Camden National Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Camden National Bank Bundle
Camden National Bank navigates a complex financial landscape where buyer power and the threat of substitutes significantly shape its competitive environment. Understanding these forces is crucial for any stakeholder looking to grasp the bank's strategic positioning.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Camden National Bank’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Camden National Bank's reliance on technology and software providers for critical functions like digital banking, core systems, and cybersecurity presents a significant factor in its operational landscape. The bargaining power of these suppliers can range from moderate to high, particularly when the bank utilizes specialized or proprietary software solutions. In such cases, the costs and complexities associated with switching to alternative providers can be substantial, giving suppliers leverage.
The bank's strategic emphasis on enhancing its digital offerings and customer experience in recent years, a trend observed across the banking sector in 2024, amplifies this dependence. For instance, a report by Gartner in late 2023 predicted that IT spending in financial services would continue to grow, with a significant portion allocated to digital transformation initiatives, underscoring the importance of these technology partnerships.
Financial data providers wield significant influence over Camden National Bank, as access to real-time market data and analytical tools is fundamental for its investment and wealth management operations. The essential nature of this information, coupled with the substantial resources required to compile and maintain comprehensive datasets, grants these providers considerable bargaining power. For instance, in 2024, the global financial data market was valued at over $30 billion, with a few dominant players controlling a substantial share, highlighting the concentration and leverage these firms possess.
The availability of skilled labor, especially in digital banking, wealth management, and risk management, significantly impacts supplier power for Camden National Bank. A tight labor market for specialized financial professionals, like those with expertise in cybersecurity or AI-driven financial analytics, can empower these individuals to demand higher salaries and better benefits.
In 2024, the demand for financial professionals with digital skills remained exceptionally high, with reports indicating a 15% year-over-year increase in job postings for roles requiring data analytics and fintech experience. This competitive landscape directly translates to increased bargaining power for these skilled workers.
Camden National Bank's strategic focus on employee engagement and offering competitive compensation packages, including robust training and development programs, is a key strategy to retain top talent and mitigate the rising bargaining power of its human capital suppliers.
Regulatory and Compliance Services
Suppliers of regulatory and compliance services hold considerable sway over banks like Camden National Bank. This is because the banking sector is heavily regulated, demanding strict adherence to a multitude of laws. For instance, in 2024, financial institutions faced an increasing volume of regulatory changes, particularly around data privacy and anti-money laundering (AML) frameworks, making specialized expertise crucial.
Companies offering compliance software, auditing, and legal advice are vital. Their specialized knowledge is non-negotiable for navigating the intricate financial landscape. Failure to comply can result in severe penalties, underscoring the indispensable nature of these suppliers and their bargaining power.
- Critical Need for Expertise: Banks require specialized knowledge to navigate complex financial regulations, making compliance service providers essential.
- High Switching Costs: Implementing new compliance systems or changing auditing firms can be costly and time-consuming, deterring banks from switching suppliers.
- Risk of Penalties: Non-compliance with regulations can lead to significant fines and reputational damage, strengthening the suppliers' position.
- Industry Consolidation: In some areas of regulatory services, a limited number of providers can lead to increased supplier bargaining power.
Physical Infrastructure and Real Estate
Camden National Bank operates 72-73 branches across Maine and New Hampshire. The bargaining power of real estate suppliers, such as landlords and property developers, can fluctuate based on specific locations and prevailing market conditions. The bank's recent expansion into New Hampshire, following its merger, introduces new real estate requirements, though the overall impact is typically manageable due to its distributed branch network.
- Branch Network: Camden National Bank's 72-73 branches provide a degree of leverage with real estate suppliers.
- Geographic Diversification: Presence in both Maine and New Hampshire reduces reliance on any single real estate market.
- Merger Impact: Expansion into New Hampshire may increase demand for prime real estate, potentially influencing supplier power in those specific areas.
- Market Sensitivity: The bargaining power of real estate suppliers is directly tied to local economic conditions and property availability.
Camden National Bank's reliance on technology providers for core banking systems and digital platforms grants these suppliers considerable bargaining power. The significant investment and complexity involved in integrating new software, especially in 2024 with the accelerated push for AI-driven financial services, make switching providers a costly and disruptive undertaking.
