Seiko Epson Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Seiko Epson Bundle
Seiko Epson navigates a competitive landscape shaped by intense rivalry among established printer manufacturers and the looming threat of digital alternatives. Understanding the bargaining power of their suppliers, particularly for specialized components, is crucial for maintaining profitability. The ease with which new entrants could disrupt the market, especially with innovative printing technologies, also presents a significant challenge.
Ready to move beyond the basics? Get a full strategic breakdown of Seiko Epson’s market position, competitive intensity, and external threats—all in one powerful analysis.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
If Seiko Epson relies on a limited number of suppliers for crucial components, such as their proprietary ink jet printheads or specialized micro-electromechanical systems (MEMS) for their robotics division, those suppliers would wield considerable influence. For instance, a single supplier providing a unique chemical compound essential for their high-performance inks could dictate terms, impacting Epson's production costs and product development timelines.
Seiko Epson faces significant supplier power due to high switching costs associated with its manufacturing processes. For instance, retooling production lines or redesigning products to integrate components from alternative suppliers can incur substantial expenses and lead times. This makes it difficult and costly for Epson to change suppliers, thereby strengthening the bargaining position of its existing component providers.
Suppliers offering highly specialized, patented, or rare components, such as specific quartz crystal devices or advanced semiconductors essential for Epson's precision engineering, hold considerable bargaining power. Epson's dependence on these unique inputs for its core technologies, like those powering its high-precision inkjet printheads, directly amplifies the leverage these suppliers wield in negotiations.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of forward integration by suppliers poses a moderate risk to Seiko Epson. If key component suppliers were to enter the finished printer or projector market, they could leverage their existing manufacturing capabilities and potentially disrupt Epson's market share. This is particularly relevant for suppliers of essential components like print heads or ink cartridges, where the technology is not excessively complex.
While Epson benefits from established brand recognition and distribution networks, a significant supplier entering the market could offer competitive pricing. For instance, a major semiconductor supplier for Epson's core chipsets could theoretically leverage its expertise to assemble and market its own devices. This would directly challenge Epson's existing business model and require strategic responses to maintain its competitive edge.
The bargaining power of suppliers is amplified when they possess the capability and willingness to integrate forward. For Seiko Epson, this means monitoring the strategic intentions of its critical upstream partners.
- Supplier Capability: Assess which suppliers possess the technical and manufacturing know-how to produce finished products comparable to Epson's offerings.
- Market Attractiveness: Evaluate if the profitability and growth potential of the printer and projector markets would incentivize suppliers to integrate forward.
- Epson's Dependence: Understand the degree to which Epson relies on specific suppliers for critical components, as this can influence a supplier's decision and leverage.
Importance of Epson to Suppliers
Epson's significance to its suppliers plays a crucial role in the bargaining power dynamic. If Epson constitutes a substantial portion of a supplier's overall revenue, that supplier's leverage diminishes because they rely heavily on Epson's continued business.
However, for suppliers who are large and have a diverse customer base, Epson's importance might be less pronounced. This means they have more flexibility and less dependence on any single client like Epson.
- Revenue Dependence: For suppliers whose revenue is heavily reliant on Epson, their bargaining power is weakened.
- Supplier Diversification: Large, diversified suppliers with many clients are less impacted by Epson's business volume, thus retaining more power.
- Epson's Procurement Volume: Epson's substantial purchasing power, especially in areas like semiconductor manufacturing where it is a significant player, can offset some supplier influence. For example, in 2023, Epson's semiconductor segment reported net sales of approximately ¥206.6 billion (around $1.4 billion USD at an average ¥150/USD exchange rate), indicating a considerable demand from Epson's side for its components.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Seiko Epson is influenced by the concentration of suppliers and the uniqueness of their offerings. When a few suppliers control critical, specialized components, like advanced printhead technology or specific microprocessors, they can command higher prices and more favorable terms. Epson's reliance on these specialized inputs, such as the proprietary ink formulations critical for its high-quality printing, directly grants these suppliers significant leverage.
