Founder Securities Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Founder Securities Bundle
Founder Securities faces intense competition, with rivals vying for market share and potential new entrants threatening established positions. Understanding the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers is crucial for navigating this landscape.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Founder Securities’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of specialized financial technology and data providers significantly influences Founder Securities. When only a handful of firms offer critical market data or trading platforms, these suppliers can dictate higher prices. For instance, in 2024, the cost of premium financial data feeds saw an average increase of 8% across the industry, directly impacting the operational expenses of firms like Founder Securities.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Founder Securities is significantly shaped by the availability of highly skilled human capital. A scarcity of talent in specialized roles like investment bankers, financial analysts, and asset managers directly translates to increased leverage for these professionals.
In competitive markets, such as China's rapidly evolving financial sector, a tight labor market for these in-demand skills can drive up salary expectations and recruitment expenses for Founder Securities. For instance, reports from 2024 indicated a persistent demand for experienced financial professionals, with average compensation packages for senior investment bankers seeing notable increases.
Access to capital from financial institutions is a key supplier dynamic for Founder Securities. In 2024, rising interest rates, with the US Federal Reserve maintaining its benchmark rate above 5% for much of the year, directly increased the cost of borrowing for firms like Founder Securities. This tightening of lending conditions signifies elevated supplier power from banks and other lenders, potentially squeezing profit margins.
Supplier Power 4
Regulatory bodies, though not direct suppliers, hold substantial sway over securities firms. Their stringent compliance mandates, often requiring specific software solutions, independent auditing, and specialized legal advice, effectively create a demand for these services. This, in turn, grants these service providers significant leverage, as securities firms must adhere to these regulations to operate.
These mandated services can represent a significant operational cost for financial institutions. For instance, in 2024, the average cost for regulatory compliance software for mid-sized financial firms was estimated to be between $50,000 and $200,000 annually, depending on the complexity of their operations and the specific regulatory frameworks they fall under. This highlights the financial dependency and the bargaining power these specialized service providers wield.
- Mandated Services: Compliance with regulations often necessitates the use of specific technologies and professional services.
- Increased Demand: Regulatory requirements drive demand for specialized software, auditing, and legal expertise.
- Supplier Leverage: This created demand empowers providers of these essential services, giving them greater bargaining power.
- Operational Costs: Compliance expenses can represent a substantial portion of a securities firm's budget, emphasizing the impact of supplier costs.
Supplier Power 5
The concentration of specialized software vendors for critical back-office functions, cybersecurity, and advanced analytics significantly impacts Founder Securities. When few alternatives exist for highly specialized systems, these vendors gain considerable leverage. This can lead to increased vendor lock-in and higher operational costs for Founder Securities, as switching providers becomes complex and expensive.
For instance, in 2024, the financial technology sector saw continued consolidation, with major players in areas like core banking systems and regulatory compliance software acquiring smaller, specialized firms. This trend limits choices for financial institutions like Founder Securities, potentially increasing the bargaining power of the remaining dominant vendors. Founder Securities may find itself paying premium prices for essential software if it lacks viable alternative solutions.
- Concentrated Vendor Landscape: A limited number of providers for specialized financial software grants them enhanced negotiation power.
- Vendor Lock-in: High switching costs and integration complexities with unique systems can trap Founder Securities with specific suppliers.
- Increased Costs: Restricted alternatives often translate to higher licensing fees, maintenance charges, and support costs for essential technology.
- Impact on Operations: Dependence on a few key vendors for critical functions can disrupt operations if supply or service is compromised.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Founder Securities is amplified by the concentration of specialized financial data providers. When few entities offer critical market intelligence or trading platforms, these suppliers can command higher prices, directly impacting Founder Securities' operational expenses. For example, in 2024, the cost of premium financial data feeds rose by an average of 8% across the industry, a trend that directly affects firms like Founder Securities.
