Chifeng Jilong Gold Mining Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Chifeng Jilong Gold Mining Bundle
Chifeng Jilong Gold Mining faces significant competitive pressures, with the threat of new entrants and the bargaining power of buyers posing notable challenges. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for navigating the gold mining landscape effectively.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Chifeng Jilong Gold Mining’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Suppliers of specialized mining equipment and advanced exploration technology hold significant bargaining power. The mining sector's dependence on unique or proprietary machinery means that providers of these critical inputs can dictate terms, especially given the substantial costs and operational disruptions associated with switching suppliers. This reliance is amplified as companies like Chifeng Jilong Gold Mining invest heavily in digital and intelligent transformation, increasing their dependence on cutting-edge technology providers.
Access to highly skilled geologists, mining engineers, and experienced labor is paramount for Chifeng Jilong Gold Mining's efficient and safe operations. A scarcity of this specialized talent can directly escalate labor expenses and amplify the negotiation leverage of these skilled professionals. For instance, in 2024, the global mining industry continued to face challenges in attracting and retaining experienced personnel, leading to increased wage demands in many regions where Chifeng Jilong operates.
Chifeng Jilong Gold Mining’s reliance on energy and raw materials significantly influences supplier bargaining power. Mining is inherently energy-intensive, consuming substantial electricity and fuel, alongside specialized chemicals crucial for ore processing. For instance, global oil prices, a key component of fuel costs, saw an average of $77.48 per barrel in 2024, impacting operational expenses directly.
Logistics and Transportation Services
The bargaining power of logistics and transportation service providers for Chifeng Jilong Gold Mining is influenced by the specialized nature of moving mined ore, processed gold, and waste materials, particularly across international borders. Limited availability of carriers equipped for these specific demands can give suppliers leverage. For instance, in 2024, the global shipping industry faced ongoing challenges with capacity constraints and rising fuel costs, which directly impacts the pricing power of transportation firms serving mining operations. Chifeng Jilong's reliance on these services for its diverse global sites means that any disruption or price hike from these suppliers can significantly affect operational costs.
- Specialized Transport Needs: Moving bulk ore and precious metals requires specific equipment and handling protocols, limiting the pool of suitable providers.
- Global Operations: Chifeng Jilong's international mining sites necessitate complex logistics chains, increasing dependence on a few key transportation partners.
- Industry Conditions (2024): Rising fuel prices and container shortages in 2024 bolstered the pricing power of shipping and logistics companies.
Environmental Compliance and Consulting Services
The bargaining power of suppliers in environmental compliance and consulting services for Chifeng Jilong Gold Mining is significant, driven by escalating ESG mandates. Companies offering specialized waste management, emissions control, and sustainability reporting are increasingly essential for the mining sector, particularly in regions like China with its robust environmental protection laws.
China's commitment to green development, as outlined in its five-year plans, directly impacts mining operations. For instance, the 14th Five-Year Plan (2021-2025) emphasizes stricter environmental standards for industries, including mining. This regulatory pressure elevates the importance and pricing power of suppliers who can ensure compliance and mitigate environmental risks for gold mining companies.
- Growing Demand for ESG Services: Global ESG investment reached an estimated $35.3 trillion in 2024, increasing the leverage of environmental consultants.
- Regulatory Stringency: China's environmental regulations, enforced rigorously, make specialized compliance services non-negotiable for mining operations.
- Specialized Expertise: The niche knowledge required for environmental permitting and remediation allows these suppliers to command higher prices.
- Limited Supplier Pool: A concentrated market of highly qualified environmental service providers further strengthens their bargaining position.
Suppliers of specialized mining equipment and advanced exploration technology hold significant bargaining power due to the sector's reliance on unique or proprietary machinery. This dependence is amplified by Chifeng Jilong's investment in digital transformation, increasing reliance on cutting-edge technology providers.
A scarcity of highly skilled geologists and mining engineers in 2024 escalated labor expenses and amplified the negotiation leverage of these professionals within the global mining industry. This talent shortage directly impacts operational costs and efficiency.
Chifeng Jilong Gold Mining's substantial energy consumption makes it vulnerable to fluctuations in fuel prices. For example, average global oil prices in 2024 were approximately $77.48 per barrel, directly affecting operational expenses for energy-intensive mining activities.
