FIDEA Holdings Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
FIDEA Holdings Bundle
FIDEA Holdings operates within an industry characterized by moderate buyer power and a significant threat from substitute products, as revealed by our Porter's Five Forces analysis. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for navigating the competitive landscape.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping FIDEA Holdings’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
FIDEA Holdings, a financial services group, sources its capital and funding from a variety of channels. These include customer deposits, which are a primary source of funds, as well as interbank lending and access to broader capital markets. The ability to attract and retain deposits is crucial, and FIDEA's deposit growth in 2023 reached 8.5%, demonstrating strong customer confidence and a competitive offering.
The bargaining power of these funding suppliers, such as depositors and lenders, is influenced by market liquidity and the overall competitiveness of the financial sector. When markets are tight or interest rates are high, suppliers can demand better terms. FIDEA's robust credit rating, maintained at A- by a leading agency in early 2024, significantly enhances its ability to secure favorable funding conditions, thereby mitigating supplier power.
A diversified funding strategy is key to reducing reliance on any single source and lessening the bargaining power of individual suppliers. FIDEA's proactive approach to managing its balance sheet and maintaining a strong capital adequacy ratio, which stood at 15.2% in Q4 2023, well above regulatory minimums, provides a solid foundation that limits the leverage of its funding sources.
In the rapidly evolving digital banking sector, FIDEA Holdings relies heavily on technology and software providers for its core operations, including digital infrastructure, robust cybersecurity measures, and innovative fintech solutions. The bargaining power of these suppliers is shaped by the distinctiveness of their products, the expense and complexity associated with switching to a different vendor, and the presence of viable alternative options in the market.
The ongoing digital transformation initiative within Japanese banking underscores FIDEA Holdings' significant dependence on these technology partners. For instance, the global IT spending in the banking sector was projected to reach $225 billion in 2024, indicating the substantial investment and reliance on external tech expertise.
The availability of skilled professionals in finance, technology, and risk management is a critical factor for FIDEA Holdings. In 2024, Japan faced a persistent shortage of IT talent, with an estimated deficit of over 400,000 workers, directly impacting companies needing specialized tech expertise.
The bargaining power of FIDEA's employees, especially those with niche financial or risk management skills, is amplified by high demand and tight labor market conditions. For instance, compensation for senior financial analysts in major Japanese cities saw increases of 5-8% in 2024, reflecting this competitive landscape.
FIDEA's ability to attract and retain top talent hinges on its compensation and benefits packages compared to other financial institutions in the Tohoku region and nationally. Competitiveness in salaries and benefits directly influences the leverage employees hold, especially in specialized fields where demand consistently outstrips supply.
Regulatory Bodies and Compliance Services
Regulatory bodies, while not direct suppliers in the traditional sense, wield considerable influence over FIDEA Holdings. For instance, the Financial Services Agency (FSA) in Japan, a key regulator for financial institutions, dictates operational standards and compliance mandates. These regulations, covering areas like capital adequacy and data protection, directly affect FIDEA's business model and investment strategies.
The bargaining power of these regulatory entities stems from their ability to impose penalties for non-compliance and to shape the very landscape in which FIDEA operates. For example, in 2024, financial institutions globally faced increased scrutiny regarding cybersecurity measures, leading to substantial investments in compliance. This necessity to adapt to evolving legal frameworks grants regulators significant leverage.
- Regulatory Impact: Compliance with banking laws and cybersecurity guidelines significantly influences FIDEA's operational costs and strategic direction.
- FSA's Authority: The Financial Services Agency's oversight imposes strict capital adequacy requirements, impacting FIDEA's financial planning.
- Evolving Landscape: The constant need to adapt to new financial regulations, as seen with increased cybersecurity demands in 2024, amplifies regulatory bodies' power.
Information and Data Providers
Financial institutions, including FIDEA Holdings, depend significantly on external information and data providers. These suppliers offer critical market insights, credit assessments, and economic forecasts essential for strategic decision-making. For instance, in 2024, the global financial data market was valued at approximately $30 billion, highlighting the substantial reliance on these services.
