Covenant Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Covenant Bundle
Covenant's competitive landscape is shaped by the bargaining power of its buyers, the intensity of rivalry among existing firms, and the threat of new entrants. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating its market effectively.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Covenant’s industry—from supplier influence to substitute threats. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Fuel, primarily diesel, represents a substantial and unavoidable expense for trucking and logistics operations such as Covenant Logistics. The price of diesel is directly influenced by global crude oil prices, geopolitical events, and the availability of refining capacity, all of which can cause significant increases in operational expenditures.
For instance, average diesel prices in the US hovered around $4.00 per gallon in early 2024, a figure that can drastically impact a logistics company's bottom line. While larger carriers like Covenant may mitigate some of this volatility through fuel surcharge mechanisms, smaller companies and independent drivers often absorb these costs directly, potentially shrinking their profit margins or forcing them out of business.
The logistics sector, encompassing truckload transport and warehousing, grappled with significant labor deficits for both skilled drivers and warehouse personnel throughout 2024. This persistent shortage directly fuels increased labor expenses and hampers operational fluidity, thereby amplifying the bargaining leverage of the available workforce.
In response, companies are accelerating investments in automation technologies and enhancing compensation packages, including wages and benefits, as crucial strategies to attract and retain essential talent in a competitive market.
Suppliers of essential equipment like trucks and trailers, as well as advanced logistics technologies such as AI, IoT, and cloud computing, wield considerable bargaining power. The industry's push for greater efficiency and sustainability means companies are increasingly dependent on these suppliers for cutting-edge vehicles and integrated tech platforms.
This heightened reliance on new equipment and technology for competitiveness and resilience directly translates to increased demand for these specialized suppliers. For instance, the global logistics technology market was valued at approximately $35 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, indicating a strong market position for providers of these vital solutions.
Maintenance and Parts Providers
The ongoing operation of a substantial truckload fleet hinges on consistent maintenance and the availability of replacement parts. Suppliers offering these essential services and components wield significant bargaining power, particularly when dealing with specialized parts or during periods of elevated demand or disruptions within the supply chain. This dynamic can directly translate into higher operational and maintenance costs for fleet operators.
For instance, in 2024, the average cost of heavy-duty truck parts saw an increase, with some specialized components experiencing price hikes of 5-10% due to global supply chain pressures and increased raw material costs. This puts pressure on companies like Covenant Porter to manage these expenses effectively.
- Specialized Parts: Suppliers of unique or proprietary truck components can command higher prices due to limited alternatives.
- Supply Chain Vulnerability: Disruptions, such as those seen in 2023-2024 affecting semiconductor chips and engine components, amplify supplier leverage.
- Maintenance Services: Skilled technicians and specialized repair facilities for complex engine or transmission systems also represent a concentration of supplier power.
- Demand Fluctuations: Increased demand for maintenance services during peak operating seasons or following adverse weather events can give service providers more pricing power.
Insurance Providers
In the trucking industry, the bargaining power of insurance providers is significant, largely due to the inherent risks and the structure of coverage. Many trucking companies operate with self-insured retentions and policy limits, meaning they bear a portion of the risk themselves. This, coupled with the increasing frequency and size of large jury awards, often referred to as 'nuclear verdicts', makes insurance a critical but often unpredictable expense. In 2023, the trucking industry saw a notable increase in insurance premiums, with some segments experiencing hikes of over 20%, directly reflecting the rising cost of claims and the providers' ability to dictate terms.
This dynamic allows insurers to exert considerable influence. Their services are indispensable for trucking operations aiming to mitigate substantial financial exposure from accidents and liability. The volatility in claims expenses, which can swing dramatically year over year, further solidifies the insurers' position. For example, a single large verdict can significantly impact an insurer's profitability, leading them to adjust premiums and coverage terms accordingly, thereby enhancing their bargaining leverage.
- Increased Premiums: Trucking insurance costs saw substantial rises in 2023, with some fleets facing premium increases exceeding 20%.
- Nuclear Verdicts Impact: The growing trend of multi-million dollar jury awards against trucking companies directly fuels higher insurance costs and strengthens provider bargaining power.
