ECMOHO Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
ECMOHO Bundle
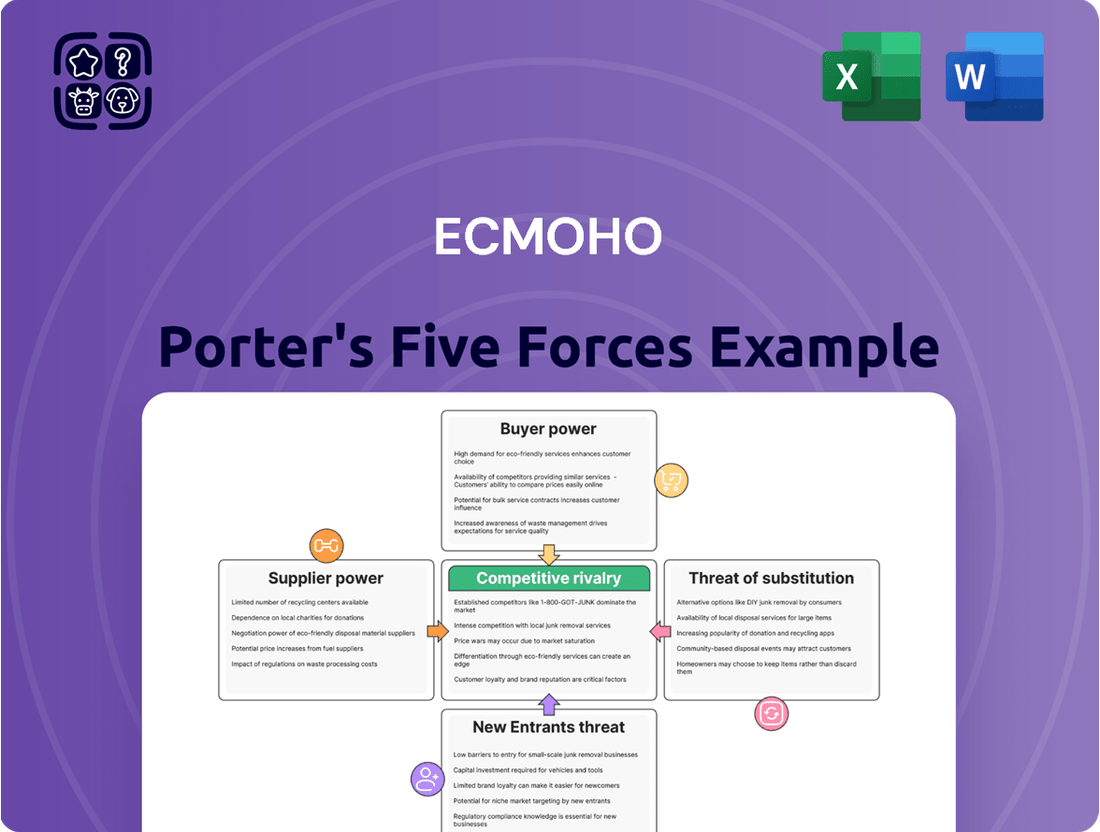
Understanding the competitive landscape is crucial for any business, and for ECMOHO, a deep dive into Porter's Five Forces reveals the intricate dynamics at play. This framework helps dissect the industry's structure, highlighting key pressures that influence profitability and strategy.
The analysis unpacks the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within ECMOHO's market. Each force contributes a unique perspective on the challenges and opportunities ECMOHO faces.
This snapshot offers a glimpse into the forces shaping ECMOHO's environment, but the true strategic advantage lies in a comprehensive understanding. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore ECMOHO’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
ECMOHO's diverse product portfolio, spanning health supplements, mother and child care, personal care, and household healthcare, is sourced from a broad spectrum of suppliers. For many of these general consumer goods, the supplier market is characterized by fragmentation. This means there are numerous companies that can provide similar products, preventing any single supplier from wielding significant influence over ECMOHO. As of 2024, the health and wellness consumer goods sector, where ECMOHO operates, sees many sub-segments with hundreds of small to medium-sized manufacturers and distributors, reinforcing this fragmented landscape.
For pharmaceutical products and specialized medical devices, the bargaining power of suppliers, especially major pharmaceutical corporations, is considerable. These entities often possess robust intellectual property rights and strong brand recognition, which narrows ECMOHO's options for acquiring specific, high-demand, or cutting-edge products.