The bargaining power of these information and data providers is influenced by several factors. Key among these are the exclusivity and accuracy of the data they offer, alongside the cost and accessibility of alternative data sources. If a provider possesses unique, highly accurate data and few viable substitutes exist, their leverage increases.
- Data Exclusivity: Providers with proprietary or unique datasets hold stronger bargaining power.
- Data Accuracy and Timeliness: The perceived reliability and speed of data delivery directly impact a provider's influence.
- Availability of Alternatives: The presence of multiple comparable data providers dilutes individual supplier power.
- Cost of Switching: High costs associated with changing data providers can lock in existing relationships, increasing supplier leverage.
FIDEA Holdings faces moderate bargaining power from its technology and software suppliers, particularly those providing specialized fintech solutions and cybersecurity. The high cost and complexity of switching, coupled with the increasing demand for advanced digital services, give these vendors significant leverage. For instance, global IT spending in the banking sector was projected to reach $225 billion in 2024, underscoring the critical role and influence of these tech partners.
What is included in the product
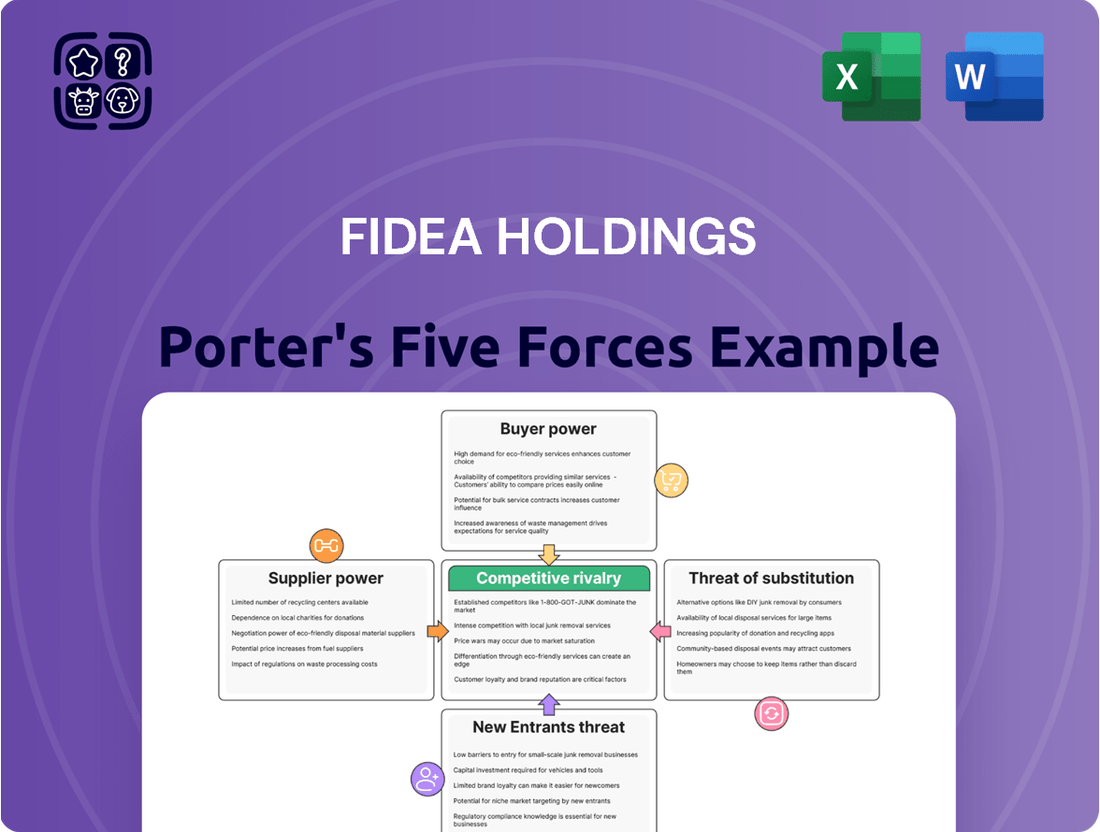
This analysis details the competitive forces impacting FIDEA Holdings, including the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry.
