Extreme Networks Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Extreme Networks Bundle
Extreme Networks operates within a dynamic networking industry, facing significant competitive pressures. Understanding the interplay of buyer power, supplier leverage, the threat of new entrants, substitutes, and existing rivalries is crucial for strategic planning.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Extreme Networks’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of suppliers for Extreme Networks is significantly shaped by supplier concentration. When a few key manufacturers dominate the supply of specialized semiconductors or network interface cards, their ability to influence pricing and terms for Extreme Networks, and indeed the entire industry, grows. This concentration means fewer alternatives for critical components.
In the high-tech networking sector, where custom-designed chips and advanced hardware are often necessary, this supplier concentration can be quite pronounced. For instance, if a handful of companies control the production of essential ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits) vital for high-speed switching and routing, they hold considerable leverage. This leverage translates into the ability to potentially demand higher prices or impose specific contractual conditions, impacting Extreme Networks' cost structure and product development timelines.
Extreme Networks' suppliers wield significant bargaining power when the inputs they provide are highly unique or proprietary. If Extreme Networks relies on specialized software, custom-designed chipsets, or patented technologies that cannot be readily sourced from alternative providers, these suppliers gain considerable leverage. This uniqueness is particularly impactful in the competitive cloud-managed networking sector, where advanced components are critical for performance and differentiation.
For instance, the reliance on specific, high-performance silicon for their Wi-Fi 6E and Wi-Fi 7 access points, or proprietary operating system software that underpins their cloud management platform, can grant suppliers substantial influence. In 2024, the demand for advanced networking hardware, driven by 5G expansion and the increasing adoption of IoT devices, has intensified the market for these specialized components, potentially increasing supplier pricing power.
The cost and complexity for Extreme Networks to switch suppliers play a significant role in how much power those suppliers hold. If it's difficult and expensive for Extreme Networks to move to a different supplier, the current suppliers have more leverage. For instance, if switching requires substantial investment in new equipment or significant changes to product designs, suppliers can often dictate terms more easily.
High switching costs can arise from various factors. These might include the expense and time involved in retooling manufacturing processes to accommodate new components or the intricate process of renegotiating complex, long-term supply chain agreements. Such barriers make Extreme Networks more dependent on its existing supplier relationships, even if those relationships come with less favorable pricing or terms.
For example, in the networking hardware sector, proprietary software integration and specialized component compatibility can create substantial switching costs. A supplier providing a critical, highly integrated component might leverage this to negotiate higher prices. Extreme Networks, by its nature as a technology provider, likely faces these kinds of embedded costs when dealing with specialized hardware or software suppliers.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into Extreme Networks' market is a significant factor influencing their bargaining power. If suppliers, particularly those providing critical components or even more integrated technology solutions, were to directly offer networking products and services to Extreme Networks' customer base, it would fundamentally alter the competitive landscape.
While component suppliers typically focus on manufacturing, larger technology conglomerates with broader portfolios could potentially leverage their existing infrastructure and customer relationships to enter the networking solutions space. This would mean they could compete directly with Extreme Networks, offering end-to-end solutions rather than just individual parts.
- Increased Competition: Forward integration by suppliers would introduce new direct competitors to Extreme Networks, potentially fragmenting market share.
- Pricing Pressure: A supplier acting as a direct competitor could exert downward pressure on pricing for networking solutions.
- Control over Value Chain: Suppliers moving into this space would gain greater control over the entire value chain, from component manufacturing to final product delivery.
- Strategic Shift: For Extreme Networks, this would necessitate a strategic response to maintain its competitive edge and market position against these potentially integrated rivals.
Importance of Extreme Networks to Suppliers
The significance of Extreme Networks as a customer directly impacts its bargaining power with suppliers. When Extreme Networks constitutes a substantial portion of a supplier's overall revenue, that supplier is more likely to offer competitive pricing and favorable contract terms to retain this valuable business.
Conversely, if Extreme Networks is a minor client for a supplier, especially a large, diversified one, its leverage diminishes. In such scenarios, suppliers may be less inclined to make concessions, as the loss of Extreme Networks' business would have a negligible impact on their financial performance.