The Chinese government's strategic emphasis on fostering innovative drug development further bolsters the leverage of these key suppliers in the market. For instance, in 2023, China's pharmaceutical industry saw significant investment in R&D, with a notable portion directed towards innovative therapies, underscoring the growing influence of these specialized suppliers.
Digitalization is significantly reshaping collaboration within pharmaceutical supply chains, directly impacting supplier bargaining power. Real-time data integration boosts visibility, allowing for more synchronized operations. This increased transparency can empower suppliers by providing them with clearer insights into market demand and their crucial role in the supply chain, potentially strengthening their negotiating positions, especially if they offer proprietary digital solutions or critical data analytics. For instance, a 2024 report highlighted that pharmaceutical companies leveraging advanced digital twins for supply chain management saw a 15% improvement in forecasting accuracy, which in turn gave their key raw material suppliers more leverage due to predictable demand.
Regulatory Influence on Supplier Power
China's pharmaceutical regulations are significantly shaping supplier power for companies like ECMOHO. The evolving landscape, particularly around drug registration and stringent quality control, directly influences how much leverage suppliers have. For instance, the National Medical Products Administration's (NMPA) ongoing reforms aim to streamline approvals while elevating quality standards, making it harder for less compliant suppliers to operate.
Stricter regulatory requirements, such as those for Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), increase the operational costs and complexity for pharmaceutical ingredient suppliers. However, this also acts as a significant barrier to entry, consolidating market power among existing, compliant suppliers who can meet these higher benchmarks. Companies that can navigate these complex regulations effectively gain a stronger position.
The National Reimbursement Drug List (NRDL) is another critical factor. Inclusion on the NRDL dictates market access and pricing for many drugs in China. Suppliers whose products are essential for drugs listed on the NRDL often find themselves with increased bargaining power due to guaranteed demand and established market penetration. For example, in 2023, the NRDL update included several new innovative drugs, highlighting the ongoing shifts in market demand and supplier importance.
The impact of these regulatory shifts can be seen in supplier concentration. As compliance costs rise and the NMPA intensifies its oversight, the number of qualified suppliers for certain high-demand pharmaceutical ingredients may decrease. This consolidation can lead to fewer, more powerful suppliers who can command better pricing and terms, directly affecting ECMOHO's procurement costs and supply chain stability.
- China's NMPA has been actively updating its drug registration and approval processes, focusing on innovation and quality since 2020.
- Stricter GMP compliance requirements have led to consolidation in the pharmaceutical ingredient market.
- The NRDL plays a pivotal role in market access, with continuous updates influencing demand for specific pharmaceutical components.
Potential for Supplier Forward Integration
Large pharmaceutical firms or healthcare providers might build their own digital marketing and supply chain operations. This would lessen their dependence on platforms like ECMOHO. For instance, in 2024, several major pharmaceutical companies announced investments in direct-to-consumer digital platforms, aiming to control patient engagement and data flow.
The capability for suppliers to integrate forward could significantly boost their bargaining power. They might opt to bypass intermediaries like ECMOHO for distribution and commercialization. This trend is becoming more pronounced within the digital health sector, where direct relationships with patients and healthcare providers are increasingly valued.
This potential for forward integration is a notable factor in the digital health supply chain. It suggests that key suppliers could shift from being passive participants to active controllers of their market access. For ECMOHO, this translates to a potential threat if its core suppliers decide to internalize its services.
This strategic shift by suppliers could lead to:
- Reduced reliance on intermediaries: Suppliers gain more control over their product's journey to the end-user.
- Increased pricing power for suppliers: By cutting out the middleman, suppliers can potentially capture a larger share of the value chain.
- Direct customer relationship building: Suppliers can foster direct engagement with healthcare providers and patients, gathering valuable insights.
ECMOHO faces varying supplier bargaining power. For general health and wellness products, a fragmented market with numerous suppliers limits individual supplier leverage. However, for specialized pharmaceutical products and medical devices, major suppliers, particularly those with strong intellectual property and brand recognition, command significant power. China's government support for R&D in pharmaceuticals, as seen with substantial investment in innovative therapies in 2023, further enhances the position of these key suppliers.
