw significant investment in plant-based alternatives and convenient meal solutions, with major players like Nestlé and Conagra Brands actively expanding their offerings in these high-growth segments.
Frial must maintain a vigilant watch on these competitor actions to effectively navigate the market. Adapting strategies is key to sustaining its position. This could involve broadening its product portfolio to cater to evolving consumer tastes, enhancing its commitment to sustainability practices, or streamlining its supply chain for greater efficiency and cost-effectiveness. The global frozen food market was valued at approximately USD 310.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow, underscoring the dynamic nature of the competitive landscape.
- New Product Launches: Competitors are consistently innovating, with a notable trend in 2024 towards premium and health-conscious frozen meals.
- Aggressive Marketing: Increased digital marketing spend and influencer collaborations are common tactics used to reach a wider audience.
- Pricing Strategies: Price sensitivity remains a factor, leading to promotional activities and value-pack offerings from various brands.
- Sustainability Initiatives: Brands are increasingly highlighting eco-friendly packaging and ethically sourced ingredients as a competitive differentiator.
The competitive rivalry in the frozen seafood market is fierce, characterized by a diverse range of players from global conglomerates to niche specialists. This intense competition is fueled by a substantial market size, valued at approximately $48.2 billion in 2023, which attracts numerous companies vying for market share. Many competitors emphasize similar quality and traceability claims, making differentiation a significant challenge for Frial.
High exit barriers, such as substantial investments in specialized processing plants and equipment, compel companies to remain in the market even when unprofitable. This persistence contributes to market overcapacity, intensifying price competition and aggressive strategies like new product launches and promotional activities. For instance, in 2024, the frozen food market saw a surge in plant-based and convenient meal options, with major brands actively expanding their portfolios to capture evolving consumer preferences.
| Competitor Action | Impact on Frial | 2024 Market Trend |
| New Product Launches | Requires Frial to innovate or risk losing market share. | Focus on premium, health-conscious, and plant-based frozen meals. |
| Aggressive Marketing & Promotions | Pressures Frial to increase marketing spend or risk reduced brand visibility. | Increased digital marketing and influencer collaborations. |
| Pricing Strategies | Can lead to price wars, impacting Frial's profit margins. | Value-pack offerings and promotional pricing remain prevalent. |
| Sustainability Initiatives | Necessitates Frial to clearly communicate its own sustainability efforts. | Emphasis on eco-friendly packaging and ethical sourcing. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Fresh seafood presents a significant threat to Frial's frozen products. Consumers and businesses often compare the convenience and extended shelf life of frozen items against the perceived better taste and texture of fresh seafood. This comparison directly impacts purchasing decisions.
The accessibility and affordability of fresh seafood are crucial factors. For instance, if the price of fresh fish drops significantly, or if new technologies improve its preservation and distribution, the appeal of frozen alternatives diminishes. In 2024, global seafood consumption saw a slight shift towards fresh, with certain regions reporting a 3-5% increase in demand for locally sourced, fresh catches, driven by consumer preference for quality and traceability.
When fresh options become more readily available and competitively priced, the threat of substitution intensifies. This can pressure Frial to innovate in terms of product quality, processing techniques, or pricing strategies to maintain its market share against the allure of fresh alternatives.
Consumers have a vast selection of protein sources beyond seafood, encompassing traditional meats like chicken, beef, and pork, alongside the booming plant-based protein market. These alternatives directly vie for consumer meal choices and dietary requirements, presenting a significant competitive challenge.
The increasing popularity of vegetarian, vegan, and flexitarian diets directly impacts seafood demand. For instance, the global plant-based meat market was valued at approximately $7.0 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach over $30 billion by 2030, indicating a substantial shift in consumer preferences that directly threatens seafood consumption.
The threat of substitutes for Frial's frozen seafood products is significant, primarily stemming from ready-to-eat meals and the dining-out experience. Consumers increasingly value convenience, and fully prepared meals, whether frozen or chilled and not containing seafood, offer a direct alternative to cooking from scratch. For instance, the global frozen ready meals market was valued at approximately USD 35 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow, indicating a strong consumer preference for convenience.
Furthermore, the option to dine out at restaurants presents another powerful substitute. This caters to consumers seeking convenience and a different culinary experience altogether, bypassing the need for home preparation of any kind. The food delivery sector's expansion, with services like DoorDash and Uber Eats reporting continued user growth and transaction volume increases throughout 2023 and into early 2024, amplifies this threat by making restaurant meals more accessible than ever.
