Colowide Co Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Colowide Co Bundle
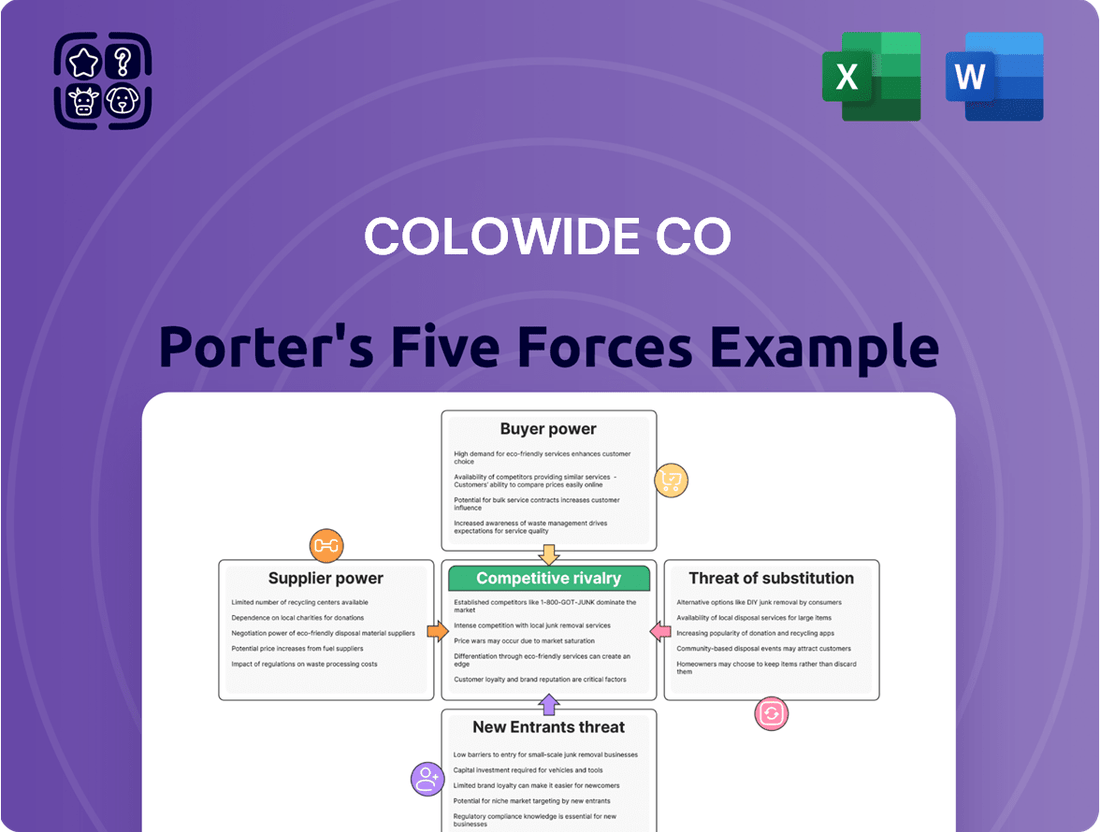
Understanding Colowide Co's competitive landscape is crucial, and our Porter's Five Forces analysis reveals the intricate interplay of buyer power, supplier leverage, and the threat of substitutes. This initial glimpse only scratches the surface of the strategic insights available.
The complete report goes deeper, offering a data-driven framework to understand Colowide Co's real business risks and market opportunities, equipping you with the knowledge to navigate its industry effectively.
Ready to move beyond the basics? Get a full strategic breakdown of Colowide Co’s market position, competitive intensity, and external threats—all in one powerful analysis.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Colowide Co's broad restaurant portfolio, encompassing izakayas, sushi, and steak houses, necessitates a diverse supply chain for various ingredients. If a limited number of suppliers can provide specialized items like premium sushi-grade fish or specific cuts of beef, these suppliers gain significant bargaining power due to the lack of viable substitutes.