High switching costs further bolster supplier power. The substantial investment required to retool manufacturing lines or redesign products to accommodate alternative components makes it economically challenging for Epson to change suppliers. This inertia strengthens the negotiating position of existing providers, particularly for components like specialized semiconductor chips essential for Epson's imaging and robotics divisions.
The threat of forward integration by suppliers presents a moderate risk. If key component manufacturers, such as those supplying advanced print heads or specialized ink, decide to enter the finished product market, they could leverage their technical expertise to compete directly with Epson. This scenario is more plausible for suppliers whose technologies are not excessively complex and can be readily adapted for consumer-facing products.
Seiko Epson's own procurement volume can mitigate supplier power, especially in areas where it represents a significant portion of a supplier's business. For instance, Epson's substantial demand for semiconductors, evidenced by its semiconductor segment's net sales of approximately ¥206.6 billion in 2023, grants it considerable purchasing influence. However, for large, diversified suppliers with many clients, Epson's business volume may be less critical, thus preserving their bargaining leverage.
| Factor | Impact on Epson | Example for Epson |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High Power | Few suppliers for proprietary printhead technology |
| Switching Costs | High Power | Costly retooling for specialized semiconductor integration |
| Component Uniqueness | High Power | Specialized chemicals for high-performance inks |
| Forward Integration Threat | Moderate Risk | Suppliers entering the printer market |
| Epson's Dependence | High Power | Reliance on specific MEMS for robotics |
| Supplier Revenue Dependence | Low Power for Supplier | Epson being a major client for a component supplier |
| Supplier Diversification | High Power for Supplier | Large suppliers with multiple customers |
| Epson's Procurement Volume | Low Power for Supplier | Significant semiconductor purchases (¥206.6 billion in 2023) |
What is included in the product
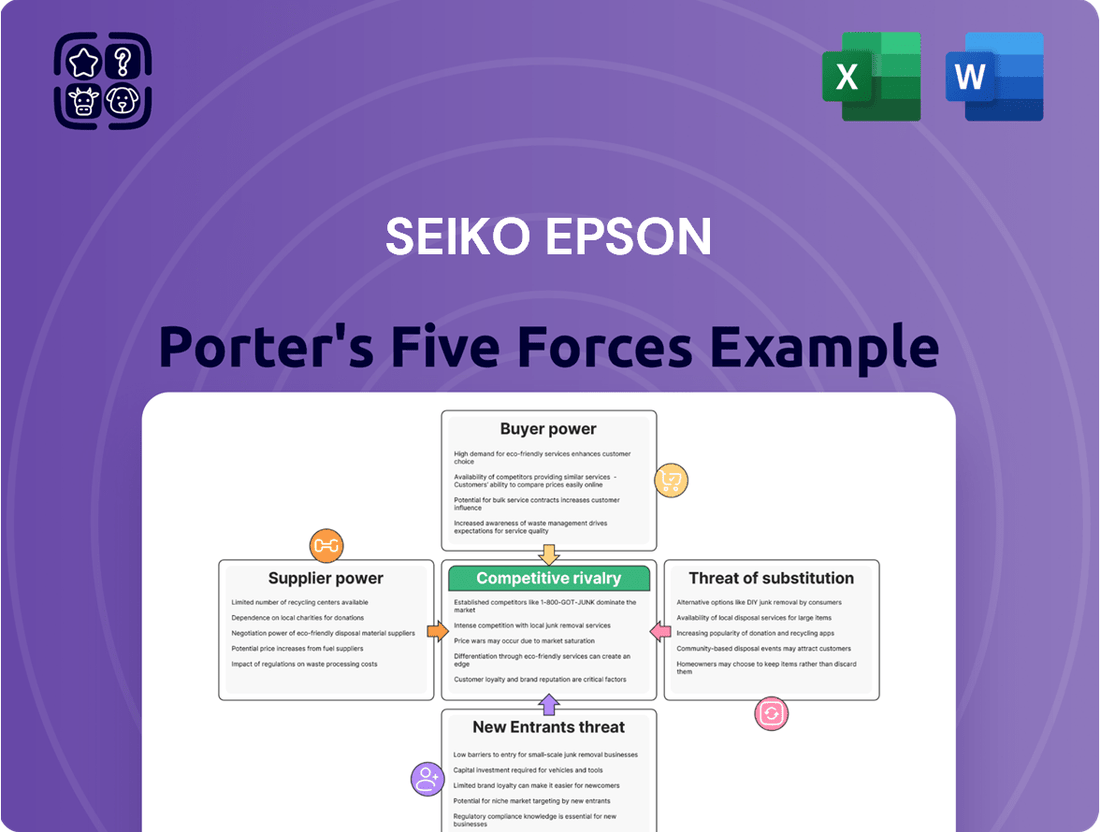
Analyzes the competitive intensity, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and substitutes impacting Seiko Epson's market position.
