Calian Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Calian Bundle
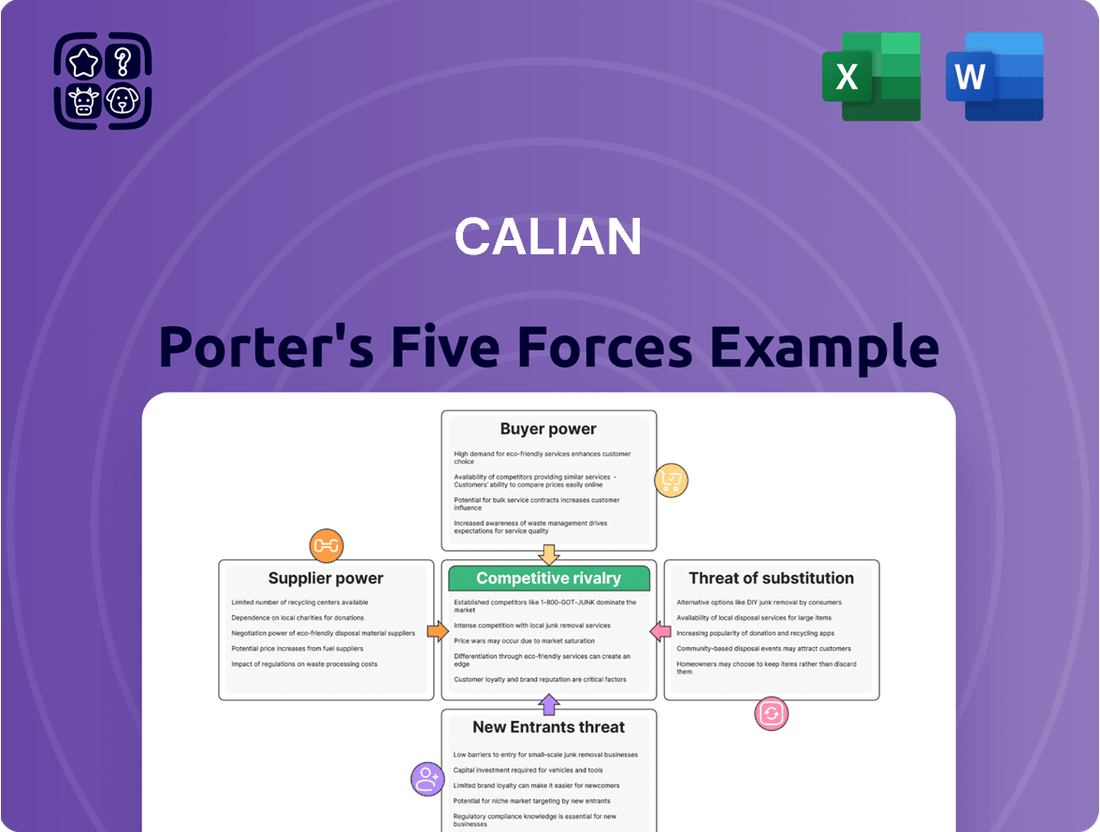
Calian's competitive landscape is shaped by five key forces: the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for strategic planning.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Calian’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Calian's position within its various operating sectors means that its dependence on any one supplier group can fluctuate. For instance, if Calian requires highly specialized technology components or unique healthcare equipment that can only be sourced from a limited number of providers, these suppliers gain considerable leverage.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Calian is significantly influenced by switching costs. If Calian faces substantial expenses or operational disruptions when changing suppliers, such as the need for extensive software integration or retraining its workforce on new equipment, existing suppliers gain considerable leverage. For instance, if a critical supplier provides proprietary technology that is deeply embedded in Calian's operations, the cost and time to transition to an alternative could be prohibitive, thereby increasing the supplier's power.
