Orient Securities Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Orient Securities Bundle
Orient Securities navigates a landscape shaped by intense rivalry and the constant threat of new entrants, impacting its pricing power and profitability. Understanding these pressures is crucial for any stakeholder.
The full analysis reveals the real forces shaping Orient Securities’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The China Securities Regulatory Commission (CSRC) and various stock exchanges are significant suppliers to Orient Securities, providing essential operating licenses and market access. Their regulatory frameworks, like the new National Nine Articles (NNA) implemented in April 2024, directly influence how securities firms conduct business, impacting operational costs and strategic choices.
Technology and data providers wield considerable bargaining power in the financial services sector, especially as firms like Orient Securities increasingly rely on digital infrastructure. Vendors offering specialized trading platforms, advanced data analytics, and robust cybersecurity solutions are crucial for maintaining competitive edge and operational integrity. For instance, the global financial technology market was valued at approximately $11.3 trillion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, indicating strong demand for these specialized services.
Critical market data providers also exert substantial influence. With growing regulatory scrutiny around data monopolization and the need for accurate, real-time information for compliance and trading strategies, these data vendors are indispensable. The cost and availability of high-quality financial data, such as real-time market feeds and historical datasets, can directly impact a firm's ability to operate efficiently and profitably.
The availability of highly skilled professionals, such as investment bankers and research analysts, is a critical factor for Orient Securities. In 2024, the financial services sector continued to see robust demand for specialized talent, leading to increased recruitment challenges and potentially higher compensation expectations.
A competitive market for top-tier talent means Orient Securities might face pressure to offer more attractive salary and benefit packages. This can directly impact operational costs, as firms vie for individuals with proven track records in areas like asset management and financial analysis, driving up the bargaining power of these skilled professionals.
Capital Providers
Capital providers, such as banks and institutional lenders, hold significant bargaining power over Orient Securities. Their ability to supply essential capital for proprietary trading, underwriting, and margin financing directly impacts Orient Securities' cost of funds and its capacity for risk-taking. For instance, in early 2024, rising interest rates globally, with the US Federal Reserve maintaining its benchmark rate, increased the cost of borrowing for financial institutions, including securities firms. This directly translated to higher funding costs for Orient Securities.
- Cost of Funds: Higher interest rates from capital providers increase Orient Securities' operational expenses.
- Market Liquidity: When market liquidity is low, capital providers can demand higher returns, reducing Orient Securities' profitability.
- Risk Appetite: The willingness of capital providers to lend influences Orient Securities' ability to engage in capital-intensive activities.
Infrastructure and Utility Providers
Infrastructure and utility providers, such as telecommunications and internet services, represent a critical input for Orient Securities. While these services are often seen as commodities, their reliability and cost directly influence operational efficiency and overall expenses. In 2024, the global spending on business internet services saw continued growth, reflecting the increasing reliance on robust connectivity.
The bargaining power of these suppliers can be significant, especially for specialized or high-speed services essential for financial trading and client communication. Disruptions, even temporary ones, can lead to substantial financial losses and reputational damage for a securities firm. For instance, a major internet outage impacting a financial hub could halt trading activities for hours.
- Essential Services: Telecommunications, internet, and physical office spaces are non-negotiable for Orient Securities' daily functions.
- Cost Impact: Price hikes from these providers can directly increase operating costs, squeezing profit margins.
- Operational Reliance: The efficiency and speed of these services are paramount for timely trade execution and client service delivery.
- Potential for Disruption: Any interruption in these core utilities can severely impact business continuity and revenue generation.
Regulators like the CSRC and exchanges are key suppliers, their rules impacting Orient Securities' operations and costs. Technology and data providers hold significant sway due to the sector's digital reliance; the global fintech market's value, around $11.3 trillion in 2023, highlights this. Skilled professionals are also powerful suppliers, with high demand in 2024 driving up compensation.
