Calder Group Ltd. Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Calder Group Ltd. Bundle
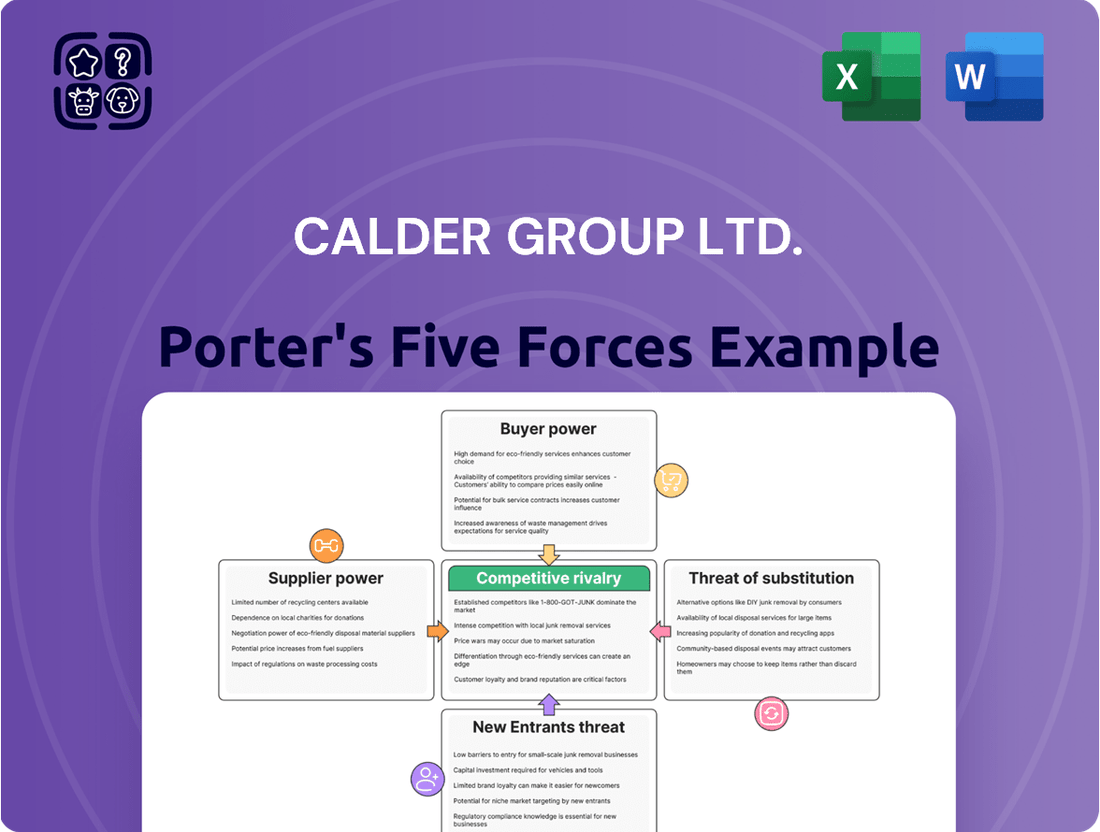
The Calder Group Ltd. Porter's Five Forces Analysis highlights significant competitive pressures, particularly in the threat of new entrants and the bargaining power of buyers. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for navigating the market effectively.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Calder Group Ltd.’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The global lead market, with Asia-Pacific leading in consumption, presents a scenario where a few dominant suppliers could wield significant influence over Calder Group Ltd. This concentration means that if these key lead providers also cater to other major industries, their leverage in negotiations with Calder Group naturally increases.
The lead market's dynamics in 2024 underscore this vulnerability. Factors such as a decrease in both primary and secondary lead supplies, coupled with China's more stringent emission regulations impacting battery manufacturers, have contributed to price volatility. This sensitivity to supply-side shifts directly amplifies the bargaining power of lead suppliers.
The availability of substitute materials for suppliers of raw lead, a key input for Calder Group, generally limits their bargaining power. This is because suppliers' primary market is companies like Calder that produce lead-based products, meaning lead has limited alternative high-demand uses outside this sector.
However, if significant alternative applications for lead emerge that Calder Group does not cater to, suppliers could redirect their supply. For instance, in 2024, the demand for lead in electric vehicle batteries continued to grow, potentially diverting supply from traditional industries and impacting Calder's costs and product availability.