Logistics and transportation providers possess considerable bargaining power, especially given the specialized nature of moving mined ore and precious metals globally. In 2024, industry-wide capacity constraints and rising fuel costs further strengthened the pricing power of these essential service providers.
| Supplier Category | Key Drivers of Bargaining Power | Impact on Chifeng Jilong | 2024 Data/Context |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mining Equipment & Technology | Proprietary technology, high switching costs | Dictated terms, potential cost escalations | Increased demand for digital transformation tech |
| Skilled Labor (Geologists, Engineers) | Talent scarcity, specialized expertise | Higher wage demands, recruitment challenges | Global shortage of experienced mining professionals |
| Energy & Raw Materials | High consumption, price volatility | Direct impact on operational costs | Average Brent Crude oil price: ~$77.48/barrel |
| Logistics & Transportation | Specialized handling, global reach, limited providers | Increased shipping costs, potential delays | Shipping capacity constraints and fuel surcharges |
| Environmental Compliance Services | Stringent regulations, ESG mandates, niche expertise | Necessity for compliance, higher service fees | Global ESG investment ~ $35.3 trillion; China's strict environmental laws |
What is included in the product
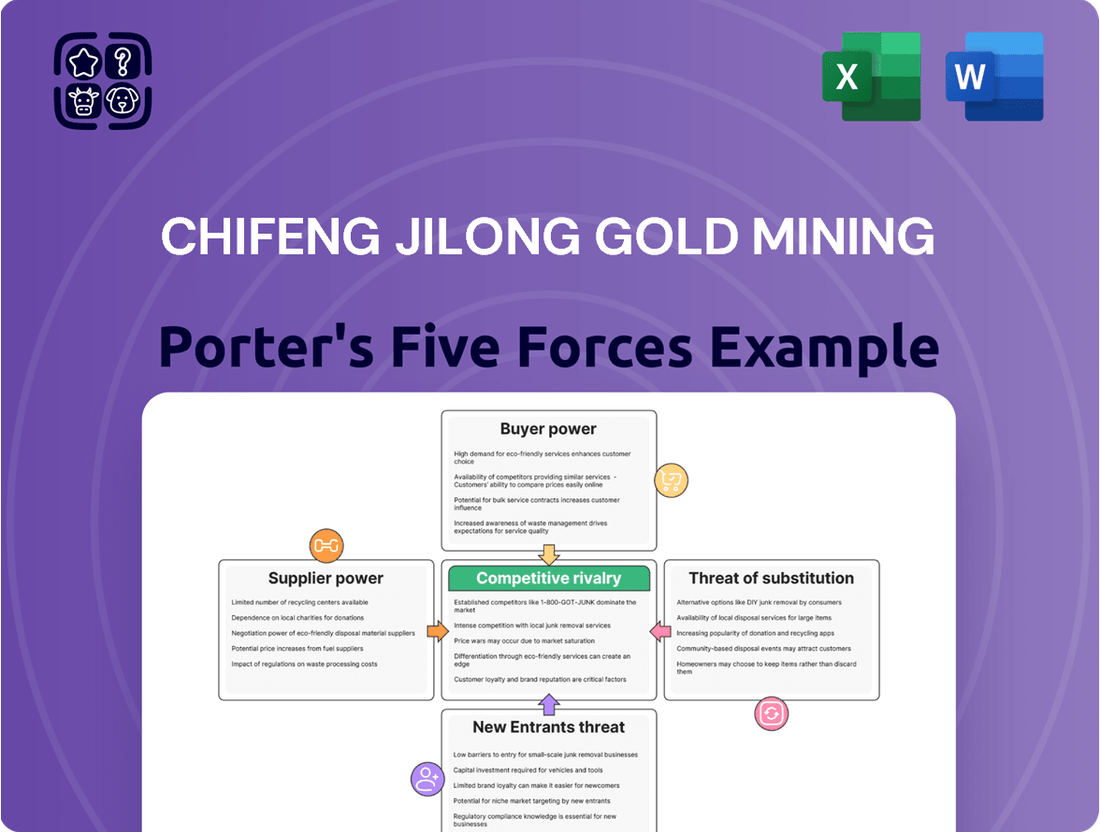
This analysis dissects Chifeng Jilong Gold Mining's competitive environment by examining the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the gold mining sector.
Instantly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a visual breakdown of Chifeng Jilong Gold Mining's Porter's Five Forces, enabling proactive strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of customers in the gold market, particularly for a producer like Chifeng Jilong Gold Mining, is quite limited. Gold is a globally traded commodity, and its price is set by broad international market forces, not by the demands of individual buyers. This means that no single customer, or even a consortium of customers, can dictate terms to a gold mining company.
