CGI Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
CGI Bundle
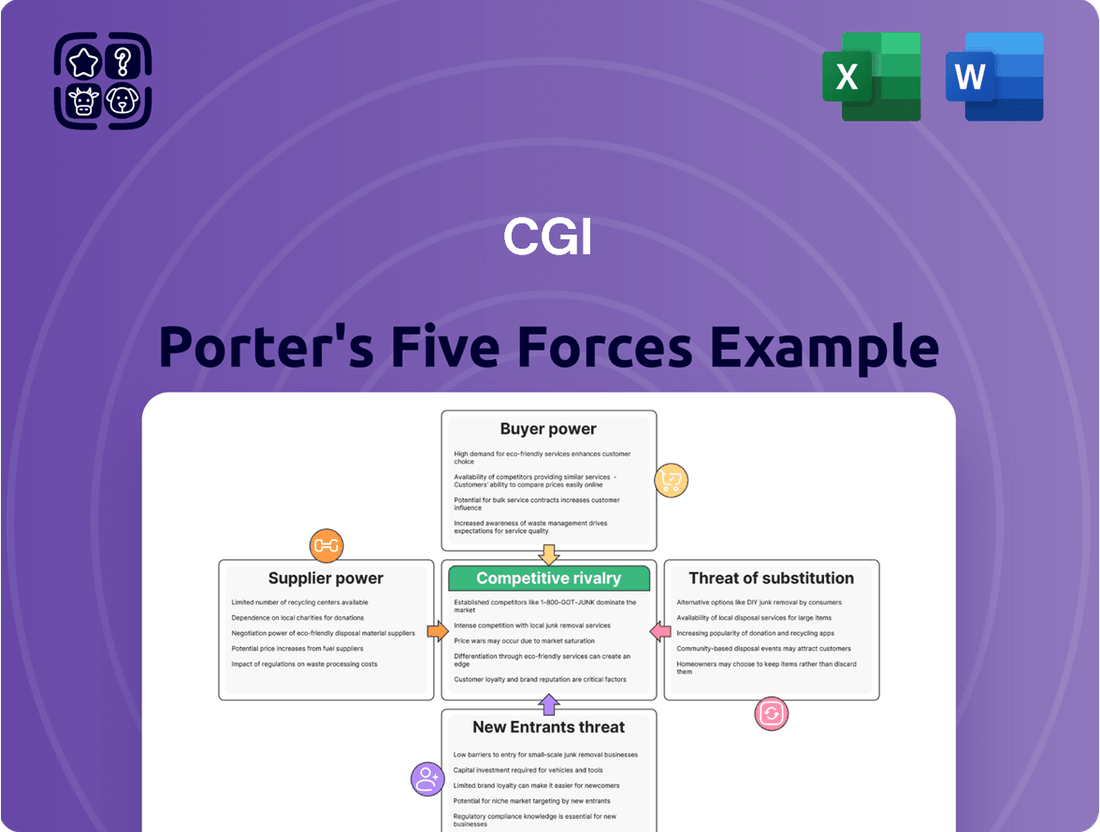
Understanding the competitive landscape is crucial for any business, and a Porter's Five Forces analysis provides that clarity. For CGI, this framework reveals the intricate web of industry rivalry, buyer and supplier power, and the ever-present threats of new entrants and substitutes.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore CGI’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The IT and business consulting industry, where CGI operates, sources from various suppliers like tech vendors and specialized talent. While the overall supplier market is quite fragmented, meaning no single supplier has overwhelming power, certain niche technology or highly skilled labor markets can see supplier concentration. This can give those specific suppliers more leverage when dealing with a large company like CGI.
For CGI, the uniqueness of supplier offerings is a key determinant of supplier power. Standardized services like cloud infrastructure from major providers such as Amazon Web Services (AWS) or Microsoft Azure have many alternatives, diminishing their individual bargaining sway. In 2024, the cloud computing market saw continued dominance by these major players, with AWS holding an estimated 31% market share and Azure 24%, indicating a competitive landscape for these foundational services.
Conversely, suppliers providing highly specialized proprietary software, unique cybersecurity solutions, or scarce technical expertise, particularly in emerging fields like advanced AI or quantum computing, can command greater leverage. The limited availability of direct substitutes for these niche offerings means CGI might face higher costs or less favorable terms when sourcing these critical components, directly impacting its operational expenses and project timelines.