Switching lead suppliers for Calder Group is a complex undertaking. It involves not only identifying a new vendor but also the rigorous process of qualifying new materials, adapting manufacturing workflows, and navigating potential supply chain interruptions. These multifaceted switching costs can significantly enhance the bargaining power of existing suppliers, as the effort and expense to change are substantial.
The capital-intensive nature of certain lead-based products, such as those used in radiation shielding, further entrenches these supplier relationships. For instance, specialized equipment and processes are often required to meet the stringent quality and safety standards for these applications, making a transition to a new supplier a considerable investment, thereby reinforcing the leverage of current providers.
Uniqueness of Lead and Lead-Based Inputs
The bargaining power of suppliers for Calder Group Ltd. is significantly influenced by the uniqueness of lead and lead-based inputs. Lead's exceptional density, malleability, and corrosion resistance make it indispensable for Calder Group's specialized products, such as radiation shielding and lead sheeting, where these properties are critical for performance and safety.
This inherent uniqueness means that alternative materials often cannot directly substitute for lead in these demanding applications, granting lead suppliers a stronger negotiating position. Calder Group's reliance on these specific characteristics for its product integrity and marketability translates into a degree of dependence on its lead suppliers.
- Lead's unique properties (high density, malleability, corrosion resistance) are difficult to replicate for specific applications like radiation shielding.
- Calder Group's reliance on these properties for product performance strengthens supplier bargaining power.
- Limited viable substitutes for lead in specialized applications increase supplier leverage.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of lead suppliers integrating forward into manufacturing engineered lead products presents a significant challenge for Calder Group Ltd. This strategic move would transform suppliers into direct competitors, potentially disrupting Calder's market position. Such integration demands considerable capital, specialized knowledge in lead engineering, and custom fabrication capabilities, making it a substantial undertaking.
While the likelihood of this specific forward integration may be low, its mere possibility can enhance supplier bargaining power. Suppliers could leverage this potential threat to negotiate more favorable terms with Calder, knowing that a loss of their supply could lead to Calder facing direct competition from them.
- Potential for Competition: Suppliers integrating forward would directly compete with Calder Group in the engineered lead products market.
- Investment Threshold: Forward integration requires significant investment in manufacturing, engineering expertise, and custom fabrication.
- Increased Bargaining Power: The threat of competition, even if not fully realized, strengthens suppliers' negotiating leverage.
The bargaining power of lead suppliers for Calder Group Ltd. is substantial due to the specialized nature of lead and the high costs associated with switching suppliers. Lead's unique physical properties make it difficult to substitute in critical applications, and the investment required to change suppliers is significant, giving existing providers considerable leverage.
| Factor | Impact on Supplier Bargaining Power | Calder Group Ltd. Implication |
|---|---|---|
| Concentration of Suppliers | High (few dominant players) | Increased negotiation leverage for suppliers |
| Switching Costs | High (material qualification, workflow adaptation) | Reinforces reliance on existing suppliers |
| Uniqueness of Input (Lead) | High (essential for specific properties) | Limits Calder's ability to source alternatives |
| Threat of Forward Integration | Moderate (potential for direct competition) | Can be used as a negotiation tactic by suppliers |
What is included in the product
This analysis of Calder Group Ltd. dissects the competitive forces shaping its industry, examining the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the intensity of rivalry, and the threat of substitute products.
Instantly identify competitive threats and opportunities with a visual breakdown of Porter's Five Forces, enabling proactive strategy adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Calder Group Ltd. serves a variety of industries, including construction, healthcare, and industrial manufacturing. This diversification is generally positive, but a concentration of large buyers within specific sectors, like major hospital construction projects or large industrial facility developments, can amplify customer bargaining power.
For instance, a significant hospital network undertaking a major expansion might leverage its substantial order volume to negotiate more favorable pricing or terms with Calder Group, especially if Calder's radiation shielding products are critical to the project's completion.
In 2024, the global healthcare construction market was valued at over $200 billion, with significant projects often involving large, sophisticated buyers who are accustomed to demanding competitive terms, potentially impacting Calder's pricing flexibility in this segment.
