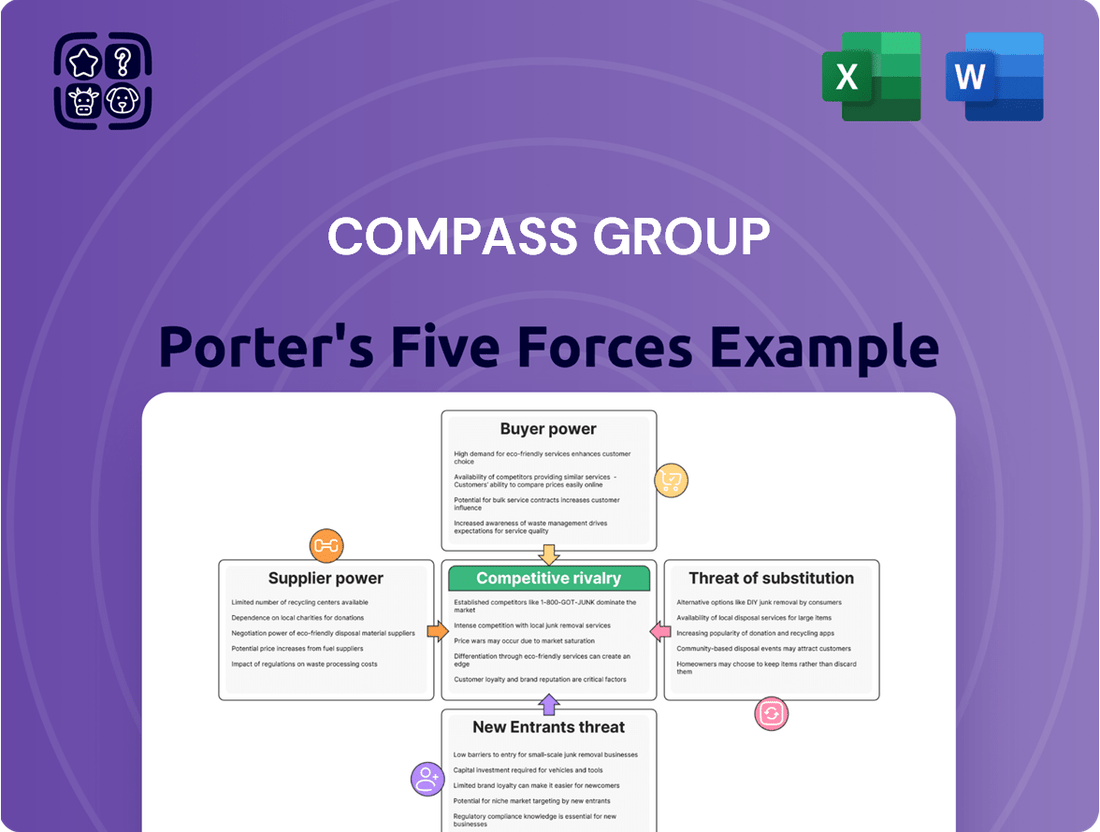
Compass Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Compass Group Bundle
Compass Group operates in a dynamic environment shaped by intense rivalry, significant buyer power, and the constant threat of substitutes. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating the competitive landscape.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Compass Group’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Compass Group's extensive global sourcing network, spanning numerous regions and product categories, inherently dilutes the bargaining power of individual suppliers. This diversification allows Compass to readily substitute suppliers for most of its needs, limiting any single vendor's leverage. For instance, in 2024, Compass managed a supply chain involving thousands of suppliers worldwide, with no single supplier representing more than 1% of its total procurement spend.
However, the power dynamic can shift for highly specialized inputs. If Compass requires unique ingredients or proprietary equipment, a concentrated supplier market for these specific items can grant those vendors significant bargaining power. This is particularly true if the switching costs for Compass are high, requiring extensive retooling or reformulation, thereby increasing the supplier's ability to dictate terms.