- Customer Concentration: If a supplier relies heavily on Extreme Networks for a significant percentage of its sales, Extreme Networks gains considerable bargaining power.
- Supplier Diversification: Conversely, if Extreme Networks represents a small fraction of a supplier's revenue stream, the supplier's willingness to negotiate is reduced.
- Market Position: Extreme Networks' overall market share and purchasing volume can influence how critical its business is to its suppliers.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Extreme Networks is influenced by the availability of substitute inputs. If alternative components or services can fulfill the same function, Extreme Networks can leverage this to negotiate better terms. The lack of readily available substitutes for highly specialized networking hardware, however, strengthens supplier power.
For example, in 2024, the demand for advanced semiconductors used in high-performance switches and routers remained robust, with limited direct substitutes for cutting-edge chipsets. This scenario grants suppliers a notable advantage in pricing negotiations. Extreme Networks’ reliance on these specialized components means that a lack of viable alternatives directly translates into increased supplier leverage.
What is included in the product
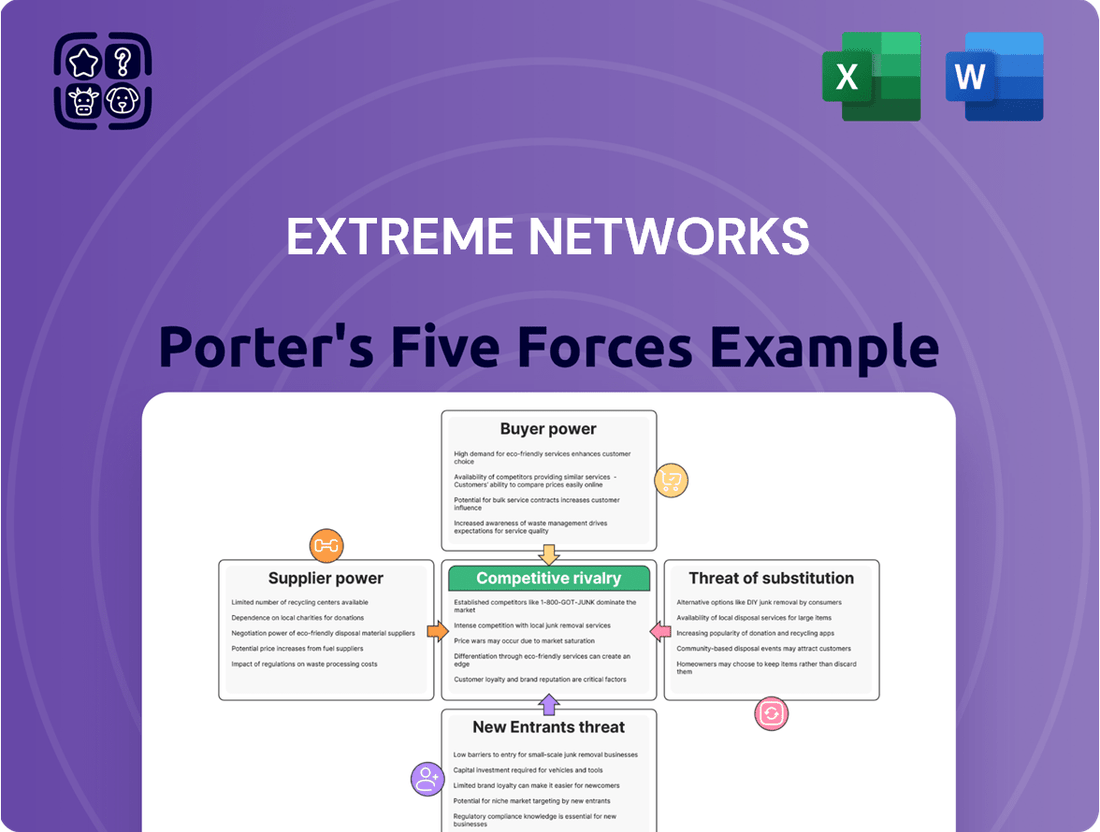
This analysis specifically examines the competitive forces impacting Extreme Networks, detailing industry rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and substitute products to understand its market position and strategic vulnerabilities.
