Corteva Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Corteva Bundle
Corteva faces moderate threats from new entrants and substitutes in the agricultural sector, largely due to high capital requirements and established brand loyalty. However, the bargaining power of buyers, primarily large distributors and farmers, presents a significant challenge.
The full Porter's Five Forces analysis reveals the real forces shaping Corteva’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Corteva Agriscience depends on a limited number of specialized suppliers for crucial components such as advanced chemical compounds, proprietary genetic material, and essential active ingredients for its agricultural products. A concentrated supplier base in these niche markets means these few providers hold considerable sway over pricing and availability. This can directly affect Corteva's operational expenses and profitability.
For example, in the agricultural biotechnology sector, where innovation and intellectual property are paramount, the suppliers of cutting-edge genetic traits or novel active ingredients are often highly specialized. If Corteva faces a situation where only a handful of companies can provide a critical input, those suppliers gain leverage. This bargaining power can manifest as higher prices or restricted access to these vital resources, impacting Corteva's ability to maintain competitive production costs.
Suppliers possessing proprietary technology, particularly in specialized areas like advanced seed genetics or novel chemical formulations, can exert significant bargaining power. Corteva, with its emphasis on research and development, frequently relies on these unique inputs. For instance, a supplier holding patents for a breakthrough biological control agent could command higher prices, as Corteva has limited alternatives for that specific innovation.
Switching suppliers for highly specialized seeds or critical crop protection components presents substantial challenges for Corteva. These challenges include the need for significant R&D adjustments to integrate new products, navigating complex and time-consuming regulatory approval processes, and potentially reconfiguring production lines to accommodate different input specifications.
The high switching costs associated with these specialized inputs directly bolster the bargaining power of Corteva's suppliers. Should Corteva decide to change its input sources, it would face considerable upfront expenses and operational disruptions, making suppliers less susceptible to price pressure or unfavorable contract terms.
Supplier's Ability to Forward Integrate
Suppliers possessing the capability to integrate forward into Corteva's core businesses, such as seed or crop protection manufacturing, represent a significant bargaining chip. This potential to become a direct competitor grants them considerable leverage during price negotiations, as they can credibly threaten to bypass Corteva and capture more of the value chain themselves. While this threat is more pronounced for suppliers of key intermediates or proprietary technologies, it underscores the importance of maintaining strong supplier relationships.
For instance, consider a hypothetical scenario where a supplier of a crucial active ingredient for a widely used herbicide could invest in its own formulation and distribution capabilities. This would directly challenge Corteva's market position. While specific forward integration threats are often proprietary, the agricultural sector has seen consolidation and strategic moves by input providers, highlighting the ongoing relevance of this dynamic. In 2024, Corteva's cost of goods sold was approximately $10.9 billion, indicating the substantial financial impact of supplier relationships.
- Potential for Direct Competition: Suppliers can threaten to enter Corteva's market by producing finished seeds or crop protection products.
- Leverage in Negotiations: The ability to forward integrate provides suppliers with a strong position to demand better terms from Corteva.
- Industry Dynamics: Consolidation and strategic investments by input providers in the agricultural sector demonstrate the real-world applicability of this threat.
- Financial Impact: Corteva's significant cost of goods sold in 2024 underscores the financial importance of managing supplier relationships effectively.
Importance of Supplier's Input to Corteva's Product Quality
The quality of raw materials and specialized components from suppliers directly influences the efficacy and yield of Corteva's seed and crop protection products. For instance, the purity and genetic integrity of seed traits, or the precise chemical composition of crop protection agents, are paramount. If a supplier provides a unique or highly specialized input that is difficult for Corteva to source elsewhere, that supplier's leverage increases significantly.
This dependence on specific, high-quality inputs grants suppliers considerable bargaining power. A disruption in the supply of a critical ingredient or seed trait could directly impact Corteva's production schedules and the performance of its end products in the market. For example, in 2024, the agricultural sector faced ongoing supply chain challenges, highlighting the importance of reliable inputs for companies like Corteva.
- Critical Inputs: Suppliers of specialized genetic traits for seeds or novel active ingredients for crop protection hold significant power due to their unique contributions to product performance.
- Quality Dependence: Corteva's reputation for product quality and farmer trust is directly tied to the consistency and reliability of its suppliers' outputs.
- Supply Chain Vulnerability: Reliance on a limited number of suppliers for key components can amplify supplier bargaining power, especially during periods of market volatility.
