Digi Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Digi Bundle
Digi faces intense competition, with significant threats from new entrants and powerful buyers influencing its market position. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for strategic planning.
The complete Porter's Five Forces Analysis dives deep into Digi’s competitive landscape, revealing the true strength of each force. Gain actionable insights to navigate these pressures and secure a competitive edge.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Digi International's reliance on a global supply chain for specialized components, such as cellular modules and semiconductors, means supplier concentration is a key factor. When only a few companies produce these critical, high-tech parts, they gain considerable leverage. For instance, a significant portion of the global cellular module market is dominated by a handful of manufacturers, giving them substantial bargaining power over companies like Digi.
Digi's bargaining power with its suppliers is significantly influenced by switching costs. If Digi relies on highly specialized or proprietary components from a limited number of suppliers, the cost and complexity of switching to an alternative can be substantial. This might involve redesigning its products, undergoing rigorous re-certification processes for new components, or re-tooling manufacturing lines, all of which can be very expensive and time-consuming.
For instance, Digi's established product lines often integrate components that are deeply embedded within their technological ecosystems. This deep integration means that changing a supplier for a critical component could necessitate extensive engineering work and validation, effectively locking Digi into existing supplier relationships and thereby increasing supplier leverage. In 2024, the semiconductor industry, a key area for Digi, continued to experience supply chain complexities and extended lead times for specialized chips, further amplifying the importance of strong supplier relationships and the costs associated with changing them.
Suppliers might consider forward integration by developing their own end-user IoT solutions, which would put them in direct competition with Digi. While component suppliers typically don't do this, major semiconductor or module manufacturers possess the technical know-how to move up the value chain.
This scenario would intensify competition for Digi and could potentially restrict their access to advanced components. For instance, a major chip manufacturer entering the IoT solutions market could leverage its existing component supply to offer integrated products at competitive prices, impacting Digi's market share and supplier relationships.
Uniqueness of Input Components
The uniqueness of input components for advanced cellular routers and embedded systems significantly impacts supplier bargaining power. If a supplier provides proprietary technology or holds patents on critical IoT connectivity elements, Digi International (DGII) faces limited alternatives, potentially leading to increased costs and less favorable contract terms. For instance, specialized chipsets or unique modem technologies essential for next-generation cellular standards like 5G mmWave could offer substantial leverage to their providers.
This differentiation can manifest in several ways:
- Proprietary Technology: Suppliers with exclusive rights to advanced processing units or wireless communication modules used in Digi's routers can dictate terms.
- Patented Components: Patents on key connectivity technologies, such as specific antenna designs or power management circuits, limit Digi's ability to source from multiple vendors.
- High Switching Costs: If integrating a supplier's unique component requires significant re-engineering or certification processes for Digi's products, the supplier gains an advantage.
Impact of Input on Product Quality/Cost
The quality and cost of components are paramount for Digi to offer dependable and competitively priced IoT solutions. If these inputs are critical for product performance or heavily impact production expenses, suppliers can exert significant influence.
Digi's financial performance, with gross profit margins rising in Q3 2024 and Q1 2025, suggests a capacity for effective cost control, even when facing potential supplier leverage.
- Component Criticality: The degree to which Digi's product performance relies on specific supplier components directly impacts supplier bargaining power.
- Cost Sensitivity: If component costs represent a substantial portion of Digi's overall manufacturing expenses, suppliers have greater leverage.
- Supplier Concentration: A market with few suppliers for essential components amplifies their bargaining power.
- Switching Costs: High costs or complexities associated with changing suppliers further strengthen their position.
Suppliers of critical components like cellular modules and semiconductors hold significant bargaining power over Digi International. This leverage stems from supplier concentration, where a few dominant manufacturers control essential parts, coupled with high switching costs for Digi due to component integration and proprietary technology. In 2024, persistent semiconductor supply chain challenges further amplified this power dynamic.