Gain immediate clarity on competitive pressures with a visual spider chart, allowing rapid assessment of how Extreme Networks' strategies address each force.
Customers Bargaining Power
Extreme Networks' customer base, which includes large enterprises, data centers, and service providers, can exert significant bargaining power, particularly if a few key clients represent a substantial portion of their revenue. For instance, if a major telecommunications company or a large cloud provider were to account for a significant percentage of Extreme Networks' sales, that customer could leverage its importance to negotiate lower prices or demand specific product customizations. This concentration is a common dynamic in business-to-business markets where substantial contracts are crucial for vendor success.
Customers wield significant bargaining power when a wide array of alternative networking solutions are readily available from competitors. Companies like Cisco, HPE, Juniper Networks, and Arista Networks offer robust and often feature-comparable products, giving customers leverage to negotiate pricing or demand better terms. This competitive landscape means Extreme Networks must continuously innovate and offer compelling value propositions to retain its customer base.
The ease with which customers can switch to a rival’s offerings directly impacts Extreme Networks’ pricing flexibility. For instance, if a competitor releases a new cloud-managed switch with comparable performance at a lower price point, customers may be inclined to migrate, forcing Extreme Networks to consider price adjustments or enhanced service bundles to remain competitive.
Extreme Networks’ strategy to differentiate through cloud-managed platforms and simplified IT operations is crucial in mitigating this customer power. By offering unique features or superior user experience, they can reduce the perceived substitutability of their solutions. However, the ongoing development of similar capabilities by competitors means this remains a constant challenge.
In 2024, the networking hardware and services market is highly competitive, with significant investment in research and development across major players. This intense innovation cycle ensures that alternative solutions with competitive pricing and features are consistently entering the market, thereby maintaining high customer bargaining power.
The costs customers incur to move from Extreme Networks to a competitor are a key factor in their bargaining power. These switching costs can be financial, operational, or technical. If it's difficult, takes a lot of time, or costs a lot to migrate a network already using Extreme Networks' equipment and software, customers will be less inclined to switch, which in turn weakens their negotiating leverage.
Extreme Networks' efforts to simplify licensing and enhance ease of use directly address these switching costs. By making their solutions more user-friendly and their licensing models straightforward, Extreme can lower the perceived difficulty and expense of switching away, potentially increasing customer bargaining power if they choose to explore other options.
Customer Price Sensitivity
Customer price sensitivity is a significant lever in the bargaining power of customers for networking solutions like those offered by Extreme Networks. If clients are highly attuned to the cost of these solutions, they will naturally push for lower prices. This sensitivity can stem from several factors, including strained IT budgets, the increasing standardization of networking hardware and software components, or intense cost pressures within their own business sectors.
For instance, in 2024, many businesses across various industries reported tighter capital expenditure on IT infrastructure due to ongoing economic uncertainties and a focus on operational efficiency. This environment amplifies the desire for cost-effective networking solutions, giving customers greater leverage to negotiate pricing with vendors like Extreme Networks. When networking becomes a more commoditized purchase, customers often shift their focus primarily to the price tag.
- High IT Budget Constraints: Many organizations in 2024 continued to manage lean IT budgets, directly impacting their willingness to pay premium prices for networking equipment and services.
- Commoditization of Components: As core networking technologies mature, many components become more standardized, allowing customers to more easily compare prices across vendors and demand lower costs.
- Competitive Industry Pressures: Industries facing significant competition often pass cost-saving pressures down the supply chain, forcing their vendors to offer more aggressive pricing.
- Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Increasingly, customers evaluate not just the upfront purchase price but the overall TCO, including maintenance, support, and energy consumption, which can also drive price negotiations.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of customers integrating backward into network solution provision significantly boosts their bargaining power against companies like Extreme Networks. This means customers could potentially start building their own networking solutions, lessening their need to buy from external providers.
While this is a remote possibility for many businesses, extremely large entities such as major service providers or hyperscale data centers possess the resources and scale to explore developing their own proprietary networking technologies. Some might even consider acquiring smaller vendors to gain immediate capabilities, thereby reducing their dependence on established players like Extreme Networks.