- Innovation Linkage: Suppliers who provide proprietary technologies or innovative materials essential for Corteva's product development pipeline can command greater influence.
The bargaining power of suppliers to Corteva Agriscience is substantial, particularly for those providing specialized chemical compounds, proprietary genetic material, and essential active ingredients. These suppliers often operate in niche markets with limited competition, allowing them to influence pricing and availability. For example, in 2024, Corteva's cost of goods sold was approximately $10.9 billion, highlighting the significant financial impact of managing these critical supplier relationships effectively.
Suppliers with unique, patented technologies, such as novel seed traits or advanced biological control agents, possess considerable leverage. Corteva's reliance on these proprietary inputs for its product innovation means suppliers can command higher prices, as alternatives are scarce. The high switching costs involved in integrating new suppliers, including R&D adjustments and regulatory hurdles, further solidify supplier power.
| Supplier Power Factor | Impact on Corteva | Example/Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Increased pricing leverage and potential supply disruptions | Few specialized providers for advanced chemical compounds and genetic material. |
| Proprietary Technology/Patents | Higher input costs, limited alternatives | Suppliers of breakthrough biological control agents or unique seed traits. |
| High Switching Costs | Reduced flexibility, increased dependence | R&D integration, regulatory approvals, production line reconfiguration. |
| Forward Integration Threat | Potential for direct competition, reduced value capture for Corteva | Suppliers of key active ingredients investing in formulation and distribution. |
What is included in the product
Corteva's Porter's Five Forces Analysis reveals the intense competition within the agricultural sector, the significant bargaining power of large distributors and farmers, and the high barriers to entry for new seed and crop protection companies.
Corteva's Porter's Five Forces analysis provides a clear, one-sheet summary of all five forces—perfect for quick decision-making on competitive strategy.
Customers Bargaining Power
Corteva's customer base, primarily farmers, is incredibly fragmented across the globe. While some large agricultural operations exist, the vast majority are individual farmers. This sheer number of buyers generally dilutes their collective power to negotiate prices with major input suppliers like Corteva, particularly for specialized seed and crop protection products.
Corteva's investment in research and development significantly bolsters its product differentiation. By focusing on unique seed traits, advanced crop protection solutions, and integrated digital farming tools, the company cultivates strong brand loyalty among farmers who value performance and innovation.
This strategic differentiation directly combats customer bargaining power. Farmers are less likely to switch to competitors solely on price when they perceive tangible benefits and proven results from Corteva's specialized offerings, effectively reducing their leverage.
Switching costs for farmers can significantly influence their bargaining power with seed and crop protection providers like Corteva. These costs can manifest in several ways, from the time and effort required to learn new application techniques for crop protection products to the potential need for machinery adjustments or even the risk of reduced yields when adopting unfamiliar seed varieties. For instance, a farmer accustomed to a specific herbicide application might face a learning curve and potential equipment recalibration if they switch to a new chemical family, adding a tangible cost to the transition.
These switching costs act as a barrier, effectively dampening the bargaining power of customers. When the perceived benefits of switching to a competitor are outweighed by the associated effort, expense, and uncertainty, farmers are more likely to remain with their current suppliers. This inertia benefits companies like Corteva by fostering customer loyalty and reducing the pressure to constantly compete on price alone. In 2024, the agricultural sector continued to see innovation in seed technology and crop protection, but the fundamental economics of switching remain a key factor in customer retention.
Customer Price Sensitivity
Customer price sensitivity significantly impacts Corteva's bargaining power of customers. While farmers prioritize product performance, their purchasing power is heavily swayed by fluctuating commodity prices and their overall farm income. For instance, during periods of low corn or soybean prices, farmers often become more budget-conscious, directly influencing their willingness to pay for Corteva's seeds and crop protection products.
This heightened price sensitivity can translate into increased bargaining power for customers. When farm incomes are squeezed, as seen in certain agricultural regions experiencing adverse weather or market downturns in 2024, farmers are more likely to seek out lower-cost alternatives or negotiate harder on pricing. This dynamic puts direct pricing pressure on Corteva, potentially impacting its profit margins.
- Farmer Income Fluctuations: In 2024, net farm income in the U.S. experienced a projected decline from previous years, impacting farmers' discretionary spending on inputs like seeds and crop protection.
