Foster Farms Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Foster Farms Bundle
Foster Farms faces significant competitive pressures, particularly from the high bargaining power of large retailers and the constant threat of substitute products like plant-based proteins. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating the poultry market.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Foster Farms’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Foster Farms' reliance on a concentrated market for essential inputs like animal feed, primarily corn and soybeans, and specialized veterinary services grants suppliers considerable leverage. When the number of suppliers for these critical components is limited, they can dictate pricing and contract terms, directly impacting Foster Farms' profitability. For instance, the volatility in global feed ingredient prices experienced in early 2025, with corn prices seeing a 15% increase due to adverse weather conditions in major producing regions, highlights the significant cost pressure suppliers can impose.
High switching costs significantly bolster the bargaining power of Foster Farms' suppliers. If Foster Farms needs to change suppliers for critical inputs, such as specialized poultry genetics or proprietary feed blends, the expenses and operational disruptions can be substantial. This isn't just about the price of new materials; it encompasses the potential for inconsistent product quality and the intricate process of re-establishing supply chain reliability.
The quality of inputs is crucial for Foster Farms, directly impacting the final product's taste and safety. For instance, the health of their breeding stock and the nutritional content of feed are fundamental. Suppliers who can consistently provide these superior inputs naturally gain more bargaining power because their products are directly linked to Foster Farms' brand image and consumer confidence.
This focus on quality means Foster Farms might be more inclined to pay a premium for suppliers offering top-tier ingredients. The company's commitment to high standards in 2024, as seen in their continued investment in animal welfare and sustainable feed practices, reinforces the importance of these supplier relationships. Reliable, high-quality sourcing becomes a competitive advantage, allowing suppliers to command better terms.
Threat of Forward Integration
The threat of forward integration by suppliers in the poultry sector, while less prevalent for raw material providers, could significantly bolster their leverage over companies like Foster Farms. Should a key supplier decide to move into direct poultry production, they would effectively become a competitor. This shift could restrict Foster Farms' access to essential inputs or drive up their operational expenses.
For instance, if a major feed producer were to establish their own processing plants, they could prioritize their own operations, potentially leaving Foster Farms with fewer options and higher prices for feed. This scenario directly impacts Foster Farms' cost structure and supply chain reliability.
- Supplier Integration Risk: A significant supplier integrating forward into poultry production could transform a partner into a direct competitor.
- Impact on Foster Farms: This move could limit Foster Farms' access to critical raw materials like feed or chicks, or lead to increased input costs.
- Example Scenario: A large feed manufacturer establishing its own processing facilities could create supply constraints or price hikes for Foster Farms.
Regulatory and Disease Impacts
Regulatory changes and disease outbreaks significantly influence the bargaining power of Foster Farms' suppliers. For example, highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) outbreaks can severely disrupt the supply of essential breeding stock, leading to scarcity and increased costs. This scarcity naturally amplifies supplier power as they face higher risks and can command premium prices for their limited, healthy inventory.
The impact of avian influenza on the poultry industry in 2024 highlights this dynamic. While specific data for Foster Farms' suppliers isn't publicly detailed, the broader industry faced significant challenges. In early 2024, the USDA reported numerous HPAI detections across multiple states, impacting commercial flocks and leading to culling. This situation directly translates to reduced availability of chicks and breeder birds for companies like Foster Farms, giving those suppliers who maintain disease-free operations greater leverage.
- Regulatory Hurdles: New environmental or animal welfare regulations can increase production costs for suppliers, potentially forcing them to pass these costs onto Foster Farms.
- Disease Outbreaks: Incidents like HPAI reduce the overall supply of poultry, strengthening the position of unaffected suppliers.
- Supply Chain Vulnerability: A concentrated supplier base, especially for specialized inputs like breeding stock, makes Foster Farms more susceptible to supplier power when disruptions occur.
- Increased Input Costs: Scarcity driven by disease or regulation directly translates to higher prices for raw materials and live birds, benefiting suppliers.
Foster Farms faces significant supplier bargaining power due to its reliance on a concentrated market for key inputs like feed grains and specialized veterinary services. The limited number of suppliers for these essential components allows them to influence pricing and contract terms, directly impacting Foster Farms' cost structure and profitability. For example, in early 2025, a 15% surge in corn prices, driven by adverse weather, underscored the cost pressures suppliers can exert.