Capital providers, such as banks, have considerable bargaining power, influencing Orient Securities' funding costs and risk-taking capacity. Rising global interest rates in early 2024, exemplified by the US Federal Reserve's stance, directly increased borrowing expenses for financial institutions.
| Supplier Type | Key Influence | 2024 Impact Example |
|---|---|---|
| Regulators (CSRC, Exchanges) | Licenses, Market Access, Operational Rules | New National Nine Articles (April 2024) affecting business conduct |
| Technology & Data Providers | Trading Platforms, Data Analytics, Cybersecurity | Global Fintech Market ~$11.3T (2023), increasing demand for specialized services |
| Skilled Professionals | Investment Banking, Research Analysis Expertise | Robust demand for talent leading to higher compensation expectations |
| Capital Providers (Banks, Lenders) | Funding for Trading, Underwriting, Margin Financing | Increased borrowing costs due to global interest rate trends |
What is included in the product
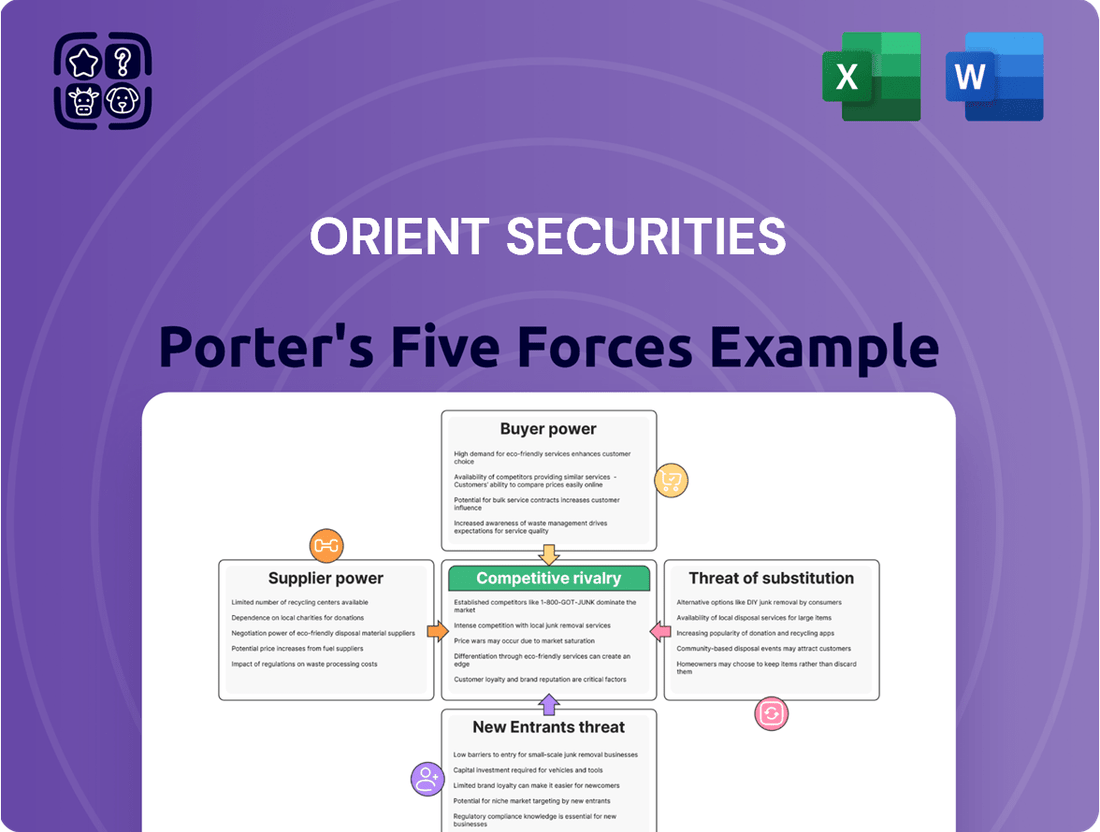
This Porter's Five Forces analysis provides a comprehensive examination of the competitive landscape for Orient Securities, detailing the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitute products.
Instantly identify and address competitive threats with a visual breakdown of Orient Securities' market pressures.
Customers Bargaining Power
Large institutional investors, such as mutual funds and pension funds, represent a significant portion of trading volume for firms like Orient Securities. In 2024, institutional investors accounted for over 60% of equity trading volume on major exchanges, according to industry reports. Their substantial transaction sizes empower them to negotiate for reduced commission rates and preferential treatment, directly impacting Orient Securities' revenue streams and profitability.
Individual retail investors, while seemingly small players, wield significant collective power, especially in a vast market like China. Their sheer volume can influence market trends and demand for brokerage services. For instance, in 2023, retail investors accounted for a substantial portion of trading volume on the Shanghai Stock Exchange, demonstrating their market presence.
The rise of online trading platforms and enhanced financial literacy have significantly boosted the bargaining power of these investors. They can now easily compare fees, research quality, and platform features offered by various securities firms. This accessibility means clients expect more value for their money, pushing firms to offer competitive pricing and superior service to retain them.