Chifeng Jilong Gold Mining's revenue is directly tied to these global price fluctuations. For instance, in 2023, gold prices reached record highs, averaging around $1,970 per ounce for the year, and continued this upward trend into early 2024, touching over $2,300 per ounce at times. Such market-driven pricing significantly diminishes any individual customer's ability to negotiate lower prices.
Chifeng Jilong Gold Mining benefits from a diverse customer base, catering to investment, jewelry, and industrial sectors. This broad appeal across different end-uses, each with unique demand drivers, significantly dilutes the bargaining power of any single customer group. For instance, in 2024, China's domestic gold consumption remained robust, with jewelry and investment demand forming substantial portions of the market.
For core demand, especially in investment and specific industrial uses, gold genuinely lacks direct substitutes that can replicate its unique properties or the immense perceived value it holds. While other precious metals like silver or platinum are available, gold's established position as a safe-haven asset and its deep cultural importance, particularly in markets such as China, significantly restrict customers' ability to easily switch away. This fundamental characteristic inherently lowers the bargaining power of customers concerning the primary gold product.
Investment Demand Dynamics
The bargaining power of customers in the gold market, particularly for a miner like Chifeng Jilong Gold Mining, is influenced by the diverse nature of gold demand. A substantial portion of gold is purchased by investors, including central banks and individual investors. These entities are swayed by broader economic indicators such as inflation, geopolitical stability, and overall market sentiment rather than direct price negotiations with individual mining companies.
This investor-driven demand means that customers are not typically focused on haggling over the price of gold from a single producer. Instead, their decisions are part of a much larger global economic narrative. For instance, in 2023, central banks continued to be significant buyers of gold, with net purchases totaling 1,080 tonnes, according to the World Gold Council. This indicates a demand driven by strategic reserve management and diversification rather than price sensitivity to a specific miner.
- Investor-Driven Demand: Central banks and individual investors are key gold purchasers, prioritizing macroeconomic factors and geopolitical stability over direct price negotiation with miners.
- Mitigated Customer Power: The broad, sentiment-driven nature of investment demand dilutes the power of any single customer to dictate terms to a specific gold producer.
- Central Bank Activity: Central banks remained net buyers in 2023, acquiring 1,080 tonnes of gold, underscoring demand driven by strategic asset allocation rather than individual supplier relationships.
Non-Ferrous Metal Buyers
Chifeng Jilong Gold Mining's customer base for non-ferrous metals like silver, bismuth, and palladium possesses varying degrees of bargaining power. For these secondary products, customer influence is largely dictated by the specific market conditions for each metal. Factors such as prevailing supply and demand, the number of available suppliers, and the ease with which customers can switch to alternatives all play a crucial role in shaping this power.
The bargaining power of customers for Chifeng Jilong's non-ferrous metal offerings beyond gold is influenced by several key market dynamics. For instance, the global silver market, while substantial, can see price volatility influenced by industrial demand and investment flows. In 2024, the price of silver experienced fluctuations, impacting the leverage buyers have. Similarly, the markets for bismuth and palladium, often niche compared to gold and silver, can exhibit different supply chain structures and fewer large-scale buyers, potentially altering customer bargaining power.
- Market Concentration: The number of significant buyers for each specific non-ferrous metal impacts their collective bargaining power. A more concentrated buyer base can exert greater influence.
- Availability of Substitutes: For industrial applications, the existence of alternative materials that can replace silver, bismuth, or palladium can significantly enhance customer bargaining power.
- Price Sensitivity: The degree to which customers are sensitive to price changes for these metals will determine how aggressively they negotiate.
- Supplier Landscape: The presence of numerous alternative suppliers for these non-ferrous metals weakens Chifeng Jilong's position, while a limited supplier pool strengthens it.
The bargaining power of customers for Chifeng Jilong Gold Mining is generally low, especially concerning gold. This is due to gold's status as a globally traded commodity whose price is dictated by international market forces, not individual buyer demands. For instance, gold prices in 2023 averaged around $1,970 per ounce and saw further increases into early 2024, exceeding $2,300 per ounce at times, limiting any single customer's ability to negotiate lower prices.