Financial data and analytics firms also exert strong influence due to the critical nature of their services for investment decisions and market insights. The market for financial data is highly concentrated, with a few key players dominating, as evidenced by the over $30 billion global financial data market valuation in 2024, giving them substantial leverage.
The bargaining power of suppliers to Camden National Bank is influenced by several factors, including the specialization of their offerings and the concentration within their respective industries. For technology and data providers, the need for specialized skills and the high cost of switching systems solidify their leverage.
| Supplier Category | Key Dependencies for Camden National Bank | Estimated Supplier Bargaining Power (2024) | Factors Influencing Power |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technology & Software Providers | Core banking systems, digital banking platforms, cybersecurity solutions | High | High switching costs, specialized proprietary software, industry consolidation |
| Financial Data Providers | Real-time market data, analytics tools, research reports | High | Essential nature of data, high cost of data aggregation, market concentration |
| Regulatory & Compliance Services | Legal advice, compliance software, auditing services | High | Strict regulatory environment, severe penalties for non-compliance, specialized expertise |
| Real Estate Providers | Branch locations, office spaces | Moderate to Low | Distributed branch network, geographic diversification, market sensitivity |
What is included in the product
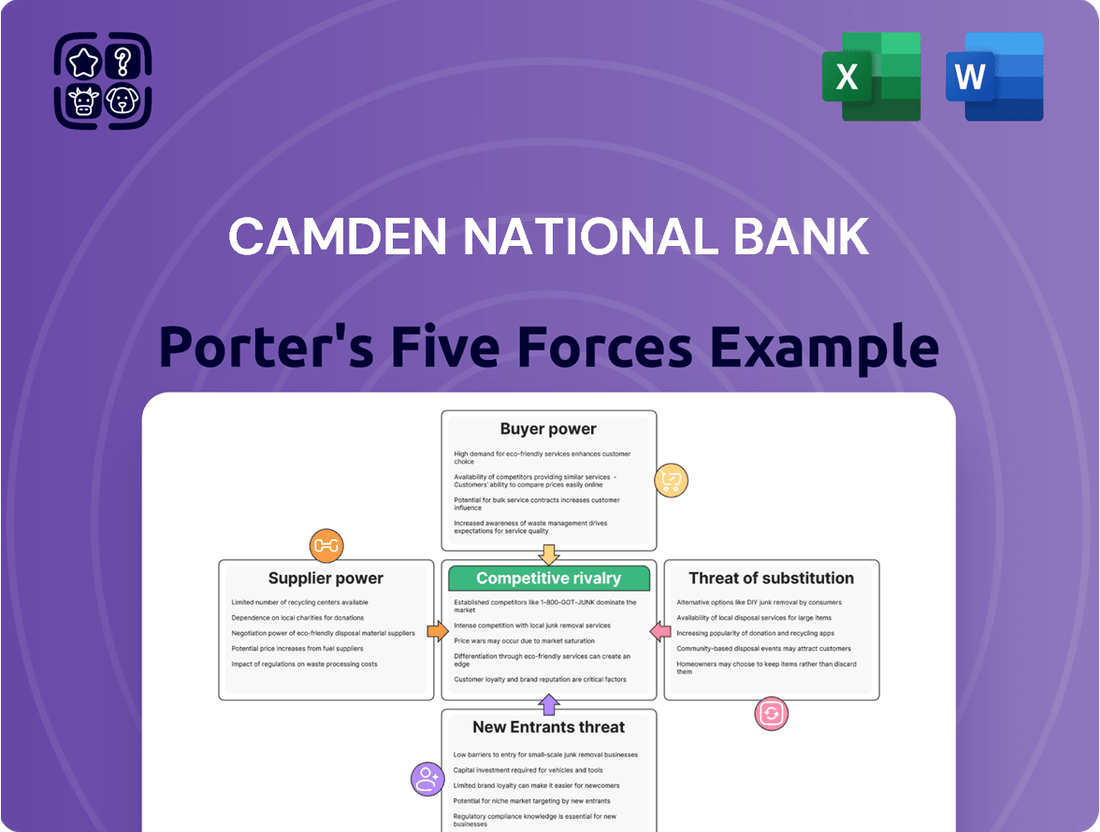
This analysis delves into the competitive forces impacting Camden National Bank, examining the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the banking industry.