FIDEA Holdings' Porter's Five Forces Analysis provides a clear, one-sheet summary of all competitive forces, perfect for quick, informed decision-making.
Customers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of individual depositors with FIDEA Holdings is typically low. This is because most basic savings and checking accounts offer standardized products with minimal differentiation. Furthermore, switching costs for these accounts are generally quite low, meaning customers can move their funds easily if they find a slightly better offer elsewhere.
However, this power shifts significantly for larger corporate clients. These entities often hold substantial balances and can leverage this to negotiate more favorable interest rates or terms. For instance, a large business might have the leverage to move millions of yen, prompting FIDEA to offer better conditions to retain their deposit business.
In Japan's current economic climate, with interest rates potentially rising in 2024, the attractiveness of deposits for customers could increase. As of early 2024, while base rates remain low, any upward movement makes holding funds in traditional accounts more appealing compared to potentially volatile investments, thereby slightly increasing depositor leverage for those seeking yield.
Borrowers, especially larger corporations or those with excellent credit histories, can exert considerable influence by negotiating for lower interest rates and more adaptable loan conditions. This bargaining power is amplified by the prevailing regional economic climate and the accessibility of alternative funding avenues, such as other financial institutions or direct capital markets.
For FIDEA Holdings, whose business model is deeply rooted in supporting local enterprises, the bargaining power of its borrowers is a critical factor. The company's performance is intrinsically linked to the health and dynamism of the regional economy, which directly impacts the financial standing and negotiating leverage of its client base.
The bargaining power of clients in leasing and other financial services for FIDEA Holdings can fluctuate. Larger clients requiring complex, customized leasing arrangements or specialized financial products often wield more influence, especially if alternative providers exist. For instance, a large corporation seeking a bespoke fleet management solution might negotiate more favorable terms than a small business leasing standard equipment.
FIDEA Holdings' strategy to diversify into various financial services, including leasing, aims to cater to a broad spectrum of client needs. This diversification can mitigate the bargaining power of any single client segment. By offering niche services or highly tailored solutions, FIDEA can differentiate itself, reducing the ease with which clients can switch to competitors, thereby strengthening its own position.
Digital-Savvy Customers
Digital-savvy customers in Japan now wield significant bargaining power. The rapid adoption of digital banking, with over 80% of Japanese consumers using online banking services as of 2024, allows them to effortlessly compare offerings from various financial institutions and fintech providers. This ease of comparison means customers can quickly switch to platforms that offer a better user experience or more competitive rates, putting pressure on incumbents like FIDEA Holdings to innovate.
FIDEA Holdings must prioritize its digital transformation strategy to counter this trend. By investing in user-friendly interfaces and seamless digital services, the company can better meet the expectations of these increasingly demanding customers. For instance, a focus on mobile banking enhancements could be crucial, as mobile payments in Japan are projected to reach over 70% of all transactions by 2025.
- Increased Digital Adoption: Japanese consumers are embracing digital banking, with a significant portion actively using online platforms for their financial needs.
- Ease of Comparison: The digital landscape enables customers to readily compare services, fees, and user experiences across different financial providers.
- Switching Behavior: Tech-savvy customers are more inclined to switch to digital-first banks or fintechs offering superior convenience and functionality.
- FIDEA's Digital Imperative: FIDEA Holdings needs substantial investment in digital transformation to retain existing customers and attract new ones in this competitive environment.
Local Businesses Seeking Revitalization Support
FIDEA Holdings' mission to revitalize the Tohoku region grants local businesses significant bargaining power. Their success is intrinsically linked to FIDEA's core objectives, potentially allowing them to negotiate more favorable terms or demand specialized support. For instance, in 2023, FIDEA Holdings provided approximately ¥240 billion in loans to support regional businesses, highlighting their commitment.