Instantly identify competitive threats and opportunities by visualizing the intensity of each of Porter's Five Forces, empowering strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
In the highly competitive printer and projector markets, Seiko Epson faces significant customer price sensitivity. Both business and individual consumers actively compare prices across brands like HP, Canon, and Xerox, making it difficult for any single player to command premium pricing.
This price sensitivity is amplified by the ease with which customers can switch suppliers, especially in the B2B segment where procurement departments often prioritize cost-effectiveness. For instance, in 2024, the global printer market saw intense price competition, with average selling prices for many consumer models remaining relatively stable or even declining year-over-year, reflecting this buyer power.
The ease with which customers can switch to alternative brands or technologies significantly influences their bargaining power. For example, the growing availability of compatible ink cartridges and refillable EcoTank systems for printers directly empowers consumers to demand lower prices or better features from traditional manufacturers like Epson.
In 2024, the printer market continues to see intense competition, with many brands offering cost-per-page solutions that challenge established models. This abundance of choice means customers can readily shift their loyalty if they perceive better value elsewhere, thereby increasing their leverage over any single supplier.
Large corporate clients and major retailers buying in bulk wield considerable influence over Epson. Their substantial order volumes give them leverage to negotiate better pricing and terms. Epson's B2B segment has been a growth driver, highlighting the importance of these high-volume purchasers.
Customer Information and Transparency
Customers today possess unprecedented access to information, readily comparing product features, pricing, and user reviews across numerous platforms. This heightened transparency significantly bolsters their bargaining power, enabling them to negotiate more favorable terms with manufacturers like Seiko Epson.
This ease of comparison means customers can quickly identify the best value, forcing companies to remain competitive in their pricing and product offerings. For instance, in the printer market, where Epson operates, consumers can easily find detailed specifications and price points for competing models, intensifying pressure on Epson to offer compelling deals.
- Increased Information Access: Consumers can easily research product specifications, pricing, and competitor offerings online.
- Price Sensitivity: Greater transparency leads to increased price sensitivity among buyers.
- Demand for Value: Customers are more likely to demand better value for their money, influencing pricing strategies.
- Switching Behavior: Informed customers are more willing to switch brands if better alternatives are available.
Low Switching Costs for Customers
When customers face minimal costs or hassle in switching from Seiko Epson products to those of a competitor, their ability to negotiate better terms or prices increases significantly. This is especially prevalent in the consumer electronics market, where brand allegiance can be less of a barrier. For instance, in 2024, the market for printers and ink cartridges is highly competitive, with many brands offering comparable features. This ease of transition empowers buyers.
The bargaining power of customers is amplified when switching costs are low. This means customers can easily shift their purchases to rival firms without facing penalties, learning new systems, or incurring substantial upfront expenses. For Epson, this dynamic is particularly relevant in segments like consumer inkjet printers, where a wide array of alternatives exist. In 2024, the global printer market saw numerous new entrants and aggressive pricing strategies, further reducing perceived switching costs for end-users.
