Dashang Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Dashang Group Bundle
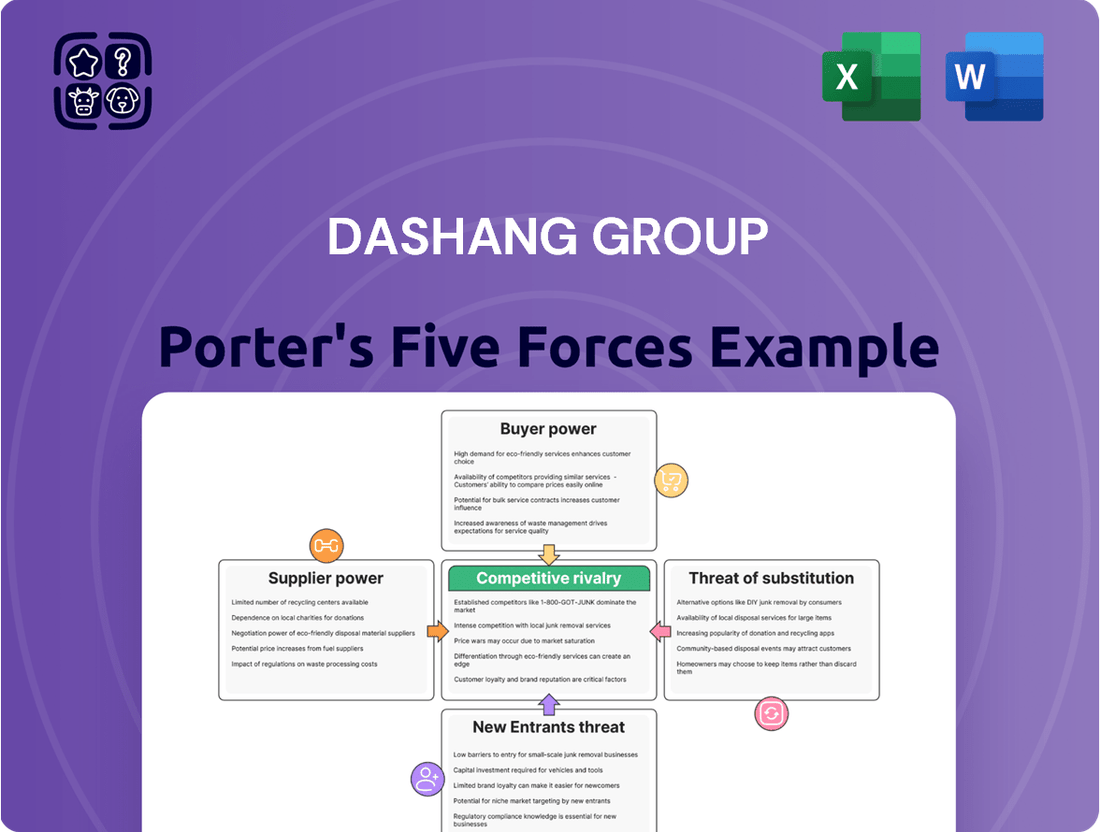
Dashang Group operates within a dynamic retail landscape, where understanding the intensity of competition and the power of buyers and suppliers is crucial. Our Porter's Five Forces analysis reveals the key pressures influencing Dashang Group's profitability and strategic options.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Dashang Group’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of suppliers for Dashang Group is significantly influenced by supplier concentration across its varied product lines, which include fashion and fresh produce. When a few dominant suppliers control a particular category, they can exert considerable influence over pricing and terms, potentially impacting Dashang's profitability.
For example, in the highly competitive fashion retail sector, if a small number of premium fabric manufacturers or well-known designer brands hold a large market share, they can command higher prices. Conversely, a broad and fragmented supplier base for items like everyday groceries or basic apparel generally offers Dashang more negotiating leverage, allowing for more favorable purchasing agreements.
