CJ Logistics Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
CJ Logistics Bundle
CJ Logistics operates in a dynamic industry shaped by intense competition and evolving customer demands. Understanding the power of buyers and the threat of substitutes is crucial for navigating this landscape.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping CJ Logistics’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of suppliers in the logistics sector, particularly for CJ Logistics, is influenced by the availability of specialized technology. A limited number of providers offer advanced solutions such as AI-driven analytics and real-time tracking, which are critical for operational efficiency. This concentration means these tech suppliers can exert significant influence.
The reliance on a few key technology vendors allows them to potentially dictate terms and pricing. For instance, approximately 70% of logistics companies in 2023 were utilizing technology from major providers like SAP and Oracle. This widespread adoption underscores the dependency and the resultant leverage these suppliers hold, impacting costs for companies like CJ Logistics.
The availability of skilled labor, especially drivers and warehouse staff, is a major challenge for logistics firms, driving up operational costs. In 2024, the U.S. logistics sector saw labor expenses climb by an estimated 9.5% year-over-year. This scarcity of qualified drivers directly enhances the bargaining power of labor suppliers, prompting companies like CJ Logistics to explore automation solutions to mitigate workforce shortages.
CJ Logistics faces considerable supplier power due to its reliance on a limited number of key transportation and courier partners. This dependence means that if these essential suppliers increase their rates, it directly impacts CJ Logistics' operational costs and pricing strategies. For instance, the third-party logistics industry often sees companies depending on just three to five reliable providers, making them vulnerable to price hikes.
Supplier Power 4
The bargaining power of fuel suppliers is a significant factor for CJ Logistics, as fuel costs are a major operational expense. In 2024, global fuel prices saw volatility, directly impacting the cost of transportation and warehousing services. This dependence on fuel makes CJ Logistics susceptible to price hikes, as seen with the average diesel price in the US fluctuating throughout the year, often exceeding $4.00 per gallon at various points.
This vulnerability is amplified by the essential nature of fuel for all logistics operations, from trucking fleets to warehouse energy consumption. When fuel prices surge, the financial strain on companies like CJ Logistics increases, highlighting their limited ability to absorb these costs without passing them on, or facing reduced profit margins.
- Fuel Price Volatility: Fluctuations in global crude oil prices directly translate to higher operational costs for CJ Logistics in 2024.
- Essential Input: Fuel is a non-substitutable cost for core logistics functions, giving suppliers leverage.
- Impact on Margins: Rising fuel expenses in 2024 squeezed profit margins for many logistics providers, including CJ Logistics.
Supplier Power 5
The bargaining power of suppliers for CJ Logistics is influenced by the availability of specialized materials. Suppliers of unique or eco-friendly packaging, for instance, can exert greater influence because there are fewer alternatives. This is a significant factor in the logistics industry.
This leverage is amplified by industry-wide sourcing difficulties. In 2023, a substantial 60% of logistics companies indicated struggles in locating alternative suppliers for their packaging needs. This dependency allows current suppliers to potentially dictate terms and pricing more effectively.
The implications for CJ Logistics include:
- Increased material costs: Suppliers with limited competition can command higher prices for specialized packaging.
- Potential supply chain disruptions: Reliance on a few suppliers for critical materials creates vulnerability.
- Limited negotiation flexibility: Fewer alternatives reduce CJ Logistics' ability to negotiate favorable terms.
The bargaining power of suppliers for CJ Logistics is notably high due to the concentrated nature of specialized technology providers. Companies like CJ Logistics rely on a limited number of vendors for critical AI and tracking systems, giving these suppliers significant leverage. For example, in 2023, roughly 70% of logistics firms utilized technology from major players like SAP and Oracle, highlighting this dependency.