- Commodity Price Volatility: Global commodity prices for key crops like soybeans and corn have shown significant volatility, directly affecting farmers' revenue streams and their ability to absorb higher input costs.
- Demand for Value: Farmers are increasingly seeking bundled solutions and demonstrable return on investment, making them more sensitive to price when comparing offerings from different agricultural input providers.
Availability of Substitutes and Customer Information
The availability of generic crop protection chemicals and conventional seeds can indeed give customers more leverage. For instance, in 2024, the agricultural sector continues to see a strong presence of established generic chemical producers, offering price-sensitive farmers alternative solutions. This broad accessibility to non-proprietary products inherently empowers buyers.
However, Corteva's strategic focus on advanced biotechnology, including genetically modified (GM) seeds and biological crop protection solutions, presents a different dynamic. These innovations often deliver distinct performance advantages, such as enhanced yield potential or improved pest resistance, which are not easily matched by off-the-shelf alternatives. Corteva reported significant growth in its Enlist™ herbicide-tolerant trait technology in 2024, demonstrating customer adoption of its differentiated offerings.
Corteva's investment in research and development, leading to proprietary technologies like CRISPR gene editing for seed development, further distinguishes its product portfolio. These advanced solutions create a value proposition that can mitigate the bargaining power of customers who might otherwise switch to simpler, less innovative substitutes. The company's 2024 pipeline includes several novel biologicals aimed at addressing specific pest and disease challenges, further solidifying its unique market position.
- Generic Availability: Farmers can access a wide range of conventional seeds and chemical crop protection products from numerous suppliers.
- Corteva's Differentiation: Advanced biotechnology, including GM traits and biologicals, offers unique benefits not easily replicated by substitutes.
- R&D Investment: Significant investment in proprietary technologies like CRISPR enhances Corteva's product distinctiveness.
- Customer Adoption: Strong uptake of technologies like Enlist™ in 2024 indicates customer willingness to pay for specialized solutions.
Corteva's customer bargaining power is generally considered moderate. While farmers, as individuals, have limited power due to their fragmented nature, collective purchasing or strong demand for specific alternatives can shift this. In 2024, factors like fluctuating commodity prices and increased price sensitivity among farmers, especially in regions facing economic headwinds, amplified their ability to negotiate or seek lower-cost options.
Corteva's product differentiation through R&D, including advanced traits like Enlist™ and novel biologicals, helps to mitigate this power by creating unique value propositions. However, the availability of generic crop protection chemicals and conventional seeds provides a baseline for comparison, allowing price-conscious buyers to exert some influence.
Switching costs, while present, are a key factor. Farmers weigh the effort and risk of adopting new technologies against the perceived benefits, often leading to a degree of customer loyalty that tempers their bargaining leverage. The overall impact is a dynamic where Corteva's innovation and branding efforts are crucial in managing customer price expectations and demands.
| Factor | Impact on Corteva's Customer Bargaining Power | 2024 Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Fragmentation | Lowers individual customer power | Continues to be a dominant characteristic of the farming sector. |