- Self-Insured Portions: The need for trucking companies to self-insure a portion of their risk makes comprehensive insurance coverage essential, increasing reliance on providers.
Suppliers of essential trucking components and maintenance services hold significant sway due to the industry's reliance on specialized parts and skilled labor. For instance, the cost of heavy-duty truck parts increased in 2024, with some specialized items seeing price hikes of 5-10% due to supply chain issues and raw material costs, impacting fleet operators.
The bargaining power of insurance providers is also substantial, driven by inherent industry risks and the increasing frequency of large legal settlements. Trucking insurance premiums rose significantly in 2023, with some sectors experiencing increases over 20%, reflecting higher claim costs and provider leverage.
| Supplier Category | Key Factors Influencing Bargaining Power | Impact on Logistics Companies (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel (Diesel) | Global oil prices, geopolitical events, refining capacity | Average US diesel prices around $4.00/gallon in early 2024, increasing operational costs. |
| Equipment & Technology | Demand for efficiency, sustainability, specialized tech (AI, IoT) | Global logistics tech market valued at ~$35 billion in 2023, indicating strong supplier position. |
| Parts & Maintenance | Availability of specialized parts, supply chain disruptions, skilled technicians | 5-10% price increases for some heavy-duty truck parts in 2024 due to supply chain pressures. |
| Insurance Providers | Industry risks, 'nuclear verdicts', self-insured retentions | Insurance premiums rose over 20% in some segments in 2023, driven by rising claims and verdicts. |
What is included in the product
Uncovers key drivers of competition, customer influence, and market entry risks tailored to Covenant's unique position in the porter industry.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each Porter's Five Forces, allowing for targeted strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Covenant Logistics' diverse customer base across North America generally moderates the bargaining power of individual customers. In 2024, the company's broad reach, serving sectors from retail to manufacturing, means no single client dictates terms to a significant degree.
However, the landscape isn't uniform. Large clients, particularly those with substantial volume contracts, can still leverage their buying power. For instance, a major retailer requiring significant freight capacity might negotiate more favorable pricing or specific service level agreements, especially during periods of economic uncertainty or oversupply in the logistics market.
Customers in the freight market have numerous options, with thousands of truckload carriers, freight brokers, and third-party logistics (3PL) providers available. This abundance of choice significantly amplifies customer bargaining power.
For instance, in 2024, the U.S. trucking industry features over 1.5 million registered carriers, many of which are small, owner-operator businesses. This sheer volume ensures that shippers can easily find alternative providers if current rates or service levels are not competitive.
The ease with which customers can compare services and pricing across these many providers means they can negotiate more favorable terms or switch to a competitor if dissatisfied, putting pressure on existing carriers to maintain high service standards and competitive pricing.
In the highly competitive freight sector, customers, particularly large shippers, wield significant bargaining power due to their price sensitivity. They actively seek the most cost-effective logistics solutions, putting pressure on carriers like Covenant Logistics to offer competitive rates. This is especially true when the market experiences overcapacity or economic downturns, as seen in recent freight market trends.
For instance, during 2023 and into early 2024, many freight markets faced overcapacity, leading to declining spot rates. This environment allowed major customers to negotiate more favorable terms, impacting carrier profitability. Covenant Logistics, like its peers, had to contend with these customer demands to maintain market share.
Demand for Integrated and Value-Added Services
Customers are increasingly seeking integrated logistics solutions that go beyond simple freight movement. They expect a bundled offering encompassing warehousing, inventory management, and advanced tracking capabilities. This shift empowers them to negotiate for better terms and higher service standards, as they can consolidate their needs with fewer providers.
The demand for value-added services, such as real-time visibility and data analytics, significantly strengthens the bargaining power of customers. For instance, a 2024 survey indicated that 75% of shippers prioritize technology integration and transparency when selecting a logistics partner. This means providers who can offer seamless, tech-enabled solutions can command better prices, but it also gives customers leverage to demand more for their money.
- Demand for integrated services: Customers want warehousing, transportation, and visibility from a single provider.
- Technology as a driver: Real-time tracking and data analytics are becoming essential expectations.
- Increased customer leverage: Bundled service expectations allow customers to negotiate more effectively.