Dashang Group faces significant switching costs when changing suppliers, particularly for specialized components or proprietary IT systems integral to its operations. These costs can include the expense of renegotiating contracts, reconfiguring complex supply chains, and adapting or replacing existing IT infrastructure. For instance, if a key supplier provides a unique, custom-built piece of machinery, the investment in finding and integrating a replacement could be substantial, potentially running into millions of dollars in setup and training alone.
When suppliers offer unique or highly differentiated products, technologies, or services, their bargaining power significantly increases. This distinctiveness means Dashang Group has fewer viable alternatives, allowing these suppliers to command higher prices and dictate more favorable terms. For instance, a supplier providing proprietary software essential for Dashang's operations, or a manufacturer of a critical component with no readily available substitutes, would wield considerable influence.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into retail operations significantly bolsters their bargaining power against Dashang Group. If suppliers, particularly those with strong brand recognition, were to establish their own direct-to-consumer channels, they could effectively disintermediate Dashang, cutting into its distribution margins and market access.
This forward integration risk is heightened for suppliers who possess established brand equity and a direct relationship with end consumers. For instance, a major apparel supplier to Dashang could, in theory, launch its own e-commerce platform or flagship stores, thereby bypassing Dashang's retail network entirely.
- Supplier Integration Threat: Suppliers may leverage their brand strength to bypass Dashang and sell directly to consumers.
- Impact on Dashang: This reduces Dashang's role in distribution and can compress profit margins.
- Key Factor: The credibility of this threat increases with the supplier's brand establishment and consumer recognition.
Importance of Dashang to the Supplier
The bargaining power of suppliers to Dashang Group is significantly influenced by Dashang's importance as a customer. If Dashang accounts for a large percentage of a supplier's total sales, the supplier is more likely to offer competitive pricing and favorable terms to secure Dashang's continued business. For instance, in 2023, major department store chains often represented over 10% of their key apparel suppliers' annual turnover, giving them considerable leverage.
Conversely, if Dashang is a minor client for a supplier, that supplier holds greater power. They may be less inclined to negotiate on price or delivery schedules, as losing Dashang's business would have a minimal impact on their overall revenue. This dynamic can lead to higher input costs for Dashang if they rely on specialized or niche suppliers who have many other customers.
- Dashang's Revenue Share: If Dashang constitutes a significant portion of a supplier's revenue, the supplier’s bargaining power is diminished.
- Supplier Dependence: Suppliers heavily reliant on Dashang for sales will likely offer more favorable terms.
- Market Concentration: The number of alternative suppliers available to Dashang impacts the bargaining power of existing suppliers.
- Input Cost Sensitivity: Suppliers with high fixed costs or unique inputs may have stronger bargaining power.
Suppliers' bargaining power for Dashang Group is influenced by the concentration of suppliers in its diverse product categories, such as fashion and fresh produce. When a few dominant suppliers control a segment, they can dictate pricing and terms, impacting Dashang's profitability.
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into retail, especially those with strong brand equity, significantly enhances their power. This could lead to disintermediation, reducing Dashang's distribution role and profit margins. For example, a major apparel supplier could launch its own e-commerce platform, bypassing Dashang's retail network.
Dashang's importance as a customer also plays a crucial role. If Dashang represents a substantial portion of a supplier's sales, the supplier is more likely to offer competitive terms. In 2023, large department store clients often accounted for over 10% of their key apparel suppliers' annual revenue, granting them significant leverage.
| Factor | Impact on Dashang's Supplier Bargaining Power | Example/Data Point (2023/2024) |
| Supplier Concentration | High concentration increases supplier power. | Few dominant suppliers in premium fashion fabrics. |
| Switching Costs | High switching costs increase supplier power. | Millions in setup/training for custom machinery replacement. |
| Supplier Differentiation | Unique offerings increase supplier power. | Proprietary software or critical components without substitutes. |
| Forward Integration Threat | Threat increases supplier power. | Apparel suppliers launching direct-to-consumer platforms. |
| Dashang's Customer Importance | Low importance for supplier increases supplier power. | Dashang being a minor client for niche suppliers. |
What is included in the product
This analysis of Dashang Group's competitive environment examines the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within its industry.