CGI's switching costs with its suppliers vary significantly. For standard IT components or widely available software, the cost to switch is minimal. However, when CGI engages with suppliers for highly specialized or deeply integrated solutions, such as custom enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems or long-term managed services, the expenses involved in data migration, retraining staff, and potential project delays can become considerable. This makes it more challenging and costly to change suppliers for these critical services.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward to compete directly with CGI is generally low. This is because becoming a comprehensive IT consulting firm requires substantial investment in service delivery infrastructure, deep client relationship management capabilities, and broad industry expertise, which are significant barriers for most software vendors.
However, a notable exception exists with large technology companies like Microsoft, IBM, and Oracle. These entities already possess established consulting divisions. This dual role means they are not only suppliers of technology but also potential competitors offering integrated solutions that include IT services, thereby blurring the lines between supplier and competitor.
For instance, in 2023, major cloud providers, who are key suppliers for many IT services firms, continued to expand their own professional services offerings. Microsoft's consulting services revenue, for example, saw continued growth, indicating their commitment to capturing more of the end-to-end IT solution market, which can directly impact companies like CGI.
- Low Integration Threat: Most software vendors lack the capital and expertise to replicate CGI's service delivery model and client engagement strategies.
- Established Competitors: Major tech giants like Microsoft, IBM, and Oracle already operate significant consulting arms, acting as both suppliers and direct competitors.
- Market Dynamics: The increasing demand for integrated solutions means these tech giants are incentivized to leverage their existing supplier relationships to offer end-to-end services.
- Strategic Implications: CGI must carefully manage relationships with these large tech firms, recognizing their dual role as crucial partners and potential rivals in the IT services landscape.
Importance of CGI to Suppliers
CGI's substantial revenue, reaching $4.09 billion in Q3 F2025, makes it a critical client for many of its suppliers, particularly smaller, specialized technology firms and talent agencies. For these entities, a contract with CGI can significantly impact their financial stability and market presence, inherently diminishing their leverage.
Conversely, larger and more diversified suppliers may find CGI to be just one of many significant clients. In such scenarios, the importance of any single contract with CGI is diluted, thereby increasing the supplier's bargaining power relative to CGI.
- CGI's Financial Scale: With $4.09 billion in Q3 F2025 revenue, CGI is a major customer for its suppliers.
- Impact on Smaller Suppliers: For niche providers, securing CGI contracts is vital for revenue and visibility, reducing their bargaining power.
- Diversified Suppliers' Position: Larger, multi-client suppliers have less dependence on CGI, enhancing their negotiation leverage.
The bargaining power of suppliers for CGI is generally moderate. While CGI's significant revenue of $4.09 billion in Q3 F2025 gives it leverage with smaller, specialized suppliers, the IT sector's reliance on a few dominant tech giants for cloud services and proprietary software can shift power. Suppliers of unique or highly specialized offerings, or those with scarce talent, can exert more influence.
Suppliers of standardized services like cloud infrastructure have limited power due to market fragmentation; AWS held an estimated 31% and Azure 24% market share in 2024. However, providers of niche, proprietary solutions or specialized expertise, such as in advanced AI, can command higher prices and more favorable terms. CGI's switching costs are low for standard components but high for deeply integrated, specialized solutions.
The threat of forward integration by suppliers is low for most, as replicating CGI's service delivery model is difficult. However, major tech firms like Microsoft, IBM, and Oracle, which have existing consulting arms, pose a greater challenge by offering integrated solutions that blur the supplier-competitor line. This dual role is amplified as these companies expand their professional services, as seen with Microsoft's continued growth in consulting revenue.
| Factor | Impact on CGI | Supporting Data/Example |
| Supplier Concentration (Standard Services) | Low Bargaining Power | AWS (31%) and Azure (24%) market share in cloud computing (2024) indicates multiple alternatives. |
| Supplier Uniqueness (Niche Services) | High Bargaining Power | Limited substitutes for specialized AI or cybersecurity solutions increase supplier leverage. |
| CGI's Client Size | Low Bargaining Power for Suppliers | CGI's Q3 F2025 revenue of $4.09 billion makes it a critical client for smaller, specialized firms. |
| Forward Integration Threat | Moderate to High (for major tech firms) | Microsoft's growing consulting services revenue demonstrates intent to offer end-to-end solutions. |
What is included in the product
Analyzes the five forces shaping CGI's competitive environment: threat of new entrants, bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, threat of substitutes, and intensity of rivalry.