These businesses, crucial for local economic development, can leverage their importance to the region's recovery. This positions them to request tailored financial products, extended repayment periods, or even investment in their growth initiatives. The bank's strategic focus on these areas means that the success of these local enterprises directly impacts FIDEA's own performance metrics related to regional contribution.
- Leveraging Regional Importance: Businesses can emphasize their role in job creation and local economic stability to FIDEA.
- Negotiating Favorable Terms: The bank's revitalization mandate may lead to more flexible loan conditions for key regional players.
- Seeking Specialized Support: Local firms might request specific advisory services or investment to enhance their competitive edge within Tohoku.
Customers' bargaining power at FIDEA Holdings is a mixed bag, largely dependent on their size and digital savviness. While individual depositors have limited sway, larger corporate clients and digitally active consumers can negotiate better terms due to their substantial funds or ease of switching. FIDEA's regional focus also grants local businesses, vital for Tohoku's revitalization, significant leverage in securing favorable conditions.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power | Key Influencing Factors | FIDEA's Response/Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Individual Depositors | Low | Standardized products, low switching costs | Focus on digital experience, competitive basic rates |
| Large Corporate Clients | High | Substantial balances, potential for large-scale fund movement | Tailored offerings, competitive interest rates |
| Digital-Savvy Customers | High | Ease of comparison, preference for convenience and functionality | Digital transformation investment, user-friendly interfaces |
| Regional Businesses (Tohoku) | High | Crucial for regional economic revitalization, FIDEA's mission alignment | Flexible loan terms, specialized support, tailored financial products |
Same Document Delivered
FIDEA Holdings Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis for FIDEA Holdings, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic implications. The document displayed here is the part of the full version you’ll get—ready for download and use the moment you buy. It meticulously examines the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within FIDEA Holdings' operating environment.
Rivalry Among Competitors
FIDEA Holdings contends with significant rivalry from other regional banks in the Tohoku area and nearby prefectures. This competitive landscape is particularly challenging given Japan's ongoing demographic shifts, which necessitate a strong focus on deposit acquisition and asset growth for these institutions.
The trend of mergers among regional banks is a clear indicator of this intense competition, as entities seek to consolidate for greater scale and operational efficiency. For instance, the merger of the Bank of Tohoku and the Daishi Bank to form FIDEA Holdings itself highlights this strategic imperative to remain competitive in a shrinking market.
While FIDEA Holdings concentrates on the Tohoku region, larger Japanese megabanks represent a significant competitive challenge. These national players boast extensive branch networks, a wider array of financial products and services, and considerable financial muscle, allowing them to absorb losses and invest heavily in growth initiatives.
The competitive rivalry is further intensified by the megabanks' aggressive push into digital transformation. By heavily investing in and expanding their digital banking platforms, they are increasingly reaching into retail markets, directly competing with FIDEA Holdings' core customer base and potentially eroding its market share through superior digital convenience and broader accessibility.
The competitive landscape for FIDEA Holdings is increasingly shaped by emerging digital banks and fintech companies in Japan. These agile players are disrupting the market with innovative services, often at lower cost structures, and delivering seamless digital experiences that strongly resonate with younger, tech-savvy consumers. For instance, by mid-2024, several neobanks had reported significant user growth, with some exceeding 1 million accounts, demonstrating their ability to quickly capture market share from traditional institutions.
Financial Cooperatives and Credit Unions
Local financial cooperatives and credit unions, though often smaller in scale, present a competitive force by offering highly personalized services and cultivating strong community connections. This is particularly relevant for small businesses and individuals within specific localities of the Tohoku region, where these institutions frequently leverage deep-rooted member relationships.
These community-focused financial entities can effectively compete by emphasizing tailored solutions and a commitment to local economic development. For instance, as of early 2024, many regional credit unions in Japan reported stable membership growth, indicating sustained trust and engagement within their operational areas.
- Personalized Service: Credit unions often excel in providing one-on-one customer support, fostering loyalty.
- Community Ties: Strong local connections can translate into preferential treatment for local businesses and residents.