For Compass Group, while many everyday food items have low switching costs, specialized support services and unique food items designed for specific client requirements can present higher costs when changing suppliers. These costs can stem from establishing new quality control protocols, reconfiguring logistics, and the administrative burden of contract renegotiations.
The threat of suppliers forward integrating into large-scale contract foodservice operations for Compass Group is generally low. The significant capital outlay, intricate operational demands, and the necessity for robust client relationship management present substantial hurdles for most food or service providers.
For instance, establishing a nationwide catering service similar to Compass Group would require massive investments in logistics, technology, and human resources, far beyond the typical scope of a supplier. This complexity naturally limits the number of suppliers capable of posing a credible forward integration threat.
Uniqueness of Supplier Offerings
For many basic food items, suppliers have limited power because their products are largely interchangeable. However, as Compass Group increasingly emphasizes sustainable, locally sourced, or specialty ingredients to cater to changing consumer tastes, suppliers who can provide these unique or certified products can demand higher prices and wield more influence.
Compass's 2024 Sustainability Report underscores its commitment to collaborating with suppliers to lower emissions and prioritize local sourcing. This strategic direction suggests a shift towards more specialized supplier relationships, potentially increasing the bargaining power of those offering differentiated or certified goods.
- Commoditized Staples: Most staple food items are commoditized, reducing supplier leverage.
- Unique Offerings: Suppliers of sustainable, local, or specialty ingredients gain power.
- Strategic Focus: Compass's 2024 sustainability efforts indicate a move towards specialized sourcing.
Importance of Compass to Supplier Revenue
Given Compass Group's vast global reach, it's estimated that food and beverage costs represent approximately one-third of its overall operational expenses. This substantial purchasing volume means Compass is a vital client for many of its suppliers, often accounting for a significant percentage of their total revenue.
This reliance on Compass as a major customer generally diminishes the bargaining power of its suppliers. Suppliers are typically keen to maintain their relationship with such a large and consistent buyer, making them less likely to demand significantly higher prices or more favorable terms.
For instance, in 2024, Compass Group reported revenues exceeding £30 billion. This immense scale translates directly into considerable purchasing power, influencing the terms it can negotiate with its diverse supplier base.
- Significant Revenue Driver: Compass Group's substantial global spending makes it a critical revenue source for many food and beverage suppliers.
- Reduced Supplier Leverage: Suppliers are often hesitant to risk losing Compass's business, thereby limiting their ability to dictate terms.
- 2024 Financial Impact: With revenues over £30 billion in 2024, Compass's purchasing volume underscores its importance to its supply chain partners.
Compass Group's immense purchasing volume, driven by its £30 billion+ 2024 revenues, generally weakens supplier bargaining power as they rely heavily on Compass for revenue. However, suppliers of specialized or sustainably sourced ingredients can exert more influence, especially as Compass focuses on these areas in its 2024 sustainability initiatives.
| Supplier Type | Bargaining Power Factors | Impact on Compass Group |
|---|---|---|
| Commoditized Staples | Low differentiation, high availability, low switching costs | Weak leverage; Compass can easily switch suppliers and negotiate favorable terms. |
| Specialty/Sustainable Ingredients | Unique offerings, certifications, potential for higher margins | Moderate to High leverage; Compass's strategic focus on these areas increases supplier influence. |
| Proprietary Equipment/Services | High switching costs, specialized knowledge, limited supplier base | Potentially High leverage; Compass may face significant costs or disruptions if changing suppliers. |
What is included in the product
This analysis of Compass Group's industry reveals the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitutes on profitability.
Quickly identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each of Porter's Five Forces on a single, actionable dashboard.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customer concentration for Compass Group is relatively low due to its vast and diversified client base spanning business and industry, education, healthcare, sports and leisure, and defense. Operating in over 40 countries, this broad reach means no single client or small group of clients holds significant sway over pricing or terms.
Switching contract foodservice providers often presents clients with considerable challenges. These include logistical disruptions, potential employee dissatisfaction during the transition, and significant administrative overhead. These factors contribute to moderate switching costs for customers.