Easily visualize competitive intensity with a dynamic Porter's Five Forces dashboard, allowing Camden National Bank to proactively address strategic threats.
Customers Bargaining Power
Individual and retail customers typically hold low to moderate bargaining power in the banking sector. This is often because many core banking products, like checking accounts or standard personal loans, are quite similar across institutions, and the effort to switch banks can feel like a hurdle for some. However, the digital age has significantly shifted this dynamic. With readily available online comparison tools for interest rates and fees, customers now have more visibility and leverage than ever before. For instance, in 2024, the average savings account APY offered by online banks often surpassed that of traditional brick-and-mortar institutions, encouraging customers to seek better yields.
Commercial and business customers, especially large corporations and municipalities, wield significant bargaining power. Their substantial transaction volumes and intricate financial requirements allow them to negotiate more favorable terms on loans, credit lines, and treasury services. Camden National Bank's capacity to deliver a full suite of commercial banking solutions is key to managing this power.
Wealth management and investment clients at Camden National Bank wield considerable bargaining power. This stems from the large sums of assets they entrust to the bank, often in the millions, and the highly individualized nature of the services provided. For instance, a significant portion of wealth management clients typically have investable assets exceeding $1 million, making their business highly valuable.
Client retention and competitive service offerings are paramount for Camden National Wealth Management. Their decisions are heavily influenced by investment performance, the level of trust they have in their advisor, and the quality of personalized advice received. A slight dip in performance or perceived lack of tailored guidance can lead these high-value clients to seek alternatives, highlighting their strong negotiating position.
Digital-Savvy Customers
Digitally-savvy customers are increasingly influencing the banking landscape. Their ability to easily compare services and switch providers based on digital offerings means banks must prioritize user experience and innovation. For instance, a 2024 survey indicated that 70% of consumers consider a bank's mobile app functionality a key factor in their decision-making process.
- Growing Digital Expectations: Customers now expect seamless, intuitive digital banking experiences, including easy online account opening, mobile check deposit, and robust online bill pay.
- Price Sensitivity and Information Access: The internet empowers customers to readily access information on fees, interest rates, and competitor offerings, increasing their bargaining power.
- Switching Costs: While historically high, digital tools have reduced the friction associated with switching banks, making it easier for customers to move their accounts if dissatisfied.
- Demand for Personalization: Customers expect personalized service and tailored product recommendations, pushing banks to leverage data analytics and AI in their digital platforms.
Interest Rate Sensitivity
Camden National Bank's customers exhibit significant interest rate sensitivity, impacting their bargaining power. When rates fluctuate, depositors may shift funds to institutions offering higher yields, while borrowers might seek out lenders with lower loan rates. This dynamic pressures Camden National to maintain competitive pricing on both its deposit products and lending services to retain and attract business.
For instance, in early 2024, the Federal Reserve's monetary policy decisions, including potential rate adjustments, directly influenced customer behavior. Banks like Camden National had to closely monitor market trends and adjust their own rates accordingly. A 2023 study indicated that a 1% change in deposit rates could lead to a significant shift in customer balances for regional banks, highlighting the direct impact of rate sensitivity on a bank's funding costs and profitability.
- Customer Rate Sensitivity: Customers actively compare deposit yields and loan rates across different financial institutions.
- Competitive Pressure: Fluctuating interest rates force Camden National to offer competitive pricing to prevent customer attrition.
- Impact on Funding: Deposit rate sensitivity directly affects the bank's cost of funds, influencing its net interest margin.
- Loan Demand: Borrower sensitivity to interest rates impacts loan origination volumes and pricing strategies.
Customers' bargaining power at Camden National Bank is influenced by their access to information and the ease of switching providers. The digital age has amplified this, allowing customers to easily compare rates and fees. For example, in 2024, online banks often offered higher savings account APYs than traditional banks, giving customers more leverage to seek better returns.