- 2024 data: 75% of shippers prioritize technology and transparency in logistics partner selection.
E-commerce Growth and Last-Mile Delivery Expectations
The rapid expansion of e-commerce has significantly amplified customer expectations for delivery speed, flexibility, and dependability, particularly concerning last-mile logistics. This heightened demand grants consumers greater influence in setting delivery terms and service standards.
As of 2024, the global e-commerce market continues its robust growth, with projections indicating a substantial increase in online sales volume. This surge directly translates to more pressure on logistics providers to meet demanding delivery windows. For instance, studies show that a significant percentage of online shoppers are willing to pay a premium for same-day or next-day delivery, underscoring their power to shape service offerings.
- Increased Demand for Speed: E-commerce growth fuels the need for faster last-mile delivery, empowering customers to choose providers based on delivery speed.
- Flexibility in Delivery Options: Customers now expect a variety of delivery choices, such as specific time slots or pickup points, giving them leverage.
- Focus on Reliability: Consistent and on-time deliveries are paramount, allowing customers to penalize or avoid companies with poor track records.
- Data-Driven Expectations: Customers are increasingly informed about delivery performance, using this knowledge to negotiate or select services.
Customers in the logistics sector possess considerable bargaining power, primarily driven by the abundance of service providers and their own price sensitivity. The ease of switching between carriers, especially for large volume shippers, allows them to negotiate favorable rates and service terms. This dynamic is further intensified by the growing demand for integrated logistics solutions and advanced technological capabilities, which customers expect as standard offerings.
In 2024, the fragmented nature of the U.S. trucking industry, with over 1.5 million registered carriers, ensures that shippers have ample choices, thereby increasing customer leverage. Furthermore, the e-commerce boom has heightened expectations for rapid and flexible deliveries, giving customers more power to dictate terms and select providers based on performance and reliability.
| Factor | Impact on Bargaining Power | 2024 Context/Data |
|---|---|---|
| Provider Availability | High; numerous carriers and 3PLs exist. | Over 1.5 million U.S. trucking carriers in 2024. |
| Customer Price Sensitivity | High; customers actively seek cost-effective solutions. | Declining spot rates in early 2024 due to overcapacity pressured carriers. |
| Demand for Integrated Services | Increases; customers consolidate needs with fewer providers. | 75% of shippers prioritize technology and transparency in 2024. |
| E-commerce Growth | Amplifies expectations for speed and flexibility. | Continued robust growth in global e-commerce sales volume. |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
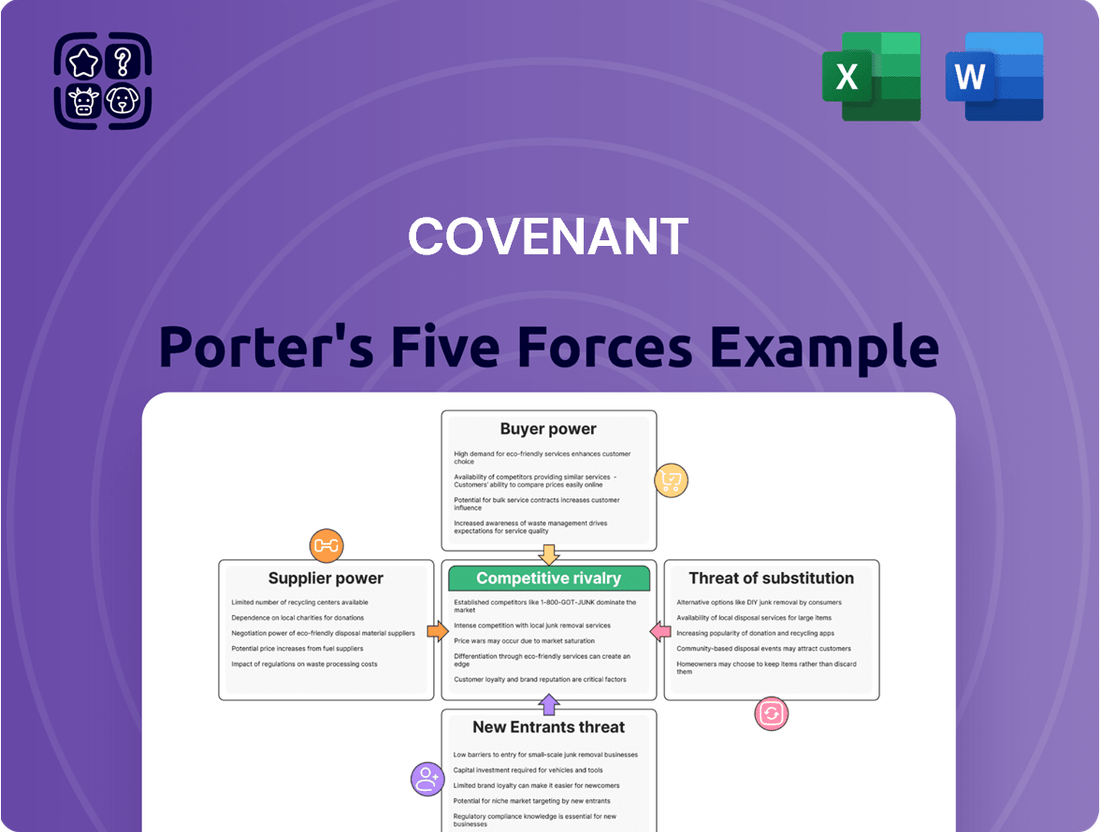
Covenant Porter's Five Forces Analysis