Customers today have unprecedented access to market information and comparison tools. This ease of access significantly amplifies their bargaining power, allowing them to thoroughly research and compare offerings from various financial service providers. For instance, in 2024, numerous online platforms and financial news outlets provided detailed performance metrics and fee structures for brokerage firms, making it simple for investors to identify cost-effective options.
This transparency directly impacts firms like Orient Securities. When clients can easily see competitive rates and superior service alternatives for standard brokerage activities, their ability to negotiate better terms or switch providers increases. This pressure compels firms to maintain competitive pricing and service quality to retain their customer base.
Low Switching Costs for Certain Services
For basic brokerage and wealth management accounts, switching costs for customers can be remarkably low, especially as the financial landscape becomes more digitized. This ease of movement allows clients to transfer their assets to other firms if they believe they can find better value or service elsewhere. For instance, a 2024 survey indicated that over 60% of retail investors would consider switching brokers for a fee reduction of just 0.25%.
This low friction in switching puts significant pressure on firms like Orient Securities to continuously offer competitive pricing and superior customer service to retain their client base. The ability for customers to easily compare and move their funds means that firms must constantly innovate and demonstrate value to avoid attrition.
Key factors contributing to low switching costs include:
- Standardized Account Transfer Processes: Industry-wide adoption of protocols like ACATS (Automated Customer Account Transfer Service) simplifies asset movement between financial institutions.
- Digital Onboarding and Management: Many firms offer online platforms for account opening and management, reducing the need for in-person interactions and making it easier to initiate a switch.
- Availability of Robo-Advisors and Online Platforms: The rise of accessible digital investment tools means customers can often replicate services from traditional brokers with greater ease and lower fees, increasing their willingness to explore alternatives.
Demand for Integrated Services
Customers increasingly desire a one-stop shop for all their financial needs, including brokerage, investment banking, and asset management. This demand for integrated services can shift power towards providers like Orient Securities if they can effectively bundle these offerings, creating significant value for clients through convenience and efficiency. For instance, in 2024, the global wealth management market, which often involves integrated services, was projected to reach over $90 trillion, indicating a strong customer preference for consolidated financial solutions.
However, this integration also raises customer expectations for seamless operation, superior quality across all services, and competitive pricing. If Orient Securities cannot deliver on these integrated expectations, customers retain considerable bargaining power, as they can easily switch to competitors offering a more cohesive or cost-effective package. The ability to switch providers easily remains a key factor in customer leverage.
- Demand for integrated financial services is growing.
- Bundling can reduce customer bargaining power if value is created.
- Customers expect seamless, high-quality, and cost-effective integrated solutions.
- Failure to meet these expectations empowers customers to switch providers.
The bargaining power of customers for Orient Securities is substantial due to increased market transparency and low switching costs. Investors can readily compare fees and services across numerous platforms, as evidenced by the significant portion of trading volume dominated by institutional investors who negotiate favorable terms. For instance, in 2024, online platforms provided detailed fee structures, enabling investors to easily identify cost-effective options.
The ease with which customers can switch providers, particularly for basic brokerage services, further amplifies their leverage. A 2024 survey revealed that a mere 0.25% fee reduction would prompt over 60% of retail investors to consider switching brokers. This environment necessitates that firms like Orient Securities maintain competitive pricing and superior service to retain their client base.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Drivers | Impact on Orient Securities |
|---|---|---|
| Institutional Investors | Large transaction volumes, negotiation for reduced commissions | Directly impacts revenue streams and profitability |
| Retail Investors | Collective market influence, ease of comparison, low switching costs | Pressure to offer competitive pricing and superior service |
| All Customers | Access to information, demand for integrated services, digital platforms | Need for value-added offerings and seamless customer experience |
Preview Before You Purchase
Orient Securities Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview displays the complete Orient Securities Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of the competitive landscape within the securities industry. You are viewing the exact, professionally formatted document that will be delivered instantly upon purchase. This comprehensive analysis provides actionable insights into the industry's structure and competitive dynamics.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The competitive rivalry within the Chinese securities market is exceptionally fierce due to a highly fragmented landscape. With over 140 securities firms, including Orient Securities, vying for market share, competition is intense across all service offerings. This crowded market means that firms like Orient Securities must constantly innovate and differentiate themselves to attract and retain clients.
The Chinese government is actively encouraging consolidation within the securities industry, aiming to forge globally competitive investment banks. This strategic push, exemplified by the potential merger between Guotai Junan and Haitong Securities, directly impacts Orient Securities by creating larger, more formidable competitors in the market.