Instantly identify and address competitive threats with a visual representation of all five forces, enabling proactive strategy adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
CGI's broad client base, spanning numerous industries and regions, typically limits the bargaining power derived from customer concentration. For instance, as of their 2023 fiscal year, CGI reported revenue from thousands of clients globally, preventing any single customer from holding disproportionate influence.
However, the situation can shift for exceptionally large, multi-year contracts within specific market segments. In such instances, a dominant client could exert greater leverage due to their substantial contribution to CGI's revenue stream.
CGI's strategic approach of maintaining a diversified portfolio and a significant global footprint is key to mitigating the risk associated with any over-reliance on a small number of major clients, thereby generally keeping customer concentration in check.
For CGI's clients, the costs associated with switching providers for complex IT services can be substantial. These switching costs are a key factor in the bargaining power of customers, often leaning in CGI's favor. For instance, in 2024, many large enterprises rely on CGI for mission-critical systems integration, where the expense and effort to move to a new vendor can run into millions of dollars.
The process of disentangling deeply embedded systems, migrating vast amounts of sensitive data, and retraining personnel for a new service provider is not only time-consuming but also inherently disruptive to ongoing business operations. This inherent stickiness of CGI's services significantly strengthens its position, making it more challenging for clients to explore alternatives without incurring considerable risk and expense.
Customers in the IT and business consulting sector are typically large, sophisticated enterprises. This sophistication means they often have access to extensive market data, can solicit competitive bids, and possess internal expertise, all of which significantly boosts their price sensitivity and overall bargaining power. For instance, in 2024, many large corporations actively benchmark IT service costs against industry averages, often leading to downward pressure on pricing for standardized services.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of customers bringing IT and consulting services in-house, known as backward integration, is a factor for CGI. However, for complex, large-scale projects, this threat is often constrained. Clients might build internal capabilities for simpler, routine tasks, but replicating CGI's specialized expertise, the scale of operations, and the constant investment in cutting-edge technologies for advanced business and IT consulting, systems integration, and extensive outsourcing is typically impractical and less economical.
For instance, while a company might manage its basic IT help desk internally, undertaking a major digital transformation project or managing a global enterprise resource planning (ERP) system implementation requires a depth of knowledge and a breadth of resources that most clients find challenging to replicate cost-effectively. In 2024, the average cost of a major IT project failure, often due to a lack of in-house expertise, can run into millions of dollars, underscoring the value of specialized external providers like CGI.
- Limited Practicality: Full backward integration is often too costly and complex for clients to manage effectively, especially for specialized IT and consulting needs.
- Expertise Gap: Clients typically lack the deep, specialized knowledge and continuous training required to match the capabilities of firms like CGI in areas like cybersecurity or cloud migration.
- Scalability Issues: The ability to scale resources up or down rapidly, a key offering from CGI, is difficult for individual clients to achieve internally.
- Focus on Core Competencies: Most businesses prefer to concentrate on their primary operations rather than diverting resources to build and maintain extensive IT and consulting departments.
Importance of CGI's Services to Customers
CGI's offerings, particularly in digital transformation, operational efficiency, and innovation, are often fundamental to their clients' strategic goals and competitive edge. This inherent criticality means clients are less inclined to prioritize price over quality when selecting a provider, diminishing their bargaining leverage.
The increasing integration of AI and cloud computing further elevates the importance of CGI's services. For instance, in 2024, many enterprises are heavily reliant on digital infrastructure for core operations, making service continuity and advanced capabilities paramount. This reliance translates to a reduced ability for customers to exert significant price pressure.
- Mission-Critical Services: CGI's expertise in areas like cybersecurity and complex IT system integration are vital for client business continuity, limiting price sensitivity.
- Value-Added Solutions: Services that drive innovation and efficiency, such as AI-powered analytics, provide tangible ROI, making switching costs higher.
- Digital Transformation Dependence: As businesses increasingly depend on digital capabilities, the strategic importance of CGI's transformation services grows, reducing customer bargaining power.
- Cloud and AI Integration: The ongoing adoption of cloud and AI technologies by clients means they are less likely to switch from established, integrated service providers like CGI due to the complexity and potential disruption.