The diverse demand for gold, spanning investment, jewelry, and industrial sectors, further dilutes customer power. Investment demand, particularly from central banks which acquired 1,080 tonnes net in 2023, is driven by macroeconomic factors and geopolitical stability rather than price sensitivity to a specific miner. This strategic buying behavior means customers are less focused on haggling with individual producers.
For Chifeng Jilong's other metals like silver, bismuth, and palladium, customer bargaining power varies. It hinges on market concentration, availability of substitutes for industrial uses, price sensitivity, and the overall supplier landscape for each specific metal. For example, in 2024, silver prices experienced fluctuations, influencing buyer leverage.
| Metal | Key Demand Driver | Customer Bargaining Power Factor | 2023/2024 Data Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gold | Investment, Jewelry, Industrial | Global commodity pricing, lack of substitutes, investor sentiment | Average price ~ $1,970/oz (2023); > $2,300/oz (early 2024) |
| Silver | Industrial, Investment | Industrial demand, investment flows, price volatility | Price fluctuations observed in 2024 |
| Bismuth | Industrial (e.g., pharmaceuticals, electronics) | Niche market, supply chain structure, buyer concentration | Market dynamics vary, less transparent than gold/silver |
| Palladium | Automotive (catalytic converters), Industrial | Specific industrial applications, supply/demand balance | Market sensitive to automotive production and emissions regulations |
Full Version Awaits
Chifeng Jilong Gold Mining Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis for Chifeng Jilong Gold Mining, offering insights into competitive rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the threat of substitutes. The document displayed here is the part of the full version you’ll get—ready for download and use the moment you buy, providing a complete and actionable strategic overview.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The gold mining sector, particularly within China, is characterized by a multitude of smaller operators, creating a fragmented landscape. However, this fragmentation is steadily giving way to consolidation as larger entities pursue mergers and acquisitions to gain scale and efficiency.
Chifeng Jilong Gold Mining exemplifies this trend, strategically acquiring mining assets to bolster its production capacity and market presence. For instance, in 2023, the company continued its expansion efforts, aiming to integrate acquired operations smoothly. This consolidation drive intensifies competition as companies battle for prime mining concessions and market share.
The gold mining industry is inherently capital intensive, demanding significant upfront investment. For instance, establishing a new mine can cost hundreds of millions, even billions, of dollars for exploration, land acquisition, equipment, and processing facilities. This high barrier to entry limits the number of new players and also means existing companies have substantial fixed costs to cover.
This capital intensity often compels mining companies, including Chifeng Jilong Gold Mining, to maintain high production levels to spread these fixed costs over a larger output. When gold prices are stable or falling, this can lead to aggressive competition, often on price, as firms strive to achieve economies of scale and profitability. Chifeng Jilong's substantial asset base, which includes significant mining rights and operational infrastructure, underscores the considerable capital commitment typical in this sector.
In the gold mining sector, competitive rivalry is intense because gold is a commodity with very little product differentiation. This means companies like Chifeng Jilong Gold Mining compete primarily on factors such as cost efficiency, the sheer volume of gold they can produce, and the quality and size of their gold reserves. For instance, in 2023, the average all-in sustaining cost for gold producers globally hovered around $1,200 per ounce, making cost control a critical battleground.
Chifeng Jilong Gold Mining, therefore, must focus on operational improvements and expanding its resource base to stand out. Rather than developing unique product features, their competitive edge comes from optimizing extraction processes and securing new, high-grade deposits. This strategic focus is essential to maintain profitability and market share in an industry where the core product is fundamentally the same across all players.
Global and Domestic Competitors
Chifeng Jilong Gold Mining contends with intense competition from both domestic giants and international powerhouses in the gold mining sector. In China, large state-owned enterprises often benefit from government support and established infrastructure, presenting a formidable challenge. Globally, major players like Barrick Gold and Newmont Corporation, with their vast resources and operational scale, directly compete with Chifeng Jilong, especially as the company expands its footprint into overseas markets.
The competitive landscape is further defined by the presence of other significant Chinese mining companies. For instance, Zijin Mining Group, another major player, actively pursues global expansion and asset acquisition, creating direct competition for resources and market share. Chifeng Jilong's strategic moves into countries like Ghana and Laos place it directly against these established global and domestic competitors, necessitating continuous innovation and efficiency to maintain its competitive edge.
- Domestic Giants: Chifeng Jilong faces strong competition from established Chinese state-owned mining enterprises.
- International Players: Major global gold producers like Barrick Gold and Newmont Corporation are direct rivals, particularly in overseas markets.