The threat of forward integration by suppliers, particularly in feed production, poses a substantial risk. If a major feed manufacturer were to establish its own poultry processing operations, Foster Farms could face restricted access to vital feed supplies or encounter increased input costs, as the supplier prioritizes its own integrated business. This strategic move could fundamentally alter the supply chain dynamics.
The bargaining power of Foster Farms' suppliers is further amplified by high switching costs associated with critical inputs like specialized genetics or proprietary feed blends. The financial and operational disruptions involved in changing suppliers, coupled with potential quality inconsistencies, make it challenging for Foster Farms to find alternative sources, thus strengthening the leverage of incumbent suppliers.
Disease outbreaks, such as highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI), critically influence supplier leverage. HPAI incidents in 2024 led to reduced availability of essential breeding stock, creating scarcity and enabling unaffected suppliers to command premium prices. This vulnerability highlights how supply chain disruptions can significantly empower suppliers, especially those maintaining disease-free operations.
| Factor | Impact on Foster Farms | Example/Data Point |
| Concentrated Input Market | Increased supplier pricing power | 15% rise in corn prices (early 2025) due to weather |
| High Switching Costs | Supplier retention & leverage | Disruptions from changing specialized genetics suppliers |
| Supplier Forward Integration | Potential competitor & supply constraint | Feed producer establishing own processing plants |
| Disease Outbreaks (HPAI) | Reduced supply, increased costs for Foster Farms | HPAI detections in 2024 impacting breeder stock availability |
What is included in the product
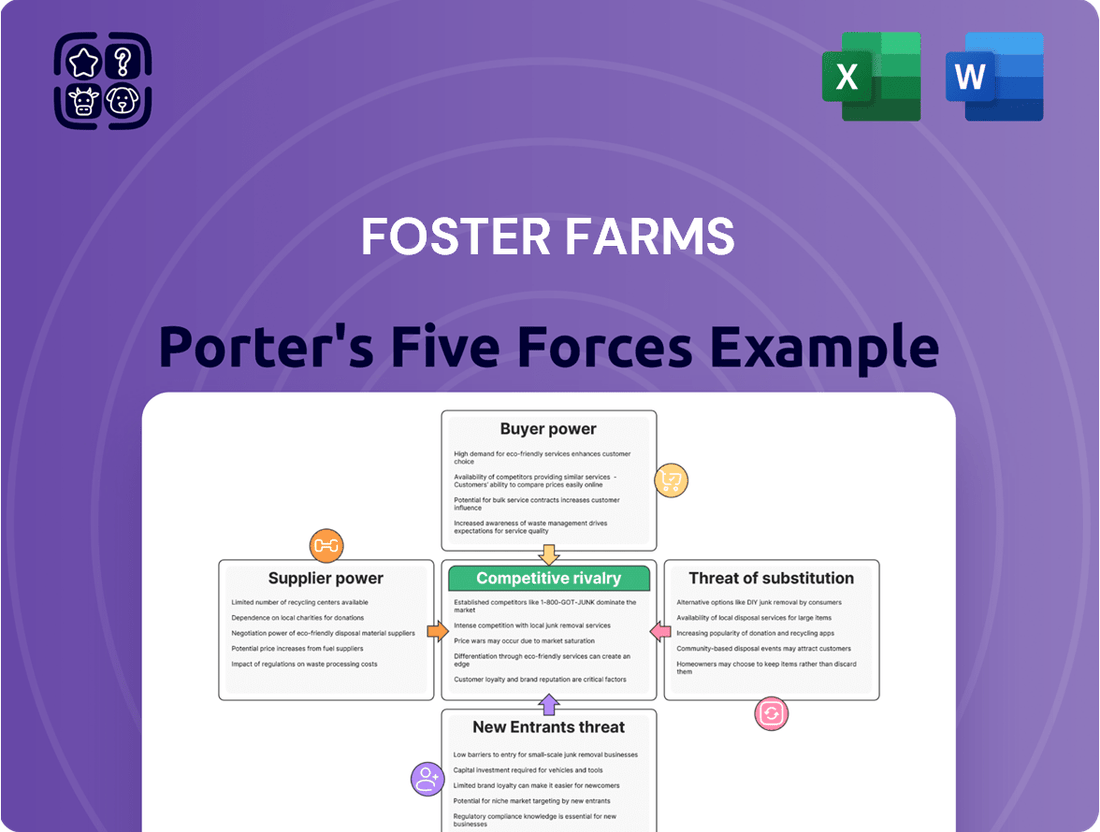
This analysis of Foster Farms' competitive environment identifies the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the risk of substitute products, providing a strategic overview of the poultry industry.
