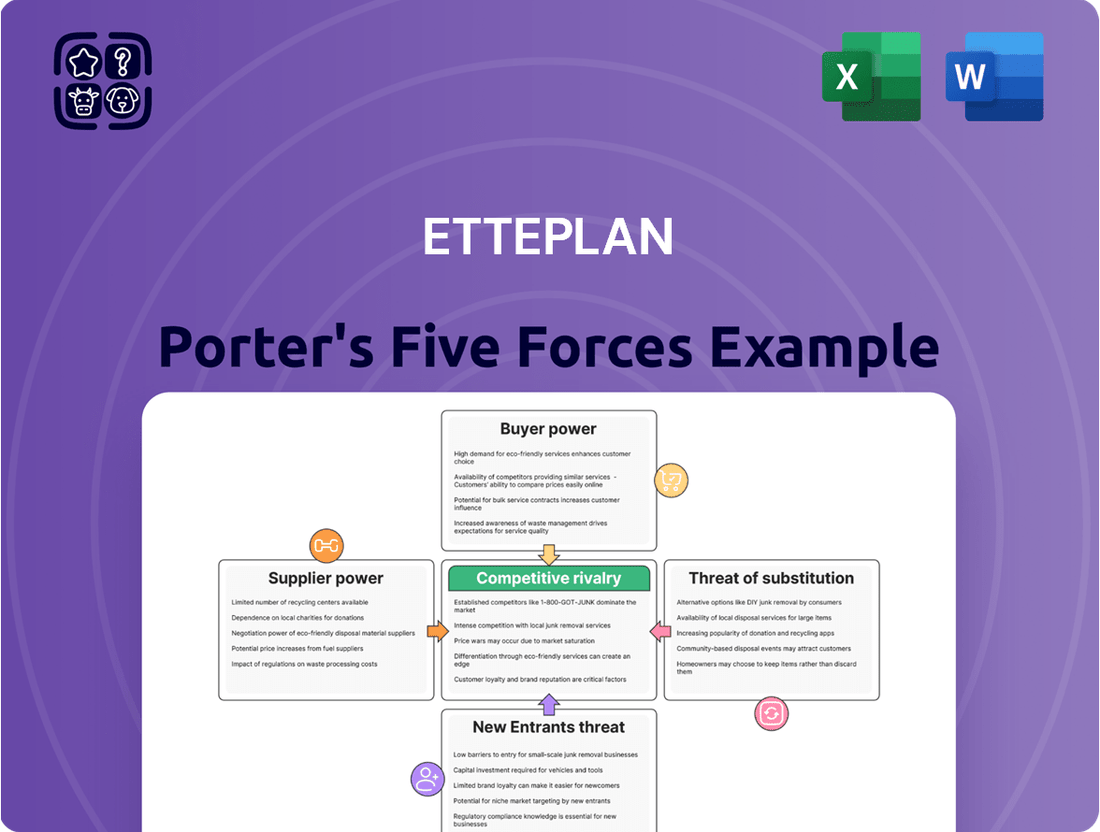
Etteplan Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Etteplan Bundle
Our Porter's Five Forces Analysis for Etteplan reveals the critical competitive landscape, highlighting how buyer power and the threat of new entrants are shaping the market.
The full report dives deeper, quantifying the intensity of each force and offering a strategic roadmap to navigate Etteplan's industry challenges and opportunities.
Ready to gain a comprehensive understanding of Etteplan's competitive environment? Unlock the complete analysis to make informed strategic decisions.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of suppliers for Etteplan is largely kept in check by the fragmented nature of the engineering talent market. This means there isn't a single dominant supplier of the highly skilled professionals Etteplan relies on, limiting any one provider's ability to dictate terms.
While certain specialized software or hardware components might originate from fewer sources, the overall availability of technical personnel and common development tools dilutes the leverage of any individual supplier. For instance, in 2024, the global IT services market, which includes engineering talent, remained highly competitive with numerous players vying for contracts, preventing undue supplier influence.