For instance, in 2024, the increasing trend of hyperscalers designing custom silicon for their data centers, as reported by industry analysts, hints at a growing inclination towards in-house solution development. This move aims to optimize performance and cost, directly impacting the market for traditional network equipment vendors.
- Increased Customer Leverage: The potential for backward integration gives large customers more leverage in negotiations.
- Reduced Reliance on Vendors: Customers developing in-house solutions decrease their dependence on external providers.
- Hyperscaler Customization: Hyperscale data centers are increasingly designing custom hardware, including networking components, to meet specific needs.
- Impact on Market: This trend can force traditional vendors like Extreme Networks to innovate and offer more competitive pricing or specialized services.
Customers hold considerable bargaining power when they represent a large portion of Extreme Networks' revenue or when switching to competitors is easy and inexpensive. In 2024, economic uncertainties led many businesses to scrutinize IT spending, amplifying price sensitivity and thus customer leverage. The availability of numerous alternative solutions from rivals like Cisco and Juniper Networks further strengthens this position.
The bargaining power of Extreme Networks' customers is significant due to market competition and the potential for lower switching costs. In 2024, many organizations faced budget constraints, making them highly price-sensitive and eager to negotiate better terms for networking solutions. The increasing commoditization of networking components also allows customers to easily compare prices and demand cost reductions, directly impacting vendors like Extreme Networks.
| Factor | Impact on Extreme Networks | 2024 Context |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High dependence on key clients can lead to price concessions. | While specific customer revenue percentages for Extreme Networks are proprietary, concentration in large enterprise and service provider sectors is common. |
| Availability of Substitutes | Numerous competitors (Cisco, HPE, Juniper) offer viable alternatives. | The networking market in 2024 remained highly competitive with continuous innovation from major players. |
| Switching Costs | Low switching costs empower customers to negotiate. | Extreme Networks' focus on simplifying operations aims to reduce perceived switching barriers, potentially increasing customer leverage. |
| Price Sensitivity | Customers with tight budgets push for lower prices. | Many businesses in 2024 managed lean IT budgets, amplifying price sensitivity and customer bargaining power. |
Same Document Delivered
Extreme Networks Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. You'll get a comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis of Extreme Networks, detailing the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors, the bargaining power of buyers, the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of suppliers, and the threat of substitute products or services. This in-depth analysis will equip you with a strategic understanding of Extreme Networks' competitive landscape.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The enterprise networking sector is a battleground with numerous strong contenders. This intense rivalry stems from the presence of giants like Cisco Systems, Arista Networks, Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE), and Juniper Networks, alongside more niche players, all vying for dominance.
This crowded field means companies must constantly innovate and compete aggressively on price and features to capture market share. For instance, Cisco, a long-standing leader, consistently invests heavily in research and development, setting a high bar for others.
The diversity of competitors, ranging from broad technology providers to specialized networking solutions firms, further intensifies this rivalry. This forces companies like Extreme Networks to differentiate themselves through specific product strengths or service offerings to stand out in a saturated market.
The networking infrastructure market is seeing robust expansion, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 8% to 10% through 2027. This healthy growth generally tempers intense rivalry, as companies can increase revenue by capturing new market share rather than solely by taking it from competitors. However, specific sub-segments within this market may exhibit different growth trajectories, leading to localized competitive pressures.
Extreme Networks' ability to differentiate its software-driven, cloud-managed networking solutions, particularly its ExtremeCloud IQ platform and AI-driven features, plays a crucial role in shaping competitive rivalry. When these offerings are perceived as unique and valuable, it naturally lessens the intensity of competition.
High switching costs for customers further serve to insulate Extreme Networks from aggressive rivalry. If it's difficult or expensive for clients to move to a competitor's platform, they are more likely to remain with Extreme, thereby reducing the pressure from rivals seeking to poach customers.
Conversely, if Extreme's products are viewed as interchangeable or commoditized, the landscape shifts dramatically. In such scenarios, competition often devolves into price wars, as companies vie for market share by offering lower costs, which can erode profitability for all players.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers in the networking sector, including substantial investments in specialized hardware and infrastructure, often lock companies into the market even when profitability wanes. These barriers, such as sunk costs in proprietary technology and significant capital tied up in physical assets, can force even struggling competitors to remain active, leading to persistent overcapacity. For instance, the substantial upfront capital expenditure required for network infrastructure development, often in the billions for major players, makes divesting or exiting a complex and costly endeavor.