When suppliers offer unique or proprietary products, their bargaining power significantly increases. For Calian, this is particularly evident in areas like specialized cybersecurity solutions or advanced satellite communication technologies. For instance, if a supplier provides a critical, one-of-a-kind component for Calian's satellite ground segment operations, that supplier holds considerable sway.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into Calian's business operations poses a significant consideration. If a supplier can credibly threaten to start offering Calian's services or products directly to its customer base, this naturally enhances the supplier's bargaining power. This scenario would allow them to capture a larger portion of the value chain, potentially cutting out Calian as an intermediary.
However, the diverse nature of Calian's operations, spanning areas like IT, health, and learning, likely limits the scope of this threat. Forward integration by suppliers might be a more pronounced risk in very specific, niche segments of Calian's market rather than across its entire business. For instance, a specialized software provider to a particular Calian division might consider such a move if the economics were favorable.
Calian's 2024 financial reports indicate a strong focus on diversified revenue streams. For example, its Health segment reported significant growth, which could make it an attractive area for a healthcare technology supplier to consider direct market entry. Conversely, its IT services segment, with its broad client base, might present a less concentrated opportunity for a single supplier to effectively integrate forward.
- Supplier Forward Integration Risk: Suppliers could potentially offer Calian's services directly to clients, thereby increasing their own market power.
- Calian's Diversification as a Mitigant: The broad range of Calian's business segments may limit the feasibility of forward integration for most suppliers.
- Niche Market Vulnerability: Specific, specialized areas within Calian's portfolio might be more susceptible to this threat.
- 2024 Financial Context: Calian's varied performance across segments in 2024 provides a backdrop for assessing where this threat might be most relevant.
Importance of Calian to Supplier
Calian's significance to a supplier's revenue stream directly impacts the supplier's bargaining power. If Calian constitutes a substantial portion of a supplier's sales, that supplier is more likely to be accommodating to Calian's terms, thereby reducing their leverage. For instance, if a specialized component supplier relies heavily on Calian for a large percentage of its business, they have less room to dictate pricing or contract conditions.
Conversely, when Calian represents a minor client for a large, diversified supplier, the supplier generally possesses greater bargaining power. Such a supplier, serving numerous clients across various industries, is less dependent on Calian and can afford to be more assertive regarding pricing, delivery schedules, and other contract terms. This is particularly true for suppliers of commoditized goods or services where Calian has many alternative sources.
- Revenue Dependence: A supplier's reliance on Calian for a significant portion of its revenue weakens its bargaining position.
- Client Diversification: Suppliers with a broad client base and less dependence on Calian gain more leverage.
- Market Dynamics: The specific industry and the supplier's position within it are crucial factors determining bargaining power.
- Strategic Importance: If Calian is a key strategic partner for a supplier, this can also influence the power balance, potentially shifting leverage towards Calian.
The bargaining power of Calian's suppliers is influenced by the concentration of their customer base. If a supplier serves many clients, Calian's business is less critical, giving the supplier more leverage. Conversely, if Calian is a major customer, the supplier's power diminishes.
In 2024, Calian's strategic sourcing initiatives likely aimed to reduce reliance on single suppliers, thereby mitigating supplier power. For example, expanding its network of IT hardware vendors in 2024 would dilute the leverage of any one provider.
Calian's ability to switch suppliers also plays a role. High switching costs, such as those associated with specialized software integration for its health services division, empower suppliers. Conversely, readily available alternatives for common components weaken supplier influence.
| Factor | Impact on Supplier Bargaining Power | Calian Context (2024 Focus) |
| Supplier Customer Concentration | High concentration = Low supplier power; Low concentration = High supplier power | Calian seeks to diversify its supplier base to reduce dependence. |
| Switching Costs | High costs = High supplier power; Low costs = Low supplier power | Investments in proprietary systems can increase switching costs for Calian. |
| Supplier Differentiation | Unique offerings = High supplier power; Commoditized offerings = Low supplier power | Specialized technology in satellite communications gives suppliers an edge. |
What is included in the product
Calian's Porter's Five Forces analysis deeply examines the competitive intensity within its operating industries, assessing the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, and the threat of substitute products.
Easily identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each of Porter's Five Forces.