Etteplan's strength lies in its skilled workforce, comprising engineers, developers, and technical writers. The company's focus on human capital means that the expertise of its employees is a critical factor in its service delivery.
While individual employees might have specialized skills, Etteplan actively develops its talent pool through internal training programs. This approach reduces reliance on any single external expert, thereby lessening the bargaining power of individual suppliers of unique skills.
Furthermore, Etteplan's global delivery model, including its investment in BJIT in Bangladesh, diversifies its talent sourcing. This strategy allows Etteplan to tap into a wider range of expertise and manage costs effectively, further diminishing the leverage of any singular unique supplier.
Switching costs for Etteplan's suppliers are generally moderate. For example, if Etteplan relies on specific proprietary software or highly specialized engineering tools from a particular vendor, transitioning to an alternative could necessitate significant investment in employee retraining and data migration. This complexity makes frequent supplier changes less appealing.
However, for suppliers of more commoditized services or individual freelance engineering contractors, the switching costs are considerably lower. Etteplan can readily onboard new talent or engage with different consulting firms if a current supplier relationship becomes unsatisfactory, indicating a degree of flexibility in this area.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into Etteplan's service areas is generally low. Individual engineers or smaller consulting firms typically lack the necessary scale, established client networks, and the broad spectrum of services, encompassing engineering, software development, and technical documentation, to directly challenge Etteplan's comprehensive offerings.
While larger technology vendors might present some integrated solutions, their core business models remain distinct from Etteplan's project-based service delivery. For instance, in 2024, Etteplan's revenue was reported at €1.1 billion, highlighting the significant operational size and market presence that aspiring forward-integrating suppliers would need to replicate to pose a substantial threat.
- Limited Supplier Scale: Most suppliers are individual professionals or small entities, lacking the capital and infrastructure for broad service integration.
- Service Portfolio Gap: Suppliers typically specialize, unlike Etteplan which offers a diverse range of integrated engineering and digital solutions.
- Business Model Divergence: Technology vendors, while capable of offering solutions, focus on product sales rather than Etteplan's project-specific service provision.
Importance of Etteplan to Suppliers
Etteplan represents a significant customer for many individual contractors, specialized small businesses, and even providers of essential software and tools. Their ongoing need for skilled personnel and specialized services offers a reliable income source for these suppliers. This consistent demand makes Etteplan a crucial partner for them, thereby diminishing the suppliers' ability to dictate terms and prices.
The bargaining power of suppliers in Etteplan's ecosystem is generally moderate. While Etteplan is a substantial client for many, the availability of alternative engineering and technology service providers limits any single supplier's leverage. For instance, in 2023, Etteplan's revenue reached €1.1 billion, indicating the scale of its operations and the potential volume of business available to its suppliers. This scale, combined with a diverse supplier base, prevents any one supplier from holding excessive power.
- Significant Client Base: Etteplan's consistent demand for engineering and design services makes it a vital revenue source for many specialized firms and individual contractors.
- Supplier Dependence: For smaller, niche suppliers, Etteplan's business can represent a substantial portion of their annual turnover, increasing Etteplan's importance to them.
- Market Availability: The engineering services market is competitive, with numerous qualified suppliers available, which naturally moderates the bargaining power of any individual supplier.
- Cost Sensitivity: While quality is paramount, Etteplan, like most large organizations, is mindful of costs, which also influences the negotiation dynamics with its suppliers.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Etteplan is generally moderate, primarily due to the fragmented nature of the engineering talent market and the company's strategic diversification of its talent sourcing. This prevents any single supplier from exerting undue influence over pricing or terms.
