BlueCity Holdings Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
BlueCity Holdings Bundle
BlueCity Holdings operates within a dynamic digital landscape, facing moderate threats from new entrants and the constant pressure of evolving substitute products. Understanding the bargaining power of both buyers and suppliers is crucial for navigating its competitive terrain effectively.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping BlueCity Holdings’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
BlueCity Holdings, operating in the digital space, depends on technology and software vendors for its platform. The bargaining power of these suppliers can be significant if a limited number of providers offer highly specialized and critical services, like advanced live-streaming capabilities or sophisticated data analytics tools. For instance, in 2024, the global market for specialized cloud infrastructure services, crucial for platforms like BlueCity, saw continued consolidation, with a few major players dominating. This concentration can give these specialized providers more leverage.
Content creators and influencers are crucial suppliers for platforms like BlueCity Holdings, especially those focused on user-generated content and live streaming. Their ability to attract and retain audiences directly impacts the platform's value. For instance, if a popular influencer with millions of followers can easily switch to a rival platform, their bargaining power increases significantly, forcing BlueCity to offer competitive incentives.
In 2024, the competition for top-tier creators intensified. Platforms are increasingly investing in creator funds and offering advanced monetization tools, such as higher revenue-sharing percentages on virtual gifts and subscriptions, to secure these vital suppliers. BlueCity's success hinges on its capacity to provide these attractive offerings and foster a supportive environment that encourages creators to remain and grow on its platform.
The bargaining power of suppliers in the data security and privacy solutions sector is substantial for companies like BlueCity Holdings. As global data privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA, continue to tighten, the demand for robust cybersecurity and data protection services escalates. In 2023, the global cybersecurity market was valued at approximately $214.1 billion, with projections indicating continued growth, underscoring the critical nature of these services.
BlueCity's reliance on these specialized providers to safeguard sensitive user information and ensure regulatory compliance grants these suppliers considerable leverage. Failure to comply with data protection mandates can result in severe penalties, making investments in advanced security solutions non-negotiable. The specialized nature of these solutions and the high stakes involved mean that BlueCity may face significant costs and limited alternatives when negotiating with key vendors in this space.
Payment Gateway Providers
Payment gateway providers hold a significant position for BlueCity Holdings, as its revenue generation from membership subscriptions and value-added services is directly tied to their services. The bargaining power of these suppliers can range from moderate to high. This is particularly true if they offer robust security, unwavering reliability, and broad acceptance of payment methods, coupled with substantial switching costs for BlueCity.
These providers’ fees directly influence BlueCity's bottom line. For instance, in 2024, transaction fees from payment gateways can represent a notable percentage of revenue for subscription-based businesses. A typical range for these fees might be between 1.5% and 3.5% of each transaction value, depending on the volume and the specific provider's terms.
- Dependency on Payment Gateways: BlueCity's revenue stream relies heavily on seamless payment processing.
- Supplier Bargaining Power Factors: Security, reliability, acceptance rates, and switching costs determine supplier leverage.
- Financial Impact: Transaction fees directly affect BlueCity's profitability margins.
- Industry Fee Benchmarks: In 2024, payment processing fees commonly fall between 1.5% and 3.5% per transaction.
Advertising Technology Providers
Advertising technology providers hold significant bargaining power over BlueCity Holdings, as advertising is a crucial revenue stream. BlueCity relies on these providers for essential functions like ad targeting, delivery, and performance analytics. While the ad tech landscape is crowded, specialized providers offering advanced targeting capabilities or innovative ad formats can command greater leverage. For instance, in 2024, companies specializing in AI-driven audience segmentation saw increased demand, potentially allowing them to negotiate more favorable terms.
The effectiveness of these ad tech tools directly influences BlueCity's capacity to generate revenue from its platform. If a provider offers superior targeting, it can lead to higher ad engagement and conversion rates, justifying higher costs for BlueCity. Conversely, a lack of differentiation among providers would weaken their individual bargaining power.
- Dependency on Ad Tech: BlueCity's revenue generation is directly tied to the performance of advertising, making it reliant on ad technology providers.
- Provider Specialization: Specialized ad tech firms with unique targeting or ad format capabilities possess greater bargaining power.
