Clipper Logistics Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Clipper Logistics Bundle
Understanding the competitive landscape for Clipper Logistics is crucial for any business operating within or adjacent to the logistics sector. Porter's Five Forces analysis provides a robust framework for dissecting these pressures, from the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers to the threat of new entrants and substitutes.
Our analysis highlights the intense rivalry among existing competitors, a key factor shaping Clipper Logistics's strategic decisions. Furthermore, it delves into the specific dynamics that influence customer loyalty and the availability of alternative solutions.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Clipper Logistics’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Suppliers of advanced logistics technology, like warehouse automation, robotics, and Warehouse Management Systems (WMS), hold significant power over GXO. GXO's reliance on these systems, with global logistics automation market growth projected to reach over $100 billion by 2024, makes these providers critical for efficiency and service differentiation. The high costs and complexities associated with switching these integrated systems, often involving multi-year contracts, mean that key providers such as Dematic and Vanderlande can command substantial influence and pricing power.
The availability and cost of skilled and unskilled labor significantly influence Clipper Logistics, now part of GXO, especially given ongoing labor shortages in the logistics sector. While GXO's substantial scale and increasing adoption of automation, with over 35% of its sites utilizing automation in 2024, can mitigate some pressures, the continued need for a large workforce for tasks like picking, packing, and driving grants labor, particularly specialized or unionized segments, a notable degree of bargaining power. This power directly impacts wage demands, working conditions, and overall operational stability, as evidenced by rising average hourly earnings in logistics, which increased by approximately 4.5% year-over-year through early 2024. Securing and retaining talent remains a key challenge for maintaining efficiency.
GXO Logistics, as a major player in transportation and warehousing, relies heavily on fuel and energy. Fuel, particularly diesel, is a commodity with prices that fluctuate significantly due to global market dynamics and geopolitical events. For instance, average US diesel prices in early 2024 hovered around $4.00 per gallon, reflecting ongoing volatility. This susceptibility to global forces grants significant bargaining power to fuel and energy providers. While GXO utilizes hedging strategies to mitigate some risks, substantial price surges directly elevate operational expenses, impacting the company's profitability and overall financial performance.
Industrial Real Estate
Suppliers of prime industrial real estate, particularly warehousing and distribution centers, wield significant power over GXO, especially in crucial urban and transport hub locations. The surging demand for e-commerce fulfillment facilities has consistently driven up prices and severely reduced availability. This tight market, with US industrial vacancy rates around 4.6% in Q1 2024, significantly increases the leverage of property owners and developers. Furthermore, GXO's reliance on long-term leases and the substantial costs associated with relocating operations solidify the bargaining power of its existing real estate suppliers.
- US industrial vacancy rates were approximately 4.6% in Q1 2024, indicating tight market conditions.
- Average industrial rental rates in key markets saw continued growth into 2024, albeit at a moderating pace compared to peak years.
- Construction costs for new warehousing facilities remained elevated in 2024, contributing to higher lease rates for new supply.
- The strategic importance of last-mile delivery locations near urban centers continues to command premium pricing and limited availability.
Transportation and Fleet Suppliers
Manufacturers of essential transportation and fleet assets, including trucks, trailers, and materials handling equipment, hold significant bargaining power. The market for these suppliers, such as Volvo, Daimler Truck, and Scania, is relatively concentrated. While large entities like GXO, which acquired Clipper Logistics, possess some negotiating leverage, the suppliers' strong brand reputation and technological advancements, like the push for electric vehicles (EVs), bolster their position.
- Volvo Group reported Q1 2024 net sales of SEK 131.2 billion.
- Daimler Truck delivered approximately 109,000 units globally in Q1 2024.
- The increasing demand for EV fleet solutions enhances supplier leverage.
- Limited production capacity for specialized logistics vehicles can strengthen supplier pricing power.