Etteplan's substantial revenue, reaching €1.1 billion in 2023, signifies its importance as a client for many specialized firms and individual contractors, thereby reducing supplier dependence. While switching costs can be moderate for specialized tools, the availability of numerous qualified suppliers in the competitive engineering services market keeps individual supplier leverage in check.
| Factor | Impact on Etteplan | Supporting Data/Reasoning |
| Supplier Concentration | Low | Fragmented engineering talent market; diverse sourcing strategies (e.g., BJIT investment). |
| Importance of Etteplan to Suppliers | High | Etteplan's €1.1 billion revenue (2023) makes it a significant customer for many niche suppliers. |
| Switching Costs for Etteplan | Moderate (for specialized tools), Low (for talent) | Potential retraining/data migration for specialized software vs. ease of onboarding new engineers. |
| Threat of Forward Integration | Low | Individual suppliers/small firms lack scale and broad service portfolios to compete directly. |
What is included in the product
Uncovers the competitive intensity, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and substitute products/services impacting Etteplan's market position.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a visually intuitive, pre-built analysis that cuts through market complexity.
Customers Bargaining Power
Etteplan's customer concentration is a key factor in their bargaining power. While serving leading manufacturing firms suggests strong client relationships, a reliance on a few major customers could grant them significant leverage. For instance, if a single client represented over 10% of Etteplan's revenue in 2024, that client would have considerable sway.
However, Etteplan's strategy of diversification across sectors like defense, energy, and automotive helps to mitigate this risk. A broad customer base across these industries means no single client can dictate terms as easily, spreading the risk and reducing the overall bargaining power of any individual customer.
Switching costs for Etteplan's clients can be substantial, especially when dealing with intricate, long-term engineering endeavors, the development of embedded software, or comprehensive technical documentation packages. These costs are amplified by Etteplan's deep integration into a client's product development cycles and the proprietary knowledge gained, making a transition to a new provider a complex and potentially disruptive undertaking.
Customer price sensitivity is a major driver of bargaining power. When the economic climate tightens, like during periods of high inflation or recession fears, customers become more hesitant to spend on engineering services. This reluctance can translate into significant price pressure on providers.
For instance, in 2024, many industries experienced elevated operating costs, forcing clients to scrutinize every expenditure. This environment directly impacts companies like Etteplan, where clients may seek to negotiate lower rates for engineering projects. Etteplan's strategic use of its global delivery model, which allows for cost-effective resource allocation, becomes crucial in mitigating this increased price sensitivity and maintaining competitiveness.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of customers performing Etteplan's services in-house, known as backward integration, is a moderate factor. Many large manufacturing clients possess their own engineering departments, potentially capable of handling some of these tasks internally.
However, the specialized knowledge, operational efficiency, and adaptability that a focused service provider like Etteplan delivers often outweigh the costs and complexities of building and maintaining comparable in-house capabilities. This is particularly true for specialized engineering needs or when demand fluctuates significantly.
For instance, in 2024, many industrial companies are prioritizing core competencies, making outsourcing non-core but critical functions like advanced engineering design and digital transformation services a strategic choice to maintain agility and focus on their primary manufacturing operations.
- Customer Capabilities: Large customers often have existing engineering departments.
- Etteplan's Value Proposition: Specialization, efficiency, and flexibility of outsourcing.
- Strategic Outsourcing: Focus on core competencies drives outsourcing decisions.
- Market Trends: Increased demand for specialized digital and engineering services in 2024.
Availability of Substitute Services for Customers
Customers can easily switch to alternative engineering service providers if they find Etteplan's pricing or service offerings unsatisfactory. This is especially true as the market for engineering services continues to grow and diversify.
The increasing availability of in-house engineering teams within client organizations also shifts bargaining power. Many companies are building their own capabilities, reducing their reliance on external providers like Etteplan.
Furthermore, advancements in artificial intelligence and automation are creating new alternatives. AI tools can now handle certain design, simulation, and documentation tasks, potentially reducing the need for specialized engineering service firms for some projects.
- High availability of alternative engineering service providers.
- Growing trend of clients developing in-house engineering capabilities.
- Emergence of AI and automation tools as substitutes for certain engineering tasks.
- Increased customer leverage due to a wider array of options.
Etteplan's customer bargaining power is influenced by several factors, including customer concentration, switching costs, price sensitivity, and the threat of backward integration. While a diversified client base helps mitigate individual customer leverage, high switching costs associated with specialized engineering projects generally reduce customer power.
