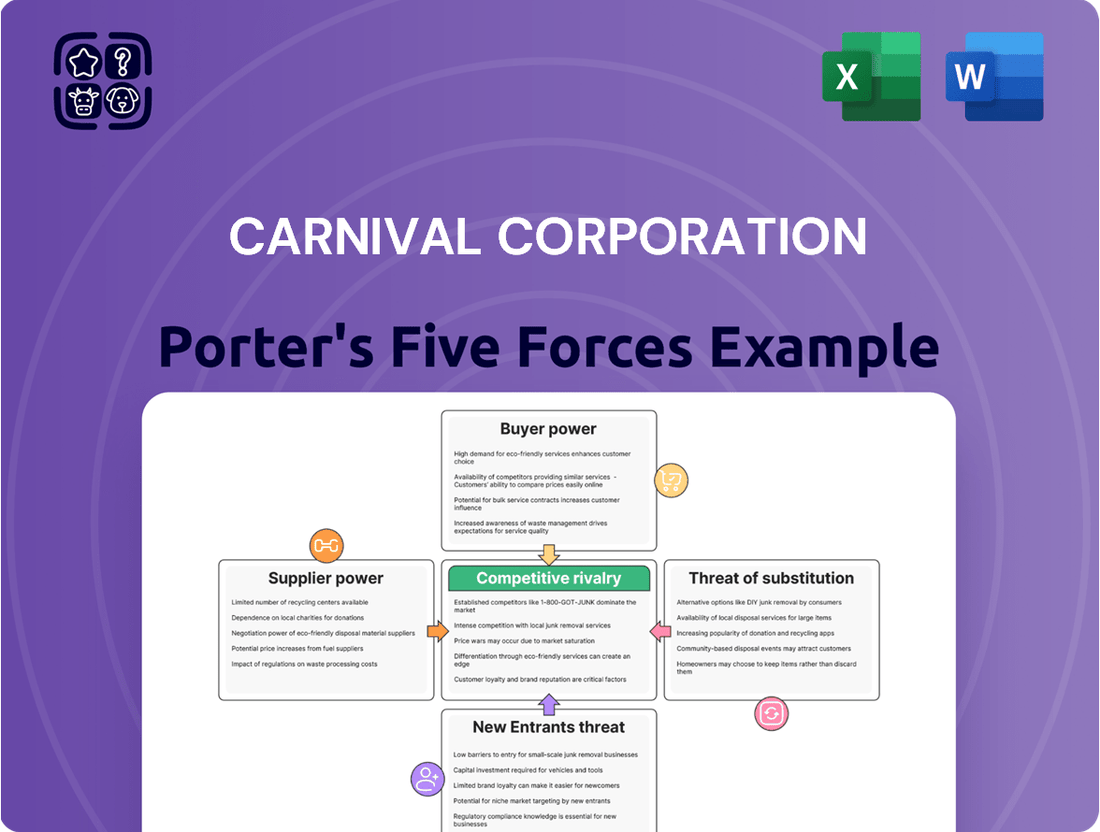
Carnival Corporation Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Carnival Corporation Bundle
Carnival Corporation navigates a complex industry shaped by intense rivalry, significant buyer power, and the constant threat of new entrants. Understanding these forces is crucial for any stakeholder looking to grasp the company's strategic landscape.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Carnival Corporation’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of specialized shipbuilders for Carnival Corporation is substantial due to the highly capital-intensive and niche nature of cruise ship construction. Only a handful of global shipyards possess the expertise and infrastructure to build these complex vessels, limiting Carnival's options. For instance, in 2024, the global order book for cruise ships reflects this concentration, with yards like Meyer Werft and Fincantieri securing significant contracts, indicating their strong negotiating position.
Carnival's dependence on these few yards for fleet expansion and upgrades means they often face significant cost pressures and extended delivery schedules. The specialized skills and advanced technology required mean that switching shipyards is not a simple or cost-effective undertaking. This reliance grants these shipbuilders considerable leverage in price negotiations and contract terms, directly impacting Carnival's capital expenditure.
Fuel is a significant cost for Carnival Corporation, directly impacted by volatile global oil prices. In 2024, the price of Brent crude oil, a key benchmark, averaged around $83 per barrel, showing the ongoing sensitivity of operating expenses to energy markets.