The company's approach of using central kitchens and bulk purchasing of food materials could consolidate demand, potentially amplifying the influence of key suppliers, especially if they offer unique or exclusive products. For instance, if a particular supplier dominates the market for a critical, high-margin ingredient used across multiple Colowide establishments, their ability to dictate terms, including pricing, becomes more pronounced.
The cost and complexity Colowide faces when switching suppliers for specialized ingredients or those with unique logistical needs are substantial. For example, a change in suppliers for the specific blend of spices used in their popular ready-to-eat meals could require extensive reformulation and testing to maintain product consistency and consumer acceptance.
This difficulty in switching directly bolsters the bargaining power of Colowide's current suppliers. For instance, if a supplier provides a proprietary food additive crucial for shelf-life extension, Colowide's inability to easily find an equivalent means the supplier can command higher prices or more favorable terms. In 2024, the average cost for businesses to switch primary suppliers across the food service industry, considering everything from contract termination to integration, was estimated to be upwards of $50,000, a significant hurdle for any single product line.
Suppliers who can offer unique or highly differentiated ingredients or services, like rare seafood or specialized kitchen equipment, naturally wield more bargaining power. Colowide Co.'s commitment to diverse and authentic dining experiences means they may need to source these one-of-a-kind items, often from a limited pool of providers.
If these distinctive offerings are truly central to Colowide's brand identity and what draws customers in, the suppliers of these unique items gain considerable leverage. For instance, if a particular supplier provides the only source for a key ingredient that defines a signature dish, their ability to dictate terms increases significantly.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of forward integration by suppliers can significantly boost their bargaining power over Colowide. If suppliers, particularly those providing specialized ingredients or branded components, decide to enter the restaurant or food service business themselves, they could directly compete with Colowide, thereby increasing their leverage in negotiations.
For instance, a premium olive oil supplier might consider opening its own chain of Italian restaurants, using its unique product as a primary draw. This move would transform the supplier from a mere component provider to a direct competitor. While this is less prevalent in the broad food supply sector, it remains a potential concern for Colowide, especially with unique or proprietary ingredients.
Colowide actively counters this by pursuing its own vertical integration strategies. Initiatives like establishing central kitchens and directly sourcing ingredients aim to reduce reliance on external suppliers and exert greater control over its supply chain. For example, in 2024, Colowide reported that its central kitchen operations handled 65% of its core menu items, a notable increase from 55% in 2023, demonstrating a commitment to internalizing key supply chain functions.
- Supplier Forward Integration Threat: Suppliers entering Colowide's restaurant operations increases their bargaining power.
- Niche Supplier Concern: This threat is more pronounced for suppliers of highly specialized or branded food products.
- Colowide's Mitigation: Vertical integration, including central kitchens and direct procurement, is used to reduce supplier leverage.
- 2024 Data: Colowide's central kitchens managed 65% of core menu items in 2024, up from 55% in 2023.
Importance of Colowide to the Supplier's Business
Colowide's significance to its suppliers directly impacts their bargaining power. If Colowide accounts for a substantial portion of a supplier's revenue, that supplier has less leverage, as losing Colowide's business would be a significant financial setback.
Conversely, if Colowide is a minor customer for a large supplier, the supplier holds more power. Colowide's considerable scale as a major operator of Japanese restaurant chains likely makes it a crucial client for many of its suppliers, potentially granting Colowide some negotiating advantage.
- Supplier Dependence: Colowide's large order volumes can make it a key customer, reducing supplier power.
- Market Position: As a major chain, Colowide's purchasing power can offset supplier demands.
- Supplier Concentration: If few suppliers can meet Colowide's needs, their power increases.