For customers in sectors like construction and healthcare, switching lead product suppliers can be a significant undertaking. Imagine needing to re-engineer building designs or re-certify specialized materials, especially when dealing with critical applications such as radiation shielding. These processes can incur substantial costs and delays, effectively locking customers in and diminishing their bargaining power.
Calder Group Ltd.'s expertise in lead engineering further solidifies these switching costs. When customers rely on Calder for custom-fabricated solutions or highly specialized lead products, the technical knowledge and established integration become barriers to switching. This is particularly true in 2024, where project timelines and regulatory compliance are paramount, making disruption a costly proposition for buyers.
Customer price sensitivity is a key factor for Calder Group Ltd. In the construction and industrial sectors, where competitive bidding and tight project budgets are common, customers often prioritize the lowest price. This can put pressure on Calder's margins if they cannot effectively differentiate their offerings.
However, Calder's position in specialized markets, such as radiation shielding for healthcare, demonstrates a different dynamic. Here, the critical nature of the application means that performance, safety, and adherence to strict regulatory standards outweigh minor price differences. For instance, in 2024, the global medical imaging market, a key area for radiation shielding, was valued at over $100 billion, with a significant portion driven by advanced safety features and compliance.
Availability of Substitute Products for Customers
The availability of substitute products significantly influences the bargaining power of customers for Calder Group Ltd. If customers can readily find alternative materials or products that fulfill the same function as Calder's lead-based offerings, their leverage increases.
While lead possesses distinct advantages, particularly in radiation shielding, the market for construction and industrial applications may present viable alternatives. For instance, in damp proofing or soundproofing, other materials could be considered, potentially diminishing customer reliance on lead and thus enhancing their bargaining power.
Consider the construction sector, where regulations and material innovation can shift preferences. For example, in 2024, the global construction market saw continued interest in sustainable and alternative materials, with advancements in polymer-based damp proofing and advanced acoustic insulation technologies offering competitive solutions.
- Lead's unique properties in radiation shielding limit direct substitutes in critical applications.
- However, in construction and industrial uses, alternative materials for damp proofing and soundproofing exist, granting customers more choice.
- The 2024 market trend towards sustainable and innovative materials in construction provides a growing array of potential substitutes.
- This availability of alternatives can empower customers to negotiate better terms with Calder Group Ltd.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of backward integration by customers, particularly large industrial manufacturers or construction conglomerates, poses a potential challenge to Calder Group Ltd. These customers could, in theory, decide to produce their own engineered lead products, thereby reducing their reliance on external suppliers like Calder Group. This would directly impact Calder Group's sales volume and pricing power.
However, this threat is significantly mitigated by substantial barriers to entry in lead manufacturing. The specialized knowledge, advanced equipment, and stringent regulatory compliance required for producing engineered lead products are considerable hurdles. For instance, lead smelting and refining operations demand significant capital investment in pollution control technology and specialized expertise to manage health and safety protocols, often exceeding the capabilities or strategic focus of typical end-users.
- High Capital Investment: Establishing a lead manufacturing facility requires substantial upfront capital, often in the tens or hundreds of millions of dollars, for specialized machinery, environmental controls, and safety infrastructure.
- Technical Expertise: The production of engineered lead products involves complex metallurgical processes and a deep understanding of material science, which most customers in sectors like construction or automotive do not possess internally.
- Regulatory Burden: Lead manufacturing is subject to rigorous environmental and health regulations globally, necessitating continuous investment in compliance and monitoring, a burden that many potential integrating customers may find prohibitive.
- Economies of Scale: Calder Group, as an established player, likely benefits from economies of scale in sourcing raw materials and production, making it difficult for a new, smaller-scale customer integration to achieve comparable cost efficiencies.
The bargaining power of customers for Calder Group Ltd. is influenced by several factors, including switching costs, price sensitivity, and the availability of substitutes. While high switching costs, particularly in specialized applications like radiation shielding, can limit customer power, price sensitivity in broader construction and industrial markets can increase it.
In 2024, the global construction market's ongoing focus on sustainable materials and innovation presents a growing landscape of potential substitutes for lead in certain applications, such as damp proofing and soundproofing. This trend empowers customers to negotiate more favorable terms with Calder Group Ltd. by providing them with more choices and leverage.