The bargaining power of CGI's customers is generally moderate, influenced by factors like switching costs and the criticality of services. While a broad client base limits individual customer leverage, large, long-term contracts can increase it. For 2024, the significant investment required for clients to switch IT service providers, often running into millions for complex integrations, acts as a strong deterrent.
| Factor | Impact on CGI | 2024 Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Switching Costs | High (Reduces power) | Millions of dollars for complex system migration. |
| Customer Concentration | Low (Reduces power) | Thousands of global clients in FY2023. |
| Availability of Substitutes | Moderate (Increases power) | Competition exists, but specialized expertise is key. |
| Customer's Price Sensitivity | Moderate (Increases power) | Sophisticated clients benchmark costs and seek competitive bids. |
| Criticality of Service | Low (Reduces power) | Services are fundamental to clients' strategic goals and digital operations. |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
CGI Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete CGI Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering an in-depth examination of competitive forces within the industry. The document you see here is precisely what you'll receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no surprises and full readiness for your strategic planning. This professionally formatted analysis provides actionable insights into industry rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threats of new entrants and substitutes, empowering your business decisions.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The IT and business consulting services market is intensely competitive. CGI faces formidable rivals, including global giants such as Accenture, Capgemini, Cognizant, DXC Technology, Infosys, IBM Consulting, and Deloitte Consulting. This diverse competitive set ranges from massive multinational corporations to specialized niche players and regional firms, all vying for market share.
The IT consulting and services market is booming, with the global market size estimated at a substantial $2.04 trillion in 2024. This robust growth is expected to continue, reaching approximately $2.98 trillion by 2034.
Specifically, the digital transformation consulting segment is a major driver, projected to expand from $383.33 billion in 2025 to an impressive $896.21 billion by 2033. While this expansion offers opportunities, the rapid evolution of technology and the surging demand for digital solutions intensify competition among industry players.
In the IT and business consulting sector, differentiating services is paramount. CGI highlights its broad spectrum of offerings, encompassing high-end business and IT consulting, systems integration, and outsourcing, aiming to provide complete solutions. This comprehensive approach is a key differentiator in a competitive landscape.
Firms often distinguish themselves through deep industry knowledge, unique operational methods, and advancements in technology like AI, cloud computing, and cybersecurity. Building robust client relationships also plays a significant role. For instance, CGI's focus on industry-specific solutions allows them to tailor their expertise, as seen in their work within the financial services or public sector, where specialized knowledge is highly valued.
Despite these efforts, a significant portion of consulting services can become standardized, intensifying competition based on price. This commoditization pressure means that while differentiation is key, maintaining competitive pricing remains a constant challenge. CGI's ability to consistently deliver value-added services beyond basic IT functions is therefore critical to its success in mitigating this trend.
Exit Barriers
Exit barriers in the IT and business consulting sector are notably high. Firms often have deep investments in their skilled workforce, which is difficult to redeploy, and long-standing client relationships that are hard to replicate. Specialized infrastructure, like proprietary software and data centers, also adds to the cost of leaving the market.
The process of winding down a substantial consulting operation is expensive. Companies face significant outlays for employee severance packages, early termination of client contracts, and the potential loss of valuable intellectual property developed over years. These substantial costs act as a deterrent, keeping many firms engaged in the market.
For instance, in 2024, the IT consulting market alone was valued at over $450 billion globally. The sheer scale of human capital and ongoing project commitments within these firms makes a swift exit economically unfeasible for many. This persistence fuels ongoing competitive rivalry as firms are incentivized to stay and compete rather than incur massive exit costs.
- High Human Capital Investment: Consulting firms invest heavily in training and developing their employees, making staff a significant, hard-to-liquidate asset.
- Client Relationship Value: Established trust and long-term partnerships with clients represent a substantial intangible asset that is lost upon exit.
- Specialized Infrastructure Costs: Investments in proprietary technology, research, and development create sunk costs that are difficult to recover.
- Significant Disbandment Expenses: Severance pay, contract penalties, and intellectual property write-offs contribute to substantial financial penalties for exiting the market.
Strategic Stakes
The IT services industry, where CGI operates, is characterized by incredibly high strategic stakes. Companies are vying for dominance in a market reshaped by rapid technological evolution, including the widespread adoption of AI, cloud computing, and automation. For CGI and its rivals, staying ahead means not just keeping pace but actively leading digital transformation initiatives for their clients.
Securing long-term contracts and attracting skilled professionals are paramount for sustained growth and profitability. This intense competition drives aggressive strategies, often involving significant investments in research and development and strategic mergers and acquisitions to expand capabilities and market reach. For instance, in 2023, the IT services market saw numerous M&A activities as firms sought to consolidate their positions and acquire new technologies.
