Delivery Hero Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Delivery Hero Bundle
Delivery Hero operates in a dynamic food delivery landscape, where buyer power is significant due to readily available alternatives and intense competition. Understanding the nuanced interplay of these forces is crucial for navigating this market.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Delivery Hero’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of individual restaurants partnering with Delivery Hero can be quite varied. For smaller, independent eateries, this power is often limited, as they depend significantly on platforms like Delivery Hero for crucial online visibility and the logistical complexities of delivery. These restaurants might have fewer options for reaching customers directly.
Conversely, highly sought-after restaurants or established chains with strong brand recognition and a loyal customer following can wield more influence. Their ability to draw a substantial customer base gives them a stronger negotiating position when it comes to commission rates or service terms.
Delivery Hero's vast network, operating in numerous markets and featuring a wide array of restaurant partners, inherently dilutes the leverage of any single restaurant. This broad supplier base means Delivery Hero is less dependent on any one partner, thereby reducing their individual bargaining power.
The bargaining power of delivery riders for Delivery Hero is a dynamic factor, heavily influenced by local labor laws and the overall economic climate. In areas with a surplus of available riders and weaker worker protections, their ability to negotiate terms is diminished. For instance, in some markets, riders are classified as independent contractors, limiting their collective bargaining rights and thus their power.
Conversely, in regions experiencing rider shortages or where labor unions are active, the bargaining power of these riders can significantly increase. This can translate into demands for higher pay, better benefits, and improved working conditions. For example, in late 2023 and early 2024, protests and strikes by delivery riders in several European cities highlighted their growing collective strength and their ability to disrupt operations if their demands are not met, potentially increasing Delivery Hero's operational costs.
While Delivery Hero builds much of its core technology internally, it still depends on external technology providers for essential services like cloud computing, mapping data, and payment processing. The influence of these suppliers can range from moderate to significant, particularly when their services are highly specialized and alternatives are scarce. For instance, providers of advanced AI-driven mapping or specialized fraud detection systems might hold considerable sway.
Delivery Hero's considerable global presence and substantial order volume, reaching over 2.4 billion orders in 2023 across its various brands, do offer some negotiation strength. This scale allows them to potentially secure more favorable pricing and service level agreements from technology vendors. However, the critical nature of these services means that switching providers can be complex and costly, maintaining a degree of supplier power.
Grocery and Quick Commerce Suppliers
As Delivery Hero ventures deeper into quick commerce, the bargaining power of grocery and essential goods suppliers gains significance. For widely available items, supplier power is generally moderate, stemming from established distribution networks and consumer brand loyalty. However, for unique or specialty products, suppliers can wield greater influence.
Delivery Hero's strategic approach to mitigate this power includes diversifying its supplier base and developing its own 'dark stores,' often referred to as Dmarts. This vertical integration allows for greater control over inventory and sourcing, thereby reducing reliance on individual suppliers. For instance, by the end of 2023, Delivery Hero operated thousands of Dmarts across various markets, providing a significant lever in supplier negotiations.
- Moderate Power for Essentials: Suppliers of everyday groceries often have moderate bargaining power due to established logistics and brand recognition, but Delivery Hero's scale can offset this.
- Higher Power for Niche Products: For specialized or less common items, suppliers can command more favorable terms.
- Mitigation through Dark Stores: Delivery Hero's network of Dmarts (e.g., thousands operational by late 2023) allows for direct sourcing and inventory management, reducing supplier dependency.
- Diversification as a Strategy: Sourcing from multiple vendors for similar product categories enhances Delivery Hero's negotiating position.
Marketing and Advertising Partners
Delivery Hero engages a variety of marketing and advertising partners to connect with its customer base. The bargaining power of these entities, which include digital advertising platforms and media buying agencies, is generally considered moderate. While the market offers numerous choices, certain highly effective platforms or specialized agencies can negotiate for premium rates, reflecting their proven ability to drive customer acquisition and engagement.