The availability of essential technologies and platforms also presents a supplier power dynamic. Limited choices for critical back-office systems, cybersecurity solutions, and advanced analytics can lead to vendor lock-in and increased costs for Founder Securities. This is exacerbated by industry consolidation, where dominant vendors in core systems can dictate terms, as seen in the financial technology sector in 2024.
| Supplier Category | Key Impact on Founder Securities | 2024 Trend/Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Specialized Data Providers | Increased cost of essential market intelligence. | Average 8% increase in premium financial data feed costs. |
| Financial Technology Vendors (Core Systems) | Potential for vendor lock-in and higher licensing/maintenance fees. | Continued consolidation in FinTech limiting alternative solutions. |
| Skilled Human Capital | Higher recruitment and compensation expenses due to talent scarcity. | Persistent demand for experienced financial professionals driving salary increases. |
| Capital Providers (Banks/Lenders) | Increased cost of borrowing and tighter lending conditions. | Benchmark interest rates remaining elevated, increasing debt servicing costs. |
What is included in the product
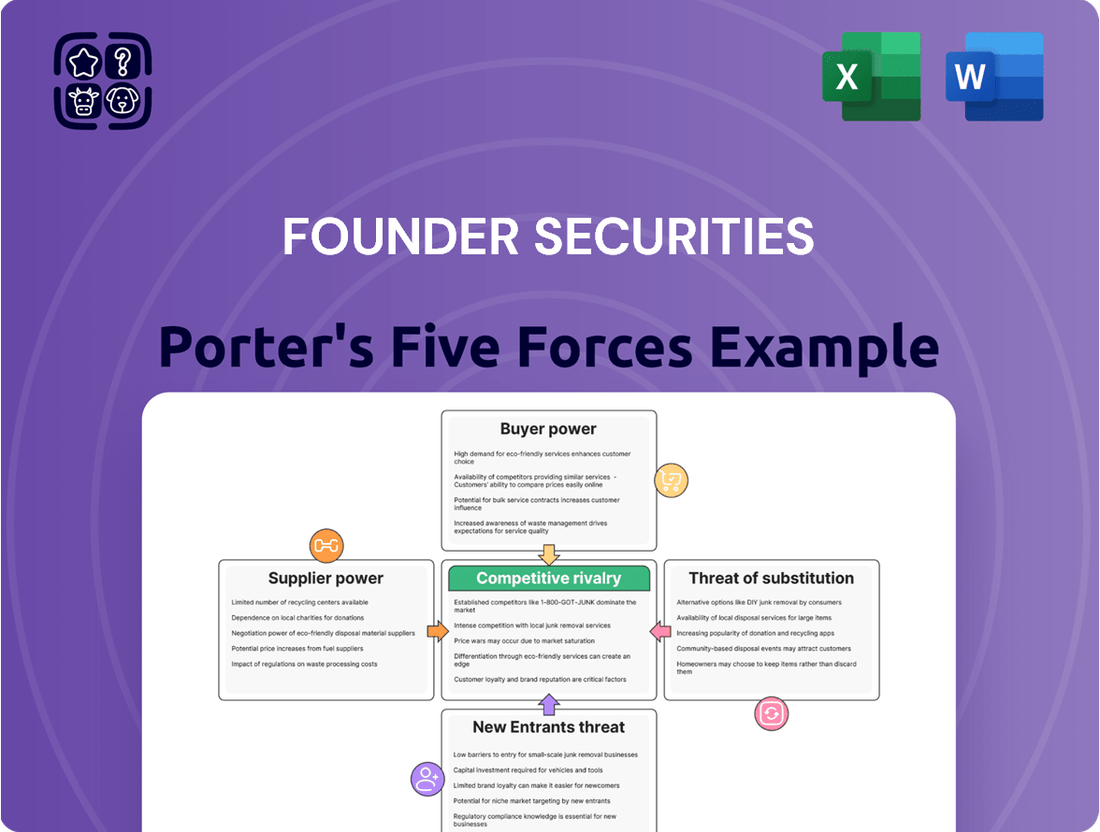
Founder Securities' Porter's Five Forces analysis delves into the competitive intensity within the securities industry, examining threats from new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the rivalry among existing firms.
Instantly identify and address competitive threats with a dynamic, interactive visualization of Founder Securities' Porter's Five Forces.