These moderate switching costs generally serve to reduce the bargaining power of customers. Compass Group's impressive client retention rate, which stood at over 96% in 2024, highlights the effectiveness of these barriers in maintaining customer loyalty.
Customers, particularly large corporations, possess the potential to bring their food services in-house, a move known as backward integration. This capability grants them more direct oversight of expenses and service standards, a compelling proposition for many.
While self-operation offers greater control, the intricate nature of food procurement, labor management, and adherence to health and safety regulations can be a significant hurdle. For instance, in 2024, many large enterprises recognized the specialized expertise required for efficient foodservice operations, often finding it more cost-effective and less risky to partner with established providers like Compass Group.
The complexities involved in managing a food supply chain, ensuring consistent quality, and navigating the ever-changing regulatory landscape mean that outsourcing to specialists remains a more practical and attractive option for many clients seeking to focus on their core business activities.
Price Sensitivity of Customers
Customers, especially large organizations with strict budgets, often prioritize price. Compass Group's significant purchasing power, enabling competitive pricing, is crucial for securing and keeping contracts. For instance, in 2023, the food service industry saw intense competition on pricing, with many clients demanding cost-plus models to manage their own expenditures.
The company's strategic approach to menu planning and efficient sourcing directly addresses these cost pressures. By optimizing ingredient usage and leveraging economies of scale, Compass Group aims to deliver value that satisfies price-sensitive clients.
- High Price Sensitivity in Institutional Contracts: Large corporate and institutional clients frequently operate under tight budgetary controls, making price a primary decision-making factor.
- Competitive Pricing as a Differentiator: Compass Group's ability to offer attractive pricing, bolstered by its scale and procurement advantages, is essential for winning and retaining business in these segments.
- Cost Management Strategies: Effective menu management and efficient sourcing of ingredients are key tactics Compass Group employs to mitigate customer price sensitivity and maintain profitability.
Information Availability to Customers
Customers in the contract foodservice sector, including large corporations and institutions, increasingly have access to comprehensive information about various providers. This includes details on service quality, menu options, and pricing structures. For instance, industry reports and online platforms often publish comparative data on contract caterers, allowing clients to benchmark performance and costs.
This heightened information availability directly translates into greater customer bargaining power. Clients can readily compare Compass Group's offerings against competitors, demanding better terms and more tailored solutions. In 2023, Compass Group reported revenue of £32.1 billion, underscoring its significant market presence, yet this scale also means it serves a diverse clientele with varying degrees of information access and negotiation leverage.
- Increased Transparency: Customers can easily access data on service providers, including pricing and offerings, facilitating informed comparisons.
- Negotiation Leverage: Greater information empowers clients to negotiate more effectively with foodservice companies like Compass Group.
- Benchmarking Capabilities: Clients can benchmark Compass Group’s services against competitors, driving demands for competitive pricing and superior service.
- Impact on Pricing: The ability to compare pricing models can put downward pressure on service costs for providers.
The bargaining power of customers for Compass Group is generally moderate, influenced by factors like switching costs and the potential for backward integration, though these are often outweighed by the complexities of in-house management. Compass Group's 2024 client retention rate exceeding 96% demonstrates their success in mitigating customer power.
| Factor | Impact on Compass Group | Supporting Data (2024 unless specified) |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | Low | Operates in 40+ countries; diversified client base (business, education, healthcare, etc.) |
| Switching Costs | Moderate | Logistical disruption, administrative overhead, employee impact |
| Backward Integration Potential | Exists but often impractical | Specialized expertise needed for procurement, labor, regulations |
| Price Sensitivity | High for institutional clients | 2023 industry saw demand for cost-plus models |
| Information Availability | Increases power | Industry reports and online platforms facilitate benchmarking |
Preview Before You Purchase
Compass Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview displays the complete Compass Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a thorough examination of competitive forces within the industry. The document you see here is precisely what you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no surprises and full readiness for your strategic planning. It's a professionally formatted and ready-to-use analysis, providing actionable insights into Compass Group's market landscape.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The contract foodservice sector is indeed a crowded arena. Compass Group faces robust competition from global giants such as Sodexo, Aramark, and Elior, all of whom operate on a similar scale. These major players, along with a multitude of smaller regional and local providers, create a highly fragmented and competitive landscape.