The significant volume of advertising expenditure by Delivery Hero, coupled with the strategic development of its internal AdTech capabilities, provides the company with a degree of leverage in its dealings with these partners. This influence can be seen in negotiations over ad placements, pricing structures, and the terms of service, allowing Delivery Hero to optimize its marketing investments. For instance, in 2023, the global digital advertising market saw substantial growth, with platforms like Google and Meta continuing to dominate, but also with increasing demand for performance-based advertising solutions where Delivery Hero's own data and technology can play a role.
- Moderate Bargaining Power: Marketing and advertising partners have moderate power due to the availability of multiple platforms, but specialized agencies or high-performing digital channels can command higher prices.
- Delivery Hero's Influence: The company's substantial advertising budget and its burgeoning AdTech business grant it negotiation advantages.
- Market Dynamics: The digital advertising landscape is competitive, with major players and emerging AdTech solutions influencing partner capabilities and pricing.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Delivery Hero is multifaceted, influenced by the type of supplier and Delivery Hero's own strategic initiatives. For technology providers, their power can be significant if their services are specialized and difficult to replace, though Delivery Hero's scale offers some leverage. In the quick commerce sector, grocery suppliers of common items have moderate power, but this increases for niche products, a dynamic Delivery Hero mitigates through its Dmart network.
Delivery Hero's vast operational scale, evidenced by over 2.4 billion orders in 2023, grants it considerable negotiation strength with suppliers, particularly in securing favorable terms for technology and logistics. However, the critical nature of some services, like advanced mapping data or cloud infrastructure, means that switching providers can be complex and costly, maintaining a degree of supplier leverage.
The company's investment in vertical integration, such as its thousands of Dmarts by the end of 2023, directly reduces its reliance on external grocery suppliers, thereby diminishing their bargaining power for essential goods. Diversifying its supplier base further strengthens Delivery Hero's negotiating position across various categories.
| Supplier Category | Bargaining Power Assessment | Delivery Hero's Mitigating Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Technology Providers (Cloud, Mapping, AI) | Moderate to Significant (depending on specialization) | Scale of operations, potential for long-term contracts, internal development capabilities |
| Grocery & Essential Goods Suppliers (Quick Commerce) | Moderate (for essentials) to High (for niche products) | Network of Dmarts, supplier diversification, direct sourcing strategies |
| Marketing & Advertising Partners | Moderate | Large advertising budget, internal AdTech development, multiple platform options |
What is included in the product
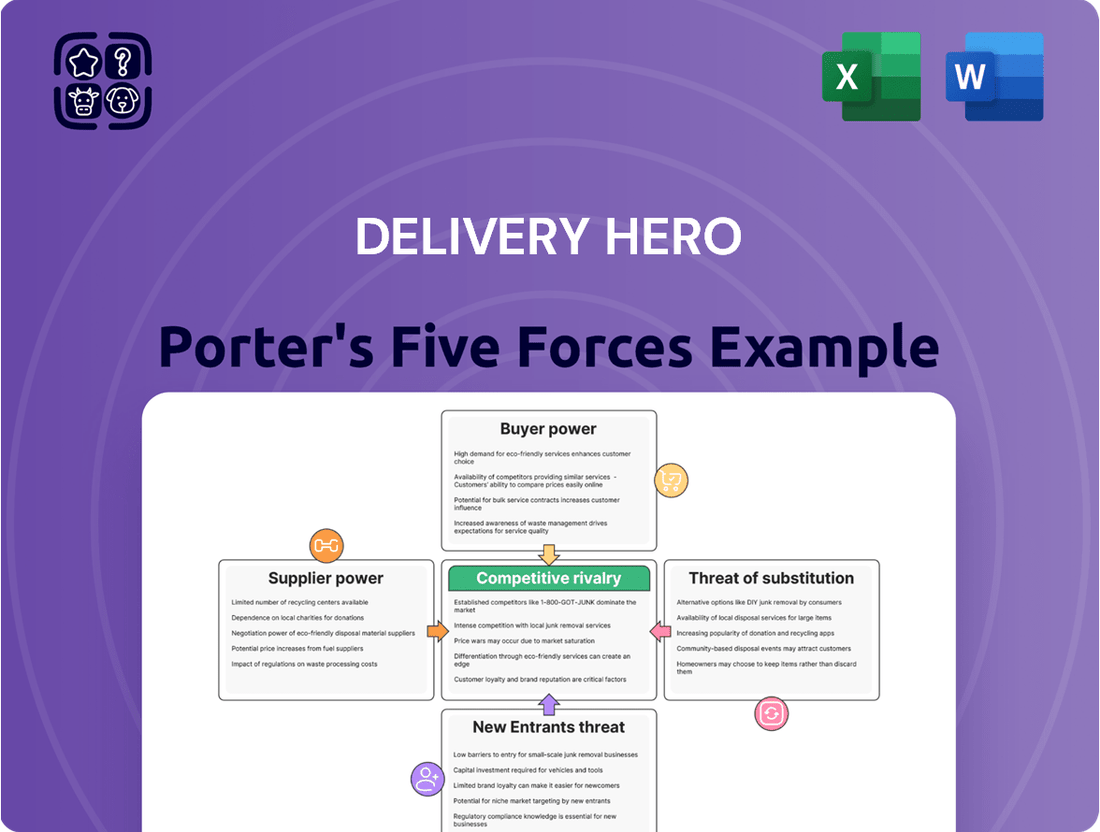
This analysis of Delivery Hero's competitive landscape reveals the intense rivalry among food delivery platforms and the significant bargaining power of both restaurants and customers, impacting profitability and strategic decisions.