| Product Differentiation | Lowers customer power | Corteva's investment in Enlist™ and biologicals in 2024 strengthens this. |
| Switching Costs | Lowers customer power | Learning curves for new seed traits and crop protection methods remain a barrier. |
| Price Sensitivity | Increases customer power | Projected declines in U.S. net farm income in 2024 heightened farmer budget consciousness. |
| Availability of Substitutes | Increases customer power | Generic crop protection chemicals remain readily available. |
What You See Is What You Get
Corteva Porter's Five Forces Analysis
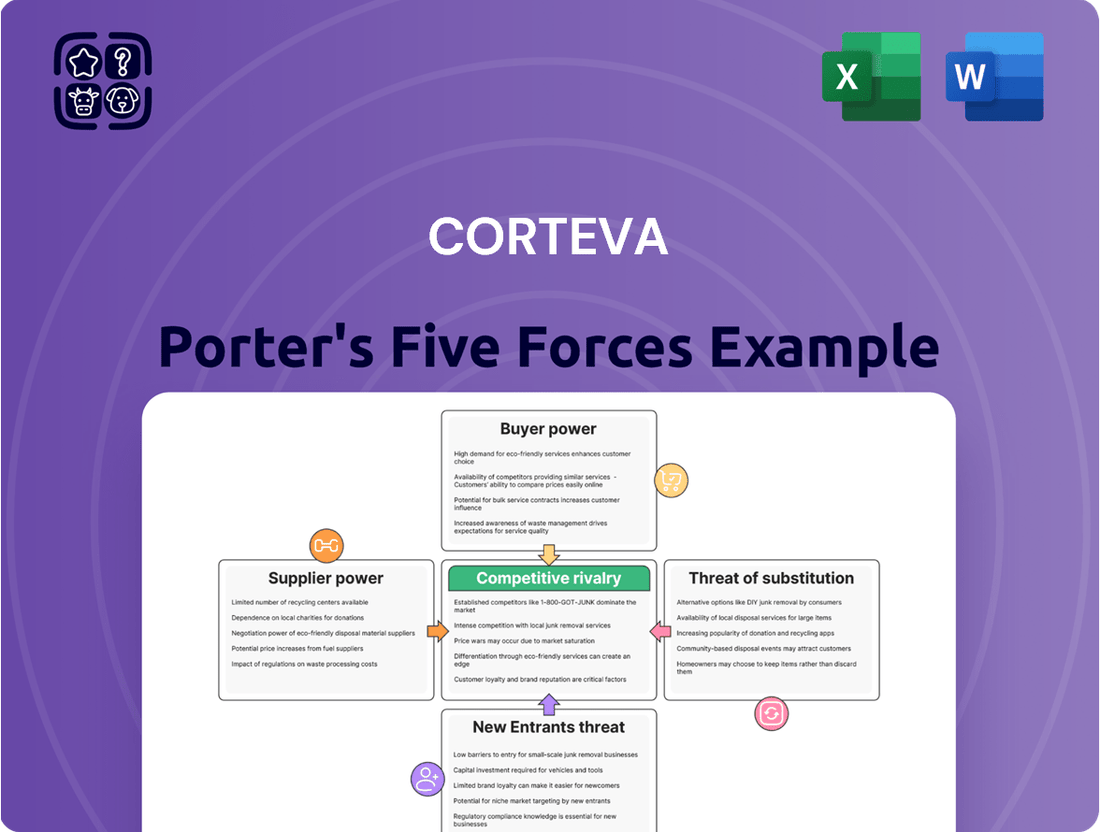
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis of Corteva, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic positioning within the agricultural sector. The document you see here is the exact, fully formatted analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring transparency and immediate utility. It meticulously examines the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors, providing actionable insights for strategic decision-making.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The global agriculture inputs market, especially for seeds and crop protection, is dominated by a handful of major corporations. Think of giants like Corteva, Bayer, Syngenta, and BASF; these companies hold significant sway. This concentration means competition is fierce, as these players constantly push for market share through new product development and strategic company buys.
Competitive rivalry in the agricultural sector, particularly for companies like Corteva, is intensely fueled by a relentless pursuit of product differentiation and innovation. This race is most evident in areas like seed genetics, where advancements can significantly impact crop yields and resilience. For instance, the development of new seed traits, such as drought tolerance or enhanced nutrient uptake, requires substantial and ongoing investment in research and development.
The competition extends deeply into crop protection chemistry, with companies constantly striving to create more effective and environmentally sound herbicides, insecticides, and fungicides. This innovation is crucial for farmers seeking to manage pests and diseases efficiently. Furthermore, the burgeoning field of digital agriculture, encompassing precision farming tools and data analytics, presents another critical battleground for differentiation, offering solutions that optimize resource use and improve farm management.
Companies are pouring billions into R&D to stay ahead. In 2023, for example, Corteva reported R&D expenses of $1.1 billion. This significant investment underscores the commitment required to develop cutting-edge products that offer tangible benefits like higher yields, superior pest resistance, or improved sustainability credentials, thereby creating a perpetual cycle of differentiation and market advantage.
Corteva faces intense competition from global players like Bayer Crop Science and Syngenta, but rivalry often heats up in specific geographic areas. These regional battles are shaped by local farming methods, differing regulations, and the types of crops grown.
For instance, pricing pressures can be more acute in Latin America, impacting Corteva's market share and profitability there. Conversely, North America might see more stable market conditions, though competition remains fierce.
Mergers and Acquisitions Activity
The agricultural sector has experienced a notable wave of mergers and acquisitions. Larger, established companies are actively acquiring smaller, innovative firms to bolster their product offerings and secure cutting-edge technologies, especially in areas like biological crop protection and digital agriculture solutions. This trend is particularly evident as companies seek to integrate advanced digital tools for precision farming and sustainable practices into their portfolios.