In 2024, economic pressures led to increased price sensitivity among Etteplan's clients. For instance, reports indicated that many industrial clients were actively seeking cost reductions, potentially leading to renegotiations on service contracts. This heightened sensitivity means Etteplan must continually demonstrate value and cost-effectiveness to retain clients and manage pricing expectations.
The availability of alternative providers and the growing trend of clients developing in-house engineering capabilities also contribute to customer bargaining power. As AI and automation tools become more sophisticated, they offer potential substitutes for certain engineering tasks, further increasing customer options and leverage.
| Factor | Impact on Etteplan | 2024 Trend/Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | Moderate to High if reliant on few large clients | Etteplan's diversification strategy aims to reduce reliance on single clients. |
| Switching Costs | Generally High due to specialized, integrated services | Long-term projects and proprietary knowledge increase costs for clients to switch providers. |
| Price Sensitivity | Increased due to economic climate | Clients in 2024 faced rising operating costs, leading to greater scrutiny of engineering service expenditures. |
| Backward Integration Threat | Moderate, as clients have own engineering departments | Clients prioritize core competencies, often outsourcing non-core but critical engineering functions. |
| Availability of Alternatives | Increasing | Growth in engineering service market and AI/automation tools offer clients more choices. |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Etteplan Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Etteplan Porter's Five Forces Analysis, identical to the document you will receive immediately after purchase. You're examining the actual, professionally formatted report, ensuring no surprises or placeholder content. What you see is precisely what you'll be able to download and utilize, ready for your strategic planning needs.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The engineering services, software, and technical documentation sectors where Etteplan operates are quite crowded. This landscape features a mix of large, established global corporations and a multitude of smaller, highly specialized companies, all vying for market share.
Etteplan faces direct competition from significant players such as Enfo, Tietoevry, and Lime. Additionally, more niche but still relevant competitors include GGS Information Services, Leadec, and Phoenix Contact, each offering distinct but overlapping services.
The engineering services market is on a solid growth trajectory, with an anticipated compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.4% from 2024 to 2025. This steady expansion, projected to continue at 3.5% CAGR from 2025 to 2029, generally eases competitive pressures.
However, the embedded software sector presents a more dynamic picture, forecasting a robust 9.6% CAGR between 2025 and 2034. While growth typically dampens rivalry, challenging market conditions can still lead to intensified competition among players, even within expanding segments.
Etteplan stands out by providing a full spectrum of services covering the entire product journey, from initial concept and design through to ongoing aftermarket care. This holistic approach aims to boost client product competitiveness and streamline their operational processes.
The company's strategic direction, updated to incorporate AI-driven solutions, is a key differentiator. Etteplan has set a target to generate 35% of its revenue from these advanced solutions by 2027, signaling a strong commitment to innovation and future growth in a competitive landscape.
Switching Costs for Customers
Switching costs for customers in the engineering services sector, like those Etteplan operates in, can significantly impact competitive rivalry. When clients have deeply integrated Etteplan's solutions or rely on specialized knowledge developed through long-term partnerships, the effort and expense to switch to a competitor become substantial. This integration often involves custom software, proprietary processes, and a workforce trained on specific systems, making a transition costly and time-consuming.
However, the intensity of rivalry can fluctuate based on the nature of the service. For new projects or less complex, standardized offerings, switching costs tend to be lower. In these scenarios, clients may have more flexibility to compare providers and opt for the most competitive pricing or features, thereby increasing competitive pressure among engineering firms.
For instance, in 2024, the demand for specialized digital engineering services, where deep integration is common, saw Etteplan report strong growth, indicating that clients in these areas were less prone to switching. Conversely, in more commoditized segments of the market, firms likely faced greater pressure to differentiate on price and speed, reflecting lower switching costs.
- High integration and specialized knowledge create significant barriers to switching for existing clients.
- Lower switching costs for new or less integrated projects intensify competition among engineering service providers.
- The nature of the service dictates the level of switching costs and, consequently, competitive rivalry.