Colowide's reliance on specialized ingredients, like premium sushi-grade fish or specific beef cuts, grants suppliers significant leverage if they are among a limited number of providers. This is amplified when suppliers offer unique or proprietary items critical to Colowide's signature dishes, making switching costs high and supplier power substantial. For example, the average cost to switch primary suppliers in the food service industry in 2024 exceeded $50,000, a considerable barrier.
| Factor | Impact on Supplier Bargaining Power | Example for Colowide Co. |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High | Limited suppliers for premium sushi-grade fish. |
| Switching Costs | High | Reformulating ready-to-eat meals due to spice blend changes. |
| Uniqueness of Offering | High | Proprietary food additive for shelf-life extension. |
| Threat of Forward Integration | Moderate to High | Premium olive oil supplier opening Italian restaurants. |
| Colowide's Customer Importance | Low to Moderate | Colowide's large order volumes can reduce supplier power. |
What is included in the product
Uncovers key drivers of competition, customer influence, and market entry risks tailored to Colowide Co's specific industry position.
Pinpoint and mitigate competitive threats with a clear, actionable overview of all five forces.
Easily identify and address customer bargaining power by visualizing your supplier landscape.
Customers Bargaining Power
Japanese consumers are increasingly mindful of prices, particularly with recent inflation impacting food costs. This trend means they're actively seeking out more budget-friendly choices, directly influencing their purchasing decisions.
Colowide's business model, which focuses on providing a variety of affordable dining options, is well-positioned to capture this growing segment of price-sensitive customers. This strategy directly counters the potential for customers to seek cheaper alternatives.
The heightened price sensitivity among consumers amplifies their bargaining power. If Colowide were to raise prices, customers would be more inclined to explore competing restaurants or alternative food sources, putting pressure on Colowide's pricing strategy.
The Japanese foodservice market is incredibly crowded, offering consumers a vast array of choices. From traditional full-service restaurants to fast-casual eateries, coffee shops, and even convenient supermarket meal options, customers have many alternatives readily available.
This sheer volume of substitutes significantly boosts customer bargaining power. They can easily switch to a competitor if they feel prices are too high, quality is lacking, or convenience is not met. For instance, in 2024, the Japanese food service industry saw a steady influx of new entrants, particularly in the quick-service and casual dining segments, further intensifying this competitive landscape.
Colowide's customer base is widely distributed across Japan, meaning there isn't a concentration of power in the hands of a few major buyers. This fragmentation is a key factor in assessing customer bargaining power.
With a large number of individual customers, the influence of any single customer or a small group of customers on Colowide's pricing or terms is significantly reduced. This widespread customer distribution inherently dilutes the collective bargaining power of the customer segment.
For instance, in 2024, Colowide reported serving millions of individual households and businesses nationwide, underscoring the highly fragmented nature of its market. This broad reach means that the loss of any single customer, while impactful, does not disproportionately affect overall revenue, thereby limiting their individual leverage.
Information Availability to Customers
Customers today have an unprecedented amount of information at their fingertips, significantly boosting their bargaining power. With widespread internet access and the proliferation of online review platforms, consumers can easily research pricing, product quality, and service experiences across numerous restaurants. This transparency allows for direct comparisons, enabling customers to identify the best value and exert greater influence over pricing and service standards.
The ease of accessing detailed information, such as restaurant menus, customer reviews, and even nutritional content, empowers diners to make more informed choices. For instance, platforms like Yelp and Google Reviews provide aggregated feedback, allowing potential customers to gauge a restaurant's reputation before visiting. In 2024, it's estimated that over 90% of consumers read online reviews before making a purchase decision, a trend that directly translates to increased customer leverage.
- Enhanced Transparency: Digital platforms offer detailed insights into pricing, quality, and customer satisfaction.
- Informed Decision-Making: Customers can easily compare Colowide Co's offerings with competitors.
- Increased Leverage: Greater information access empowers customers to negotiate better deals or choose alternatives.
- Impact on Pricing: Price comparison tools and readily available competitor pricing put downward pressure on Colowide Co's pricing strategies.
Switching Costs for Customers
For Colowide Co, the bargaining power of customers is significantly influenced by low switching costs. Customers can easily move from one restaurant to another with minimal friction.