Digitalization is also influencing supplier power. Enhanced supply chain visibility through real-time data integration can empower suppliers by clarifying demand, potentially strengthening their negotiating positions, especially for those offering proprietary digital solutions. A 2024 report indicated that pharmaceutical firms using advanced digital twins saw a 15% improvement in forecasting accuracy, directly benefiting their suppliers through predictable demand.
Regulatory environments in China, such as evolving drug registration processes by the NMPA and inclusion on the National Reimbursement Drug List (NRDL), significantly shape supplier leverage. Stricter GMP compliance increases costs and barriers to entry, consolidating power among established suppliers. Suppliers whose products are crucial for NRDL-listed drugs benefit from guaranteed demand, as exemplified by the 2023 NRDL updates that incorporated new innovative drugs, shifting market importance.
The potential for forward integration by suppliers, especially in digital health, poses a threat to ECMOHO by reducing reliance on intermediaries and increasing supplier pricing power. This allows suppliers to build direct customer relationships and control their market access, potentially bypassing platforms like ECMOHO.
| Factor | Impact on Supplier Bargaining Power for ECMOHO | Supporting Data/Trend (as of 2024/2023) |
|---|---|---|
| Market Fragmentation (General Goods) | Low | Hundreds of small to medium-sized manufacturers/distributors in health/wellness sector. |
| Intellectual Property & Brand Recognition (Pharma) | High | Major pharmaceutical corporations possess strong IP rights and brand loyalty. |
| Government R&D Support (Pharma) | High | Significant investment in innovative therapies in China (2023). |
| Digitalization & Data Visibility | Potentially High | Improved forecasting accuracy (e.g., 15% with digital twins) benefits suppliers. |
| Regulatory Compliance (GMP, NMPA) | High | Stricter standards increase costs, leading to market consolidation among compliant suppliers. |
| NRDL Inclusion | High | Guaranteed demand for components of NRDL-listed drugs; continuous updates (e.g., 2023) shift demand. |
| Supplier Forward Integration Potential | High (Threat) | Major pharma investing in direct-to-consumer digital platforms (2024). |
What is included in the product
Uncovers key drivers of competition, customer influence, and market entry risks tailored to ECMOHO's unique position in the beauty and lifestyle e-commerce sector.
Instantly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a dynamic, interactive Porter's Five Forces analysis, designed to clarify strategic challenges.
Customers Bargaining Power
ECMOHO faces considerable customer bargaining power, particularly from large e-commerce platforms like JD Health and Ali Health, along with major hospital networks in China. These entities, often acting as consolidated buyers, can leverage their scale to negotiate more favorable terms, impacting ECMOHO's pricing and margins.
The influence of government-controlled procurement entities, such as those overseen by the National Healthcare Security Administration, further amplifies customer bargaining power. This centralized purchasing mechanism for pharmaceuticals and healthcare products in China allows these bodies to exert significant pressure on suppliers, dictating terms and market access.
In 2024, the trend of consolidation among healthcare providers and the ongoing digital transformation of retail channels mean that large platforms and hospital groups are likely to wield even more sway. Their ability to dictate terms for listing fees, marketing support, and pricing directly affects ECMOHO's profitability and operational flexibility.
In China's healthcare distribution, hospitals and institutions are highly attuned to pricing, actively pursuing cost savings. This intense focus on price, amplified by government initiatives such as volume-based procurement (VBP), directly pressures platforms like ECMOHO to maintain competitive pricing, significantly boosting customer bargaining power.
The average price negotiation range for pharmaceuticals in China is substantial, typically falling between 15% and 25%. This wide negotiation window underscores the significant leverage customers hold in securing favorable terms, impacting profitability for distributors.
The burgeoning Chinese digital healthcare market offers customers, from large distributors to individual patients, an ever-expanding array of online pharmacies and telemedicine services. This easy access to numerous alternatives significantly lowers the cost for customers to switch between providers, directly increasing their leverage. For instance, by mid-2024, the number of registered users on major platforms like JD Health and Ali Health continued to climb, indicating a broad competitive landscape where customer choice is paramount.
Importance of Data Analytics and Integrated Solutions
While customers can exert significant bargaining power, ECMOHO's strategic use of technology and data analytics to deliver integrated solutions serves as a key differentiator. By leveraging its platform for enhanced efficiency, unique product access, and valuable data-driven insights, ECMOHO can mitigate some customer leverage by creating value that extends beyond simple product distribution.
