Campus Activewear Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Campus Activewear Bundle
Campus Activewear navigates a dynamic market, facing moderate threats from new entrants and the availability of substitutes in the activewear sector. Understanding the bargaining power of both buyers and suppliers is crucial for their strategic positioning.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Campus Activewear’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Campus Activewear's bargaining power of suppliers is influenced by the concentration of its raw material sources. If the company relies on a few dominant suppliers for key inputs like specialized synthetic fabrics or unique sole components, these suppliers gain significant leverage. For instance, a 2024 report indicated that the global market for performance athletic footwear materials is increasingly consolidated, with a handful of chemical and textile manufacturers holding substantial market share.
The uniqueness of these raw materials also plays a crucial role. If Campus Activewear sources components that are highly specialized and not readily available from multiple vendors, suppliers can command higher prices or dictate terms. Conversely, if the materials are standardized and easily substitutable, like basic rubber or common synthetic fabrics, Campus Activewear can switch suppliers more readily, reducing supplier power.
Campus Activewear's bargaining power of suppliers is influenced by switching costs. If Campus Activewear needs to change suppliers, they might incur significant expenses related to retooling machinery or adapting to new material specifications. For instance, if a supplier provides unique fabric blends or specialized manufacturing equipment, the cost and time to transition to a new supplier could be substantial. This makes it harder for Campus Activewear to switch, thus strengthening the supplier's position.
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into footwear manufacturing represents a significant potential increase in their bargaining power against Campus Activewear. If key material suppliers, such as those providing specialized rubber soles or performance fabrics, were to establish their own footwear production lines, they could directly challenge Campus Activewear's market share.
This forward integration would allow suppliers to capture a larger portion of the value chain, potentially offering their own branded footwear directly to consumers or retailers. For instance, a major sole manufacturer with advanced material science capabilities might leverage its expertise to create its own line of athletic shoes, thereby becoming a direct competitor.
In 2023, the Indian footwear market was valued at approximately $12 billion, with the sports footwear segment showing robust growth. Should a significant supplier decide to enter this lucrative market, it would not only disrupt the supply chain but also intensify competition, forcing Campus Activewear to contend with new, potentially well-resourced rivals who understand the intricacies of material sourcing.
Importance of Campus Activewear to Suppliers
The significance of Campus Activewear to its suppliers plays a crucial role in determining supplier bargaining power. If Campus Activewear constitutes a substantial portion of a supplier's total sales, that supplier might have less leverage. This is because the supplier's revenue stream would be heavily reliant on Campus, making them more accommodating to Campus's demands.
For instance, if a key fabric supplier for Campus Activewear generates 30% of its revenue from Campus, that supplier is likely to be more sensitive to Campus's pricing and terms. Conversely, if Campus represents only a small fraction of a supplier's business, the supplier has less incentive to concede to Campus's requests, thus increasing their bargaining power.
- Supplier Dependence: The degree to which suppliers depend on Campus Activewear for their revenue directly influences their bargaining power. A higher dependence generally leads to lower supplier power.
- Revenue Concentration: If a significant percentage of a supplier's annual revenue comes from Campus Activewear, the supplier may be more inclined to offer favorable terms to maintain the business relationship.
- Market Share of Supplier: For suppliers who are relatively small or specialized, Campus Activewear might represent a larger share of their market, amplifying Campus's influence.
Availability of Substitute Inputs
The availability of substitute inputs significantly impacts supplier bargaining power for Campus Activewear. If alternative materials or components are readily accessible and comparable in quality and price, Campus Activewear can switch suppliers, thereby limiting the leverage of any single supplier. For instance, if the primary synthetic fabric supplier faces issues, having easily sourced alternatives like recycled polyester or other performance blends would reduce the pressure from the original supplier.
In 2023, the global textile market saw increased interest in sustainable and recycled materials, indicating a growing availability of substitute inputs. This trend can empower companies like Campus Activewear to negotiate better terms with their existing suppliers or explore new sourcing options. The ease with which Campus Activewear can find comparable alternatives directly correlates to how much power its suppliers can wield.
- Availability of Substitutes: The presence of multiple suppliers for key materials like synthetic fabrics, rubber for soles, and dyes reduces the dependence on any single source.