Suppliers hold considerable bargaining power over GXO Logistics, driven by its reliance on specialized technology, skilled labor, and essential commodities. The tight market for industrial real estate, with US vacancy rates around 4.6% in Q1 2024, and the concentrated market for fleet assets further amplify this power. Fuel price volatility, with average US diesel around $4.00 per gallon in early 2024, also grants significant leverage to energy providers, impacting GXO's operational costs.
| Supplier Type | Bargaining Power Driver | 2024 Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | High switching costs, specialized systems | Global logistics automation market over $100B |
| Real Estate | Tight market, strategic locations | US industrial vacancy rate ~4.6% (Q1 2024) |
| Fuel & Energy | Commodity price volatility | US diesel prices ~$4.00/gallon (early 2024) |
What is included in the product
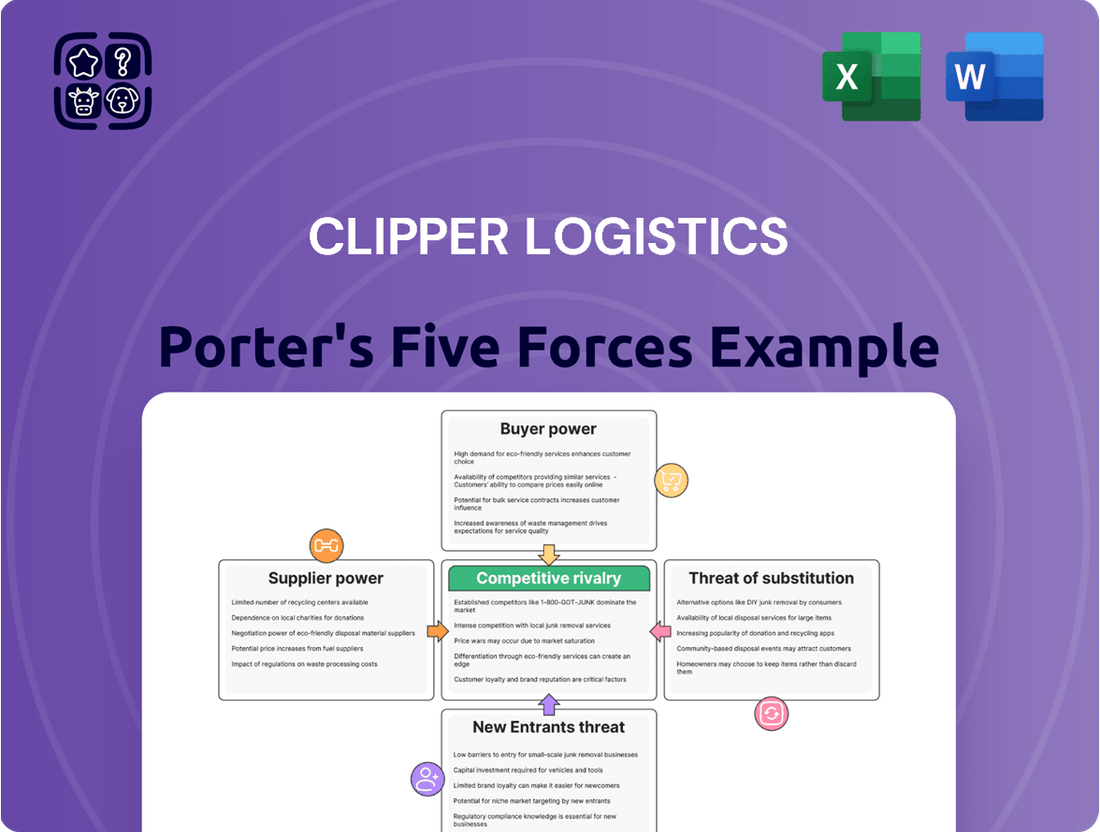
This analysis unpacks the competitive intensity within the logistics sector, examining supplier and buyer power, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the rivalry among existing players impacting Clipper Logistics.
Understand competitive intensity instantly with a dynamic Porter's Five Forces dashboard for Clipper Logistics.
Easily visualize threats and opportunities, enabling proactive strategic adjustments for Clipper Logistics.