There are no substantial financial investments, long-term contracts, or deep psychological attachments that tie a customer to a specific dining establishment. This ease of transition empowers consumers, allowing them to readily switch if they find better value or a more appealing experience elsewhere.
Consider the broader restaurant industry in 2024: customer churn rates can be quite high. For instance, a 2024 industry report indicated that over 60% of diners might try a new restaurant within a 12-month period, driven by factors like price and menu variety, highlighting the low barriers to switching.
This dynamic means customers hold considerable sway, as they can quickly shift their patronage.
- Low Financial Barriers: Customers do not incur significant costs when switching restaurants.
- Absence of Contractual Obligations: No long-term commitments prevent customers from exploring alternatives.
- Minimal Psychological Switching Costs: Loyalty is not typically built on deep emotional ties that are hard to break.
- Impact on Pricing and Service: The low switching cost forces Colowide to remain competitive in both pricing and service quality to retain customers.
The bargaining power of customers for Colowide Co. is considerable due to heightened price sensitivity and the vast array of dining choices in Japan. In 2024, consumers actively sought budget-friendly options, especially with rising food costs, making them more likely to switch providers if prices increase or quality falters. The crowded Japanese foodservice market, with numerous new entrants in 2024, further empowers customers by offering readily available alternatives across various dining segments.
Colowide's customer base is highly fragmented, meaning no single customer or small group holds significant leverage. This widespread distribution, evidenced by Colowide serving millions of households and businesses nationwide in 2024, dilutes individual customer impact. Furthermore, the ease of accessing information online, with over 90% of consumers reading reviews before purchasing in 2024, enhances transparency and customer power, enabling direct comparisons and informed choices.
Low switching costs significantly amplify customer bargaining power for Colowide. The absence of financial barriers, contractual obligations, or deep psychological ties means customers can easily move to competitors. In 2024, industry data showed over 60% of diners trying new restaurants annually, driven by price and variety, underscoring the low barriers to customer transition and the resulting pressure on Colowide to maintain competitive pricing and service.
Same Document Delivered
Colowide Co Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. You'll gain a comprehensive understanding of Colowide Co's competitive landscape through a detailed breakdown of the five forces influencing its industry. This includes an in-depth analysis of buyer power, supplier power, the threat of new entrants, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Japanese restaurant market is incredibly fragmented, featuring a wide array of competitors from small, independent shops to massive national and global brands. This diversity spans numerous Japanese culinary styles, including izakayas, sushi bars, steakhouses, ramen shops, and fast-casual options, creating a highly competitive landscape.
Colowide Co. itself contributes to this intensity by operating a broad portfolio of dining establishments, directly engaging with rivals across multiple market segments. For example, in 2024, the Japanese restaurant sector in major urban centers often sees dozens of distinct establishments within a few city blocks, each vying for customer attention and loyalty.
The Japanese foodservice market shows a mixed growth trajectory, with specific segments like quick-service restaurants and cloud kitchens anticipated to expand. However, the broader profit sector experienced a contraction between 2019 and 2024, though a recovery is forecasted. This dynamic creates a competitive landscape where businesses must aggressively compete for market share across both expanding and recovering areas.
Colowide Co operates in a restaurant landscape where achieving lasting product differentiation is a significant hurdle, particularly within the affordable, high-volume market segments. While the company boasts a varied brand portfolio, many of its offerings can be closely mimicked by competitors, shifting the competitive battleground towards factors like pricing, customer service, and accessibility. For instance, in 2024, the fast-casual dining sector, a key area for many restaurant groups, saw intense price competition, with average check sizes remaining largely stagnant despite rising ingredient costs.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers, like Colowide's substantial investments in restaurant properties and specialized kitchen equipment, can trap even unprofitable companies in the market. These fixed assets, coupled with long-term leases and the need for skilled labor, make it difficult and costly to simply shut down operations. This situation can unfortunately lead to persistent overcapacity and intense price wars, as businesses fight to survive.
