Broad Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Broad Bundle
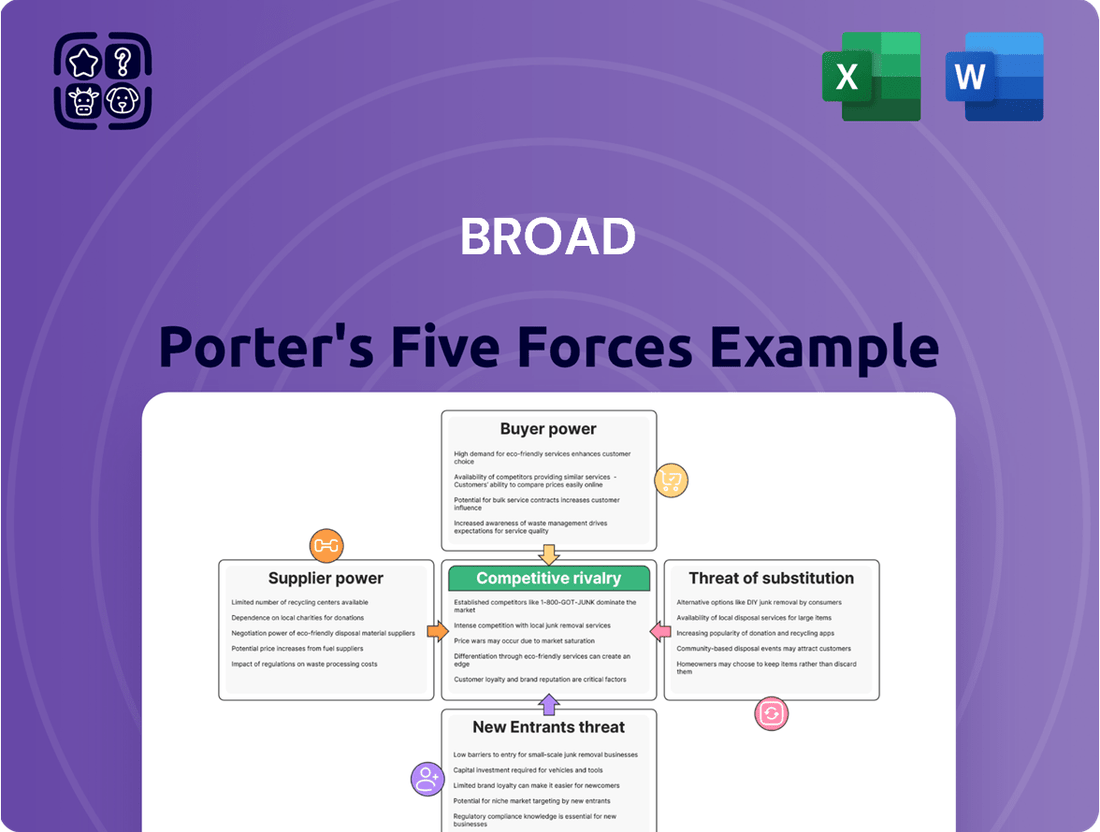
Porter's Five Forces Analysis helps understand the competitive landscape. It examines the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. This framework is crucial for assessing an industry's attractiveness and a company's strategic positioning.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Broad’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
BROAD Group's reliance on specialized inputs like lithium bromide for its absorption chillers and advanced materials for prefabricated buildings significantly influences supplier power. The uniqueness and scarcity of these components can grant suppliers considerable leverage.
The growing demand for sustainable building materials, such as low-carbon concrete and engineered wood, is reshaping supplier dynamics. For example, the global market for engineered wood was valued at approximately $115.6 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow, potentially increasing the bargaining power of suppliers in this niche.
Suppliers who possess unique technology or patents for essential parts, particularly in sophisticated absorption chiller systems or specialized prefabricated building components, can wield considerable influence. This often involves proprietary heat recovery technologies or advanced materials for building envelopes.