This consolidation directly impacts competitive rivalry. When major players absorb smaller, specialized companies, they often emerge as more formidable competitors with broader technological capabilities and expanded market reach. For instance, in 2024, the agrochemical and seed industry continued to see strategic acquisitions aimed at enhancing digital platforms and biological product lines, creating larger entities with diversified revenue streams and increased market power.
- Consolidation Drivers: Expansion of portfolios and acquisition of technological capabilities, particularly in biologicals and digital farming.
- Impact on Rivalry: Reshapes the competitive landscape by creating larger, more diversified competitors, potentially intensifying rivalry.
- 2024 Trends: Continued strategic acquisitions focused on digital platforms and biological product lines within the agrochemical and seed sectors.
Regulatory and Environmental Pressures
Increasing regulatory scrutiny and the growing demand for sustainable agricultural practices intensify competitive rivalry. Companies are increasingly judged not just on product efficacy but also on their environmental footprint. This dynamic is pushing significant investment into research and development for biological solutions and other eco-friendly innovations, forcing competitors to adapt or risk falling behind.
For instance, in 2024, the European Union's Farm to Fork strategy continued to influence agricultural markets, pushing for a 50% reduction in pesticide use by 2030. This regulatory push directly impacts companies like Corteva, encouraging a competitive race to develop and market lower-impact crop protection and enhancement products. Companies demonstrating strong sustainability credentials often gain a competitive edge, attracting environmentally conscious customers and investors.
- Regulatory Scrutiny: Heightened government oversight on product safety and environmental impact.
- Sustainability Demand: Growing consumer and farmer preference for eco-friendly agricultural solutions.
- Innovation Investment: Increased R&D spending on biologicals and sustainable agricultural technologies.
- Competitive Differentiation: Companies compete on their ability to offer environmentally responsible products and practices.
Competitive rivalry within the agricultural sector, especially for companies like Corteva, is characterized by intense innovation and a constant drive for differentiation. This is evident in the seed and crop protection markets, where substantial R&D investments, such as Corteva's $1.1 billion in 2023, are crucial for developing advanced traits and sustainable solutions. The industry also sees significant consolidation, with major players acquiring smaller firms to enhance their technological capabilities, particularly in digital agriculture and biologicals, thereby reshaping the competitive landscape and often intensifying rivalry.
| Competitor | 2023 Seed Revenue (USD Billion) | 2023 Crop Protection Revenue (USD Billion) | Approximate R&D Investment (2023, USD Billion) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corteva | 6.5 | 9.8 | 1.1 |
| Bayer Crop Science | 11.2 | 12.5 | 2.5 (Group) |
| Syngenta Group | 7.1 | 10.2 | 1.4 |
| BASF Agricultural Solutions | 8.3 | 8.9 | 0.9 |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The most direct substitutes for Corteva's advanced seeds and synthetic crop protection products are conventional seeds and traditional farming methods. These alternatives may involve less reliance on biotechnology or advanced chemicals, offering a simpler approach for some growers.
While often less efficient in terms of yield or pest control, these conventional approaches can serve as a substitute, particularly for price-sensitive farmers. For instance, in 2024, a significant portion of global agriculture still utilizes open-pollinated varieties or older seed technologies, representing a substantial substitute market.
The increasing consumer preference for organic and sustainably grown food directly fuels the market for biological crop protection products and biostimulants. These alternatives offer a viable substitute for traditional synthetic chemicals, potentially reducing reliance on Corteva's core offerings.
Corteva recognizes this shift and is strategically bolstering its biologicals segment. For instance, in 2023, the company announced significant investments in its biologicals research and development pipeline, aiming to expand its portfolio of naturally derived solutions to counter this substitution threat.
Advances in digital agriculture and precision farming, leveraging AI and IoT, are transforming how farmers manage their crops. These technologies allow for highly targeted application of inputs, potentially reducing the overall volume of crop protection products needed. For instance, sensors and data analytics can identify specific pest or disease outbreaks in localized areas, enabling spot treatments rather than blanket spraying.
While many digital agriculture tools are designed to complement existing crop protection solutions, they can, in certain scenarios, substitute for broader-spectrum chemical applications. By optimizing application timing and dosage, farmers can achieve similar or even improved efficacy with less product. This shift could impact the demand for traditional, high-volume chemical solutions as precision farming gains wider adoption.