Carnival's reliance on traditional marine fuels for its extensive fleet limits its ability to quickly pivot to alternative energy sources. This dependence grants fuel providers substantial bargaining power, as the company cannot easily substitute these essential inputs for its current operations.
The bargaining power of suppliers in port services and infrastructure for Carnival Corporation is significant. Access to key port destinations and essential services like docking, pilotage, and waste disposal are critical for Carnival's global operations. Many ports operate as regional monopolies or face limited competition, enabling them to set terms and fees that can impact Carnival's costs.
Carnival's reliance on a wide array of these local service providers across its extensive itinerary network amplifies the collective power of these suppliers. For instance, in 2023, Carnival Corporation operated a fleet of 90 ships calling at over 400 ports worldwide, highlighting the broad dependency on diverse port service providers.
Highly Skilled Labor (Officers and Crew)
The cruise industry, including Carnival Corporation, depends heavily on a global talent pool for specialized maritime roles. Positions like captains, chief engineers, and experienced hospitality managers require specific certifications and extensive experience, giving these skilled individuals and their representatives a degree of leverage.
While the overall labor market might be vast, the scarcity of highly qualified and certified officers can translate into increased recruitment and retention costs for cruise lines. For instance, the International Maritime Organization (IMO) continually updates training standards, further emphasizing the need for specialized expertise.
Carnival Corporation, like its peers, invests significantly in training and development programs to cultivate and retain its skilled workforce. This focus on internal development helps to mitigate the bargaining power of external suppliers of highly skilled labor.
- Specialized Maritime Roles: Demand for certified captains, engineers, and hospitality managers creates leverage for these workers.
- Global Workforce Dependency: Cruise lines rely on international talent for critical operational and service functions.
- Training and Retention Investments: Companies like Carnival invest in employee development to secure and maintain a skilled labor force, thereby managing supplier power.
Food, Beverage, and Entertainment Suppliers
Carnival Corporation's bargaining power with food, beverage, and entertainment suppliers is influenced by its massive scale. While a broad base of suppliers exists, Carnival's substantial purchasing volume allows for negotiation of favorable terms and long-term contracts, particularly for standard goods. For instance, in 2024, Carnival continued to leverage its purchasing power to secure competitive pricing for core food and beverage components across its fleet.
However, the bargaining power can shift towards suppliers of unique or premium products, such as specialty culinary ingredients or specific, high-demand entertainment acts. These specialized suppliers may command higher prices due to their limited availability and distinct value proposition, giving them more leverage in negotiations with Carnival.
Effectively managing this diverse supply chain is crucial for Carnival to mitigate supplier power. This involves strategic sourcing, building strong supplier relationships, and diversifying procurement to avoid over-reliance on any single supplier.
- Scale Advantage: Carnival's large order volumes grant significant negotiation leverage for commodity items.
- Premium Niche: Suppliers of unique or high-quality entertainment and specialty foods can exert greater influence.
- Strategic Sourcing: Diversifying suppliers and fostering relationships helps manage supplier power effectively.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Carnival Corporation is a multifaceted issue, with key areas including specialized shipbuilders, fuel providers, port services, and specialized labor. While Carnival's scale offers some leverage, the unique nature of cruise operations and the limited pool of qualified providers in certain sectors grant significant power to many suppliers.
| Supplier Category | Key Factors Influencing Bargaining Power | Impact on Carnival | 2024 Data/Context |
|---|---|---|---|
| Specialized Shipbuilders | Limited number of global yards with expertise, high capital intensity, long lead times. | Significant cost pressures, extended delivery schedules, limited options for fleet expansion/maintenance. | Concentrated order book with major players like Fincantieri and Meyer Werft securing key contracts. |
| Fuel Providers | Volatility of global oil prices, dependence on traditional marine fuels. | Direct impact on operating expenses, sensitivity to energy market fluctuations. | Brent crude oil averaged around $83 per barrel in 2024, highlighting ongoing cost sensitivity. |
| Port Services & Infrastructure | Regional monopolies or limited competition in many ports, critical operational necessity. | Ability to set terms and fees, impacting operational costs across a global network. | Carnival's fleet of 90 ships called at over 400 ports worldwide in 2023, indicating broad dependency. |
| Specialized Labor | Scarcity of certified maritime officers and experienced hospitality managers. | Increased recruitment and retention costs, need for specialized training. | International Maritime Organization (IMO) updates emphasize ongoing need for specialized expertise. |
| Food, Beverage & Entertainment (Premium) | Limited availability and distinct value proposition of unique/premium products or acts. | Potential for higher prices due to specialized offerings. | Carnival leverages purchasing power for standard goods but faces higher costs for niche entertainment. |
What is included in the product
This analysis delves into the competitive forces shaping the cruise industry, examining Carnival Corporation's position against rivals, the bargaining power of customers and suppliers, and the threat of new entrants and substitutes.