These entrenched competitors, despite potentially weak financial performance, continue to exert pressure through aggressive pricing strategies. This situation is exacerbated by long-term customer contracts and the significant costs associated with employee severance and retraining, further complicating any exit strategy. The result is a market where even underperforming entities contribute to intense price competition, impacting overall industry profitability.
- Significant Capital Investments: Networking companies often have billions tied up in R&D and physical infrastructure.
- Specialized Equipment: High costs associated with proprietary or highly specialized networking hardware are difficult to recoup.
- Long-Term Contracts: Existing service agreements and support commitments can bind companies to markets for extended periods.
- Employee Severance Costs: Layoffs in a specialized field like networking can incur substantial severance packages.
Strategic Stakes and Aggressiveness
The strategic stakes in the networking industry are incredibly high, influencing how aggressively companies compete. Competitors like Cisco, Aruba (HPE), and Juniper Networks are deeply invested in maintaining or expanding their market share, especially in lucrative segments like cloud-managed networking and the burgeoning field of AI integration in network management.
This drive for market dominance often leads to intense rivalry. Companies frequently engage in price wars to capture customers, particularly for large enterprise deals. Aggressive marketing campaigns and a relentless pace of innovation are also hallmarks of this competition, as firms strive to establish themselves as leaders in next-generation technologies.
- Market Share Defense: Cisco, a dominant player, is heavily motivated to protect its substantial market share against aggressive challengers.
- Growth Aspirations: Companies like Aruba (HPE) and Juniper are actively pursuing growth, targeting areas like Wi-Fi 6E and AI-driven network operations to gain ground.
- Technological Leadership: The race to integrate AI for predictive analytics, automated troubleshooting, and enhanced security is a key battleground, with significant strategic implications for future revenue streams.
- Price Sensitivity: In certain segments, particularly for commodity hardware or managed services, price remains a significant competitive lever, leading to potential price wars.
Competitive rivalry within the enterprise networking sector is fierce, characterized by the presence of major players like Cisco, Arista, HPE, and Juniper Networks. These companies continuously innovate and compete on price and features, with Cisco, for example, dedicating substantial R&D to maintain its leadership. The market's projected 8-10% CAGR through 2027 offers some buffer, allowing for revenue growth through market expansion rather than solely through competitive gains. However, specific niches may still experience intense localized competition.
| Competitor | Approximate Market Share (2024 Estimate) | Key Competitive Focus Areas |
|---|---|---|
| Cisco Systems | ~30-35% | Cloud networking, security, AI integration, enterprise switching and routing |
| Arista Networks | ~10-15% | High-performance data center networking, cloud networking, campus networks |
| Hewlett Packard Enterprise (Aruba) | ~10-12% | Campus and branch networking, Wi-Fi, edge computing, AI-driven operations |
| Juniper Networks | ~5-7% | AI-driven enterprise networking, cloud-native solutions, AI for IT operations |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Extreme Networks' offerings is significant, primarily stemming from the increasing availability of alternative technologies. Customers can increasingly opt for networking services provided natively by major public cloud providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform. These cloud-native solutions often cater to similar needs for connectivity, security, and management, presenting a direct substitute for on-premises or hybrid networking infrastructure that Extreme Networks traditionally serves.
Furthermore, the rise of open-source networking software presents another potent substitute. Solutions like ONAP or SONiC allow organizations to build and manage their networks with greater flexibility and potentially lower upfront costs, bypassing the need for proprietary hardware and software from traditional vendors. This trend is particularly relevant for cost-conscious enterprises and service providers looking to avoid vendor lock-in and leverage community-driven innovation.
For instance, cloud providers are not just offering basic connectivity; they are increasingly providing sophisticated Software-Defined Networking (SDN) capabilities and managed network services. In 2024, the global cloud networking market was valued at over $10 billion, with substantial growth projected, indicating a strong customer shift towards these integrated solutions. This directly competes with Extreme Networks’ hardware and software sales for enterprise data centers and campus networks.
