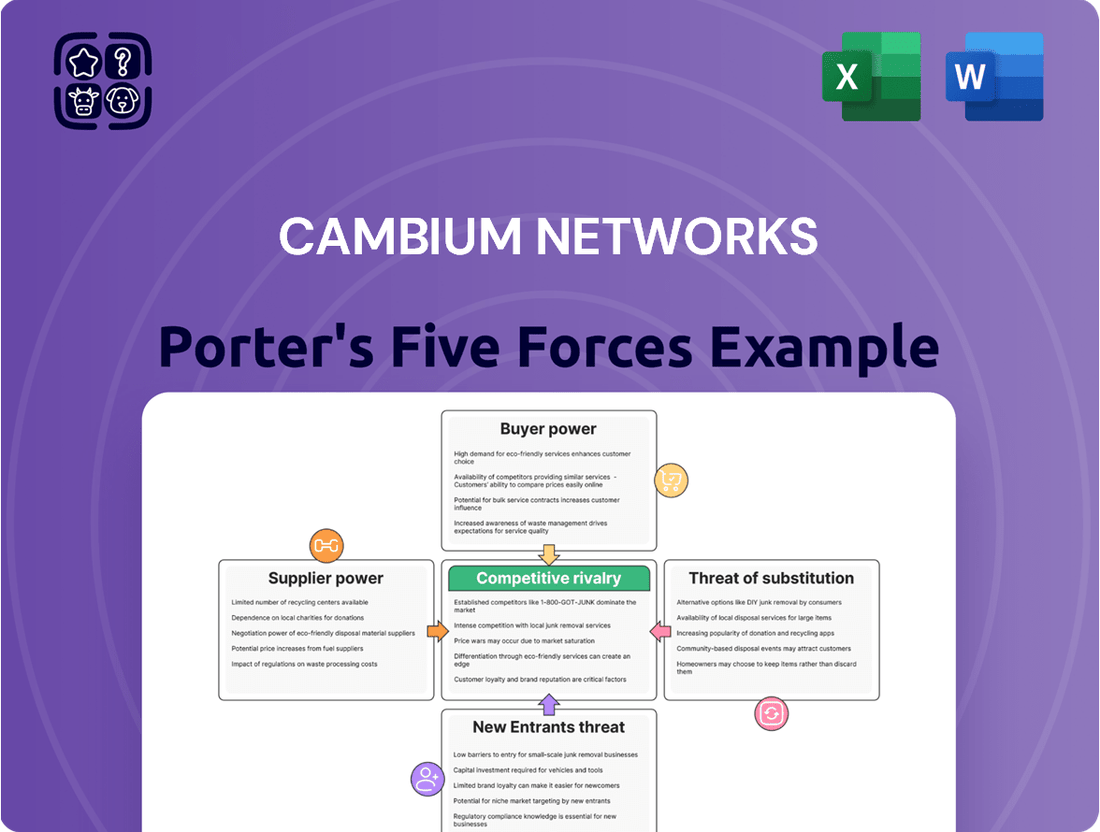
Cambium Networks Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Cambium Networks Bundle
Cambium Networks navigates a dynamic wireless connectivity landscape, facing moderate threats from new entrants and the bargaining power of buyers. Understanding the intensity of these forces is crucial for strategic planning.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Cambium Networks’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The concentration of suppliers significantly impacts Cambium Networks' bargaining power. If a limited number of companies provide essential wireless components, such as advanced chipsets or specialized antenna modules, these suppliers gain considerable leverage. For instance, in 2024, the market for certain high-performance wireless semiconductors remained relatively consolidated, with a few key players dominating production.
Cambium Networks' suppliers gain leverage when they offer inputs that are truly one-of-a-kind or significantly different from what others provide, especially if these are vital for Cambium's offerings and lack readily available alternatives. This uniqueness might stem from patented technology or specialized production methods.
For instance, if a key component for Cambium's wireless networking solutions, like a specific type of radio frequency chip, is only available from a single manufacturer due to its advanced design or exclusive licensing, that supplier's bargaining power increases substantially. In 2023, the global semiconductor market saw continued consolidation, with specialized chip manufacturers holding significant sway over their customer base due to high R&D costs and complex production.