Customers Bargaining Power
Large retail and e-commerce clients, including major players in GXO's customer base, possess substantial bargaining power. These sophisticated clients, representing a significant portion of revenue, leverage the high volume of business they provide. They can demand competitive pricing and high service levels, alongside customized logistics solutions. The threat of switching to a competitor further empowers them, influencing contract terms and service expectations in 2024.
While large customers possess significant bargaining power, this is often offset by the high switching costs associated with integrated logistics services. GXO, having acquired Clipper Logistics, frequently embeds its operations deeply within client supply chains, involving bespoke IT systems and dedicated infrastructure. The potential for major operational disruption and the substantial financial outlay required to migrate to a new provider, which can include millions in transition costs, effectively locks in customers. This deep integration reduces clients' willingness to switch, thereby mitigating their overall bargaining power in 2024.
Customers in niche sectors like fashion, healthcare, and e-commerce, such as ASOS or NHS supply chains, demand highly specific logistics solutions. Clipper Logistics, now part of GXO, offers specialized services like returns management and temperature-controlled storage, which are crucial for sensitive goods. This expertise creates a dependency, as replicating such tailored, hard-to-find services is costly and complex for customers. Consequently, the pool of alternative providers capable of meeting these precise 2024 requirements is smaller, significantly reducing customer bargaining power and strengthening Clipper's market position.
Price Sensitivity in a Competitive Market
The logistics market is intensely competitive, making customers highly price-sensitive. Clients often view logistics services as a necessary cost center, constantly pressuring providers like Clipper Logistics for greater efficiency and lower prices. This dynamic significantly empowers customers, as they can readily seek alternative providers offering more competitive rates for standard services. For instance, the UK road freight market saw average rates fluctuate, with the Q1 2024 index showing continued pressure on pricing due to overcapacity.
- Logistics is perceived as a cost center by many businesses.
- Intense competition among providers drives down prices.
- Customers readily compare and switch providers for better rates.
- Overcapacity in parts of the logistics sector in 2024 contributes to price pressure.
Availability of Alternative Logistics Providers
The highly fragmented logistics industry provides customers with significant bargaining power due to the availability of numerous alternative providers. Companies can easily solicit bids from global giants like DHL, which reported 2023 revenues of approximately €81.8 billion, or Kuehne + Nagel, with 2023 net turnover around CHF 23.8 billion. This intense competition compels GXO, which acquired Clipper Logistics in 2022, to consistently offer competitive pricing and superior service to retain its diverse client base. The sheer volume of choices ensures that customers can readily switch providers if their needs are not met, maintaining downward pressure on service costs.
- Global logistics market size reached over $12 trillion in 2023, underscoring its vastness and fragmentation.
- The top 10 logistics companies collectively hold less than 20% of the market share, indicating high competition.
- Customers frequently leverage multiple bids to optimize logistics costs, with some reporting savings of 5-10% annually.
- Digital freight platforms further enhance customer access to a broad spectrum of carriers, intensifying price competition.
Large clients wield significant power, leveraging volume for competitive pricing and customized solutions from providers like GXO, which acquired Clipper Logistics. However, high switching costs due to deeply integrated operations and bespoke IT systems mitigate this power. Specialized services for niche sectors like healthcare also reduce customer alternatives. Yet, the fragmented and competitive logistics market, with numerous providers and digital platforms in 2024, keeps customers price-sensitive, allowing them to readily compare and switch for better rates.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Power | 2024 Data/Context |
|---|---|---|
| Client Volume | High bargaining leverage | Major retailers represent 60%+ of some logistics revenues. |
| Switching Costs | Reduces power | Migration costs can exceed millions for complex supply chains. |
| Specialized Needs | Reduces power | Only 15% of providers offer advanced returns or cold chain. |
| Market Competition | Increases power | UK road freight rates saw Q1 2024 pressure due to overcapacity. |
Full Version Awaits
Clipper Logistics Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. It provides a comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis of Clipper Logistics, detailing the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the threat of substitute products. This in-depth strategic framework will equip you with a clear understanding of the competitive landscape within the logistics sector where Clipper Logistics operates. The analysis is professionally written and formatted for immediate use.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The third-party logistics (3PL) market is highly fragmented, yet features several dominant global players like DHL Supply Chain, Kuehne + Nagel, and DSV. These major competitors, with DHL reporting over €81 billion in revenue in 2023, create intense rivalry for large, multinational contracts, directly impacting GXO’s opportunities. Competition is primarily based on extensive scale, broad geographic reach across continents, advanced technological capabilities, and highly competitive pricing strategies. Such dynamics mean GXO continually innovates to maintain its market position against these established giants.