Quickly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a visual breakdown of Delivery Hero's bargaining power, supplier power, threat of new entrants, threat of substitutes, and rivalry.
Customers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of individual consumers is typically quite strong in the food delivery sector. This is largely because switching between different apps is incredibly easy, with minimal effort or cost involved for the user. For instance, a consumer can easily compare the offerings of Delivery Hero's brands against competitors like Uber Eats or DoorDash in seconds, simply by opening another application on their phone.
This ease of switching, combined with a vast array of available restaurants and delivery options, means consumers have significant leverage. They can readily shop around for the best deals, looking at factors like delivery fees, estimated arrival times, and available discounts. This constant comparison pushes platforms to offer competitive pricing and frequent promotions to attract and retain customers, as evidenced by the ongoing promotional wars seen across the industry in 2024.
Corporate clients and businesses that place substantial, ongoing orders, such as for employee meal programs, can wield significant bargaining power. Their ability to negotiate for better pricing, dedicated customer service, or tailored service agreements stems directly from the consistent volume of business they represent. Delivery Hero's strategic push into workplace meal solutions underscores its recognition of this influential customer segment.
Customers in the food delivery sector exhibit significant price sensitivity, frequently comparing options based on promotions, discounts, and delivery charges. This behavior directly pressures Delivery Hero to offer competitive pricing, potentially affecting its profit margins.
Preference for Convenience and Speed
Customers today prioritize convenience and speed, often valuing these attributes as much as, or even more than, a lower price. This means that food delivery platforms offering quicker delivery times and a smoother, more intuitive app experience can build strong customer loyalty, even if they aren't always the cheapest option.
This preference for seamlessness significantly influences customer bargaining power. For instance, in 2024, reports indicated that over 60% of consumers would switch to a competitor for faster delivery, highlighting the tangible impact of speed on customer retention.
- Speed as a Differentiator: Platforms that invest in logistics and technology to reduce delivery times gain a competitive edge.
- User Experience Matters: An easy-to-navigate app and straightforward ordering process enhance customer satisfaction and reduce the likelihood of switching.
- Balancing Price and Convenience: While price remains a consideration, the willingness to pay a premium for superior convenience shifts some bargaining power away from the customer based solely on cost.
Access to Multiple Platforms
The widespread availability of numerous food and quick commerce delivery apps significantly amplifies customer bargaining power. Customers can easily compare services, pricing, and product selections across various platforms, including rivals to Delivery Hero. This ease of switching means customers can readily abandon a platform if they encounter dissatisfaction, forcing Delivery Hero to remain competitive to retain them.
In 2024, the global online food delivery market continued to see robust competition. For instance, the market size was projected to reach over $200 billion, with a significant portion of this growth driven by the proliferation of delivery platforms. This intense competition directly translates to customers having more choices than ever before, enhancing their ability to negotiate better terms or simply move to a competitor offering superior value.
- Increased Choice: Customers can easily access and compare offerings from Delivery Hero and its numerous competitors.