Visualize competitive intensity with a dynamic Porter's Five Forces dashboard, allowing Carnival Corporation to proactively address threats and capitalize on opportunities.
Customers Bargaining Power
Cruise vacations are a major discretionary purchase, and consumers are keenly aware of the cost, particularly when economic conditions are uncertain. In 2024, for instance, many travelers continued to seek value, making price a primary driver in their booking decisions. This sensitivity means Carnival Corporation must constantly monitor and adjust its pricing to remain attractive.
The ease with which customers can compare offerings across various cruise lines and even alternative vacation types intensifies this price pressure. For example, a quick online search can reveal numerous options for a similar travel experience, forcing Carnival to offer competitive pricing and appealing promotions to capture market share. This dynamic directly impacts Carnival's ability to command higher prices without losing significant customer volume.
The sheer volume of vacation alternatives available to consumers significantly bolsters their bargaining power. Beyond cruises, travelers can choose from beach resorts, adventure tours, city breaks, and even staycations. This wide spectrum of substitutes means that if Carnival Corporation's pricing or product doesn't align with customer desires, switching to a different type of holiday is remarkably easy.
In 2024, the travel industry continued to see robust demand for diverse vacation experiences. For instance, the all-inclusive resort market has shown consistent growth, offering a bundled price that can be highly attractive. This competitive landscape forces cruise lines like Carnival to continually innovate and offer compelling value propositions to retain their customer base.
The internet has dramatically shifted the balance of power towards customers in the cruise industry. With countless online travel agencies and review sites, travelers can easily access comprehensive information on pricing, itineraries, and past passenger experiences. This ease of information access allows them to compare offerings from Carnival Corporation and its competitors side-by-side, significantly increasing their bargaining power.
In 2024, the proliferation of user-generated content and independent review platforms means that customer opinions carry substantial weight. For instance, platforms like TripAdvisor and Cruise Critic provide detailed insights that can heavily influence booking decisions. Carnival must therefore invest in managing its online reputation and optimizing its presence across these channels to effectively guide customer choices and mitigate the impact of negative feedback.
Impact of Group Bookings and Travel Agencies
While individual travelers hold some sway, the bargaining power of customers escalates significantly with large group bookings and through established travel agencies. These agencies, acting as aggregators of demand, can negotiate favorable commission rates or secure exclusive package deals, directly impacting Carnival's pricing flexibility. In 2024, travel agencies remained a crucial distribution channel for Carnival, handling a substantial portion of bookings, which inherently limits direct pricing control.
- Group Bookings: Large group reservations, often for corporate events or special occasions, provide customers with leverage to negotiate bulk discounts.
- Travel Agency Influence: Travel agencies, by consolidating customer demand, can exert considerable pressure on cruise lines for better rates and higher commissions.
- Distribution Dependence: Carnival's reliance on these intermediaries for a significant share of its sales means that agency demands can influence pricing strategies.
Switching Costs are Relatively Low
For Carnival Corporation, the bargaining power of customers is amplified by relatively low switching costs. Travelers can easily move between different cruise lines or opt for alternative vacation types without facing significant penalties or contractual lock-ins. This freedom to choose means Carnival must continually earn customer loyalty through superior experiences and competitive pricing.
The ease with which customers can switch vacation providers is a key factor. For instance, a customer booking a Caribbean cruise in 2024 can readily compare prices and itineraries across Carnival, Royal Caribbean, and Norwegian Cruise Line, or even decide on a land-based resort vacation. There are no substantial upfront investments or specialized equipment required to change cruise lines, unlike in some B2B industries.
- Low Switching Costs: Customers can readily switch between Carnival and competitors like Royal Caribbean or Norwegian Cruise Line, or choose alternative vacation types.
- No Significant Penalties: Unlike long-term contracts in other sectors, cruise bookings typically do not involve penalties for cancellation or switching for future travel.
- Focus on Loyalty: Carnival's need to retain customers is high, driving investment in loyalty programs and personalized offers to mitigate the impact of low switching costs.