The uniqueness of input components, such as specialized chipsets for 5G, grants suppliers considerable leverage by limiting Digi's alternatives and potentially leading to less favorable contract terms.
Digi's ability to manage costs, as seen in its gross profit margin improvements in Q3 2024 and Q1 2025, indicates some capacity to navigate supplier influence, though the underlying power imbalance remains.
| Factor | Impact on Digi | 2024/2025 Context |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High leverage for few key suppliers | Dominance in cellular modules and semiconductors |
| Switching Costs | High due to product integration and re-engineering | Deeply embedded components in established product lines |
| Component Uniqueness | Limited alternatives, potential for higher costs | Proprietary tech and patents on connectivity elements |
| Supplier Forward Integration | Potential for direct competition | Major manufacturers could enter IoT solutions market |
What is included in the product
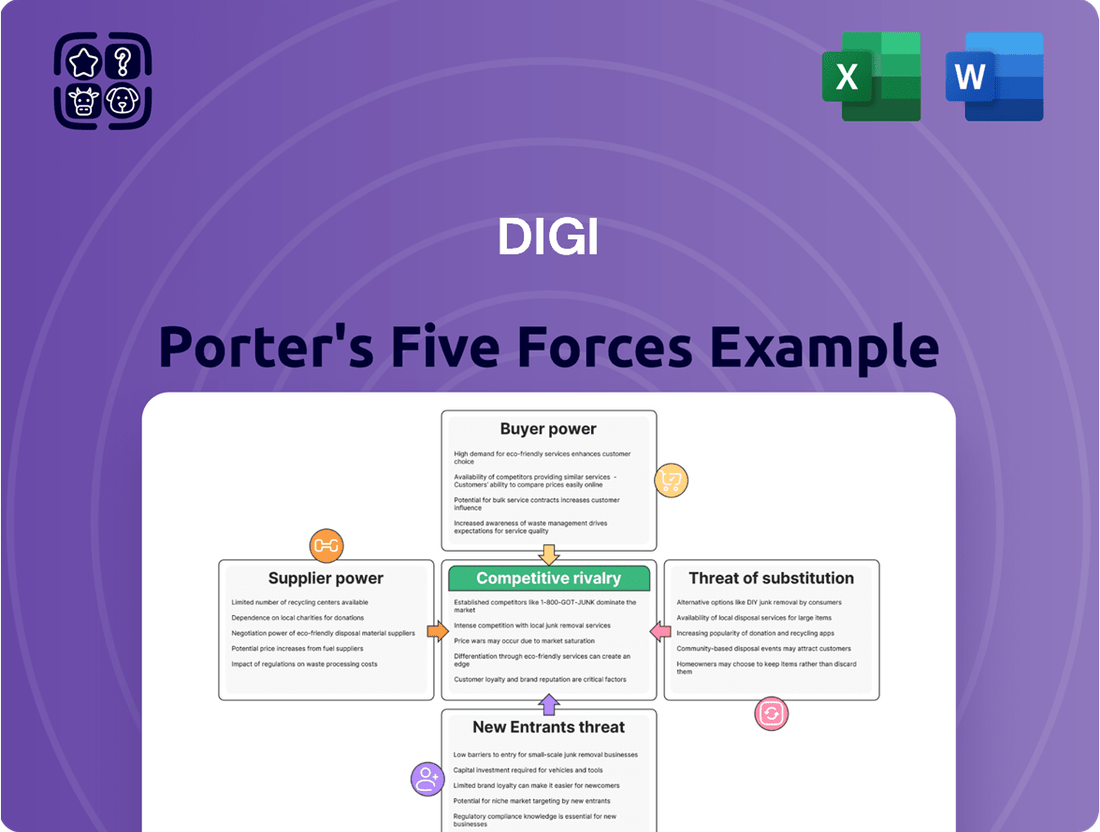
This analysis dissects the competitive landscape for Digi by examining the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitute products.
Instantly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a dynamic, interactive visualization of all five forces.