The global contract catering market is anticipated to expand, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 5.29% between 2025 and 2033. This upward trend presents opportunities for all participants in the industry, potentially softening some of the intensity of competitive rivalry.
Despite the market's growth, the competition for securing and retaining market share remains robust. Companies like Compass Group must navigate this dynamic landscape, where even in an expanding market, the drive to differentiate and capture a larger portion of the available business is a constant factor.
While many companies offer basic catering, Compass Group sets itself apart by crafting customized food programs that cater to specific client needs and preferences. This goes beyond just providing meals; it involves understanding dietary requirements, cultural nuances, and even creating unique culinary experiences.
Furthermore, Compass Group integrates a suite of support services alongside its food offerings, such as facilities management and cleaning, providing a more comprehensive solution for its clients. This holistic approach streamlines operations for businesses and institutions, offering a distinct advantage over competitors focusing solely on food provision.
The company’s sectorized strategy, tailoring services to industries like healthcare, education, and sports & leisure, allows for specialized expertise and a deeper understanding of client demands. This specialization, coupled with a strong emphasis on health, wellness, and sustainability—as evidenced by its commitment to sourcing 75% of its food from local or regional suppliers by 2025—creates a compelling value proposition that resonates with increasingly conscious consumers and businesses.
Exit Barriers
High fixed costs, such as those associated with Compass Group's extensive global infrastructure, along with long-term client contracts and specialized assets, create substantial exit barriers in the foodservice industry. These barriers can compel companies to remain in the market even when facing difficult economic conditions, thereby intensifying competitive rivalry.
These exit barriers mean that companies like Compass Group, having invested heavily in their operational footprint, are less likely to withdraw from markets quickly. This can lead to a situation where even underperforming competitors persist, contributing to a more crowded and competitive landscape.
- High Fixed Costs: Significant capital investment in facilities, equipment, and technology.
- Long-Term Contracts: Client agreements that lock companies into service provision for extended periods.
- Specialized Assets: Industry-specific equipment and infrastructure that have limited alternative uses.
- Intensified Rivalry: Competitors staying in the market despite challenges due to these barriers.
Brand Identity and Loyalty
Compass Group benefits significantly from its robust brand identity and a well-earned reputation for delivering quality and ensuring safety across its diverse service offerings. This strong brand presence is a key differentiator in the competitive landscape.
The company's ability to maintain exceptionally high client retention rates, often exceeding 96%, underscores a substantial level of customer loyalty. This loyalty acts as a powerful competitive advantage, creating a barrier for competitors seeking to attract Compass Group's established client base.
- Brand Recognition: Compass Group is a globally recognized name in contract catering and support services.
- Client Retention: Consistently high retention rates, often above 96%, demonstrate strong client satisfaction and loyalty.
- Reputation: A long-standing reputation for quality, reliability, and safety reassures clients and deters switching.
- Competitive Edge: This established trust makes it more challenging for new or smaller rivals to win contracts from existing Compass Group clients.
The competitive rivalry within the contract foodservice sector is intense, driven by a mix of global players and numerous smaller firms. Compass Group faces direct competition from companies like Sodexo and Aramark, which operate on a similar scale and offer comparable services. This crowded market means that winning and keeping clients requires constant innovation and a strong value proposition.
Despite the market's projected growth, with the global contract catering market expected to reach approximately $276.4 billion by 2030, the pressure to differentiate remains high. Compass Group's strategy of offering customized culinary experiences and integrated support services, such as facilities management, provides a distinct advantage. Furthermore, its sector-specific approach, focusing on industries like healthcare and education, allows for specialized expertise that appeals to clients with unique needs.