Crop Rotation and Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
Farmers can significantly reduce their reliance on specific seed traits or chemical inputs by adopting cultural practices. For instance, crop rotation helps break pest and disease cycles, making it harder for specific pathogens to establish. In 2024, studies indicated that well-implemented crop rotation can decrease pest-related yield losses by up to 20% in certain staple crops, directly impacting the demand for targeted pest-resistance traits in seeds.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) strategies offer another potent substitute. IPM combines biological controls, cultural practices, and judicious use of pesticides, aiming to manage pests sustainably. This approach can lower the overall volume and frequency of chemical applications. For example, the adoption of IPM in corn production in the US has shown potential to reduce insecticide use by 15-30% in some regions, affecting the market share for certain crop protection products.
- Crop Rotation Benefits: Can reduce specific pest populations by up to 20% in staple crops, lessening the need for specialized seed traits.
- IPM Impact: Integrated Pest Management can lead to a 15-30% reduction in insecticide usage in crops like corn.
- Intercropping Advantage: Planting multiple crops together can deter pests and improve soil health, acting as a natural defense.
- Reduced Chemical Reliance: These practices collectively decrease dependence on proprietary chemical solutions, posing a threat to Corteva's crop protection segment.
Alternative Food Production Systems
The long-term emergence of alternative food production systems poses a potential, albeit distant, threat of substitution. Innovations like vertical farming, lab-grown meat, and novel protein sources could fundamentally shift consumer demand away from traditional agricultural outputs. While these technologies do not directly substitute Corteva's current seed and crop protection offerings, they represent a future trend that could reshape the agricultural industry.
The growth trajectory of these alternative systems is noteworthy. For instance, the global market for cultured meat was projected to reach approximately $1.5 billion by 2025, with significant growth anticipated thereafter. Similarly, vertical farming, which can produce crops with significantly less land and water, is seeing substantial investment. These advancements suggest a gradual but impactful alteration in how food is produced and consumed, potentially impacting the demand for conventional agricultural inputs that Corteva provides.
- Vertical Farming: Offers controlled environments, reducing reliance on traditional land and weather patterns.
- Lab-Grown Meat: Aims to produce meat from cell cultures, bypassing traditional animal agriculture.
- Novel Protein Sources: Includes plant-based alternatives and insect protein, diversifying protein consumption.
- Market Growth: The alternative protein market, for example, is experiencing rapid expansion, indicating shifting consumer preferences.
The threat of substitutes for Corteva's offerings is multifaceted, encompassing conventional farming methods, biological alternatives, and evolving food production systems. While Corteva focuses on advanced seeds and synthetic crop protection, growers can opt for less technologically intensive approaches. For example, in 2024, a substantial portion of global agriculture still relies on conventional seeds and traditional pest management, representing a significant substitute market.
The increasing demand for organic and sustainable products also drives the adoption of biological crop protection and biostimulants, directly challenging synthetic chemical solutions. Corteva is actively investing in this area, with significant R&D investments announced in 2023 to expand its biologicals portfolio.
Furthermore, advancements in digital agriculture and precision farming enable more targeted input application, potentially reducing the overall volume of chemicals needed. Integrated Pest Management (IPM) and cultural practices like crop rotation also offer viable alternatives, with crop rotation shown to reduce pest-related yield losses by up to 20% in certain staple crops as of 2024.
| Substitute Category | Description | Impact on Corteva | Example Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional Farming | Use of non-GMO seeds, traditional pest control methods. | Lower adoption of advanced seed traits and synthetic chemicals. | Significant portion of global agriculture still uses conventional methods (2024). |
| Biologicals & Organic | Biopesticides, biostimulants, organic farming practices. | Direct competition for crop protection market share. | Corteva invested significantly in biologicals R&D in 2023. |
| Precision Agriculture | AI, IoT for targeted input application. | Reduced overall volume of synthetic chemicals required. | IPM can reduce insecticide use by 15-30% in some crops. |
| Cultural Practices | Crop rotation, intercropping, IPM. | Decreased reliance on specific seed traits and chemical treatments. | Crop rotation can reduce pest losses by up to 20% in staple crops (2024). |
Entrants Threaten
The agriculture inputs industry, especially in seeds and crop protection, demands massive capital for research and development, manufacturing plants, and extensive distribution channels. For instance, bringing a new crop protection product to market can cost upwards of $250 million and take a decade or more. This significant financial commitment acts as a substantial hurdle for potential new competitors.