Customers Bargaining Power
Digi International's diverse customer base spans industrial automation, smart cities, and healthcare, but a concentration of large enterprise clients or major government contracts can significantly amplify their bargaining power. These high-volume purchasers, such as a major automotive manufacturer or a national smart grid initiative, can leverage their substantial order sizes to negotiate more favorable terms, including customized product configurations and pricing discounts. For instance, if a single client represented over 10% of Digi's 2024 revenue, their ability to influence pricing and product development would be considerably higher.
Customer switching costs are a key factor in how much power buyers have. For Digi's customers, moving from one IoT connectivity provider to another can be quite expensive. Think about the effort involved in reconfiguring all the devices already in place, moving any important data, and then training staff on new systems. These are not small tasks.
Digi actively works to make switching harder for its customers. By offering secure and dependable communication solutions, and providing expert help for setting up IoT projects, they build loyalty. Services like Digi 360 and LifeCycle Assurance are designed to lock customers in, making it less appealing to switch. This strategy directly boosts customer retention and, in turn, lessens the bargaining power of those customers.
Customer price sensitivity is a significant factor for Digi, especially within the diverse IoT landscape. In highly competitive or cost-conscious industries, customers are likely to scrutinize pricing closely for general IoT connectivity solutions, potentially leading them to seek out lower-cost alternatives. For instance, in the smart home sector, which saw significant growth in 2024 with an estimated global market size of over $100 billion, consumers often prioritize affordability.
However, this sensitivity can be less pronounced in specialized or mission-critical applications. Sectors like industrial automation or healthcare IoT, where reliability and performance are paramount, may exhibit lower price sensitivity. In 2024, investments in industrial IoT continued to climb, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate of over 15% through 2030, suggesting a willingness to pay for robust solutions.
Digi's strategy to counter price sensitivity hinges on its capacity to clearly articulate and demonstrate a strong return on investment (ROI). By highlighting tangible benefits such as enhanced operational efficiency, reduced downtime, and improved cybersecurity, Digi can justify its pricing. For example, a successful industrial IoT deployment can lead to efficiency gains of 10-20%, directly impacting a company's bottom line and making the initial investment more palatable.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
Large customers, particularly those possessing substantial in-house technical expertise, may contemplate developing their own Internet of Things (IoT) connectivity solutions or embedded systems. This potential for backward integration could lessen their dependence on external suppliers like Digi.
However, the inherent complexity and specialized knowledge required for designing and manufacturing cellular routers and intricate embedded systems present a significant barrier to entry for the majority of customers. For instance, the development of a custom IoT gateway can involve substantial R&D investment, specialized firmware engineering, and rigorous testing, often exceeding the capabilities of many end-users.
- High R&D Costs: Developing proprietary IoT hardware and software can cost millions of dollars, a prohibitive expense for most.
- Specialized Expertise: Creating reliable cellular connectivity solutions demands deep knowledge in radio frequency engineering, embedded systems, and cybersecurity.
- Manufacturing Scale: Achieving cost-effective production requires significant manufacturing infrastructure and supply chain management, which most customers lack.
- Time to Market: The lengthy development cycle for custom solutions means customers might miss critical market windows compared to using off-the-shelf components.
Availability of Substitute Products/Services for Customers
Customers can choose from a wide range of IoT connectivity solutions, impacting Digi's pricing power. This includes alternative hardware manufacturers, various wireless communication protocols like Wi-Fi and LoRaWAN, and even specialized managed service providers. The sheer volume of options available means customers are less reliant on any single vendor.
The IoT market's dynamic nature, characterized by rapid expansion and technological advancement, continuously introduces new substitutes. For instance, in 2024, the market saw continued growth in low-power wide-area network (LPWAN) technologies alongside established options, presenting customers with increasingly sophisticated and often cost-effective alternatives to traditional cellular IoT. This means Digi faces constant pressure to enhance its value proposition.