Changing Consumer Preferences and Health Trends
Evolving consumer tastes and a heightened focus on health significantly impact the threat of substitutes. As people become more health-conscious, they may actively seek out unprocessed foods, potentially reducing demand for certain processed or frozen seafood options. For instance, a growing aversion to specific additives or a desire for more natural ingredients could push consumers towards fresh produce or plant-based alternatives.
Dietary trends also play a crucial role. Concerns about specific nutritional profiles, such as mercury levels in certain fish species, can drive consumers to explore other protein sources like poultry, legumes, or even lab-grown meats. This shift in preference directly increases the viability and attractiveness of these substitutes.
- Shifting Dietary Habits: A 2024 report indicated a 15% year-over-year increase in consumer spending on plant-based protein alternatives, signaling a growing preference away from traditional animal proteins, including seafood.
- Health and Wellness Focus: Surveys from early 2024 revealed that 60% of consumers actively read ingredient labels, with a primary concern being the absence of artificial preservatives and a preference for "clean label" products, impacting demand for some processed seafood.
- Convenience vs. Naturalness: While convenience remains a factor, a notable segment of consumers (around 40% in recent polls) prioritize natural, minimally processed foods, creating a competitive pressure from fresh food categories and whole ingredients.
- Alternative Protein Growth: The global alternative protein market, encompassing plant-based and cultivated options, was projected to reach over $160 billion by 2030, underscoring the increasing threat from these substitutes to traditional food sectors, including seafood.
Cross-Category Competition within Frozen Foods
The threat of substitutes for Frial is significant due to the broad spectrum of choices available to consumers within the frozen food category. Beyond direct competitors in frozen seafood, Frial's offerings must contend with a wide array of other frozen items, including vegetables, pizzas, and ready-to-eat meals. This cross-category competition means consumers allocate a portion of their grocery budget to frozen goods, and Frial needs to demonstrate superior value and appeal to secure a share of this spending.
For instance, in 2024, the global frozen food market was valued at approximately $320 billion, with a projected compound annual growth rate of around 5.5% through 2030. This growth is fueled by convenience and variety, highlighting the intense competition Frial faces from diverse frozen product segments. Consumers often view frozen vegetables or ready meals as equally convenient and potentially more budget-friendly substitutes for frozen seafood.
- Broad Frozen Food Landscape: Frial's products are not isolated; they compete against a vast array of frozen items, from vegetables and fruits to pizzas and complete meals, all vying for consumer attention and budget allocation.
- Consumer Budget Allocation: Shoppers often have a set budget for frozen foods, making Frial's pricing and perceived value critical when compared to other frozen alternatives.
- Convenience as a Differentiator: While Frial offers convenience, so do many other frozen categories, making it challenging to stand out solely on this attribute.
- Market Growth Dynamics: The overall growth in the frozen food sector, projected to reach over $440 billion by 2030, underscores the intense competition as more players and product types emerge.
The threat of substitutes for Frial is significant, as consumers have numerous protein alternatives beyond seafood, including poultry, beef, pork, and the rapidly expanding plant-based protein market. These alternatives directly compete for mealtime decisions and dietary needs, posing a substantial challenge to seafood's market share.
The growth of plant-based diets is a key driver here; the global plant-based meat market was valued around $7.0 billion in 2023 and is expected to surpass $30 billion by 2030. This trend indicates a clear shift in consumer preferences that directly impacts demand for traditional protein sources like seafood.
Moreover, convenience-driven substitutes like ready-to-eat meals and dining out are increasingly popular. The global frozen ready meals market alone was valued at approximately $35 billion in 2023, highlighting a strong consumer preference for easy meal solutions that bypass the need for home cooking, including seafood preparation.
Consumer choices are also influenced by evolving tastes and a heightened focus on health and wellness. A growing preference for natural, unprocessed foods and concerns about specific nutritional profiles, such as mercury levels in certain fish, can steer consumers towards other protein sources, thereby increasing the attractiveness of substitutes.
| Substitute Category | 2023 Market Value (Approx.) | Projected Growth Driver |
| Plant-Based Proteins | $7.0 billion | Increasing health consciousness and ethical consumerism |
| Frozen Ready Meals | $35 billion | Demand for convenience and time-saving meal solutions |
| Dining Out/Food Delivery | Continued user growth (2023-2024) | Accessibility and desire for varied culinary experiences |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the frozen seafood market demands significant capital. Think about the costs for processing plants, specialized freezing gear, and maintaining that all-important cold chain for transport and storage. These upfront expenses can easily run into millions, creating a formidable hurdle for newcomers.
For instance, establishing a modern frozen seafood processing facility can cost upwards of $10 million to $50 million, depending on capacity and automation. Add to that the investment in refrigerated trucks, cold storage warehouses, and navigating complex regulatory compliance, and the barrier to entry becomes exceptionally high.