- Price Sensitivity: The availability of alternatives makes customers more sensitive to pricing differences, potentially leading to demands for discounts or lower fees.
- Service Expectations: Customers expect high levels of service across all platforms and will switch if Delivery Hero fails to meet these expectations.
- Platform Loyalty: Low switching costs mean customer loyalty is not guaranteed, requiring Delivery Hero to constantly innovate and offer compelling reasons to stay.
The bargaining power of customers in the food delivery sector remains substantial, driven by low switching costs and an abundance of choices. In 2024, the market continued to be characterized by intense competition among numerous platforms, including Delivery Hero's various brands and rivals like Uber Eats and DoorDash. This competitive landscape empowers consumers to readily compare prices, delivery times, and promotions, often opting for the most attractive deals.
Customers are highly price-sensitive, frequently leveraging discounts and comparing delivery fees across apps. This behavior pressures Delivery Hero to maintain competitive pricing, potentially impacting profit margins. Furthermore, a significant portion of consumers, over 60% as indicated by 2024 industry reports, are willing to switch to a competitor for faster delivery, highlighting speed and convenience as key factors influencing customer loyalty.
| Factor | Impact on Delivery Hero | Customer Behavior Example (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Low Switching Costs | Weakens customer loyalty, increases churn risk | Users easily switch between apps for promotions. |
| Price Sensitivity | Pressures margins, necessitates constant promotions | Customers actively seek out discount codes and free delivery offers. |
| Demand for Speed/Convenience | Requires investment in logistics and user experience | Over 60% of consumers would switch for faster delivery. |
| Numerous Competitors | Intensifies competition, limits pricing power | Proliferation of platforms in a market projected over $200 billion in 2024. |
Preview Before You Purchase
Delivery Hero Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Delivery Hero Porter's Five Forces Analysis, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic implications for the company. You're viewing the exact, professionally formatted document that you will receive instantly upon purchase. This comprehensive analysis covers the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the threat of substitute products, providing a thorough understanding of Delivery Hero's market position.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The online food and quick commerce delivery sector is incredibly crowded, featuring a multitude of global giants and smaller, regional players. This high density of competitors means Delivery Hero constantly faces pressure to innovate and attract both customers and restaurant partners.
Global powerhouses such as Uber Eats and Just Eat Takeaway.com, which itself operates Foodpanda in several key regions, are major rivals. Their extensive networks and brand recognition create a formidable challenge, forcing Delivery Hero into aggressive market strategies.
In 2024, the landscape continues to be shaped by these large entities, alongside a persistent presence of local and niche delivery services. This intense rivalry often leads to price wars and heavy marketing spend as companies battle for dominance in each market they operate.
Delivery Hero operates in a fiercely competitive landscape where price wars and aggressive promotions are commonplace. This intense rivalry forces the company to constantly offer discounts and special deals to win and keep customers, which can put a strain on its profitability. For example, in 2023, many food delivery platforms globally, including those in regions where Delivery Hero operates, saw increased promotional spending as companies battled for market share.
Competitors in the food delivery sector are heavily investing in technology, with companies like DoorDash and Uber Eats pouring billions into AI for personalized recommendations and sophisticated real-time tracking systems. This arms race in technological advancement means Delivery Hero must continually innovate in areas like route optimization and predictive demand forecasting to maintain its competitive edge and customer satisfaction.
Geographic Expansion and Market Exits
Delivery Hero and its competitors are constantly expanding into new territories and sometimes pulling back from unprofitable ones. This constant movement means that the intensity of competition can vary greatly from one country to another.
For example, in 2023, Delivery Hero continued its strategic focus on core markets, leading to divestments in certain regions. This allows them to concentrate resources where they see the most potential for growth and profitability, directly impacting how fiercely they compete in their chosen operational areas.
- Geographic Expansion: Delivery Hero actively enters new markets, aiming to capture market share and diversify revenue streams.
- Market Exits: The company strategically exits underperforming or non-core markets to streamline operations and improve financial performance.
- Competitive Intensity: The dynamic nature of expansion and exits means competitive pressures can be very high in some markets and less so in others.