The emergence of cutting-edge insulation materials, such as those utilizing aerogel technology or vacuum insulated panels, is poised to strengthen the negotiating position of these suppliers. For instance, by 2024, the global aerogel market was projected to reach over $1.5 billion, indicating a significant value placed on such advanced materials.
BROAD Group faces a reduction in its bargaining power with suppliers if switching key components or materials incurs substantial costs. These costs can include retooling manufacturing lines, redesigning existing products, or the lengthy process of qualifying new suppliers, especially critical in integrated energy solutions where system compatibility is paramount.
The company's reliance on specialized software and hardware for AI and machine learning-driven system optimization in waste heat recovery further solidifies this dependency. For instance, if a proprietary control system requires extensive custom programming or hardware upgrades for a new vendor's components, the switching costs for BROAD Group would be significant, thereby increasing the supplier's leverage.
Supplier Concentration and Industry Consolidation
When a few large suppliers control the essential inputs for an industry, their bargaining power increases significantly. For instance, if there are only a handful of companies that produce specialized components for absorption chillers or provide critical sustainable building materials, they can more easily dictate pricing and terms to manufacturers.
The global absorption chiller market, projected to reach approximately $1.5 billion by 2024, exhibits a moderate level of supplier concentration for certain specialized components. This means that manufacturers relying on these specific parts may face greater pressure from a limited number of suppliers.
- Supplier Concentration: A market dominated by a few key suppliers grants them leverage over buyers.
- Impact on Pricing: Limited suppliers for critical inputs like absorption chiller components can lead to price increases.
- Market Dynamics: The absorption chiller market's growth, coupled with the presence of major players, influences supplier power for specific parts.
Forward Integration Threat by Suppliers
Suppliers can significantly increase their bargaining power if they possess the capability to integrate forward into BROAD Group's operations. This means suppliers could potentially start manufacturing similar non-electric air conditioning systems or prefabricated building solutions themselves, directly competing with BROAD. For instance, a major supplier of steel framing for modular construction might decide to assemble entire prefabricated modules, bypassing BROAD's assembly process. This threat compels BROAD Group to nurture strong supplier relationships and ensure its pricing remains competitive to deter such moves.
The modular construction market's expansion presents a clear avenue for material suppliers to enhance their own market position. As demand for prefabricated building solutions grows, suppliers of key components like insulation, structural panels, or even specialized fasteners are well-positioned to move up the value chain. Consider the global modular construction market, projected to reach over $150 billion by 2027, a significant increase from previous years. This growth signals a fertile ground for suppliers to consider expanding into prefabricated module assembly, thereby increasing their leverage over companies like BROAD Group.
- Forward Integration Threat: Suppliers moving into direct competition with BROAD Group by producing similar non-electric AC systems or prefabricated building solutions.
- Impact on Bargaining Power: This capability directly elevates supplier influence, pushing BROAD to maintain favorable terms.
- Market Growth as a Catalyst: The expanding modular construction sector, with its projected growth, provides a strong incentive for material suppliers to explore assembly operations.
Suppliers hold significant bargaining power when they provide critical, specialized inputs that are difficult for buyers like BROAD Group to substitute. This power is amplified if there are few suppliers for these essential materials, allowing them to dictate terms and prices. For instance, the market for advanced materials used in BROAD's high-efficiency absorption chillers may be concentrated among a limited number of producers, giving them considerable leverage.
The cost for BROAD Group to switch suppliers for these specialized components is a key factor in supplier power. High switching costs, including retooling or redesigning products, strengthen the supplier's position. Additionally, if suppliers have the potential to integrate forward and compete directly with BROAD, their bargaining power increases substantially, pushing BROAD to maintain favorable relationships and competitive pricing.
| Factor | Impact on Supplier Bargaining Power | Example for BROAD Group |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High | Few suppliers for specialized absorption chiller components |
| Switching Costs | High | Redesigning products for alternative materials |
| Forward Integration Threat | High | Suppliers entering the prefabricated building market |
What is included in the product
Porter's Five Forces Analysis provides a framework to understand the competitive intensity and attractiveness of an industry, by examining the threat of new entrants, bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, threat of substitute products or services, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors.