Customers constantly weigh the cost against the capabilities of alternative solutions. If a substitute provides similar functionality for less money, or better features for the same price, the pressure on Extreme Networks intensifies. This forces Extreme Networks to ensure its offerings remain competitive in terms of value.
For instance, the increasing sophistication and cost-effectiveness of software-defined networking (SDN) solutions, particularly those leveraging open-source components, present a clear substitute threat. These alternatives can offer greater flexibility and potentially lower capital expenditure compared to traditional hardware-centric network infrastructure, which Extreme Networks historically specialized in.
The rise of managed service providers (MSPs) who bundle networking services with hardware from various vendors also represents a substitute. Customers might opt for an all-inclusive service package that simplifies operations and potentially offers predictable monthly costs, bypassing the need to procure and manage individual network components directly from a vendor like Extreme Networks.
In 2024, the market saw continued growth in cloud-managed networking solutions, with many businesses prioritizing ease of deployment and ongoing management. This trend directly challenges traditional on-premises solutions, highlighting the importance for Extreme Networks to offer robust cloud-based alternatives that match or exceed the price-performance of these competing models.
Customers are increasingly willing to consider Network-as-a-Service (NaaS) or fully managed solutions, especially if these alternatives simplify IT operations or offer tangible cost savings. For instance, Gartner predicted in 2024 that NaaS adoption would accelerate, with many organizations seeking to reduce upfront capital expenditure and leverage flexible operational spending models.
The perceived risk associated with switching to a substitute is a key determinant. If a new service offers robust security and reliable performance, customers are more likely to embrace it, especially as data breaches become a more significant concern. This ease of adoption, coupled with clear value propositions, directly impacts the propensity for customers to move away from traditional networking hardware and support models.
Emergence of New Business Models
New business models are emerging that function as substitutes for traditional networking hardware and software solutions. For instance, Network-as-a-Service (NaaS) and Security Service Edge (SASE) offer integrated networking and security capabilities on a consumption basis. This approach allows customers to access these functions without significant upfront investment in on-premise infrastructure, potentially diminishing the demand for Extreme Networks' core offerings.
The shift towards cloud-native and as-a-service models presents a significant threat. By bundling networking, security, and management into a single, scalable service, these new models can offer greater flexibility and potentially lower total cost of ownership for businesses. For example, the SASE market, which combines network security functions with wide-area networking capabilities, is projected to grow substantially. Gartner predicted that by 2025, 70% of new network access control deployments will be cloud-based, up from 15% in 2020, highlighting the growing acceptance of these substitute models.
- Network-as-a-Service (NaaS): Offers flexible, subscription-based access to networking infrastructure and services.
- Security Service Edge (SASE): Integrates network security functions with WAN capabilities, delivered as a cloud service.
- Market Growth: The SASE market is experiencing rapid expansion, indicating strong customer adoption of these integrated, cloud-delivered solutions.
- Reduced Hardware Dependence: These models can lessen customer reliance on purchasing and managing physical networking hardware, a core revenue stream for traditional vendors.
Do-It-Yourself Solutions
For some organizations, particularly smaller ones or those with highly specialized needs and internal expertise, building or maintaining their own networking solutions using generic hardware and open-source software could serve as a substitute for Extreme Networks' offerings. This DIY approach, while often more complex, can present significant cost savings and a high degree of customization for specific use cases. For instance, businesses might opt for commodity servers running Linux distributions and open-source routing software to bypass the need for proprietary hardware and support contracts.
The potential for DIY solutions is amplified by the increasing availability and maturity of open-source networking software. Projects like SONiC (Software for Open Networking in the Cloud) and Cumulus Linux are enabling companies to build sophisticated network infrastructures without relying on traditional vendors. This trend is particularly relevant for hyperscalers and large enterprises who have the technical talent to manage such environments. In 2023, the global open-source software market was valued at over $30 billion, indicating a strong and growing adoption of these alternative approaches.
- DIY networks can offer substantial cost reductions compared to enterprise-grade solutions.
- Organizations with in-house technical expertise are better positioned to leverage DIY networking.
- Open-source software platforms are making it more feasible for companies to build their own networks.