- Cost of Switching: If the cost and effort involved in switching to a new supplier are low, Campus Activewear's bargaining power increases.
- Material Innovation: Advances in material science offering new, cost-effective, or performance-enhancing alternatives can further dilute supplier power.
- Supplier Concentration: A fragmented supplier base for essential components generally leads to lower supplier bargaining power compared to a concentrated market.
The bargaining power of Campus Activewear's suppliers is influenced by the concentration and uniqueness of raw materials. If key inputs are sourced from a few dominant manufacturers, as seen in the consolidated global athletic footwear material market in 2024, these suppliers gain significant leverage, especially if the materials are specialized and not easily substituted. High switching costs for Campus Activewear, such as retooling for new materials, further strengthen supplier positions.
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into manufacturing, potentially becoming direct competitors, poses a substantial risk. For example, a major sole manufacturer entering the growing Indian sports footwear market (valued around $12 billion in 2023) could intensify competition. Conversely, if Campus Activewear represents a large portion of a supplier's revenue, the supplier's dependence on Campus reduces their bargaining power.
The availability of substitute inputs, such as recycled materials which saw increased interest in 2023, empowers Campus Activewear to negotiate better terms. A fragmented supplier base for essential components generally leads to lower supplier bargaining power, as Campus can more easily switch sources if terms become unfavorable.
| Factor | Impact on Supplier Bargaining Power | Campus Activewear's Position (2024 Estimate) |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High concentration increases power | Moderate to High (depending on specific material) |
| Uniqueness of Materials | High uniqueness increases power | Varies; some proprietary materials, some standard |
| Switching Costs | High costs increase power | Moderate (can be high for specialized components) |
| Threat of Forward Integration | High threat increases power | Moderate (potential for material suppliers to enter footwear) |
| Supplier Dependence on Campus | Low dependence increases power | Varies; some suppliers likely highly dependent |
| Availability of Substitutes | High availability decreases power | Growing (especially with sustainable materials) |
What is included in the product
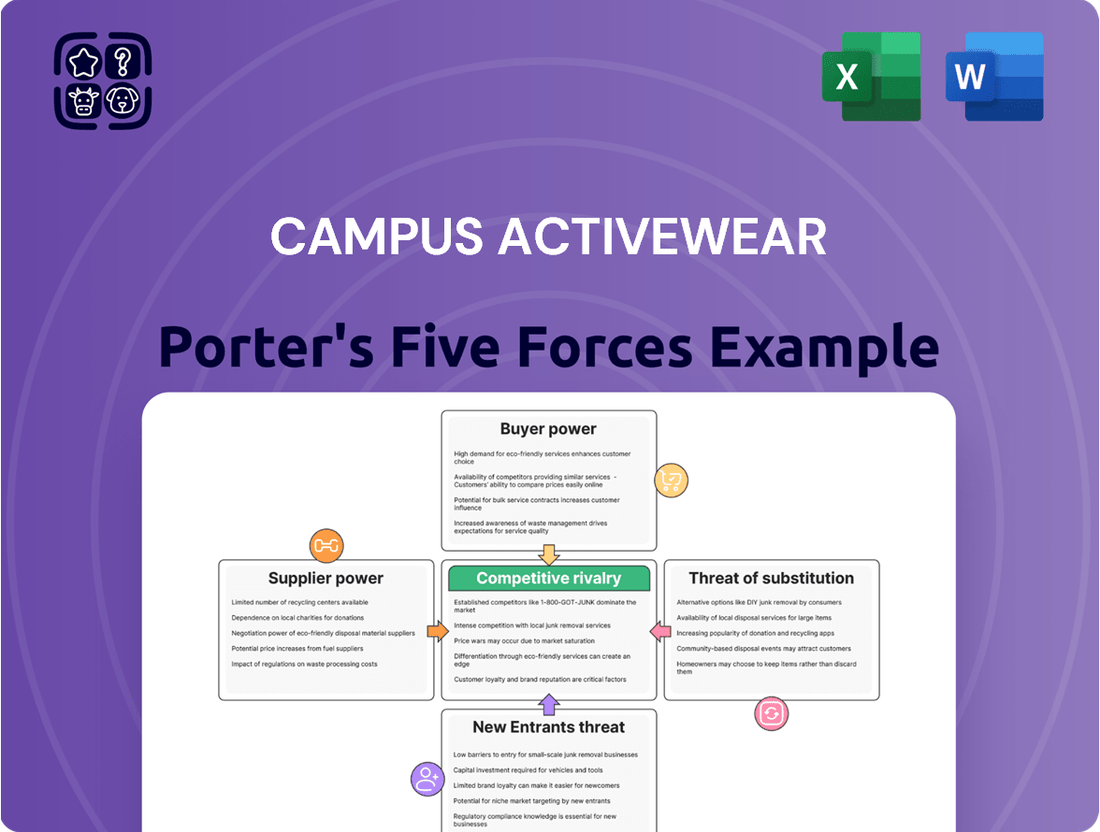
This analysis of Campus Activewear's competitive environment examines the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitute products, providing strategic insights into its market position.