- Impact on Monetization: The quality of ad tech services directly affects BlueCity's ability to effectively monetize its user base through advertising.
The bargaining power of suppliers for BlueCity Holdings is influenced by the essential nature of their services and the level of competition within those supply markets. For instance, providers of critical infrastructure, such as cloud computing services, can wield significant power if the market is dominated by a few large players, as was evident in the consolidation trends observed in 2024.
Content creators and influencers represent another key supplier group whose leverage is amplified by their ability to attract and retain audiences, with platforms increasingly competing for top talent in 2024 by offering enhanced monetization and support.
The reliance on specialized vendors for data security and payment processing also grants these suppliers considerable bargaining power, especially given the escalating importance of regulatory compliance and the direct impact on revenue streams.
| Supplier Category | Key Dependencies for BlueCity | Factors Influencing Bargaining Power | 2024 Data/Trends |
| Technology & Software Vendors | Platform infrastructure, live-streaming, data analytics | Market concentration, specialization of services | Continued consolidation in specialized cloud infrastructure services |
| Content Creators/Influencers | User engagement, platform value | Audience size, portability to rival platforms | Intensified competition for top creators; increased investment in creator funds and monetization tools |
| Data Security & Privacy Solutions | User data protection, regulatory compliance | Stringency of data privacy regulations, criticality of services | Global cybersecurity market valued at ~$214.1 billion in 2023; increasing demand for robust protection |
| Payment Gateway Providers | Revenue generation (subscriptions, services) | Security, reliability, payment method acceptance, switching costs | Transaction fees typically range from 1.5% to 3.5% in 2024 |
| Advertising Technology Providers | Advertising revenue stream | Effectiveness of targeting, ad formats, differentiation | Increased demand for AI-driven audience segmentation tools |
What is included in the product
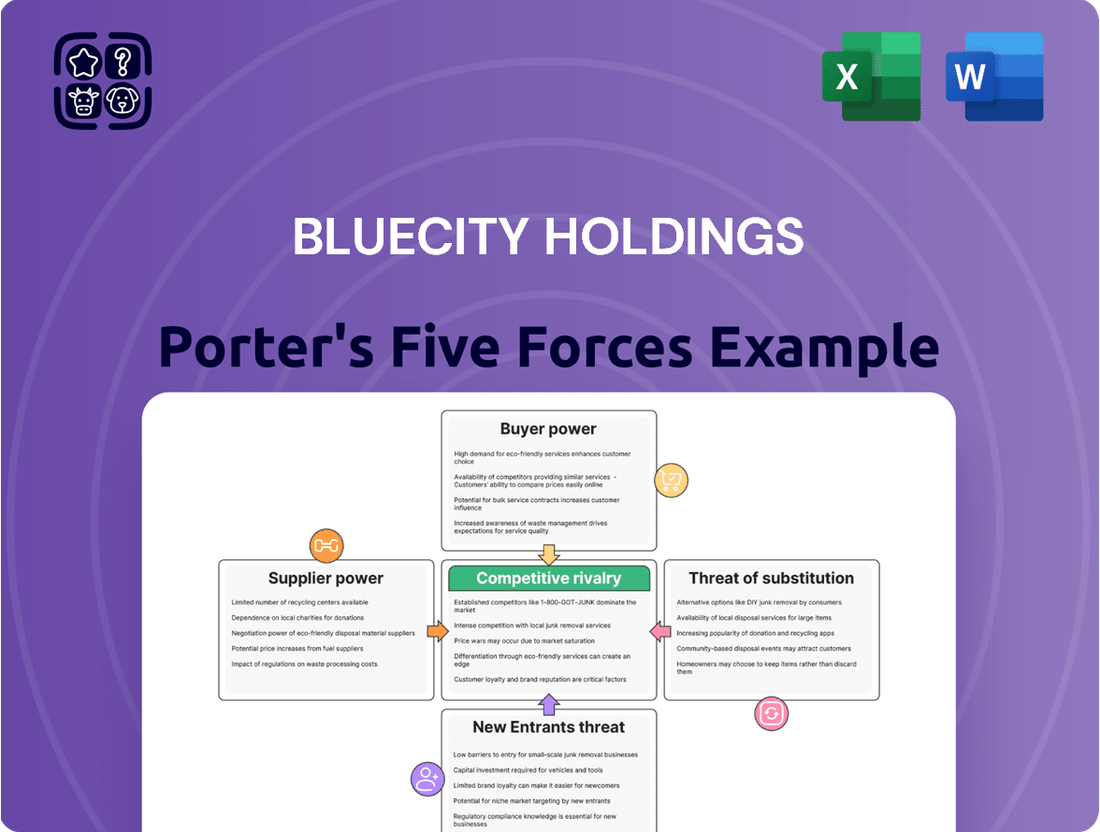
This analysis of BlueCity Holdings reveals the intensity of rivalry, the power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitutes, all within the context of its specific market.