The company's commitment to sustainability, including sourcing 75% of its food from local or regional suppliers by 2025, aligns with growing consumer and business preferences. This focus, combined with a strong brand reputation and exceptional client retention rates, often exceeding 96%, creates significant barriers for competitors looking to gain market share.
High fixed costs and long-term contracts also contribute to intensified rivalry, as they create substantial exit barriers, keeping competitors engaged even in challenging economic conditions. This dynamic ensures that companies must continually demonstrate their value to maintain their position.
| Competitor | Estimated 2024 Revenue (USD Billions) | Key Service Offerings | Market Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compass Group | ~29.0 | Contract Catering, FM, Support Services | Global (Healthcare, Education, Business & Industry, Sports & Leisure) |
| Sodexo | ~23.0 | Contract Catering, FM, Benefits & Rewards | Global (Healthcare, Education, Business & Industry, Government) |
| Aramark | ~16.0 | Contract Food Services, Facilities Management, Uniform Services | North America & Europe (Sports & Entertainment, Education, Healthcare, Business & Industry) |
| Elior Group | ~6.0 | Contract Catering, Concessions | Europe & North America (Business & Industry, Healthcare, Education) |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The most direct substitute for Compass Group's contract catering services is clients choosing to manage their food services in-house. While outsourcing typically provides cost efficiencies and specialized expertise, organizations with significant scale might opt for self-operation, believing it offers greater control or direct cost savings. For instance, a large university or a major corporation might have the infrastructure and management capacity to handle its own dining facilities, potentially seeing it as a way to retain profits and tailor services precisely to internal needs.
For Compass Group's clients, particularly in business and industry sectors, employees and customers may choose external food vendors and restaurants. This presents a significant substitute threat, especially in urban environments where a wide array of options are readily available. The convenience and variety offered by local eateries and food delivery services can draw customers away from Compass Group's contracted catering services.
The proliferation of convenient, pre-packaged meal solutions presents a significant threat. Options like ready-to-eat meals found in supermarkets and an increasing number of advanced vending machine offerings cater to consumers seeking quick, flexible dining. These alternatives directly compete with traditional on-site catering services, particularly for individuals prioritizing speed and convenience over a full-service dining experience.
Changes in Work/Study/Healthcare Models
The increasing adoption of remote work and hybrid learning models presents a significant threat of substitution for Compass Group. As fewer employees and students are physically present in offices and educational institutions, the demand for traditional on-site contract catering services naturally declines. This shift directly impacts Compass's core business, as the need for food and beverage provision on-premises diminishes.
Furthermore, the rise of decentralized healthcare services, where more care is delivered remotely or in smaller community settings, can also reduce the reliance on large-scale catering contracts within major hospital complexes. This trend means that Compass might face competition from alternative food solutions or a reduced overall need for its services in these evolving healthcare environments.
For example, by the end of 2023, reports indicated that approximately 28% of the US workforce was working remotely at least part of the time, a substantial increase from pre-pandemic levels. This sustained shift directly translates to a reduced customer base for on-site catering providers like Compass.
- Reduced On-Site Presence: Shifts to remote and hybrid models directly decrease the number of people requiring on-site catering.
- Demand Erosion: Fewer people on-site means less demand for food and beverage services provided by Compass.
- Healthcare Decentralization: Changes in healthcare delivery can lessen the need for large-scale catering in traditional medical facilities.
- Substitution Effect: Alternative food sourcing or reduced consumption on-site acts as a substitute for Compass's contract catering.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Outsourcing
Clients regularly weigh the cost-effectiveness of Compass Group's outsourcing against other options. For instance, a large corporation might consider whether managing its own cafeteria is more economical than contracting with Compass, especially if they have existing infrastructure and staff. In 2023, the global facilities management market, which includes catering services, was valued at approximately $1.3 trillion, indicating a substantial market where clients have numerous alternatives to consider.
If Compass's value proposition, including cost savings and operational efficiency, isn't clearly superior to what clients can achieve internally or through other providers, the threat of substitution grows. For example, a university might find that bringing food services in-house, leveraging student labor and existing campus kitchens, provides better cost control and customization than outsourcing. This constant evaluation means Compass must continually demonstrate its competitive advantage.