The threat of backward integration by customers is generally low due to the significant capital investment, technical expertise, and stringent regulatory compliance required for lead product manufacturing. These barriers make it economically unfeasible for most of Calder's customers to produce their own engineered lead products.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power | Calder Group Ltd. Context |
|---|---|---|
| Switching Costs | High in specialized applications (radiation shielding) | Technical integration and custom fabrication create significant switching barriers. |
| Price Sensitivity | Moderate to High in construction/industrial sectors | Competitive bidding and budget constraints can pressure pricing. |
| Availability of Substitutes | Low for radiation shielding; Moderate for construction/industrial uses | Alternative materials exist for damp proofing and soundproofing, increasing customer options. |
| Backward Integration Threat | Low | High capital, expertise, and regulatory hurdles deter customer self-production. |
Same Document Delivered
Calder Group Ltd. Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis for Calder Group Ltd., detailing the competitive landscape and strategic implications. The document you see here is the exact, fully formatted report you will receive immediately after purchase, offering actionable insights without any placeholders or surprises. It meticulously examines the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of existing rivalry within Calder Group Ltd.'s industry, providing a complete strategic overview for informed decision-making.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The market for engineered lead products, including lead sheet and radiation shielding, features several established competitors. The medical radiation shielding sector, a key area for Calder Group Ltd., is particularly dynamic, with numerous companies actively participating and driving competition.
This competitive landscape includes both large, diversified manufacturers and smaller, specialized firms focusing on niche applications. For instance, the global market for radiation shielding was valued at approximately USD 5.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, indicating a robust but also crowded market where rivalry is naturally heightened as companies compete for increasing demand.
The medical radiation shielding market is poised for substantial expansion, with projected compound annual growth rates (CAGRs) between 6.6% and over 21% from 2024 through 2029. Similarly, the lead sheet market is anticipated to experience robust growth during this period.
This industry expansion can moderate competitive intensity by creating a larger pie for all participants. However, it also acts as a magnet for new companies entering the market and spurs existing competitors to increase their investment in capacity and innovation, potentially intensifying rivalry.
Calder Group Ltd. distinguishes itself through deep expertise in lead engineering and custom fabrication, moving beyond standard lead sheet offerings. This specialization allows them to provide tailored solutions and bespoke designs, particularly in critical sectors like radiation shielding.
By focusing on high-quality products and unique customization, Calder Group can lessen direct competition based purely on price. This strategy helps secure a more robust market position, as clients value the specialized capabilities and engineered solutions that address specific needs, rather than commodity products.
Exit Barriers
Calder Group Ltd. faces a competitive landscape intensified by high exit barriers. These barriers, stemming from substantial investments in specialized assets like lead manufacturing facilities and significant sunk costs in ongoing research and development, make it difficult and costly for firms to leave the market. This reluctance to exit, even when profitability is low, means that rivalry remains persistently high, as companies are essentially locked into the industry.
The presence of these exit barriers significantly impacts the competitive dynamic. Companies are compelled to continue operating and competing, even in challenging economic conditions. For instance, in the lead industry, the specialized nature of production equipment represents a considerable sunk cost. If a company were to attempt to exit, these assets would likely have very little resale value, effectively trapping capital within the sector.
- Specialized Assets: Calder Group's lead manufacturing facilities are highly specialized, with limited alternative uses, creating a significant barrier to exiting the market.
- Sunk Costs in R&D: Long-term investments in research and development for lead-based products represent substantial sunk costs, making withdrawal financially unviable.
- Long-term Contracts: Existing long-term supply contracts with customers further bind companies like Calder Group to the market, deterring early exit.
- Industry Entrenchment: The cumulative effect of these factors entrenches existing players, ensuring sustained competitive rivalry as firms are reluctant to divest from the sector.
Cost Structure and Capacity Utilization
Industries with significant fixed costs and a strong need to keep production lines running at high capacity often see intense price competition. Companies in these sectors, like Calder Group’s engineered lead products manufacturing, face pressure to cover their substantial asset investments. This often translates into aggressive pricing strategies to maximize sales volume and maintain operational efficiency, thereby heightening rivalry among competitors.