- Niche Market Focus: Their ability to cater to specific local needs can be a significant advantage against larger, more generalized competitors.
Non-Bank Financial Service Providers
FIDEA Holdings faces competition from a diverse array of non-bank financial service providers. These include specialized leasing companies, consumer finance firms, and rapidly growing online lending platforms.
These competitors often differentiate themselves by offering niche products or more adaptable terms, which can appeal to customers seeking alternatives to conventional banking. For instance, in 2024, the online lending market continued its expansion, with fintech platforms facilitating billions in loans, often with quicker approval processes than traditional banks.
FIDEA Holdings' own leasing subsidiary operates within this dynamic environment, directly contending with other leasing entities that may offer specialized equipment financing or more flexible lease structures. The competitive pressure from these non-bank players underscores the need for continuous innovation and customer-centric solutions in the financial services sector.
- Leasing Companies: Offer specialized financing for assets, often with tailored terms.
- Consumer Finance Companies: Focus on personal loans and credit, sometimes with faster approval.
- Online Lending Platforms: Utilize technology for efficient loan origination and servicing, attracting digital-savvy customers.
- FIDEA's Leasing Subsidiary: Directly competes with these entities, requiring competitive product offerings and service levels.
FIDEA Holdings operates in a highly competitive banking sector, facing pressure from both large national megabanks and smaller, community-focused financial institutions. The ongoing trend of mergers among regional banks, exemplified by FIDEA's own formation, highlights the intense rivalry and the drive for scale in a consolidating market. Digital transformation is a key battleground, with megabanks aggressively expanding their online platforms, directly challenging FIDEA's customer base.
Emerging digital banks and fintech companies are further intensifying this rivalry by offering innovative, cost-effective services and superior digital experiences, particularly appealing to younger demographics. Even local financial cooperatives and credit unions compete effectively through personalized service and strong community ties, especially with small businesses and residents in the Tohoku region. Additionally, non-bank financial service providers, including leasing companies and online lenders, offer specialized and flexible alternatives, capturing market share with efficient processes.
| Competitor Type | Key Competitive Strengths | Impact on FIDEA Holdings | 2024 Market Trends/Data |
|---|---|---|---|
| Regional Banks | Consolidation for scale, operational efficiency | Direct competition for deposits and loans in Tohoku | Mergers continue, e.g., FIDEA's formation |
| Megabanks | Extensive networks, broad product offerings, digital investment | Erosion of market share through digital channels, greater resources | Significant investment in AI and digital platforms reported by major Japanese banks |
| Digital Banks & Fintech | Agility, lower costs, seamless digital experiences | Attracting tech-savvy customers, disrupting traditional models | Neobanks reporting over 1 million accounts by mid-2024 |
| Financial Cooperatives/Credit Unions | Personalized service, strong community ties | Retaining local customer loyalty, niche market focus | Stable membership growth reported by many credit unions in early 2024 |
| Non-Bank Financial Services | Niche products, flexible terms, efficient processes | Offering alternatives to traditional banking, capturing specific customer needs | Online lending market facilitated billions in loans in 2024 |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Larger businesses often have alternatives to traditional bank financing, such as directly accessing capital markets by issuing corporate bonds or securing private equity. This bypasses banks, particularly for companies with strong credit ratings. Recent trends in Japan, including increased merger and acquisition activity and significant capital expenditure, further highlight the viability of these substitutes.
Fintech lending platforms, including online lenders and peer-to-peer (P2P) networks, present a growing threat of substitution for traditional bank lending in Japan. These platforms often provide quicker application processes and more adaptable loan terms, appealing to a segment of borrowers who might find conventional bank requirements restrictive. The Japanese government's active promotion of fintech innovation is likely to further bolster the appeal and accessibility of these alternative financing channels.
The rise of digital payment systems and e-wallets presents a significant threat of substitution for traditional banking services. These platforms, often provided by tech companies rather than established banks, offer consumers a convenient alternative to cash and conventional bank accounts. For instance, by the end of 2023, global mobile payment transaction values were projected to exceed $1.5 trillion, highlighting a substantial shift in consumer behavior.