- Diverse Connectivity Options: Customers can select from cellular (2G, 3G, 4G LTE, 5G), LPWAN (LoRaWAN, Sigfox), Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and satellite technologies for IoT deployments.
- Hardware Vendor Competition: Numerous companies offer IoT gateways, modules, and end-device hardware, providing customers with choices beyond Digi's product lines.
- Managed Service Providers: The rise of IoT platform-as-a-service (PaaS) and managed connectivity providers offers customers integrated solutions, reducing their need to manage individual components.
- Price Sensitivity: The availability of substitutes often leads to increased price sensitivity among customers, forcing vendors like Digi to maintain competitive pricing and demonstrate clear differentiation.
The bargaining power of customers for Digi International is influenced by several factors, including the concentration of buyers and customer switching costs. A few large clients can exert significant influence, as seen if a single customer represented over 10% of Digi's 2024 revenue, giving them leverage in negotiations. High switching costs, stemming from the expense and complexity of reconfiguring devices and retraining staff, generally reduce customer power.
Customer price sensitivity is another key determinant. While cost-conscious sectors like smart homes may prioritize affordability, critical applications in industrial automation or healthcare often exhibit lower price sensitivity, especially given the projected 15% CAGR for industrial IoT investments through 2030. Digi counters this by emphasizing a strong ROI, highlighting efficiency gains of 10-20% from successful deployments.
The potential for customers to develop their own solutions is limited by high R&D costs, specialized expertise in areas like RF engineering, and the need for manufacturing scale. The availability of numerous substitutes, from different hardware vendors to alternative wireless protocols, also increases customer choice and can drive price competition.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power | Digi's Mitigation Strategy |
| Buyer Concentration | High for large enterprise clients | Focus on value-added services and differentiation |
| Switching Costs | High due to integration complexity | Build loyalty through reliable solutions and support |
| Price Sensitivity | Varies by industry; higher in cost-sensitive sectors | Demonstrate clear ROI and tangible benefits |
| Threat of Backward Integration | Low due to high R&D and expertise requirements | Maintain technological leadership and innovation |
| Availability of Substitutes | High due to diverse market options | Emphasize unique features and ecosystem integration |
Full Version Awaits
Digi Porter's Five Forces Analysis
You're looking at the actual Digi Porter's Five Forces Analysis. Once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact file, providing a comprehensive breakdown of competitive forces within the digital industry to inform your strategic decisions.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Internet of Things (IoT) connectivity market is a crowded space with many different types of companies vying for market share. You'll find major telecommunications providers and huge technology corporations alongside smaller companies that focus on specific hardware, like cellular routers or embedded systems.
Digi International, for instance, faces competition from a wide array of businesses across various parts of the IoT ecosystem. This includes companies like Sierra Wireless, which offers a broad portfolio of cellular modules and gateways, and Advantech, a significant player in industrial IoT solutions and embedded computing.
In 2024, the global IoT market was valued at approximately $1.1 trillion, with connectivity being a fundamental component. This vast market size naturally attracts a diverse range of competitors, from established players in networking and telecommunications to newer entrants specializing in niche IoT applications and services.
The global Internet of Things (IoT) market is a hotbed of activity, with its size anticipated to reach hundreds of billions of dollars by 2025 and continue its upward climb. This impressive expansion isn't limited to the overall market; both cellular IoT and industrial IoT sectors are demonstrating equally strong growth patterns. For instance, the industrial IoT market alone was valued at approximately $214 billion in 2023 and is projected to surge to $349 billion by 2028, showcasing a compound annual growth rate of over 10%.
While such rapid growth is generally a positive sign, it also acts as a magnet for new companies eager to capture a piece of the expanding pie. This influx of new players, coupled with the ambitions of existing ones, naturally escalates the competition for market share. Companies are vying for dominance, leading to an increasingly dynamic and often fierce competitive landscape as they strive to innovate and gain an edge.