While Calder Group’s precise cost structure isn't publicly itemized, the nature of producing engineered lead products suggests considerable upfront investment in plant, machinery, and specialized equipment. These are typically high fixed costs. Consequently, achieving high capacity utilization becomes a critical factor for profitability. If Calder Group, or its competitors, operate below optimal capacity, the per-unit cost of production rises, creating a powerful incentive to secure more orders, even at lower margins.
- High Fixed Costs: Industries producing engineered lead products often require significant capital expenditure on manufacturing facilities and equipment.
- Capacity Utilization Pressure: To offset high fixed costs, companies must operate at or near full capacity, leading to potential price wars if demand falters.
- Competitive Pricing: The drive to utilize capacity can force companies to engage in aggressive pricing to gain market share and cover overheads, intensifying rivalry.
Calder Group Ltd. operates in a competitive market characterized by numerous established players and a dynamic radiation shielding sector. The global radiation shielding market was valued at approximately USD 5.5 billion in 2023, with projected growth rates between 6.6% and over 21% annually from 2024 to 2029, indicating a robust but crowded environment. This expansion, while beneficial, also attracts new entrants and encourages existing firms to invest more, thereby intensifying rivalry.
High exit barriers, including substantial investments in specialized lead manufacturing assets and ongoing R&D, lock companies into the industry, ensuring sustained competition. For example, the specialized nature of production equipment in the lead industry often results in low resale value, making withdrawal financially unviable for firms like Calder Group.
The industry's high fixed costs and the need for high capacity utilization also drive aggressive pricing strategies. Companies must cover significant capital expenditures, leading to a focus on maximizing sales volume, which can result in price wars and heightened competitive rivalry as firms strive to maintain operational efficiency and cover overheads.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Calder Group Ltd. |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Competitors | Many established firms and specialized niche players. | Intense competition for market share, especially in the growing medical radiation shielding segment. |
| Market Growth | Global radiation shielding market ~USD 5.5 billion (2023), with projected CAGR 6.6%-21%+ (2024-2029). | Attracts new entrants and spurs existing competitors to expand, increasing rivalry despite market expansion. |
| Exit Barriers | High sunk costs in specialized assets (e.g., lead manufacturing facilities) and R&D. | Companies are reluctant to exit, leading to persistent rivalry and pressure to maintain operations even in challenging conditions. |
| Cost Structure | High fixed costs associated with specialized manufacturing. | Pressure for high capacity utilization can lead to aggressive pricing and potential price wars to cover overheads. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
For roofing and damp proofing, lead sheet faces competition from synthetic membranes and other metals. If lead prices rise significantly, or if environmental regulations tighten further, these alternatives become more attractive. For instance, the global roofing market was valued at approximately USD 120 billion in 2023, with membranes holding a substantial and growing share.
In radiation shielding, lead's effectiveness is hard to match with cost-efficient substitutes, though safety and environmental concerns are driving interest in lead-free options. For example, bismuth and tungsten-based shielding are emerging, but their widespread adoption in critical applications like medical facilities or nuclear power plants is still developing, and their cost-effectiveness compared to lead remains a key consideration.
The threat of substitutes for Calder Group Ltd. hinges on whether these alternatives can match lead's performance, particularly in radiation shielding, at a similar or reduced cost. While advancements in lead-free materials are ongoing, their current efficacy in attenuation and overall cost-effectiveness compared to traditional lead remains a significant consideration.
In the construction sector, the long-standing durability and established effectiveness of lead sheeting are crucial benchmarks. Potential substitutes must demonstrate comparable longevity and protective capabilities, while also offering a compelling initial cost advantage to truly challenge lead's market position. For instance, the global market for radiation shielding materials, excluding lead, was projected to reach $1.5 billion in 2024, indicating growing interest in alternatives, but lead continues to hold a substantial share due to its proven track record and cost-efficiency in many applications.
Customer willingness to switch away from Calder Group Ltd.'s products is a key factor in the threat of substitutes. This willingness hinges on several elements, including the perceived risk associated with a new product, how readily regulatory bodies accept it, and how simple it is for customers to start using it.
For instance, in high-stakes sectors such as medical radiation shielding, where lives are on the line, customers place immense value on established efficacy and safety. This makes them inherently hesitant to adopt unproven alternatives, significantly lowering their willingness to switch. In 2023, the global market for medical imaging and radiation therapy equipment was valued at approximately $40 billion, highlighting the critical nature of reliability in this segment.
