Coventry Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Coventry Group Bundle
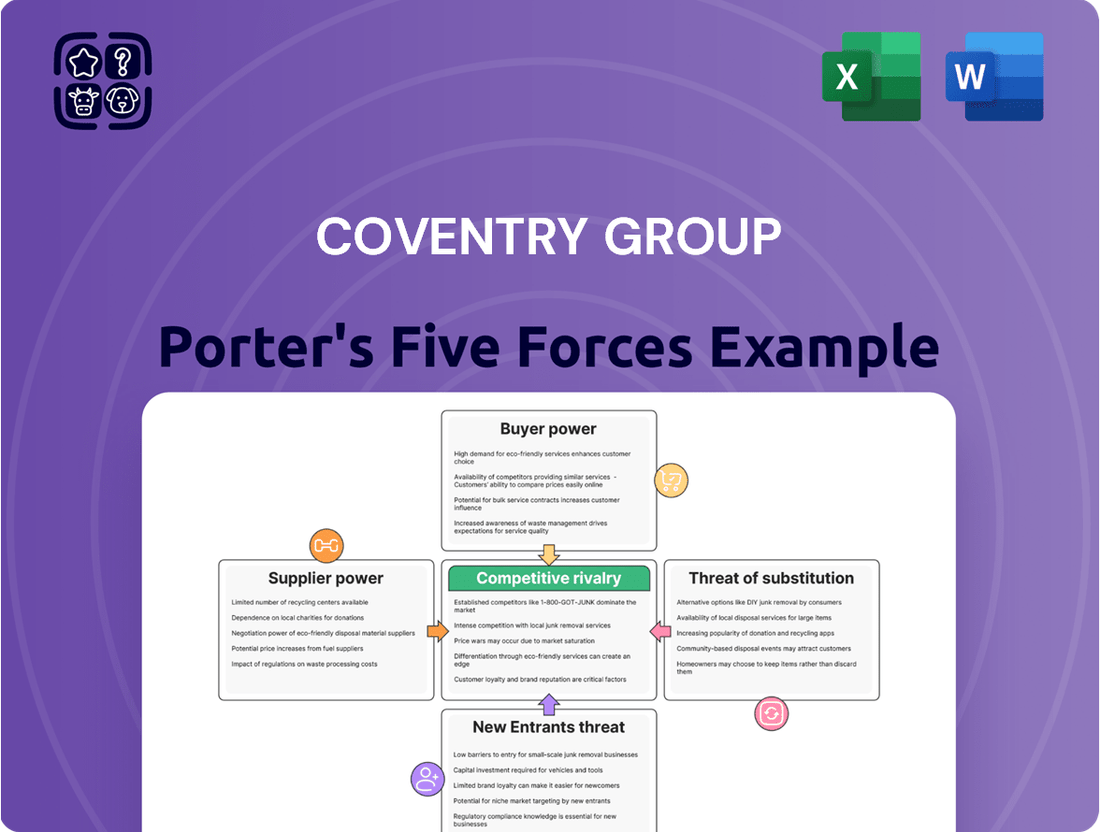
Coventry Group faces moderate competitive rivalry, with established players and potential for product differentiation. Understanding the threat of new entrants and the bargaining power of buyers is crucial for their strategic positioning.
The full Porter's Five Forces Analysis delves into the intricate details of Coventry Group's industry landscape, revealing the true intensity of each force and its impact on profitability. Unlock actionable insights to navigate these pressures and secure a competitive edge.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Supplier concentration for fasteners, industrial hardware, and fluid transfer products in Australia and New Zealand significantly impacts Coventry Group's bargaining power. A limited number of key suppliers for essential components can lead to increased pricing leverage for those suppliers, potentially raising Coventry Group's cost of goods sold.
Coventry Group's ability to switch suppliers significantly impacts their bargaining power. If it's difficult and costly for Coventry Group to change suppliers, perhaps due to specialized equipment or lengthy integration processes, suppliers gain leverage. For instance, if a new supplier requires substantial re-tooling of Coventry Group's manufacturing lines, this creates high switching costs, strengthening the supplier's position.