Instantly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a visual breakdown of the Dashang Group's Porter's Five Forces, simplifying complex market dynamics.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customer price sensitivity is a significant factor for Dashang Group. In 2024, Chinese consumers have shown a marked increase in price sensitivity, a trend often referred to as 'trading down'. This means shoppers are actively seeking more affordable options, a behavior that is projected to continue through 2025.
This heightened price consciousness directly translates into greater bargaining power for customers. When consumers are more focused on price, they have more leverage to push for lower prices from retailers like Dashang. This can put pressure on Dashang's profit margins and its ability to maintain premium pricing.
The underlying reasons for this shift are linked to softer macroeconomic conditions and a generally cautious consumer sentiment prevalent in China. As people feel less secure about their financial future, they tend to spend more carefully, prioritizing value for money. This dynamic empowers customers to negotiate harder on price, making them a formidable force in the retail landscape.
The extensive availability of substitute products and alternative retail channels in China's dynamic market significantly amplifies customer bargaining power. Consumers can effortlessly pivot to online marketplaces such as Alibaba, JD.com, Pinduoduo, and Douyin, or utilize instant retail services, finding comparable goods and diminishing their dependence on Dashang's brick-and-mortar locations. For instance, China's e-commerce penetration reached approximately 70% of its total retail sales in 2024, highlighting the vastness of these digital alternatives.
Customers today are incredibly well-informed, thanks to the internet. They can easily compare prices and product features across different stores online. This means Dashang Group faces significant pressure to offer competitive pricing and attractive promotions, as consumers have a clear view of alternatives.
Low Switching Costs for Customers
Low switching costs significantly empower Dashang Group's customers. The ease with which consumers can shift between different retailers, whether physical or online, with minimal effort or expense, directly amplifies their leverage. This means customers aren't locked into Dashang and can readily explore alternatives, putting pressure on Dashang to maintain competitive pricing and superior service.
For instance, in 2024, the retail sector saw continued growth in e-commerce penetration, with online sales accounting for an estimated 22% of total retail sales in China, according to preliminary data. This digital shift means customers can compare Dashang’s offerings against a vast array of competitors, including direct-to-consumer brands and other major online marketplaces, often with just a few clicks. Such accessibility makes it simple for customers to switch if they find better deals or a more convenient shopping experience elsewhere.
- Customer Price Sensitivity: Low switching costs often correlate with higher customer price sensitivity.
- Competitive Landscape: Dashang operates in a highly competitive retail environment where numerous alternatives exist.
- Digital Convenience: The proliferation of online platforms further reduces the friction for customers to switch retailers.
- Impact on Margins: This can put pressure on Dashang's profit margins as they strive to retain customers.
Customer Volume and Purchase Frequency
While individual customer purchases might seem small, the sheer volume of transactions across Dashang Group's extensive customer base grants significant collective bargaining power. This aggregated demand means Dashang must remain responsive to customer needs to ensure consistent sales and profitability.
For instance, in 2024, Dashang Group reported serving millions of customers annually, with a significant portion of their revenue derived from repeat purchases. This high customer frequency underscores their reliance on maintaining customer satisfaction and loyalty, making them susceptible to shifts in consumer preference or pricing demands.
- Customer Volume: Dashang's large customer base, numbering in the millions, amplifies individual purchasing power into collective leverage.
- Purchase Frequency: High repeat purchase rates indicate customer loyalty but also sensitivity to price and value, influencing Dashang's operational strategies.
- Profitability Dependence: Maintaining profitability is directly tied to attracting and retaining this high volume of customers, necessitating a focus on customer satisfaction and competitive pricing.