Conversely, in less demanding areas like general construction, customers might be more open to switching if the cost savings are substantial. If a substitute product offers a significant price advantage without compromising essential performance, the likelihood of a switch increases. For example, a 10% reduction in material costs for non-specialized building components could drive considerable customer migration, especially in a competitive market where profit margins are tight.
Technological Advancements in Substitute Materials
Ongoing advancements in materials science pose a significant threat of substitutes for lead. For instance, research into new composite shielding materials could offer comparable or superior performance with reduced environmental impact, potentially displacing lead in applications like radiation shielding. Innovations in nanomaterials are also being explored for their potential in various sectors, which could further diversify the substitute landscape.
The threat is amplified by the continuous drive for more sustainable and safer alternatives across industries. As of early 2024, the global market for advanced materials, including composites and nanomaterials, is projected to grow substantially, indicating increasing investment and development in areas that could directly challenge lead's market share. For example, the market for advanced composites was valued at over $100 billion in 2023 and is expected to see robust growth.
- Emergence of Novel Materials: Continued R&D in materials science may yield new substitutes for lead in applications such as batteries and construction.
- Performance Improvements: New materials could offer enhanced properties like lighter weight or greater durability, making them more attractive alternatives.
- Environmental and Regulatory Pressures: Growing concerns about lead's toxicity are driving demand for safer, eco-friendly substitutes, a trend expected to continue through 2025.
- Cost Competitiveness: As substitute material production scales, their cost-effectiveness relative to lead is likely to improve, increasing their competitive threat.
Regulatory Pressure for Lead Alternatives
Increasing environmental regulations and growing concerns about lead's toxicity are significantly boosting the demand for lead-free alternatives. This trend is particularly pronounced in sectors like healthcare and construction, where safety standards are paramount.
Regulations targeting hazardous substances are making substitutes more appealing and accelerating their adoption. For instance, the European Union's Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) directive, continually updated, impacts the use of lead in electronics, a market where Calder Group Ltd. may operate.
- Growing demand for lead-free materials in construction and healthcare.
- Impact of environmental regulations like RoHS on product design.
- Increased attractiveness and adoption of substitute materials due to regulatory pressure.
The threat of substitutes for Calder Group Ltd. is moderate, primarily due to lead's unique properties in specific applications like radiation shielding. While alternatives exist in roofing and construction, their ability to match lead's performance and cost-effectiveness remains a key differentiator. For example, the global market for radiation shielding materials, excluding lead, was projected to reach $1.5 billion in 2024, indicating a growing but still niche market for alternatives.
Customer willingness to switch is influenced by perceived risk and regulatory acceptance, particularly in critical sectors like healthcare. In less sensitive areas, significant cost savings from substitutes could drive adoption, especially if initial cost advantages are substantial, as seen in the broader construction materials market where a 10% cost reduction can be a strong motivator.
Advancements in materials science, including composites and nanomaterials, present a growing threat, fueled by environmental and safety concerns. The global market for advanced materials, valued at over $100 billion in 2023, demonstrates significant investment in areas that could yield superior or more sustainable substitutes for lead.
Entrants Threaten
Entering the engineered lead products market, particularly for sophisticated uses like radiation shielding or bespoke fabrication, demands substantial capital. Newcomers must invest heavily in advanced manufacturing plants, specialized equipment, and ongoing research and development, creating a formidable hurdle.
Newcomers to the lead-acid battery market face significant hurdles in securing consistent and competitively priced access to raw lead. This essential material, subject to global market fluctuations, presents a substantial barrier for any new player aiming to establish a foothold.
Established companies, such as Calder Group Ltd., often benefit from long-standing supplier relationships and bulk purchasing power, creating an advantage that is challenging for new entrants to overcome. For instance, in 2023, lead prices saw considerable volatility, with the LME Lead price fluctuating between approximately $2,000 and $2,500 per metric ton, underscoring the importance of secured supply chains.