- High Stakes in Dynamic Market: CGI and competitors face intense pressure in an industry driven by rapid technological advancements like AI and cloud computing.
- Digital Transformation Imperative: Client demand for digital transformation creates a high-stakes environment for IT service providers to demonstrate value and innovation.
- Talent and Contract Acquisition: Attracting and retaining top talent, alongside securing lucrative long-term contracts, are critical for maintaining market leadership and profitability.
- Aggressive Competitive Strategies: The pursuit of market share fuels aggressive tactics, including substantial R&D investments and strategic mergers and acquisitions, as seen throughout 2023 and early 2024.
Competitive rivalry is a defining characteristic of the IT and business consulting sector, where CGI operates. The market is populated by a broad range of players, from global powerhouses like Accenture and Deloitte to specialized niche firms, all vying for client business. This intense competition is fueled by a booming global IT consulting market, estimated at $2.04 trillion in 2024, with significant growth projected in areas like digital transformation consulting, expected to reach $896.21 billion by 2033.
Firms differentiate themselves through specialized expertise, innovative technologies such as AI and cloud computing, and strong client relationships, exemplified by CGI's focus on industry-specific solutions. However, the potential for service commoditization puts constant pressure on pricing, making value-added services crucial for maintaining a competitive edge.
High exit barriers, including substantial investments in human capital and long-term client relationships, mean that firms tend to persist in the market, intensifying ongoing rivalry. The strategic stakes are exceptionally high, with companies competing fiercely to lead in digital transformation and secure critical talent and contracts, driving aggressive strategies like mergers and acquisitions, which were prevalent throughout 2023 and into 2024.
| Key Competitors | Market Position | Differentiation Strategy |
| Accenture | Global Leader | Broad service portfolio, digital transformation expertise |
| Deloitte Consulting | Major Player | Industry specialization, advisory services integration |
| Infosys | Global IT Services | Digital services, cost-efficiency, talent pool |
| CGI | Global IT and Business Services | Industry-specific solutions, end-to-end capabilities, client proximity |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The most significant substitute for external IT and business consulting services, like those offered by CGI, is for companies to develop these capabilities internally. This means building in-house IT departments or dedicated consulting teams to manage tasks such as digital transformation, system integration, or IT outsourcing.
However, the need for specialized expertise, the scale of projects, and the urgency of deployment often favor external providers. For instance, in 2023, companies globally spent an estimated $1.3 trillion on IT services, with a significant portion allocated to external consultants for complex digital initiatives, highlighting the continued reliance on outside expertise for specialized needs.
The cost-effectiveness of using internal teams versus external consultants hinges on project specifics. For straightforward, recurring tasks, an in-house team often proves more economical. However, for highly specialized or complex projects, the expense of recruiting, developing, and retaining niche expertise internally can become a significant burden, making external providers a more viable option.
External consulting firms frequently offer greater scalability, allowing companies to access specialized skills on demand without the long-term commitment of hiring. Furthermore, these firms often provide access to advanced technologies and methodologies that would be prohibitively expensive for a single organization to develop independently. For example, in 2024, the average cost of a senior IT consultant could range from $150-$300 per hour, while building a comparable in-house team might involve substantial overheads in recruitment and training.
Buyer propensity to substitute is a key factor in assessing the threat of substitutes. For instance, budget constraints can drive clients to seek less expensive alternatives, while a desire for greater control or concerns about data security might push them towards in-house solutions.
However, the IT landscape's growing complexity and the rapid evolution of technology often make external expertise more appealing. In 2024, the persistent talent shortage in specialized fields like AI and cybersecurity further amplifies this trend, making it challenging for many organizations to manage these critical functions internally.
Ease of Substitution for Customers
The ease with which customers can switch to alternative solutions significantly impacts CGI's competitive landscape. For routine IT services, like basic help desk support or standard software installation, the threat of substitution is higher. Many businesses can leverage their internal IT departments or opt for readily available, off-the-shelf software solutions, potentially reducing reliance on external consultants. For example, in 2024, the global IT services market saw continued growth, but also increased competition from specialized niche players and in-house IT teams taking on more complex tasks.