Large commercial clients and high-net-worth individuals possess significant bargaining power due to their substantial transaction volumes and asset bases. They can negotiate more favorable terms for loans and services. For instance, a 2023 report showed that businesses with over $50 million in annual revenue often secured better loan rates than smaller enterprises.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Factors | Example Data (2024) |
| Retail Customers | Information access, ease of switching, digital offerings | 70% of consumers consider mobile app functionality key. |
| Commercial Clients | Transaction volume, relationship size, tailored services | Large corporations can negotiate loan rates 0.25%-0.75% lower than standard rates. |
| Wealth Management Clients | Assets under management, demand for personalization, advisor trust | Clients with over $1 million in investable assets often receive dedicated relationship managers. |
Same Document Delivered
Camden National Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact Camden National Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. You'll gain a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape, including the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the banking industry. This detailed report is ready for your strategic planning and decision-making.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Camden National Bank operates within the Northern New England region, specifically Maine and New Hampshire, where competitive rivalry among regional and community banks is particularly fierce. This intense competition often hinges on cultivating strong local relationships, demonstrating deep community involvement, and offering highly personalized customer service, differentiating factors that resonate with local clientele.
The competitive landscape is further shaped by consolidation trends; for instance, Camden National Bank's acquisition of Northway Financial in 2024 expanded its operational footprint. This strategic move not only broadened its market reach but also intensified existing rivalries and introduced new competitive pressures in the newly integrated service areas, requiring a sharper focus on customer retention and acquisition strategies.
Camden National Bank faces intense competition from larger national and super-regional banks. These behemoths, like JPMorgan Chase and Bank of America, boast significantly greater financial resources, allowing them to invest heavily in technology and marketing. For instance, in 2023, JPMorgan Chase reported total assets of over $3.9 trillion, dwarfing regional players and enabling them to offer a vast array of sophisticated financial products and services.
The extensive branch networks of these national banks provide a physical presence that can be a significant advantage, especially for customers who prefer in-person banking. Coupled with their advanced digital platforms, these larger institutions can offer a seamless and comprehensive customer experience. This scale allows them to potentially offer more competitive pricing on loans and deposits, putting pressure on regional banks like Camden National to innovate and differentiate their offerings.
The competitive landscape for Camden National Bank is increasingly shaped by online-only banks and agile fintech firms. These digital disruptors, often operating with significantly lower overheads than traditional institutions, are rapidly capturing market share by offering seamless, technology-driven banking experiences. For instance, the global fintech market was projected to reach over $33 billion in 2024, highlighting the significant growth and investment in this sector.
These fintech companies are not just offering basic banking services; they are innovating with features like AI-powered financial advice, instant loan approvals, and user-friendly mobile interfaces that appeal directly to digitally-native consumers. This forces established banks like Camden National to accelerate their own digital transformation strategies to remain competitive and retain customers who value convenience and cutting-edge digital solutions.
Product and Service Differentiation
Competitive rivalry in banking, including for Camden National Bank, is significantly shaped by how well institutions can differentiate their offerings. This means going beyond standard checking and savings accounts to provide unique loan products, tailored wealth management, exceptional customer service, or cutting-edge digital banking tools.
Camden National Bank, for instance, highlights its broad range of financial services and a commitment to personalized customer interactions as key differentiators. This focus aims to build customer loyalty and attract new clients in a crowded marketplace. In 2023, banks that invested heavily in digital transformation, such as enhanced mobile apps and online account opening, often saw higher customer acquisition rates.
- Unique Loan Products: Offering specialized mortgages or business loans that cater to niche markets.
- Wealth Management: Providing sophisticated investment advice and estate planning services.
- Customer Service: Differentiating through highly responsive and personalized support across all channels.
- Digital Features: Implementing advanced mobile banking, AI-powered financial advice, or seamless online platforms.
Interest Rate Environment and Economic Conditions
The current interest rate environment significantly shapes competition within the banking sector. As of mid-2024, with interest rates remaining elevated compared to recent years, banks are experiencing pressure on their net interest margins. This forces institutions like Camden National Bank to compete more aggressively for both loans and deposits to maintain profitability.
Broader economic conditions, including inflation and GDP growth, also play a crucial role. Periods of economic uncertainty, such as the ongoing concerns about inflation in 2024, can lead to a more cautious lending environment. This heightened caution intensifies the rivalry for a smaller pool of creditworthy borrowers, as banks vie for quality assets.