Corteva's robust patent portfolio, covering unique seed traits and crop protection chemistries, presents a significant hurdle for newcomers. For instance, in 2024, the agricultural biotechnology sector continued to see substantial R&D investments, with major players like Corteva allocating billions to innovation, further solidifying their IP advantage. This extensive intellectual property makes it exceptionally challenging for new entrants to develop and market comparable, differentiated products without incurring massive research and development costs or securing costly licensing deals.
The agricultural sector, particularly concerning genetically modified seeds and chemical crop protection, is a minefield of regulations. For any new company looking to enter this space, navigating these complex rules is a significant barrier. For instance, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) have rigorous approval processes for new agricultural chemicals and biotech traits, often requiring years of safety and efficacy testing.
These lengthy and expensive approval pathways act as a powerful deterrent to potential new entrants. Companies must invest substantial capital and time, often a decade or more, in research, development, and regulatory submissions before a product can even reach the market. This high upfront cost and extended timeline significantly reduce the threat of new competitors challenging established players like Corteva.
Established Distribution Channels and Customer Relationships
Corteva Agriscience benefits significantly from deeply entrenched relationships with farmers, built over years of trust and direct engagement. This loyalty is a formidable barrier for any new competitor attempting to enter the agricultural solutions market.
The company also possesses a vast and efficient global distribution network. Establishing comparable channels, capable of reaching farmers worldwide with timely delivery of seeds and crop protection products, would require immense capital investment and time for new entrants.
Consider these points regarding established distribution channels and customer relationships:
- Farmer Trust: Corteva's long-standing presence fosters trust, making farmers hesitant to switch to unproven new suppliers.
- Global Reach: The company's established logistics and supply chain infrastructure are difficult and costly for newcomers to replicate.
- Direct Engagement: Corteva's sales force and agronomic support teams provide direct farmer interaction, a critical component for adoption of new technologies.
- Market Access: Existing channels provide immediate access to a broad customer base, a hurdle new entrants must overcome through extensive marketing and sales efforts.
Brand Recognition and Scale Economies
Corteva, a significant player in the agricultural sector, benefits immensely from established brand recognition and substantial economies of scale. This allows them to spread fixed costs over a larger production volume, leading to lower per-unit costs in manufacturing, research and development, and marketing. For instance, in 2023, Corteva reported net sales of $17.1 billion, underscoring its massive operational footprint.
New entrants face a considerable hurdle in matching Corteva's cost efficiencies. The capital investment required to build comparable production facilities, establish a global distribution network, and fund extensive marketing campaigns is immense. This financial barrier makes it difficult for newcomers to compete effectively on price or to build the same level of trust and perceived value with customers that Corteva has cultivated over years.
- Brand Loyalty: Corteva's long-standing presence has fostered strong brand loyalty among farmers, who often rely on trusted seed and crop protection brands.
- Economies of Scale: Their large-scale operations in seed production and chemical manufacturing translate into significant cost advantages per unit.
- R&D Investment: Corteva's substantial investment in research and development, exceeding $1 billion annually, creates a pipeline of innovative products that are hard for new entrants to replicate quickly.
- Distribution Network: An extensive and efficient distribution network ensures product availability and support, a critical factor for farmers.
The threat of new entrants for Corteva is relatively low due to significant barriers. High capital requirements for R&D, manufacturing, and distribution, coupled with stringent regulatory approvals, deter new players. Corteva's established patent portfolio and strong farmer relationships further solidify its market position.
New companies entering the agriculture inputs market face immense financial hurdles, needing hundreds of millions for product development and regulatory compliance. For example, bringing a new crop protection product to market can cost over $250 million and take more than a decade. This extensive investment, along with the need to build trust and distribution networks, makes the threat of new entrants manageable for Corteva.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High costs for R&D, manufacturing, and distribution. | Significant financial hurdle. |
| Intellectual Property | Corteva's patent portfolio on seed traits and crop protection. | Difficult to replicate differentiated products. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex and lengthy approval processes for agricultural products. | Requires substantial time and investment. |
| Brand Loyalty & Distribution | Established farmer trust and extensive global distribution networks. | Challenging to gain market access and farmer adoption. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Corteva Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, drawing from Corteva's annual reports, SEC filings, and investor presentations. We also incorporate insights from leading agricultural industry research firms and market intelligence reports.