Identify and neutralize competitive threats before they impact profitability, offering a clear roadmap to sustainable advantage.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customers, whether industrial clients for absorption chillers or developers for prefabricated buildings, are often price-sensitive, especially given the significant investment involved in large-scale cooling systems or construction projects. For instance, in the commercial building sector, the upfront cost of HVAC systems can represent a substantial portion of a project's budget, making price a critical factor in purchasing decisions.
The growing demand for energy-efficient solutions and lower operational costs, as offered by absorption chillers, suggests that customers are looking for long-term value beyond initial purchase price. In 2024, the emphasis on sustainability and operational expenditure (OPEX) reduction continues to drive purchasing behavior, with many businesses prioritizing total cost of ownership over mere acquisition cost for major capital equipment.
Customers for cooling and construction solutions have a wide array of alternatives. These include not only traditional HVAC systems but also conventional building methods and various air purification products. This broad selection directly enhances customer bargaining power, compelling companies like BROAD Group to focus on competitive pricing and delivering strong value.
The global HVAC system market itself underscores this diversity, showing substantial growth and a multitude of choices available to consumers. For instance, the global air conditioning market was valued at approximately $130 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow, indicating a dynamic landscape where customer options are plentiful.
If BROAD Group's customer base is dominated by a few major clients, like large industrial firms or significant property developers, these customers hold substantial bargaining power. This is especially relevant in the industrial sector, a key market for absorption chillers, where large orders can significantly influence pricing and terms.
Switching Costs for Customers
The cost and complexity associated with customers transitioning from BROAD Group's products to those of a competitor directly impact their leverage. For significant undertakings like large-scale construction projects or comprehensive energy solutions, switching can involve substantial expenses and intricate integration challenges, especially concerning long-term operational compatibility.
While high switching costs can limit customer bargaining power, shifts towards modular designs and accelerated construction methodologies in the building sector may gradually lower these barriers. This evolving landscape could empower customers by making it easier to adopt alternative solutions.
For instance, in the construction industry, the average cost to switch building information modeling (BIM) software can range from 10% to 25% of the software's annual license fee, factoring in training and data migration. BROAD Group's ability to minimize these transition frictions for its clients will be crucial in managing customer bargaining power.
Consider these factors influencing switching costs:
- Integration Complexity: The degree to which BROAD Group's solutions are embedded within a customer's existing systems and processes.
- Learning Curve: The time and resources required for customers to become proficient with a competitor's offerings.
- Contractual Obligations: Any long-term service agreements or warranties that might incur penalties upon early termination.
- Supplier Relationships: The established trust and service levels that customers have with BROAD Group, which are difficult to replicate.
Customer Information and Transparency
Customers armed with readily available market data, competitive pricing information, and detailed product reviews are in a much stronger position to negotiate favorable terms. This increased access to information significantly amplifies their bargaining power.
The growing transparency within sectors like sustainable building materials and energy efficiency empowers customers to easily compare different offerings. This allows them to scrutinize pricing and performance, leading them to demand better value and more advantageous contract conditions.
For instance, in 2024, the global green building materials market was valued at approximately $270 billion, with significant growth driven by customer demand for transparency and verifiable sustainability. Certifications such as LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) provide customers with standardized metrics for evaluating the environmental performance of buildings and the materials used.
- Informed Customers: Access to price comparison sites and user reviews in 2024 gave consumers unprecedented leverage.
- Market Transparency: The energy efficiency market saw a 15% increase in customer inquiries about lifecycle costs in 2024, driven by transparent data.
- Certification Impact: LEED-certified projects in 2024 often reported lower operational costs, influencing customer demands for similar performance.
Customers possess significant bargaining power when they are price-sensitive, have numerous alternatives, or face low switching costs. In 2024, the emphasis on total cost of ownership and readily available market data empowers buyers, particularly in large-scale projects where initial investment is substantial.
For example, the global HVAC market, valued around $130 billion in 2023, offers a wide array of choices, thereby increasing customer leverage. Similarly, the green building materials market, estimated at $270 billion in 2024, highlights customer demand for transparency and verifiable performance.