This reliance translates into potential pricing power for these tech suppliers, impacting CJ Logistics' operational costs. Furthermore, the scarcity of skilled labor, particularly drivers, saw wage increases of an estimated 9.5% year-over-year in the U.S. logistics sector in 2024. This labor shortage directly empowers labor suppliers, pushing companies to explore automation.
| Supplier Type | Key Factors Influencing Power | Impact on CJ Logistics | 2023/2024 Data Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technology Providers | Limited number of specialized vendors (AI, tracking) | Higher software/licensing costs, potential vendor lock-in | ~70% of logistics firms used major tech providers in 2023 |
| Skilled Labor (Drivers) | Labor shortages, high demand | Increased wage costs, operational disruptions | Estimated 9.5% YoY wage increase in U.S. logistics (2024) |
| Fuel Suppliers | Global price volatility, essential input | Increased transportation and operational costs | Average US diesel prices exceeded $4.00/gallon at points in 2024 |
| Specialized Packaging Suppliers | Limited alternatives, sourcing difficulties | Higher material costs, potential supply chain risks | 60% of logistics companies struggled to find alternative packaging suppliers (2023) |
What is included in the product
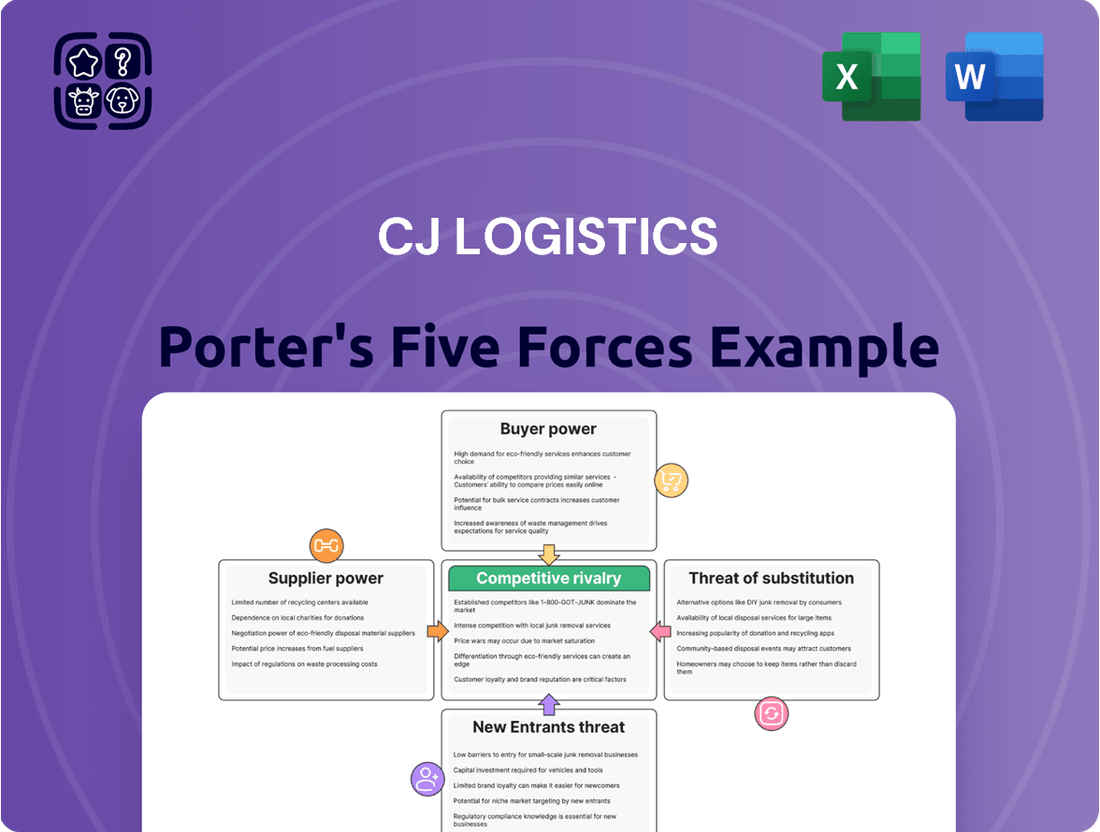
This Porter's Five Forces analysis for CJ Logistics examines the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the threat of substitute services within the logistics industry.