- Low Switching Costs: Customers can readily move to competing brands without significant financial or operational disruption.
- Consumer Market Impact: This is especially true for consumer-grade products where brand loyalty is often less pronounced.
- Competitive Landscape: In 2024, the printer market, for example, is characterized by numerous alternatives, intensifying customer bargaining power.
- Price Sensitivity: Reduced switching costs often correlate with increased customer price sensitivity and demand for better value.
Seiko Epson's customers possess considerable bargaining power due to widespread product availability and low switching costs, particularly in the consumer printer segment. The ease with which buyers can compare prices and features online, coupled with the availability of compatible consumables, forces Epson to maintain competitive pricing. Large B2B clients further amplify this power through bulk purchasing, negotiating favorable terms. In 2024, the printer market's intense competition, with stable or declining average selling prices for many consumer models, underscores this customer leverage.
| Factor | Impact on Epson | Supporting Data (2024 Context) |
|---|---|---|
| Information Access | Increased price sensitivity and demand for value | Consumers readily compare specs and prices across brands like HP, Canon, Xerox. |
| Switching Costs | Empowers customers to negotiate better terms | Availability of compatible ink and refillable systems lowers barriers to switching. |
| Market Competition | Intensifies pressure on pricing and offerings | Global printer market saw stable to declining average selling prices in 2024. |
| Buyer Concentration | Large clients wield significant influence | Epson's B2B segment growth highlights the importance of high-volume purchasers. |
What You See Is What You Get
Seiko Epson Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact, comprehensive Seiko Epson Porter's Five Forces Analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase, detailing the competitive landscape of the printer and electronics industry. You'll gain a deep understanding of the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the market. No surprises, no placeholders—just the fully formatted and ready-to-use analysis for your strategic planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Seiko Epson operates in highly competitive printer and projector markets, facing formidable rivals like HP, Canon, Ricoh, and Xerox. This crowded landscape, particularly in high-volume product segments, fuels intense price wars and a constant drive for technological advancement.
The overall growth rate for the IT product group, which includes many of Epson's offerings, has been relatively subdued. For instance, the global printer market, a key segment for Epson, experienced a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of only 1.5% from 2020 to 2023, according to market research firm IDC. This slower growth environment naturally fuels more intense rivalry as companies vie for existing market share rather than expanding into new, rapidly growing territories.
Seiko Epson actively differentiates its products through proprietary technologies such as PrecisionCore printhead technology and its EcoTank ink system, emphasizing benefits like operational efficiency, reduced size, and environmental sustainability. For instance, Epson's EcoTank printers, launched in 2010, have seen significant adoption, with global sales reaching over 100 million units by early 2024, highlighting a successful differentiation strategy focused on lower long-term printing costs.
Despite Epson's efforts, the printer market is characterized by intense competition, where rivals like Canon and HP also invest substantially in research and development. This continuous innovation means competitors are constantly introducing new features and improving existing ones, making sustained product differentiation a challenging, ongoing battle for market share.
High Fixed Costs
The electronics manufacturing sector, which encompasses products like Seiko Epson's printers and projectors, is characterized by substantial upfront investments. These include significant outlays for research and development, the establishment and maintenance of advanced manufacturing facilities, and the creation of robust distribution channels.
These high fixed costs create a strong incentive for companies to maximize their production capacity utilization. To achieve this, firms often engage in aggressive pricing strategies, leading to intense price competition as they strive to maintain sales volumes and cover their overheads.
- R&D Investment: Companies in the printer market, for instance, invest heavily in developing new technologies, with major players dedicating billions annually to innovation.
- Capital Expenditure: Establishing and maintaining state-of-the-art manufacturing plants for electronics requires hundreds of millions, if not billions, of dollars in capital expenditure.