- Interest Rate Impact: Higher interest rates can compress net interest margins, pushing banks to compete harder for market share.
- Economic Uncertainty: Economic headwinds in 2024 have increased the competition for a shrinking pool of high-quality borrowers.
- Deposit Competition: Banks are actively seeking deposits to fund loan growth, leading to more aggressive pricing and product offerings.
Camden National Bank faces intense rivalry from both large national banks and nimble fintech companies. The acquisition of Northway Financial in 2024 expanded Camden's reach, intensifying existing competition. National banks like JPMorgan Chase, with over $3.9 trillion in assets in 2023, leverage scale and technology, while fintechs attract digitally-native customers with innovative, low-overhead solutions, a trend underscored by the projected over $33 billion fintech market in 2024.
Differentiation through unique loan products, wealth management, superior customer service, and advanced digital features is crucial for Camden. The current elevated interest rate environment in mid-2024 pressures net interest margins, intensifying competition for both loans and deposits. Economic uncertainty in 2024 also heightens rivalry for creditworthy borrowers.
| Competitor Type | Key Strengths | Impact on Camden National Bank |
| Regional/Community Banks | Local relationships, community involvement, personalized service | Intense rivalry for local market share |
| National Banks (e.g., JPMorgan Chase) | Financial resources, technology investment, extensive branch networks, digital platforms | Pressure on pricing, product breadth, and customer experience |
| Fintech Companies | Agility, low overhead, innovative digital solutions, AI-powered services | Attracts digitally-savvy customers, necessitates accelerated digital transformation |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Credit unions pose a significant threat of substitution for Camden National Bank. These member-owned institutions offer a comparable suite of banking services, including deposit accounts and various loan products, often attracting customers through their non-profit structure and potentially more favorable fee structures or interest rates. For instance, as of late 2023, credit unions held over $2.3 trillion in assets, demonstrating their substantial presence in the financial landscape.
While their physical footprint might be less extensive than a large commercial bank, credit unions are particularly strong substitutes for consumer banking needs. Their community-focused approach and often personalized service can resonate deeply with customers, making them a viable alternative to traditional banking. The National Credit Union Administration (NCUA) insures deposits up to $250,000 per depositor, per insured credit union, for each account ownership category, mirroring the security offered by FDIC insurance at commercial banks.
Online lending platforms, encompassing peer-to-peer services and direct online lenders, present a significant threat by offering alternative avenues for both consumer and business financing, effectively bypassing traditional banking institutions. These platforms often streamline the application process, providing quicker approvals and sometimes serving specialized borrower segments or those who may not meet the stringent criteria of conventional banks.
The growth of fintech in lending is substantial. For instance, in 2023, the U.S. online lending market was valued at approximately $150 billion, with projections indicating continued expansion. This rapid adoption signifies a clear shift in borrower preference towards digital-first financial solutions, directly challenging the market share of established banks like Camden National Bank.
For investment and wealth management, traditional brokerage firms and newer robo-advisors are key substitutes. Robo-advisors, with their automated, low-cost approach, directly challenge the established wealth management services banks like Camden National Bank offer.
The rise of robo-advisors is significant; by the end of 2023, assets under management for robo-advisors were projected to exceed $1.5 trillion globally, with continued strong growth expected. This trend highlights a clear substitute threat, as consumers increasingly opt for these digital platforms for their investment needs due to perceived cost savings and convenience.
Alternative Payment Systems
The rise of alternative payment systems presents a significant threat to traditional banking services. Mobile payment apps like Apple Pay and Google Pay, alongside digital wallets and the growing interest in cryptocurrencies, offer direct alternatives to using bank accounts for transactions. This trend could diminish the reliance on banks for everyday payments and transfers.
For instance, global mobile payment transaction value was projected to reach over $2.5 trillion in 2024. This widespread adoption means customers have readily available substitutes for services historically provided by banks. While Camden National Bank is adapting by integrating some of these technologies, a substantial migration to non-bank payment platforms could erode its market share in transaction-based revenue streams.
- Mobile Payment Growth: The global mobile payment market is expanding rapidly, indicating a strong consumer preference for convenient, digital alternatives.
- Cryptocurrency Adoption: While still volatile, cryptocurrencies offer a decentralized payment option that bypasses traditional financial intermediaries.