Instantly visualize competitive intensity with a clear, actionable Porter's Five Forces analysis, simplifying complex market pressures for strategic clarity.
Customers Bargaining Power
Campus Activewear's customer price sensitivity is a key factor in their bargaining power. With a significant portion of their customer base being value-conscious students and young professionals, fluctuations in price can directly impact purchasing decisions. For instance, in the fiscal year 2023, Campus Activewear reported a revenue of ₹1,141 crore, indicating a substantial market presence where even small price shifts can resonate across many transactions.
The degree of product differentiation and the strength of brand loyalty play a crucial role here. While Campus offers a wide range of footwear, the athletic and casual footwear market is competitive, with many alternatives available. If customers perceive little difference between Campus products and those of competitors, or if their loyalty isn't deeply ingrained, they are more likely to switch brands for a lower price, thereby increasing their bargaining leverage.
Customers today have access to an unprecedented amount of information about product features, quality, and pricing, thanks to the internet. This transparency allows them to easily compare offerings from various brands, including Campus Activewear, and understand what constitutes fair value.
For instance, online reviews, detailed product specifications, and price comparison websites empower consumers. In 2024, a significant portion of apparel purchases are influenced by online research, with many consumers consulting multiple sources before making a decision. This readily available data strengthens their bargaining position.
The bargaining power of customers is significantly influenced by the availability of substitute products. For Campus Activewear, this means that if customers can easily find similar athletic, casual, or lifestyle footwear from other brands, their ability to negotiate better prices or terms increases.
The athletic footwear market, in particular, is crowded with numerous domestic and international players, offering a wide spectrum of choices. This abundance of alternatives empowers consumers, as they can readily switch brands if Campus Activewear's pricing or product offerings are not perceived as competitive. For instance, in 2023, the Indian footwear market saw strong growth, with a significant portion attributed to the athleisure segment, indicating robust competition.
Customer Concentration and Volume
Campus Activewear primarily serves a highly fragmented individual consumer base, which generally dilutes the bargaining power of any single customer. This widespread customer reach means that no single buyer accounts for a significant portion of overall sales.
However, large multi-brand retailers or institutional buyers can still exert some influence due to the volume they represent. For instance, if a major retail chain decides to reduce its order volume of Campus Activewear products, it could impact the company's revenue streams, although not to the same extent as if the company had only a handful of such clients.
- Customer Base: Campus Activewear's sales are predominantly driven by individual consumers, indicating a fragmented customer landscape.
- Impact of Large Buyers: While individual consumers have minimal power, large retailers or institutional buyers can wield influence through their purchase volumes.
- Leverage: The company's broad distribution network and direct-to-consumer sales channels help to mitigate the concentrated bargaining power of large buyers.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of backward integration by customers poses a significant challenge to Campus Activewear. Large retail partners, such as major sporting goods chains or department stores, could potentially leverage their market access and capital to develop their own private label footwear lines. This capability directly enhances their bargaining power, as they can credibly threaten to produce similar products internally, thereby reducing their reliance on Campus Activewear.
If these key customers were to engage in backward integration, they could capture a larger portion of the value chain. For instance, a large retailer might decide to invest in its own manufacturing facilities or contract with manufacturers directly to produce footwear under its brand. This would allow them to control costs, design, and supply more effectively, potentially leading to lower prices for consumers but squeezing Campus Activewear's margins.