Conversely, if Cambium Networks can readily find comparable inputs from a wide array of vendors, the suppliers' ability to dictate terms or raise prices is considerably weakened. The ease of switching suppliers directly impacts the bargaining power they possess.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Cambium Networks is significantly influenced by switching costs. If Cambium faces high costs and complexity in moving from one supplier to another, for instance, due to the need for retooling production lines or recertifying specific components, existing suppliers gain considerable leverage. For example, a supplier providing a highly specialized chipset that requires extensive integration and testing would command more power.
Conversely, if switching suppliers is relatively straightforward and inexpensive, Cambium Networks can negotiate more favorable terms. This often occurs when components are standardized or readily available from multiple sources. In 2023, Cambium Networks reported that its cost of goods sold was approximately $370 million, highlighting the importance of managing supplier relationships and costs across its diverse component needs.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into Cambium Networks' wireless networking solutions significantly amplifies their bargaining power. If a key component supplier, for instance, possesses the capability and strategic intent to manufacture their own end-to-end wireless products, they can directly compete with Cambium. This scenario becomes more potent when the supplier's existing operations are highly complementary to Cambium's market.
Consider the semiconductor industry, a critical supplier to networking equipment manufacturers. Companies like Qualcomm, a major supplier of chipsets for wireless devices, have the technical expertise and manufacturing infrastructure to potentially develop and market their own complete networking solutions. In 2024, the global semiconductor market reached an estimated $689 billion, indicating the substantial financial resources and technological depth available to such suppliers.
- Forward Integration Threat: Suppliers can leverage their existing capabilities to enter Cambium's market directly.
- Industry Overlap: The risk is heightened when a supplier's core business naturally aligns with Cambium's product offerings.
- Supplier Financial Strength: The substantial size of markets like semiconductors ($689 billion in 2024) provides ample resources for potential forward integration.
Importance of Cambium Networks to Suppliers
Cambium Networks' significance as a customer directly impacts its bargaining power with suppliers. When Cambium represents a substantial portion of a supplier's overall sales, that supplier is more likely to offer competitive pricing and favorable contract terms to retain this valuable business. This is a common dynamic in the technology sector where large orders can significantly influence a supplier's financial performance.
Conversely, if Cambium is a minor client for a supplier, its ability to negotiate advantageous terms diminishes considerably. Suppliers with a diverse customer base have less incentive to accommodate the specific demands of a smaller client. For instance, if a key component supplier's revenue is heavily diversified across many customers, Cambium's individual order volume might not warrant special concessions.
- Customer Dependence: Suppliers who rely heavily on Cambium Networks for a significant percentage of their revenue are more amenable to negotiation.
- Market Share Impact: If Cambium secures a large market share in its product categories, its purchasing power increases, influencing supplier pricing.
- Supplier Diversification: Suppliers with a broad customer base exhibit less sensitivity to Cambium's purchasing volume, reducing Cambium's leverage.
The bargaining power of Cambium Networks' suppliers is influenced by the availability of substitute inputs. If alternative components can fulfill similar functions, suppliers face reduced leverage. For example, if Cambium can source comparable wireless chipsets from multiple manufacturers, no single supplier can command excessive prices.
Suppliers also gain power when their products are critical to Cambium's operations and lack close substitutes. This is particularly true for specialized components where R&D investment is high, making it difficult for new entrants or existing players to offer viable alternatives. The global semiconductor market, valued at approximately $689 billion in 2024, illustrates the high barriers to entry for specialized chip production.
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into Cambium's market also strengthens their position. If a key component provider, like a major chipset manufacturer, can develop and sell complete networking solutions, they can directly compete. The substantial financial resources within the semiconductor industry, evidenced by its 2024 market size, empower such suppliers to pursue this strategy.
| Factor | Impact on Supplier Bargaining Power | Example/Data Point (2023-2024) |
| Supplier Concentration | High if few suppliers dominate | Consolidated market for high-performance wireless semiconductors in 2024 |
| Input Uniqueness | High if inputs are differentiated and vital | Patented RF chips with no readily available alternatives |
| Switching Costs | High if changing suppliers is complex/costly | Extensive integration and recertification for specialized chipsets |
| Forward Integration Threat | High if suppliers can enter Cambium's market | Semiconductor giants like Qualcomm potentially offering end-to-end solutions |
| Cambium's Customer Significance | Low if Cambium is a small customer | Suppliers with diversified customer bases are less sensitive to Cambium's volume |
What is included in the product
This analysis unpacks the competitive forces impacting Cambium Networks, detailing the intensity of rivalry, the power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the potential for substitute products.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats with Cambium Networks' Porter's Five Forces analysis, providing a clear roadmap to navigate industry pressures.