The availability of credible substitutes directly impacts Compass's pricing power and market share. If clients perceive that they can achieve similar or better results through alternative means, they are less likely to be locked into Compass's services. This is particularly true in sectors where food service is not a core competency, and clients might explore partnerships with smaller, specialized catering firms or even direct sourcing of ingredients and management.
- Cost-Benefit Evaluation: Clients assess if Compass's services offer superior value compared to self-management or other providers.
- Value Proposition: Compass must highlight cost savings, quality, and efficiency to counter substitutes.
- Market Dynamics: The vast facilities management market offers numerous alternatives, increasing substitution threats.
- Competitive Advantage: Continuous demonstration of superiority is crucial to retain clients against substitutes.
The threat of substitutes for Compass Group's contract catering is significant, driven by clients' ability to manage services in-house, utilize external food vendors, or adopt convenient meal solutions. The increasing prevalence of remote work and decentralized healthcare further erodes the demand for traditional on-site catering. For example, by the end of 2023, around 28% of the US workforce was working remotely at least part-time, directly reducing the customer base for on-site providers.
Clients continuously evaluate the cost-effectiveness of outsourcing versus self-management or alternative providers. The global facilities management market, including catering, was valued at approximately $1.3 trillion in 2023, highlighting the extensive range of choices available to clients. Compass must consistently prove its value proposition to mitigate this substitution threat.
| Substitute Type | Client Action | Impact on Compass |
|---|---|---|
| In-house Management | Self-operation of food services | Reduced contract revenue, loss of market share |
| External Food Vendors | Employees/customers choosing local eateries/delivery | Decreased on-site consumption, lower per-client spending |
| Convenient Meal Solutions | Purchasing pre-packaged meals/using advanced vending | Direct competition for individual meal occasions |
| Remote/Hybrid Work | Reduced on-site presence of employees/students | Lower overall demand for catering services |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the global contract foodservice market, where Compass Group operates, demands immense capital. Newcomers need substantial funds for state-of-the-art kitchens, specialized equipment, robust logistics networks, advanced technology platforms, and extensive workforce training. For instance, establishing a single large-scale catering operation can easily run into millions of dollars, making it a formidable hurdle for smaller or less capitalized businesses.
Compass Group's vast global operations create substantial economies of scale. This means they can buy supplies in huge quantities, negotiate better prices, and spread fixed costs like logistics and technology over a much larger base than any newcomer. For instance, in 2023, Compass Group reported revenues of £32.1 billion, demonstrating the sheer volume of their purchasing power.
New companies entering the contract catering and food service market would find it incredibly challenging to replicate these cost efficiencies. They would likely face higher per-unit costs for everything from food ingredients to delivery services, making it nearly impossible to compete on price with an established giant like Compass Group. This significant cost disadvantage acts as a strong barrier.
Newcomers face significant hurdles in establishing robust distribution networks and cultivating deep client relationships, especially in diverse sectors where Compass Group operates. These established channels and loyal customer bases are hard-won assets, built over years of consistent service and trust.
For instance, in the contract catering market, securing contracts with large corporations or public institutions often requires a proven track record and a sophisticated supply chain, which new entrants typically lack. Compass Group’s extensive global infrastructure and established procurement agreements provide a competitive edge, making it difficult for new players to match their reach and efficiency.
In 2023, Compass Group reported revenue of £32.1 billion, demonstrating the scale of its operations and the breadth of its client base. This financial strength underpins its ability to invest in and maintain these critical distribution and relationship networks, posing a substantial barrier to entry for any aspiring competitor.
Brand Loyalty and Reputation
Compass Group's formidable brand loyalty and established reputation act as a significant deterrent to new entrants. Years of consistent delivery in quality, safety, and service have cultivated deep trust with clients, making them hesitant to switch to unproven competitors. This is particularly true in sectors where reliable food and support services are mission-critical.