Digi International distinguishes itself in the competitive IoT landscape by prioritizing security, reliability, and user-friendly deployment for its connectivity products and services. Their offerings, like secure communication solutions and remote console management devices, aim to address critical customer needs. Digi also provides professional services to enhance the customer experience.
Innovation is a cornerstone of Digi's strategy to stay ahead. The company actively introduces new products, with significant developments expected in 2024, to maintain its competitive edge. This focus on continuous improvement and new feature sets is crucial for capturing market share and meeting evolving industry demands.
Switching Costs for Customers
High customer switching costs can dampen competitive rivalry by making it more difficult for customers to defect to rivals. Digi’s strategy focuses on embedding its services deeply into customer workflows, thereby increasing the effort and expense associated with changing providers. For instance, by offering integrated cloud solutions and robust customer support, Digi aims to create a sticky ecosystem that discourages customers from seeking alternatives.
Conversely, if switching costs are low, competitive rivalry often escalates as companies vie for market share through price reductions or enhanced feature sets. The digital services market, in general, has seen a trend towards increased integration, with companies like Microsoft and Google offering bundled solutions that raise the barrier to switching for businesses reliant on their platforms. In 2024, the average cost for a small business to migrate its data and operations to a new cloud provider can range from several thousand to tens of thousands of dollars, depending on complexity and data volume.
- Increased switching costs for customers inherently reduce the intensity of competitive rivalry.
- Digi’s strategy to boost switching costs involves creating integrated solutions and providing superior customer support.
- Low switching costs typically lead to fiercer competition among service providers.
- The digital services sector is witnessing a rise in bundled offerings, which naturally elevates customer switching costs.
Exit Barriers for Competitors
High exit barriers in the IoT sector, stemming from specialized hardware investments and extensive R&D commitments, can trap even underperforming companies. This situation often forces them to maintain aggressive pricing strategies or continue competing intensely, even when market conditions are unfavorable. For instance, companies heavily invested in proprietary IoT chipsets or complex network infrastructure face substantial losses if they attempt to exit, thereby prolonging competitive pressure.
The persistence of unprofitable competitors due to these barriers directly fuels rivalry. In 2024, the global IoT market, valued at an estimated $1.1 trillion, continues to see players with significant sunk costs in specialized infrastructure. These sunk costs act as a powerful deterrent to exiting the market, compelling them to fight for market share through price reductions or innovative, albeit potentially low-margin, product offerings.
- Specialized Assets: Significant capital expenditure on custom IoT sensors, gateways, and cloud infrastructure creates high switching costs for companies.
- Long-Term Contracts: Commitments to service providers or clients for IoT solutions often lock companies into the market for extended periods.
- R&D Investment: Ongoing research and development in areas like AI integration for IoT devices require substantial, ongoing financial commitment, making abandonment costly.
- Brand Loyalty and Reputation: Established brands in the IoT space may find it difficult to divest without impacting their overall corporate reputation, thus preferring to weather downturns.
The competitive rivalry within the IoT connectivity market is intense, fueled by a vast array of players from global telecommunications giants to niche hardware specialists. The sheer size of the global IoT market, estimated at $1.1 trillion in 2024, attracts constant new entrants and aggressive strategies from established firms. Companies like Digi International face direct competition from entities such as Sierra Wireless and Advantech, each offering diverse IoT solutions.
Innovation and customer retention are key battlegrounds. Digi International, for example, emphasizes security, reliability, and user-friendly deployment, alongside professional services, to differentiate itself. The company’s commitment to introducing new products in 2024 underscores the need to stay ahead in this dynamic sector. Furthermore, strategies to increase customer switching costs, such as embedding services deeply into client workflows, are crucial for maintaining market position.