Conversely, if Coventry Group can easily source materials or components from multiple vendors without incurring significant expenses or disruptions, their bargaining power increases. For example, if Coventry Group's key inputs are standardized commodities readily available from numerous providers, they can more effectively negotiate pricing and terms. This flexibility is crucial for maintaining profitability and operational efficiency.
Suppliers offering highly specialized or unique products, for which there are few viable substitutes, inherently possess a stronger position in dictating terms. Coventry Group's dependence on such distinct components or proprietary technologies from a limited number of suppliers would significantly curtail its ability to negotiate favorable pricing or contract conditions.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
If suppliers possess a credible threat of integrating forward into distribution, they can directly compete with Coventry Group, thereby increasing their bargaining power. This situation can compel Coventry Group to accept less favorable terms to preserve essential supply relationships.
For instance, a key component supplier to Coventry Group might consider establishing its own retail outlets or distribution channels. Such a move would not only capture a larger share of the value chain but also put direct pressure on Coventry Group’s existing business model. In 2024, many industries saw suppliers exploring vertical integration to gain greater market control, a trend that could significantly impact companies like Coventry Group if their suppliers are similarly positioned.
- Supplier Integration Threat: Suppliers moving into distribution directly challenges Coventry Group's market presence.
- Impact on Terms: This threat forces Coventry Group to negotiate from a weaker position, potentially accepting less favorable terms.
- Industry Trend: Forward integration by suppliers is a growing concern across various sectors, as evidenced by supplier strategies observed in 2024.
Importance of Coventry Group to Suppliers
Coventry Group's significance as a customer directly impacts supplier bargaining power. If Coventry Group constitutes a large percentage of a supplier's total sales, that supplier will likely be more amenable to favorable terms to secure continued business. This is particularly relevant given the supply chain challenges Australian businesses faced in 2024, with disruptions and rising input costs persisting into 2025, making customer retention crucial for suppliers.
The bargaining power of suppliers is influenced by Coventry Group's purchasing volume and the availability of alternative suppliers. A high volume of purchases can give Coventry Group leverage to negotiate better pricing and terms. However, if there are few suppliers for essential components or raw materials, or if those suppliers have strong market positions, their bargaining power increases, potentially leading to higher costs for Coventry Group.
- Customer Dependence: Coventry Group's substantial revenue contribution to certain suppliers can lead to more favorable negotiations.
- Market Concentration: The number of available suppliers for critical inputs directly affects their individual bargaining power.
- Supply Chain Volatility: Ongoing supply chain disruptions and cost increases in 2024-2025 amplify the importance of supplier relationships for Coventry Group.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Coventry Group is shaped by the concentration of suppliers in its key markets. With a limited number of providers for specialized industrial hardware and fluid transfer products in Australia and New Zealand, these suppliers can exert significant pricing influence. This concentration was a notable factor in 2024, as companies grappled with ongoing supply chain pressures and rising input costs, making it harder for buyers like Coventry Group to negotiate favorable terms.
Coventry Group's ability to switch suppliers is a critical determinant of supplier leverage. High switching costs, stemming from specialized integration requirements or unique product specifications, empower suppliers by limiting Coventry Group's alternatives. Conversely, access to a broad base of suppliers for standardized components grants Coventry Group greater negotiation power, a flexibility that became even more valuable amidst the supply chain volatility experienced throughout 2024.
The threat of forward integration by suppliers, where they move into distribution, directly enhances their bargaining power. This strategic move by suppliers can create a competitive dynamic, forcing Coventry Group to accept less favorable terms to maintain essential supply relationships. In 2024, many suppliers across various sectors explored vertical integration, a trend that could directly impact Coventry Group if its own suppliers pursue similar strategies to gain greater market control.