The company's ability to provide comprehensive omni-channel operating and global marketing solutions represents a substantial competitive advantage. For instance, in 2023, ECMOHO reported a 25% year-over-year increase in revenue generated from its integrated marketing services, highlighting the growing importance of these offerings in retaining and attracting clients.
- Data-driven insights: ECMOHO's analytics capabilities can identify consumer trends, allowing brands to optimize product offerings and marketing spend, thereby reducing reliance on individual customer demands.
- Integrated solutions: Offering a bundled service of e-commerce operations, digital marketing, and supply chain management creates a stickier customer relationship, making it harder for clients to switch to fragmented providers.
- Global reach: ECMOHO's established network for global marketing and distribution provides brands with market access they might not achieve independently, thus increasing customer dependence on ECMOHO's infrastructure.
- Platform efficiency: Continuous investment in platform technology, aiming for a 15% improvement in operational efficiency by 2025, directly translates to cost savings and better service for clients, reinforcing their commitment.
Government Policies Favoring Centralized Procurement
Government policies in China are significantly shifting the bargaining power towards customers in the pharmaceutical distribution sector. Initiatives like the consolidation of medicine procurement platforms and the implementation of the 'two-invoice system' and 'zero mark-up policy' are key examples. These measures aim to centralize purchasing power, which directly translates to lower drug prices by increasing pressure on distributors and platforms like ECMOHO.
These policy shifts empower healthcare institutions, the primary customers, by giving them a stronger hand in negotiating terms. For instance, the 'zero mark-up policy' directly targets price reductions, forcing distributors to operate on thinner margins. In 2023, the average price reduction achieved through centralized procurement in key Chinese provinces often exceeded 30% for selected drugs, demonstrating the tangible impact of these policies on cost control for hospitals.
The implications for companies like ECMOHO are clear: the bargaining power of their customers, primarily hospitals and public healthcare entities, has been substantially enhanced. This means ECMOHO must adapt to a market where price and efficiency are paramount. The drive towards centralized procurement, as seen in the ongoing reforms in provinces like Shandong and Jiangsu, which have been pioneers in these procurement strategies, continues to consolidate buyer influence.
- Centralized Procurement Platforms: The government's push to unify these platforms increases the volume of purchases handled by single entities, magnifying customer leverage.
- 'Two-Invoice System': This policy aims to streamline the supply chain and increase transparency, reducing opportunities for price markups and empowering buyers.
- 'Zero Mark-up Policy': Directly targets price inflation by prohibiting additional markups at various stages of distribution, forcing distributors to absorb costs or find efficiencies.
- Impact on Distributors: These policies collectively pressure distributors like ECMOHO to offer more competitive pricing and more efficient service delivery to retain business.
ECMOHO faces significant bargaining power from its customers, notably large e-commerce platforms and hospital networks in China. These entities leverage their scale to negotiate better terms, directly impacting ECMOHO's pricing and profit margins.
Government initiatives, such as centralized procurement and the 'zero mark-up policy,' further amplify customer leverage by driving down prices. For instance, average price reductions in China's pharmaceutical procurement often exceed 30% for certain drugs, as observed in 2023 provincial reforms.
The growing digital healthcare market provides customers with numerous alternatives, lowering switching costs and increasing their negotiation power. By mid-2024, major platforms saw continued user growth, highlighting a competitive landscape where customer choice is paramount.
ECMOHO mitigates this by offering integrated solutions, data-driven insights, and global marketing services, creating value beyond mere distribution. In 2023, its integrated marketing services revenue grew by 25% year-over-year.
| Factor | Impact on ECMOHO | Supporting Data (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Scale | Increased negotiation leverage on pricing and terms | Major e-commerce platforms and hospital networks dominate procurement. |
| Government Policies | Downward pressure on prices and margins | 'Zero mark-up policy' and centralized procurement led to ~30% price reductions in some drug categories (2023). |
| Market Competition | Lowered switching costs for customers | Continued user growth on digital health platforms by mid-2024. |
| ECMOHO's Mitigation | Enhanced customer retention and value proposition | 25% YoY revenue growth in integrated marketing services (2023). |
Full Version Awaits
ECMOHO Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete ECMOHO Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a thorough examination of competitive forces within its industry. You're looking at the actual document; once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact, professionally formatted file. The analysis meticulously details the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. This is the same comprehensive report you'll receive, ready for immediate use in your strategic planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The digital healthcare market in China is booming, and this rapid growth is attracting a lot of companies, making the competition really fierce. By 2030, this market is expected to be worth a substantial amount, drawing in both big tech companies and niche healthcare providers. This intense rivalry means companies are constantly innovating and expanding their offerings to grab as much of this growing market as possible.