The bargaining power of customers is amplified when they possess the ability to integrate backward. This threat compels suppliers like Campus Activewear to offer more competitive pricing and favorable terms to retain these valuable relationships. Consider the broader athletic footwear market where some large retailers have indeed launched successful private label brands, demonstrating the viability of this strategy.
- Customer Integration Threat: Large retailers can develop private label brands or even manufacture footwear themselves, increasing their bargaining power.
- Impact on Suppliers: This threat forces suppliers like Campus Activewear to offer better pricing and terms to maintain customer loyalty.
- Market Precedent: The athletic footwear sector has seen instances of retailers successfully launching private label lines, validating the potential for backward integration.
The bargaining power of customers for Campus Activewear is moderate. While individual consumers have limited power due to the fragmented nature of the customer base, large retailers and institutional buyers can exert influence through their purchase volumes.
The company's broad distribution network and direct-to-consumer sales channels help to mitigate the concentrated bargaining power of large buyers. However, the threat of backward integration by customers, such as large retailers developing private label brands, remains a factor that compels Campus Activewear to offer competitive pricing and terms.
| Factor | Impact on Campus Activewear | Supporting Data/Observation |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Fragmentation | Lowers individual customer power | Predominantly individual consumer base |
| Large Retailer Influence | Moderate power through volume | Key retail partners can impact sales |
| Backward Integration Threat | Moderate power through potential private labels | Market precedent of retailers launching own brands |
Preview Before You Purchase
Campus Activewear Porter's Five Forces Analysis
The document you see is your deliverable. It’s ready for immediate use—no customization or setup required. This comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis of Campus Activewear delves into the competitive landscape, examining the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the athletic apparel market. You’ll gain strategic insights into the factors shaping Campus Activewear's profitability and market position.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Indian sports and lifestyle footwear market is a crowded space, featuring a mix of established global giants like Nike and Adidas, alongside strong domestic players such as Relaxo Footwears and Paragon Footwear. This diverse competitive landscape, with brands employing varied strategies from premium positioning to mass-market accessibility, significantly heightens the rivalry.
The Indian footwear market, especially the activewear segment, is experiencing robust growth. This expansion, however, can intensify competitive rivalry as companies strive to capture a larger share of this expanding pie.
In 2023, the Indian footwear market was valued at approximately $11.1 billion and is projected to reach $22.8 billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 15.4%. This healthy growth rate suggests that while opportunities abound, the fight for consumer attention and loyalty will remain fierce, particularly for brands like Campus Activewear.
Campus Activewear faces intense competition, but its focus on product differentiation and building brand loyalty helps mitigate direct rivalry. By offering unique designs, innovative features, and a strong emphasis on comfort and style, Campus aims to stand out in the crowded athletic footwear market. This strategy is crucial in a sector where many competitors offer similar products.
The company's efforts to cultivate brand loyalty are evident in its marketing campaigns and customer engagement initiatives. For instance, Campus Activewear has been actively expanding its retail presence and online channels to reach a wider audience. As of the fiscal year ending March 31, 2023, Campus Activewear reported a revenue of ₹1,190.7 crore, showcasing its significant market presence and the effectiveness of its brand-building strategies in attracting and retaining customers.
Exit Barriers for Competitors
The Indian footwear market presents several exit barriers that can trap competitors, even those experiencing losses. Specialized manufacturing equipment, particularly for sports and performance footwear, represents a significant sunk cost. For instance, companies heavily invested in proprietary sole-molding technology or advanced stitching machinery would find it difficult to recoup their investment if they exited.
Furthermore, brand loyalty and established distribution networks act as substantial hurdles. A competitor that has spent years building brand recognition and securing shelf space in major retail chains across India, as many established players like Bata and Relaxo have, faces considerable challenges in divesting these assets without substantial write-downs. The emotional and strategic commitment to the Indian market also plays a role; many firms view India as a long-term growth opportunity, making a premature exit less likely.
- High Capital Investment: Specialized footwear manufacturing machinery and tooling represent significant sunk costs, making it financially punitive to exit the market.
- Brand Equity and Distribution: Established brands and extensive retail networks are difficult to sell off without significant depreciation, trapping firms with existing market presence.