The bargaining power of customers is a significant force for Carnival Corporation, driven by price sensitivity and the abundance of vacation alternatives. In 2024, travelers remained highly attuned to value, making price a critical factor in their decisions. This means Carnival must consistently offer competitive pricing and attractive promotions to secure bookings.
The ease of comparison across numerous cruise lines and other vacation types further empowers customers. Online platforms allow for straightforward price and itinerary comparisons, forcing Carnival to remain vigilant about its pricing strategies. This dynamic directly limits Carnival's ability to increase prices without risking customer loss.
In 2024, the travel market saw continued growth in diverse offerings, such as all-inclusive resorts, which present a bundled value proposition that competes directly with cruise packages. This broad range of substitutes means that if Carnival's offerings do not meet customer expectations, consumers can easily opt for different types of holidays, underscoring the substantial bargaining power they hold.
Preview Before You Purchase
Carnival Corporation Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. It details Carnival Corporation's competitive landscape through Porter's Five Forces, analyzing the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers, the bargaining power of suppliers, the threat of substitute products or services, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The global cruise industry is a tightly concentrated market, with Carnival Corporation, Royal Caribbean Group, and Norwegian Cruise Line Holdings being the dominant forces. This oligopolistic landscape means that any strategic move by one of these giants, like adjusting ticket prices or launching new vessels, directly influences the competitive environment for the others. For instance, in 2023, Carnival Corporation reported total revenues of $21.6 billion, highlighting its significant market share and the substantial resources available for competitive maneuvers.
Carnival Corporation, like other major cruise lines, grapples with immense fixed costs tied to its massive fleet, port facilities, and extensive crew. These substantial overheads necessitate a constant focus on filling as many cabins as possible. For instance, in 2023, Carnival reported operating costs exceeding $17 billion, underscoring the financial imperative of high capacity utilization.
This pressure to maintain high occupancy, often targeting rates above 100% of available lower berths, directly fuels intense competition. Cruise lines frequently resort to aggressive pricing strategies, offering significant discounts and promotional packages to attract passengers, especially when the industry experiences overcapacity or during seasonal lulls in demand.
Carnival Corporation actively differentiates its offerings across its extensive brand portfolio. For instance, while the core product is cruising, brands like Cunard target the luxury segment with a more traditional, refined experience, whereas Carnival Cruise Line focuses on a fun, value-oriented, contemporary market. This strategic segmentation, evident in their diverse fleet and destination strategies, aims to reduce head-to-head price wars by appealing to distinct customer preferences.
Slow Industry Growth and Mature Market Segments
In mature market segments of the cruise industry, growth is often achieved by taking share from rivals, intensifying competitive rivalry. Carnival Corporation, like its peers, faces this dynamic where expansion relies on outmaneuvering competitors rather than capitalizing on broad market expansion.
While emerging markets present opportunities, the overall pace of industry growth remains slower compared to other travel and tourism sectors. This limited growth forces companies to compete more fiercely for existing customers.
The struggle for market share in these established areas frequently translates into aggressive marketing campaigns and price-sensitive strategies. For instance, in 2024, the cruise industry continued to focus on promotional offers to attract passengers, particularly in North America and Europe, which represent its most mature markets.
- Intensified Competition: Mature markets necessitate aggressive tactics to gain market share.
- Limited Overall Growth: Slower industry expansion compared to other tourism sectors fuels rivalry.
- Strategic Focus: Companies rely on marketing and pricing to differentiate and capture customers.
Exit Barriers are Extremely High
Carnival Corporation faces extremely high exit barriers due to the massive capital required for its fleet. The specialized nature of cruise ships, with their extensive customization and regulatory compliance, makes them difficult to repurpose or sell quickly. This means even struggling entities often remain in the market, prolonging competitive intensity rather than easing it through natural attrition.
The sheer cost of divesting or dismantling a cruise ship can be prohibitive. For instance, a new large cruise ship can cost upwards of $1 billion, and their resale value is heavily dependent on the specific market conditions and the ship's age and features. This financial commitment acts as a significant deterrent to exiting the industry, even when facing financial headwinds.
- Immense Capital Investment: The cost of building and maintaining a modern cruise ship fleet represents a substantial financial commitment, often running into billions of dollars.
- Specialized Assets: Cruise ships are highly specialized assets with limited alternative uses, making their disposal or sale a complex and often loss-making proposition.