Customers Bargaining Power
The Chinese securities market is highly competitive, with numerous alternative companies offering similar financial services. This abundance of choice for both individual and institutional investors significantly lowers switching costs, amplifying customer bargaining power, especially for standard brokerage services.
Large institutional clients, like pension funds and major corporations, wield considerable negotiation power with Founder Securities because of the substantial volume of business they represent. This leverage allows them to negotiate for more favorable terms, potentially including reduced fees or specialized service packages, to ensure their continued patronage.
Retail investors, particularly those focused on straightforward services like stock trading, exhibit significant price sensitivity. This means they are more likely to switch providers based on cost alone, granting them considerable bargaining power. For instance, in 2023, the average commission fee for online stock trading in China saw a continued downward trend, reflecting this intense price competition.
The proliferation of online trading platforms and increasingly competitive fee structures within China directly impacts firms like Founder Securities. To remain attractive and retain their customer base, these companies are compelled to maintain aggressive pricing strategies. This pressure forces them to constantly evaluate and optimize their service costs to prevent client attrition to lower-cost alternatives.
Buyer Power 4
Customers at Founder Securities are increasingly empowered due to enhanced financial literacy and readily available information. This allows them to easily compare services and pricing from various financial institutions, putting pressure on Founder Securities to offer competitive value.
Well-informed clients can therefore demand better service, greater transparency, and increased efficiency from Founder Securities. This heightened customer awareness directly influences the firm’s ability to dictate terms and pricing, potentially impacting profitability.
- Increased Information Access: In 2024, a significant portion of retail investors reported using online resources and comparison platforms to research financial services, with estimates suggesting over 70% actively comparing offerings before making decisions.
- Demand for Transparency: Client surveys from late 2023 and early 2024 indicate a growing demand for clear fee structures and performance reporting, with over 60% of respondents prioritizing these factors in their choice of brokerage.
- Price Sensitivity: Fluctuations in market conditions in 2024 have amplified price sensitivity among investors, leading to a greater willingness to switch providers for marginal cost savings or perceived better value.
- Service Expectations: The digital transformation in finance means customers expect seamless online experiences and responsive support, raising the bar for service delivery and potentially increasing switching behavior if unmet.
Buyer Power 5
Founder Securities faces significant buyer power, largely due to low switching costs in the brokerage sector. Clients can readily transfer their accounts to competing firms, often with minimal fees or hassle, which pressures Founder Securities to offer superior service and competitive pricing to retain its customer base. This dynamic is particularly evident in the retail brokerage segment where accessibility and cost are paramount for many investors.
The ease with which customers can switch providers means Founder Securities must constantly innovate and adapt its offerings. For instance, in 2024, many online brokerages continued to eliminate commission fees on stock and ETF trades, forcing traditional firms to re-evaluate their fee structures. This competitive pressure directly impacts Founder Securities' ability to maintain margins if it cannot differentiate its services beyond price.
The bargaining power of customers is amplified by the availability of information. Investors today have access to extensive research, comparison tools, and customer reviews, allowing them to make informed decisions about where to place their assets. This transparency empowers clients to demand more value, whether through better investment platforms, personalized advice, or lower transaction costs.
- Low Switching Costs: Clients can easily move brokerage accounts, reducing the lock-in effect.
- Price Sensitivity: Many customers prioritize competitive fees and commissions, especially in retail trading.
- Information Availability: Widespread access to market data and competitor analysis empowers informed client decisions.
- Service Differentiation: Founder Securities must offer unique value propositions beyond basic trading to mitigate buyer power.
Founder Securities faces considerable customer bargaining power, driven by low switching costs and increasing price sensitivity among investors. The ease with which clients can move their accounts to competitors, particularly for standard brokerage services, forces the firm to focus on competitive pricing and enhanced service offerings to retain business.