Coventry Group's significance as a customer plays a key role in supplier negotiations. When Coventry Group represents a substantial portion of a supplier's sales, that supplier is more incentivized to offer favorable terms to retain the business. This customer dependence is amplified by the 2024-2025 supply chain environment, where supplier retention became a priority amidst disruptions and cost escalations.
| Factor | Impact on Coventry Group | 2024 Context |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Increases supplier leverage, potentially higher costs | Limited suppliers for specialized products in ANZ |
| Switching Costs | High costs empower suppliers; low costs empower Coventry Group | Specialized integration needs can create high switching costs |
| Forward Integration Threat | Weakens Coventry Group's negotiating position | Suppliers exploring vertical integration for market control |
| Customer Dependence | Coventry Group's volume can lead to better terms | Supplier retention crucial due to supply chain volatility |
What is included in the product
This analysis unpacks the competitive forces impacting Coventry Group, evaluating the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the intensity of rivalry, and the threat of substitutes.
Quickly identify and neutralize competitive threats with a visually intuitive breakdown of Porter's Five Forces, enabling proactive strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Coventry Group's customer concentration and the sheer volume of purchases by key clients significantly influence their bargaining power. Major players in sectors like construction, mining, and infrastructure, who represent substantial order volumes, can leverage this to negotiate more favorable pricing and service agreements. For instance, in 2024, a significant portion of Coventry Group's revenue was derived from a handful of large industrial clients, giving these customers considerable sway.
Customer switching costs significantly influence their bargaining power with Coventry Group. If customers can easily switch to another distributor of fasteners, industrial hardware, or fluid transfer products without incurring substantial expenses or facing major disruptions, their ability to negotiate better terms increases. For instance, if Coventry Group’s clients can find comparable products and services from competitors with minimal effort and cost, they hold more sway.
The presence of substitute products significantly amplifies customer bargaining power. When customers can easily switch to alternative offerings, their reliance on Coventry Group diminishes, allowing them to demand better terms and pricing.
In the Australian and New Zealand industrial fasteners market, this dynamic is evident. While the market is projected for growth, the increasing adoption of alternatives like advanced pressure-sensitive tapes and adhesives presents a direct challenge.
For instance, certain applications previously requiring mechanical fasteners can now be effectively addressed by high-strength adhesives, offering comparable performance with potential benefits in weight reduction and assembly speed.
Customer Price Sensitivity
Coventry Group's customers exhibit varying degrees of price sensitivity. This sensitivity is shaped by how much the purchased products impact their own costs and the final value of their own offerings. For instance, if a customer's core business heavily relies on Coventry's components, they might be less sensitive to minor price fluctuations. Conversely, if Coventry's products represent a significant portion of a customer's overall expenditure and are easily substitutable, price becomes a major deciding factor.
The willingness of customers to pay directly correlates with their price sensitivity. When customers are highly sensitive to price, they will actively seek out lower-cost alternatives or negotiate aggressively, putting considerable pressure on Coventry Group's profit margins. In 2024, for example, many industries faced inflationary pressures, leading to increased price scrutiny from buyers across the board, including those who purchase from Coventry.
- Customer Price Sensitivity: Directly impacts the pressure on Coventry Group's pricing strategies and profitability.
- Cost Structures: Customers whose own cost structures are tight will likely be more price-sensitive towards Coventry's offerings.
- Importance to Final Output: Products that are critical to a customer's end product may see lower price sensitivity compared to ancillary items.
- Market Conditions (2024): General economic conditions in 2024, marked by inflation and supply chain adjustments, heightened price sensitivity for many of Coventry's customer segments.
Customer Information and Transparency
Coventry Group's customers, particularly in the competitive retail and trade sectors, possess significant bargaining power when they have access to comprehensive information. This includes detailed knowledge of product pricing, the cost structures of suppliers, and a clear understanding of available alternative offerings from competitors. The more informed customers are, the more leverage they have to negotiate favorable terms.
The increasing transparency in the Australian market, driven by online platforms and consumer review sites, directly impacts Coventry Group. Customers can readily compare prices and product features, leading them to demand more competitive deals. For instance, in the building materials sector, where Coventry Group operates, price comparison tools are widely used by both professional tradespeople and DIY consumers.
- Informed Customers: Customers armed with pricing data and knowledge of alternatives can effectively challenge Coventry Group's pricing strategies.
- Market Transparency: Websites and industry reports that detail supplier costs and market benchmarks empower customers.
- Competitive Landscape: The availability of numerous substitutes for Coventry Group's products amplifies customer bargaining power.