Concentrated customer bases, where a few large clients dominate, also amplify their bargaining power. This is evident in sectors like industrial absorption chillers, where major orders can dictate pricing and terms. However, high integration complexity and learning curves can mitigate this power by increasing switching costs.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power | 2024 Relevance Example |
|---|---|---|
| Price Sensitivity | High | Upfront cost of HVAC systems for commercial buildings |
| Availability of Alternatives | High | Diverse options in the global HVAC and green building materials markets |
| Switching Costs | Low to Moderate | Integration complexity and learning curves vs. modular construction trends |
| Customer Concentration | High (if few large clients) | Large industrial firms or property developers influencing pricing |
| Information Availability | High | Price comparison sites and user reviews driving demand for better value |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Broad Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. You'll gain a comprehensive understanding of Porter's Five Forces, including the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers, the bargaining power of suppliers, the threat of substitute products or services, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. This detailed analysis will equip you with the strategic insights needed to evaluate industry attractiveness and competitive dynamics.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The absorption chiller market is populated by significant players such as Thermax Ltd, Shuangliang Eco-Energy Systems Co. Ltd., Carrier Corporation, Johnson Controls, and Broad Group, showcasing a robust competitive environment. This array of established companies suggests a dynamic market where innovation and efficiency are paramount for gaining an edge.
Further intensifying this rivalry, the prefabricated building and air purification sectors, where Broad Group also operates, are characterized by a high number of diverse participants. This broad base of competitors across its key business areas means Broad Group faces constant pressure to differentiate its offerings and secure market share through strategic pricing and product development.
The absorption chiller market is anticipated to expand at a compound annual growth rate of 4.9% between 2024 and 2034. This robust growth, coupled with a similar upward trend in the modular construction sector, creates fertile ground for increased competition as companies vie for market share.
Furthermore, the burgeoning green building market is a significant driver of this expansion, attracting more players and intensifying the competitive landscape. Companies are likely to engage in aggressive strategies to capture a larger portion of these expanding markets.
BROAD Group's emphasis on non-electric absorption chillers and sustainable building technologies offers a unique market position. For instance, their commitment to eco-friendly solutions like air purification systems sets them apart. However, the competitive landscape is dynamic, with rivals introducing advancements such as hydrogen-powered absorption chillers and intelligent HVAC systems, intensifying rivalry.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers can significantly intensify competitive rivalry. When it's difficult or costly for companies to leave an industry, they may continue operating even with low profits, leading to prolonged price wars or overcapacity. This is particularly true in sectors requiring substantial sunk costs.
For instance, the manufacturing of absorption chillers and prefabricated building solutions often involves specialized machinery and dedicated production lines. These assets have limited alternative uses, making them difficult to sell or redeploy. Companies invested in such infrastructure face considerable financial penalties if they attempt to exit.
Consider the capital expenditure involved. In 2024, the global market for HVAC systems, which includes absorption chillers, was valued at over $120 billion. The significant investment in manufacturing facilities and technology creates a strong incentive for firms to remain operational, even during economic downturns, thereby increasing the pressure on existing players.
- Specialized Assets: Absorption chiller plants require highly specific components and manufacturing processes, limiting resale value.
- Long-Term Contracts: Companies may be bound by service agreements or supply contracts that extend for years, preventing a swift exit.
- Capital Investments: The upfront cost of establishing a factory for prefabricated building solutions can run into tens of millions of dollars, deterring quick departures.
- Employee Severance: Laying off a skilled workforce, especially in specialized manufacturing, can incur substantial severance costs and reputational damage.
Strategic Commitments and Market Share Goals
Competitors with aggressive market share goals, such as those aiming to capture a larger portion of the growing renewable energy market, will intensify rivalry. For instance, in 2024, major energy companies are committing billions to develop and deploy green building solutions, signaling a strong intent to dominate this segment.