- Emotional and Strategic Commitment: Many companies view the Indian market as a crucial long-term growth engine, deterring quick exits even in the face of temporary unprofitability.
Fixed Costs and Capacity Utilization
The footwear manufacturing industry, including companies like Campus Activewear, often carries significant fixed costs associated with setting up production facilities, machinery, and research and development. These high fixed costs create a strong incentive for manufacturers to operate at high capacity utilization to spread these costs over a larger volume of output. When capacity utilization is low, the cost per unit increases, making it harder to compete on price.
This pressure to maintain high production volumes can lead to intense price competition among rivals. Companies may engage in price wars to capture market share and keep their factories running efficiently. In 2023, for instance, the Indian footwear market saw increased promotional activities and discounts from major players as they aimed to boost sales volumes amidst a competitive landscape.
- High Fixed Costs: Investments in manufacturing plants and equipment represent substantial fixed costs for footwear producers.
- Capacity Utilization Imperative: Achieving high capacity utilization is crucial to lower per-unit production costs and maintain profitability.
- Price Competition Driver: The need to cover fixed costs and utilize capacity often fuels aggressive pricing strategies among competitors.
- Market Dynamics: In 2023, the Indian footwear sector experienced heightened competition, with companies employing promotional tactics to drive sales volumes.
Campus Activewear operates in a fiercely competitive Indian footwear market, characterized by numerous players vying for market share. The presence of global giants like Nike and Adidas, alongside strong domestic brands such as Relaxo and Paragon, intensifies this rivalry. This crowded environment means companies must constantly innovate and differentiate to capture consumer attention. The market's projected growth, from $11.1 billion in 2023 to an estimated $22.8 billion by 2028, fuels this competition as firms aim to secure a larger slice of the expanding pie.
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Campus Activewear is significant, as consumers have a wide array of non-activewear footwear options. This includes formal shoes for professional settings, traditional Indian footwear like juttis or sandals for cultural events, and even the practical choice of going barefoot in certain informal or domestic situations. The availability of these diverse alternatives directly impacts the demand for specialized activewear.
In 2024, the Indian footwear market, valued at approximately INR 60,000 crore, saw a substantial contribution from non-athletic segments. For instance, the formal and casual wear segments, which directly compete with activewear for discretionary spending on footwear, continue to hold a significant market share. This broad spectrum of readily available alternatives means consumers can easily switch to different footwear types based on occasion, comfort, or price, thereby posing a constant challenge to activewear brands like Campus.
The threat of substitutes for Campus Activewear is influenced by the price-performance trade-off. If other footwear brands, like Bata or Relaxo, offer comparable comfort and durability at a significantly lower price point, consumers might switch. For instance, if a substitute shoe provides 80% of the performance of a Campus shoe but costs 30% less, the threat is elevated.
Consumers generally face low switching costs when moving from Campus Activewear footwear to substitutes. The effort, time, and financial investment required to change brands are minimal, as athletic footwear is a widely available commodity. For instance, a consumer might spend less than $50 to switch from a Campus running shoe to a comparable model from a competitor like Skechers or Puma, with no significant time commitment beyond browsing online or in-store.
Consumer Preferences and Trends
Evolving consumer preferences present a significant threat of substitutes for Campus Activewear. A growing trend towards minimalist footwear, prioritizing comfort and simplicity over specialized athletic features, could divert consumers. For instance, the global minimalist shoe market was valued at approximately $1.7 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow, indicating a potential shift away from traditional activewear.
Furthermore, shifts in lifestyle and leisure activities can reduce the demand for dedicated activewear. As more consumers engage in activities like yoga, Pilates, or even casual walking that don't necessitate high-performance footwear, the need for specialized activewear diminishes. This trend is supported by data showing a 15% increase in participation in at-home fitness and wellness activities in 2024, often requiring less specialized gear.
- Shifting Footwear Trends: Growing consumer interest in minimalist or barefoot-style shoes, which offer a different sensory experience and perceived health benefits, can draw customers away from traditional athletic footwear brands like Campus.
- Lifestyle Activity Changes: An increase in participation in low-impact or non-sporting activities such as yoga, meditation, or even casual athleisure wear that prioritizes comfort over performance can reduce the necessity for specialized activewear.