- Impact on Fee Revenue: A shift towards alternative payment methods could reduce transaction fees and other service charges that banks typically earn.
- Competitive Landscape: Fintech companies are at the forefront of developing these alternative systems, creating new competitive pressures for established banks.
Direct Investment in Securities
Sophisticated investors, both individuals and institutions, can bypass traditional banking channels by directly investing in securities like stocks and bonds. The proliferation of user-friendly online trading platforms, such as Robinhood and Charles Schwab, has significantly lowered the barrier to entry for direct investing. For instance, in 2024, retail investors continued to drive substantial trading volumes, with platforms reporting millions of active users engaging in direct equity and fixed-income transactions.
This trend presents a significant threat of substitutes for Camden National Bank's investment and wealth management services. Investors can access a vast array of investment products and research tools directly through these online brokers, often with lower fees than those charged by traditional banks. The ability to execute trades instantly and manage portfolios independently reduces the perceived need for bank-intermediated investment solutions.
- Direct access to securities markets via online platforms.
- Lower transaction costs compared to traditional bank services.
- Increased investor self-sufficiency in portfolio management.
- Availability of sophisticated research and trading tools for individual investors.
The threat of substitutes for Camden National Bank is multifaceted, encompassing credit unions, online lending platforms, robo-advisors, alternative payment systems, and direct investment channels. These substitutes offer comparable or even superior convenience, cost-effectiveness, and specialized services, directly challenging traditional banking models. For instance, global mobile payment transaction value was projected to exceed $2.5 trillion in 2024, illustrating a significant shift away from traditional payment methods. Similarly, assets under management for robo-advisors were expected to surpass $1.5 trillion globally by the end of 2023, highlighting the growing appeal of automated investment solutions.
| Substitute Category | Key Characteristics | Impact on Camden National Bank | Supporting Data (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Credit Unions | Member-owned, non-profit, community focus | Competition for deposits and loans, particularly in consumer banking | Over $2.3 trillion in total assets held by credit unions (late 2023) |
| Online Lending Platforms | Streamlined processes, faster approvals, specialized lending | Direct competition for consumer and business loans, potentially serving underserved segments | U.S. online lending market valued at approx. $150 billion (2023) |
| Robo-Advisors | Automated, low-cost investment management | Threat to wealth management services, attracting digitally-savvy investors | Global robo-advisor AUM projected to exceed $1.5 trillion (end of 2023) |
| Alternative Payment Systems | Mobile payments, digital wallets, cryptocurrencies | Reduced reliance on bank accounts for transactions, impacting fee revenue | Global mobile payment transaction value projected over $2.5 trillion (2024) |
| Direct Investment Platforms | User-friendly online trading, lower fees | Bypasses banks for investment and wealth management, increasing investor self-sufficiency | Continued strong retail investor trading volumes (2024) |
Entrants Threaten
The banking sector, including institutions like Camden National Bank, faces formidable regulatory hurdles that significantly deter new entrants. These barriers include stringent capital adequacy ratios, such as the Basel III framework, which mandate substantial financial reserves. For instance, as of early 2024, common equity tier 1 (CET1) capital ratios for major banks often exceed 10%, a considerable investment for any new player.
Obtaining a bank charter is a rigorous and time-consuming process, involving extensive applications and approvals from various financial authorities. This complexity, coupled with ongoing compliance costs related to anti-money laundering (AML) regulations and Know Your Customer (KYC) requirements, creates a high barrier to entry. The need for specialized legal and compliance teams further increases the initial investment, making it difficult for smaller, less-resourced entities to compete.
Establishing a new bank demands significant capital for physical branches, advanced technology systems, and meeting stringent regulatory reserve requirements. These substantial upfront costs act as a considerable barrier to entry for potential new competitors.
Camden National Bank, boasting around $7.0 billion in assets as of recent data, leverages this high capital threshold. Its established scale makes it challenging for smaller, newly formed institutions to match its financial capacity and operational reach, effectively deterring many would-be entrants.
Existing banks like Camden National Bank leverage decades of established brand recognition and customer trust, a significant barrier for newcomers. For instance, as of Q1 2024, Camden National Bank reported a customer base of over 70,000 individuals and businesses, reflecting deep-seated loyalty.