However, for highly specialized and complex projects, such as large-scale digital transformation initiatives, intricate cloud migration strategies, or cybersecurity architecture design, the switching costs and risks for customers are considerably higher. These projects often require deep domain expertise, established client relationships, and significant investment in understanding specific business processes, making direct substitution difficult and potentially disruptive. In 2024, companies undertaking major digital overhauls often found it challenging to quickly or easily replace established IT partners due to the embedded knowledge and ongoing project dependencies.
- High Substitution Risk for Basic Services: For standard IT support and simple software deployments, customers can often utilize internal resources or alternative, less specialized providers, increasing the threat of substitution.
- Low Substitution Risk for Complex Projects: In areas like complex systems integration or large-scale business process re-engineering, the specialized knowledge and high switching costs make substitution more difficult and risky for clients.
- Impact of Digital Transformation: While digital transformation creates opportunities, it also means that companies seeking to innovate may more readily consider new, agile providers if existing partners cannot keep pace, especially for less integrated components of their strategy.
Impact of Technological Advancements on Substitutes
Technological advancements, especially in automation and AI, significantly shape the threat of substitutes for companies like CGI. As these technologies mature, they can automate tasks previously handled by human consultants, potentially diminishing demand for certain services. For instance, AI-powered analytics platforms can now perform data analysis that once required extensive human input.
However, this evolution also presents new avenues for growth. CGI can leverage its expertise to offer consulting services focused on the implementation and management of these advanced technologies. This strategic pivot allows the company to address the changing market landscape, with demand for AI integration consulting expected to rise. By 2024, the global AI market was projected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars, highlighting the significant opportunity.
- Automation of Routine Tasks: AI can now handle data analysis, report generation, and even some customer service functions, reducing the need for human intervention in these areas.
- Emergence of New Service Models: Technology enables new ways of delivering services, such as SaaS platforms offering self-service analytics or AI-driven chatbots for initial client engagement.
- CGI's Strategic Response: CGI is investing in AI and automation capabilities to offer specialized consulting on digital transformation and the integration of these technologies for clients.
- Market Growth in AI Services: The increasing adoption of AI across industries creates a growing market for consulting services that help businesses navigate and implement these solutions effectively.
The threat of substitutes for CGI's services is primarily driven by the option for clients to develop capabilities in-house or use alternative, less specialized providers. For routine IT tasks, this threat is significant, as companies can leverage internal teams or simpler solutions. However, for complex, specialized projects, the cost and risk of substitution increase considerably due to the need for deep expertise and established relationships.
Technological advancements, particularly in AI and automation, are reshaping this threat by automating tasks and creating new service models. While this can reduce demand for certain traditional services, it also opens opportunities for CGI to offer consulting on implementing these new technologies. The growing market for AI services, projected to reach hundreds of billions in 2024, underscores this evolving landscape.
| Service Type | Substitution Risk | Key Factors Influencing Substitution |
|---|---|---|
| Basic IT Support (e.g., help desk) | High | Availability of internal IT staff, off-the-shelf software solutions. |
| Complex Systems Integration | Low | Need for specialized expertise, high switching costs, project complexity, embedded client knowledge. |
| Digital Transformation Consulting | Medium to High | Client's internal capabilities, agility of alternative providers, client's willingness to adopt new technologies. |
| AI and Automation Implementation | Medium | Rapid evolution of technology, availability of specialized AI talent (internal vs. external), cost of developing in-house AI expertise. |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the global IT and business consulting arena, particularly at CGI's expansive level, demands significant upfront capital. Newcomers must be prepared for substantial expenditures in recruiting and nurturing skilled professionals, creating a worldwide operational infrastructure, and developing unique service offerings and intellectual property.
The need for considerable investment in talent, global delivery capabilities, and brand building presents a formidable hurdle. For instance, a new firm aiming to replicate CGI's market presence would likely require billions in initial funding, a sum that deters many potential competitors from even attempting to enter the market.
For IT and business consulting firms like CGI, access to distribution channels is a significant barrier for new entrants. These channels are often built on direct sales, deep client relationships, and a demonstrable history of success. New players must overcome the hurdle of establishing trust and securing access to major enterprise clients, who typically favor established providers with extensive experience and comprehensive service offerings.
CGI's established relationships and extensive global footprint present a formidable challenge for emerging firms seeking to quickly gain market share. In 2023, CGI reported revenues of approximately $12.5 billion, underscoring its substantial market presence and the entrenched nature of its client base.