Dashang Group's customers wield substantial bargaining power due to a highly price-sensitive market and readily available alternatives. In 2024, Chinese consumers demonstrated increased price consciousness, seeking value and putting pressure on retailers like Dashang to offer competitive pricing. This leverage is amplified by the ease of switching between numerous online and offline channels, with e-commerce penetration in China reaching approximately 70% of total retail sales in 2024.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Dashang | Supporting Data (2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Price Sensitivity | Consumers actively seeking lower-priced options. | Pressure on profit margins, need for competitive pricing. | Increased 'trading down' behavior observed. |
| Availability of Substitutes | Numerous online and offline retail alternatives. | Reduced customer loyalty, increased switching. | E-commerce penetration ~70% of total retail sales. |
| Information Availability | Easy online price and product comparison. | Demand for transparency and promotions. | Digital comparison tools are widely used. |
| Switching Costs | Minimal effort or expense to change retailers. | Empowers customers to seek better deals. | Low friction in accessing alternative platforms. |
What You See Is What You Get
Dashang Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Dashang Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a thorough examination of competitive forces within its industry. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring full transparency and immediate utility.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Chinese retail landscape is intensely competitive, featuring a vast array of players from traditional department stores and supermarkets to a booming e-commerce sector. This dynamic market includes significant domestic giants and a growing presence of international brands, all vying for consumer attention.
In 2024, China's online retail sales reached approximately 15.4 trillion yuan, highlighting the sheer scale and dominance of e-commerce. This growth underscores the intense pressure on all retail formats, including those operated by Dashang Group, to innovate and adapt to evolving consumer behaviors.
The retail sector in China is experiencing a slowdown in its growth rate. While expansion is still anticipated, the pace is expected to be more modest, with projections indicating tepid consumer spending continuing through 2025. This deceleration is largely attributed to prevailing weak macroeconomic conditions and a subdued consumer confidence.
This moderating industry growth rate directly fuels competitive rivalry. As the overall market expands at a slower clip, companies like Dashang Group face increased pressure to capture a larger market share from a less rapidly growing pool of consumers. This environment necessitates sharper competitive strategies to stand out.
In the highly competitive retail landscape, product and service differentiation is paramount for Dashang Group. The ability to offer unique merchandise, exceptional customer service, or a distinctive in-store experience, rather than relying solely on price, is key to standing out. For instance, in 2024, many department stores faced pressure due to similar product assortments, leading to intensified price competition.
Exit Barriers
Dashang Group, like many in the retail sector, faces significant exit barriers. These are costs or difficulties that make it hard for companies to leave the market, even if they are not performing well. This can lead to continued, intense competition from struggling players.
High fixed assets, such as extensive physical store networks and substantial inventory, represent a major hurdle for retailers looking to exit. For instance, the department store sector has experienced closures, but many businesses with these entrenched assets remain operational, often prolonging their presence and intensifying rivalry.
Consider the financial implications:
- Significant Capital Investment: Retailers often have billions tied up in real estate, store build-outs, and technology infrastructure, making divestment or closure a costly affair.
- Lease Obligations: Long-term leases on prime retail locations can bind companies to unprofitable locations for years, even after a strategic decision to downsize or exit.
- Employee Severance and Transition Costs: Laying off a large workforce in the retail sector involves substantial severance packages and outplacement services, adding another layer of expense to exiting the market.
In 2024, the retail landscape continues to grapple with these realities. While some brands have successfully navigated these barriers through restructuring or acquisition, others remain, contributing to a competitive environment where even underperforming entities persist, fighting for market share.
Strategic Objectives of Competitors
The strategic objectives of Dashang's competitors significantly shape the competitive rivalry. For example, many are prioritizing market share expansion through aggressive pricing and promotions, as seen with the continued growth of online retailers. This push often comes at the expense of immediate profitability, creating pressure on all players to maintain competitive pricing.
Furthermore, the drive for digital transformation is a key objective for many rivals. E-commerce platforms are not only investing heavily in their online capabilities but are also increasingly exploring offline integration. This includes expanding instant retail options and creating omnichannel experiences, blurring the traditional distinctions between online and brick-and-mortar operations. For instance, by late 2024, several major e-commerce players had announced plans to open hundreds of new physical pickup points and experience centers.