Customers Bargaining Power
Calian's customer base spans both government and commercial sectors worldwide, a diverse mix that can impact customer bargaining power. The presence of large government contracts or a few major commercial clients grants these entities significant leverage due to the substantial revenue they contribute to Calian.
The bargaining power of Calian's customers is significantly influenced by the availability of substitutes for its diverse service offerings. If clients can readily find alternative providers for healthcare staffing, satellite ground systems, learning solutions, or cybersecurity, their leverage naturally increases. This ease of finding comparable services means customers can demand better pricing or terms, knowing other options exist.
The cost and complexity associated with switching from Calian to a competitor are critical factors. For instance, in the healthcare staffing sector, if onboarding a new agency is straightforward and inexpensive, a hospital facing staffing shortages might have more power to negotiate rates with Calian. Conversely, if switching involves significant retraining or integration costs, Calian's position strengthens.
In 2023, the Canadian IT and cybersecurity market saw increased competition, with many smaller firms offering specialized services. This environment potentially gives clients more choices for cybersecurity solutions, thereby enhancing their bargaining power with larger providers like Calian. Similarly, the global satellite ground segment is evolving, with new players emerging, which could offer alternatives for ground system management.
Customer price sensitivity significantly impacts bargaining power, especially in commoditized sectors or when clients face budget constraints. For instance, in the IT services sector, where many providers offer similar solutions, clients can easily switch for a lower price, giving them considerable leverage. This was evident in 2024 as many businesses tightened IT spending, leading to increased price negotiations.
Calian can counter this by emphasizing its unique value proposition and specialized expertise. By offering innovative solutions or niche services that competitors cannot easily replicate, Calian can reduce its customers' perception of substitutability. This differentiation strategy is crucial for commanding premium pricing and mitigating the downward pressure on prices driven by price-sensitive customers.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
Customers can indeed wield significant bargaining power by threatening to develop capabilities in-house, a concept known as backward integration. This means a client might decide to build its own solutions or services rather than continuing to purchase them from Calian. For example, a substantial government entity with a pressing need for specialized IT support or cybersecurity might explore establishing its own internal team to manage these functions directly.
The credibility of this threat is directly proportional to the client’s size and available resources. Larger organizations, particularly those with substantial budgets and a clear strategic imperative, are more likely to possess the financial and human capital necessary to undertake such an endeavor. For instance, a major telecommunications company might consider developing its own network management software if it perceives Calian's offerings as too costly or inflexible for its specific, large-scale operational requirements.
- Customer Threat of Backward Integration: Clients may develop services internally, reducing reliance on Calian.
- Example Scenario: A large government agency could build its own cybersecurity team instead of outsourcing.
- Resource Dependency: This threat is more potent for large clients possessing significant financial and technical resources.
- Strategic Impact: Successful backward integration by a major client could lead to a substantial loss of revenue for Calian.
Information Availability to Customers
Customers armed with readily available information about pricing, competitor offerings, and service quality possess significant leverage. This heightened market transparency for Calian's services directly translates into customers being able to negotiate more favorable terms and conditions, potentially impacting Calian's pricing power and profitability.
- Increased Information Access: The digital age has democratized information, making it easier for customers to compare Calian's services against alternatives.
- Price Sensitivity: With easy access to pricing data, customers can more readily identify and exploit price discrepancies, putting pressure on Calian's margins.
- Service Quality Benchmarking: Online reviews and comparison platforms allow customers to assess the quality of Calian's services relative to competitors, influencing their willingness to pay premium prices.
Calian's customers possess considerable bargaining power due to the availability of substitutes and the ease of switching providers. For instance, in 2024, the competitive landscape for IT and cybersecurity services saw numerous smaller firms offering specialized solutions, giving clients more options and thus increasing their leverage. This trend suggests that customers can more readily negotiate pricing and terms by leveraging alternative service providers.
The threat of backward integration, where customers develop services in-house, is a significant factor. Large government agencies or major commercial clients with substantial resources may choose to build their own capabilities, particularly in areas like cybersecurity or IT support, to gain more control or reduce costs. This is more potent for clients with significant financial and technical capital, potentially leading to substantial revenue loss for Calian if realized.