Significant strategic commitments to specific technologies, like advanced waste heat recovery systems, also fuel fierce competition. Companies heavily investing in R&D and production capacity for these innovations are positioning themselves for leadership, creating a more dynamic competitive landscape.
The global imperative for sustainability and energy efficiency is a major driver. Many players are heavily invested in these areas, leading to increased rivalry as they vie for market dominance. This investment surge means more companies are actively competing on price, innovation, and service quality.
- Aggressive Market Share Goals: Companies targeting significant growth in sustainable technologies are increasing competitive intensity.
- Strategic Technology Investments: Major commitments to areas like waste heat recovery signal a drive for technological leadership and market share.
- Sustainability Imperative: The global push for energy efficiency is causing widespread investment, intensifying rivalry across the sector.
- Increased Competition Drivers: Players compete on innovation, pricing, and service to capture market share in efficiency-focused segments.
The competitive rivalry within the absorption chiller and broader building solutions market is intense, driven by numerous established players and a high number of participants in related sectors. This dynamic environment forces companies like Broad Group to constantly innovate and differentiate to maintain market share.
The significant growth projected for the absorption chiller market, with a 4.9% CAGR expected between 2024 and 2034, coupled with expansion in modular construction and green buildings, attracts more competitors. This creates a scenario where companies aggressively pursue market dominance through various strategies.
High exit barriers, such as specialized assets and substantial capital investments in manufacturing facilities, trap companies in the industry. This can lead to prolonged price competition and overcapacity as firms strive to recoup their investments, intensifying rivalry among existing players.
Companies with aggressive market share objectives, particularly in the burgeoning renewable energy and sustainable building sectors, are escalating competitive pressures. Strategic investments in advanced technologies like waste heat recovery further fuel this rivalry, as firms aim for leadership in efficiency-focused segments.
| Industry Segment | Key Competitors (Examples) | Competitive Intensity Drivers |
|---|---|---|
| Absorption Chillers | Thermax Ltd, Shuangliang Eco-Energy, Carrier Corporation, Johnson Controls | Market growth (4.9% CAGR 2024-2034), innovation in sustainability, high capital investment |
| Prefabricated Buildings | Various global and regional manufacturers | High number of diverse participants, significant capital expenditure for facilities |
| Air Purification | Numerous specialized and diversified companies | High number of participants, focus on health and environmental regulations |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Traditional vapor compression chillers, powered by electricity, represent a significant threat of substitution to BROAD Group's non-electric absorption chillers. These conventional systems are deeply entrenched in the market, often boasting lower initial purchase prices, which can be a strong draw for many buyers despite the long-term energy savings of absorption technology.
The global HVAC market is robust and diverse, with a wide array of air conditioning solutions available, further intensifying the competitive landscape. In 2024, the global air conditioning market was valued at approximately $130 billion, with conventional systems holding a substantial share.
Traditional on-site construction methods serve as a significant substitute for BROAD Group's prefabricated building solutions. While BROAD's BSB structures offer advantages like speed and energy efficiency, conventional building remains a strong competitor, often seen as more adaptable for specific project needs.
Despite the increasing adoption of modular construction, traditional building techniques still hold a dominant position in the overall construction industry. In 2023, the global construction market was valued at approximately $13.4 trillion, with prefabricated construction representing a growing but still smaller segment of this vast market.
While BROAD Group's absorption chillers leverage waste heat, alternative technologies like Organic Rankine Cycle (ORC) systems and thermoelectric generators also convert waste heat into usable energy. These can serve as substitutes, particularly in different scales or application niches within the broader energy solutions market.
The global waste heat recovery market is experiencing robust growth, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 5.5% through 2028, reaching an estimated value of over $70 billion. This expansion signifies a dynamic landscape with diverse and evolving technological solutions available.
DIY Solutions and Smaller-Scale Alternatives
For air purification products, the threat of substitutes is present, especially from DIY solutions and smaller-scale alternatives. Consumers might opt for less sophisticated but cheaper methods like opening windows for natural ventilation, particularly in residential or smaller commercial settings where the need for advanced filtration might be perceived as lower. This is a significant consideration in a market driven by growing awareness of air quality issues.