- Etteplan's 2024 performance suggests clients in specialized digital engineering areas exhibit higher loyalty due to integration.
Exit Barriers
Exit barriers in the engineering services sector are substantial, keeping firms engaged even when profitability wanes. These include the need to maintain highly specialized assets, such as advanced testing equipment, and the commitment to long-term customer contracts. Furthermore, the imperative to retain a skilled workforce, a critical component of service delivery, acts as a significant deterrent to exiting the market, thereby perpetuating intense competition.
Etteplan's strategic decisions have further solidified these exit barriers. The company's considerable investments in its state-of-the-art test laboratory, a crucial asset for quality assurance and innovation, represent a sunk cost that is difficult to recover. Additionally, Etteplan's history of strategic acquisitions, aimed at expanding its capabilities and market reach, also creates substantial barriers to exit. These investments tie up capital and expertise, making it challenging for the company to disengage from its operations without significant financial repercussions, thus contributing to ongoing competitive rivalry.
- Specialized Assets: High capital expenditure on unique testing equipment and facilities.
- Long-Term Contracts: Commitments to clients that span multiple years, requiring continued service provision.
- Skilled Personnel: The necessity of retaining experienced engineers and technical staff, who are difficult to replace or redeploy.
- Acquisition Integration: The operational and financial complexities of integrating acquired businesses.
The competitive landscape for Etteplan is characterized by a high degree of rivalry due to the presence of numerous global corporations and specialized firms. This intense competition is further fueled by relatively low switching costs in certain market segments, encouraging clients to explore various providers. However, the complexity and integration of services in areas like digital engineering can create stickiness for existing clients, moderating rivalry.
Etteplan's strategy of offering end-to-end product lifecycle services and its focus on AI-driven solutions are key differentiators in this crowded market. The engineering services sector is expected to grow steadily, with embedded software showing particularly strong growth, which can either ease or intensify competition depending on market dynamics.
The engineering services sector is projected to grow at a CAGR of 3.4% from 2024 to 2025, and 3.5% from 2025 to 2029. The embedded software segment is expected to see a CAGR of 9.6% between 2025 and 2034.
| Competitor | Service Focus | Market Presence |
|---|---|---|
| Enfo | Digitalization, IT Services | Nordic Region |
| Tietoevry | IT & Digital Services | Nordic Region, Global |
| Lime | CRM, Sales & Marketing Software | Nordic Region |
| GGS Information Services | Technical Documentation | Global |
| Leadec | Industrial Services, Engineering | Global |
| Phoenix Contact | Industrial Automation, Connectivity | Global |
SSubstitutes Threaten
While Etteplan's integrated engineering services offer a comprehensive solution, potential substitutes do exist. Customers might opt for a fragmented approach, engaging multiple specialized vendors for distinct project phases, rather than a single, all-encompassing provider. This could fragment project management but potentially allow for sourcing best-in-class expertise for each specific need.
Another significant substitute is the enhancement of in-house capabilities. As of 2024, many companies are investing in upskilling their existing workforce and expanding their internal engineering departments to gain more control and reduce reliance on external partners. This trend is driven by a desire for greater agility and cost management, especially in sectors facing rapid technological shifts.
Customers may look for less expensive, simpler alternatives or even decide to handle tasks internally if the value proposition doesn't strongly favor Etteplan's offerings. This is particularly true if they can achieve a satisfactory outcome at a lower overall cost.
The growing sophistication and accessibility of artificial intelligence tools are a significant factor. For instance, AI-powered design automation or content generation platforms can offer a more cost-effective substitute for specific components of the engineering and digital solutions Etteplan provides, potentially impacting demand for traditional service models.
Customer propensity to substitute for Etteplan's services hinges on project specifics, budget, and risk appetite. For mission-critical or intricate engineering tasks, Etteplan's established expertise and reliability often trump the allure of cheaper alternatives, as seen in their significant role in complex industrial automation projects. In 2024, the demand for specialized engineering services remained robust, with clients prioritizing proven track records for high-stakes ventures.