Customer price sensitivity, especially in commoditized sectors, directly amplifies their bargaining power. In 2024, many businesses tightened IT spending, leading to increased price negotiations. Calian counters this by highlighting its unique value proposition and specialized expertise to mitigate downward price pressure.
| Factor | Impact on Calian | Mitigation Strategies |
| Availability of Substitutes | Increases customer leverage, potentially lowering prices. | Emphasize unique value proposition, specialized expertise. |
| Switching Costs | Low switching costs empower customers to negotiate. | Build customer loyalty through superior service and integrated solutions. |
| Backward Integration Threat | Potential loss of revenue if major clients develop services internally. | Offer flexible solutions, demonstrate cost-effectiveness and superior performance. |
| Customer Information Access | Heightened transparency allows for better price negotiation. | Transparent pricing, clear communication of service benefits. |
What You See Is What You Get
Calian Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Calian Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering an in-depth examination of the competitive landscape. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted report you will receive immediately upon purchase. You can be confident that no placeholders or sample content are included; this is the full, ready-to-use analysis for your strategic planning needs.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Calian Technology's competitive landscape is shaped by its operations across diverse sectors like healthcare, advanced technologies, learning, and cybersecurity. This multi-sector presence means Calian faces a broad spectrum of rivals, ranging from highly specialized niche providers to large, established multinational corporations. For instance, in the advanced technologies segment, Calian might compete with companies focused on specific defense or aerospace solutions, while in healthcare, it could be up against major IT service providers for healthcare systems.
The sheer number and variety of competitors in each of these markets significantly intensify rivalry. In 2024, the global IT services market, a key area for Calian, was projected to reach over $1.3 trillion, indicating a highly competitive environment with numerous players vying for market share. Similarly, the cybersecurity market, another core Calian business, saw significant investment and growth, with hundreds of companies offering specialized solutions, further fragmenting the competitive field.
The industry growth rate significantly influences competitive rivalry. In rapidly expanding sectors, companies can often increase sales by capturing new demand, which typically lessens the pressure to directly challenge competitors for existing market share. This dynamic can lead to more collaborative or less aggressive competitive behavior as the overall market pie is getting bigger.
Conversely, in mature or slow-growth industries, the competitive landscape intensifies. Companies must fight harder for every customer, leading to increased price competition, promotional activities, and a greater focus on differentiation to steal market share. For instance, the global IT services market, a sector often experiencing moderate to strong growth, saw its revenue increase by approximately 7.5% in 2024, reaching an estimated $1.4 trillion, which generally helps to temper the most aggressive forms of rivalry.
Calian's competitive rivalry is influenced by its ability to differentiate its products and services. By offering innovative solutions and specialized expertise, Calian can lessen the pressure from competitors who might otherwise engage in price-based competition. For instance, Calian's focus on advanced cybersecurity solutions and integrated managed services in its IT and cybersecurity segment sets it apart from more commoditized IT providers.
If Calian's services were more standardized, the rivalry would intensify. Customers would likely switch based on price alone, eroding profit margins. However, Calian's strategy of providing end-to-end solutions, such as its work in advanced communications and healthcare technology, creates customer stickiness and reduces the likelihood of direct price wars.
High Fixed Costs and Storage Costs
Industries requiring substantial investment in fixed assets, like advanced technology or specialized infrastructure, often see intense competition. Companies with high fixed costs, such as those operating complex satellite ground systems, may engage in aggressive pricing to maximize capacity utilization, thereby intensifying rivalry among existing players. Calian's diversified business model, spanning sectors from space and defense to health and IT, helps mitigate this risk by spreading these significant operational costs across various segments.
For instance, in the satellite communications sector, the initial capital outlay for ground stations and network infrastructure is immense. Companies must ensure these assets are consistently utilized to achieve profitability. This pressure can lead to price wars, especially when demand fluctuates. Calian's strategy of operating in multiple, less correlated markets allows it to absorb the impact of downturns in any single sector, providing a more stable financial footing.