Instantly gauge competitive intensity and identify strategic vulnerabilities with a visually intuitive Porter's Five Forces analysis, simplifying complex market dynamics for BlueCity Holdings.
Customers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of BlueCity's customers is significantly amplified by the low switching costs inherent in the social networking and dating app market. Users can readily transition to competing platforms if they find BlueCity's offerings lacking in features, community engagement, or overall user experience. This ease of movement places considerable pressure on BlueCity to consistently deliver value and maintain high levels of user satisfaction to retain its customer base.
The market for LGBTQ+ social networking and dating applications is quite crowded, meaning users have plenty of other options. This abundance of choices, from major worldwide apps to smaller, specialized ones, significantly boosts customer power. Users can easily switch to a different platform if BlueCity Holdings doesn't meet their expectations.
In BlueCity's case, the bargaining power of customers is amplified because users aren't just consumers; they are also creators of the platform's core value. When users generate content, they directly contribute to the appeal and engagement of BlueCity. This dynamic means that if a substantial portion of users, particularly those with significant influence or a large following, were to depart, the platform's overall attractiveness would suffer, thereby strengthening the remaining users' leverage.
This situation highlights a critical challenge for BlueCity: maintaining a vibrant and sticky community. The platform's success hinges on its ability to foster a sense of belonging and continuous engagement among its user base. By making users feel valued and connected, BlueCity can mitigate the risk of mass departures and the subsequent increase in customer bargaining power. For instance, in 2024, platforms that prioritized community features and user-generated content saw higher retention rates, with some reporting a 15% increase in user engagement compared to those with less interactive models.
Demand for Privacy and Safety
Users, particularly within the LGBTQ+ community, are increasingly vocal about their need for strong privacy and safety features on online platforms. This demand is a significant factor in their bargaining power.
Recent analyses in 2024 have shown that some major social media platforms are not adequately addressing safety concerns for LGBTQ+ individuals, with certain platforms scoring poorly on safety metrics. This underscores the user's ability to influence platform policies.
This heightened user awareness translates directly into greater power for customers to demand improved data protection and more effective content moderation from companies like BlueCity Holdings.
- Increased Demand for Privacy: Users are more aware of data usage and actively seek platforms with robust privacy controls.
- Safety Concerns Drive Choice: Negative experiences or perceived lack of safety can lead users to switch platforms.
- Community Advocacy: LGBTQ+ advocacy groups and users are actively pushing for safer online environments, influencing platform standards.
Influence of Community and Network Effects
While individual users of platforms like BlueCity Holdings might possess significant bargaining power due to the availability of alternatives, the strength of its community and network effects can serve as a powerful counterforce. A vibrant and engaged user base, actively contributing content and fostering interactions, creates unique value that transcends mere functionality. For instance, if BlueCity's community actively shares specialized knowledge or facilitates valuable connections, users may find it difficult to replicate this experience elsewhere, thus reducing their propensity to switch even if faced with slightly better pricing from competitors.
However, this loyalty is not absolute. A single negative experience, such as a significant policy shift that alienizes a core user group or a perceived decline in content quality, can rapidly diminish the perceived value of the community. This erosion of trust can quickly lead to a mass exodus, as users realize the network effects are not strong enough to retain them when the core value proposition is compromised. For example, a platform experiencing a sudden surge in spam or a poorly implemented algorithm change could see user engagement plummet, weakening the collective bargaining power of the community itself.