- Focus on Profitability: These strategic moves are driven by a desire to optimize resource allocation and focus on sustainable, profitable growth.
Diversification into Quick Commerce
The competitive arena for Delivery Hero has significantly broadened. It's no longer solely about food delivery; quick commerce, encompassing groceries and everyday items, is now a major factor. This means Delivery Hero faces rivals not just in food delivery but also from grocery delivery platforms and established retailers venturing into rapid fulfillment.
This multi-vertical competition intensifies rivalry. For instance, in 2024, the quick commerce sector saw substantial investment and growth, with companies like Gorillas and Flink expanding their operations across numerous European cities. Delivery Hero’s own Dm-drogerie markt partnership in Germany exemplifies this shift, directly competing with grocery-focused players.
- Increased Competition: Delivery Hero now competes with a wider array of businesses, including grocery delivery services and traditional retailers with online presence.
- Market Expansion: The move into quick commerce means competing for customer loyalty across different everyday purchase categories, not just meals.
- Strategic Partnerships: Collaborations, such as Delivery Hero's involvement with Dm-drogerie markt, highlight the strategic importance of diversifying beyond food to capture a larger share of the rapid delivery market.
Delivery Hero faces intense competition from global giants like Uber Eats and Just Eat Takeaway.com, alongside numerous regional and niche players. This crowded market necessitates continuous innovation and aggressive strategies, often leading to price wars and substantial marketing expenditures. For instance, in 2023, promotional spending across the food delivery sector saw a significant uptick as companies vied for market share.
The rivalry extends into quick commerce, forcing Delivery Hero to compete with grocery delivery services and retailers. This multi-vertical competition intensifies pressure. In 2024, the quick commerce sector experienced considerable investment, with companies like Gorillas and Flink expanding rapidly, directly challenging Delivery Hero's diversified offerings.
| Competitor | Primary Focus | Key Markets |
|---|---|---|
| Uber Eats | Food Delivery, Groceries | Global |
| Just Eat Takeaway.com | Food Delivery | Europe, North America |
| DoorDash | Food Delivery, Groceries | North America |
| Gorillas | Quick Commerce (Groceries) | Europe |
| Flink | Quick Commerce (Groceries) | Europe |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Customers increasingly bypass third-party delivery platforms by ordering directly from restaurants for pickup or through the restaurant's own delivery services. This trend is fueled by a desire to avoid commission fees, which can range from 15% to 30% for platforms like DoorDash or Uber Eats, directly impacting restaurant margins.
Many restaurants are actively investing in their own online ordering systems and delivery infrastructure. For instance, in 2024, numerous independent and chain restaurants expanded their in-house delivery fleets and optimized their websites and apps for direct orders, aiming to retain a larger portion of their revenue.
The most fundamental substitute for ordering delivered food is, of course, cooking meals at home. This option offers significant cost savings; for instance, the average cost of a home-cooked meal can be considerably lower than a restaurant delivery, especially for families. Consumers also value the control over ingredients and dietary needs that home cooking provides, a factor that gains importance during economic slowdowns or for health-conscious individuals. The increasing popularity of meal kit services further strengthens this substitute, making home cooking more convenient.
While the convenience of online food delivery is undeniable, traditional takeaway and dine-in options continue to serve as significant substitutes for platforms like Delivery Hero. These established methods offer distinct advantages, such as the absence of delivery fees, which can make them more cost-effective for consumers. For instance, in 2024, many consumers still prioritize picking up their orders directly from restaurants to avoid these charges, especially for smaller orders.
Furthermore, the social aspect of dining in provides an experience that online delivery cannot replicate. Restaurants often offer unique ambiances and the opportunity for immediate consumption without waiting for a delivery driver. This can be particularly appealing for spontaneous meal decisions or when seeking a specific dining atmosphere, presenting a persistent challenge to the dominance of delivery-only models.
Grocery Delivery Services
The increasing prevalence of dedicated online grocery delivery platforms presents a significant threat of substitutes for Delivery Hero's quick commerce operations. These services, while often offering longer delivery windows, cater to the same fundamental customer need: convenient grocery acquisition without leaving home. This directly challenges Delivery Hero's expansion into the grocery delivery market.