- High Fixed Costs: Industries like satellite ground systems demand significant upfront investment, creating pressure for high capacity utilization.
- Aggressive Pricing: To cover fixed costs, companies may lower prices, intensifying competition.
- Calian's Diversification: Calian's broad portfolio helps spread high fixed and storage costs across different business units, reducing the impact of any single segment's performance.
- Risk Mitigation: Operating in diverse markets provides a buffer against sector-specific economic downturns or competitive pressures.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers, like specialized assets or long-term commitments, can trap companies in a market, even when they're not making money. This situation often fuels persistent, tough competition. For Calian, this factor is generally less impactful because its business model is quite diverse and adaptable, allowing for easier shifts in strategy or resource allocation.
Calian's operational flexibility means it doesn't typically face significant hurdles when exiting specific market segments or divesting certain business units. This contrasts with industries reliant on highly specialized, non-transferable assets, where leaving can be prohibitively expensive.
- Calian's diversified service offerings reduce the risk of being tied to unprofitable segments.
- The company's adaptable business model allows for strategic pivots, minimizing the impact of high exit barriers.
- Unlike heavy manufacturing, Calian's reliance on human capital and flexible technologies means lower asset-specific exit costs.
Calian's competitive rivalry is characterized by a broad spectrum of competitors across its diverse sectors, including healthcare, advanced technologies, learning, and cybersecurity. The sheer volume of players in markets like global IT services, projected to exceed $1.3 trillion in 2024, and the fragmented cybersecurity landscape, with hundreds of specialized firms, intensifies this rivalry.
Industry growth rates play a crucial role; faster-growing sectors can temper direct competition as companies focus on expanding demand. However, mature markets necessitate more aggressive strategies like price competition and differentiation to capture market share. Calian's ability to offer end-to-end solutions and specialized expertise, particularly in areas like advanced cybersecurity, helps it stand out and reduces reliance on price alone.
High fixed costs in sectors such as satellite ground systems can drive aggressive pricing to ensure capacity utilization, a pressure Calian mitigates through its diversified business model. This diversification across multiple, less correlated markets provides stability and reduces the impact of sector-specific downturns. Furthermore, Calian's adaptable structure and lower asset-specific exit costs compared to heavy industries mean it is less susceptible to being trapped by high exit barriers.
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Calian's diverse service offerings is significant, as customers can often find alternative ways to fulfill their needs. In the healthcare sector, for instance, clients might choose to bolster their in-house staffing capabilities rather than outsourcing to Calian, or they could invest in different medical technologies that reduce the reliance on specialized personnel.
Similarly, within the learning and development space, organizations might opt for readily available online learning platforms or strengthen their internal training departments as substitutes for Calian's tailored programs. This availability of alternative solutions directly impacts Calian's pricing power and market share, as customers can switch to more cost-effective or readily accessible options if Calian's value proposition isn't sufficiently compelling. For example, the global e-learning market was valued at approximately $250 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow, indicating a robust and competitive landscape for learning solutions.
The threat of substitutes for Calian is amplified when alternative solutions offer a compelling price-performance ratio. For example, if clients can find less expensive cybersecurity services that still meet their basic needs, or if readily available, off-the-shelf training programs prove adequate for many, Calian's premium offerings may face increased pressure. This dynamic was evident in the IT services sector in 2024, where a significant portion of small to medium-sized businesses prioritized cost savings, opting for cloud-based solutions that offered a more palatable entry price point compared to traditional on-premise deployments.
Calian's customers' willingness to switch to substitute solutions is influenced by several key factors. Brand loyalty plays a significant role; a strong, established relationship with Calian can make customers hesitant to explore alternatives. Perceived risk is also crucial; if switching involves uncertainty about performance, security, or integration, customers are less likely to make the change. The ease of transition is another major determinant. If moving to a competitor requires substantial investment in new infrastructure, retraining staff, or complex data migration, the propensity to substitute is considerably lower.