Consider the impact of user-generated content on platforms. In 2024, social media platforms that fostered strong creator communities, like TikTok, demonstrated how engaged users can drive significant platform growth and stickiness. If BlueCity Holdings can cultivate a similar environment where users feel invested in the platform's success through their contributions, it directly impacts the bargaining power of individual customers by making the collective experience more valuable and harder to abandon.
- Community Value: Engaged users create unique value that makes leaving the platform less appealing.
- Network Strength: A large and active user base enhances the platform's utility for all members.
- Vulnerability to Change: Negative policy changes or user experiences can quickly weaken community loyalty.
- User-Generated Content: Platforms with strong creator ecosystems often benefit from increased user retention.
The bargaining power of BlueCity's customers is substantial due to low switching costs and a competitive market landscape, offering users numerous alternative platforms. This ease of migration means BlueCity must continuously innovate and prioritize user experience to retain its audience. For instance, in 2024, the social networking market saw a proliferation of niche apps, increasing user choice and leverage.
Customers also act as content creators, directly contributing to BlueCity's value proposition. A significant departure of influential users could diminish the platform's appeal, thereby empowering remaining users. In 2024, platforms that effectively leveraged user-generated content reported higher engagement, underscoring this dynamic.
Furthermore, heightened user awareness regarding privacy and safety, particularly within the LGBTQ+ community, grants customers greater power to demand robust data protection and content moderation. Reports from 2024 indicated that some major platforms failed to meet these safety expectations, reinforcing users' ability to influence platform policies.
| Factor | Impact on BlueCity | 2024 Relevance |
| Low Switching Costs | High customer power; easy to move to competitors. | Increased availability of specialized apps in 2024 amplified choice. |
| User-Generated Content | Users are key value creators; their departure weakens the platform. | Platforms fostering creator communities in 2024 saw better retention. |
| Privacy & Safety Demands | Customers can demand better data protection and moderation. | 2024 safety reports showed gaps, empowering user advocacy. |
Same Document Delivered
BlueCity Holdings Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis for BlueCity Holdings, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic positioning of the company within its industry. You're looking at the actual document; once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact file, which includes an in-depth examination of the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors.
Rivalry Among Competitors
BlueCity Holdings operates within a fiercely competitive landscape, facing rivalry from both broad-reaching social media giants and specialized LGBTQ+ platforms. General platforms like TikTok, with its massive 1.7 billion global monthly active users as of early 2024, and Instagram, boasting over 2 billion, increasingly offer features that can attract LGBTQ+ users seeking connection, diluting the market share for dedicated apps.
The dedicated LGBTQ+ dating and social app sector itself is highly fragmented and competitive. Apps such as Grindr, HER, Scruff, and Taimi all vie for user attention, each with its own unique selling proposition and user base. This intense rivalry means BlueCity must continually innovate and differentiate its offerings to maintain and grow its user engagement and market position.
The digital platform sector is a hotbed of innovation, meaning companies like BlueCity Holdings must constantly stay ahead of the curve. Competitors are adept at quickly copying successful features, forcing BlueCity to continuously invest in new ideas and unique offerings to stand out.
This dynamic means BlueCity must always be thinking about what's next, whether it's enhancing social networking, improving live streaming, or expanding its health-related services. For instance, by the end of 2024, the global live streaming market was projected to reach over $247 billion, highlighting the intense competition and the need for differentiation in such a lucrative space.
BlueCity Holdings faces intense competition not just on user engagement but also on how it makes money. This includes competing for advertising dollars against a crowded digital landscape and convincing users to pay for premium features or memberships. For instance, in 2023, the global digital advertising market was projected to reach over $600 billion, a significant pool that BlueCity aims to capture.
The company must offer compelling value propositions to stand out in this monetization battle. This means competitive pricing for its subscription tiers and ensuring its value-added services are genuinely attractive to users, differentiating them from free alternatives or lower-cost competitors. BlueCity's ability to balance user acquisition with effective monetization is crucial for its financial health.
Global vs. Local Competition
BlueCity Holdings navigates a competitive arena where global players coexist with localized rivals. While international platforms offer broad reach, regional and country-specific LGBTQ+ platforms often possess a deeper understanding of local cultural nuances and regulatory landscapes, creating a fragmented yet intense competitive dynamic.