The document you see is your deliverable. It’s ready for immediate use—no customization or setup required. This preview showcases the complete Covenant Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a comprehensive examination of the competitive landscape, including threats of new entrants, bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, threat of substitute products, and intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. You'll receive this exact, professionally formatted document upon purchase, providing actionable insights for strategic decision-making.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The transportation and logistics sector, especially truckload and freight brokerage, is incredibly fragmented. We're seeing a vast number of companies competing, including those that own their trucks and those that primarily arrange shipments. This sheer volume of players means there's constant pressure on freight prices and, consequently, on everyone's profit margins.
In 2024, the U.S. trucking industry alone comprises over 100,000 registered carriers, with the vast majority being small businesses operating fewer than six trucks. This level of fragmentation directly contributes to intense price competition, making it challenging for any single entity to command premium rates.
Competition in the truckload spot market is intensely price-driven. Shippers often engage in aggressive rate-shopping, which directly impacts carrier profitability and necessitates stringent cost management. For instance, the DAT Truckload Capacity Index for the van spot market in early 2024 showed significant rate fluctuations, with average dry van spot rates dipping below $2.00 per mile at times, highlighting the pressure on carriers to optimize operations.
The truckload market frequently grapples with overcapacity, a situation where more trucks are available than there are goods needing transport. This imbalance directly fuels intense competition among trucking companies.
When supply outstrips demand, freight rates, both on the spot market and through contracts, tend to fall. For instance, in early 2024, the U.S. truckload spot market saw rates significantly below previous years, with some dry van rates dipping below $2.00 per mile, a stark contrast to the higher rates seen during peak demand periods.
This oversupply forces carriers to compete more aggressively for every available load, often at lower profit margins, to keep their assets utilized and drivers employed. This dynamic intensifies rivalry as companies fight for market share and survival.
Diversified Service Offerings
Companies like Covenant Logistics, which offer a wide range of services such as expedited shipping, dedicated fleet management, freight brokerage, and warehousing, face competition not just within each of these individual service areas but also from other providers who can bundle these services. This broad service portfolio is designed to build a more robust business, yet it necessitates going head-to-head with highly specialized firms in every segment.
For instance, in the freight brokerage segment, Covenant Logistics competes with pure-play brokers who may have deeper networks or more specialized technology. Similarly, in dedicated fleet services, they contend with companies solely focused on optimizing and managing dedicated fleets. This creates a complex competitive landscape where success depends on excelling across multiple service dimensions.
- Broad Service Spectrum: Covenant Logistics competes across expedited, dedicated, brokerage, and warehousing, facing specialists in each.
- Integrated Solutions vs. Specialization: The company offers integrated solutions, but this means competing against niche providers who excel in single service areas.
- Resilience Through Diversification: This strategy aims to create a more stable business model by not relying on a single service offering.