Competitive rivalry in the securities industry, particularly for foundational services like underwriting and brokerage, is fierce. This intense competition has led to a significant downward trend in fees, pushing them to levels that are difficult to sustain. For instance, in 2024, average brokerage commissions for online trades have continued to hover near zero for many retail investors, a stark contrast to previous decades.
This aggressive pricing environment directly translates into considerable pressure on profit margins for firms like Orient Securities. Companies are compelled to find ways to operate more efficiently and achieve greater scale to remain profitable. The drive for scale is evident in the ongoing consolidation within the financial services sector, as larger entities aim to leverage their size to absorb lower margins and invest in technology.
Homogeneity of Basic Services
The fundamental services provided by many securities firms, like executing stock trades and offering straightforward wealth management, often appear quite similar. This lack of distinctiveness forces companies to engage in intense price competition or to pour resources into enhancing service quality and technological capabilities to differentiate themselves.
For instance, in 2024, the average trading commission for online retail investors in the US remained near zero for many major brokerages, highlighting the aggressive pricing strategies prevalent in the market. This homogeneity pressures firms like Orient Securities to innovate beyond basic offerings.
- Undifferentiated Core Services: Basic stock trading and wealth management are often seen as commodities in the securities industry.
- Price Competition: The similarity of services drives down prices, forcing firms to compete on cost.
- Differentiation Strategies: Firms must invest in superior customer service, advanced technology, or specialized advice to stand out.
- Impact on Profitability: Intense rivalry on price can erode profit margins for securities companies.
Market Volatility and Regulatory Changes
Fluctuations in the Chinese capital market, exemplified by the Shanghai Composite Index's performance, create a dynamic landscape for securities firms. For instance, in 2024, the index experienced periods of significant volatility, impacting trading volumes and commission revenues for all players.
Ongoing regulatory overhauls, such as the 'new National Nine Articles' introduced in 2023 and further refined through 2024, introduce an uncertain operating environment. These policy shifts necessitate rapid adaptation to new compliance requirements and capital adequacy rules, intensifying competition.
Firms like Orient Securities must navigate these shifts, adapting their strategies to policy changes and evolving market sentiment. This dynamic environment fuels a scramble for market share and the pursuit of stable, diversified revenue streams amidst the inherent unpredictability.
- Market Volatility: The Shanghai Composite Index saw significant swings in 2024, impacting revenue streams for securities firms.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: The 'new National Nine Articles' and subsequent clarifications in 2024 mandate quick adaptation to new compliance standards.
- Competitive Pressure: Firms are intensifying efforts to capture market share and secure stable revenue in response to policy shifts and market sentiment.
The competitive rivalry within China's securities sector is intense, driven by over 140 firms, including Orient Securities, all vying for market share. This fragmentation pushes down fees, with brokerage commissions for online retail trades in 2024 often approaching zero, squeezing profit margins.
The government's push for consolidation, aiming to create larger, globally competitive players, intensifies this rivalry. Firms must differentiate through service quality and technology or risk being outpaced by larger, merged entities.
Market volatility, as seen with the Shanghai Composite Index in 2024, adds another layer of pressure, impacting trading volumes and revenues. Navigating regulatory changes, such as the refined 'new National Nine Articles' through 2024, further heightens the competitive landscape as firms adapt to new compliance demands.
| Key Metric | 2023 (Approx.) | 2024 (Estimate/Trend) |
| Number of Securities Firms in China | ~140+ | Continued consolidation expected |
| Average Online Retail Brokerage Commission | Very Low (sub-basis points) | Near Zero for many |
| Shanghai Composite Index Volatility | Significant | Continued volatility observed |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Chinese commercial banks are a significant threat to securities firms' wealth management business. In 2023, the total assets of commercial banks in China reached ¥250.5 trillion, with a substantial portion allocated to wealth management products.
These bank-offered wealth management products often present themselves as stable and easily accessible alternatives, particularly for risk-averse investors who are comfortable with traditional banking channels. This broad appeal directly competes with the investment products offered by securities firms.
Individual and institutional investors are increasingly bypassing traditional securities firms by directly accessing alternative assets. For instance, in 2024, the global alternative investment market was valued at over $14 trillion, with significant growth in areas like private equity and real estate, according to industry reports. This direct investment route allows investors to avoid intermediary fees, potentially enhancing returns.
This trend offers investors more control over their portfolios and access to different risk-return profiles. Many are drawn to the potential for higher yields and diversification benefits offered by assets like direct real estate holdings or private equity funds, which don't always require a securities firm as an intermediary.