Technological Advancements Enabling Substitutes
Rapid technological advancements are a significant threat, as they can quickly introduce new solutions that compete with Calian's offerings. For instance, the rise of AI and machine learning presents a direct substitute threat to traditional human-led training and IT support services. This could impact Calian's Learning and IT & Cyber Solutions segments by offering more cost-effective or efficient alternatives.
The increasing sophistication of these technologies means that what was once a core competency for companies like Calian can be replicated or even surpassed by software and automated systems. This trend is accelerating, with significant investments being poured into AI development globally, projected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars in the coming years.
- AI-powered learning platforms can offer personalized and scalable training, potentially displacing traditional classroom or instructor-led modules.
- Automated IT helpdesks and cybersecurity solutions are becoming more capable, reducing the need for human intervention in routine tasks.
- Cloud-based collaboration tools can substitute for some on-premise IT infrastructure and support services.
- Low-code/no-code development platforms enable faster application creation, potentially reducing demand for custom IT development services.
Regulatory or Policy Changes Favoring Substitutes
Changes in government regulations or policies can significantly impact the competitive landscape by favoring substitute solutions. For instance, new legislation or incentives designed to promote cloud-based data analytics could reduce the reliance on on-premises solutions, a segment Calian might serve. In 2024, many governments globally are focusing on digital transformation initiatives, which often include subsidies for adopting new technologies that could compete with existing offerings.
Consider the cybersecurity sector. A hypothetical policy change in 2024 mandating the use of open-source security protocols could directly challenge proprietary solutions. This would increase the threat of substitutes by making them more cost-effective and widely adopted. For example, if a major government contract in 2024 specified open-source components for critical infrastructure, it would divert potential clients away from traditional, licensed software providers.
- Policy Favoring Open-Source: A 2024 directive promoting open-source software for government IT projects could decrease demand for Calian's proprietary solutions.
- Digital Transformation Incentives: Government subsidies for cloud migration in 2024 might boost cloud-based analytics, acting as a substitute for on-premises data management.
- Data Localization Laws: Emerging data localization regulations in 2024 could push companies towards local, potentially less sophisticated, but compliant substitute service providers.
- Cybersecurity Standards: New cybersecurity standards in 2024 that prioritize interoperability with open platforms could make open-source security tools more attractive than integrated proprietary suites.
The threat of substitutes for Calian is substantial, particularly as technological advancements and evolving market demands present readily available alternatives. For instance, the proliferation of AI-driven platforms in learning and development offers scalable, personalized training that can compete with Calian's tailored programs. Similarly, in IT and cybersecurity, automated solutions and cloud-based services are increasingly capable of handling tasks previously requiring specialized human expertise.
The cost-effectiveness and accessibility of these substitutes are key drivers of their adoption. In 2024, many organizations, especially small to medium-sized businesses, prioritized budget efficiency, leading them to opt for cloud-based IT solutions that offered a lower entry price point compared to traditional deployments. This trend highlights how substitutes with a favorable price-performance ratio can directly challenge established service providers.
The global e-learning market, valued at around $250 billion in 2023, demonstrates the competitive pressure from readily available online learning platforms. Furthermore, the significant investments in AI development globally, projected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars, underscore the potential for these technologies to disrupt traditional service models across various sectors Calian operates in.
Factors such as brand loyalty, perceived switching risks, and the ease of transition influence customer decisions regarding substitutes. However, rapid technological evolution, particularly in AI and automation, continuously lowers the barrier to entry for new, competitive solutions, thereby intensifying the threat of substitution for Calian's offerings.
Entrants Threaten
The capital required to enter Calian's diverse sectors, particularly advanced technologies and satellite ground systems, presents a substantial barrier. For instance, developing and deploying sophisticated satellite communication infrastructure demands hundreds of millions of dollars in upfront investment, significantly deterring smaller players.