This substantial financial commitment naturally limits the number of companies that can realistically enter this competitive space. It favors established players with existing infrastructure and deep pockets, thereby reducing the immediate threat of new, smaller competitors disrupting the market significantly.
Gaining access to established distribution channels presents a significant hurdle for new companies looking to enter the frozen food market. Securing prime shelf space in major grocery chains and building relationships with foodservice distributors requires substantial investment and time. For instance, in 2024, the average listing fee for a new product in a large supermarket chain could range from $5,000 to $50,000, with additional slotting allowances often expected.
Existing players, like Frial, have cultivated long-standing partnerships with distributors and retailers, creating a strong competitive advantage. These established networks ensure consistent product availability and visibility, making it exceedingly difficult for newcomers to compete for market access. In 2023, the top five frozen food distributors in the US controlled over 70% of the market share, highlighting the concentrated nature of the distribution landscape.
The frozen seafood industry faces significant regulatory hurdles, particularly concerning food safety and traceability. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) continued to emphasize stringent oversight of imported seafood, requiring detailed documentation to ensure compliance with U.S. standards.
New companies entering this market must invest heavily in understanding and adhering to these complex regulations, which include obtaining certifications and establishing robust quality assurance systems. These compliance costs can act as a substantial barrier, deterring potential new entrants who may lack the capital or expertise to navigate such requirements effectively.
Brand Loyalty and Established Reputation
Brand loyalty is a significant barrier for new entrants. Established companies, like Frial, have cultivated strong brand recognition and consumer trust, often built over decades. This trust is frequently linked to perceptions of quality and reliability, which are crucial in the food industry where safety is a top concern. Frial's emphasis on traceability, for instance, directly contributes to this consumer confidence.
Newcomers must overcome the substantial hurdle of building a reputation from the ground up. This necessitates considerable investment in marketing and a lengthy period to earn consumer trust, especially in a market where food safety is non-negotiable. For example, in 2024, the global food and beverage market saw marketing expenditures reach trillions of dollars, highlighting the scale of investment required to make an impact.
- Brand Recognition: Existing players have spent years and significant resources building recognizable brands.
- Consumer Trust: Long-standing companies often benefit from established trust, particularly concerning product safety and quality.
- Marketing Investment: New entrants need substantial capital for marketing to even begin competing with established brand awareness.
- Time to Build Reputation: Gaining consumer confidence in a sensitive sector like food can take a considerable amount of time.
Economies of Scale and Experience Curve
Incumbent companies often leverage significant economies of scale, which translates to lower per-unit costs for raw materials, production, and distribution. For instance, in the automotive sector, major manufacturers in 2024 benefit from bulk purchasing discounts that smaller, new entrants simply cannot access. This cost advantage makes it difficult for newcomers to compete on price.
The experience curve further solidifies the position of established players. Through years of operation, these firms have optimized their processes and supply chains, leading to greater efficiency and reduced waste. A 2024 report highlighted that legacy tech companies, with decades of product development, possess highly streamlined manufacturing and R&D pipelines compared to emerging startups.
- Economies of Scale: Lower unit costs due to large-scale operations in purchasing, production, and marketing.
- Experience Curve: Improved efficiency and cost reduction through accumulated knowledge and refined processes over time.
- Cost Disadvantage for New Entrants: Newcomers struggle to match the cost efficiencies of established firms, impacting their pricing power.
- Barriers to Entry: These factors create substantial barriers, deterring potential new competitors.
The threat of new entrants in the frozen seafood market is significantly mitigated by substantial capital requirements for processing, freezing, and maintaining cold chain logistics, often exceeding tens of millions of dollars.
Securing distribution channels and shelf space in major retailers presents another major hurdle, with listing fees alone potentially reaching $50,000 in 2024, alongside the need to build trust and brand recognition against established players.
Stringent regulatory compliance for food safety and traceability, coupled with the cost of marketing to overcome established brand loyalty, further deters new companies, as seen in the trillions spent on global food marketing in 2024.
Economies of scale and the experience curve enjoyed by incumbents create a significant cost advantage, making it difficult for newcomers to compete on price and efficiency.
| Barrier Type | Estimated Cost/Factor (2024 Data) | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Investment (Processing Plant) | $10M - $50M+ | Very High |
| Distribution Channel Access (Listing Fee) | $5K - $50K per product | High |
| Marketing & Brand Building | Trillions (Global F&B Market) | Very High |
| Regulatory Compliance | Significant Investment | High |
| Economies of Scale | Lower Unit Costs | High |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, including publicly available company financial statements, industry-specific market research reports, and government economic indicators.