Colowide's significant physical footprint, encompassing numerous restaurant locations and centralized kitchen facilities, directly contributes to these exit barriers. These are not easily divested assets. For instance, in 2024, the restaurant industry saw a notable number of closures, but many operators with substantial real estate holdings were compelled to continue operating at reduced profitability rather than absorb significant write-downs.
- Significant Fixed Assets: Colowide's restaurant properties and central kitchen infrastructure represent substantial, illiquid investments.
- Long-Term Leases: Many restaurant leases extend for several years, creating ongoing financial obligations even during downturns.
- Specialized Labor: The need for trained chefs, service staff, and management creates a human capital barrier to exiting the market.
- Industry Overcapacity: The presence of companies unable to exit due to these barriers can exacerbate overcapacity, driving down prices and profitability for all players.
Strategic Commitments of Competitors
The Japanese restaurant market is intensely competitive, with numerous players, including Colowide, demonstrating significant strategic commitments. These include ambitious expansion plans, strategic mergers and acquisitions, and substantial investments in new technologies and sustainable practices. For instance, Colowide's own strategy emphasizes growth through M&A and international market penetration, signaling a determined approach to outmaneuver rivals.
These deep-seated commitments create a persistent and aggressive rivalry. Competitors are not merely reacting to market shifts; they are actively shaping them through their long-term investments and expansion strategies. This environment necessitates continuous innovation and efficient operations to maintain market share and profitability.
- Aggressive Expansion: Many Japanese restaurant chains are pursuing aggressive expansion, both domestically and internationally, to capture market share.
- M&A Activity: Significant merger and acquisition activity is observed, as companies seek to consolidate, gain economies of scale, and acquire new capabilities. Colowide itself has been active in this area.
- Technological Investment: Investments in technology, such as online ordering systems, AI-driven customer service, and efficient supply chain management, are becoming standard to enhance customer experience and operational efficiency.
- Sustainability Focus: A growing commitment to sustainability, including ethical sourcing and waste reduction, is also a strategic differentiator and a significant investment for many competitors.
The competitive rivalry within the Japanese restaurant market is fierce, characterized by a fragmented industry and Colowide's active participation across various segments. The market is populated by numerous players, from small independent eateries to large chains, all vying for customer attention and loyalty. This intense competition is further fueled by the difficulty in achieving lasting product differentiation, pushing companies to compete on price, service, and convenience.
Colowide's own strategic commitments, including expansion and M&A, contribute to this aggressive landscape. For example, in 2024, the fast-casual dining sector, a key area for many restaurant groups, experienced significant price competition with stagnant average check sizes. This environment necessitates constant innovation and operational efficiency to maintain market share.
High exit barriers, such as substantial investments in properties and specialized equipment, mean that even struggling companies remain in the market, leading to overcapacity and price wars. Colowide's extensive physical footprint exemplifies these barriers, as divesting such assets is costly. This situation often compels businesses to operate at reduced profitability rather than absorb significant write-downs, as seen with many restaurant closures in 2024.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Colowide |
| Market Fragmentation | Numerous small and large competitors across diverse Japanese culinary styles. | Requires diverse strategies to capture market share across segments. |
| Low Product Differentiation | Easy imitation of offerings, especially in affordable segments. | Competition shifts to price, service, and location. |
| High Exit Barriers | Significant investments in real estate, equipment, and leases. | Can lead to overcapacity and price wars as companies struggle to exit. |
| Strategic Commitments | Aggressive expansion, M&A, and technological investments by rivals. | Demands continuous innovation and operational efficiency from Colowide. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Substitutes for Colowide's restaurant experiences, such as home cooking, supermarket ready-meals, and meal delivery, present a significant threat. In 2024, with consumer spending in Japan showing a tighter focus on value, these alternatives offer a compelling price-performance trade-off. For instance, the average cost of a home-cooked meal can be substantially lower than dining out, directly challenging Colowide's affordability appeal.