- Operational Continuity: High exit barriers compel even unprofitable companies to continue operations to avoid realizing significant asset write-downs, contributing to industry overcapacity.
- Sustained Competitive Pressure: The inability of firms to easily exit the market ensures a constant level of competition, as struggling players remain active participants rather than exiting and reducing supply.
The competitive rivalry within the cruise industry is fierce, primarily driven by a concentrated market structure dominated by a few major players like Carnival Corporation. This oligopoly means that strategic decisions, such as pricing or fleet expansion, directly impact competitors. For instance, Carnival Corporation's 2023 revenue of $21.6 billion underscores its significant market presence and capacity for competitive action.
High fixed costs associated with maintaining a large fleet and extensive infrastructure compel cruise lines to prioritize high occupancy rates. In 2023, Carnival's operating costs exceeded $17 billion, emphasizing the need for constant customer acquisition. This pressure often leads to aggressive pricing and promotional activities, especially in mature markets where growth is achieved by taking share from rivals.
Carnival Corporation mitigates direct price competition through brand segmentation, offering distinct experiences across its portfolio, from luxury with Cunard to value-oriented with Carnival Cruise Line. This strategy aims to capture different customer segments and reduce direct head-to-head battles, though competition for overall market share remains intense, particularly in established regions like North America and Europe, which saw continued promotional efforts in 2024.
| Company | 2023 Revenue (USD Billions) | 2023 Operating Costs (USD Billions) | Key Competitive Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carnival Corporation | 21.6 | >17 | Brand segmentation, aggressive marketing, pricing promotions |
| Royal Caribbean Group | 13.1 | N/A | Fleet modernization, premium experiences |
| Norwegian Cruise Line Holdings | 8.5 | N/A | Focus on contemporary market, diverse itineraries |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Land-based all-inclusive resorts present a significant threat of substitution for Carnival Corporation's cruise offerings. These resorts provide a comparable all-in-one vacation experience, encompassing lodging, dining, drinks, and entertainment, often with a clear, upfront price. This makes them a direct competitor for travelers prioritizing convenience and predictable budgeting.
For individuals who prefer a single destination and the opportunity for deeper exploration on land, all-inclusive resorts are a compelling alternative to a cruise. This segment of the travel market, which values a stationary vacation base, directly substitutes the cruise experience. For instance, in 2024, the all-inclusive resort sector continued its strong recovery, with occupancy rates in popular Caribbean destinations frequently exceeding 80%, indicating robust demand.
Major theme parks and integrated destination resorts offer compelling, immersive vacation experiences that directly compete with cruise lines for consumer leisure spending. For instance, in 2024, the global theme park market was projected to reach over $70 billion, demonstrating a significant draw for families and thrill-seekers. These land-based alternatives provide a concentrated form of entertainment, often appealing to the same demographic that might otherwise consider a cruise, especially for shorter, domestic trips.
A significant portion of the travel market opts for independent travel, booking flights, accommodations, and activities separately. This DIY approach offers unparalleled flexibility and personalization, allowing travelers to craft unique itineraries that often involve a deeper immersion into local culture. For instance, in 2023, the global online travel market was valued at over $800 billion, with a substantial share attributed to individual bookings for flights and hotels, highlighting the scale of this substitute.
The increasing popularity of vacation rental platforms like Airbnb and Vrbo further strengthens this competitive force. These platforms provide travelers with diverse lodging options, from apartments to entire homes, often at competitive prices and with the added benefit of local living experiences. This trend directly competes with the packaged nature of cruise offerings by providing a more authentic and customizable travel experience.
Adventure Travel and Specialized Tours
For consumers looking for truly unique experiences, adventure travel and specialized tours present a significant threat of substitution to Carnival Corporation's offerings. These niche travel segments, such as safaris, extensive trekking expeditions, or deep cultural immersion tours, appeal to a different set of traveler motivations but compete for the same discretionary travel budgets. For instance, in 2024, the global adventure tourism market was valued at approximately $285 billion, demonstrating a substantial pool of spending that could be diverted from traditional cruising.
These specialized options often provide a level of exclusivity and personalized engagement that a large-scale cruise might not match. Travelers prioritizing exploration and authentic cultural encounters may find these alternatives more fulfilling. The growth in this sector is robust, with projections indicating continued expansion as more individuals seek out distinctive and memorable travel experiences beyond the conventional.