- Distribution Networks: Building and managing global distribution and service networks also represents a considerable fixed cost for electronics manufacturers.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers can trap companies, even those struggling, in a market, which naturally fuels more intense competition. Think of specialized machinery or long-term supply agreements; these make it difficult and costly to simply shut down operations and leave. For a company like Seiko Epson, which operates in manufacturing, these kinds of barriers are often a given.
While specific data on Epson's exit barriers isn't publicly detailed, the electronics and precision manufacturing sectors typically involve significant investments in specialized production lines and R&D. These assets often have limited resale value outside their specific industry, making a complete exit a substantial financial undertaking.
- Specialized Assets: Manufacturing plants for printers, semiconductors, and micro-devices require highly specialized equipment that is difficult to repurpose or sell off.
- Long-Term Contracts: Commitments to suppliers, distributors, or even customers can create ongoing obligations that are costly to break.
- Workforce Skills: The specialized skills of its workforce might not be easily transferable to other industries, adding a human capital exit barrier.
- Brand Reputation: A long-established brand like Epson has built significant equity, and a disorderly exit could damage this, impacting other business lines or future ventures.
The competitive rivalry within Seiko Epson's markets, particularly printers and projectors, is intense due to the presence of major global players like HP, Canon, and Brother. This rivalry is exacerbated by a relatively slow market growth rate; for instance, the global printer market saw a CAGR of just 1.5% between 2020 and 2023, forcing companies to fight harder for market share. Epson differentiates through technologies like PrecisionCore printheads and EcoTank, with EcoTank sales exceeding 100 million units by early 2024, demonstrating a successful strategy to stand out amidst the competition.
| Competitor | Printer Market Share (2023 Estimate) | Projector Market Share (2023 Estimate) |
|---|---|---|
| HP | ~20-25% | N/A (Minor Player) |
| Canon | ~15-20% | ~15-20% |
| Epson | ~10-15% | ~30-35% |
| Brother | ~10-15% | N/A (Minor Player) |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for traditional printing is significant, stemming from digital document management systems and cloud-based solutions that offer similar functionality without physical output. For instance, the global digital transformation trend continues to accelerate, with businesses increasingly adopting paperless workflows. By 2024, it's estimated that over 80% of enterprise data will be stored digitally, reducing the reliance on printed documents.
Furthermore, the growing prevalence of digital displays in communication and information sharing presents another substitute. Think about how many reports or presentations are now viewed solely on screens rather than being printed. This shift is driven by convenience and environmental concerns, directly impacting the demand for printing hardware and consumables.
Customer willingness to switch to alternatives for printing solutions is influenced by convenience, cost savings, and growing environmental awareness. For instance, the increasing adoption of digital workflows and cloud-based communication significantly diminishes the demand for physical documents.
Technological advancements significantly amplify the threat of substitutes for Epson. For instance, the rapid evolution of virtual collaboration platforms and sophisticated digital signage solutions can directly challenge Epson's traditional projector and display markets. As of 2024, the global market for video conferencing solutions alone was projected to reach over $20 billion, indicating a substantial shift towards digital interaction that may reduce reliance on physical display hardware.
Indirect Substitutes (e.g., Digital Transformation)
The overarching trend of digital transformation presents a significant indirect threat to traditional printing and projection markets. As government organizations, small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), and e-commerce platforms increasingly adopt digital workflows and communication methods, the demand for physical output diminishes. This shift, accelerating through 2024, means less reliance on printers and projectors for everyday operations.
For instance, the global digital transformation market was valued at approximately $620 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach over $1.7 trillion by 2028, indicating a substantial move away from physical media. This broad adoption of digital solutions means that tasks previously requiring printed documents or in-person presentations can now be handled entirely through digital channels, such as cloud-based document sharing, virtual meetings, and digital signage.
- Digital Transformation Market Growth: The digital transformation market is experiencing robust growth, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 17% from 2023 to 2028.
- Shift in Business Operations: By 2024, a significant percentage of businesses, particularly SMEs, are prioritizing cloud adoption and digital collaboration tools, reducing their dependence on physical document management.