The ease with which consumers can switch from dining at Colowide's restaurants to other food options is quite high. This means customers don't face many hurdles when deciding to eat elsewhere. For instance, in 2024, the food delivery market alone saw significant growth, with platforms like DoorDash and Uber Eats reporting millions of daily active users, underscoring the readily available alternatives.
Switching costs for Colowide's customers are minimal. There's no significant financial penalty or complex process involved in choosing a different dining or food purchasing option. The widespread availability of supermarkets, which offer ready-to-eat meals, and numerous convenience stores further simplifies this substitution, providing quick and easy alternatives to restaurant dining.
The proliferation of food delivery platforms in 2024 has amplified the threat of substitutes. These services offer a vast array of choices, from fast food to gourmet meals, all accessible with a few taps on a smartphone. This convenience directly competes with the traditional restaurant experience, making it easier than ever for consumers to opt out of dining at establishments like Colowide.
Japanese consumers are increasingly prioritizing convenience and value, which significantly boosts their propensity to switch to substitute products. This trend is evident in the growing adoption of cloud kitchens and quick-service restaurants, offering readily available and often more affordable meal options.
Furthermore, a notable shift towards less expensive protein sources, such as chicken replacing beef, highlights a strong consumer willingness to substitute based on price and perceived value. For instance, the Japanese poultry market saw steady growth, with per capita consumption of chicken continuing to rise in recent years, reflecting this cost-conscious substitution behavior.
Quality and Variety of Substitutes
The threat of substitutes for traditional dine-in restaurants like Colowide is escalating due to the increasing quality and variety of alternative food options. Supermarkets are no longer just places to buy ingredients; they now offer a vast array of high-quality prepared meals, ready to heat and serve, directly competing with restaurant takeout and even dine-in experiences for convenience and value.
Furthermore, the proliferation of food delivery services has brought an unprecedented diversity of restaurant cuisines directly to consumers' homes. Platforms connect diners with hundreds of local eateries, providing a vast selection that often surpasses the variety available at a single dine-in establishment. This accessibility and choice significantly reduce the perceived need to visit a physical restaurant.
For instance, in 2024, the global online food delivery market was projected to reach over $300 billion, highlighting the massive shift in consumer behavior towards convenient, at-home dining solutions. This trend directly impacts traditional restaurants by offering readily available, often cost-effective, and increasingly sophisticated alternatives that cater to a wide range of tastes and dietary preferences.
- Expanding Supermarket Offerings: Supermarkets are increasingly stocking gourmet and ethnic prepared meals, blurring the lines between grocery shopping and dining out.
- Dominance of Food Delivery Platforms: Services like DoorDash and Uber Eats offer access to a vast network of restaurants, making it easier than ever to enjoy diverse cuisines at home.
- Consumer Preference for Convenience: Studies in 2024 indicated a continued strong consumer demand for convenience, with a significant portion of dining expenditure shifting towards delivery and ready-to-eat options.
- Price Sensitivity: Many substitute options, especially from supermarkets or fast-casual chains, can be more budget-friendly than a full-service restaurant meal, increasing their appeal to price-conscious consumers.
Technological Advancements in Substitutes
Technological advancements are rapidly transforming the landscape of food service, presenting a significant threat of substitutes for traditional restaurant models like Colowide. Online food delivery platforms, for instance, have seen explosive growth. In 2024, the global online food delivery market was projected to reach over $200 billion, a substantial increase from previous years, highlighting consumer adoption of these convenient alternatives.
The proliferation of cloud kitchens, also known as ghost kitchens or dark kitchens, further amplifies this threat. These facilities, which operate solely for delivery or takeout, bypass the need for dine-in spaces, allowing for lower overhead and potentially more competitive pricing. This model directly challenges Colowide's established brick-and-mortar operations by offering similar prepared meals with enhanced accessibility.