- Negotiation Leverage: Greater information access allows customers to push for discounts, better payment terms, and enhanced service levels.
Coventry Group's customers wield significant bargaining power due to their ability to switch suppliers, especially when switching costs are low. In 2024, the industrial hardware market continued to offer numerous alternatives, allowing major clients to negotiate for better pricing and terms. The ease with which customers can source comparable products from competitors directly translates into leverage, pressuring Coventry Group to maintain competitive offerings and service levels.
The bargaining power of Coventry Group's customers is also amplified by the availability of substitute products. For example, in construction and manufacturing, advanced adhesives are increasingly replacing traditional fasteners for certain applications. This trend, evident throughout 2024, means customers have viable alternatives, reducing their dependence on Coventry's core product lines and increasing their ability to demand favorable pricing and service agreements.
Customer price sensitivity, heightened by economic conditions in 2024, further empowers buyers. When Coventry's products represent a significant portion of a customer's costs or are easily substitutable, customers become more aggressive in seeking lower prices. This was particularly true for sectors experiencing margin pressures, leading to more rigorous negotiations with suppliers like Coventry Group.
| Factor | Impact on Coventry Group | 2024 Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Low Switching Costs | Increased customer leverage for better pricing. | Many customers could readily find comparable products from competitors. |
| Availability of Substitutes | Reduced customer reliance, enabling negotiation for favorable terms. | Rise of adhesives and alternative materials challenged traditional fastener markets. |
| Price Sensitivity | Pressure on profit margins and pricing strategies. | Inflationary pressures in 2024 made buyers more cost-conscious across industries. |
Same Document Delivered
Coventry Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
The document you see is your deliverable. It’s ready for immediate use—no customization or setup required. This comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis of the Coventry Group delves into the competitive landscape, evaluating the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the industry. Understanding these forces is crucial for strategic decision-making and identifying opportunities for sustained competitive advantage.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Australian and New Zealand industrial distribution market, encompassing fasteners, industrial hardware, and fluid transfer products, is populated by a diverse array of competitors. The intensity of rivalry is significantly shaped by whether the market is fragmented with many similarly sized players or dominated by a few large entities.
Coventry Group navigates a competitive landscape, facing numerous companies within the mining and industrial machinery wholesaling, as well as hardware wholesaling sectors. For instance, in the 2023 financial year, Coventry Group reported revenue of AUD 330.5 million, highlighting its position within this competitive arena.
The growth rate within Australia and New Zealand's industrial hardware and fluid transfer sectors directly influences competitive intensity. When these markets expand, there's more room for all players, potentially easing rivalry. However, a slower growth rate, or even a contraction, forces companies to compete more aggressively for existing market share, often leading to price wars or increased marketing spend.
In 2024, the Australian fasteners market, a key segment for industrial hardware, is expected to see positive growth. This expansion suggests that while competition will remain, the overall market size is increasing, offering opportunities for companies like Coventry Group to grow their revenue and market presence without necessarily taking share directly from rivals.
Coventry Group's ability to differentiate its offerings significantly impacts competitive rivalry. By emphasizing technical expertise and a broad product range, the company aims to stand out from competitors who may focus solely on price. This strategy can foster customer loyalty and reduce the pressure of direct price wars.
Exit Barriers
Coventry Group, like many in industrial distribution, faces significant exit barriers. These can include highly specialized machinery and equipment that have little resale value outside the specific industry, making it costly for a struggling firm to simply shut down and liquidate assets. Furthermore, long-term supply agreements or customer contracts can obligate companies to continue operations even when unprofitable, simply to fulfill existing commitments. This can trap capital and resources, prolonging the presence of weaker players.
These high exit barriers often lead to intensified competitive rivalry. When firms cannot easily exit the market, they may resort to more aggressive pricing or operational strategies to cover their fixed costs and maintain market share, even if it means operating at a loss. This dynamic can suppress overall industry profitability and create a challenging environment for more efficient competitors.