- Market Size: The global adventure tourism market was valued around $285 billion in 2024.
- Growth Potential: This segment is experiencing significant growth, attracting travelers seeking unique experiences.
- Consumer Motivation: Adventure and specialized tours cater to a desire for exploration and cultural immersion, differing from mass-market cruising.
- Spending Competition: These alternatives draw from the same discretionary travel spending pool as cruise lines.
Staycations and Local Leisure Activities
The rise of staycations and local leisure activities presents a significant threat of substitutes for cruise lines like Carnival Corporation. In times of economic uncertainty or for budget-conscious consumers, opting for domestic travel or engaging in local entertainment becomes a more attractive alternative to expensive international vacations.
This trend was particularly evident in 2024, with many consumers prioritizing value and convenience. For instance, a significant portion of travelers explored domestic destinations, reducing the demand for long-haul travel often associated with cruises. This shift means that Carnival must contend with a broader range of leisure spending options, from weekend getaways to cultural events closer to home.
- Increased Domestic Travel: Reports in 2024 indicated a strong preference for domestic travel, with many individuals choosing to explore national parks, beaches, and cities within their own countries, offering a direct alternative to cruise itineraries.
- Growth in Local Entertainment: Spending on local attractions, dining, and entertainment also saw a rise, diverting discretionary income that might otherwise have been allocated to a cruise.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Staycations and local activities often represent a more cost-effective way to enjoy leisure time, especially when factoring in the all-inclusive nature of many cruise packages but also considering the additional costs of flights and pre/post-cruise accommodations for cruises.
The threat of substitutes for Carnival Corporation is substantial, as numerous alternative vacation experiences compete for consumer dollars. Land-based all-inclusive resorts offer a comparable convenience and predictable budgeting, with the sector showing strong recovery in 2024, frequently exceeding 80% occupancy in Caribbean destinations. Similarly, major theme parks and integrated resorts, which saw the global market projected to exceed $70 billion in 2024, attract families and thrill-seekers with immersive entertainment.
Independent travel, facilitated by online booking platforms valued at over $800 billion in 2023, provides flexibility and customization that cruises may not match. Vacation rental platforms like Airbnb also offer diverse lodging and local experiences, directly challenging the packaged nature of cruise vacations. Furthermore, the adventure tourism market, valued at approximately $285 billion in 2024, caters to travelers seeking unique, immersive experiences, diverting spending from traditional cruising.
| Substitute Category | Key Characteristics | 2024 Market Relevance/Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| All-Inclusive Resorts | Convenience, predictable budgeting, single destination | High occupancy rates (often >80%) in Caribbean in 2024 |
| Theme Parks & Integrated Resorts | Immersive entertainment, family appeal | Global market projected >$70 billion in 2024 |
| Independent Travel (Online Bookings) | Flexibility, personalization, local immersion | Global online travel market valued >$800 billion in 2023 |
| Vacation Rentals (e.g., Airbnb) | Diverse lodging, local living experience, customization | Continual growth in platform user base and bookings |
| Adventure & Specialized Tours | Unique experiences, exploration, cultural immersion | Global market valued ~$285 billion in 2024 |
Entrants Threaten
The cruise industry presents a formidable barrier to entry due to the sheer magnitude of capital investment required. Building a single modern cruise ship can easily cost between $500 million and over $1 billion, a sum that deters most potential newcomers.
This prohibitive cost means that any new entrant must secure substantial funding just to acquire even a modest fleet, making it incredibly challenging to achieve the economies of scale enjoyed by giants like Carnival Corporation. For instance, Carnival's 2023 annual report details significant ongoing capital expenditures for fleet modernization and expansion, highlighting the continuous investment needed to remain competitive.
The cruise industry is heavily regulated, with international maritime laws, environmental standards, and safety protocols creating significant barriers. For instance, the International Maritime Organization (IMO) continuously updates its safety and environmental regulations, such as the Ballast Water Management Convention, which requires substantial investment in new technologies for compliance. New entrants must navigate these complex legal landscapes and secure numerous certifications before even launching operations, a process that can take years and millions of dollars.
Carnival Corporation, like other major players in the cruise industry, benefits significantly from deeply ingrained brand loyalty and extensive distribution networks. For instance, Carnival's brands such as Carnival Cruise Line, Princess Cruises, and Holland America Line have cultivated decades of customer relationships, often reinforced by robust loyalty programs. As of 2024, these established brands continue to leverage their reputations to attract repeat business, making it a formidable barrier for newcomers.