Navigate the complex competitive landscape of logistics with a simplified, actionable Porter's Five Forces analysis for CJ Logistics, offering immediate insights into competitive pressures.
Customers Bargaining Power
The increasing demand for speed and dependability in deliveries, fueled by the booming e-commerce sector, significantly bolsters customer bargaining power. Consumers' willingness to pay a premium for expedited shipping, with a McKinsey study revealing that 70% of them will do so, pressures logistics companies like CJ Logistics to constantly upgrade their services.
The bargaining power of customers for CJ Logistics is significant due to the highly competitive nature of the logistics industry. With over 9,551 active competitors, customers have a vast selection of providers, enabling them to easily switch if unsatisfied with pricing or service. This abundance of choice directly translates into greater leverage for customers when negotiating contracts and terms.
The sheer number of alternatives available means customers can readily compare offerings and secure more favorable deals. As the global logistics and transportation services market was projected to reach $1.3 trillion in 2023, the intense competition within this massive market further amplifies customer negotiation power. Businesses can effectively play providers against each other to achieve cost savings and better service level agreements.
Customers in the logistics sector are demanding more transparency, expecting detailed reports on everything from real-time shipment tracking to the environmental impact of their deliveries. This heightened expectation significantly strengthens their bargaining power.
Companies that can offer sophisticated data analytics and reporting often see improved customer retention, with some studies indicating rates can increase by as much as 25%. This ability to provide valuable data insights becomes a key differentiator and a lever for customers.
Buyer Power 4
The bargaining power of customers in the logistics sector, particularly for companies like CJ Logistics, is significantly amplified by the burgeoning e-commerce landscape. With a substantial portion of online purchases, often exceeding 30% in many markets, being returned, customers wield considerable influence over reverse logistics operations.
This high volume of returns necessitates that logistics providers and their clients, the e-commerce businesses, invest heavily in efficient and customer-friendly return processes. Customers are acutely aware of their leverage, as a poor returns experience can directly impact their future purchasing decisions and brand loyalty. This awareness translates into a stronger negotiating position with logistics partners regarding the cost and efficiency of handling returns.
- E-commerce Returns: Over 30% of online purchases are returned, a figure that grants significant power to consumers in shaping reverse logistics services.
- Customer Expectations: Buyers expect seamless and often free return processes, pushing logistics companies to optimize their operations.
- Negotiating Leverage: The ability to easily return goods empowers customers to demand better service and pricing from both retailers and their logistics providers.
Buyer Power 5
Large businesses and major e-commerce platforms wield considerable bargaining power over logistics providers like CJ Logistics. This is primarily due to their substantial shipping volumes, which translate into large, high-value contracts. For instance, in 2024, major retailers often account for a significant portion of a logistics company's revenue, giving them leverage.
These clients can effectively negotiate for more favorable terms, including reduced pricing and the development of customized logistics solutions tailored to their specific needs. This dynamic is crucial for CJ Logistics as it aims to secure and renew contracts with these key players, ensuring continued business and favorable financial arrangements.
- High Volume Contracts: Large clients represent a substantial portion of CJ Logistics' business, giving them significant negotiation leverage.
- Customized Solutions: Buyers demand and receive tailored services, influencing pricing and operational models.
- Price Sensitivity: Due to scale, even small percentage discounts on logistics services can result in considerable savings for large buyers.
The bargaining power of customers for CJ Logistics is substantial, driven by intense market competition and evolving consumer demands. With numerous logistics providers available, customers can easily switch, forcing companies to offer competitive pricing and superior service. This dynamic is further intensified by the growth of e-commerce, where customer expectations for speed, transparency, and efficient returns are paramount.