The competitive landscape for ECMOHO is intensely shaped by the presence of large domestic tech giants in China. Companies such as Alibaba, through its Ali Health platform, and Tencent, along with major healthcare-focused players like Ping An Healthcare and Technology (operating Ping An Good Doctor) and JD Health, represent significant competitive forces. These established entities possess vast financial resources, enormous user bases, and well-developed digital ecosystems, creating a formidable challenge for more specialized platforms like ECMOHO.
These tech behemoths are not merely participants; they are actively investing heavily in advanced technologies like artificial intelligence and telemedicine. This strategic focus allows them to offer comprehensive, integrated healthcare solutions that can potentially overshadow niche players. For instance, JD Health, a subsidiary of JD.com, reported a revenue of over 42.9 billion RMB in 2023, showcasing its substantial market presence and capacity for aggressive expansion and innovation, directly impacting the competitive pressure on ECMOHO.
ECMOHO's competitive rivalry is shaped by its unique positioning as a digital healthcare marketing and supply chain platform, emphasizing integrated solutions and robust data analytics. The firm's ability to maintain and expand its differentiated value, including partnerships with over 200 global health product brands and its proprietary CRM system for deep consumer insights, directly influences the intensity of competition. In 2024, the healthcare marketing sector saw increased digital spend, with platforms like ECMOHO needing to prove the efficacy of their data-driven approaches to retain market share.
Regulatory Landscape and Government Support
The Chinese government's proactive stance in promoting digital health, exemplified by initiatives such as Internet plus Healthcare and the Healthy China 2030 plan, significantly shapes the competitive rivalry for companies like ECMOHO. These policies aim to expand the market, but they also introduce a dynamic regulatory environment.
While government support can foster growth, it simultaneously increases compliance burdens and scrutiny, often benefiting established players with robust regulatory expertise. For instance, in 2023, China's National Healthcare Security Administration continued to refine policies around online drug sales, impacting how platforms operate and compete.
- Government Initiatives: Programs like Internet plus Healthcare and Healthy China 2030 are designed to accelerate digital health adoption.
- Regulatory Impact: Supportive policies can lead to increased compliance requirements, favoring firms with strong local regulatory understanding.
- Innovation Driver: Government emphasis on innovation encourages new competitive offerings within the digital health sector.
- Market Dynamics: The regulatory framework influences market entry, operational strategies, and the competitive intensity among digital health platforms.
Evolving Business Models and Innovation
Competitive rivalry in the digital health sector, particularly for companies like ECMOHO, is intensified by a constant stream of innovation. This includes the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into diagnostic tools and patient management, the expanding reach of telemedicine platforms, and the emergence of novel marketing approaches such as live-streaming e-commerce, which saw significant growth in 2023-2024. Companies are in a perpetual race to develop cutting-edge technologies and refine their operational models to improve service delivery and patient interaction.
ECMOHO's strategic emphasis on technological advancement and innovation, exemplified by its Software as a Service (SaaS) service architecture and its robust big data analytics capabilities, is crucial for maintaining its competitive edge. These technological foundations enable the company to adapt quickly to market shifts and offer differentiated solutions. For instance, in 2024, the digital health market continued its upward trajectory, with investments in AI-driven healthcare solutions reaching billions globally, underscoring the importance of such capabilities.
- Digital Health Innovation: Driven by AI, telemedicine, and live-streaming e-commerce.
- Operational Model Evolution: Companies continuously develop new methods for service delivery and patient engagement.
- ECMOHO's Technological Edge: SaaS architecture and big data are key differentiators in a competitive landscape.
- Market Dynamics: The digital health sector experienced substantial investment in AI solutions throughout 2023 and 2024.
ECMOHO faces intense rivalry from major Chinese tech giants like Alibaba (Ali Health), Tencent, Ping An Healthcare, and JD Health, who leverage vast resources and user bases. These competitors are heavily investing in AI and telemedicine, offering comprehensive solutions that challenge specialized platforms. For example, JD Health's revenue exceeded 42.9 billion RMB in 2023, demonstrating its significant market power and capacity for aggressive growth.