Instantly visualize competitive intensity with a dynamic Porter's Five Forces analysis, simplifying complex market dynamics for Foster Farms.
Customers Bargaining Power
Foster Farms serves a wide array of customers, from major grocery chains and large foodservice operators to smaller independent delis and restaurants. This broad customer base, while including powerful buyers like national supermarket chains, is largely fragmented. This fragmentation means that no single customer or small group of customers holds an overwhelming amount of power to dictate terms.
While major retailers and foodservice conglomerates can exert considerable influence due to their volume, the sheer number of smaller clients dilutes this collective leverage. Foster Farms' strategy of balancing sales across retail, foodservice, and export markets further diversifies its customer portfolio, thereby mitigating the bargaining power of any single segment.
Foster Farms' customers, particularly large grocery chains and foodservice companies, exhibit significant price sensitivity. These businesses operate in competitive environments themselves and are constantly looking for ways to manage their own costs, directly impacting their willingness to pay for poultry. For instance, in 2024, major supermarket chains reported average net profit margins often below 3%, highlighting their need to secure favorable pricing from suppliers like Foster Farms.
The digital age has dramatically increased the transparency of pricing information. Customers can now readily access data on commodity prices, competitor pricing, and production costs, allowing them to negotiate more effectively. This ease of comparison empowers buyers, putting downward pressure on Foster Farms' pricing power and potentially impacting its profit margins.
Beyond wholesale buyers, the end consumer's cost consciousness is also a major driver. With inflation impacting household budgets throughout 2024 and into early 2025, affordability remains a paramount concern for shoppers. This means that Foster Farms must remain competitive on price to capture market share, as consumers are more likely to opt for cheaper alternatives if prices rise significantly.
Customer switching costs for Foster Farms are a mixed bag. For large institutional buyers, such as major grocery chains or foodservice distributors, shifting to a different poultry supplier can incur expenses related to adjusting logistics, reconfiguring supply chains, and managing potential operational disruptions. This can give Foster Farms some leverage.
However, for the average consumer, the effort and cost involved in switching between poultry brands are quite minimal. This low barrier means consumers have significant power, as they can easily opt for a competitor if Foster Farms' pricing or product offerings are not to their liking. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. poultry market is highly competitive, with numerous brands available in most supermarkets, reinforcing consumer choice.
Volume of Purchases
Large volume customers, like major supermarket chains and national foodservice distributors, wield considerable bargaining power over Foster Farms. Their substantial purchase volumes allow them to negotiate for lower prices, more advantageous payment terms, and even specialized product offerings. For instance, in 2024, major U.S. grocery retailers such as Walmart and Kroger continued to represent a significant portion of the food industry's sales, often dictating terms due to their market share.
Foster Farms, to secure these crucial large contracts, might find itself compelled to make concessions, impacting its profit margins. The company's strategy to maintain a strong presence in physical retail channels is directly linked to maximizing sales volume, which in turn influences its ability to meet the demands of these powerful buyers.
- Customer Concentration: The concentration of Foster Farms' customer base among a few large buyers increases their leverage.
- Price Sensitivity: Large buyers often operate on thinner margins, making them highly sensitive to price fluctuations and demanding competitive pricing from suppliers like Foster Farms.
- Contractual Agreements: The terms of long-term supply contracts with major retailers can lock Foster Farms into specific pricing or product specifications, limiting flexibility.
- Alternative Suppliers: The availability of alternative poultry suppliers means large customers can switch if their demands are not met, further enhancing their bargaining power.
Threat of Backward Integration
While backward integration by major customers is relatively uncommon in the poultry industry, its mere possibility can empower buyers. For instance, a large supermarket chain could, in theory, invest in its own processing facilities, thereby diminishing its dependence on suppliers like Foster Farms. This potential threat, even if not actively pursued, grants customers significant leverage during price and supply negotiations.