- Zijin Mining Group: This prominent Chinese competitor also engages in aggressive global expansion, intensifying rivalry.
- Market Dynamics: Competition is fierce for mining concessions, skilled labor, and capital, especially in emerging markets where Chifeng Jilong is expanding.
Regulatory and ESG Pressures
Increasing regulatory scrutiny, especially concerning environmental and social governance (ESG) standards, intensifies competition within the mining sector. Companies demonstrating strong ESG performance and sustainable practices, like those aligning with China's emphasis on green mining, can secure a competitive edge and attract preferential investment.
For instance, in 2024, the global mining industry saw a significant uptick in ESG-related investments, with many funds actively divesting from companies with poor environmental records. Chifeng Jilong Gold Mining, like its peers, faces pressure to adapt its operations to meet these evolving global and domestic expectations.
- Growing ESG Demands: Investors and regulators are increasingly prioritizing companies with robust ESG frameworks.
- Competitive Advantage: Superior ESG performance can translate into better access to capital and enhanced brand reputation.
- China's Green Mining Initiative: This national focus creates a specific regulatory environment that mining companies must navigate.
Competitive rivalry in the gold mining sector is characterized by a lack of product differentiation, forcing companies like Chifeng Jilong Gold Mining to compete primarily on cost efficiency, production volume, and reserve quality. The industry's capital-intensive nature, with new mine development costing hundreds of millions, creates high barriers to entry and significant fixed costs. This compels firms to maximize output, often leading to price-based competition, especially when gold prices are stagnant or declining. Chifeng Jilong's strategy of asset acquisition and operational optimization is crucial for maintaining profitability in this environment.
Chifeng Jilong Gold Mining faces robust competition from both domestic Chinese mining giants, such as Zijin Mining Group, and major international players like Barrick Gold and Newmont Corporation. These global entities possess substantial resources and operational scale, directly challenging Chifeng Jilong, particularly as it expands into international markets like Ghana and Laos. The competition extends beyond production to securing prime mining concessions, attracting skilled labor, and accessing capital, especially in developing regions.
The increasing emphasis on Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) standards is reshaping the competitive landscape. Companies demonstrating strong ESG performance and sustainable practices gain a competitive edge, attracting preferential investment and enhancing their reputation. For instance, 2024 saw a notable rise in ESG-focused investments within the mining sector, with many funds divesting from companies with poor environmental records. Chifeng Jilong, like its peers, must adapt its operations to meet these evolving global and domestic expectations, including China's push for green mining initiatives.
| Competitor Type | Key Players | Competitive Factors |
| Domestic Giants | Zijin Mining Group | Scale, government support, established infrastructure |
| International Players | Barrick Gold, Newmont Corporation | Vast resources, operational scale, global presence |
| Emerging Markets | Local and regional operators | Access to concessions, labor, capital, regulatory navigation |
SSubstitutes Threaten
While gold is often seen as distinct, other precious metals like silver, platinum, and palladium can act as substitutes. These metals can be used in similar industrial applications or as alternative stores of value for investors. For instance, platinum and palladium are crucial in catalytic converters, competing with gold's use in some electronics. In 2024, the price of silver, for example, experienced significant fluctuations, impacting its attractiveness relative to gold for certain investment portfolios.
For investors, gold faces significant competition from a diverse range of financial assets. Stocks, bonds, and real estate, for example, offer different risk-reward profiles and can attract capital away from gold depending on prevailing market conditions. In 2024, as interest rates remained a key consideration, the yield on government bonds, such as the U.S. 10-year Treasury, fluctuated, influencing investor decisions about holding non-yielding assets like gold.
Gold jewelry faces significant competition from substitutes like silver, platinum, and diamonds, each offering different aesthetic appeal and price points. For instance, in 2023, the global silver jewelry market was valued at approximately USD 27.5 billion, demonstrating its substantial presence and appeal to a broad consumer base.
Consumer preferences are dynamic, influenced by fashion trends and economic conditions, which can shift demand away from gold. The rise of lab-grown diamonds, offering a more accessible luxury option, also presents a growing substitute threat, impacting traditional diamond and gold sales.
In the crucial Chinese market, while gold remains a cultural staple, there's a noticeable trend towards more contemporary designs and a wider acceptance of fashion jewelry made from less precious materials. This evolving taste landscape means that gold's dominance isn't absolute, as consumers explore a diverse range of jewelry options.