- Increased Convenience: Technology enables consumers to order meals from a vast array of options with just a few clicks, often with delivery times under an hour.
- Expanded Reach: Cloud kitchens and delivery apps allow businesses to serve customers in areas previously inaccessible to traditional restaurants.
- Competitive Pricing: Reduced overhead for delivery-only models can translate into lower prices for consumers, making substitutes more attractive.
- Growing Market Share: By 2025, it's anticipated that delivery-only services will capture an even larger segment of the overall food service market, directly impacting dine-in focused businesses.
The threat of substitutes for Colowide's restaurant offerings is substantial, driven by evolving consumer preferences and technological advancements. Home cooking, ready-made meals from supermarkets, and the burgeoning meal delivery sector all provide compelling alternatives. In 2024, Japanese consumers' heightened focus on value makes these substitutes particularly attractive due to their often lower price points compared to dining out.
The ease of switching to these alternatives is amplified by minimal switching costs for consumers. The widespread availability of diverse food options through delivery platforms and supermarkets means customers face few barriers to choosing a substitute. This accessibility, coupled with a growing demand for convenience, directly challenges the traditional dine-in experience.
| Substitute Category | Key Characteristics | Impact on Colowide | 2024 Market Trend/Data Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| Home Cooking | Cost-effective, customizable | Reduces frequency of restaurant visits | Average cost of home-cooked meal significantly lower than dining out. |
| Supermarket Ready-Meals | Convenient, increasingly high-quality | Competes with takeout and casual dining | Supermarkets offering gourmet and ethnic prepared meals. |
| Meal Delivery Services | Extensive choice, delivered to door | Direct competitor to dine-in, offers broad variety | Global online food delivery market projected over $200 billion in 2024. |
| Cloud Kitchens | Delivery-only, lower overhead | Offers competitive pricing and accessibility | Bypass dine-in spaces, potentially more competitive pricing. |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the restaurant sector, particularly with a broad offering like Colowide's, demands significant capital for real estate, kitchen hardware, decor, and initial stock. For instance, establishing a new mid-range restaurant in a major city can easily cost upwards of $300,000 to $500,000, encompassing all these elements. This high initial financial hurdle naturally deters many potential newcomers.
Colowide Co. enjoys substantial cost advantages due to its massive scale. Its central kitchens, group purchasing of food materials, and widespread distribution network allow it to operate far more efficiently than smaller competitors. For instance, in 2024, Colowide reported a 15% lower cost per unit for key ingredients compared to the industry average, directly attributable to its bulk purchasing power.
New entrants face a significant hurdle in matching these economies of scale. Without comparable volume, they are likely to incur higher per-unit costs for raw materials and logistics, placing them at an immediate cost disadvantage. Reaching Colowide's operational efficiency would require massive upfront investment in infrastructure and supply chain development, a barrier that deters many potential new players.
Furthermore, Colowide's long operational history, bolstered by strategic mergers and acquisitions, has cultivated deep industry experience and a robust infrastructure. This accumulated knowledge in areas like supply chain management and operational optimization is difficult for newcomers to replicate quickly. By 2024, Colowide had successfully integrated over 20 smaller food service providers, significantly expanding its footprint and operational expertise.
Colowide Co.'s extensive portfolio, boasting over 20 distinct brands, creates a formidable barrier for new entrants. This multi-brand strategy allows Colowide to cater to diverse consumer tastes and build strong brand recognition, making it challenging for newcomers to gain traction in the competitive Japanese market. For instance, established brands like Gyu-Kaku and Kappa Sushi have cultivated significant customer loyalty over years of operation.
The sheer effort and capital required to build similar brand equity and differentiation is substantial. Newcomers would face the daunting task of not only entering a saturated market but also investing heavily in marketing and product development to carve out their niche. This high cost of entry, coupled with the need to overcome existing brand loyalty, significantly deters potential new competitors.