The increasing prevalence of private label brands further amplifies customer power. Retailers are increasingly focused on developing and promoting their own-brand products, which often involves greater control over sourcing and production. This trend allows them to exert more pressure on suppliers to meet specific price points and quality standards, directly impacting companies like Foster Farms.
In 2024, the grocery retail sector saw continued consolidation and a strong emphasis on private label growth. Major retailers are actively seeking to expand their private label offerings, with some reporting that these brands now constitute over 30% of their total sales volume. This strategic shift underscores the growing bargaining power of these large customers.
- Backward Integration Threat: While rare, large customers like major grocery chains possess the financial capacity to invest in their own poultry processing operations, reducing reliance on external suppliers.
- Customer Leverage: The potential for backward integration, even if not fully realized, provides customers with significant bargaining power in price and contract negotiations with poultry producers.
- Private Label Growth: The expanding market share of private label brands, which represented over 30% of sales for many major retailers in 2024, empowers retailers to dictate terms and exert greater control over their supply chains.
Foster Farms faces considerable bargaining power from its customers, particularly large retail chains and foodservice operators. These buyers, driven by their own tight margins, often demand lower prices and favorable terms, a trend exacerbated by increasing price transparency in the digital age. For instance, in 2024, major U.S. grocery retailers like Walmart and Kroger, which command significant market share, often dictated terms to their suppliers.
The growth of private label brands, now exceeding 30% of sales for many major retailers in 2024, further empowers these customers. They can exert greater control over sourcing and pricing, putting downward pressure on Foster Farms. The threat of backward integration, though uncommon, also grants these large buyers leverage in negotiations.
| Customer Type | Bargaining Power Factors | Impact on Foster Farms |
|---|---|---|
| Major Retailers (e.g., Walmart, Kroger) | High volume purchases, Price sensitivity (avg. net profit <3% in 2024), Private label growth (>30% sales in 2024), Potential for backward integration | Downward pressure on pricing, demand for favorable terms, reduced flexibility |
| Large Foodservice Operators | Significant purchase volumes, Price sensitivity, Contractual agreements | Negotiating power for lower prices and specific product requirements |
| End Consumers | Low switching costs, High price consciousness (due to inflation in 2024-2025) | Need for competitive pricing, sensitivity to price increases |
Full Version Awaits
Foster Farms Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Foster Farms Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of competitive forces within the poultry industry. You are viewing the exact, professionally formatted document that will be delivered instantly upon purchase, ensuring you receive a ready-to-use, comprehensive strategic assessment.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The poultry sector is quite crowded, featuring significant players like JBS S.A., Tyson Foods, and Pilgrim's Pride Corporation, all of whom are substantial competitors to Foster Farms. This concentration of large companies means there's a constant, vigorous competition for market dominance and customer loyalty.
The global poultry industry is projected for steady growth, with demand anticipated to rise significantly in the coming years. For instance, the U.S. broiler production was forecast to reach 45.2 billion pounds in 2024, a slight increase from the previous year, indicating an expanding market.
While this expansion presents opportunities, it also fuels intense competition. Companies are actively vying for market share, especially in high-demand segments like value-added products and organic offerings, leading to aggressive strategies among players.
Foster Farms actively pursues product differentiation to stand out in the often commoditized poultry market. They focus on quality, safety certifications, and increasingly, on ethical sourcing and sustainability claims, aiming to build brand loyalty beyond price.
This strategy is evident in their expansion into value-added products like pre-marinated meats and organic lines, which command higher margins and appeal to specific consumer segments. For instance, in 2024, the demand for organic and sustainably produced foods continued to rise, with industry reports indicating a significant portion of consumers willing to pay a premium for these attributes.
Exit Barriers
Exit barriers for poultry companies like Foster Farms are substantial, primarily due to the immense fixed costs involved in operations. These include the capital investment in specialized poultry farms, advanced processing plants, and the establishment of extensive, often temperature-controlled, distribution networks. These high upfront and ongoing costs make it economically challenging for a company to simply shut down and exit the market, even when facing periods of low profitability. This situation forces businesses to remain operational, thereby intensifying competition as players fight to survive and maintain market share.