High exit barriers in the IoT sector, including significant investments in specialized hardware and R&D, compel companies to remain competitive even in challenging conditions. This can lead to aggressive pricing and continuous innovation efforts to secure market share. For instance, companies with substantial sunk costs in proprietary IoT infrastructure are less likely to exit, thereby perpetuating market competition.
| Competitor | Key Offerings | 2024 Market Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Sierra Wireless | Cellular modules, gateways | Expanding industrial IoT connectivity solutions |
| Advantech | Industrial IoT solutions, embedded computing | Strengthening edge computing and AI integration for IoT |
| Digi International | Secure communication, remote management | Enhanced security features and cloud integration for 2024 product line |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Beyond cellular networks, a diverse array of alternative connectivity technologies poses a significant threat to Digi Porter. Options like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, LoRaWAN, and satellite IoT are increasingly viable substitutes, especially for specific use cases. For instance, Wi-Fi and Bluetooth excel in short-range, low-power applications, offering cost-effective connectivity without the recurring fees associated with cellular plans.
LoRaWAN, a low-power wide-area network technology, provides a compelling alternative for applications requiring long-range communication with minimal power consumption, often seen in smart city initiatives or agricultural monitoring. In 2024, the growth of LoRaWAN deployments, particularly in industrial IoT and smart agriculture, continued to expand, providing a viable alternative for many asset tracking and sensor network needs that might otherwise rely on cellular. Satellite IoT is also emerging as a crucial substitute for remote or hard-to-reach locations where cellular coverage is nonexistent, offering global reach.
The growing trend towards cloud-native IoT platforms and software-defined networking presents a significant threat of substitutes. As more solutions become software-centric, the demand for specialized hardware, a core offering for companies like Digi, could diminish.
Competitors focusing solely on software could offer integrated solutions that reduce or eliminate the need for specific hardware components. This shift is particularly relevant as the software segment captured the largest market share in the Internet of Things (IoT) sector in 2024, a trend projected to continue its upward trajectory.
The increasing power of general-purpose computing devices, like advanced edge devices and industrial PCs, presents a significant threat of substitution for specialized IoT hardware. These devices can often integrate IoT functionalities through software updates or by adding specific modules, allowing customers to utilize existing IT infrastructure instead of purchasing dedicated IoT solutions. For instance, a powerful industrial PC might be programmed to handle sensor data and connectivity, mimicking the role of a purpose-built IoT gateway.
Internal Development by Large Enterprises
Large enterprises, particularly those with substantial R&D budgets and existing technical infrastructure, may explore developing their own IoT connectivity solutions. This internal development can range from custom embedded hardware to managing proprietary network segments. For instance, major automotive manufacturers might develop specialized connectivity modules for their vehicles, integrating them directly into their production lines.
While this offers a degree of control, the significant investment in specialized talent, infrastructure, and ongoing maintenance often makes it a less efficient route compared to leveraging established IoT specialists. The ongoing evolution of IoT standards and security protocols also presents a continuous challenge for in-house development teams. For example, the global IoT market was valued at approximately $1.1 trillion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, indicating the rapid pace of innovation that can be difficult for individual companies to match internally.
- Internal Development Costs: Building custom IoT solutions can incur substantial upfront capital expenditure and ongoing operational expenses.
- Expertise Gap: Specialized knowledge in areas like wireless protocols, cybersecurity, and cloud integration is critical and often scarce.
- Time-to-Market: Developing proprietary solutions can significantly lengthen the time it takes to deploy IoT capabilities compared to using existing platforms.
- Scalability Challenges: In-house solutions may struggle to scale efficiently with growing data volumes and device numbers.
Evolving Industry Standards and Protocols
The rapidly changing landscape of IoT standards and protocols presents a significant threat of substitutes. As new communication protocols and interoperability frameworks emerge, they can quickly render existing technologies obsolete or less desirable.
For Digi, this means a constant need to adapt and innovate. For instance, the proliferation of low-power wide-area network (LPWAN) technologies like LoRaWAN and NB-IoT, alongside evolving cellular standards such as 5G mMTC (massive Machine Type Communications), creates opportunities for new entrants offering solutions built on these newer, more efficient protocols. Digi's 2024 product roadmap must actively incorporate support for these emerging standards to remain competitive.