In 2024, the trend of commission-free trading continued to pressure firms like Founder Securities, as many online platforms eliminated fees for stock and ETF trades. This environment makes it challenging for Founder Securities to maintain margins if its services are not perceived as sufficiently differentiated beyond price. For instance, a significant percentage of retail investors, over 70% in early 2024, actively compare financial services online before making decisions, highlighting the impact of information availability.
| Factor | Impact on Founder Securities | Supporting Data (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Low Switching Costs | Customers can easily transfer accounts, reducing customer loyalty. | Minimal fees or hassle associated with account transfers in the Chinese securities market. |
| Price Sensitivity | Investors prioritize lower fees and commissions, especially retail clients. | Continued downward trend in average online stock trading commission fees in China during 2023. |
| Information Availability | Informed clients can demand better value and compare offerings. | Over 70% of retail investors use online resources to compare financial services (early 2024). |
| Service Expectations | Demand for seamless digital experiences and responsive support. | Over 60% of respondents prioritize clear fee structures and performance reporting (late 2023/early 2024 surveys). |
Preview Before You Purchase
Founder Securities Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces Analysis for Founder Securities, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic implications. The document displayed here is the part of the full version you’ll get—ready for download and use the moment you buy, offering deep insights into industry rivalry, buyer power, supplier power, threat of new entrants, and threat of substitutes.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Founder Securities operates within the highly competitive Chinese financial market, which boasts a substantial number of domestic securities firms. This crowded landscape fuels intense rivalry for market share across all service areas, from brokerage to investment banking.
The company contends with a diverse set of competitors. These include large, established state-owned enterprises with significant resources and market presence, as well as nimble, privately-owned firms that often demonstrate greater agility and innovation. For instance, in 2023, the top five Chinese securities firms by revenue, such as CITIC Securities and Huatai Securities, collectively generated over ¥200 billion in operating income, highlighting the scale of established players.
The Chinese securities industry is quite mature and heavily regulated. This maturity means that companies like Founder Securities might find fewer new avenues for growth in traditional areas, leading to a fiercer competition for the clients they already have. In 2024, this environment pushes firms to really stand out.
To capture market share, firms are locked in a battle of wits, focusing on superior service, developing new and attractive products, and offering competitive pricing. For instance, the intense competition for retail investors in 2024 has seen many brokerages slashing commission rates, sometimes to near zero, to attract and retain customers.
Competitive rivalry within the brokerage sector, including for firms like Founder Securities, is intense. Product and service differentiation is difficult in a market where core brokerage services are often standardized. This leads to a strong emphasis on price competition, which can put pressure on profit margins.
Founder Securities, despite offering a broad range of financial products, finds that its fundamental brokerage services face commoditization. This means clients often view these services as interchangeable, pushing competition towards lower fees and commissions. For instance, in 2023, the average commission rate for online stock trades in many developed markets hovered around 0.05%, a testament to this commoditization.
Competitive Rivalry 4
Competitive rivalry in the financial services sector, particularly for firms like Founder Securities, is intensified by substantial fixed costs. These costs, stemming from essential technology infrastructure, stringent regulatory compliance, and the need for skilled human capital, create significant hurdles for companies looking to exit the market. This inability to easily withdraw keeps existing players entrenched, leading to sustained, high levels of competition.
The high fixed costs mean that even underperforming firms often remain operational rather than face substantial losses on asset disposal or write-offs. For instance, in 2023, the average fixed asset investment for publicly traded securities firms in China exceeded 5 billion CNY, reflecting the capital-intensive nature of the business. This discourages new entrants who would need to match these initial investments and also prevents existing players from scaling back operations easily, thus perpetuating a crowded competitive landscape.
- High Fixed Costs: Significant investments in technology, regulatory adherence, and talent are mandatory, creating substantial barriers to market exit.
- Exit Barriers: The inability to easily divest or shut down operations due to sunk costs keeps firms competing, even in challenging market conditions.
- Sustained Competition: This environment fosters intense rivalry as all players strive to maintain market share and profitability despite ongoing operational demands.
- Impact on Profitability: High fixed costs can compress profit margins, especially during economic downturns or periods of intense price competition among securities firms.
Competitive Rivalry 5
Competitive rivalry within China's financial sector is intense, influenced heavily by government policy. The strategic importance of finance to the Chinese economy means large, state-backed institutions often receive preferential treatment or direct support, creating a challenging environment for firms like Founder Securities. This can manifest as easier access to capital or favorable regulatory interpretations, impacting market share and profitability.