- Competitive Intensity: The need to compete across multiple fronts intensifies rivalry, requiring strong performance in each distinct service category.
Technological Advancements and Digitalization
The logistics industry is experiencing a significant shift driven by technological advancements and digitalization. Companies are rapidly adopting technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and digital freight platforms to enhance operations. For instance, in 2024, the global logistics market size was valued at approximately $10.3 trillion, with technology playing a crucial role in its growth and efficiency.
These innovations are directly impacting competitive rivalry. Firms that invest in and effectively utilize these technologies gain a distinct advantage. This edge comes from improved efficiency, greater visibility across supply chains, and increased automation of processes. Conversely, companies that are slow to adopt these digital tools face mounting pressure from more technologically adept competitors.
- AI-powered route optimization can reduce fuel consumption by up to 15% in 2024.
- IoT sensors provide real-time tracking and condition monitoring, improving cargo security.
- Digital freight platforms connect shippers and carriers more efficiently, reducing empty miles.
- Companies investing in these areas are better positioned to manage costs and customer expectations.
The transportation and logistics sector is characterized by intense competition, largely due to its fragmented nature. With numerous companies, from large carriers to small owner-operators, vying for business, price wars are common, squeezing profit margins across the board.
In 2024, the U.S. trucking industry alone features over 100,000 registered carriers, the majority being small operations. This high density of participants fuels aggressive price competition, making it difficult for any single entity to dictate terms or command premium rates.
The truckload spot market, in particular, is highly sensitive to price. Shippers frequently engage in rate shopping, which directly impacts carrier profitability and necessitates rigorous cost control. For example, in early 2024, average dry van spot rates on the DAT Truckload Capacity Index dipped below $2.00 per mile at times, underscoring the pressure on carriers to maintain operational efficiency.
| Factor | Description | 2024 Data/Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Market Fragmentation | High number of competitors, many small. | Over 100,000 U.S. carriers, mostly small fleets. |
| Price Sensitivity | Shippers actively compare rates. | Spot rates for dry van fell below $2.00/mile in early 2024. |
| Overcapacity | More trucks than available freight. | Contributes to rate declines and intense rivalry. |
| Service Diversification | Companies offer multiple logistics services. | Covenant Logistics competes across expedited, dedicated, brokerage, and warehousing, facing specialized rivals. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
For certain types of freight, particularly long-haul or bulk goods, rail and intermodal transportation present a significant threat of substitution to pure trucking services. These alternatives can offer substantial cost savings, especially on established, high-volume routes. In 2024, the intermodal sector continued to grow, with truck-rail intermodal volume increasing by approximately 3% year-over-year, demonstrating its increasing appeal as a cost-effective alternative for shippers.
For urgent or high-value goods, air cargo offers a quicker alternative to traditional truckload shipping, though it comes at a higher price point. This speed advantage is a key substitute, especially for industries where time is critical.
However, the rising cost of jet fuel, a major component of air cargo expenses, could temper the attractiveness of this substitute. For instance, jet fuel prices saw significant volatility in late 2023 and early 2024, impacting overall air freight costs.
Large shippers increasingly consider managing their logistics internally with private fleets, directly substituting for third-party providers like Covenant Logistics. This trend is driven by a desire for greater control over costs and service quality. For instance, in 2024, many large retail and manufacturing companies continued to evaluate or expand their private fleet operations to better manage supply chain disruptions and ensure timely delivery.
Shipper-Carrier Direct Relationships
The rise of shipper-carrier direct relationships is a significant threat to freight brokerage services. Shippers are increasingly bypassing traditional intermediaries to negotiate directly with carriers, aiming to reduce costs and gain more control over their logistics. This trend pressures brokers to demonstrate their unique value beyond simple transaction facilitation.
This shift is driven by a desire to cut out the middleman's margin and streamline operations. For instance, in 2024, many large shippers reported increased direct contracting with trucking companies, particularly for dedicated lanes, to ensure capacity and predictable pricing. This bypasses the traditional brokerage model, which historically provided access to a broader carrier network and managed the complexities of freight matching.
- Direct Negotiation: Shippers can negotiate rates and terms directly with carriers, potentially securing better pricing and service levels.