This duality means BlueCity must not only contend with established global brands but also with emerging or entrenched local competitors who may cater more precisely to specific community needs or operate within distinct market conditions. For instance, in certain Asian markets, local social networking apps might have a stronger cultural resonance, even if they aren't exclusively LGBTQ+ focused, presenting a unique challenge.
- Global Reach vs. Local Nuance: International competitors offer scalability, but local players often win on cultural relevance and community understanding.
- Fragmented Market: The presence of both types of competitors means BlueCity faces a diverse set of challenges, requiring tailored strategies for different regions.
- Regulatory Adaptation: Local competitors may be more adept at navigating specific national regulations, giving them an advantage in compliance and market access.
Brand Reputation and Trust
In the LGBTQ+ community, where trust is paramount, BlueCity Holdings' brand reputation and commitment to user safety and privacy are key competitive advantages. Negative publicity or security breaches can severely hinder user growth and retention, amplifying the competitive pressures within this niche market.
For instance, in 2024, a significant data privacy concern reported by a competing dating app led to a substantial drop in its user base, highlighting the critical importance of robust security measures and transparent data handling practices. BlueCity's proactive approach to user safety, including verified profiles and clear community guidelines, directly addresses these sensitivities.
- Brand Reputation: BlueCity's long-standing presence and positive association with the LGBTQ+ community foster strong brand loyalty.
- User Trust: Demonstrated commitment to user privacy and safety, including investments in security infrastructure, builds essential trust.
- Competitive Impact: Negative incidents affecting competitors underscore the financial and reputational risks associated with compromised user data, making trust a vital differentiator.
BlueCity Holdings faces intense rivalry from both global social media behemoths and numerous specialized LGBTQ+ platforms. Major players like TikTok, with over 1.7 billion global monthly active users in early 2024, and Instagram, exceeding 2 billion users, increasingly incorporate features that attract LGBTQ+ individuals, thereby fragmenting the user base for dedicated apps. This broad competition necessitates constant innovation from BlueCity to maintain user engagement and market share.
The dedicated LGBTQ+ dating and social app sector itself is highly competitive, featuring established names like Grindr, HER, Scruff, and Taimi, each with distinct offerings. This crowded space demands that BlueCity continuously differentiates its services to retain and grow its user base, especially as the global live streaming market, a key area for engagement, was projected to surpass $247 billion by the end of 2024.
Monetization strategies also fuel competitive pressures, as BlueCity contends for advertising revenue and premium subscriptions against a vast digital advertising market, projected to reach over $600 billion in 2023. Competitors quickly replicate successful features, forcing BlueCity to invest heavily in new ideas and unique value propositions to stand out and secure its financial health.
| Competitor Type | Key Characteristics | Impact on BlueCity |
| Global Social Media Platforms | Massive user bases (e.g., TikTok >1.7B MAU 2024), broad feature sets | Dilutes specialized LGBTQ+ user attention, requires feature differentiation |
| Specialized LGBTQ+ Apps | Niche focus, established communities (e.g., Grindr, HER) | Direct competition for user engagement and premium subscriptions |
| Emerging Digital Platforms | Rapid innovation, feature replication | Requires continuous investment in new offerings and user experience |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The most significant substitute for online social networking and dating platforms like those BlueCity Holdings operates is traditional, face-to-face social interaction. While digital platforms offer unmatched convenience and the ability to connect with a wider array of people, especially those with very specific interests, the enduring appeal of in-person connections cannot be overlooked.
Real-world meetups, community events, and organic personal connections forged through shared activities or existing social circles continue to serve as powerful alternatives. For instance, data from 2024 indicates a continued strong participation in local community events and hobby groups, suggesting that a portion of the population still prioritizes these offline avenues for social engagement and relationship building.
Generic communication apps like WhatsApp and Telegram present a significant threat of substitution for BlueCity's social networking functions. These platforms offer robust messaging, voice, and video call capabilities, allowing users to maintain social connections without needing a dedicated social media platform. For instance, WhatsApp boasts over two billion monthly active users globally as of early 2024, demonstrating its widespread adoption and utility as a primary communication tool.