Major clients, particularly large e-commerce platforms, exert significant influence due to their high shipping volumes and the substantial revenue they represent. These clients can negotiate for reduced rates and customized solutions, impacting CJ Logistics' profitability and operational strategies. For example, in 2024, securing contracts with these major players often involves concessions on pricing to maintain market share.
| Factor | Impact on CJ Logistics | Supporting Data/Example (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Market Competition | High customer bargaining power | Over 9,551 active competitors in the logistics sector |
| E-commerce Growth | Increased demand for speed and returns management | 70% of consumers willing to pay more for expedited shipping |
| Customer Expectations | Demand for transparency and data analytics | Companies offering data insights can see customer retention increase by 25% |
| Volume Buyers | Significant leverage for large clients | Major retailers often constitute a large portion of a logistics provider's revenue |
| Returns Management | Customer influence over reverse logistics | Over 30% of online purchases are returned, impacting service demands |
Preview Before You Purchase
CJ Logistics Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive CJ Logistics Porter's Five Forces Analysis, detailing the competitive landscape of the logistics industry. You're looking at the actual document; once purchased, you'll gain instant access to this exact, professionally formatted analysis, ready for immediate use and strategic planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Competitive rivalry within the global logistics sector is fierce, with CJ Logistics navigating a landscape populated by over 9,551 active competitors. This high degree of fragmentation means that established giants like DHL, XPO Logistics, and UPS Supply Chain Solutions are constantly vying for market share.
The expansion of the global third-party logistics (3PL) market, projected to reach $1.7 trillion by 2027, intensifies this rivalry. As more businesses outsource their logistics needs, customer expectations for faster delivery times and greater operational transparency are escalating, putting pressure on all players to innovate and optimize.
The logistics industry is experiencing intense competitive rivalry, largely fueled by rapid technological advancements. Companies are investing heavily in AI, automation, and real-time tracking to gain an edge. These technologies are crucial for optimizing operations, boosting efficiency, and cutting costs.
CJ Logistics exemplifies this trend, demonstrating strong growth in Q1 2025. This performance was significantly driven by technology-enabled new orders and strategic investments in robotics. Such technological adoption allows logistics providers to offer superior service and competitive pricing, intensifying the rivalry among players.
The logistics industry is experiencing heightened competitive rivalry, largely driven by the explosive growth of e-commerce. As online sales continue to surge, projected to hit $7.4 trillion globally by 2025, the demand for rapid and adaptable delivery services, especially for last-mile logistics, has intensified significantly.
In response, logistics companies are pushing innovation, developing new strategies and technologies to meet these evolving customer expectations. This dynamic environment means that companies like CJ Logistics face fierce competition from both established players and emerging disruptors vying for market share in this rapidly expanding sector.
Competitive Rivalry 4
The logistics industry is experiencing heightened competitive rivalry, particularly as sustainability and Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) compliance emerge as key differentiators. Companies that proactively adopt eco-friendly practices, such as transitioning to electric vehicle fleets and optimizing delivery routes to reduce emissions, are gaining a significant competitive edge. This trend is underscored by the fact that 57% of logistics companies are targeting net-zero emissions by 2050, indicating a widespread industry commitment to greener operations.
This focus on sustainability translates into tangible competitive advantages. For instance, a logistics provider with a demonstrably lower carbon footprint can attract environmentally conscious clients, potentially securing long-term contracts. The pressure from both regulators and consumers to reduce environmental impact is intensifying, forcing all players to re-evaluate their operational strategies and invest in sustainable technologies. This creates a dynamic where innovation in eco-friendly solutions becomes a crucial battleground for market share.
- Growing Importance of ESG: Sustainability is no longer a niche concern but a core competitive factor, influencing client selection and operational investment.
- Industry-Wide Net-Zero Goals: A significant majority of logistics firms, 57%, are committed to achieving net-zero emissions by 2050, driving innovation and competition in green logistics.
- Eco-Friendly Fleet Adoption: The shift towards electric vehicles and optimized routing is a direct response to competitive pressures and regulatory demands, creating a divide between leaders and laggards.
- Consumer and Regulatory Pressure: Intensifying demand for sustainable services from both end-consumers and governing bodies compels companies to invest in and showcase their ESG credentials.
Competitive Rivalry 5
The logistics landscape is intensifying as e-commerce behemoths increasingly develop their own in-house delivery networks. In South Korea, for instance, Coupang Logistics Service's expansion directly challenges established players like CJ Logistics by capturing market share and setting new service standards.