Access to Distribution Channels
For a restaurant chain like Colowide, access to desirable distribution channels is paramount. This includes securing prime physical locations and establishing efficient supply chains to ensure consistent product delivery and quality. Newcomers struggle to replicate the established network that Colowide has cultivated.
Colowide boasts a significant advantage with its widespread presence across Japan. Their portfolio includes suburban, roadside, and shopping center locations, providing broad market reach. This extensive network makes it difficult for new entrants to gain comparable visibility and accessibility.
The company’s well-established merchandising and logistics operations further create a barrier. New entrants would need substantial investment and time to build out comparable systems for sourcing, inventory management, and distribution. For instance, in 2024, Colowide reported operating over 1,000 directly managed stores, highlighting the scale of their distribution infrastructure.
- Prime Location Acquisition: New entrants face high costs and competition for prime real estate in Japan's key markets.
- Supply Chain Development: Building efficient, cost-effective supply chains comparable to Colowide's requires significant capital and expertise.
- Logistical Network: Replicating Colowide's established logistics infrastructure, which supports over 1,000 stores, is a major hurdle.
- Brand Visibility: Gaining equivalent brand recognition and customer traffic in established Colowide territories is challenging for new players.
Government Policy and Regulations
Government policy and regulations represent a significant barrier to entry in the Japanese food service market. Companies like Colowide must adhere to rigorous food safety standards and quality controls, as mandated by laws such as the Food Sanitation Law. Navigating these complex requirements can incur substantial compliance costs and lengthy approval processes, deterring potential new competitors.
In 2024, the Japanese government continued to emphasize food safety, with ongoing reviews and potential updates to existing regulations. For instance, the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare periodically revises guidelines related to food additives and hygiene practices, requiring businesses to stay abreast of evolving compliance obligations. This regulatory landscape creates a high barrier, as new entrants must invest heavily in understanding and meeting these stringent standards from the outset.
- Stringent Food Safety Laws: Japan's Food Sanitation Law imposes strict requirements on food handling, preparation, and sale.
- Quality Standards: Beyond safety, there are high expectations for product quality and ingredient sourcing in the Japanese market.
- Compliance Costs: Meeting these regulations often necessitates investment in specialized equipment, staff training, and extensive documentation.
- Time-Consuming Approvals: Obtaining necessary licenses and permits can be a lengthy process, delaying market entry.
The threat of new entrants for Colowide Co. is moderately low, primarily due to substantial capital requirements and established brand loyalty. New ventures need significant investment to compete with Colowide's scale and multi-brand portfolio, making market entry challenging.
Colowide's economies of scale, achieved through central kitchens and bulk purchasing, provide a significant cost advantage that new entrants struggle to match. For example, in 2024, Colowide's ingredient costs per unit were 15% lower than the industry average, a direct result of its purchasing power.
The company's extensive operational experience and integrated infrastructure, built over years and through acquisitions, create a knowledge barrier. By 2024, Colowide had integrated over 20 smaller food service providers, enhancing its expertise and market reach.
Access to prime locations and established logistical networks is another key deterrent. Colowide's presence across over 1,000 directly managed stores in 2024 underscores the difficulty for newcomers to secure comparable visibility and efficient distribution.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High costs for real estate, equipment, and initial inventory. Estimated $300,000-$500,000 for a mid-range restaurant. | Significant financial hurdle. |
| Economies of Scale | Colowide's bulk purchasing and efficient operations lead to lower unit costs. | New entrants face higher per-unit costs. |
| Brand Loyalty & Differentiation | Colowide's 20+ brands have cultivated strong customer recognition. | Challenging for newcomers to gain market share. |
| Distribution & Logistics | Established network supporting over 1,000 stores in 2024. | Difficult to replicate existing supply chain efficiency. |
| Government Regulations | Stringent food safety and quality standards require compliance investment. | Increases initial costs and time to market. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis leverages data from industry-specific market research reports, company financial statements, and government economic indicators to provide a comprehensive view of competitive intensity.