For instance, in the broader industrial distribution sector, companies often invest heavily in large, dedicated warehouses and specialized logistics networks. The resale market for such assets can be very limited, representing a substantial sunk cost. In 2023, reports indicated that capital expenditures for warehousing and distribution infrastructure across various industrial sectors remained robust, suggesting ongoing investment in specialized assets that contribute to higher exit barriers.
- Specialized Assets: High investment in industry-specific machinery and infrastructure with limited alternative uses.
- Long-Term Contracts: Commitments to suppliers and customers that can prevent immediate market withdrawal.
- Operational Interdependence: Supply chains and customer relationships that are difficult to untangle quickly.
- Brand Loyalty and Reputation: The cost and time required to build and maintain a brand can be a disincentive to exit.
Market Share and Strategic Objectives
Coventry Group faces intense rivalry, with competitors often prioritizing aggressive market share expansion. For instance, in the Australian retail landscape, key players frequently engage in price wars and extensive promotional activities to capture a larger portion of the consumer market.
Coventry Group's own strategic objectives, including plans for new store openings and potential acquisitions, demonstrate an intent to actively compete and grow. This proactive approach suggests a dynamic environment where strategic maneuvers directly influence competitive intensity.
- Competitor Focus: Many rivals in the Australian retail sector are aggressively pursuing market share growth, which can lead to price competition and increased marketing spend.
- Coventry's Strategy: Coventry Group is actively expanding its footprint through new store openings and exploring acquisition opportunities, signaling a commitment to a competitive market position.
- Market Dynamics: The strategic objectives of both Coventry Group and its competitors directly shape the intensity of rivalry, influencing pricing, product offerings, and promotional efforts throughout the industry.
Competitive rivalry within Coventry Group's operating markets remains a significant factor, driven by the presence of numerous players across industrial distribution, mining, and hardware sectors. The intensity of this rivalry is further amplified by high exit barriers, such as specialized assets and long-term contracts, which can keep less profitable firms in the market, forcing them to compete aggressively. In 2024, anticipated growth in segments like Australian fasteners suggests that while competition persists, opportunities for market expansion exist for proactive companies like Coventry Group.
| Market Segment | Key Competitors (Examples) | Competitive Intensity Drivers | 2024 Outlook (Growth) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Industrial Distribution (Fasteners, Hardware) | Various Wholesalers | Market fragmentation, Price competition, Differentiation efforts | Positive Growth Expected |
| Mining Support Services | Specialized Service Providers | Project-based competition, Technical expertise | Varies with mining activity |
| Fluid Transfer Products | Specialized Distributors | Product range, Technical support, Supply chain efficiency | Stable to Moderate Growth |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Coventry Group's offerings, which include fasteners, industrial hardware, and fluid transfer products, is significant. Customers can often find alternative solutions to meet their needs, potentially impacting Coventry's market share and pricing power. For instance, in the construction and manufacturing sectors, innovative adhesive technologies are increasingly being developed as a direct replacement for traditional mechanical fasteners like bolts and screws. These advanced adhesives can offer comparable or even superior bonding strength in certain applications, while also potentially reducing assembly time and weight.
The threat of substitutes for Coventry Group's offerings hinges significantly on their price and performance relative to alternatives. If competing products or services provide comparable or superior functionality at a more attractive price point, Coventry Group faces a substantial risk of customer attrition. For instance, in the industrial services sector, the availability of more cost-effective or technologically advanced equipment from competitors could directly erode Coventry Group's market share and pricing flexibility.
Coventry Group's customers show a moderate propensity to substitute, influenced by the availability of alternative building material suppliers. In 2024, the construction industry saw increased competition, with new entrants offering similar product lines, potentially making switching easier for some of Coventry's clientele. The perceived risk of using less established brands and the cost associated with changing suppliers remain key factors mitigating this threat.
Technological Advancements
Ongoing technological advancements present a significant threat of substitutes for Coventry Group. Innovations in materials science, for example, could lead to new joining technologies that bypass the need for traditional hardware solutions.
Consider the rapid evolution in areas like advanced adhesives or novel welding techniques, which may offer comparable or superior performance at a lower cost. For instance, the global market for adhesives and sealants was projected to reach over $70 billion in 2024, indicating a robust and innovative sector capable of producing disruptive alternatives.