By mid-2024, the online grocery market continued its robust growth. For instance, in the US, online grocery sales were projected to reach over $150 billion for the year, indicating a substantial addressable market for substitute services. This growth is fueled by evolving consumer preferences for convenience and a wider selection of goods available through specialized platforms.
- Dedicated online grocery platforms offer a direct substitute for quick commerce.
- These services cater to the same customer need for convenient grocery delivery.
- The US online grocery market was projected to exceed $150 billion in sales in 2024.
- This segment directly competes with Delivery Hero's grocery delivery expansion.
Meal Kit Delivery Services
Meal kit delivery services, offering pre-portioned ingredients and recipes, present a notable substitute for prepared food delivery. These services appeal to consumers seeking the convenience of home meal preparation without the hassle of extensive grocery shopping or the full effort of cooking from scratch.
For instance, in 2024, the global meal kit delivery market was valued at approximately USD 15 billion, with projections indicating continued growth. This segment directly competes with food delivery platforms by fulfilling the need for convenient, home-cooked meals.
- Convenience Factor: Meal kits offer a middle ground between full grocery shopping and restaurant-quality takeout.
- Cost-Effectiveness: While not always cheaper than cooking from scratch, meal kits can be more cost-effective than frequent restaurant orders or prepared meals.
- Dietary Customization: Many services allow for specific dietary needs and preferences, a feature that can be more limited with general food delivery.
- Consumer Preference Shift: A growing segment of consumers in 2024 is prioritizing home cooking for health and cost reasons, making meal kits an attractive alternative.
The threat of substitutes for Delivery Hero is significant, encompassing direct restaurant ordering, home cooking, and meal kits. Consumers are increasingly opting for direct orders to bypass third-party commissions, with restaurants in 2024 expanding their own delivery infrastructure. Home cooking remains a fundamental substitute, offering cost savings and control over ingredients, a trend bolstered by convenient meal kit services.
Traditional takeaway and dine-in options also pose a threat, as they eliminate delivery fees and offer immediate consumption and social experiences. Furthermore, the expanding online grocery delivery market, projected to exceed $150 billion in US sales in 2024, directly competes with Delivery Hero's quick commerce initiatives by fulfilling the need for convenient grocery acquisition.
| Substitute Type | Key Driver | 2024 Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Direct Restaurant Orders | Avoiding commission fees (15-30%) | Restaurants investing in own delivery (2024) |
| Home Cooking | Cost savings, ingredient control | Meal kit popularity increasing convenience |
| Takeaway/Dine-in | No delivery fees, immediate consumption | Consumer preference for cost-effectiveness |
| Online Grocery Delivery | Convenient grocery acquisition | US market projected >$150 billion (2024) |
Entrants Threaten
Launching a food delivery service, while seemingly straightforward, demands significant financial investment to truly compete. Building a sophisticated app, establishing a reliable network of couriers, and marketing effectively to gain traction all require substantial upfront capital. For instance, in 2024, major players continue to pour billions into technology and expansion, making it incredibly challenging for newcomers to match this scale without deep pockets.
Delivery Hero benefits from significant brand recognition and ingrained customer loyalty, cultivated through years of marketing and reliable service delivery. New entrants must invest heavily in promotions to even begin chipping away at this established trust, a substantial hurdle in acquiring market share.
Network effects are a significant barrier for new entrants in the food delivery market. Delivery Hero, like its competitors, benefits from a virtuous cycle where a larger restaurant selection attracts more users, and a larger user base incentivizes more restaurants to join. For instance, in 2024, platforms with established user bases and extensive restaurant partnerships, such as DoorDash in the US, continued to leverage these network effects to maintain market dominance, making it difficult for smaller, newer platforms to gain traction.
Regulatory Hurdles and Labor Laws
The threat of new entrants in the food delivery sector is significantly influenced by regulatory hurdles and labor laws. As of 2024, governments worldwide are intensifying their focus on the gig economy, particularly concerning worker classification and benefits. This evolving regulatory landscape presents a substantial barrier for new companies aiming to enter the market.