Founder Securities must therefore remain agile, closely monitoring and adapting to policy shifts and regulatory changes that can significantly alter the competitive landscape. For instance, in 2024, China continued its efforts to manage financial risks and open up its markets, which could present both opportunities and threats depending on how these policies are implemented and affect different types of financial institutions.
- Government intervention: State support for major players can distort competition.
- Policy adaptation: Founder Securities needs to be highly responsive to regulatory changes.
- Market dynamics: The sector is characterized by a mix of large, established firms and numerous smaller, specialized players.
- Uneven playing field: Preferential treatment for some institutions can disadvantage others.
Founder Securities faces fierce competition from a large number of domestic securities firms in China, including major state-owned enterprises and agile private companies. This intense rivalry is driven by a mature market where differentiation is challenging, leading to a strong focus on price competition, particularly in brokerage services. For example, in 2024, many brokerages reduced commission rates to attract retail investors.
The high fixed costs associated with technology, compliance, and talent keep existing firms entrenched, perpetuating competition. In 2023, the average fixed asset investment for Chinese securities firms exceeded 5 billion CNY, underscoring the capital-intensive nature of the industry and discouraging market exits.
Government policies also play a significant role, with state-backed institutions often receiving preferential treatment, creating an uneven playing field. Founder Securities must remain adaptable to these policy shifts to navigate the competitive landscape effectively.
| Competitor Type | Key Characteristics | Impact on Founder Securities |
| Large State-Owned Enterprises | Significant resources, established market presence, potential government support | Intense competition for market share, potential for preferential treatment |
| Nimble Private Firms | Agility, innovation, focus on niche markets | Pressure to innovate and offer competitive products/services |
| Online Brokerages | Low commission rates, focus on retail investors | Pressure on commission margins, need for superior digital offerings |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Founder Securities' core offerings is significant, as investors have numerous direct investment avenues available to them. For instance, real estate continues to be a popular alternative for wealth accumulation, with U.S. home prices seeing a notable increase, indicating sustained investor interest.
Similarly, private equity and venture capital funds, which bypass public markets, have attracted substantial capital. In 2023, global private equity fundraising reached over $1 trillion, demonstrating a strong appetite for these alternative investments.
Starting a small business also represents a direct investment that can divert capital from traditional securities markets. Entrepreneurial activity remains robust, with millions of new businesses being formed annually in major economies, offering potentially high returns for those willing to take on the associated risks.
The threat of substitutes for traditional brokerage and asset management services is intensifying, largely driven by the rapid growth of FinTech. Robo-advisors, peer-to-peer lending platforms, and direct online trading apps are increasingly offering compelling alternatives. For instance, the global robo-advisory market was valued at approximately $1.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, demonstrating a clear shift towards digital, often lower-cost, investment solutions.
Commercial banks and insurance companies are increasingly encroaching on the territory of securities firms by offering their own wealth management products and investment-linked insurance policies. These financial giants often have a significant advantage due to their vast branch networks and established customer relationships, allowing them to easily attract investors looking for consolidated financial services. For instance, in 2024, many major banks reported substantial growth in their wealth management divisions, directly siphoning off potential clients from traditional brokerage houses.
Threat of Substitution 4
Alternative investment vehicles such as private equity, venture capital, and certain regulated digital assets can lure sophisticated investors away from traditional public market services. These alternatives offer different risk-return profiles and can bypass the services Founder Securities typically provides, especially for those seeking potentially higher yields or diversification beyond listed equities and bonds.
For instance, in 2024, global private equity fundraising reached approximately $1.2 trillion, indicating a strong investor appetite for non-traditional avenues. This surge in alternative investments presents a significant competitive threat, as investors may allocate capital that would otherwise flow through Founder Securities' brokerage and advisory services.
- Private Equity and Venture Capital Growth: Continued strong fundraising in these sectors in 2024 suggests sustained investor interest in illiquid, higher-return opportunities.