The sheer scale of investment required means that selling off assets can be difficult and often results in significant losses. Consequently, companies are incentivized to continue competing, even in a saturated or declining market, rather than incur the full cost of exit. This persistence among competitors is a key driver of ongoing rivalry within the industry. For instance, in 2023, the U.S. broiler industry faced overcapacity and price pressures, leading some producers to adjust operations rather than exit entirely.
Foster Farms itself has demonstrated strategic responses to market conditions rather than outright exits from core operations. The company's decision to close a turkey processing plant in Iowa, for example, highlights a tactical adjustment in response to specific market dynamics and demand shifts, rather than a complete withdrawal from the broader poultry sector. Such moves are common in industries with high exit barriers, where companies seek to optimize their remaining assets and operations to mitigate losses and stay competitive.
- High Fixed Costs: Significant investments in farming infrastructure, processing facilities, and distribution networks create substantial financial hurdles for exiting the poultry market.
- Asset Specificity: Specialized equipment and facilities for poultry production have limited alternative uses, reducing their resale value and increasing exit costs.
- Intensified Rivalry: High exit barriers encourage companies to remain in the market, leading to sustained competitive pressure even during downturns.
- Strategic Adjustments: Companies like Foster Farms often opt for operational adjustments, such as plant closures, rather than complete market exits to manage costs and adapt to changing demand.
Strategic Alliances and Acquisitions
Competitors in the poultry industry, including those vying with Foster Farms, frequently pursue strategic alliances, mergers, and acquisitions. These moves are designed to bolster market share, unlock economies of scale, and broaden product portfolios. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. poultry sector continued to see consolidation, with companies looking to streamline operations and enhance efficiency in a challenging cost environment.
Such corporate maneuvers can significantly alter the competitive dynamics. By creating larger, more integrated entities, these actions can intensify rivalry, forcing remaining players to adapt or risk falling behind. The pursuit of greater scale is particularly relevant in an industry where input costs, such as feed and energy, can fluctuate considerably.
- Consolidation Trends: The poultry industry has experienced ongoing consolidation, with larger players acquiring smaller ones to gain market access and operational efficiencies.
- Economies of Scale: Mergers and acquisitions allow companies to spread fixed costs over a larger production volume, potentially lowering per-unit costs.
- Product Diversification: Alliances and acquisitions can enable companies to expand into new product lines or value-added offerings, catering to a wider consumer base.
- Market Share Growth: A primary driver for these strategic moves is the ambition to capture a larger share of the domestic and international poultry markets.
The competitive rivalry within the poultry sector is intense, driven by a concentrated market with major players like Tyson Foods and JBS S.A. actively seeking market share. This high level of competition is further amplified by the industry's projected growth, with U.S. broiler production expected to reach 45.2 billion pounds in 2024, creating an environment where companies aggressively pursue customers through product differentiation and value-added offerings.
| Key Competitors | Market Share (Estimated 2023) | Key Strategies |
| Tyson Foods | ~20% | Product innovation, value-added products, international expansion |
| JBS S.A. | ~18% | Vertical integration, cost leadership, global sourcing |
| Pilgrim's Pride Corporation | ~15% | Operational efficiency, brand building, focus on private label |
| Foster Farms | ~5% | Quality and safety focus, organic and sustainable offerings, brand loyalty |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Consumers have a broad spectrum of protein options available, ranging from traditional meats like beef and pork to seafood. This extensive choice means that Foster Farms isn't solely reliant on its poultry products for consumer demand. For instance, in 2024, the average price per pound for boneless, skinless chicken breast remained competitive, but fluctuations in beef or pork prices could sway consumer choices.
The relative affordability of poultry is a significant driver of its demand, but this advantage can be eroded. If the prices of alternative proteins like beef or pork become more attractive, or if consumer preferences shift away from poultry due to health trends or ethical concerns, it presents a substantial threat to Foster Farms. For example, a 2024 USDA report indicated that while chicken consumption remained high, pork saw a notable increase in its share of total meat consumption in certain markets.
The burgeoning plant-based protein sector poses a significant threat of substitution for traditional poultry products. This market's rapid expansion, fueled by consumer interest in health, sustainability, and evolving dietary preferences, directly challenges Foster Farms' core offerings. For instance, the global plant-based meat market was valued at approximately $7.0 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach over $27 billion by 2030, indicating substantial consumer adoption of these alternatives.