Customers Bargaining Power
Cambium Networks' customer concentration directly impacts its bargaining power. If a few major clients, like large telecommunications companies or enterprise clients, represent a substantial percentage of Cambium's sales, these customers gain significant leverage. For instance, if the top 10 customers represented over 30% of revenue in 2023, they could more easily negotiate for lower prices or more favorable terms, potentially squeezing Cambium's profit margins.
Cambium Networks' customers generally face relatively low switching costs. This is largely because many of its wireless networking solutions utilize standardized protocols and technologies, making it easier for businesses to transition to or integrate with alternative providers. For instance, in the fixed wireless access market, interoperability between different vendors' equipment can be a key factor, reducing the pain of switching.
The ease with which a customer can move to a competitor directly impacts their leverage. If Cambium's clients can easily swap out equipment or software with minimal disruption to their operations, they are empowered to demand better pricing or terms. This is a common dynamic in the competitive telecommunications infrastructure space, where rapid technological advancements can sometimes lead to commoditization.
Customer price sensitivity is a key driver of their bargaining power. When customers are highly sensitive to price, they tend to shop around for the best deals, which can put pressure on companies like Cambium Networks to lower their prices. For instance, in sectors where connectivity solutions are seen as a commodity, or where clients have strict budget limitations, this sensitivity is amplified.
Cambium Networks can counter this by focusing on product differentiation. By offering superior performance, enhanced reliability, or innovative features that address specific customer needs, Cambium can reduce the emphasis on price alone. This strategy helps to build customer loyalty and allows the company to command a premium, thereby lessening the direct impact of price-driven bargaining.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of backward integration by customers significantly influences Cambium Networks. If major clients, particularly large enterprises or service providers, possess the technical expertise and financial clout to develop their own wireless networking solutions, their bargaining power increases. This possibility forces Cambium to remain competitive in pricing and innovation to retain these key accounts.
For instance, a telecommunications giant with substantial R&D capabilities might consider developing in-house solutions if they perceive Cambium's offerings as too costly or lacking specific features. This potential for self-production acts as a constant pressure point, compelling Cambium to demonstrate superior value. In 2024, the increasing complexity and specialization of wireless technologies, such as 5G private networks, could make backward integration more feasible for well-resourced customers.
- Customer Integration Capability: Large enterprise clients and service providers with strong technical teams and financial resources are more likely to consider backward integration.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: Customers will weigh the cost of developing their own solutions against the ongoing expense of purchasing from Cambium.
- Market Dynamics: Advances in wireless technology, like the expansion of private 5G networks, can lower the barrier to entry for customers looking to produce their own solutions.
Availability of Substitute Products for Customers
The availability of substitute products significantly impacts Cambium Networks' bargaining power with its customers. When customers have numerous alternative wireless broadband and Wi-Fi solutions readily accessible from competitors, they are empowered to negotiate for more favorable terms, including lower prices and enhanced features. This pressure forces Cambium to remain competitive in its offerings.
For instance, the proliferation of Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 6E technologies from various manufacturers provides businesses and consumers with readily available alternatives to Cambium's fixed wireless access solutions for certain use cases. In 2024, the global Wi-Fi market is expected to continue its robust growth, with numerous vendors offering a wide array of access points and network management systems, increasing customer choice.
- Increased Customer Choice: The market offers a broad spectrum of wireless connectivity solutions, from other fixed wireless providers to mesh Wi-Fi systems and even cellular backhaul options, all serving as potential substitutes.
- Price Sensitivity: When substitutes are abundant, customers are more likely to switch providers based on price differences, putting downward pressure on Cambium's pricing strategies.
- Feature Competition: To retain customers, Cambium must continuously innovate and match or exceed the feature sets offered by competing technologies, such as improved range, speed, and security.
- Market Dynamics: The competitive landscape in wireless networking is dynamic, with new technologies and vendors emerging, constantly reinforcing the bargaining power of customers seeking the best value.