- Reduced Costs: Eliminating the broker fee can lead to substantial cost savings for shippers.
- Enhanced Control: Direct relationships offer shippers greater visibility and control over their shipments and carrier performance.
- Carrier Efficiency: Carriers can also benefit by securing more consistent freight volumes and building stronger, long-term partnerships.
Emerging Delivery Methods (Drones, Autonomous Vehicles)
While still in early development for broad commercial application, future advancements in drone and autonomous vehicle technology hold the potential to become significant substitutes for conventional transportation methods. These innovations could reshape last-mile delivery and even impact certain long-haul logistics as the technology matures and regulatory frameworks adapt.
The ongoing development in drone and autonomous vehicle logistics suggests a future where these technologies could offer alternative delivery solutions. For instance, by 2024, companies are investing heavily in these areas; Amazon's Prime Air drone delivery service is expanding its reach, and numerous autonomous trucking pilots are underway across the United States, demonstrating tangible progress.
- Drone Delivery Expansion: Companies like Wing, operating in select US markets, completed hundreds of thousands of deliveries in 2023, showcasing the growing viability of drone-based logistics.
- Autonomous Trucking Pilots: Major logistics firms are actively testing autonomous trucks, with some reporting significant mileage accumulated in real-world conditions, indicating future cost-saving potential.
- Regulatory Evolution: Government bodies are actively working on frameworks for these new delivery methods, with the FAA continuing to approve more drone operations, paving the way for wider adoption.
- Cost Efficiency Potential: As these technologies scale, they are projected to reduce labor costs and potentially fuel expenses, making them attractive substitutes for traditional shipping methods.
The threat of substitutes for freight transportation is multifaceted, encompassing alternative modes and evolving business models. Rail and intermodal services offer cost advantages for bulk and long-haul freight, with intermodal volume up about 3% in 2024. Air cargo provides speed for time-sensitive goods but faces rising fuel costs, which saw volatility in late 2023 and early 2024.
Large shippers increasingly utilize private fleets for greater control, a trend that continued in 2024. Direct shipper-carrier relationships are also growing, bypassing brokers to reduce costs and improve visibility. This shift is evident in increased direct contracting for dedicated lanes, aiming for predictable pricing and capacity assurance.
Emerging technologies like drones and autonomous vehicles represent future substitutes, with significant investment and pilot programs underway. Companies like Amazon's Prime Air are expanding, and autonomous trucking pilots are accumulating substantial mileage, signaling potential future cost efficiencies and operational changes.
| Substitute Type | Key Advantage | 2024 Data/Trend | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rail/Intermodal | Cost savings for bulk/long-haul | Intermodal volume increased ~3% YoY | Reduces demand for pure trucking on specific lanes |
| Air Cargo | Speed for urgent/high-value | Jet fuel price volatility impacts cost-effectiveness | Limits substitution for cost-sensitive time-critical freight |
| Private Fleets | Control over costs & service | Continued evaluation/expansion by large shippers | Directly replaces third-party logistics providers |
| Direct Shipper-Carrier Relationships | Reduced costs, enhanced control | Increased direct contracting for dedicated lanes | Threatens freight brokerage models |
| Drones/Autonomous Vehicles | Future efficiency, speed | Expansion of drone delivery (e.g., Wing deliveries in 2023), autonomous trucking pilots | Potential to disrupt last-mile and long-haul segments |
Entrants Threaten
Establishing an asset-based truckload transportation company, like Covenant Logistics Group, demands substantial upfront capital. This includes purchasing a fleet of trucks and trailers, as well as investing in maintenance facilities and technology, often running into millions of dollars. For instance, a new Class 8 truck can cost upwards of $150,000, and a fleet of 100 such vehicles alone represents a $15 million investment before even considering trailers or operational infrastructure. This high capital requirement acts as a significant deterrent for potential new entrants aiming to compete at scale in the dedicated fleet segment.
However, the threat of new entrants is somewhat mitigated by the rise of asset-light business models within the broader transportation industry. Companies focusing on freight brokerage or managed transportation services require considerably less capital, as they leverage third-party assets rather than owning them. This allows smaller, more agile players to enter the market with lower barriers, though their impact on large, asset-heavy operators like Covenant's dedicated fleet segment is less direct.