Shifting consumer tastes pose a significant threat. A growing number of consumers are embracing flexitarian diets, reducing their overall meat consumption, and exploring plant-based alternatives. This trend is amplified by increasing awareness of the health and environmental impacts associated with food choices, directly impacting demand for traditional poultry products.
The demand for 'clean label' and natural ingredients is also on the rise, pushing consumers towards products perceived as healthier and more ethically produced. For instance, in 2024, plant-based meat alternatives continued to see robust growth, with the global market projected to reach over $100 billion by 2028, indicating a clear substitution away from conventional proteins.
Innovation in Substitute Products
Ongoing innovation in plant-based protein technologies is significantly enhancing the appeal and accessibility of meat alternatives. Companies are investing heavily in improving taste, texture, and the variety of these products, making them increasingly competitive with traditional meat. For instance, by mid-2024, the plant-based meat market was projected to reach over $10 billion globally, demonstrating substantial consumer adoption and ongoing product development.
These advancements directly challenge traditional meat providers like Foster Farms by offering consumers compelling alternatives that can satisfy similar dietary needs and preferences. The continuous improvement in plant-based options means that the threat of substitution is not static but is actively growing, requiring established players to adapt their strategies.
- Increased Consumer Acceptance: Plant-based alternatives are becoming more mainstream, with a growing percentage of consumers incorporating them into their diets regularly.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in ingredient sourcing, processing, and flavor development are closing the gap between plant-based and animal proteins.
- Market Growth: The plant-based food sector experienced robust growth in 2023, with sales continuing to climb, indicating a sustained shift in consumer demand.
Price and Accessibility of Substitutes
The increasing affordability and accessibility of plant-based alternatives directly impact the threat of substitutes for Foster Farms. As these options become more widespread in supermarkets and restaurants, they present a more compelling challenge to traditional poultry consumption.
For instance, in early 2024, the retail price of many plant-based chicken substitutes often remained higher than conventional chicken, creating a price barrier for some consumers. However, this gap is narrowing, with promotions and larger production scales driving down costs.
The availability of these substitutes has surged, with major grocery chains significantly expanding their plant-based protein sections. This widespread presence makes it easier for consumers to choose alternatives, thereby increasing the threat to poultry sales.
- Price Parity: While plant-based chicken prices were, on average, 20-30% higher than conventional chicken in early 2024, this differential is shrinking due to improved production efficiency and increased competition.
- Retail Availability: By mid-2024, over 80% of major US grocery retailers reported an increase in their plant-based product offerings, making substitutes more accessible than ever before.
- Foodservice Integration: Major fast-food chains have continued to expand their plant-based menu options, normalizing these alternatives and further challenging traditional meat consumption patterns.
The threat of substitutes for Foster Farms is significant, driven by a wide array of protein choices available to consumers. Beyond traditional meats like beef and pork, the burgeoning plant-based protein sector presents a substantial challenge, fueled by growing consumer interest in health, sustainability, and evolving dietary preferences. For example, the global plant-based meat market was valued at approximately $7.0 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach over $27 billion by 2030, indicating substantial consumer adoption of these alternatives.
Shifting consumer tastes, including the rise of flexitarian diets and a preference for 'clean label' ingredients, further amplify this threat. Innovations in plant-based protein technologies are also enhancing the appeal and accessibility of meat alternatives, making them increasingly competitive. By mid-2024, the plant-based meat market was projected to reach over $10 billion globally, demonstrating ongoing product development and consumer adoption.
| Protein Source | 2023 Market Value (USD Billion) | Projected 2030 Market Value (USD Billion) | Key Growth Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plant-Based Meat | 7.0 | 27.0+ | Health, Sustainability, Dietary Trends |
| Poultry (Foster Farms' Core) | N/A (Industry Data) | N/A (Industry Data) | Price Competitiveness, Convenience |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the poultry industry, particularly with a vertically integrated approach similar to Foster Farms, demands significant financial outlay. This includes substantial investments in land, breeding stock, feed production facilities, processing plants, and an extensive distribution infrastructure.
These considerable capital requirements act as a significant deterrent, effectively limiting the number of new players who can realistically enter and compete in this market.
For instance, establishing a modern, efficient poultry processing plant alone can cost tens of millions of dollars, a sum that many aspiring competitors simply cannot afford.