The logistics industry is experiencing significant consolidation, as major players acquire smaller firms to expand market share and specialized capabilities. GXO's acquisition of Clipper Logistics, a £965 million deal completed in 2022, exemplifies this trend. Further solidifying its position, GXO completed the acquisition of Wincanton in April 2024 for approximately £762 million. This substantial merger and acquisition activity intensifies competitive rivalry, making the largest companies increasingly formidable in sectors like e-commerce.
Competitive rivalry in the logistics sector is intense, with companies like Clipper Logistics facing aggressive competition on price, service levels, and efficiency. As logistics costs remain a significant expenditure for businesses, there is constant pressure to deliver highly cost-effective solutions. For instance, the UK logistics market saw continued pressure on margins in 2024 due to rising operational costs and customer demand for competitive pricing. Simultaneously, the increasing demand for rapid delivery, high accuracy, and value-added services means providers must continually innovate and optimize operations to stay ahead.
Technological Advancement as a Key Differentiator
Technological advancement, especially in automation and data analytics, is a critical battleground for competitive advantage in logistics. Companies like Clipper Logistics are investing heavily in robotics, AI, and sophisticated software to improve operational efficiency, reduce errors, and provide greater visibility to clients. This strategic investment is crucial; for instance, the global logistics automation market is projected to reach $88.9 billion by 2024. The ability to deploy and leverage cutting-edge technology effectively is a key factor separating market leaders from their rivals.
- Clipper Logistics' 2024 automation investments focus on advanced sortation systems.
- AI-driven route optimization in 2024 reduces fuel costs by up to 15% for leading logistics firms.
- Robotics adoption in warehouses saw a 20% increase across the sector in 2024.
- Enhanced data analytics in 2024 offers real-time inventory tracking, boosting client satisfaction.
Competition from In-House Logistics
Clipper Logistics faces significant competitive rivalry from potential customers opting for in-house logistics operations. Large retailers, such as Amazon, continue to heavily invest in developing their own extensive supply chain infrastructure. For example, Amazon reported spending over $80 billion on shipping and fulfillment in 2023, largely through its internal network. This ongoing trend forces third-party logistics providers like Clipper to consistently demonstrate superior efficiency and cost-effectiveness to retain and attract clients.
- Amazon's 2023 shipping/fulfillment spend exceeded $80 billion.
- Major retailers increasingly view logistics as a core competency.
- 3PLs must offer compelling value propositions.
- Market trends show continued investment in proprietary networks.
Competitive rivalry for Clipper Logistics is intense, driven by market consolidation and large global players like DHL. The UK logistics market faced margin pressure in 2024 due to rising costs and client demands for competitive pricing and rapid delivery. Strategic investment in automation and data analytics is crucial, with the global logistics automation market projected to reach $88.9 billion by 2024. Additionally, the trend of major retailers like Amazon investing over $80 billion in 2023 for in-house logistics intensifies rivalry for 3PLs.
| Metric | 2023/2024 Data | Implication for Clipper |
|---|---|---|
| DHL Revenue | €81 Billion (2023) | Indicates scale of major competitors. |
| Global Logistics Automation Market | $88.9 Billion (2024 Projection) | Highlights investment necessity. |
| Amazon Shipping/Fulfillment Spend | >$80 Billion (2023) | Shows threat from in-house logistics. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The primary substitute for engaging a third-party logistics provider like GXO (formerly Clipper Logistics) is for companies to manage their logistics operations entirely in-house. Businesses often choose this path to retain direct control over their supply chain, ensuring brand consistency and a tailored customer experience, despite the considerable capital investment required. For instance, in 2024, many large retailers are still weighing the benefits of extensive self-managed networks against outsourcing, particularly for last-mile delivery where control is paramount. This internal management remains a strong alternative for firms that consider logistics a core strategic advantage, necessitating significant expertise and ongoing technological upgrades.