The air purifier market itself is diverse, offering a wide range of products that can be seen as substitutes for one another, from basic HEPA filters to more advanced ionizers and UV-C light purifiers. This product proliferation means that a customer looking for air purification might find a viable, and potentially less expensive, alternative from a different segment of the market. For instance, the global air purifier market was valued at approximately $10.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach $20.7 billion by 2030, indicating substantial competition and a broad spectrum of offerings that can act as substitutes.
- Natural Ventilation: Simple, cost-free methods like opening windows can reduce reliance on powered air purifiers, especially in mild weather.
- Consumer-Grade Purifiers: Smaller, less powerful, and more affordable units serve as substitutes for high-end, industrial-grade systems.
- DIY Filtration: Basic filtration setups using readily available materials can offer a rudimentary level of air cleaning at a fraction of the cost.
- Plant-Based Solutions: While less impactful, some consumers turn to houseplants, believing they contribute to indoor air quality improvement, acting as a perceived substitute.
Energy Conservation Measures
Customers might choose less complex energy conservation measures instead of investing in new cooling systems or advanced building solutions. For instance, improved insulation, better sealing of windows and doors, or incorporating passive design strategies can significantly reduce energy consumption.
The emphasis on energy efficiency within the sustainable building materials market can also diminish the demand for sophisticated active cooling technologies. This shift towards more fundamental efficiency improvements presents a viable substitute for more capital-intensive upgrades.
- Reduced Demand for Active Cooling: Simple insulation upgrades can lower energy bills by up to 20% for homeowners, as reported by the U.S. Department of Energy.
- Passive Design Strategies: Utilizing natural ventilation and strategic window placement can decrease reliance on mechanical cooling systems, potentially saving businesses significant operational costs.
- Sustainable Materials Impact: The growing market for sustainable building materials, valued at over $250 billion globally in 2023, often prioritizes inherent energy efficiency, thereby reducing the need for supplementary active systems.
The threat of substitutes for BROAD Group's offerings is multifaceted, encompassing both direct technological alternatives and simpler, lower-cost solutions.
For chillers, traditional electric vapor compression systems remain a primary substitute, often favored for their lower upfront cost despite higher long-term energy expenses. In the broader HVAC market, valued at approximately $130 billion in 2024, these conventional units hold a substantial market share.
In construction, traditional on-site building methods are a significant substitute for BROAD's prefabricated solutions. While modular construction is growing, the global construction market, worth around $13.4 trillion in 2023, is still dominated by conventional techniques.
Other waste heat recovery technologies, like ORC systems, also present substitution threats in the energy solutions market. The waste heat recovery sector is projected to exceed $70 billion by 2028, indicating a competitive and evolving technological landscape.
For air purification, DIY solutions and basic filtration methods, alongside natural ventilation, act as substitutes for advanced purifiers. The air purifier market, valued at $10.5 billion in 2023, features a wide array of products that can serve as alternatives.
Furthermore, basic energy conservation measures like improved insulation, which can reduce energy bills by up to 20%, offer a substitute for investing in new cooling systems or advanced building technologies.
Entrants Threaten
Entering the manufacturing of non-electric air conditioning systems, prefabricated buildings, or integrated energy solutions demands significant capital. For instance, establishing a state-of-the-art manufacturing facility for prefabricated buildings can easily run into tens of millions of dollars, factoring in machinery, automation, and specialized construction equipment. This high upfront investment acts as a formidable barrier, deterring many potential new players from entering these capital-intensive sectors.
The threat of new entrants in the absorption chiller and sustainable building solutions market, where BROAD Group operates, is significantly mitigated by the high barriers to entry related to proprietary technology and specialized expertise. Developing advanced absorption chiller technology, for instance, requires substantial investment in research and development, a process that has historically led to patents and unique operational efficiencies for established players. BROAD Group’s focus on innovations like waste heat recovery systems and advanced sustainable building materials necessitates deep engineering knowledge and skilled personnel, which are not easily replicated by newcomers. For example, the development of their highly efficient absorption chillers, which can utilize low-grade waste heat, represents years of accumulated technical knowledge and significant R&D expenditure, making it a formidable challenge for any new company to match without comparable resources and time.