Cambium Networks' customers possess significant bargaining power, primarily driven by low switching costs and high price sensitivity in the competitive wireless networking market. The availability of numerous substitute products further amplifies this leverage. For example, the widespread adoption of Wi-Fi 6 and 6E technologies in 2024 provides readily available alternatives for many fixed wireless access applications, allowing customers to easily compare pricing and features. This dynamic necessitates continuous innovation and competitive pricing from Cambium to retain its customer base.
| Factor | Impact on Cambium | Customer Action |
|---|---|---|
| Switching Costs | Low | Customers can easily migrate to competitors. |
| Price Sensitivity | High | Customers actively seek lower prices. |
| Substitute Availability | High | Customers have many alternative solutions. |
| Backward Integration Potential | Moderate to High (for large clients) | Customers may develop in-house solutions. |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Cambium Networks Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact Cambium Networks Porter's Five Forces Analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic positioning within the wireless networking industry. It thoroughly examines the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors, and the threat of substitute products. This comprehensive analysis is ready for your immediate use, offering actionable insights into Cambium Networks' market dynamics.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The wireless networking infrastructure market, where Cambium Networks operates, is a battlefield with a multitude of competitors. This includes giants like Cisco, which reported over $57 billion in revenue for its fiscal year ending July 2024, and HPE Aruba, a significant player in enterprise networking. The sheer number of companies, from these global behemoths to niche providers specializing in specific wireless technologies, creates a dynamic and often aggressive competitive landscape.
This rivalry is further amplified by the diversity of these players. Competitors vary significantly in their size, from multinational corporations with vast resources to smaller, agile firms focused on particular market segments or technologies. Their product portfolios also differ, with some offering comprehensive end-to-end solutions while others concentrate on specific components like access points or management software. This wide spectrum of offerings and strategic approaches means Cambium faces competition on multiple fronts, from broad-based providers to highly specialized disruptors.
Cambium Networks operates in markets with varying growth trajectories. While segments like Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) and Industrial IoT (IIoT) are experiencing robust expansion, the broader enterprise Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) market has seen periods of slower growth and volatility. This dynamic means that in the more mature segments, companies are likely to engage in more intense competition for market share.
Cambium Networks' ability to differentiate its wireless broadband and Wi-Fi solutions significantly influences competitive rivalry. When products are easily substitutable, price wars become common, squeezing profit margins. For instance, if a competitor offers a similar performance at a lower cost, Cambium faces pressure.
However, Cambium has focused on differentiating its offerings through advanced features like enhanced security protocols and specialized solutions for challenging environments, such as fixed wireless access in rural areas. This differentiation allows them to command better pricing and reduce direct competition based solely on cost, as seen in their consistent revenue growth, with reported revenues of $231.5 million for the fiscal year 2023, indicating market acceptance of their differentiated products.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers in the wireless networking sector, like specialized equipment and ongoing service agreements, can trap less profitable companies. This situation often means these firms remain in the market even when they aren't doing well, contributing to an oversupply of products and services. Consequently, this leads to aggressive price wars as companies fight to stay afloat.
The persistence of these struggling companies intensifies competition. They may continue to offer products at lower prices to generate any revenue, putting pressure on more financially stable competitors. This dynamic can significantly erode profit margins across the entire industry.
For Cambium Networks, this means that even if a competitor is performing poorly, they might not exit the market quickly. This sustained presence can keep competitive pressure high, impacting Cambium's ability to command premium pricing or gain market share without facing significant price resistance. For instance, in 2023, the global wireless networking market saw continued investment, but also reports of price erosion in certain segments due to competitive pressures.
- Specialized Assets: Significant investment in proprietary hardware and software makes it difficult for companies to pivot or sell off assets quickly.
- Long-Term Contracts: Customer agreements for network services or equipment often bind companies for extended periods, hindering a swift exit.
- Brand Reputation: Companies invest heavily in building brand loyalty, making it challenging to divest operations without impacting brand value elsewhere.
- Employee Expertise: The highly specialized nature of wireless technology means retaining skilled personnel is crucial, and their departure can be a significant cost.
Strategic Stakes
The wireless networking market holds significant strategic importance for many companies, acting as a key driver for future growth and innovation. This perceived criticality intensifies competitive rivalry as major players are motivated to invest aggressively to secure market share and technological leadership. For instance, in 2024, the global wireless networking market was projected to reach over $100 billion, a substantial figure that underscores its strategic value.