These technological shifts can create entirely new ways of achieving desired outcomes, potentially rendering existing Coventry Group products less competitive. The threat is amplified as these advancements mature and become more accessible to a wider range of industries.
Key areas of technological advancement that could impact Coventry Group include:
- Advanced Adhesives and Sealants: Offering lighter weight and potentially stronger bonding solutions.
- Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing): Enabling the creation of complex geometries and integrated components, reducing the need for multiple hardware parts.
- New Fluid Transfer Technologies: Innovations in microfluidics or contactless fluid handling could replace traditional pipe and fitting systems.
Changes in Customer Needs or Preferences
Changes in customer needs or preferences represent a significant threat of substitutes for Coventry Group. As consumer and industrial demands shift, new alternatives emerge that can better meet these evolving requirements. For instance, a heightened focus on sustainability and energy efficiency could lead customers to seek out solutions that reduce environmental impact or operational costs, potentially bypassing traditional industrial hardware.
This trend is already visible across various sectors. In 2024, the global market for sustainable industrial solutions saw substantial growth, with many companies actively investing in greener technologies. For Coventry Group, this means that if their product offerings do not adapt to these changing preferences, customers may readily switch to substitutes that align with newer priorities, such as reduced carbon footprints or enhanced operational flexibility.
- Evolving Preferences: Customers increasingly prioritize factors like environmental impact, energy efficiency, and technological advancement.
- Example: A shift towards lighter, more resource-efficient materials in manufacturing could favor alternative components over traditional metal parts.
- Market Data: The demand for eco-friendly industrial equipment is projected to grow significantly, with some segments experiencing double-digit annual growth rates by 2024.
- Impact on Coventry Group: Failure to innovate and align with these evolving needs could lead to a loss of market share to substitute providers.
The threat of substitutes for Coventry Group's fasteners, hardware, and fluid transfer products remains a key consideration. While traditional mechanical fasteners are prevalent, advancements in areas like high-performance adhesives and additive manufacturing continue to offer viable alternatives. For example, the global adhesives and sealants market was valued at approximately $70 billion in 2024, highlighting the significant innovation and customer adoption of these substitute technologies.
The propensity for Coventry's customers to switch to substitutes is influenced by factors like cost-effectiveness, performance improvements, and evolving industry standards. In 2024, the construction sector saw a notable increase in competition from new suppliers, potentially easing the transition for some clients. However, concerns about reliability and the cost of changing suppliers can moderate this substitution threat.
Technological progress is a primary driver of substitute threats. Innovations in materials science and manufacturing processes, such as advanced welding or 3D printing, can create integrated solutions that bypass the need for conventional hardware. The growing demand for sustainable industrial solutions, with some segments experiencing double-digit growth by 2024, further encourages the adoption of alternative, environmentally friendly options.
| Substitute Area | Potential Impact on Coventry Group | 2024 Market Context |
|---|---|---|
| Advanced Adhesives | Reduced demand for mechanical fasteners; potential for lighter, stronger assemblies. | Global Adhesives & Sealants Market: ~$70 billion. |
| Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing) | Decreased need for standard hardware components; opportunity for customized solutions. | Significant growth in industrial 3D printing applications. |
| New Fluid Transfer Tech | Disruption of traditional pipe and fitting systems; adoption of microfluidics or contactless solutions. | Emerging technologies gaining traction in specialized industrial applications. |
| Sustainable Solutions | Shift in customer preference away from traditional materials/processes; demand for eco-friendly alternatives. | Strong growth in eco-friendly industrial equipment segments. |
Entrants Threaten
The substantial capital investment needed to build a robust distribution network across Australia and New Zealand presents a significant hurdle for potential new entrants in the fastener, industrial hardware, and fluid transfer products market. This capital outlay covers essential infrastructure like warehouses, maintaining adequate inventory levels, establishing efficient logistics operations, and acquiring specialized equipment necessary for handling and distributing these goods.