This dynamic forces traditional logistics companies to adapt rapidly. To stay competitive and profitable, CJ Logistics must not only innovate its service offerings but also aggressively pursue international market expansion, as seen in its ongoing global growth strategies.
- E-commerce Integration: Companies like Coupang are vertically integrating logistics, directly impacting traditional providers.
- Market Share Erosion: The rise of in-house logistics for e-commerce giants directly siphons market share from incumbent logistics firms.
- Global Expansion Necessity: To counter domestic competitive pressures, companies like CJ Logistics are prioritizing overseas ventures.
- Innovation Imperative: Continuous service improvement and technological adoption are crucial for maintaining profitability in this evolving market.
Competitive rivalry in the logistics sector is intense, with over 9,551 active competitors globally, including giants like DHL and UPS. The expansion of the third-party logistics market, projected to reach $1.7 trillion by 2027, further fuels this competition, pushing companies to innovate and optimize to meet rising customer expectations for speed and transparency.
Technological advancements, particularly in AI and automation, are critical differentiators, enabling efficiency gains and cost reductions. CJ Logistics' Q1 2025 performance, driven by technology and robotics investments, highlights this trend. Sustainability is also a key battleground, with 57% of logistics companies aiming for net-zero emissions by 2050, influencing client choices and operational investments.
The rise of e-commerce, with global online sales expected to hit $7.4 trillion by 2025, intensifies the need for rapid last-mile delivery. This has led e-commerce giants like Coupang to develop in-house logistics, directly challenging established players and necessitating continuous innovation and global expansion for companies like CJ Logistics to maintain market share.
| Competitor Type | Market Share Driver | Key Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Global Logistics Giants (DHL, UPS) | Extensive networks, technology investment | Service diversification, efficiency optimization |
| E-commerce Integrated Logistics (Coupang) | In-house delivery capabilities | Vertical integration, setting new service standards |
| Tech-Focused Logistics Providers | AI, automation, real-time tracking | Operational efficiency, cost reduction, enhanced visibility |
| Sustainability-Focused Companies | ESG compliance, EV fleets | Attracting environmentally conscious clients, regulatory adherence |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Emerging alternative transport methods, like drones and bicycles for last-mile deliveries, present a significant threat of substitution for traditional logistics services. For instance, drone delivery is projected to cut logistics costs by as much as 20% in certain urban environments.
Bicycle couriers are also gaining traction as an eco-friendly alternative for navigating congested city centers, offering a nimble and sustainable approach to parcel movement.
The threat of substitutes for CJ Logistics is amplified by the growing prevalence of digital platforms that facilitate direct shipping from manufacturers to consumers. This disintermediation bypasses traditional logistics providers entirely, reducing the reliance on services like those offered by CJ Logistics. For example, e-commerce marketplaces are increasingly offering integrated fulfillment solutions, allowing sellers to ship directly without needing a third-party logistics company for warehousing and distribution.
Large corporations and e-commerce giants are increasingly developing their in-house logistics capabilities, presenting a significant substitute threat to third-party logistics (3PL) providers like CJ Logistics. Companies like Amazon, with its extensive fulfillment network, demonstrate how building internal capacity can offer greater control over the supply chain and potentially lead to cost efficiencies.
This trend is driven by a desire for direct oversight of warehousing, transportation, and last-mile delivery, allowing businesses to tailor operations to their specific needs and customer expectations. For instance, by managing their own fleets and distribution centers, companies can aim to reduce reliance on external partners and capture more value within their operations.
4
Traditional logistics providers, often offering non-eco-friendly services, present a significant threat of substitutes. These established players leverage existing networks and economies of scale, enabling them to provide services at lower price points, which is particularly appealing in cost-sensitive segments of the market.
The sheer size of the logistics industry underscores the availability of these alternatives. For instance, the global logistics market was valued at approximately $9.6 trillion in 2022, with a substantial portion of this value stemming from conventional, less environmentally focused services.