Established players like Foster Farms leverage substantial economies of scale in their operations. This means they can produce and distribute poultry at a much lower cost per unit than a newcomer could hope to achieve. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. poultry industry saw significant consolidation, with the top 10 companies controlling a large portion of the market, indicating the power of scale.
New entrants face a daunting challenge in matching these cost efficiencies. Without the same production volume, they would likely incur higher per-unit costs, making it difficult to offer competitive pricing against established brands. This cost disadvantage acts as a significant barrier, deterring new companies from entering the market.
The poultry industry is heavily regulated, with strict rules covering food safety, animal welfare, and environmental impact. For any new company looking to enter this market, navigating these complex and often changing regulations presents a substantial barrier. This compliance burden translates to higher initial operating costs and a longer period before they can even begin selling their products.
Think about the sheer effort and investment required to meet all these standards. For instance, recent updates from the USDA concerning poultry grower contracts and transparency demand even more meticulous adherence to new protocols. These additional layers of compliance can significantly deter potential new entrants who may lack the capital or expertise to manage them effectively.
Brand Loyalty and Distribution Channels
Foster Farms benefits from significant brand loyalty, making it difficult for newcomers to capture market share. Their established presence means consumers often reach for their products first, a hurdle new entrants must overcome through substantial marketing efforts.
The company also commands extensive distribution channels, securing prime shelf space in grocery stores and strong relationships with foodservice providers, especially in the Western United States. For any new poultry producer, replicating this widespread access and securing comparable placement is a formidable and costly undertaking.
- Established Brand Recognition: Foster Farms has cultivated a strong consumer following over decades.
- Extensive Distribution Network: Access to major grocery chains and foodservice contracts is a key barrier.
- High Initial Investment: New entrants face significant costs for marketing and building distribution.
Access to Supply Chain and Expertise
Foster Farms benefits from a vertically integrated model, controlling its supply chain from hatching to distribution. This integration ensures product consistency and safety, a significant barrier for newcomers. For instance, in 2023, the US poultry industry saw significant consolidation, with major players like Tyson Foods and Perdue Farms dominating market share, making it harder for new entrants to establish comparable supply chain control.
New entrants face the daunting task of building or securing access to a similarly complex and reliable supply chain. This includes establishing relationships with feed suppliers, hatcheries, growers, processing facilities, and distribution networks. Furthermore, acquiring the deep expertise required for efficient poultry farming, humane processing, and sophisticated logistics is a substantial hurdle.
- Vertical Integration: Foster Farms' control over its entire supply chain creates a significant barrier to entry.
- Supply Chain Complexity: New entrants must invest heavily to replicate or secure access to a comparable supply chain.
- Expertise Requirement: Deep knowledge in poultry farming, processing, and logistics is essential and difficult to acquire quickly.
- Industry Consolidation: The already consolidated nature of the poultry market in 2023 makes it challenging for new, smaller players to gain traction.
The threat of new entrants in the poultry sector, particularly for a company like Foster Farms, is generally considered low. This is primarily due to the substantial capital required to establish a vertically integrated operation, which includes everything from breeding stock and feed production to processing plants and distribution networks. For example, building a state-of-the-art poultry processing facility in 2024 could easily cost upwards of $50 million, a significant barrier for most aspiring companies.
Furthermore, established players like Foster Farms benefit from significant economies of scale, allowing them to produce poultry at a lower cost per unit. In 2023, the U.S. poultry industry saw continued consolidation, with the top five companies accounting for over 50% of the market share, underscoring the advantage of scale and making it difficult for newcomers to compete on price. Navigating complex regulations, securing prime retail shelf space, and building brand loyalty also present formidable challenges for any new entrant.
| Barrier to Entry | Estimated Cost/Impact (Illustrative) | Relevance to New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Investment (Processing Plant) | $50 million+ (2024 estimate) | High barrier due to massive upfront costs. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit cost for large producers | New entrants struggle to match pricing of established players. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Significant ongoing costs for food safety, etc. | Adds to initial operating expenses and time-to-market. |
| Distribution & Shelf Space Access | Millions in marketing and slotting fees | Difficult and expensive to replicate existing networks. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Foster Farms leverages data from industry-specific market research reports, company financial statements, and government agricultural statistics. This blend provides a comprehensive view of competitive intensity, buyer and supplier power, and the threat of new entrants and substitutes in the poultry market.