Calian's established operations, spanning healthcare, advanced technologies, learning, and cybersecurity, create significant economies of scale and scope. This means they can spread their fixed costs over a larger output and leverage their expertise across different sectors, driving down per-unit costs. For instance, their diversified service model in 2023, with revenues reaching $714.5 million, demonstrates this breadth, making it difficult for newcomers to match their cost efficiency.
Calian's decades-long history, particularly its deep roots in serving government and commercial sectors, has cultivated a robust brand identity and significant customer loyalty. This established trust is a formidable barrier for newcomers. For instance, Calian's extensive contract history, evidenced by its consistent revenue streams from long-term government agreements, demonstrates the difficulty new entrants face in replicating this level of client confidence and operational integration.
Access to Distribution Channels and Supply Chains
Newcomers often struggle to access established distribution channels and secure dependable supply chains, which can be a significant hurdle. Calian's established relationships, especially within the government contracting sector and for specialized technology, act as a formidable barrier to entry for potential competitors.
For instance, Calian's extensive experience in delivering complex solutions to federal agencies, as evidenced by its numerous multi-year contracts, solidifies its position. In 2023, Calian reported significant growth in its Health and IT segments, driven by these established relationships, making it harder for new players to replicate that market penetration.
- Established Distribution Networks: Calian leverages its long-standing partnerships with key government bodies and large enterprises, which are difficult for new entrants to penetrate.
- Supply Chain Integration: The company's integrated supply chain for specialized technology ensures reliability and efficiency, a critical advantage over less experienced competitors.
- Procurement Expertise: Calian's deep understanding of complex procurement processes, particularly in defense and healthcare, creates a significant knowledge gap for new entrants.
Government Policy and Regulation
Government policy and regulation significantly impact the threat of new entrants. Strict regulations, licensing requirements, and compliance standards in sectors where Calian operates, such as healthcare and defense, create substantial barriers. For instance, obtaining necessary certifications and approvals can be a lengthy and costly process, deterring potential new competitors.
Calian's established expertise in navigating these complex regulatory landscapes is a key advantage. The company's long history of compliance and successful engagement with government agencies means it understands the intricate requirements and can adapt more readily to changes. This deep understanding reduces the risk and uncertainty for Calian compared to a new entrant facing these hurdles for the first time.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Sectors like healthcare and defense often require specific certifications, licenses, and adherence to stringent quality and safety standards, which new entrants must meet.
- Compliance Costs: The expense associated with meeting these regulatory demands, including audits and legal fees, can be a significant deterrent for smaller or less capitalized new companies.
- Calian's Advantage: Calian's proven track record in managing regulatory compliance and its existing relationships with governing bodies provide a competitive edge against potential new market participants.
The threat of new entrants for Calian is generally low due to significant capital requirements, particularly in its advanced technology and satellite sectors, where initial investments can run into hundreds of millions. Calian's established economies of scale, demonstrated by its $714.5 million in revenue in 2023, and strong brand loyalty built over decades, especially with government clients, further deter new competition. Navigating complex regulatory environments and securing established distribution channels also pose substantial barriers that new companies find difficult to overcome.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Calian's Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High upfront investment for advanced tech/satellite infrastructure. | Substantial deterrent, requiring significant funding. | Established financial capacity and access to capital. |
| Economies of Scale & Scope | Calian's diversified operations and large output reduce per-unit costs. | New entrants struggle to match cost efficiency. | Leverages broad service model for cost leadership. |
| Brand Loyalty & Reputation | Decades of serving government/commercial sectors build trust. | Difficult for newcomers to replicate client confidence. | Extensive contract history and proven reliability. |
| Distribution & Supply Chain | Access to established channels and integrated supply chains. | New entrants face challenges in market penetration. | Strong relationships with key government and enterprise clients. |
| Regulatory Environment | Strict licensing, compliance, and certifications in key sectors. | Costly and time-consuming for new players to navigate. | Proven track record in compliance and government engagement. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Calian Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, including Calian's annual reports, investor presentations, and financial statements. We also incorporate industry-specific market research, competitor news, and relevant government publications to provide a comprehensive view.