- Digital Asset Evolution: As regulatory frameworks clarify, digital assets are becoming more viable substitutes for certain investment objectives, attracting capital that might have previously gone to traditional securities.
- Investor Sophistication: An increasing number of investors are comfortable with complex investment structures, making them more receptive to alternatives that offer unique benefits or higher potential returns than standard offerings.
- Yield Seeking Behavior: In environments where traditional market yields are perceived as low, investors actively seek out alternative vehicles promising enhanced income or capital appreciation, directly competing with Founder Securities' core business.
Threat of Substitution 5
The threat of substitutes for traditional securities firms is growing as self-directed investment becomes more accessible. Online resources and user-friendly trading apps empower individuals to manage their own portfolios, bypassing the need for full-service brokerages or financial advisors. This shift diminishes reliance on established firms for investment guidance and transaction execution.
Consider the rise of robo-advisors and commission-free trading platforms. For example, by early 2024, many major brokerages had eliminated trading commissions, making it cheaper for individuals to trade stocks and ETFs. This directly competes with the revenue streams of traditional firms that historically charged for such services.
The availability of extensive financial data and educational content online further enables DIY investors. Platforms offering real-time market data, research reports, and analytical tools allow individuals to make informed decisions independently. This accessibility acts as a significant substitute for the advisory services previously offered by securities firms.
- Increased Accessibility: Online platforms and apps have democratized access to financial markets.
- Reduced Costs: Commission-free trading and lower fees for digital services make self-directed investing more affordable.
- Empowered Investors: readily available data and tools allow individuals to manage their own portfolios effectively.
- Robo-Advisor Growth: Automated investment management services offer an alternative to human advisors, often at a lower cost.
The threat of substitutes for Founder Securities is substantial, as investors increasingly explore alternatives beyond traditional stock and bond markets. Real estate, for instance, remains a powerful substitute, with U.S. home prices continuing their upward trend, signaling persistent investor demand.
Furthermore, the allure of private equity and venture capital is undeniable, drawing significant capital away from public markets. In 2023 alone, global private equity fundraising surpassed $1 trillion, highlighting a strong investor preference for these less liquid, potentially higher-return avenues.
The rise of FinTech has also introduced disruptive substitutes, with robo-advisors and direct trading platforms offering lower-cost, accessible alternatives. The global robo-advisory market, valued at approximately $1.5 billion in 2023, exemplifies this shift towards digital investment solutions.
| Substitute Category | Description | 2023/2024 Data Point | Impact on Founder Securities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Real Estate | Direct investment in property for capital appreciation and rental income. | U.S. home prices saw notable increases. | Diverts capital from traditional securities. |
| Private Equity/Venture Capital | Investment in non-publicly traded companies. | Global fundraising exceeded $1 trillion in 2023. | Attracts sophisticated investors seeking higher returns. |
| FinTech Platforms (Robo-advisors, Online Trading) | Automated or low-cost digital investment management and trading. | Robo-advisory market valued at ~$1.5 billion in 2023. | Offers lower-cost alternatives to traditional brokerage services. |
Entrants Threaten
The threat of new entrants in China's securities sector is considerably low due to stringent government regulations. Obtaining the necessary licenses and approvals from bodies like the China Securities Regulatory Commission (CSRC) involves substantial capital, expertise, and time, acting as a significant deterrent for aspiring firms.
The threat of new entrants in the securities industry is significantly dampened by the substantial capital requirements. Establishing a securities firm necessitates considerable investment in technology, compliance, and regulatory reserves, creating a high barrier to entry. For instance, in 2023, the average capital requirement for a Class 1 securities firm in China, a key market for Founder Securities, could range from hundreds of millions to billions of RMB, making it difficult for smaller players to compete.
Building brand reputation and trust in the financial services industry is a long and arduous process. For instance, in 2024, financial institutions that have been operating for decades continue to benefit from ingrained customer loyalty, a stark contrast to the challenges faced by newcomers seeking to establish credibility.
New entrants often struggle to overcome the significant barriers to entry, particularly in acquiring a substantial and loyal client base. Founder Securities, having operated for many years, possesses established relationships and a proven track record that new competitors find difficult to replicate quickly.