- The trend towards open networking is driven by the desire for customization and avoidance of vendor lock-in.
The threat of substitutes for Extreme Networks is substantial, largely driven by the migration of networking functions to cloud-native services and the rise of flexible consumption models. Major cloud providers offer integrated networking, security, and management, directly competing with traditional hardware-centric solutions. For instance, the global cloud networking market exceeded $10 billion in 2024, reflecting a strong customer preference for these consolidated offerings.
Furthermore, Network-as-a-Service (NaaS) and Security Service Edge (SASE) models are gaining traction, providing networking and security capabilities on a subscription basis. Gartner projected in 2024 that NaaS adoption would accelerate, with many organizations seeking to reduce upfront capital expenditure. This shift reduces reliance on purchasing and managing physical networking hardware, a core revenue area for companies like Extreme Networks.
Open-source software and do-it-yourself (DIY) networking approaches also pose a threat, offering customization and potential cost savings. Projects like SONiC enable companies with in-house expertise to build sophisticated networks, bypassing proprietary solutions. The global open-source software market, exceeding $30 billion in 2023, underscores the growing adoption of these alternative, more flexible strategies.
| Substitute Category | Key Characteristics | Customer Appeal | Market Trend Example (2024) |
| Cloud-Native Networking | Integrated connectivity, security, and management within cloud platforms. | Simplified operations, scalability, reduced capex. | Cloud networking market valued over $10 billion. |
| NaaS & SASE | Subscription-based, consumption-driven access to network and security functions. | Flexibility, predictable opex, reduced upfront investment. | Accelerated NaaS adoption predicted. |
| Open-Source & DIY | Customizable network infrastructure using commodity hardware and open software. | Cost savings, vendor independence, high degree of control. | Open-source software market exceeding $30 billion (2023). |
Entrants Threaten
The networking infrastructure market, where companies like Extreme Networks operate, demands massive upfront capital. We're talking about significant investments in research and development to create cutting-edge technology, building and maintaining advanced manufacturing facilities, and establishing robust global distribution and sales networks. For instance, major players often spend hundreds of millions annually on R&D alone.
This creates a substantial barrier for any new company looking to enter the fray. A new entrant would need access to considerable financial resources, likely in the billions, to even begin to compete with established giants that already have these infrastructures in place and proven track records. Think about the sheer cost of developing next-generation switching and routing hardware or cloud-based network management software.
Without this deep well of capital, a new competitor would struggle to match the product innovation, pricing power, and widespread market presence that incumbents like Extreme Networks possess. This financial hurdle effectively limits the number of viable new entrants, making it a significant deterrent.
Existing players, such as Extreme Networks, have a significant advantage due to their established economies of scale. This means they can produce and procure components at lower per-unit costs than a newcomer. For instance, in 2024, major networking equipment providers often operate with gross margins in the 50-60% range, a feat difficult for a new entrant to match from the outset.
New entrants would face substantial hurdles in replicating these cost efficiencies. Without the existing volume of production and established supplier relationships, a new company would likely incur higher costs for raw materials, manufacturing, and even research and development. This cost disadvantage would make it challenging to compete on price with established firms like Extreme Networks.
Furthermore, the experience curve plays a crucial role. Companies that have been in the market longer have refined their processes, optimized their supply chains, and gained invaluable knowledge in product development and customer support. In 2024, the networking industry is highly competitive, and the learning curve for a new entrant to achieve operational excellence is steep and capital-intensive.
Extreme Networks, like many established players in the networking industry, benefits from significant brand loyalty. Customers have grown accustomed to the reliability and performance associated with established vendors, leading to a preference that new entrants must actively overcome.
The switching costs for enterprise networking solutions are substantial. These include the expense and time associated with migrating data, retraining IT staff on new systems, and ensuring compatibility with existing hardware and software. For instance, a complex multi-vendor network environment could take months, even years, to fully transition, representing a significant barrier.
In 2024, the networking market continued to see customers prioritize continuity and proven solutions. This preference for stability, driven by the high cost of disruption, makes it particularly difficult for new entrants to penetrate the market and gain significant traction against well-entrenched brands like Extreme Networks.