The rise of fintech platforms and robo-advisors presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional financial services. These digital alternatives, like Wealthfront and Betterment, offer automated investment management, often at a fraction of the cost of human advisors. For instance, robo-advisors typically charge annual management fees around 0.25%, compared to the 1% or more common for traditional financial planners. This cost advantage, coupled with increased accessibility and user-friendly interfaces, makes them an attractive option for a growing segment of investors, particularly younger demographics.
Insurance and Trust Products
Insurance policies that include investment features and various trust products present a significant threat of substitution for traditional securities. These alternatives offer different ways for individuals to grow and protect their wealth, and plan for the future. For instance, in 2024, the global life insurance market alone was valued at over $3 trillion, with a substantial portion of this involving investment-linked products.
These substitute products often appeal to investors seeking diversification, tax advantages, or specific estate planning benefits that might not be as readily available or as prominently marketed through standard brokerage accounts. The appeal lies in their ability to bundle financial services, potentially simplifying wealth management for some consumers.
The threat is amplified as these products can cater to a broad spectrum of risk appetites and financial goals, drawing capital away from the securities market. For example, unit-linked insurance plans allow policyholders to invest in various funds, mirroring some of the functions of mutual funds or ETFs, but within an insurance wrapper.
- Investment-linked insurance policies offer a blend of protection and wealth accumulation, often with tax benefits.
- Trust products provide mechanisms for asset management, wealth preservation, and estate planning, serving as alternatives to direct investment in securities.
- In 2024, the global insurance market's immense size, exceeding $6 trillion, highlights the significant capital pool available to these substitute products.
- These substitutes can attract funds that might otherwise be channeled into stocks, bonds, or other traditional investment vehicles managed by securities firms.
Overseas Investment Opportunities
For sophisticated investors, direct investment in international markets or through qualified domestic institutional investor (QDII) schemes presents a compelling alternative to domestic opportunities. This allows for crucial diversification, mitigating risks tied to a single market. For instance, as of early 2024, the MSCI World Index offered a broad exposure to developed markets, contrasting with the performance of China's CSI 300 index.
Geopolitical tensions and domestic market sentiment significantly influence the attractiveness of these overseas substitutes. For example, heightened trade disputes or shifts in regulatory environments within China can drive capital towards perceived safer or higher-growth international markets. Investors closely monitor global economic indicators and political stability when evaluating these options.
The availability and performance of overseas investment vehicles are key considerations. QDII quotas, which limit the amount of capital that can be invested abroad by Chinese institutions, directly impact the accessibility of these substitutes. Fluctuations in QDII approvals and the overall performance of international asset classes, such as emerging market equities which saw varied performance in 2023, play a vital role in investor decisions.
- Diversification Benefits: Direct overseas investment and QDII schemes offer a crucial hedge against domestic market volatility.
- Geopolitical Impact: International relations and trade policies can significantly alter the appeal of foreign markets.
- Market Sentiment Influence: Investor confidence in the domestic versus international economic outlook drives capital flows.
- Regulatory and Quota Constraints: QDII limits and evolving regulations impact the ease of accessing foreign investment opportunities.
Commercial banks in China pose a significant threat to securities firms' wealth management services, with their ¥250.5 trillion in total assets in 2023 and substantial wealth management product allocations.
These bank products are often perceived as stable and accessible, particularly by risk-averse investors, directly competing with securities firm offerings.
Furthermore, investors are increasingly bypassing traditional intermediaries for direct investments in alternative assets, a market valued at over $14 trillion globally in 2024, seeking to enhance returns by avoiding fees.
The rise of fintech and robo-advisors, charging around 0.25% annually versus traditional advisors' 1%+, also presents a substantial substitute threat due to cost-effectiveness and accessibility.
| Substitute Type | Key Appeal | Market Size/Growth Indicator (2024 Data) |
|---|---|---|
| Commercial Bank Wealth Management | Perceived Stability, Accessibility | ¥250.5 Trillion Total Assets (China, 2023) |
| Direct Alternative Investments | Higher Potential Returns, Fee Avoidance | >$14 Trillion Global Market Value |
| Fintech/Robo-Advisors | Lower Fees (e.g., 0.25% vs 1%+), Accessibility | Rapidly Growing Investor Adoption |
| Investment-Linked Insurance/Trusts | Diversification, Tax Benefits, Estate Planning | >$6 Trillion Global Insurance Market |
Entrants Threaten
The securities industry, particularly for firms offering a full suite of services like Orient Securities, presents a formidable barrier to entry due to extremely high capital requirements. Establishing robust operational infrastructure, securing necessary licenses, and ensuring rigorous compliance with financial regulations necessitate significant upfront investment. For instance, in 2024, regulatory capital requirements for securities firms in major markets often run into the tens of millions of dollars, making it exceptionally difficult for smaller, less-capitalized entities to compete.