This trend is amplified by government push for cashless economies and increasing consumer preference for speed and ease in transactions. As more users adopt these digital solutions, the reliance on traditional payment methods, and by extension, the core services of entities like FIDEA Holdings, can diminish, thereby increasing competitive pressure.
Alternative Investment Vehicles
For depositors, alternative investment vehicles like securities and investment trusts present a significant threat of substitution. In environments with low interest rates, individuals often look beyond traditional bank deposits for higher returns. FIDEA Holdings, by managing its own securities, directly competes in this space, offering alternatives that can siphon funds away from its core deposit-taking business.
The attractiveness of these substitutes is amplified when they offer perceived advantages in yield, liquidity, or diversification. For instance, as of early 2024, many money market funds and short-term bond ETFs were yielding significantly more than typical savings accounts, making them compelling alternatives for risk-averse investors seeking better returns on their cash.
- Securities and investment trusts offer potentially higher yields than traditional bank deposits.
- Low-interest-rate environments increase the appeal of alternative investment vehicles.
- FIDEA Holdings’ own management of securities positions it as a direct competitor to its deposit products.
- Investor demand for diversification and yield drives the adoption of substitute financial products.
Internal Financing by Businesses
Established businesses with robust cash flows, like many in the technology and consumer staples sectors, increasingly favor internal financing through retained earnings. This practice directly substitutes for traditional bank lending, especially when economic conditions are favorable. For instance, in 2024, many large corporations reported significant increases in retained earnings, allowing them to self-fund capital expenditures and research and development without needing external debt.
This trend is particularly pronounced in sectors where profitability is high and predictable. Companies can reinvest profits to expand operations, acquire competitors, or return capital to shareholders, bypassing the need for bank loans. The availability of substantial internal funds acts as a powerful substitute, diminishing the bargaining power of banks and other external financiers.
- Reduced Reliance on Banks: Strong internal cash generation allows businesses to fund growth without incurring debt, lessening their dependence on traditional lending institutions.
- Cost Efficiency: Retained earnings avoid interest payments and associated fees, making them a more cost-effective financing option.
- Flexibility: Internal financing offers greater flexibility in terms of timing and project selection, as it is not subject to external approval processes.
The threat of substitutes for FIDEA Holdings' core banking services is significant, stemming from both alternative financing methods for businesses and investment options for depositors. Fintech platforms and direct capital markets access offer businesses alternatives to traditional bank loans, while digital payments and various investment vehicles present substitutes for consumers' banking needs. FIDEA Holdings, by managing its own securities, also directly competes with its deposit products.
| Substitute Type | Description | Impact on FIDEA Holdings | Example/Data Point (as of early 2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alternative Financing | Corporate bonds, private equity, retained earnings | Reduces demand for bank loans, particularly for creditworthy firms. | Many large corporations in 2024 reported significant increases in retained earnings, enabling self-funding of growth. |
| Fintech Lending | Online lenders, P2P platforms | Offers faster, more flexible loan options, attracting borrowers seeking alternatives to traditional banks. | Japanese government actively promotes fintech innovation, increasing accessibility of these channels. |
| Digital Payments | E-wallets, mobile payment systems | Provides convenient alternatives to cash and traditional bank accounts for transactions. | Global mobile payment transaction values projected to exceed $1.5 trillion by end of 2023. |
| Alternative Investments | Securities, investment trusts, money market funds | Attracts depositors seeking higher yields than traditional savings accounts. | Money market funds and short-term bond ETFs often yielded significantly more than savings accounts in early 2024. |
Entrants Threaten
The threat of new entrants in Japan's financial sector, particularly from fintech startups and digital banks, is substantial. Regulatory advancements have fostered an environment conducive to innovation, offering a clearer pathway for new financial service providers. These agile companies can capitalize on technology to deliver niche services, achieve leaner operational expenses, and target specific customer demographics, thereby posing a challenge to established banking institutions.