Evolution of Technology
The rapid evolution of technology, especially in areas like artificial intelligence (AI) and automation, presents a growing threat of substitutes for Etteplan's services. As these technologies become more sophisticated, they can increasingly perform tasks traditionally handled by human engineers and technical writers.
For instance, AI-powered tools are already capable of generating code, analyzing data, and even drafting technical documentation, potentially reducing the need for certain human-led services. This trend is expected to accelerate. In 2024, the global AI market was valued at approximately $200 billion, with significant growth projected for automation solutions within engineering and content creation sectors.
- AI-driven code generation platforms are becoming more adept, potentially reducing demand for junior developer roles.
- Automated technical writing tools can now produce user manuals and documentation, impacting traditional technical writing services.
- Robotic process automation (RPA) is increasingly used in engineering workflows, automating repetitive tasks.
- The global market for AI in engineering is projected to see substantial growth, indicating a strong trend towards technological substitution.
Regulatory and Industry Standards
Evolving regulatory requirements, such as the EU's AI Act, can significantly influence the threat of substitutes. These new mandates often demand specialized expertise and documentation that only a few firms can offer, effectively limiting the availability of less specialized alternatives.
For instance, new digital machinery instructions might require specific compliance protocols. Companies unable to meet these stringent standards would find their options for outsourcing or using alternative solutions severely restricted, thereby strengthening the position of compliant providers.
- Regulatory Landscape: The EU's AI Act, expected to have a significant impact on AI development and deployment, could create barriers for companies not adhering to its specific guidelines.
- Industry Standards: New digital machinery instructions may necessitate specialized software or hardware integration, favoring established players with proven compliance records.
- Documentation Requirements: Increased demand for rigorous documentation and validation processes in regulated sectors can be a significant hurdle for potential substitutes.
- Market Access: Non-compliance with emerging standards could restrict market access for certain products or services, making specialized providers the only viable option.
The threat of substitutes for Etteplan's services is multifaceted, encompassing both alternative service delivery models and technological advancements. Companies can choose to build in-house capabilities, a trend observed in 2024 as businesses sought greater control and cost efficiency by upskilling their workforce. This internal investment can reduce reliance on external engineering partners.
Furthermore, the increasing sophistication of AI and automation tools presents a direct substitute for certain tasks. AI-powered platforms can now handle aspects of design, data analysis, and technical writing, offering a potentially more cost-effective solution for specific project components. The global AI market's substantial growth, reaching approximately $200 billion in 2024, underscores this trend.
The choice between Etteplan and substitutes often depends on project complexity, budget constraints, and the client's risk tolerance. For highly specialized or critical engineering endeavors, Etteplan's established expertise and reliability remain a significant advantage. In 2024, demand for these specialized services remained strong, with clients prioritizing proven track records for high-stakes projects.
| Substitute Type | Description | Impact on Etteplan | 2024 Market Insight |
|---|---|---|---|
| In-house Capabilities | Companies developing or expanding internal engineering teams. | Reduces demand for outsourced services. | Increased investment in employee training and development. |
| AI & Automation Tools | Software for code generation, data analysis, and technical writing. | Automates tasks traditionally performed by engineers. | Global AI market valued at ~$200 billion, with significant growth in automation. |
| Fragmented Vendor Approach | Engaging multiple specialized firms for different project phases. | Competes with integrated service offerings. | Clients seek best-in-class expertise for specific tasks. |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the industrial engineering services, software, and technical documentation sector demands substantial capital. Newcomers must invest heavily in acquiring highly skilled engineers, software developers, and technical writers, alongside advanced technology and specialized infrastructure like testing labs. For instance, building a robust R&D department and acquiring necessary software licenses can easily run into millions of euros, creating a significant hurdle.
Established players like Etteplan leverage significant economies of scale derived from their expansive global delivery network and diverse service portfolio. This allows them to spread fixed costs over a larger output, leading to lower per-unit production costs and more competitive pricing. For instance, in 2024, Etteplan reported revenues of €314.4 million, demonstrating the scale of its operations.