The transportation sector faces stringent and ever-changing regulations, encompassing safety protocols, environmental standards, and operational licensing. For instance, in 2024, the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA) continued to emphasize compliance with Hours of Service regulations, a key area where new entrants must invest heavily to ensure adherence.
Successfully navigating this complex web of rules, including emissions standards like those being phased in for heavy-duty vehicles, presents a substantial barrier. The cost and expertise required for compliance can deter potential competitors looking to enter the market, particularly those without established systems.
Covenant Logistics benefits from deeply entrenched customer relationships, built over years of dependable service. This loyalty creates a significant barrier for newcomers aiming to capture market share, especially in niche areas like expedited freight where trust is paramount.
New entrants must overcome the hurdle of establishing their own reputation and building a comparable customer base. For instance, in 2024, the logistics sector saw continued consolidation, highlighting the advantage incumbents hold due to their established networks and proven track records.
Access to Driver Pool and Labor Challenges
The ongoing scarcity of qualified drivers and warehouse personnel presents a significant hurdle for new entrants. This labor deficit directly impacts their ability to rapidly assemble a competent operational team, thereby limiting their potential for swift expansion and efficient capacity management.
For instance, in 2024, the American Trucking Associations reported a shortage of over 78,000 drivers, a figure projected to worsen. This persistent labor challenge means new companies entering the logistics space will struggle to secure the necessary human capital to scale their operations effectively.
- Driver Shortage: In 2024, the estimated truck driver shortage in the US reached approximately 78,000, according to the American Trucking Associations.
- Warehouse Labor: The warehousing sector also faces significant staffing issues, with many facilities operating below optimal capacity due to a lack of available workers.
- Impact on New Entrants: This tight labor market makes it costly and time-consuming for new companies to recruit and retain the skilled workforce required for competitive operations.
Technological Investment and Integration
The threat of new entrants is significantly influenced by the capital required for technological investment and integration. Companies looking to enter sectors reliant on advanced logistics, for instance, must consider the substantial costs associated with implementing technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and sophisticated Transportation Management Systems (TMS). The complexity of integrating these disparate systems also presents a hurdle, demanding specialized expertise that new players may lack.
For example, in the e-commerce fulfillment sector, established players have already made considerable investments in automated warehousing and real-time tracking. A new entrant in 2024 would face the challenge of matching this technological sophistication, which could easily require millions in upfront capital. According to a 2023 report by Statista, global spending on supply chain management software was projected to reach over $25 billion, highlighting the significant financial commitment involved.
- High Capital Outlay: New entrants need substantial funds for AI, IoT, and TMS implementation.
- Integration Complexity: Merging various advanced technological systems requires specialized knowledge and resources.
- Competitive Disadvantage: Lack of advanced tech can put new companies at a significant disadvantage against incumbents.
The threat of new entrants in the asset-based truckload transportation sector, like Covenant Logistics Group, is generally low due to significant barriers. High capital requirements for fleet acquisition, estimated at over $150,000 per Class 8 truck in 2024, coupled with stringent regulations and established customer loyalty, deter many potential competitors.
Despite these challenges, asset-light models and specialized niches offer avenues for smaller players. However, the substantial investment needed for technology, such as AI and TMS, and the persistent driver shortage, with an estimated 78,000 deficit in the US in 2024, continue to favor established operators like Covenant.
| Barrier Type | Description | 2024 Data/Example |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Cost of acquiring trucks, trailers, and facilities. | Class 8 truck cost: ~$150,000+ |
| Regulatory Compliance | Adherence to safety, environmental, and operational laws. | FMCSA Hours of Service regulations. |
| Customer Loyalty | Established relationships and trust in service. | Niche markets like expedited freight require high trust. |
| Labor Shortage | Difficulty in recruiting and retaining drivers and staff. | US truck driver shortage: ~78,000 drivers. |
| Technological Investment | Costs for AI, IoT, and TMS integration. | Global SCM software spending projected over $25 billion (2023). |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, incorporating information from industry-specific market research reports, company annual filings, and expert interviews with industry professionals.