Access to Distribution Channels
New competitors in the networking sector face significant hurdles in securing robust distribution channels. Extreme Networks has cultivated strong relationships with value-added resellers (VARs), system integrators, and a direct sales force, which are essential for reaching a diverse customer base. For instance, in fiscal year 2023, Extreme Networks reported a substantial increase in partner-driven revenue, highlighting the importance of these established networks.
Establishing equivalent distribution partnerships requires considerable time, investment, and demonstrated market success, making it a formidable barrier for new entrants. Without these established channels, newcomers would struggle to gain the necessary market penetration and customer access that Extreme Networks currently enjoys.
- Distribution Channel Importance: Access to VARs, system integrators, and direct sales forces is crucial for market reach in the networking industry.
- Extreme Networks' Advantage: The company possesses existing, broad-reaching partnerships that new entrants would find difficult to replicate.
- Barrier to Entry: New companies need significant time and capital to build comparable distribution networks, posing a substantial threat.
Intellectual Property and Regulatory Hurdles
The networking industry, including companies like Extreme Networks, is heavily protected by intellectual property. This includes patents covering everything from the physical hardware to the intricate software algorithms and communication protocols that make networks function. For any new company wanting to enter this space, they face a significant challenge: either they need to license existing technologies, which can be costly, or invest heavily in developing their own proprietary solutions from scratch. This R&D investment alone presents a substantial barrier.
Beyond intellectual property, navigating the complex web of regulations and compliance standards adds another layer of difficulty for new entrants. Different regions and countries have specific requirements for network equipment, data security, and interoperability. Meeting these standards demands considerable expertise and resources, often requiring extensive testing and certification processes. For instance, in 2024, the global cybersecurity market was valued at over $270 billion, underscoring the critical importance and regulatory scrutiny placed on network security technologies.
These combined factors – the need to license or develop IP and the requirement to adhere to stringent regulations – create significant cost and time barriers. New entrants must be prepared for substantial upfront investment in research and development, legal counsel, and compliance efforts. This makes it challenging for smaller or less-funded companies to compete effectively against established players like Extreme Networks, which have already built extensive patent portfolios and established compliance frameworks.
- Intellectual Property: Patents for hardware, software algorithms, and network protocols are a major barrier to entry in the networking sector.
- Licensing vs. Development: New entrants must either license existing technologies or invest heavily in developing their own, both demanding significant capital.
- Regulatory Landscape: Compliance with diverse international regulations for network equipment and data security adds complexity and cost.
- Market Entry Costs: The combined IP and regulatory hurdles translate into substantial upfront expenses and extended time-to-market for newcomers.
The threat of new entrants in the networking infrastructure market, where Extreme Networks operates, is generally low due to substantial barriers. High capital requirements for R&D, manufacturing, and global distribution, often in the hundreds of millions annually for R&D alone, make it difficult for newcomers. Established players benefit from economies of scale, achieving gross margins of 50-60% in 2024, a cost advantage new entrants struggle to match.
Brand loyalty and high switching costs for enterprise networking solutions also deter new companies. Customers prioritize proven reliability, and migrating complex network environments can take months or years, representing significant disruption costs. Furthermore, intellectual property protection through patents and the need to navigate complex global regulations for data security and interoperability add further layers of cost and time barriers for potential market entrants.
| Barrier Category | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example Data Point (2024/2023) |
| Capital Requirements | High upfront investment for R&D, manufacturing, and distribution. | Limits the number of well-funded competitors. | Annual R&D spending in hundreds of millions for major players. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs due to high production volume. | New entrants face higher initial operating costs. | Gross margins of 50-60% for established networking equipment providers. |
| Brand Loyalty & Switching Costs | Customer preference for established, reliable vendors; cost/time of migration. | Makes it hard to win over existing customer bases. | Enterprise network migration projects can span months to years. |
| Intellectual Property & Regulation | Patents on technology and compliance with global standards. | Requires significant investment in legal, R&D, and certification. | Global cybersecurity market valued over $270 billion in 2024, indicating regulatory focus. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Extreme Networks Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon comprehensive data from company annual reports, investor presentations, and industry analyst reports. We also incorporate market research databases and financial news outlets for a well-rounded view of the competitive landscape.