For BlueCity Holdings' live streaming and entertainment services, substitutes like traditional television, movies, and music remain a significant threat. Despite the digital shift, these non-digital forms still command substantial viewership and engagement. For instance, in 2024, global broadcast television revenue is projected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars, demonstrating its continued market presence.
Specialized Health and Wellness Platforms
For health-related services, substitutes can be found in traditional healthcare providers, general telehealth platforms, and various digital wellness apps. These options offer alternative ways for individuals to manage their health, though they may lack the specific focus and cultural competency of specialized platforms.
However, it's important to note that specialized LGBTQ+ telehealth platforms are increasingly becoming direct competitors rather than mere substitutes. This shift indicates a growing market where tailored services are directly challenging broader offerings. For instance, in 2024, the digital health market saw significant growth, with telehealth services alone projected to reach over $200 billion globally by the end of the year, highlighting the competitive landscape.
- Traditional Healthcare Providers: Offer in-person consultations and established medical services, but may lack specialized LGBTQ+ cultural competency.
- General Telehealth Platforms: Provide convenient remote access to healthcare, but often do not cater to the unique needs of the LGBTQ+ community.
- Broad Digital Wellness Apps: Focus on general fitness, nutrition, or mental well-being, but miss the specific health concerns relevant to LGBTQ+ individuals.
- Emerging LGBTQ+ Telehealth Platforms: Represent direct competitors, offering specialized care and community-specific support, thereby increasing the threat of substitution for platforms not offering such tailored services.
Offline LGBTQ+ Community Resources
The threat of substitutes for BlueCity Holdings, particularly concerning its offline LGBTQ+ community resources, is moderate. While BlueCity offers a digital hub for connection and information, traditional offline avenues remain significant alternatives. These include community centers, various support groups, and local LGBTQ+ organizations that have long served as vital spaces for individuals seeking connection, emotional support, and access to essential information.
These physical and organized groups offer a different, often more intimate, form of community building and resource sharing that digital platforms may not fully replicate. For instance, in 2024, many cities saw a resurgence in in-person LGBTQ+ events and meetups, indicating a continued demand for face-to-face interaction. These offline resources provide direct access to counseling services, health clinics, and social events, directly substituting some of the core functions BlueCity aims to fulfill online.
- Community Centers: Offer physical safe spaces for socializing, events, and access to services.
- Support Groups: Provide peer-to-peer emotional and practical assistance for specific needs within the LGBTQ+ community.
- Local Organizations: Act as crucial hubs for information dissemination, advocacy, and direct service provision.
For BlueCity's core social networking and dating services, substitutes are primarily other digital platforms and traditional offline interactions. While generic communication apps like WhatsApp, boasting over two billion monthly active users as of early 2024, offer robust messaging, they lack the specialized dating and community-building features. Similarly, traditional face-to-face interactions and community events, which saw strong participation in 2024, provide an alternative but less scalable way to connect.
| Substitute Type | Key Features | User Base (Approx. 2024) | Impact on BlueCity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Generic Communication Apps | Messaging, Voice/Video Calls | WhatsApp: 2B+ MAU | Offers basic connection, but lacks specialized features |
| Traditional Socializing | In-person events, community groups | High participation in local events | Provides organic connections, but limited reach and scalability |
| Other Dating Apps | Dating, social networking | Market leader user numbers vary | Direct competitors with similar functionality |
Entrants Threaten
While building a complex platform like Blued demands substantial capital, the technical hurdles for creating simpler social or dating applications are surprisingly low. This is largely due to the widespread availability of user-friendly development tools and scalable cloud computing resources, which democratize app creation. For instance, the global cloud computing market was valued at over $600 billion in 2023, a figure projected to grow significantly, making infrastructure more accessible than ever.
The primary hurdle for new competitors in BlueCity Holdings' market isn't necessarily the technology itself, but rather establishing a significant user base and fostering strong network effects. For instance, in the social media landscape, companies like Meta (Facebook, Instagram) have demonstrated how deeply entrenched network effects can be; acquiring users on a comparable scale requires immense investment and time, often exceeding billions in marketing and development. This makes it exceptionally difficult for newcomers to overcome the initial 'empty platform' problem where a lack of users deters further adoption.