When competitors view this sector as fundamental to their long-term vision or as a cornerstone of their technological offerings, they are often prepared to engage in aggressive competition. This can manifest as significant R&D spending, price wars, or strategic acquisitions, even if it means accepting lower short-term profits. Companies like Cisco, Juniper Networks, and Aruba (a Hewlett Packard Enterprise company) consistently demonstrate this by investing heavily in 5G, Wi-Fi 6E, and other advanced wireless technologies.
- Market Growth: The wireless networking market is a high-growth sector, attracting substantial investment from established technology giants and emerging players alike.
- Technological Advancement: Companies see leadership in wireless technology as crucial for maintaining a competitive edge and driving future revenue streams.
- Strategic Investment: Aggressive investment in R&D and market penetration is common as firms vie for dominance in this strategically vital area.
- Competitive Intensity: The high stakes involved mean that rivalry among key players is often intense, impacting pricing and innovation cycles.
Competitive rivalry in the wireless networking market is intense, driven by a large number of diverse players, including giants like Cisco with over $57 billion in fiscal year 2024 revenue. This broad competitive base, ranging from large corporations to niche specialists, creates a dynamic environment. Cambium Networks faces this rivalry across various product segments, from rapidly growing Fixed Wireless Access to more mature enterprise Wi-Fi markets, where competition for market share is particularly fierce.
Product differentiation is key, as easily substitutable offerings can lead to price wars. Cambium's focus on advanced features and specialized solutions, like those for rural fixed wireless access, helps mitigate direct cost-based competition. Despite revenue growth to $231.5 million in 2023, the company must continuously innovate to maintain its edge against competitors who may be investing heavily in areas like 5G and Wi-Fi 6E, with the global wireless networking market projected to exceed $100 billion in 2024.
High exit barriers, such as specialized assets and long-term contracts, mean that even struggling companies remain in the market, contributing to price pressures. This sustained presence intensifies competition, potentially eroding profit margins for all players. Companies must navigate this landscape where strategic importance and market growth incentivize aggressive investment and a constant drive for technological leadership.
| Competitor | Fiscal Year End | Reported Revenue | Key Focus Areas |
| Cisco | July 2024 | Over $57 billion | Enterprise Networking, 5G, Wi-Fi 6E |
| HPE Aruba | N/A | N/A | Enterprise Wireless Networking |
| Cambium Networks | 2023 | $231.5 million | Fixed Wireless Access, Wi-Fi, IIoT |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Cambium Networks' wireless solutions is significant, particularly when alternatives present a more attractive price-performance ratio. For example, while Cambium focuses on fixed wireless access (FWA) and enterprise Wi-Fi, advancements in fiber optic broadband continue to push the boundaries of speed and reliability. In some scenarios, particularly in densely populated urban areas or for high-demand enterprise applications, the long-term total cost of ownership and superior performance of fiber might outweigh the initial deployment advantages of wireless, making it a potent substitute.
Cambium Networks faces a moderate threat from substitutes, largely influenced by how readily customers perceive alternative solutions as offering comparable or superior value. This propensity to switch hinges on factors like the ease of adopting a new technology and the specific benefits it provides. For instance, if a competing wireless technology offers significantly lower upfront costs or superior bandwidth for a particular application, it could entice customers to switch.
The cost sensitivity of Cambium's customer base plays a crucial role. If organizations are under pressure to reduce capital expenditures, they might explore lower-cost wireless solutions, even if they come with minor performance trade-offs. Similarly, if specific performance metrics, such as latency or data throughput, are paramount for a customer's operations and a substitute can demonstrably meet or exceed these requirements more affordably, the threat intensifies. For example, in sectors like industrial IoT where real-time data is critical, a substitute offering lower latency could be highly attractive.
Traditional wired networking solutions, like Ethernet and fiber optics, remain strong substitutes, particularly for businesses and industrial settings demanding high bandwidth and minimal delay. These wired options offer established reliability and performance benchmarks that wireless technologies must consistently match or exceed.
The ongoing evolution of wired infrastructure, including the increasing deployment of 10 Gigabit Ethernet and advancements in fiber optic speeds, presents a persistent threat. For instance, in 2024, the global Ethernet switch market was projected to reach over $30 billion, highlighting its continued dominance and investment.
Emerging Technologies as Substitutes
New and evolving technologies present a significant threat of substitution for Cambium Networks. Advanced cellular technologies, like 5G Standalone, are increasingly offering high speeds and low latency, directly competing with Cambium's fixed wireless access solutions in certain markets. For instance, the global 5G market is projected to reach over $1.3 trillion by 2030, indicating substantial growth and adoption that could displace existing wireless infrastructure.