Technological Advancements in Material Science
Ongoing advancements in material science pose a potential threat of substitution for gold, particularly in industrial applications. New materials with comparable or even superior properties at a lower cost could emerge, gradually reducing gold's demand in sectors reliant on its unique characteristics. For example, research into advanced ceramics and high-performance polymers continues to explore alternatives for electronics and specialized industrial components, areas where gold has traditionally held a strong position due to its conductivity and corrosion resistance.
While this threat is more of a long-term concern, continuous innovation across various industries means companies like Chifeng Jilong Gold Mining must remain vigilant. The development of cost-effective substitutes could impact gold's market share in specific technological applications. The company's strategic diversification into other non-ferrous metals, such as copper and zinc, helps to mitigate this risk by broadening its revenue streams beyond a sole reliance on gold.
- Material Science Innovation: Emerging materials may offer similar or better performance than gold in industrial uses at a reduced price point.
- Technological Application Impact: Innovations in sectors like electronics could decrease gold demand in specific high-tech applications.
- Company Mitigation Strategy: Chifeng Jilong Gold Mining's focus on diverse non-ferrous metals helps buffer against potential shifts in gold demand due to substitutes.
Digital Currencies and Blockchain Assets
The emergence of digital currencies and blockchain assets, often dubbed 'digital gold,' poses a potential, albeit nascent, threat of substitution. While not a direct replacement for physical gold, these digital assets are gaining traction as alternative stores of value. For instance, Bitcoin, a leading digital currency, saw its market capitalization fluctuate significantly in 2024, reaching highs that attracted considerable investor interest, potentially siphoning capital that might otherwise flow into traditional assets like gold.
This trend is particularly relevant for attracting younger investors who may be more inclined towards digital-native assets. As of mid-2024, a substantial portion of cryptocurrency holders are under the age of 40, a demographic that also represents a growing segment of the investment market. The increasing institutional adoption and regulatory clarity surrounding some digital assets could further accelerate this shift.
- Digital Gold Narrative: Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin are increasingly discussed as a digital store of value, drawing parallels to gold's traditional role.
- Investor Demographics: Younger investors, often more comfortable with digital assets, represent a growing segment of the investment pool.
- Capital Diversion: The growing acceptance of digital assets could divert investment capital away from traditional safe-haven assets like physical gold.
- Market Evolution: The increasing institutional adoption and evolving regulatory landscape for digital assets are key factors to monitor.
The threat of substitutes for gold mining companies like Chifeng Jilong is multi-faceted, encompassing both industrial applications and investment alternatives. While gold holds unique properties, advancements in material science and the appeal of other precious metals or financial instruments can chip away at its dominance.
In industrial sectors, new materials might offer comparable conductivity or corrosion resistance at a lower cost, impacting gold's use in electronics or specialized components. For investors, assets like silver, platinum, palladium, stocks, bonds, real estate, and even digital currencies present alternative avenues for wealth preservation and growth, especially when market conditions favor yields or different risk profiles.
The jewelry market also sees competition from other precious metals and gemstones, with evolving consumer tastes influencing demand. Chifeng Jilong's diversification into other metals is a strategic move to mitigate these substitution risks.
| Substitute Category | Example | 2024 Market Context/Data Point | Impact on Gold Demand |
|---|---|---|---|
| Precious Metals | Silver | Silver prices fluctuated significantly in 2024, affecting its attractiveness relative to gold for investors. | Potential diversion of investment capital. |
| Financial Assets | Government Bonds (e.g., U.S. 10-Year Treasury) | Bond yields remained a key consideration for investors in 2024, influencing decisions on holding non-yielding assets like gold. | Capital may shift to yield-generating assets. |
| Jewelry Alternatives | Silver Jewelry | The global silver jewelry market was valued at approximately USD 27.5 billion in 2023. | Competition for consumer spending in the luxury goods sector. |
| Digital Assets | Bitcoin | Bitcoin's market capitalization saw significant fluctuations in 2024, attracting considerable investor interest. | Potential siphoning of capital from traditional safe-haven assets. |
Entrants Threaten
The gold mining sector demands immense upfront capital for exploration, mine development, and processing infrastructure. For instance, major gold producers often invest billions of dollars in new projects. This financial hurdle makes it incredibly difficult for newcomers to challenge established companies like Chifeng Jilong Gold Mining, which has demonstrated its commitment through substantial investments in growth and strategic acquisitions.