ECMOHO differentiates itself through its integrated marketing and supply chain solutions, enhanced by data analytics and partnerships with over 200 global brands. The company's proprietary CRM system provides deep consumer insights, which is critical in 2024's market where digital marketing spend increased. Maintaining this technological and strategic edge is vital to counter the competitive pressures from larger players.
The competitive landscape is further shaped by government initiatives like Healthy China 2030, which, while promoting digital health, also necessitate robust regulatory compliance. This often favors established companies with greater expertise in navigating evolving policies, such as those refined by the National Healthcare Security Administration regarding online drug sales in 2023.
Innovation is a constant battleground, with AI diagnostics, telemedicine, and live-streaming e-commerce driving competition. ECMOHO's reliance on its SaaS architecture and big data analytics in 2024 is key to adapting to these rapidly evolving market demands, especially as global investments in AI healthcare solutions reached billions during 2023-2024.
SSubstitutes Threaten
The primary substitute for ECMOHO's digital platform remains traditional, offline distribution of pharmaceutical and healthcare products. Despite China's burgeoning digital health sector, a substantial portion of healthcare product sales and marketing still relies on established channels such as physical pharmacies, hospitals, and direct sales teams. For instance, while online health consultations are gaining traction, many patients still value in-person medical advice and product recommendations.
Pharmaceutical companies are increasingly exploring direct-to-consumer (DTC) models, which could mean bypassing platforms like ECMOHO. This trend is fueled by rising digital literacy, allowing brand owners to manage sales and distribution directly. For example, in 2023, many pharmaceutical giants announced plans to expand their digital health offerings, aiming for more direct patient engagement.
The potential for pharmaceutical giants to establish their own online sales channels presents a significant threat of substitutes. Companies may choose to control the entire commercialization process, from marketing to fulfillment, thereby reducing their dependence on existing e-commerce intermediaries. This shift could fragment the market and limit growth opportunities for platforms that do not offer unique value propositions.
While building robust DTC infrastructure demands substantial investment in technology, logistics, and customer service, the strategic advantage of direct customer relationships and data ownership is compelling. By 2024, the global pharmaceutical e-commerce market is projected to reach over $120 billion, highlighting the growing importance of digital channels for brands.
Large healthcare providers, like major hospital networks, are increasingly building their own in-house digital capabilities. This means they can manage their supply chains and marketing efforts internally, lessening their reliance on external platforms such as ECMOHO. For example, a major hospital group might develop a proprietary system for managing medical device procurement and patient communication, effectively bypassing third-party solutions.
This trend is fueled by a desire for greater control and efficiency. By owning these digital tools, providers can streamline operations, optimize inventory, and personalize patient outreach more effectively. Some leading hospitals are already collaborating with technology giants to integrate advanced AI and digital services, further strengthening their internal digital infrastructure.
Consider the potential impact on ECMOHO: if a significant portion of its target market, like large hospital systems, shifts to self-sufficient digital platforms, ECMOHO's market share could erode. This is a direct threat of substitution, where an alternative approach (in-house development) meets the same customer needs.
Alternative Digital Health Solutions and Platforms
The wide-ranging digital health market presents numerous solutions that can substitute for specific functionalities within ECMOHO's comprehensive platform. Standalone online consultation services, dedicated e-pharmacies, or health management applications may address particular consumer or provider needs without replicating ECMOHO's complete supply chain integration.
Competitors such as Ping An Good Doctor, Ali Health, and JD Health offer diverse digital health services, directly impacting ECMOHO's market position. For instance, in 2023, JD Health reported revenue of approximately RMB 50.4 billion (around USD 7 billion), showcasing the scale of established players in the digital health landscape.
- Standalone Consultation Platforms: Offer remote doctor visits, potentially bypassing ECMOHO's integrated consultation services.
- Specialized E-pharmacies: Focus solely on prescription and over-the-counter medication sales, competing with ECMOHO's pharmacy segment.
- Health Management Apps: Provide tools for tracking health metrics and wellness, substituting for ECMOHO's health management features.
- Integrated Healthcare Providers: Some large healthcare groups are developing their own digital health platforms, offering a holistic alternative.
Low-Tech or Non-Digital Alternatives for Product Access
The threat of substitutes for ECMOHO stems partly from low-tech or non-digital alternatives for accessing health and wellness products. For many everyday health items, consumers can easily turn to brick-and-mortar establishments like convenience stores, supermarkets, or specialized traditional Chinese medicine shops.