Satellite internet services, particularly low-Earth orbit (LEO) constellations, are also emerging as powerful substitutes. These services are rapidly expanding their reach and improving performance, offering viable alternatives for remote and underserved areas where Cambium has traditionally focused. Starlink, a prominent LEO provider, reported over 2 million users globally by late 2023, showcasing the rapid market penetration and disruptive potential of this technology.
- Advancing Cellular Networks: Technologies like 5G Standalone offer speeds and latency improvements that can substitute for fixed wireless access in urban and suburban environments.
- Satellite Internet Growth: LEO satellite services are expanding coverage and performance, providing a direct substitute for Cambium's solutions in remote and hard-to-reach locations.
- Increasing Speeds and Coverage: Both cellular and satellite advancements are continuously improving their capabilities, making them more attractive alternatives across a wider range of applications.
Do-It-Yourself (DIY) Solutions or Open-Source Alternatives
The threat of substitutes for Cambium Networks is amplified by the availability of Do-It-Yourself (DIY) solutions and open-source alternatives. For smaller deployments or specific use cases, customers might opt for less sophisticated, off-the-shelf consumer-grade Wi-Fi equipment or open-source networking solutions. These can serve as low-cost substitutes, particularly for less demanding environments, even if they lack enterprise-grade features or scalability.
For instance, in 2024, the global market for consumer Wi-Fi routers was valued at over $10 billion, indicating a substantial segment of users prioritizing cost-effectiveness over advanced features. Similarly, the growing adoption of open-source networking software, such as OpenWrt, provides a viable alternative for businesses and individuals looking to build custom network solutions without the licensing costs associated with proprietary systems.
- DIY and Open-Source Threat: Lower-cost, less feature-rich alternatives exist for simpler network needs.
- Consumer-Grade Wi-Fi: The large consumer Wi-Fi market, exceeding $10 billion in 2024, represents a potential substitute for smaller business deployments.
- Open-Source Solutions: Software like OpenWrt offers customization and cost savings, appealing to budget-conscious users.
- Feature Trade-offs: These substitutes often sacrifice enterprise-grade capabilities and scalability for lower prices.
The threat of substitutes for Cambium Networks' offerings is multifaceted, encompassing both wired and wireless technologies, as well as emerging satellite solutions. Advancements in fiber optics and 5G cellular continue to raise the performance bar, while satellite internet is rapidly expanding its reach. These alternatives present a significant challenge, especially when they offer compelling price-performance ratios or cater to specific market needs more effectively.
| Substitute Technology | Key Characteristics | Impact on Cambium Networks |
| Fiber Optics | High bandwidth, low latency, established reliability | Strong substitute for high-demand enterprise and urban FWA deployments. Global Ethernet switch market exceeded $30 billion in 2024. |
| 5G Cellular | Increasing speeds, lower latency, mobile flexibility | Direct competitor to FWA, especially in urban/suburban areas. Global 5G market projected over $1.3 trillion by 2030. |
| LEO Satellite Internet | Expanding coverage, improving performance | Viable alternative for remote and underserved markets. Starlink reported over 2 million users globally by late 2023. |
| DIY/Open-Source Wi-Fi | Lower cost, less complexity | Substitute for smaller or less demanding deployments. Consumer Wi-Fi router market valued over $10 billion in 2024. |
Entrants Threaten
The capital required to enter the wireless networking infrastructure market, like that served by Cambium Networks, acts as a substantial barrier. Developing, manufacturing, and distributing high-performance wireless broadband and Wi-Fi products demands significant investment in research and development, state-of-the-art production facilities, and robust distribution channels. This high capital outlay deters many potential new entrants from challenging established players.
Established players like Cambium Networks leverage significant economies of scale in manufacturing and procurement. This allows them to achieve lower per-unit costs for their wireless networking solutions, a crucial advantage in a competitive market.
For instance, in 2023, Cambium Networks reported a gross profit margin of 49.1%, indicating efficient cost management that new entrants would find difficult to replicate immediately.
New companies entering the market would face substantial hurdles in matching these cost efficiencies, as they would lack the established supply chains and high-volume production capabilities that drive down expenses for incumbents.