Calder Group Ltd.'s significant expertise in lead engineering and custom fabrication acts as a substantial barrier to new entrants. This deep, specialized knowledge, honed over years of operation, represents a form of proprietary technology that is difficult and time-consuming for newcomers to replicate. For instance, in the critical field of radiation shielding, where precision and material science are paramount, Calder’s established capabilities in designing and manufacturing complex lead components are a key differentiator.
Economies of Scale
Calder Group Ltd. faces a significant threat from new entrants due to entrenched economies of scale. Established players in the lead products market leverage these scale advantages across production, procurement, and distribution, resulting in a lower cost per unit. For instance, in 2024, major automotive manufacturers like Toyota, with a global production volume exceeding 8 million vehicles annually, benefit from massive purchasing power for raw materials and components, which new, smaller entrants cannot easily replicate.
New entrants would find it incredibly challenging to match the cost efficiencies enjoyed by incumbents. This initial disadvantage in cost structure would place them in a precarious competitive position from the outset. Consider the semiconductor industry, where companies like Intel and TSMC invest billions in advanced manufacturing facilities, creating a high barrier to entry; a new entrant would need comparable capital investment to achieve similar production costs.
- Economies of Scale: Established firms in lead product markets benefit from lower per-unit costs due to large-scale operations in production, procurement, and distribution.
- Cost Disadvantage for New Entrants: Newcomers struggle to achieve initial cost efficiencies, creating a competitive hurdle.
- Capital Investment Barrier: Industries requiring substantial upfront investment for efficient production, like semiconductors, present a high barrier to entry.
- Procurement Power: Large volumes allow established companies to negotiate better prices with suppliers, a benefit not readily available to new entrants.
Regulatory Hurdles and Environmental Compliance
The manufacturing and handling of lead products, like those produced by Calder Group Ltd., are heavily regulated due to lead's inherent toxicity. New companies entering this market would face substantial regulatory hurdles, including obtaining numerous licenses and permits, which can significantly increase upfront costs and time-to-market. For instance, in 2024, compliance costs for environmental protection and worker safety in the chemical manufacturing sector, which often overlaps with lead product manufacturing, can easily reach millions of dollars for new facilities.
These stringent environmental and safety regulations act as a significant deterrent to potential new entrants. Compliance with standards set by bodies like the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the United States or similar agencies globally requires substantial investment in pollution control technology and rigorous safety protocols. In 2023, the average cost for a new manufacturing plant to meet all environmental compliance requirements was estimated to be between $5 million and $20 million, depending on the scale and specific processes involved.
- Significant Capital Investment: New entrants must allocate substantial funds towards meeting environmental standards, including waste treatment and emission control systems.
- Licensing and Permitting Complexity: Navigating the complex web of federal, state, and local licenses and permits for handling hazardous materials like lead is a time-consuming and costly process.
- Ongoing Compliance Costs: Beyond initial setup, continuous monitoring, reporting, and adherence to evolving regulations represent a perpetual financial burden.
- Potential for Fines and Penalties: Non-compliance can result in severe financial penalties, further discouraging market entry. In 2024, penalties for environmental violations can range from thousands to millions of dollars per infraction.
New entrants face significant capital investment requirements for advanced manufacturing and R&D, creating a high barrier. Securing consistent, competitively priced raw lead is also a major challenge, especially given price volatility, as seen with LME lead prices fluctuating between approximately $2,000 and $2,500 per metric ton in 2023. Furthermore, stringent environmental and safety regulations, with compliance costs for new facilities potentially reaching $5 million to $20 million in 2023, add substantial complexity and expense.
| Barrier Type | Description | Example Data/Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Investment | Need for advanced manufacturing, specialized equipment, and R&D. | High upfront costs for sophisticated production facilities. |
| Raw Material Access | Securing consistent and competitively priced lead supply. | LME Lead prices fluctuated ~$2,000-$2,500/metric ton in 2023. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Meeting environmental and safety standards for lead handling. | New facilities could face $5M-$20M compliance costs (2023 estimate). |
| Proprietary Knowledge | Calder Group's expertise in lead engineering and fabrication. | Difficult and time-consuming for new entrants to replicate. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Calder Group Ltd. is built upon a robust foundation of data, including publicly available financial statements, industry-specific market research reports, and insights from reputable trade publications. This comprehensive approach ensures an accurate assessment of competitive intensity and strategic positioning.