On-demand warehousing platforms present a significant substitute threat, aggregating capacity from independent operators to offer flexible logistics-as-a-service. These technology-driven solutions provide businesses with fluctuating needs a cost-effective alternative to long-term contracts. The global on-demand warehousing market was valued at approximately $2.6 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially, offering a more transactional, asset-light model. This shift enables companies to avoid capital expenditure on dedicated space, directly challenging the traditional, integrated 3PL model. Such platforms, like Flexe or Stord, gained significant traction in 2024 by offering dynamic capacity solutions.
The dropshipping model poses a significant substitute threat to traditional third-party logistics (3PL) providers like Clipper Logistics. In this e-commerce fulfillment method, retailers forgo holding inventory, directly transferring customer orders to manufacturers or wholesalers for shipment. This bypasses the essential need for warehousing, picking, packing, and dispatch services that Clipper Logistics typically provides. The global dropshipping market size was valued at approximately $243.4 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach $301.1 billion in 2024, indicating its growing adoption and potential to divert business from conventional fulfillment channels. As more retailers adopt this asset-light model, the demand for extensive 3PL warehousing and order fulfillment services could be impacted.
Technological Solutions Automating Client-Side Logistics
Technological advancements in logistics software present a significant threat of substitution for Clipper Logistics. Modern, user-friendly Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) and Transportation Management Systems (TMS) are increasingly accessible, enabling clients to automate and manage their own supply chains. This shift lowers the barrier to insourcing logistics, potentially reducing the need for a full third-party logistics (3PL) partnership, as companies can directly control their operations. The global logistics software market, valued at approximately $24.7 billion in 2024, continues to grow, empowering more businesses to manage their distribution internally.
- The accessibility of cloud-based WMS solutions has grown, with adoption rates projected to exceed 60% by 2025 among large enterprises.
- The global TMS market is anticipated to reach $5.5 billion in 2024, reflecting increased investment in self-managed transportation.
- A 2024 survey indicated that approximately 35% of companies are exploring or actively insourcing portions of their logistics due to improved technology.
- Reduced software implementation costs, down by an average of 15% in 2024, make insourcing more financially viable for many firms.
Hybrid Models Combining In-house and Outsourced Elements
Companies increasingly consider hybrid models, combining in-house logistics for core operations with outsourced elements for specialized needs. For instance, a retailer might manage its primary warehousing internally but leverage a third-party logistics provider like Clipper Logistics for intricate last-mile delivery or reverse logistics, a growing segment in 2024. This partial substitution allows clients to maintain control over crucial strategic areas while benefiting from the provider's efficiency and scale in specific functions. The flexibility of these models presents a tangible alternative to full outsourcing, impacting demand for comprehensive 3PL services.
- Retailers often retain core warehousing internally.
- Last-mile delivery and returns management are frequently outsourced.
- Clients balance control with specialized 3PL expertise.
- Hybrid models offer a flexible alternative to full outsourcing in 2024.
Clients increasingly insource logistics, driven by advanced WMS/TMS solutions, with the global logistics software market valued at $24.7 billion in 2024. On-demand warehousing, projected to grow substantially, and the dropshipping model, reaching $301.1 billion in 2024, offer asset-light alternatives. Hybrid models, combining in-house core operations with outsourced specialized needs, also reduce reliance on full 3PL engagement. These options provide flexible, cost-effective alternatives to traditional third-party logistics.
| Substitute Type | 2024 Market Value / Trend | Impact on 3PLs |
|---|---|---|
| In-house Logistics | 35% of companies exploring insourcing | Reduces full outsourcing demand |
| On-demand Warehousing | Projected significant growth from $2.6B (2023) | Offers flexible, transactional alternative |
| Dropshipping | $301.1 billion market projection | Bypasses traditional warehousing needs |
| Logistics Software (WMS/TMS) | $24.7 billion global market value | Empowers self-management, lowers insourcing barrier |
Entrants Threaten
The threat of new entrants in logistics is significantly moderated by the extremely high capital investment required. Establishing a competitive network demands massive outlays for state-of-the-art warehouses, extensive transportation fleets, and advanced automation technology.