Existing players in wireless networking, like Cambium Networks, benefit from strong brand recognition and established customer trust, making it challenging for newcomers. For instance, in 2023, major networking equipment providers reported significant brand value, indicating the uphill battle new entrants face in capturing market share through brand building alone.
New entrants must also contend with the substantial investment required for product differentiation and the long, arduous process of cultivating customer loyalty. Companies that have successfully entered this market often do so with highly innovative technology or a significantly lower cost structure, yet even then, overcoming established relationships and proven reliability remains a key hurdle.
Access to Distribution Channels
Gaining access to established distribution channels, such as service providers, enterprise resellers, and system integrators, presents a significant hurdle for new entrants in the networking equipment market. These established channels often have deep-rooted relationships and exclusive contracts with incumbent players like Cambium Networks.
New companies must either invest heavily in building their own distribution networks from scratch, a time-consuming and capital-intensive process, or persuade existing channels to adopt their offerings. This often requires offering competitive pricing, superior technology, or substantial incentives to overcome the inertia of existing partnerships.
For instance, in 2024, the global IT distribution market was valued at hundreds of billions of dollars, with a significant portion dedicated to networking hardware. New entrants often find it difficult to secure shelf space or mindshare within these established ecosystems.
- Channel Exclusivity: Many service providers and large resellers have exclusive or preferred vendor agreements, limiting access for newcomers.
- Relationship Building: Developing trust and strong working relationships with channel partners takes considerable time and effort.
- Investment in Partner Programs: New entrants need to invest in robust partner programs offering training, marketing support, and attractive margins to incentivize channel adoption.
- Demonstrating Value: New companies must clearly articulate the unique value proposition of their products to convince channels to displace existing, proven solutions.
Regulatory and Licensing Requirements
The wireless networking sector, including companies like Cambium Networks, faces substantial barriers to entry due to stringent regulatory and licensing requirements. Navigating these complexities, particularly for spectrum usage, can be both time-consuming and expensive. For instance, obtaining FCC licenses in the United States or similar approvals in other regions involves significant application fees and adherence to technical standards.
These regulatory hurdles directly impact the threat of new entrants by increasing the initial investment and delaying market entry. New players must not only develop competitive technology but also secure the necessary permits, which can take months or even years. This compliance burden adds a considerable cost layer that established players have already absorbed.
- Spectrum Licensing Costs: Fees for acquiring and maintaining radio spectrum licenses can run into millions of dollars, deterring smaller entrants.
- Technical Compliance: Meeting standards set by bodies like the FCC or ETSI requires significant R&D and testing investment.
- Regional Variations: Different countries have unique regulatory frameworks, necessitating localized compliance efforts and increasing complexity for global market entry.
- Time to Market: The lengthy approval processes can significantly extend the time it takes for a new product to reach the market.
The threat of new entrants in the wireless networking market, where Cambium Networks operates, remains moderate. Significant capital investment is required for R&D, manufacturing, and distribution, creating a substantial barrier.
Established players benefit from economies of scale, strong brand recognition, and existing distribution channels, making it difficult for newcomers to compete on cost and customer loyalty. For example, in 2023, the average R&D spending for major networking equipment manufacturers exceeded hundreds of millions of dollars.
Stringent regulatory and licensing requirements, particularly for spectrum usage, further increase the cost and time to market for new companies. In 2024, the cost of acquiring spectrum licenses in key markets can easily reach millions of dollars.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example Data (2023-2024) |
| Capital Requirements | High R&D, manufacturing, and distribution costs. | Significant deterrent. | R&D spending for top players in hundreds of millions USD. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs due to high-volume production. | Price disadvantage for newcomers. | Cambium's 2023 gross profit margin of 49.1% indicates cost efficiency. |
| Brand Recognition & Loyalty | Established trust and relationships. | Difficult to capture market share. | Major networking brands hold significant market value. |
| Distribution Channels | Access to service providers, resellers, integrators. | Limited access for new entrants. | Global IT distribution market valued in hundreds of billions USD. |
| Regulatory & Licensing | Spectrum licenses, technical compliance. | Increased cost and time to market. | Spectrum license costs can be millions of USD. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Cambium Networks Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including Cambium's own annual reports, investor presentations, and publicly available financial statements. This is supplemented by industry-specific market research reports from firms specializing in wireless networking and telecommunications, alongside analyses of competitor strategies and product launches.