Major technology firms, often referred to as Big Tech, represent a significant threat to established financial services providers like FIDEA Holdings. These companies possess vast customer bases and sophisticated data analytics, which they could leverage to swiftly enter and disrupt the financial sector. For instance, in 2024, companies like Apple and Google continued to expand their financial offerings, such as Apple Pay and Google Wallet, demonstrating a growing interest in this space.
While FIDEA Holdings benefits from its regional focus, the threat of new entrants from foreign banks and financial institutions looms. Japan's financial sector, characterized by its stability and significant market size, remains an attractive prospect for international players. For instance, in 2023, foreign banks operating in Japan reported total assets exceeding ¥100 trillion, indicating a substantial presence and potential for further expansion.
Should regulatory barriers ease or if specific niche markets within Japan present compelling opportunities, foreign entities could increase their penetration. This is particularly true if they can leverage technological advancements or offer specialized services that are currently underserved. The prospect of lower capital requirements or streamlined licensing processes could accelerate such entries, intensifying competition for FIDEA Holdings.
Non-Financial Companies Diversifying into Financial Services
The threat of new entrants is amplified as non-financial companies increasingly venture into financial services. These companies, often possessing vast customer bases and rich data troves, are well-positioned to offer embedded finance and specialized lending. For instance, major tech companies with extensive user data are exploring partnerships or developing their own financial products, potentially disrupting traditional banking models.
This diversification blurs industry lines, creating new competitive pressures. Consider the retail sector, where large chains are now offering credit cards and buy-now-pay-later options, directly competing with established financial institutions. This trend is accelerating, with many non-financial firms leveraging their existing digital infrastructure and customer relationships to enter the financial services arena.
The impact on companies like FIDEA Holdings is significant. New entrants can leverage their existing customer ecosystems to offer integrated financial solutions, potentially at lower costs due to their non-financial core business. This can lead to:
- Increased competition for lending and payment services.
- Erosion of market share in traditional financial product segments.
- Pressure on profit margins as new players introduce innovative, often lower-cost, offerings.
- Redefined customer expectations for integrated financial experiences.
New Regional Bank Mergers and Alliances
While not entirely new players, the consolidation of regional banks through mergers and alliances presents a significant threat. These combined entities can leverage increased scale and operational efficiencies to offer more competitive pricing and a broader suite of services, directly challenging established regional banks like FIDEA Holdings. For instance, in 2023, the US saw several notable regional bank mergers, with the total value of announced deals reaching tens of billions of dollars, indicating a trend towards greater consolidation and competitive intensity.
These strengthened regional players can exert greater pricing power and invest more heavily in technology and product development. This enhanced competitive capability means existing players must innovate and adapt to maintain market share.
- Increased Scale: Merged entities benefit from larger asset bases and customer networks.
- Operational Efficiencies: Consolidation often leads to cost savings through shared resources and streamlined operations.
- Broader Service Offerings: Combined banks can provide a more comprehensive range of financial products, attracting a wider customer base.
- Competitive Pressure: These stronger regional banks can intensify competition on pricing and service quality.
The threat of new entrants for FIDEA Holdings stems from agile fintech startups, Big Tech firms, and even consolidated regional banks. Fintechs can offer niche services with lower overhead, while Big Tech leverages vast customer data and digital ecosystems. For example, in 2024, major tech companies continued to expand their financial services, like payment solutions, directly challenging incumbent banks.
Foreign financial institutions also pose a threat, particularly if regulatory barriers in Japan decrease. In 2023, foreign banks in Japan held over ¥100 trillion in assets, indicating a significant existing presence and potential for growth. Furthermore, non-financial companies entering the financial services space, such as retailers offering buy-now-pay-later options, blur industry lines and intensify competition.
Consolidation among regional banks creates larger, more efficient competitors. These merged entities can offer more competitive pricing and a wider array of services, as evidenced by the tens of billions of dollars in US regional bank mergers announced in 2023, a trend that increases competitive intensity.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our FIDEA Holdings Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of industry-specific market research reports, company filings, and expert interviews.