New entrants face a substantial hurdle in replicating these cost efficiencies. Building a comparable global infrastructure and service breadth requires immense capital investment and time, making it difficult for them to match the pricing or comprehensive offerings of incumbents. This barrier significantly dampens the threat of new entrants by increasing the cost and risk associated with market entry.
Gaining access to the established client base of leading manufacturing firms is a formidable barrier for newcomers. Etteplan's long-standing relationships with these entities, built over years of trust and demonstrated performance, are not easily replicated. For instance, in 2024, the engineering and technology services sector continued to see consolidation, making it harder for smaller, unproven firms to break into the supply chains of major industrial players.
Proprietary Technology and Expertise
Etteplan's accumulated expertise and specialized methodologies, such as their AI-powered HyperSTE for technical documentation, create a significant barrier for new entrants. These proprietary tools and developed intellectual property require substantial investment and time to replicate.
New competitors would need to invest heavily in research and development to build comparable capabilities, making it challenging to match Etteplan's established efficiency and quality. This technological and knowledge-based advantage deters potential new market participants.
- Proprietary Technology: Etteplan's AI-powered HyperSTE for technical documentation is a key differentiator, requiring significant R&D investment to replicate.
- Accumulated Expertise: Years of experience and specialized methodologies are difficult for new entrants to acquire quickly.
- Intellectual Property: The need to develop or acquire comparable intellectual property presents a substantial hurdle.
Government Policy and Regulation
Government policy and regulation can present a nuanced threat to new entrants in the engineering services sector, particularly for companies like Etteplan that serve specialized industries. While general engineering services might have low barriers, sectors such as defense or energy often impose stringent licensing, certification, and compliance standards. For instance, in 2024, the European Union continued to emphasize stricter environmental regulations across various industries, potentially requiring new engineering firms to invest heavily in specialized knowledge and compliance infrastructure to even bid on projects, thereby favoring established firms with existing expertise and certifications.
These regulatory hurdles can act as indirect barriers to entry.
- Specific industry certifications: Companies entering sectors like aerospace or medical device engineering must obtain approvals that can take years and significant investment.
- Compliance with national standards: Adherence to varying national technical standards and safety regulations adds complexity for new, potentially international, entrants.
- Government procurement policies: In some regions, government tenders may implicitly or explicitly favor suppliers with a proven track record or local presence, making it harder for newcomers to secure initial contracts.
- Data security and privacy laws: Increasingly stringent data protection regulations, like GDPR, require substantial investment in IT infrastructure and compliance protocols, which can be a significant upfront cost for new firms.
The threat of new entrants for Etteplan is relatively low due to high capital requirements for skilled personnel and technology, coupled with significant economies of scale enjoyed by established players. For instance, Etteplan's 2024 revenue of €314.4 million highlights its operational breadth. Furthermore, long-standing client relationships and proprietary technology like HyperSTE create substantial barriers, making it difficult and costly for newcomers to compete effectively.
Regulatory compliance, especially in specialized sectors like defense or energy, adds another layer of difficulty. In 2024, evolving environmental regulations in the EU, for example, necessitate significant investment in expertise and infrastructure for new engineering firms. This complex regulatory landscape favors established companies with existing certifications and proven track records.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
| Capital Requirements | High costs for skilled labor, software, and infrastructure. | Significant financial hurdle. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs due to large-scale operations (e.g., Etteplan's €314.4M revenue in 2024). | Difficult for new entrants to match pricing. |
| Customer Relationships | Established trust and performance with key clients. | Hard for newcomers to gain access. |
| Proprietary Technology & IP | Unique tools (e.g., HyperSTE) and accumulated expertise. | Requires substantial R&D to replicate. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Strict certifications and compliance in specialized industries. | Favors firms with existing expertise and approvals. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Etteplan Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, including Etteplan's own financial statements, investor relations materials, and publicly available industry reports. We also incorporate insights from market research firms specializing in the industrial B2B sector to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