New entrants into the online community space, especially those targeting sensitive demographics like the LGBTQ+ community, face significant regulatory and data privacy compliance challenges. These hurdles require substantial upfront investment in legal counsel and robust data security infrastructure, potentially acting as a barrier to entry.
For instance, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and similar legislation worldwide impose strict rules on data collection, processing, and storage. Companies operating in this space must invest heavily to ensure compliance, with fines for violations reaching up to 4% of global annual revenue, as seen in cases involving major tech firms.
Need for Trust and Brand Building in Niche Markets
In niche markets like the LGBTQ+ consumer space, establishing trust and a strong brand is crucial for any new entrant. This isn't just about selling a product; it's about demonstrating authenticity and cultural understanding.
New companies must invest significant resources in building a reputation and proving their genuine commitment to the community. For instance, a 2024 report indicated that 78% of LGBTQ+ consumers are more likely to support brands that visibly and consistently advocate for their community, highlighting the substantial barrier to entry in terms of brand loyalty and perception.
- Brand Loyalty: Existing, trusted brands in the LGBTQ+ market benefit from high customer loyalty, making it difficult for newcomers to gain market share.
- Authenticity Barrier: New entrants face the challenge of proving genuine commitment, as superficial attempts at inclusivity are often quickly identified and rejected by the community.
- Reputational Investment: Building a positive and trustworthy brand in this segment requires sustained effort and investment in community engagement, not just marketing campaigns.
Competition from Diversifying Existing Players
Existing tech giants like Meta and Google can swiftly enter or bolster their presence in emerging niche markets. They possess substantial financial reserves, massive existing user communities, and advanced technological infrastructure, making it challenging for smaller, specialized newcomers to compete. For instance, Meta's significant investment in virtual reality, including its Meta Quest line, demonstrates its ability to leverage existing platforms and user engagement to capture new market segments.
These established players can also enhance their offerings by integrating new features or acquiring promising startups. In 2024, we've seen continued M&A activity in the tech sector, with larger companies strategically purchasing innovative smaller firms to quickly gain market share and technological advantages. This strategy allows them to bypass the lengthy development cycles and customer acquisition costs that new entrants face.
The threat is amplified by their capacity to cross-subsidize new ventures with profits from their core businesses. This financial muscle enables them to offer services at lower price points or invest heavily in marketing, creating barriers to entry. For example, a large social media platform could launch a new specialized service and offer it free to its existing user base, effectively undercutting any independent competitor.
- Resource Advantage: Large tech firms can deploy vast capital and talent into new markets.
- User Base Leverage: Existing user networks provide immediate reach and data for new services.
- Acquisition Strategy: Buying out innovative startups is a common tactic to enter niche areas.
- Cross-Subsidization: Profits from established services can support the launch of new, potentially unprofitable ventures.
While the technical creation of a dating app might seem straightforward, the real barrier for new entrants in BlueCity Holdings' space is building a critical mass of users and establishing strong network effects. This is a significant hurdle, as seen in the social media world where companies invest billions to achieve similar reach.
Newcomers also face substantial costs related to data privacy regulations, such as GDPR, with potential fines reaching up to 4% of global annual revenue for non-compliance. Furthermore, building trust and authenticity within niche communities, like the LGBTQ+ demographic, is paramount, with reports indicating that 78% of these consumers favor brands with visible and consistent advocacy.
| Barrier Type | Description | Example/Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Network Effects | Difficulty in attracting users to an "empty" platform. | Social media giants like Meta leverage vast existing user bases. |
| Capital Requirements | High investment needed for marketing and user acquisition. | Billions spent by established players on growth. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Adherence to data privacy laws like GDPR. | Fines up to 4% of global annual revenue for violations. |
| Brand Trust & Authenticity | Proving genuine commitment to niche communities. | 78% of LGBTQ+ consumers favor supportive brands. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for BlueCity Holdings is built upon a foundation of publicly available financial reports, industry-specific market research, and regulatory filings. We also incorporate insights from reputable business news outlets and competitor disclosures to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