Coventry Group, like many established players, leverages significant economies of scale and scope. This means their large-scale operations, encompassing a broad product range and diverse customer base, allow them to achieve cost advantages that new entrants would struggle to match. For instance, in 2024, Coventry Group's extensive distribution network, a result of years of investment and expansion, provides a critical barrier to entry by offering superior logistical efficiency and potentially lower per-unit distribution costs.
Coventry Group's established relationships with key distributors and suppliers present a significant barrier for new entrants. Building these networks from scratch requires substantial time and investment, making it difficult for newcomers to reach customers effectively. For instance, in the competitive Australian retail landscape where Coventry operates, securing prime shelf space or reliable logistics partnerships can take years and considerable capital outlay.
Product Differentiation and Brand Loyalty
The threat of new entrants for Coventry Group is significantly mitigated by the high barriers to product differentiation and brand loyalty in the industrial components sector. Established players like Coventry Group have cultivated customer trust over years, making it difficult for newcomers to gain traction. For instance, in 2024, the industrial distribution market continued to see customers prioritizing reliability and established supplier relationships for mission-critical parts.
New entrants face an uphill battle in convincing customers to switch from trusted brands for essential industrial supplies. This customer preference for known and dependable suppliers creates a strong moat for companies like Coventry Group. Many industrial clients, particularly in sectors like manufacturing and mining, cannot afford disruptions caused by unproven component quality or unreliable delivery.
Coventry Group's ability to offer a wide range of specialized industrial products and maintain consistent quality further solidifies its market position. This comprehensive offering, coupled with a reputation for dependability, makes it challenging for new entrants to carve out a significant market share. The cost and time required to build comparable brand recognition and product portfolios are substantial deterrents.
- High Customer Switching Costs: Industrial clients often face considerable costs and risks associated with changing suppliers for critical components.
- Established Brand Reputation: Coventry Group benefits from years of building trust and a reputation for quality and reliability.
- Product Complexity and Specialization: The industrial components market often involves highly specialized products where deep technical expertise and proven performance are paramount.
- Economies of Scale in Distribution: Established distributors like Coventry Group likely benefit from economies of scale in logistics and purchasing, which can be difficult for new entrants to match.
Government Policy and Regulations
Government policy and regulations significantly influence the threat of new entrants for companies like Coventry Group in Australia and New Zealand. Stringent licensing requirements, industry-specific standards, and environmental regulations can act as substantial barriers. For instance, in the construction and building materials sector, adherence to the National Construction Code (NCC) and various state-based building regulations necessitates significant upfront investment and expertise, making it challenging for new players to enter.
Compliance costs associated with these regulations can deter potential competitors. New entrants must invest in understanding and meeting these requirements, which can include obtaining permits, ensuring product compliance, and implementing safety protocols. These financial and administrative burdens can make the Australian and New Zealand markets less attractive compared to less regulated environments, thereby reducing the threat of new entrants.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Compliance with the National Construction Code (NCC) and state-specific building standards in Australia creates a barrier.
- Licensing Requirements: Obtaining necessary licenses for construction and material supply can be a complex and costly process for new entrants.
- Environmental Standards: Meeting evolving environmental regulations in both Australia and New Zealand adds to the cost and complexity of market entry.
- Compliance Costs: The financial outlay for regulatory adherence can deter smaller, less capitalized potential competitors.
The threat of new entrants for Coventry Group is generally low due to substantial capital requirements for establishing distribution networks and inventory. High customer switching costs, driven by the need for reliable, specialized industrial components, further protect Coventry's market position. Established brand reputation and economies of scale in operations also act as significant deterrents.
In 2024, the industrial hardware and fluid transfer sectors continued to demand proven supplier relationships and product reliability, making it difficult for new, unproven entities to gain traction. For instance, companies in the mining and manufacturing sectors often prioritize suppliers with a track record of consistent quality and on-time delivery, which Coventry Group has cultivated over many years.
Regulatory compliance in Australia and New Zealand, such as adhering to the National Construction Code and environmental standards, adds another layer of complexity and cost for potential new entrants. These factors collectively create significant barriers to entry, safeguarding Coventry Group's competitive advantage.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Coventry Group is built upon a foundation of robust data, including company annual reports, investor presentations, and relevant industry association publications. This ensures a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape.