- Lower Cost: Traditional providers often undercut eco-friendly options due to established infrastructure and operational efficiencies.
- Market Penetration: Their long-standing presence means they serve a broad customer base, making them readily accessible substitutes.
- Price Sensitivity: In markets where cost is the primary decision driver, these substitutes are highly attractive.
- Scale Advantages: Economies of scale allow traditional players to absorb costs and offer competitive pricing.
5
The threat of substitutes for CJ Logistics' services is evolving, particularly with advancements in decentralized production. The increasing adoption of 3D printing technology allows for goods to be manufactured closer to consumers, potentially shortening delivery routes and diminishing the reliance on traditional logistics networks. This shift could reduce the demand for extensive transportation and warehousing, offering a viable alternative for certain product categories.
This trend implies that companies might bypass traditional logistics providers for localized production needs. For instance, in 2024, the global 3D printing market was valued at approximately $20.5 billion, with significant growth projected in industrial and consumer applications. This expansion directly impacts the volume of goods requiring traditional, long-haul logistics.
Key implications for CJ Logistics include:
- Reduced demand for last-mile delivery: As production moves closer to the end-user, the need for extensive last-mile networks may decrease.
- Shift in warehousing needs: Localized production could lessen the requirement for large, centralized distribution centers.
- Increased competition from localized solutions: Businesses may opt for in-house or local 3D printing services over outsourcing to large logistics firms.
- Potential for new service offerings: CJ Logistics could explore partnerships or services supporting localized manufacturing ecosystems.
The threat of substitutes for CJ Logistics is multifaceted, encompassing new delivery technologies, disintermediation through digital platforms, and the rise of in-house logistics capabilities by major corporations. Emerging alternatives like drone and bicycle deliveries offer cost and efficiency advantages in specific contexts, with drone delivery potentially cutting logistics costs by up to 20% in urban areas. E-commerce marketplaces increasingly integrate fulfillment, allowing direct shipping and bypassing third-party providers. For instance, Amazon's extensive network exemplifies how companies can build internal logistics, reducing reliance on external partners.
| Substitute Type | Key Characteristics | Impact on CJ Logistics | Example/Data Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| Emerging Delivery Tech | Cost savings, agility in urban areas | Potential reduction in demand for traditional last-mile services | Drone delivery cost savings up to 20% in urban settings |
| Digital Platforms/Disintermediation | Direct shipping, bypass of 3PLs | Reduced need for warehousing and distribution services | E-commerce marketplaces offering integrated fulfillment |
| In-house Logistics | Greater control, potential cost efficiencies | Loss of business from large clients | Amazon's extensive fulfillment network |
| 3D Printing/Decentralized Production | Localized manufacturing, shorter routes | Diminished reliance on long-haul transport and large distribution centers | Global 3D printing market valued at $20.5 billion in 2024 |
Entrants Threaten
The threat of new entrants in the logistics sector, particularly for a global player like CJ Logistics, is generally considered moderate. A significant barrier is the substantial initial capital required to establish the necessary infrastructure. This includes building or leasing warehouses, acquiring and maintaining a diverse transportation fleet (trucks, ships, planes), and investing in advanced technology for tracking, management, and automation. For instance, setting up a sophisticated warehousing and distribution network can easily run into tens or hundreds of millions of dollars, making it challenging for smaller entities to compete effectively.
The threat of new entrants in the logistics sector, including for a player like CJ Logistics, is generally moderate due to significant capital requirements and established infrastructure. However, advancements in technology are reshaping this landscape. By 2025, it's projected that 80% of logistics firms will be utilizing AI solutions, creating a substantial technological barrier for newcomers. Existing companies leverage AI, IoT, and blockchain for operational optimization, demanding considerable investment from potential new entrants to match this efficiency.
Established logistics providers like CJ Logistics benefit significantly from economies of scale. For instance, in 2024, major global logistics players reported substantial revenue figures, allowing them to negotiate better rates with carriers and invest in advanced technology. This cost advantage makes it challenging for new entrants to match the pricing and service levels offered by incumbents, especially in a sector often characterized by thin profit margins.