The mining industry, particularly gold, is heavily burdened by extensive regulatory hurdles and permits. Aspiring new entrants must navigate a labyrinth of environmental impact assessments, safety standards, and operational licenses, a process that is both time-consuming and financially demanding. For instance, obtaining a single mining permit in some jurisdictions can take years and involve millions in upfront costs.
Compliance requirements vary significantly across different countries, adding another layer of complexity for international expansion. China's recent action plan for the gold industry, for example, underscores a commitment to stringent compliance and sustainable development, signaling a tougher environment for new players seeking to enter the market.
The threat of new entrants into the gold mining industry, particularly concerning access to high-quality gold deposits, remains a significant barrier for companies like Chifeng Jilong Gold Mining. Finding economically viable and high-grade gold deposits is increasingly challenging, with many of the most accessible and richest resources already under the control of established players. For instance, in 2023, global gold exploration budgets saw a notable increase, reflecting the ongoing competition for new discoveries, yet the success rate for finding new, large-scale deposits remains low.
Economies of Scale and Experience Curve
Established players like Chifeng Jilong Gold Mining leverage significant economies of scale. This translates to lower per-unit costs in areas such as exploration, extraction, processing, and logistics. For instance, in 2023, Chifeng Jilong's substantial production volume allowed for more efficient use of heavy machinery and bulk purchasing of consumables, a cost advantage unavailable to smaller, new operations.
New entrants would face a considerable disadvantage due to the absence of these scale efficiencies. Their initial operating costs would be higher, and they would need to navigate a steep learning curve to optimize processes. This makes it challenging to compete on price or operational efficiency against a well-established entity like Chifeng Jilong.
- Economies of Scale: Chifeng Jilong's large-scale operations in 2023 reduced its average cost per ounce of gold produced compared to smaller competitors.
- Experience Curve: The company's years of operation have allowed it to refine its mining techniques, leading to improved efficiency and lower costs over time.
- Procurement Power: Bulk purchasing of mining equipment and supplies by Chifeng Jilong in 2023 likely secured more favorable pricing than a new entrant could achieve.
- Capital Intensity: The high capital investment required for modern, large-scale gold mining acts as a significant barrier to entry for new companies.
Brand Recognition and Market Access
Brand recognition and established relationships with refiners, industrial buyers, and investment channels create significant barriers for new entrants in the gold mining sector. Chifeng Jilong Gold Mining, with its long-standing market presence, has cultivated these crucial connections, making it difficult for newcomers to gain comparable market access.
For instance, in 2024, the global gold market continued to be influenced by established supply chains and buyer commitments. New entrants would face the considerable challenge of building trust and securing contracts with major downstream partners, a process that often takes years and substantial investment.
- Established relationships with refiners and industrial buyers offer preferential terms and consistent demand.
- New entrants must invest heavily in building credibility and market access, a time-consuming and costly endeavor.
- Chifeng Jilong's historical market participation provides a distinct advantage in securing favorable off-take agreements.
The significant capital required for exploration, development, and infrastructure presents a formidable barrier. For example, establishing a new gold mine can easily cost hundreds of millions, if not billions, of dollars. This financial commitment, coupled with the long lead times for project development, deters many potential new entrants. Furthermore, the industry is characterized by substantial economies of scale, where larger operations benefit from lower per-unit production costs, making it difficult for smaller, new companies to compete on price.
| Factor | Impact on New Entrants | Relevance to Chifeng Jilong |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Intensity | High barrier due to massive upfront investment needed for exploration and mine development. | Chifeng Jilong's established financial strength allows it to undertake large-scale projects. |
| Economies of Scale | New entrants lack cost efficiencies in procurement, processing, and logistics compared to established players. | Chifeng Jilong's significant 2023 production volumes likely resulted in lower average costs per ounce. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Navigating complex permitting, environmental, and safety regulations is time-consuming and costly. | Chifeng Jilong has experience and resources to manage compliance across its operational regions. |
| Access to Deposits | Securing economically viable, high-grade gold deposits is increasingly challenging as prime locations are often already claimed. | Chifeng Jilong's existing concessions and exploration success provide a competitive advantage in resource acquisition. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Chifeng Jilong Gold Mining is built upon a foundation of official company filings, including annual reports and SEC submissions, alongside reputable industry research from sources like S&P Global Market Intelligence and Wood Mackenzie.