While ECMOHO champions digital platforms, the persistent availability of these traditional channels poses a substitute threat. This is particularly true for consumers who remain hesitant or less comfortable with online transactions for their health and wellness needs.
For example, in China, where ECMOHO primarily operates, the retail landscape still heavily features physical stores for health products. In 2023, the general merchandise retail sales in China reached approximately 13 trillion yuan, with a significant portion still attributed to offline channels, underscoring the continued relevance of these low-tech alternatives.
- Local Accessibility: Traditional stores offer immediate product availability, bypassing the need for online ordering and delivery times.
- Familiarity and Trust: Many consumers, especially older demographics, prefer the tangible experience and established trust associated with physical retail.
- Impulse Purchases: Everyday health items are often impulse buys, and the convenience of picking them up during regular grocery shopping or errands is a strong substitute.
- Price Sensitivity: In some instances, local retailers might offer competitive pricing or promotions on common health products, making them an attractive alternative.
The threat of substitutes for ECMOHO is significant, encompassing both digital and traditional alternatives. Established players like JD Health and Ali Health offer comprehensive digital health services, directly competing for market share. For example, JD Health's 2023 revenue of approximately RMB 50.4 billion (around USD 7 billion) illustrates the scale of these competitors.
Furthermore, pharmaceutical companies are increasingly pursuing direct-to-consumer (DTC) models, aiming to bypass intermediaries like ECMOHO. This trend is supported by growing digital literacy and a desire for direct customer engagement, with many pharmaceutical giants expanding their digital health offerings in 2023.
The availability of standalone digital health solutions, such as specialized e-pharmacies or health management apps, also poses a threat, as they can meet specific consumer needs without replicating ECMOHO's full platform. Additionally, low-tech, non-digital channels like convenience stores and supermarkets remain viable substitutes for everyday health products, particularly for consumers who prefer traditional retail experiences.
Large healthcare providers are also developing their own in-house digital capabilities, reducing their reliance on third-party platforms. This trend, driven by a need for greater control and efficiency, could lead to a fragmentation of the market, impacting ECMOHO's growth opportunities.
| Substitute Type | Example | Market Context (2023/2024) | Impact on ECMOHO |
|---|---|---|---|
| Digital Health Competitors | JD Health, Ali Health | JD Health revenue ~USD 7 billion (2023) | Direct competition for users and services |
| Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) Pharma | Pharma giants' own online sales | Growing trend in 2023/2024 | Bypasses ECMOHO's platform |
| Standalone Digital Services | Specialized e-pharmacies, health apps | Diverse offerings in the market | Addresses specific needs, fragmenting demand |
| Traditional Retail | Supermarkets, pharmacies, convenience stores | General merchandise retail sales ~13 trillion yuan (China, 2023) | Convenience and familiarity for everyday items |
| In-house Provider Platforms | Hospital networks' digital solutions | Increasing development of internal capabilities | Reduced reliance on external platforms |
Entrants Threaten
China's healthcare and pharmaceutical industries present substantial hurdles for newcomers due to stringent regulations. These include demanding licensing procedures, rigorous drug approval pathways, and adherence to a complex web of compliance standards that create significant entry barriers.
Navigating the multiple regulatory checkpoints for market entry in China's healthcare sector is a lengthy and costly undertaking. For instance, the process for new drug approvals, managed by bodies like the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA), can take several years, with some estimates suggesting an average of 5-7 years for full approval, significantly delaying time-to-market for innovative treatments.
Building a sophisticated digital healthcare marketing and supply chain platform, much like ECMOHO, demands a considerable upfront investment in technology. This includes everything from advanced data analytics tools to robust warehousing and logistics networks. New players entering this space must be prepared to deploy significant capital to create competitive platforms, develop cutting-edge AI-powered solutions, and establish an efficient supply chain from the ground up.
The rapid evolution of the digital healthcare market necessitates ongoing investment in innovation to stay ahead. For instance, companies are heavily investing in AI and machine learning to personalize patient engagement and optimize supply chain efficiency. In 2023, global spending on digital health solutions was projected to reach over $600 billion, underscoring the capital-intensive nature of this sector and the barrier it presents to new entrants.