- Sustainability Concerns: Some consumers may opt for more sustainable or ethically produced footwear alternatives, even if they aren't specifically designed for athletic performance, if these align better with their values.
Innovation in Substitute Industries
Technological advancements in adjacent sectors can introduce compelling alternatives to activewear. For example, the rise of athleisure, blurring the lines between athletic and casual apparel, presents a significant substitute. In 2024, the global athleisure market continued its robust growth, with projections indicating it could reach over $326 billion by 2026, demonstrating a strong consumer preference for comfortable, versatile clothing that can serve dual purposes.
Innovations in material science are also fostering new substitutes. Fabrics that offer enhanced breathability, moisture-wicking properties, and comfort are increasingly found in everyday wear, reducing the need for specialized activewear for light activities. This trend is further amplified by the growing emphasis on sustainable and eco-friendly materials, which are being adopted across the apparel industry, including casual wear segments.
- Athleisure Market Growth: Projected to exceed $326 billion by 2026, indicating strong consumer adoption of versatile apparel.
- Material Science Advancements: Innovations in casual wear fabrics offer comfort and performance features previously exclusive to activewear.
- Sustainability Trend: Increased use of eco-friendly materials in casual wear makes them more appealing substitutes for activewear in many contexts.
The threat of substitutes for Campus Activewear is substantial, given the wide array of non-athletic footwear options available to consumers. These include formal shoes, traditional Indian footwear, and even casual sandals, all of which compete for consumer spending on footwear. In 2024, the broader Indian footwear market, valued at approximately INR 60,000 crore, saw significant demand across these non-athletic segments, highlighting the accessibility of alternatives.
Consumers can easily switch to substitutes due to low switching costs, often involving minimal time and financial investment. For instance, a consumer might spend less than $50 to try a different brand of casual shoe. Furthermore, evolving trends like minimalist footwear, with a global market valued at around $1.7 billion in 2023, and the rise of athleisure, projected to reach over $326 billion by 2026, further dilute the necessity for specialized activewear.
| Substitute Category | Examples | Key Differentiator | Impact on Campus Activewear |
| Formal & Casual Footwear | Leather shoes, loafers, sandals | Occasion-specific styling, price point | Reduces demand for activewear in non-athletic settings |
| Minimalist/Barefoot Shoes | Vibram FiveFingers, Xero Shoes | Comfort, natural feel, perceived health benefits | Appeals to a segment seeking different sensory experiences |
| Athleisure Apparel & Footwear | Stylish sneakers, comfortable slides | Versatility, comfort, fashion-forward design | Blurs lines between athletic and casual wear, offering dual utility |
Entrants Threaten
Establishing a footwear manufacturing and distribution business in India demands substantial capital. This includes significant outlays for setting up modern factories, acquiring advanced machinery, managing extensive inventory, and launching robust marketing campaigns. For instance, a new player might need to invest upwards of ₹500 crore to ₹1,000 crore to build a competitive operation from the ground up, covering land, plant, machinery, and initial working capital.
Campus Activewear has built significant brand loyalty, particularly among its target demographic, making it harder for new entrants to capture market share. This loyalty is cultivated through consistent product quality, effective marketing campaigns, and a strong retail presence. For instance, in the fiscal year ending March 31, 2024, Campus Activewear reported a revenue of ₹1,462 crore, demonstrating its established market position and customer trust.
The perceived and actual costs for consumers to switch from Campus Activewear to a new brand are considerable. These costs can include the loss of familiarity with product fit and performance, the effort involved in researching and testing new brands, and the potential disappointment if a new brand fails to meet expectations. This inertia, coupled with the positive brand association Campus has fostered, acts as a substantial barrier to entry for newcomers.
New players entering the Indian activewear market face a significant hurdle in gaining access to established distribution channels. Securing shelf space in popular multi-brand retail outlets, which are dominated by existing brands, proves exceptionally difficult. For instance, major retailers like Lifestyle and Shoppers Stop often have long-standing relationships and volume commitments with established players, making it challenging for newcomers to break in.
Establishing exclusive brand stores is also capital-intensive and time-consuming, requiring substantial investment in prime retail locations and store fit-outs across India. Furthermore, building a robust and trusted online e-commerce presence, comparable to platforms like Myntra or the direct-to-consumer sites of established brands, demands significant marketing spend and logistical capabilities that nascent companies may lack.