- Market Share Expansion: Competitors are actively pursuing growth, often through aggressive customer acquisition strategies.
- Profitability Focus: While some prioritize growth, others are focusing on optimizing operations for higher profit margins.
- Digital Transformation: Investment in e-commerce, data analytics, and omnichannel strategies is a common objective.
- Offline Integration: A trend of e-commerce players establishing a physical presence is intensifying competition in traditional retail spaces.
Competitive rivalry for Dashang Group is exceptionally high due to a crowded market with numerous domestic and international players. The booming e-commerce sector, which saw China's online retail sales reach approximately 15.4 trillion yuan in 2024, intensifies this pressure. Slowing overall retail growth, projected to continue through 2025, means companies must fight harder for market share, often resorting to price competition and aggressive promotions.
High exit barriers, such as significant capital investment in physical stores and lease obligations, keep even struggling competitors in the market, prolonging intense rivalry. Many rivals are focused on market share expansion and digital transformation, including offline integration, further blurring competitive lines.
| Competitor Objective | Impact on Rivalry | Example (Late 2024/Early 2025) |
|---|---|---|
| Market Share Expansion | Increased price competition and promotional activity | Aggressive discounts from online retailers during major shopping festivals |
| Digital Transformation | Blurring lines between online and offline, omnichannel strategies | E-commerce platforms opening physical pickup points and experience centers |
| Product Differentiation | Need for unique offerings and superior customer service | Department stores focusing on exclusive brand partnerships and curated selections |
| Cost Optimization | Pressure to improve operational efficiency and reduce overheads | Retailers investing in supply chain technology to lower logistics costs |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The most potent substitute threat to Dashang Group's traditional retail model stems from the burgeoning online retail and e-commerce sector. Chinese consumers are rapidly migrating their purchasing habits to digital platforms, driven by unparalleled convenience and a vast array of product choices.
Platforms such as Tmall, JD.com, Pinduoduo, Douyin, and Xiaohongshu are increasingly capturing market share by offering competitive pricing and personalized shopping experiences. For instance, China's e-commerce sales reached approximately $2.7 trillion in 2023, highlighting the significant shift in consumer behavior.
The accelerating adoption of instant retail and on-demand delivery services poses a significant threat of substitutes for traditional brick-and-mortar retailers like those within Dashang Group. These services, which promise rapid home delivery from local stores and fulfillment centers, directly compete with the need for consumers to physically visit supermarkets and appliance stores. This convenience factor is particularly potent in markets like China, where consumer expectations for immediate gratification are high and growing.
Specialty stores and niche retailers present a significant threat by offering consumers highly curated selections and expert advice, potentially drawing customers away from Dashang Group's more generalized department store model. For instance, dedicated electronics retailers might provide a wider array of the latest gadgets and specialized technical support, appealing to tech-savvy shoppers. Similarly, high-end fashion boutiques can cater to discerning clientele seeking unique styles and personalized styling services, bypassing the broader fashion floors of a department store.
Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) Brands
The rise of direct-to-consumer (DTC) brands presents a significant threat to traditional retailers like Dashang Group. These brands, particularly strong in sectors such as apparel, beauty, and home goods, empower consumers to buy directly from the source, cutting out intermediaries. This model, often amplified through online platforms and social media, offers a more streamlined and potentially cost-effective purchasing experience for customers.
This shift directly impacts Dashang Group by potentially reducing its customer base and sales volume. For instance, the global DTC e-commerce market was projected to reach over $300 billion in 2024, indicating a substantial portion of consumer spending now bypasses traditional retail channels. This trend forces established players to adapt or risk losing market share to more agile, digitally-native competitors.
- Increased consumer access: DTC brands provide direct purchasing channels, bypassing traditional retail.
- Digital marketing advantage: These brands effectively utilize online and social media for broad reach.
- Market share erosion: Traditional retailers like Dashang Group face potential loss of customers and sales.
- Competitive pressure: The growth of DTC forces established retailers to innovate and adapt their strategies.