- E-commerce Digitalization: The e-commerce sector's continued digital evolution means more transactions and customer interactions are occurring online, lessening the need for printed marketing materials and physical receipts.
- Government Digital Initiatives: Many governments are actively promoting e-governance and digital public services, which inherently reduces the volume of paper-based transactions and official documents.
Alternative Viewing/Communication Methods
For projectors, substitutes like large interactive flat panel displays and smart TVs present a significant threat, especially in business and education settings. These alternatives offer integrated solutions for visual communication, often with better ambient light performance and simpler setup compared to traditional projectors. For instance, the global interactive flat panel display market was valued at approximately $10.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach over $17 billion by 2028, indicating strong growth in competing technologies.
Furthermore, emerging technologies such as virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) are beginning to offer immersive alternatives for collaboration and visual experiences, potentially reducing reliance on projected images for certain applications. While the portable projector market itself is experiencing robust growth, with shipments increasing by double-digit percentages year-over-year in recent periods, the rapid advancement and increasing affordability of these alternative display technologies pose a continuous challenge to projector manufacturers like Epson.
- Interactive Flat Panels: Offering integrated, all-in-one visual solutions, they compete directly with projectors in meeting rooms and classrooms.
- Smart TVs: Increasingly larger screen sizes and advanced features make them viable substitutes for smaller-scale projection needs.
- VR/AR Solutions: These immersive technologies are carving out niches in collaboration and training, offering an alternative to shared visual displays.
- Market Trends: The continued innovation and cost reduction in alternative display technologies directly impact the demand for projectors.
The threat of substitutes for Epson's printing and display products is substantial, driven by digital alternatives and evolving consumer preferences. Digital document management systems and cloud solutions are increasingly replacing the need for physical printouts, a trend amplified by the global push for paperless workflows. By 2024, it's estimated that over 80% of enterprise data will be digitally stored, directly impacting print volumes.
For projectors, substitutes like interactive flat panel displays are gaining traction. These devices offer integrated visual communication solutions, often outperforming projectors in ambient light conditions. The interactive flat panel display market was valued at approximately $10.5 billion in 2023, with projections indicating growth to over $17 billion by 2028, highlighting the competitive landscape.
Emerging technologies such as virtual and augmented reality also present alternative ways to experience visual content and collaborate, potentially reducing reliance on traditional projection methods. The broad adoption of digital solutions across sectors, from e-commerce to government, underscores a significant shift away from physical media and towards digital interaction.
| Substitute Technology | Market Value (2023 Estimate) | Projected Growth (CAGR 2023-2028) | Impact on Epson |
| Digital Document Management | N/A (Integrated into broader software markets) | High (Driven by digital transformation) | Reduced demand for printers and consumables |
| Interactive Flat Panel Displays | $10.5 billion | ~10.5% | Direct competition for projector market share |
| Virtual/Augmented Reality | $20.1 billion (VR market) | ~35% (VR market) | Potential long-term shift in visual collaboration and entertainment |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the competitive electronics manufacturing sector, especially for sophisticated items like printers and projectors, demands significant upfront capital. This includes substantial investments in research and development to innovate, building state-of-the-art manufacturing plants, and establishing robust global distribution networks. For instance, the global semiconductor manufacturing equipment market alone was valued at approximately $115 billion in 2023, highlighting the immense scale of investment needed even for component suppliers.
Established companies like Epson leverage significant economies of scale in their manufacturing and supply chains. For instance, Epson's substantial production volumes for inkjet printheads and printers allow them to negotiate better prices for raw materials and components, driving down their per-unit cost. This cost advantage makes it incredibly challenging for newcomers to enter the market and compete on price.
Seiko Epson benefits from strong brand loyalty, particularly with its innovative EcoTank printers. This established recognition means new competitors face a significant hurdle; they must not only introduce comparable products but also invest substantially in marketing to persuade consumers to switch from trusted Epson models. For instance, in 2023, Epson reported a 16.5% increase in operating profit, underscoring the effectiveness of its brand strategy in a competitive market.