The fragmentation in IoT communication standards also plays a role. While this can be a challenge, it also favors platform-agnostic solutions that can integrate with various protocols. Companies offering flexible middleware or gateways that bridge different standards could emerge as strong substitutes to more proprietary or single-protocol solutions.
- Evolving Standards: The IoT sector saw significant activity in 2024 with ongoing standardization efforts by bodies like the IoTivity Alliance and the Matter standard's continued adoption, impacting device interoperability.
- Emergence of New Protocols: Technologies like Thread and Wi-Fi HaLow gained traction in 2024, offering alternative low-power, mesh networking capabilities that could substitute for traditional Wi-Fi or Bluetooth in certain IoT applications.
- Platform Agnosticism: The demand for solutions that can seamlessly connect devices regardless of their underlying communication protocol is growing, creating a threat from companies specializing in universal IoT platforms.
- Impact on Legacy Systems: Digi's existing product lines must demonstrate backward compatibility or upgrade paths to avoid being directly substituted by newer, more integrated solutions that leverage the latest industry protocols.
The threat of substitutes for Digi's connectivity solutions is substantial, driven by the increasing availability and capability of alternative technologies. Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and LoRaWAN offer cost-effective, low-power options for specific use cases, while satellite IoT addresses connectivity gaps in remote areas. The market's shift towards software-centric IoT platforms also diminishes the reliance on specialized hardware.
The rise of powerful, general-purpose computing devices capable of integrating IoT functionalities through software presents a direct substitute for Digi's dedicated hardware. Furthermore, large enterprises with significant R&D resources may opt for in-house development of connectivity solutions, though this often proves less efficient than leveraging specialized providers. The rapid evolution of IoT standards and protocols, such as the growing adoption of Matter and Thread in 2024, necessitates continuous innovation from Digi to avoid obsolescence.
| Substitute Technology | Key Advantages | Potential Impact on Digi |
|---|---|---|
| Wi-Fi & Bluetooth | Low cost, short-range, low power | Substitution for specific, localized IoT applications |
| LoRaWAN | Long-range, low power, cost-effective | Viable alternative for smart city and agricultural monitoring |
| Satellite IoT | Global coverage, remote access | Direct substitute for cellular in areas with no coverage |
| Software-Centric Platforms | Flexibility, integration, reduced hardware need | Diminishes demand for specialized hardware components |
| General-Purpose Computing Devices | Versatility, existing infrastructure utilization | Replaces need for dedicated IoT gateways and modules |
Entrants Threaten
The threat of new entrants into the IoT connectivity hardware and embedded systems market is significantly dampened by high capital requirements. Companies like Digi, with its established presence, benefit from substantial upfront investments in research and development, advanced manufacturing facilities, and robust supply chain networks. For instance, developing cutting-edge, secure, and certified embedded systems for industrial applications often necessitates millions of dollars in R&D alone, a considerable hurdle for newcomers.
New entrants into the industrial automation and connected systems market, like Digi, face significant hurdles in establishing widespread distribution channels and cultivating deep customer relationships. Building trust with enterprise clients across sectors such as manufacturing, healthcare, and transportation requires time and a proven track record, which newcomers often lack. For instance, in 2024, the average sales cycle for complex industrial IoT solutions can extend to 12-18 months, highlighting the difficulty in quickly gaining market traction.
Digi, with its decades of operation, has cultivated robust partnerships and distribution networks, giving it a substantial advantage. New companies must invest heavily in sales infrastructure and marketing to even begin competing for initial contracts, a process that is both time-consuming and capital-intensive. For example, a report from late 2023 indicated that establishing a dedicated B2B sales force for specialized technology can cost upwards of $500,000 annually, excluding marketing and channel development costs.