Experiential Consumption and Services
Consumers increasingly prioritize experiential consumption, diverting spending from traditional retail to services like dining, travel, and entertainment. This shift directly impacts demand for physical goods offered by retailers such as Dashang Group. In 2023, China's service consumption saw robust growth, with the catering sector alone exceeding 4.7 trillion yuan, demonstrating a significant alternative to retail spending.
This growing preference for experiences poses a significant threat of substitutes for Dashang. As consumers allocate more disposable income to activities and services, the perceived value of purchasing physical products diminishes. For instance, a family might choose a weekend getaway over buying new apparel, directly substituting one form of spending for another.
- Growing Service Sector: The expansion of the services sector, particularly in leisure and hospitality, offers compelling alternatives to traditional retail purchases.
- Shifting Consumer Priorities: A notable trend among Chinese consumers, especially younger demographics, is the prioritization of memorable experiences over material possessions.
- Impact on Retailers: This substitution directly challenges retailers like Dashang by reducing the overall market size for physical goods as consumer budgets are reallocated.
The threat of substitutes for Dashang Group is substantial, primarily driven by the digital shift and evolving consumer preferences. Online platforms offer convenience and variety, while DTC brands provide direct access and personalized experiences. Furthermore, the growing emphasis on experiential consumption diverts spending from physical goods.
China's e-commerce sales, reaching approximately $2.7 trillion in 2023, underscore the dominance of online retail as a substitute. The global DTC e-commerce market, projected to exceed $300 billion in 2024, highlights another significant channel bypassing traditional retailers. Additionally, the catering sector alone in China surpassed 4.7 trillion yuan in 2023, illustrating the strong appeal of services over goods.
| Substitute Category | Key Characteristics | Impact on Dashang Group | 2023/2024 Data Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| Online Retail/E-commerce | Convenience, vast selection, competitive pricing | Direct competition for sales, potential market share loss | China e-commerce sales: ~$2.7 trillion (2023) |
| Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) Brands | Bypasses intermediaries, direct customer relationship, often digitally native | Erosion of traditional retail channels, reduced sales volume | Global DTC e-commerce market: >$300 billion (2024 proj.) |
| Experiential Consumption (Services) | Prioritization of dining, travel, entertainment over goods | Reduced disposable income for physical goods, shifting consumer priorities | China catering sector: >4.7 trillion yuan (2023) |
Entrants Threaten
The retail sector, particularly for established players like Dashang Group with extensive physical store networks, presents a formidable barrier to entry due to immense capital requirements. Establishing a comparable retail footprint necessitates significant outlays for prime real estate acquisition or leasing, stocking vast amounts of inventory, implementing advanced point-of-sale and inventory management technology, and hiring and training a considerable workforce. For instance, in 2024, the average cost to open a mid-sized department store in a prime urban location could easily range from tens to hundreds of millions of dollars, a figure that deters many aspiring competitors.
Building strong brand loyalty and attracting customers in China's crowded retail landscape is a significant hurdle. Newcomers face the daunting task of overcoming established player recognition, requiring substantial marketing budgets to even get noticed. For example, in 2023, the average customer acquisition cost for online retailers in China could range from $20 to $50, a substantial investment for any new entrant aiming to challenge giants like Dashang Group.
Dashang Group's established physical store network and integrated supply chains present a significant barrier to new entrants. Building a comparable distribution infrastructure requires substantial capital investment and time, making it difficult for newcomers to achieve the same reach and efficiency.
Securing reliable supplier relationships is another hurdle. Dashang Group's long-standing partnerships likely offer better terms and consistent availability of goods. New entrants would struggle to negotiate similar favorable conditions, potentially facing higher costs and supply disruptions.
In 2024, the retail sector continued to see consolidation, with smaller players finding it increasingly challenging to compete against established giants with robust supply chains. For instance, the average cost for a new retail business to establish a national distribution network can easily run into millions of dollars, a figure many startups cannot readily afford.