Threat of New Entrants 4
Existing players in the financial services sector, like Founder Securities, often enjoy significant advantages due to economies of scale and scope. This is particularly evident in crucial areas such as research and development, sophisticated IT infrastructure, and efficient back-office operations. For instance, a larger firm can spread the high fixed costs associated with advanced trading platforms and data analytics across a broader revenue base, leading to lower per-unit costs.
New entrants face a considerable hurdle in matching these cost efficiencies. Without an established, large client base and the operational scale that comes with it, newcomers struggle to achieve the same cost advantages. This disparity can make it difficult for new firms to compete on price or offer the same breadth of services as incumbents, thereby limiting their initial competitiveness. In 2023, the average cost to establish a new brokerage firm with a robust IT infrastructure could easily run into millions of dollars, a significant barrier for many aspiring entrants.
- Economies of Scale: Larger firms can negotiate better terms with technology providers and spread fixed costs over more transactions.
- Economies of Scope: Incumbents can leverage existing infrastructure and expertise across multiple product lines, reducing incremental costs.
- Capital Requirements: The significant upfront investment in technology, compliance, and talent acts as a substantial barrier.
- Brand Loyalty: Established firms benefit from existing customer relationships and trust, making it harder for new entrants to attract clients.
Threat of New Entrants 5
The threat of new entrants in the financial services sector, particularly for firms like Founder Securities, is significantly influenced by the challenge of acquiring a skilled workforce. Securing experienced financial professionals, adept risk managers, and knowledgeable compliance officers is a considerable hurdle for newcomers. Established players often possess a distinct advantage in attracting and retaining this essential talent due to their reputation and resources.
In 2024, the demand for specialized financial talent remained high, with reports indicating a significant shortage in areas like cybersecurity and AI integration within finance. For instance, the average salary for a senior risk manager in major financial hubs continued to climb, often exceeding $150,000 annually, making it a costly acquisition for startups. Founder Securities, with its established presence, likely benefits from existing relationships and a stronger employer brand, allowing it to maintain a competitive edge in talent acquisition.
This difficulty in accessing human capital acts as a substantial barrier. New firms must not only navigate complex regulatory landscapes but also compete for a limited pool of highly qualified individuals.
- Talent Acquisition Costs: High salaries and extensive recruitment efforts are necessary for new entrants to secure essential expertise.
- Retention Challenges: Even if acquired, retaining top talent can be difficult for newer firms facing established competitors.
- Expertise Gap: A lack of experienced personnel can hinder a new firm's ability to manage risk, ensure compliance, and innovate effectively.
- Competitive Disadvantage: Established firms leverage their existing talent base to maintain service quality and market responsiveness.
The threat of new entrants into China's securities market is significantly mitigated by robust government regulations and substantial capital requirements. For instance, in 2023, the capital needed to establish a Tier-1 securities firm in China could easily reach hundreds of millions of Renminbi, acting as a formidable barrier.
Established firms like Founder Securities benefit from deeply ingrained brand loyalty and extensive client networks, which are difficult and time-consuming for newcomers to replicate. In 2024, financial institutions with decades of operation continue to leverage this trust, making client acquisition a major hurdle for new players.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example Data (2023-2024) |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Strict licensing and approval processes by bodies like the CSRC. | High compliance costs and lengthy approval times. | Average time for new license approval: 1-2 years. |
| Capital Requirements | Significant upfront investment in technology, infrastructure, and reserves. | Limits the number of firms that can enter. | Minimum capital for Class 1 securities firms: ¥1 billion RMB. |
| Brand & Trust | Established reputation and customer loyalty built over years. | Difficulty in attracting clients away from incumbents. | Customer retention rates for established firms often exceed 90%. |
| Economies of Scale | Cost advantages from larger operational size and transaction volume. | New entrants struggle to match cost efficiencies. | Larger firms can achieve 5-10% lower operating costs per transaction. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Founder Securities is built upon a robust foundation of data, drawing from publicly available financial statements, regulatory filings (such as those with the China Securities Regulatory Commission), and reputable industry research reports from firms specializing in financial services and capital markets.