Access to Distribution Channels
New companies entering the printer market face significant hurdles in securing access to established distribution channels. Existing players like Seiko Epson have cultivated strong relationships with retailers, both brick-and-mortar and online, as well as robust B2B sales networks.
These established relationships often come with exclusive contracts and preferential placement, making it difficult for newcomers to gain visibility and reach customers effectively. For instance, in 2024, major electronics retailers continued to prioritize established brands, often requiring substantial marketing investments from new entrants to even be considered for shelf space.
- Established Retail Networks: Securing shelf space in major electronics stores and office supply chains remains a primary challenge.
- Online Platform Dominance: Gaining prominent placement on e-commerce giants like Amazon requires significant marketing spend and favorable seller terms.
- B2B Channel Access: Penetrating corporate and government procurement channels often necessitates long-standing relationships and certifications.
- Distribution Costs: The cost of building and maintaining a competitive distribution network can be prohibitive for startups.
Proprietary Technology and Patents
Seiko Epson's significant investment in proprietary technology, such as its PrecisionCore printhead technology, acts as a formidable barrier to new entrants. The company holds numerous patents protecting these core innovations, making it difficult and expensive for newcomers to replicate Epson's performance and quality without substantial R&D or licensing agreements. For instance, Epson's commitment to innovation is reflected in its consistent R&D spending, which has historically represented a significant portion of its revenue, underscoring the capital required to compete technologically.
The threat of new entrants is thus mitigated by the high cost and complexity associated with developing comparable technological capabilities. New companies would need to either invest heavily in their own research and development to create unique, patentable technologies or secure licenses for existing advanced systems, both of which present considerable financial and time hurdles. This technological moat means that potential competitors face a steep climb to even reach parity, let alone gain a competitive edge.
- Proprietary Technology: Epson's PrecisionCore technology is a key differentiator, protected by a robust patent portfolio.
- High R&D Investment: The continuous innovation required to match Epson's technological advancements demands substantial financial commitment from new players.
- Intellectual Property Barriers: Patents create legal and practical obstacles for new entrants seeking to utilize similar advanced printing technologies.
- Licensing Costs: Acquiring licenses for existing cutting-edge technology can be prohibitively expensive for smaller or emerging companies.
The threat of new entrants into Seiko Epson's market is generally low. The industry demands substantial capital for research and development, manufacturing facilities, and global distribution, creating high upfront investment barriers. For example, the capital expenditure for advanced semiconductor manufacturing equipment, crucial for many electronic components, can run into billions of dollars, a figure that new entrants often struggle to match.
Economies of scale enjoyed by established players like Epson, coupled with strong brand loyalty, further deter new competition. Epson's significant production volumes allow for cost advantages, making it difficult for newcomers to compete on price. In 2023, Epson's robust financial performance, with a reported operating profit increase of 16.5%, highlights the strength of its market position and brand equity.
Access to established distribution channels and proprietary technology, protected by extensive patent portfolios, also presents significant hurdles. New entrants would need to invest heavily in marketing to gain shelf space and develop or license advanced technologies, a costly and time-consuming endeavor.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High investment needed for R&D, manufacturing, and distribution. | Significant financial hurdle. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs due to high production volumes. | Price competition disadvantage for newcomers. |
| Brand Loyalty | Established customer trust and recognition. | Difficulty in customer acquisition. |
| Proprietary Technology | Patented innovations like PrecisionCore printhead technology. | Technological parity or superiority is hard to achieve. |
| Distribution Channels | Strong relationships with retailers and B2B networks. | Limited market access for new players. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Seiko Epson leverages data from annual reports, investor presentations, and reputable industry analysis firms like IDC and Gartner. We also incorporate market research reports and competitor financial disclosures to thoroughly assess the competitive landscape.