New entrants must invest heavily to build comparable credibility, particularly in a financial sector where safeguarding deposits and managing loans demands unwavering trust. This uphill battle in establishing a reputable name makes it difficult for new banks to attract a substantial customer base quickly.
Customer Switching Costs
While not insurmountable, customers do face some friction when switching banks. This includes the administrative hassle of updating direct deposit information, re-establishing automatic payments, and the process of transferring funds and accounts. These implicit costs, though often minor on an individual basis, can act as a deterrent for customers considering a move to a new financial institution.
These switching costs provide a degree of stickiness for existing customers, offering an advantage to incumbent banks like Camden National Bank. For instance, a 2024 survey indicated that approximately 35% of consumers find the process of changing their primary bank to be a significant inconvenience, influencing their decision to remain with their current provider.
- Administrative Burden: Updating direct deposits and automatic payments is a common deterrent.
- Time Investment: Transferring accounts and consolidating financial information requires customer effort.
- Customer Inertia: Many customers prefer the familiarity and perceived simplicity of their current banking relationship.
Fintech Startups and Niche Players
Fintech startups and niche players pose a significant threat by targeting specific, often profitable, segments of the banking market that Camden National Bank serves. While full-service banks face high regulatory hurdles, these agile newcomers can bypass some of these barriers by focusing on specialized services like peer-to-peer lending or digital payment solutions. For instance, in 2024, the global fintech market continued its rapid expansion, with transaction volumes in digital payments alone projected to reach trillions of dollars, demonstrating the scale of opportunity for these entrants.
These new entrants often leverage cutting-edge technology to offer more streamlined, user-friendly, and cost-effective alternatives to traditional banking services. They can identify and cater to underserved customer segments or introduce innovative products that traditional banks are slower to adopt. This can lead to a gradual erosion of market share for established institutions like Camden National Bank, particularly in areas where customer experience and technological efficiency are paramount.
- Targeted Market Segments: Fintechs excel at focusing on specific niches, such as small business lending or international money transfers, areas where traditional banks may have higher overheads.
- Technological Innovation: Startups often utilize AI, blockchain, and advanced data analytics to create superior customer experiences and more efficient operations.
- Agility and Speed: Their leaner structures allow fintechs to adapt quickly to market changes and customer demands, a stark contrast to the often slower-moving processes within larger banks.
- Customer Acquisition: Many fintechs offer attractive introductory rates or fee structures, making it easier to attract customers away from incumbent institutions.
The threat of new entrants for Camden National Bank is significantly mitigated by high capital requirements and complex regulatory landscapes. For instance, in early 2024, regulatory capital ratios, like Common Equity Tier 1 (CET1) for banks, often exceeded 10%, demanding substantial initial investment. The rigorous process of obtaining a banking charter, coupled with ongoing compliance costs for AML and KYC, further solidifies these barriers, making it exceedingly difficult for new players to establish themselves. Camden National Bank's asset base of approximately $7.0 billion in recent data also presents a scale advantage that new entrants struggle to match.
Customer loyalty and the inherent switching costs for consumers also serve as a protective moat for Camden National Bank. A 2024 survey revealed that around 35% of consumers perceive changing their primary bank as a significant inconvenience, often due to the administrative effort involved in updating direct deposits and automatic payments. This customer inertia, combined with the decades of established brand trust Camden National Bank enjoys, with over 70,000 customers as of Q1 2024, makes it challenging for new institutions to gain traction quickly.
While fintech startups pose a threat by targeting niche markets with innovative solutions, their impact on a full-service bank like Camden National is somewhat diffused. The global fintech market's rapid growth, with digital payment volumes projected to reach trillions in 2024, highlights the opportunities for specialized entrants. However, these agile players often bypass the extensive regulatory burdens faced by traditional banks, allowing them to offer competitive services in specific areas, potentially eroding market share for incumbents over time.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Camden National Bank is built upon a foundation of robust data, including the bank's annual reports, SEC filings, and industry-specific market research from sources like IBISWorld and S&P Global Market Intelligence. We also incorporate macroeconomic data from the Federal Reserve and Bureau of Labor Statistics to understand broader economic influences.