Digi International's strong portfolio of proprietary technology and patents in areas like cellular routers and embedded systems acts as a significant hurdle for potential new entrants. These intellectual property assets, including numerous patents filed and granted, make it difficult and costly for competitors to develop comparable products or services. The inherent complexity of developing robust IoT solutions further necessitates substantial technical expertise, which new players often lack.
Economies of Scale and Experience Curve
Established players in the digital solutions sector, like Digi, leverage significant economies of scale. This allows them to achieve lower per-unit costs in manufacturing, procurement, and research and development compared to potential new entrants. For instance, in 2024, major tech firms often reported billions in R&D spending, a figure difficult for startups to replicate. This cost advantage makes it challenging for new companies to compete on price without substantial initial investment and market penetration.
The experience curve also acts as a formidable barrier. Companies that have been in the market longer, developing and deploying complex IoT solutions, have honed their processes and expertise. This accumulated knowledge translates into greater efficiency and fewer errors. By 2024, the complexity of integrating diverse digital platforms means that practical, hands-on experience is invaluable, giving incumbents a distinct edge in delivering reliable and scalable solutions.
- Economies of Scale: Digi's established infrastructure and high production volumes in 2024 enable cost efficiencies that new entrants struggle to match.
- Procurement Power: Large-scale purchasing by incumbents leads to better pricing on components and services, a significant advantage over smaller, newer firms.
- R&D Investment: Billions invested annually by leading tech companies in 2024 in R&D create a knowledge and innovation gap that new entrants find difficult to bridge quickly.
- Experience Curve Benefits: Decades of experience in deploying and refining digital solutions give established players a competitive edge in efficiency and problem-solving.
Regulatory Hurdles and Certifications
The threat of new entrants in the IoT connectivity sector is significantly impacted by regulatory hurdles and the need for certifications. For products targeting critical infrastructures such as healthcare or transportation, these requirements are particularly stringent.
Navigating these complex regulatory landscapes and securing the necessary approvals can be a substantial barrier, demanding significant time and financial investment from potential new players. Digi's commitment to high security and reliability standards, meeting demanding industry benchmarks, effectively raises this entry threshold.
For instance, in the medical IoT space, devices often require FDA clearance, a process that can take months or even years and involve substantial testing and documentation. Similarly, automotive IoT components must comply with standards like ISO 21434 for cybersecurity, adding another layer of complexity.
- Regulatory Compliance Costs: New entrants face substantial costs for legal counsel, testing, and certification processes, potentially running into hundreds of thousands of dollars for specialized IoT devices.
- Time to Market Delays: Obtaining certifications can add 6-18 months to product development timelines, allowing established players like Digi to maintain market share.
- Industry-Specific Standards: Adherence to standards like HIPAA for healthcare data or automotive safety regulations creates a high barrier to entry for less experienced companies.
The threat of new entrants into the industrial IoT and embedded systems market is substantially mitigated by high switching costs for existing customers. Businesses relying on Digi's established solutions often face significant expenses and operational disruptions if they were to transition to a new provider.
These costs can include re-engineering hardware, rewriting software, retraining personnel, and the potential for extended downtime during migration. For example, in 2024, the cost of migrating a complex industrial control system to a new IoT platform could easily run into millions of dollars, making customer retention a strong defensive moat for incumbents.
Furthermore, the integration of Digi's devices into existing enterprise resource planning (ERP) and manufacturing execution systems (MES) creates deep dependencies. This intricate web of integration means that switching providers is not just a hardware replacement but a comprehensive system overhaul, further solidifying customer loyalty and deterring new entrants.
| Factor | Impact on New Entrants | Example Data (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Switching Costs | High | Estimated $1M+ for complex industrial system migration. |
| Integration Complexity | Significant | Deep dependencies with ERP/MES systems. |
| Customer Lock-in | Strong | Long-term contracts and proven reliability reduce willingness to switch. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, including publicly available company financial statements, industry-specific market research reports, and government economic indicators. This ensures a comprehensive understanding of competitive pressures.