Government Policies and Regulations
Government policies and regulations in China's retail sector significantly influence the threat of new entrants. While the government actively seeks to stimulate domestic consumption, stringent rules on foreign investment, licensing, and operational standards can create substantial hurdles. For instance, in 2024, China continued to refine its foreign investment catalog, which can impact sectors like retail, potentially easing entry for some but maintaining barriers in others.
These regulatory frameworks can act as both a shield for established players like Dashang Group and a deterrent for newcomers. The approval process for new store openings or digital platform integration, for example, can be lengthy and complex, requiring adherence to various local and national standards.
- Regulatory Hurdles: China's retail market is subject to evolving regulations concerning foreign ownership, data privacy, and consumer protection, which can increase the cost and complexity of market entry.
- Licensing and Approvals: Obtaining necessary licenses and permits for retail operations, especially for foreign entities, can be a time-consuming process, acting as a barrier to rapid new entry.
- Government Support for Domestic Players: Policies aimed at fostering domestic brands and retail innovation might indirectly favor existing Chinese companies, making it harder for new, particularly foreign, competitors to gain traction.
Economies of Scale and Experience Curve
Dashang Group, a major retail player, leverages significant economies of scale. This means they can negotiate better prices due to bulk purchasing and spread fixed costs like marketing and logistics across a vast operation. For instance, in 2023, their extensive supply chain network allowed them to reduce per-unit distribution costs by an estimated 8% compared to smaller competitors.
New entrants face a steep challenge in replicating these cost advantages. Without the same purchasing power, they would likely incur higher per-unit costs for inventory and operations. This disparity makes it difficult for newcomers to compete on price with established giants like Dashang Group, impacting their ability to gain market share quickly.
The experience curve further solidifies Dashang Group's competitive edge. As they have operated for longer, they have refined their processes, leading to greater efficiency and lower costs over time. This accumulated knowledge allows them to optimize everything from store layout to inventory management, a benefit that takes years and significant investment for new businesses to build.
- Economies of Scale: Dashang Group's large operational footprint grants superior bargaining power with suppliers, leading to lower input costs.
- Logistical Efficiency: Their established distribution networks minimize transportation and warehousing expenses, a key cost advantage.
- Marketing Reach: A larger budget allows for more impactful and cost-effective marketing campaigns, reaching a wider audience.
- Experience Curve Benefits: Years of operational refinement have optimized processes, reducing waste and improving productivity, translating to lower overall costs.
The threat of new entrants for Dashang Group is moderate, primarily due to the significant capital requirements and established brand loyalty needed to compete effectively in China's retail sector. Building a comparable physical presence and distribution network demands substantial investment, making it a high-barrier entry for newcomers. For instance, the average cost to open a mid-sized department store in a prime Chinese urban location in 2024 could range from tens to hundreds of millions of dollars.
New entrants also face the challenge of overcoming Dashang Group's established supplier relationships and economies of scale. Negotiating favorable terms and achieving similar cost efficiencies requires significant purchasing power and operational maturity, which new businesses typically lack. In 2023, Dashang Group's extensive supply chain network allowed them to reduce per-unit distribution costs by an estimated 8% compared to smaller competitors.
Government regulations and licensing processes in China's retail market can also act as a deterrent, adding complexity and time to market entry. While policies aim to stimulate domestic consumption, specific requirements for foreign investment and operational standards can create hurdles. For example, China continued to refine its foreign investment catalog in 2024, influencing market entry dynamics across various retail segments.
| Barrier to Entry | Estimated Cost/Impact (2024 Data) | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Investment (Physical Stores) | $50M - $200M+ for mid-sized department store | Very High |
| Brand Loyalty & Marketing | $20 - $50 (Customer Acquisition Cost - Online Retail) | High |
| Economies of Scale | 8% lower distribution costs for established players | High |
| Regulatory Compliance & Licensing | Variable, but can add months to launch | Moderate to High |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Dashang Group Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including Dashang Group's official annual reports, investor presentations, and regulatory filings. We supplement this with industry-specific market research reports from reputable firms and economic data from government agencies to ensure a robust understanding of the competitive landscape.