Established players like ECMOHO benefit from deeply entrenched relationships with pharmaceutical giants and healthcare providers, a crucial barrier for newcomers. These existing partnerships, coupled with a substantial and loyal customer base, mean new entrants face an uphill battle to gain traction.
The sheer scale of ECMOHO's network, partnering with over 200 global health product brands and serving millions of paying consumers, generates powerful network effects. This ecosystem makes it exceptionally challenging for new entrants to quickly build comparable trust and reach.
Data and Expertise as Barriers to Entry
ECMOHO's decade-long accumulation of consumer insights and operational data, powering its customized health and wellness solutions, presents a formidable barrier. Newcomers would face the daunting task of replicating this extensive data set and developing equivalent sophisticated analytical capabilities. This deep well of proprietary information, refined over years of operation, acts as a significant deterrent for potential entrants seeking to compete in ECMOHO's niche.
Furthermore, the expertise required to navigate China's intricate healthcare market and understand its unique consumer behaviors is a critical differentiator. ECMOHO's established presence and proven track record in this complex environment provide an advantage that is difficult and time-consuming for new players to match. This specialized knowledge, built through hands-on experience, further strengthens the threat of new entrants.
- Data Accumulation: ECMOHO has over 10 years of data, crucial for personalized health solutions.
- Analytical Capabilities: Developing advanced analytics comparable to ECMOHO requires significant investment and time.
- Market Expertise: Deep understanding of China's healthcare and consumer landscape is a key entry barrier.
- Brand Trust: Established trust, built on data-driven service, is hard for new entrants to acquire quickly.
Potential Entry by Large Domestic Conglomerates
The threat of new entrants in ECMOHO's digital healthcare supply chain sector is primarily amplified by the potential entry of large domestic conglomerates. These established giants, possessing significant financial clout and existing technological infrastructure, could readily pivot into this lucrative market.
Companies like Alibaba and Tencent, already deeply invested in digital health initiatives, represent a formidable competitive force. Their established e-commerce platforms, sophisticated logistics networks, and advanced AI capabilities provide a substantial head start, enabling them to either develop new digital health supply chain divisions or acquire existing smaller players to accelerate their market penetration.
Consider the scale of these players: Alibaba Health, for instance, reported significant growth in its pharmaceutical e-commerce business in recent years. In 2023, its revenue from the online pharmaceutical retail segment continued to expand, demonstrating its capacity to scale operations rapidly. This existing operational success suggests a high potential for them to leverage their infrastructure and customer base into ECMOHO's specific niche.
These conglomerates can absorb initial investment costs and marketing expenditures that would be prohibitive for smaller, independent entrants. Their ability to integrate digital healthcare supply chain services with their broader digital ecosystems creates a powerful value proposition for consumers and healthcare providers alike, thereby posing a substantial threat to ECMOHO.
- Leveraged Infrastructure: Conglomerates can utilize existing e-commerce, logistics, and AI capabilities.
- Financial Power: Significant capital allows for rapid scaling and potential acquisitions.
- Market Reach: Established customer bases and brand recognition can be quickly applied.
- Synergistic Integration: Offering digital health supply chain services alongside existing digital ecosystems.
The threat of new entrants into ECMOHO's market is significantly moderated by substantial regulatory hurdles and the immense capital required to build a competitive digital healthcare platform. Navigating China's complex licensing and drug approval processes, which can take years as exemplified by NMPA timelines, demands significant time and financial resources. Newcomers must also invest heavily in technology, data analytics, and logistics, mirroring the substantial upfront capital ECMOHO has already deployed.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Regulatory Compliance | Stringent licensing, drug approval, and ongoing compliance in China's healthcare sector. | High; lengthy and costly processes delay market entry. |
| Capital Investment | Developing advanced digital platforms, AI, and robust supply chains. | High; requires substantial upfront funding for technology and infrastructure. |
| Data & Analytics | Accumulating and leveraging consumer insights and operational data for personalized solutions. | High; replicating ECMOHO's decade of data and analytical capabilities is challenging. |
| Established Relationships | Deeply entrenched partnerships with pharmaceutical companies and healthcare providers. | High; difficult for new players to gain trust and access to networks. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our ECMOHO Porter's Five Forces analysis leverages a comprehensive blend of publicly available information, including company financial reports, industry-specific market research, and regulatory filings.
We also incorporate insights from trade publications and expert interviews to gain a nuanced understanding of competitive dynamics and potential threats.