Economies of Scale in Production and Marketing
Campus Activewear, like many established players in the athletic footwear sector, benefits significantly from economies of scale in production and marketing. Large-scale manufacturing allows for lower per-unit costs due to bulk purchasing of raw materials and more efficient production processes. For instance, in 2023, the Indian athletic footwear market was valued at approximately INR 25,000 crore, with major brands leveraging their size to negotiate better terms with suppliers and optimize distribution networks.
New entrants attempting to penetrate this market would likely face a substantial cost disadvantage. Operating at a smaller scale means higher per-unit costs for manufacturing, procurement, and crucially, marketing. The significant advertising spend required to build brand awareness and compete with established players like Campus Activewear, which likely invests heavily in celebrity endorsements and widespread retail presence, presents a formidable barrier. This cost disparity makes it less attractive for new, smaller companies to enter the market and compete effectively on price or reach.
- Economies of Scale in Production: Established firms like Campus Activewear can achieve lower production costs per unit by operating larger, more efficient manufacturing facilities and securing bulk discounts on raw materials.
- Marketing Cost Disadvantage: New entrants face higher per-unit marketing costs to achieve comparable brand visibility and consumer reach against established brands that have built significant brand equity and marketing infrastructure.
- Procurement Advantages: Larger companies benefit from greater bargaining power with suppliers, leading to more favorable pricing for components and materials, a benefit not readily available to smaller, new competitors.
- Distribution Network Efficiency: Existing players have developed extensive and cost-effective distribution networks, which are costly and time-consuming for new entrants to replicate.
Government Policy and Regulations
Government policy and regulations in India can significantly impact the threat of new entrants in the activewear market. For instance, the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) mandates certain quality certifications for footwear, which can be a hurdle for new players needing to invest in compliance. In 2023, the government also continued its focus on 'Make in India,' potentially offering incentives for domestic manufacturing, which could lower barriers for some local entrants but might pose challenges for those relying heavily on imports due to tariffs or import restrictions.
Licensing requirements and trade policies play a crucial role. New companies might face complexities in obtaining necessary business licenses and navigating import duties if they plan to source materials or finished goods from abroad. Conversely, trade agreements or government support for specific sectors could ease entry. For example, policies aimed at boosting the textile and apparel industry, which includes activewear, could indirectly facilitate new entrants by improving the overall business environment.
Favorable policies for established players or stringent regulations can act as significant entry barriers. Companies that have already invested in meeting BIS standards or have established relationships with government bodies might find it easier to operate. For example, in 2024, the government's emphasis on sustainable manufacturing practices could require new entrants to make substantial upfront investments in eco-friendly production, thereby raising the barrier.
- BIS Certification: Mandatory quality standards for footwear increase compliance costs for new entrants.
- 'Make in India' Initiative: Incentives for domestic manufacturing can favor local players but might increase costs for importers.
- Licensing and Trade Policies: Navigating business licenses and import/export regulations can be complex and costly for new firms.
- Sustainability Regulations: Growing focus on eco-friendly production in 2024 necessitates upfront investment in sustainable practices.
The threat of new entrants for Campus Activewear is moderate to high, primarily due to substantial capital requirements for manufacturing and distribution, alongside strong brand loyalty and high switching costs for consumers. Established players benefit from economies of scale in production and procurement, making it difficult for newcomers to compete on cost. Additionally, navigating regulatory landscapes and securing efficient distribution channels present significant hurdles.
| Barrier to Entry | Impact on New Entrants | Campus Activewear's Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High (₹500-1000 crore for competitive operation) | Established infrastructure and financial resources |
| Brand Loyalty & Switching Costs | High (Consumer inertia and preference for known brands) | Strong brand equity and customer trust |
| Economies of Scale | Disadvantageous (Higher per-unit costs) | Lower production and marketing costs |
| Distribution Access | Challenging (Securing shelf space and building online presence) | Extensive and efficient distribution network |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our analysis of Campus Activewear's competitive landscape is built upon a foundation of industry-specific market research reports, financial statements from publicly traded competitors, and consumer behavior surveys. We also leverage insights from trade publications and economic data to understand broader market trends.