4
The threat of new entrants in the logistics sector, particularly for a major player like CJ Logistics, is generally considered moderate to low. This is primarily due to the substantial capital investment required for infrastructure, technology, and global operational capabilities.
Established players benefit from significant brand recognition and deeply entrenched customer relationships, built over many years. For instance, CJ Logistics has cultivated a reputation for reliability and comprehensive service offerings, making it difficult for newcomers to immediately attract and retain clients. This loyalty is a powerful deterrent.
Furthermore, the extensive service networks and economies of scale that companies like CJ Logistics possess create substantial barriers. Building a comparable network of warehouses, transportation fleets, and skilled personnel takes considerable time and resources. In 2024, the global logistics market, valued at trillions, is characterized by these high entry costs.
- High Capital Requirements: Setting up a global logistics operation demands significant investment in warehouses, fleets, and technology, estimated in the billions for comprehensive coverage.
- Established Brand Loyalty: Customer trust in established providers like CJ Logistics is hard-won and difficult for new entrants to replicate quickly.
- Economies of Scale: Existing large players benefit from cost efficiencies that new entrants cannot match initially, impacting pricing competitiveness.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Navigating diverse international regulations and compliance standards adds complexity and cost for new market participants.
5
The threat of new entrants in the logistics sector, specifically for a company like CJ Logistics, is moderately low due to significant regulatory and capital barriers. Navigating complex international trade agreements and adhering to stringent environmental standards, such as evolving emissions regulations for fleets, requires substantial upfront investment and expertise. For instance, the push towards greener logistics in 2024 means new players must consider investments in electric or alternative fuel vehicles, which carry higher initial costs.
Compliance with these evolving environmental mandates presents a considerable challenge.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Obtaining necessary licenses and permits for warehousing, transportation, and cross-border operations can be time-consuming and costly, especially with varying regulations across different countries.
- Environmental Standards: Increasing pressure for sustainable logistics, including stricter emissions targets and waste management protocols, necessitates significant capital outlay for compliant technologies and practices.
- Capital Intensity: Establishing a logistics network requires substantial investment in infrastructure, vehicles, technology, and skilled personnel, creating a high barrier for potential new entrants.
- Economies of Scale: Established players like CJ Logistics benefit from existing scale, which allows for more competitive pricing and operational efficiencies that are difficult for newcomers to match.
The threat of new entrants for CJ Logistics is moderate to low, primarily due to the immense capital required to establish a global logistics network. Newcomers face significant hurdles in acquiring fleets, building or leasing extensive warehouse facilities, and investing in advanced tracking and automation technologies. For example, the global logistics market, valued at over $9 trillion in 2024, demands such substantial upfront investment that it deters many potential competitors.
Beyond capital, established players like CJ Logistics benefit from strong brand recognition and long-standing customer relationships, making it difficult for new entrants to gain market share quickly. Economies of scale also play a crucial role; larger companies can negotiate better rates with carriers and suppliers, offering more competitive pricing. Furthermore, navigating the complex web of international regulations and compliance standards, including evolving environmental mandates for fleets, adds another layer of difficulty and cost for any new player entering the market.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example Data (2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Investment in infrastructure, fleets, and technology | High | Setting up a single large distribution center can cost $50M+ |
| Brand Loyalty & Relationships | Customer trust and existing contracts | Moderate | Customer retention rates for established players often exceed 90% |
| Economies of Scale | Cost advantages from large-scale operations | High | Major logistics firms report operating margins that are 2-5% higher due to scale |
| Regulatory & Compliance | Navigating international trade laws and environmental standards | Moderate | Compliance costs for emissions standards can add 5-10% to fleet operating expenses |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our CJ Logistics Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including publicly available financial reports, industry-specific market research from firms like IBISWorld, and insights from reputable business news outlets.
We leverage a combination of company disclosures, analyst reports, and government economic data to thoroughly assess the competitive landscape, supplier and buyer power, and the threat of new entrants and substitutes for CJ Logistics.