New companies entering the cruise market face the immense challenge of replicating Carnival's established presence. Building comparable brand trust and securing access to effective sales channels, which include a vast array of travel agents and online travel agencies that Carnival has nurtured over time, requires substantial investment and time. This existing infrastructure and customer affinity significantly deter potential new entrants by making market penetration exceedingly difficult and costly.
Limited Port Infrastructure and Slot Availability
The threat of new entrants is significantly amplified by limited port infrastructure and the scarcity of available berthing slots, particularly in high-demand cruise destinations. Established players like Carnival Corporation often secure long-term contracts and preferential access, creating a barrier for newcomers. For instance, in 2024, major Caribbean ports like St. Maarten and Cozumel reported near-capacity utilization during peak seasons, making it difficult for new cruise lines to secure consistent docking privileges. This constraint directly impacts the ability of new entrants to develop competitive and appealing itineraries, as reliable port access is fundamental to operational success.
New entrants would face substantial hurdles in securing adequate berthing and operational support in key global markets. This is not just about finding a space to dock; it involves negotiating with port authorities, often competing with established cruise lines that have built strong relationships over years. In 2023, the average waiting time for a new cruise line seeking premium port access in the Mediterranean reportedly increased by 15% compared to previous years. Such challenges can delay launch timelines and increase initial capital expenditure, making the market entry financially precarious.
The difficulty in obtaining sufficient port slots directly hinders the creation of attractive cruise itineraries, a critical factor for market penetration. Without guaranteed access to desirable ports, new entrants struggle to offer the varied and appealing destinations that consumers expect. For example, a new entrant might find it impossible to secure the necessary port calls in Alaska during the 2025 season due to existing commitments from major operators, forcing them to offer less desirable routes. This limitation makes it challenging to compete with the established product offerings of companies like Carnival, which can leverage their extensive port agreements to provide comprehensive and desirable cruise experiences.
- Limited Port Infrastructure: Key cruise destinations in 2024, such as parts of the Caribbean and Mediterranean, experienced high port utilization rates, limiting available docking space for new operators.
- Slot Availability Challenges: Established cruise lines often hold preferential access to prime port slots through long-term agreements, making it difficult for new entrants to secure necessary berthing.
- Itinerary Development Hindrance: The inability to guarantee port access in popular locations directly impedes new entrants' ability to craft competitive and appealing cruise itineraries.
- Increased Operational Costs: Securing limited port access can lead to higher operational costs and extended planning cycles for new cruise businesses, impacting profitability and market entry viability.
Operational Complexity and Specialized Expertise
The cruise industry presents a formidable barrier to entry due to its inherent operational complexity. New companies must master intricate logistics, from port operations to itinerary planning, alongside sophisticated hospitality management to cater to a diverse global clientele. Maritime operations require adherence to stringent international safety regulations and the management of large, complex vessels, demanding highly specialized skills.
Furthermore, establishing a global supply chain capable of supporting multiple ships and destinations is a monumental task. New entrants would need to build this expertise from scratch, a process that takes years and significant capital investment. For instance, Carnival Corporation, a major player, benefits from decades of accumulated knowledge in areas like fuel procurement, waste management, and crew training, which are critical for efficient and compliant operations.
- Logistics Mastery: Managing global port calls, shore excursions, and passenger flow requires extensive experience.
- Hospitality Excellence: Delivering consistent high-quality service across numerous onboard venues is a core competency.
- Maritime Compliance: Navigating complex international maritime laws and safety standards is non-negotiable.
- Supply Chain Integration: Sourcing and delivering provisions, fuel, and maintenance parts efficiently across a fleet is vital.
The threat of new entrants into the cruise industry is significantly low, primarily due to the immense capital required to build and operate even a single modern cruise ship, with costs often exceeding $500 million. This financial hurdle, coupled with stringent international regulations and the need for established brand loyalty and extensive distribution networks, creates substantial barriers. For instance, in 2024, the ongoing need for fleet modernization and compliance with evolving environmental standards like the IMO's Ballast Water Management Convention demands continuous, significant investment, a challenge most new players cannot readily meet.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Carnival Corporation is built upon a foundation of industry-specific market research reports, financial filings from Carnival and its competitors, and data from reputable travel industry associations.