Established players like CGI leverage significant economies of scale, boasting a global workforce of over 90,000 employees as of Q1 2024, enabling them to spread fixed costs across a vast operational base. This scale allows for standardized processes and a broad client portfolio, driving down per-unit costs.
Furthermore, CGI benefits from economies of scope by offering a comprehensive suite of services, from consulting to managed IT and business process services. This integrated approach makes it more cost-effective for CGI to deliver a wider array of solutions compared to specialized new entrants, creating a formidable cost advantage.
The ability to undertake large, complex projects, often requiring substantial upfront investment and risk management capabilities, acts as a significant barrier. New entrants would find it challenging to match CGI's capacity and financial muscle, limiting their ability to compete for major contracts.
Brand Identity and Reputation
In the consulting sector, a firm's brand identity and reputation are incredibly important. Clients frequently select consulting firms based on their perceived expertise, dependability, and track record of success. CGI, having operated for a considerable period and maintaining a global reach, has cultivated a robust brand and a strong market reputation.
Newcomers would require substantial time and financial resources to build a similar level of trust and credibility. This makes it difficult for them to effectively compete for lucrative, high-value contracts that are often awarded to established players like CGI.
- Brand Equity: CGI's established brand equity acts as a significant barrier, as clients associate it with consistent quality and successful project outcomes.
- Client Loyalty: Long-standing client relationships, built on trust and proven performance, reduce the likelihood of clients switching to unproven new entrants.
- Perceived Risk: Engaging with a new, unknown consulting firm often carries a higher perceived risk for clients compared to partnering with a reputable, globally recognized entity like CGI.
- Market Perception: In 2024, the consulting market continues to value established reputations, with many large-scale digital transformation projects favoring firms with a demonstrable history of delivering complex solutions.
Government Policy and Regulation
Government policy and regulation can act as a significant deterrent to new entrants in the IT and business consulting space. While not universally stringent, specific areas like data privacy, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) impacting operations in the European Union, and cybersecurity mandates create compliance hurdles. For a company like CGI, which operates globally, the need to adhere to a patchwork of differing national and regional regulations, including sector-specific rules in areas like defense or healthcare, can be a substantial barrier to entry for newcomers unfamiliar with these complexities.
Navigating these varied regulatory landscapes requires considerable investment in legal counsel and compliance infrastructure. For instance, the increasing focus on data sovereignty means that data processing and storage must often occur within specific geographic borders, adding operational complexity for new firms. The potential for fines and reputational damage due to non-compliance further elevates the risk for new entrants attempting to establish a foothold in regulated markets.
- Data Privacy Regulations: Compliance with frameworks like GDPR and CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) necessitates robust data handling protocols.
- Cybersecurity Standards: Adherence to evolving cybersecurity standards, such as those mandated by NIST or ISO 27001, is crucial for client trust and data protection.
- Industry-Specific Compliance: Sectors like finance and healthcare have stringent regulatory requirements that new entrants must meet, often involving specialized certifications.
- International Regulatory Divergence: Operating across multiple jurisdictions means managing a complex web of differing legal and compliance obligations, a significant barrier for new, smaller firms.
The threat of new entrants for CGI is relatively low due to substantial capital requirements for talent acquisition, global infrastructure, and service development. For instance, replicating CGI's market presence would likely demand billions in initial funding, a significant deterrent.
Established client relationships, brand reputation, and economies of scale further solidify CGI's position. With over 90,000 employees globally as of Q1 2024 and revenues around $12.5 billion in 2023, CGI benefits from cost advantages and client loyalty, making it difficult for newcomers to gain traction.
Regulatory complexities, particularly around data privacy and cybersecurity, add another layer of difficulty for new firms. Navigating diverse international regulations, like GDPR, requires significant investment in compliance infrastructure, increasing the risk for emerging competitors.
| Barrier | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High upfront costs for talent, infrastructure, and IP development. | Significant financial hurdle, limiting the number of potential entrants. |
| Economies of Scale & Scope | CGI's large workforce (90,000+ employees) and broad service offerings reduce costs. | New entrants struggle to match cost efficiencies and integrated solutions. |
| Brand Equity & Client Loyalty | Established reputation and long-standing client relationships. | New firms face challenges in building trust and acquiring clients. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Adherence to diverse data privacy and cybersecurity laws. | Requires substantial investment and expertise, increasing operational complexity. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of robust data, encompassing company annual reports, industry-specific market research, and publicly available financial filings. We also leverage insights from reputable trade publications and economic databases to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape.