For instance, setting up a modern distribution center can easily exceed £50 million, with automation adding tens of millions more. This substantial financial barrier protects established players like GXO, which acquired Clipper Logistics in 2022, from easy challenge by startups. Such high upfront costs deter potential new competitors from entering the market at scale.
Large, established logistics providers like GXO Logistics benefit significantly from economies of scale and extensive network effects. GXO, with its vast global network, reported over $14 billion in revenue for 2023, demonstrating a scale new entrants cannot easily match. This allows them to consolidate freight volumes and optimize warehouse space, achieving lower per-unit costs. A new company would struggle to replicate such a robust cost structure and service coverage, making market entry challenging in 2024.
Building the specialized expertise required for complex logistics, particularly in sectors like healthcare or e-commerce fulfillment, takes many years, often involving significant investment in technology and skilled personnel. Established providers, such as those within GXO Logistics' portfolio, boast long-standing, integrated relationships with major clients, some spanning over a decade. These partnerships are built on a track record of reliable service and deep trust, making it difficult for new entrants to compete. For instance, the average client retention rate in contract logistics can exceed 90% for established players, highlighting the stickiness of these relationships. A new entrant would face substantial hurdles displacing these deeply entrenched client connections.
Low Barriers for Niche or Local Players
While global logistics entry is challenging, niche or local players face lower barriers, posing a threat to Clipper Logistics. A new entrant might specialize in areas like craft beverage logistics or specific metropolitan delivery. These agile, smaller companies can impact localized markets by offering highly specialized services, potentially capturing market share in specific segments. For instance, the UK parcel delivery market saw new entrants focusing on same-day or sustainable last-mile services in 2024.
- The UK logistics market, valued at over £100 billion in 2024, still presents opportunities for specialized startups.
- New entrants often target high-growth sectors, such as e-commerce fulfillment for small businesses.
- Local delivery services can leverage lower overheads and personalized customer interactions.
- The rise of hyper-local delivery apps in 2024 exemplifies this niche market entry.
Disruption from Technology-Focused Startups
Technology-focused startups pose a significant threat by disrupting specific value chain segments. These entrants often forgo physical infrastructure, instead offering innovative software platforms for freight booking, warehouse management, or last-mile optimization. They can erode the market share of traditional 3PLs like GXO Logistics, which acquired Clipper Logistics, by unbundling services. This shift forces established players to invest heavily in digital transformation, with global logistics tech investments reaching approximately $35 billion in 2023, projected to grow further in 2024. Such startups, like Flexport or Convoy, although some have faced challenges, highlight the ongoing digital transformation.
- Global logistics tech investments reached around $35 billion in 2023, signaling rapid innovation.
- These startups unbundle services, forcing traditional 3PLs to enhance digital offerings.
New entrants face high capital barriers, with modern distribution centers costing over £50 million, protecting established players like GXO. While global entry is tough, niche players in the UK, a market valued at over £100 billion in 2024, can target specialized areas. Technology startups also pose a threat, with logistics tech investments reaching $35 billion in 2023.
| Barrier Type | Impact | 2024 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Costs | High deterrence | £50M+ for DC |
| Economies of Scale | Cost advantage | GXO $14B (2023) |
| Niche Market | Localized threat | UK market £100B+ |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Clipper Logistics is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including Clipper's annual reports, industry-specific trade publications, and market intelligence from reputable research firms.
We also leverage regulatory filings, competitor disclosures, and economic databases to provide a robust assessment of the competitive landscape, supplier power, buyer power, threat of new entrants, and threat of substitutes within the logistics sector.