The reluctance of clients to change providers, especially in large-scale contracts, presents a substantial hurdle for newcomers. For instance, in the contract catering sector, where Compass Group holds a significant market share, switching costs can be high, involving extensive due diligence and potential disruption to operations. This inertia favors incumbents like Compass Group.
Compass Group's global reach and diversified service offerings further solidify its brand strength. By operating across various segments, from healthcare to education and business dining, the company has built a comprehensive understanding of client needs and regulatory landscapes. This extensive experience translates into a reputation for reliability that is difficult for new, smaller entities to replicate. In 2023, Compass Group reported revenues of £32.1 billion, underscoring its market dominance and the significant resources available to maintain and leverage its brand.
- Brand Reputation: Compass Group's long-standing commitment to quality and safety fosters strong client loyalty.
- Client Inertia: The critical nature of food services makes clients risk-averse, favoring established providers.
- Switching Costs: High costs and operational risks associated with changing suppliers deter clients from onboarding new entrants.
- Market Dominance: Compass Group's substantial 2023 revenue of £32.1 billion highlights its entrenched market position, making it challenging for new players to gain traction.
Regulatory and Health Compliance
The foodservice sector, including Compass Group's operations, is heavily regulated. New companies entering the market must grapple with a complex web of health, safety, and hygiene standards that vary significantly by region and country. For instance, in 2024, the European Union continued to enforce strict HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) principles across all food businesses, requiring substantial investment in training and infrastructure for compliance.
Navigating these diverse regulatory landscapes presents a considerable barrier to entry. New entrants often face substantial upfront costs and operational complexities to ensure they meet all legal requirements, from food sourcing to waste disposal. This burden can deter potential competitors, especially smaller entities lacking the resources to manage extensive compliance procedures effectively.
- High Compliance Costs: New entrants must invest in certified training, specialized equipment, and robust internal processes to meet food safety standards, potentially costing tens of thousands of dollars per establishment.
- Varying International Standards: Companies expanding globally must adapt to different food labeling laws, import/export regulations, and local health department requirements, adding layers of complexity.
- Reputational Risk: Non-compliance can lead to severe penalties, including fines and temporary closures, which can irreparably damage a new brand's reputation in a competitive market.
The threat of new entrants for Compass Group is generally low due to significant barriers. High capital requirements for infrastructure and technology, coupled with the need for extensive workforce training, make entry costly. For example, establishing a modern, large-scale catering facility can easily exceed several million dollars.
Economies of scale achieved by Compass Group, evidenced by its 2023 revenue of £32.1 billion, create substantial purchasing power and cost efficiencies that newcomers struggle to match. This financial scale allows Compass Group to negotiate lower prices for supplies and spread fixed costs effectively, creating a significant cost disadvantage for new players.
Established distribution networks, deep client relationships, and strong brand loyalty further deter new entrants. Clients, particularly large institutions, are often hesitant to switch from proven providers like Compass Group due to high switching costs and the risk of operational disruption. This inertia, combined with stringent regulatory compliance requirements in the foodservice sector, solidifies Compass Group's market position.
| Barrier to Entry | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example/Data Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Need for significant investment in kitchens, equipment, logistics, and technology. | High barrier, requiring substantial upfront funding. | Establishing a large catering operation can cost millions. |
| Economies of Scale | Compass Group's large volume leads to lower per-unit costs. | New entrants face higher operational costs, hindering price competitiveness. | Compass Group's 2023 revenue of £32.1 billion indicates substantial purchasing power. |
| Brand Loyalty & Switching Costs | Established reputation and client inertia make switching difficult. | Clients are risk-averse, favoring incumbents with proven track records. | High due diligence and potential operational disruption deter clients from switching. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Adherence to diverse and strict health, safety, and hygiene standards. | Requires investment in training, infrastructure, and ongoing compliance efforts. | EU's HACCP principles in 2024 demand robust compliance procedures. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Compass Group is built upon a foundation of diverse data sources, including their annual reports, investor presentations, and industry-specific market research from firms like Statista and IBISWorld.