Established players like BROAD Group leverage significant economies of scale, meaning they can produce goods at a lower per-unit cost due to their large production volumes. For instance, in 2024, BROAD Group's extensive manufacturing facilities likely operate at peak efficiency, a feat difficult for newcomers to replicate quickly.
Furthermore, the experience curve effect grants incumbent firms an advantage; as they produce more over time, they become more efficient and identify cost-saving opportunities. This accumulated knowledge means BROAD Group can optimize processes, potentially reducing costs by 15-30% over their production lifespan, a substantial barrier for any new entrant aiming to compete on price.
Brand Recognition and Customer Loyalty
Building a strong brand and fostering customer loyalty in the HVAC and construction sectors is a long and resource-intensive process. New entrants face significant hurdles in establishing trust and recognition against established players like BROAD Group.
BROAD Group's established reputation for sustainable and energy-efficient solutions acts as a substantial barrier. New companies would need to commit significant capital to marketing and cultivating relationships to even begin to rival BROAD's market standing.
- Brand Equity: Companies with high brand equity, like BROAD, benefit from customer preference, which is difficult and costly for new entrants to replicate.
- Customer Loyalty: Repeat business and positive word-of-mouth are critical in these industries, and new entrants must invest heavily to earn this trust.
- Marketing Investment: In 2024, the global HVAC market saw significant marketing spend, with companies like BROAD leveraging their sustainability credentials to attract customers.
- Switching Costs: For consumers and businesses, the perceived risk and effort involved in switching HVAC or construction providers can be a deterrent to new entrants.
Regulatory Hurdles and Environmental Standards
The industries where BROAD Group operates face significant regulatory challenges. For instance, in 2024, the global green building market was valued at over $1.3 trillion, with stringent energy efficiency standards becoming commonplace. New entrants must invest heavily in research and development to comply with these evolving regulations, such as China's updated building energy efficiency standards which aim to reduce energy consumption by 20% in new buildings by 2025.
Navigating complex environmental standards and building codes presents a substantial barrier to entry. Companies looking to enter the prefabricated building sector, a key area for BROAD Group, must adhere to diverse local and international codes. For example, the European Union's Green Deal initiatives are driving stricter requirements for sustainable construction materials and practices, adding considerable cost and complexity for newcomers.
- Stringent Regulations: Compliance with energy efficiency, environmental impact, and building codes is mandatory.
- High Entry Costs: Meeting these standards requires significant investment in R&D and specialized materials.
- Evolving Standards: Continuous updates to regulations, such as those driven by decarbonization goals, necessitate ongoing adaptation.
- Green Certifications: Obtaining certifications like LEED or BREEAM adds another layer of complexity and cost for new market participants.
The threat of new entrants in markets like absorption chillers and sustainable building solutions is generally low due to substantial barriers. These include high capital requirements for manufacturing and R&D, proprietary technology, established economies of scale, strong brand equity, and complex regulatory landscapes. For instance, the global green building market's growth to over $1.3 trillion by 2024, coupled with evolving energy efficiency standards, necessitates significant upfront investment for compliance.
| Barrier Type | Description | Example Impact |
| Capital Requirements | High initial investment for manufacturing and technology development. | Establishing a new absorption chiller plant can cost tens of millions USD. |
| Proprietary Technology | Unique, patented technologies are difficult to replicate. | BROAD's waste heat recovery systems require deep R&D expertise. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs due to high production volumes. | Established players in 2024 benefit from efficient, large-scale operations. |
| Brand Equity & Loyalty | Customer trust and repeat business are hard-won. | New entrants need significant marketing investment to build recognition. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Adherence to stringent energy and environmental standards. | Meeting EU Green Deal requirements adds complexity and cost. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of robust data, drawing from financial disclosures, industry expert interviews, and comprehensive market research reports to capture the nuances of competitive intensity.