Stringent regulatory hurdles, particularly the complex licensing procedures mandated by the China Securities Regulatory Commission (CSRC), significantly deter new entrants into the Chinese securities market. These rigorous requirements necessitate substantial investment in compliance infrastructure and demonstrate robust risk management capabilities, effectively acting as a formidable barrier to entry.
Established firms like Orient Securities benefit from years of building strong brand recognition and client trust. Newcomers must overcome the significant hurdle of gaining credibility and attracting customers who are loyal to these entrenched players. For example, in 2023, the top five securities firms in China, including those with long histories, held over 60% of the market share in brokerage services, indicating the power of established reputations.
Extensive Distribution Networks and Client Relationships
Existing securities firms boast robust distribution networks, including physical branches and advanced online platforms, alongside strong ties with individual and institutional clients. Establishing comparable channels and client trust is a significant hurdle for newcomers, requiring substantial investment and time. For instance, in 2024, major Chinese securities firms like CITIC Securities reported extensive branch networks, with CITIC Securities alone operating hundreds of physical locations across China, facilitating broad client access.
The threat of new entrants is therefore moderated by the immense cost and time required to replicate these established distribution capabilities and cultivate deep client relationships. New players face the challenge of building brand recognition and a loyal customer base against incumbents who have spent years solidifying their market presence.
- Established Infrastructure: Incumbent firms have invested heavily in physical and digital distribution, creating significant barriers to entry.
- Client Loyalty: Deep-seated relationships with existing clients make it difficult for new entrants to attract and retain business.
- Brand Reputation: Years of operation have allowed established firms to build trust and a strong brand image, which new entrants must overcome.
Governmental Support for Incumbents and Consolidation
The Chinese government's strategic objective to cultivate a select group of 'world-class' investment banks through industry consolidation inherently benefits incumbent firms. This policy actively erects higher entry barriers for smaller, independent entities seeking to establish themselves in the market.
Policy initiatives, including preferential treatment and encouragement of strategic mergers, serve to solidify the market position and competitive advantage of already dominant players. For instance, the push for consolidation in China's securities industry has seen significant merger activity, with larger state-backed firms often acquiring smaller ones, thereby concentrating market share.
- Government Mandate: China aims for a few globally competitive investment banks.
- Consolidation Trend: Policy actively encourages mergers and acquisitions, favoring larger entities.
- Barrier Creation: This consolidation increases capital and regulatory hurdles for new, independent entrants.
The threat of new entrants for a firm like Orient Securities is significantly mitigated by the immense capital requirements and complex regulatory landscape in the securities industry. For example, in 2024, obtaining the necessary licenses and establishing compliant operations in major financial markets often demands tens of millions of dollars in initial investment.
Established players like Orient Securities also benefit from strong brand recognition and deep client relationships, built over years of operation. Newcomers face the daunting task of gaining trust and market share against incumbents who, as of 2023, held substantial market dominance, with the top five Chinese securities firms controlling over 60% of brokerage services.
Furthermore, government policies in China, aimed at fostering a few globally competitive investment banks, encourage industry consolidation. This trend, evidenced by significant merger activity where larger firms acquire smaller ones, inherently raises entry barriers for independent new entities.
| Barrier Type | Description | 2024 Data/Example |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High upfront investment needed for infrastructure, licenses, and compliance. | Tens of millions of dollars in regulatory capital for major markets. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex licensing and compliance procedures, especially in China (CSRC). | Rigorous compliance infrastructure and risk management demonstration required. |
| Brand Reputation & Client Loyalty | Difficulty in attracting clients away from established, trusted firms. | Top 5 Chinese securities firms held >60% market share in brokerage (2023). |
| Distribution Networks | Need to replicate extensive physical and digital client access points. | CITIC Securities operates hundreds of branches across China. |
| Government Policy | Focus on industry consolidation favors larger, established entities. | Merger activity concentrates market share, increasing barriers for new entrants. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Orient Securities is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including the company's annual reports, investor presentations, and official regulatory filings. We also incorporate insights from reputable financial news outlets and industry-specific market research reports to capture the competitive landscape.