New players must contend with complex and often inconsistent labor laws across various regions. For instance, the ongoing debate around whether delivery riders should be classified as employees or independent contractors can lead to vastly different operational costs and legal liabilities. Companies like Uber Eats and DoorDash have faced numerous legal challenges and regulatory changes in 2024 concerning worker rights and minimum wage requirements in key markets, demonstrating the significant financial and legal risks involved.
- Worker Classification: Jurisdictions are increasingly pushing for employee status for gig workers, which would mandate benefits like health insurance and paid time off, increasing costs for new entrants.
- Minimum Wage Laws: Compliance with varying minimum wage laws, which can differ significantly by city or state, adds complexity and cost to new delivery operations.
- Safety Regulations: New regulations concerning rider safety, such as mandatory insurance or equipment standards, can also represent upfront investment and ongoing compliance costs.
- Data Privacy: Stricter data privacy laws, like GDPR or similar emerging regulations in 2024, require new entrants to invest in robust data protection measures from the outset.
Economies of Scale in Logistics
Economies of scale in logistics present a significant barrier for new entrants in the food delivery market. Delivery Hero, as a large incumbent, leverages its extensive network to optimize delivery routes, manage its vast rider fleet efficiently, and ultimately lower the cost per delivery. This operational efficiency is difficult for smaller, newer companies to replicate, making it challenging for them to compete on pricing.
For instance, in 2024, major food delivery platforms have invested heavily in sophisticated route optimization software and data analytics to maximize driver utilization. This allows them to absorb a larger portion of delivery costs, offering more competitive fees to customers and potentially lower commission rates to restaurants, squeezing margins for any new player trying to enter the market without comparable scale.
- Scale Advantage: Incumbents like Delivery Hero benefit from lower per-delivery costs due to optimized logistics and fleet management.
- Cost Barrier: New entrants struggle to achieve similar efficiencies, leading to higher operating costs and less competitive pricing.
- Investment Needs: Reaching the scale required to match incumbent logistics efficiency demands substantial upfront investment in technology and infrastructure.
The threat of new entrants in the food delivery sector remains moderate to high, primarily due to the substantial capital required for technology development, courier networks, and marketing. While the digital nature of the business theoretically lowers entry barriers, the reality of competing with established giants like Delivery Hero necessitates significant financial backing. By 2024, the ongoing global investment in logistics technology and expanding service areas by incumbents further solidifies this barrier.
Established brand loyalty and the powerful network effects enjoyed by incumbent platforms like Delivery Hero present a considerable challenge for newcomers. Overcoming customer inertia and building a comparable restaurant selection requires extensive time and resources. In 2024, platforms with strong user bases and deep restaurant partnerships continued to benefit from these self-reinforcing advantages, making it difficult for new entrants to gain meaningful traction.
Regulatory complexities, particularly concerning the gig economy and worker classification, add another layer of difficulty for potential new entrants. As of 2024, evolving labor laws and increased scrutiny on worker benefits in key markets mean that new companies must navigate significant legal and financial risks. These evolving regulations can drastically alter operational costs and compliance requirements, acting as a deterrent to market entry.
Economies of scale in logistics and operations create a significant cost advantage for established players like Delivery Hero. Their ability to optimize routes, manage large fleets efficiently, and leverage data analytics leads to lower per-delivery costs. New entrants struggle to achieve this level of efficiency without comparable scale, making it challenging to compete on price and service quality in 2024.
| Factor | Impact on New Entrants | Mitigation Strategy for Incumbents | 2024 Relevance |
| Capital Investment | High (Tech, Logistics, Marketing) | Leverage existing infrastructure and brand recognition | Continued high investment by incumbents |
| Brand Loyalty & Network Effects | High (Difficult to overcome) | Focus on customer retention and exclusive partnerships | Strengthening through data and personalized offers |
| Regulatory Landscape | Moderate to High (Worker classification, data privacy) | Proactive compliance and adaptation to evolving laws | Increased government oversight globally |
| Economies of Scale | High (Cost disadvantage for newcomers) | Continuous optimization of logistics and operational efficiency | Investment in AI for route planning and fleet management |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Delivery Hero Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, including company annual reports, investor presentations, and financial news outlets. We also leverage industry-specific market research reports and publicly available competitor data to provide a comprehensive view.
