Berkshire Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Berkshire Bank Bundle
Berkshire Bank navigates a landscape shaped by intense rivalry, the looming threat of new entrants, and the significant power of buyers and suppliers. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for any stakeholder seeking to grasp their competitive position.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Berkshire Bank’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Berkshire Bank's reliance on specialized technology providers for its core banking systems, digital interfaces, and cybersecurity creates a moderate to high bargaining power for these suppliers. This is particularly true when their solutions involve proprietary technologies or highly specialized functionalities. For instance, in 2024, the average cost for a financial institution to switch core banking platforms can range from tens to hundreds of millions of dollars, reflecting the significant switching costs that limit a bank's flexibility and embolden these vendors.
The financial services sector, including regional banks such as Berkshire Bank, relies heavily on a specialized talent pool. This is especially true for roles in technology, wealth management, and risk assessment. A scarcity of these qualified individuals, particularly in emerging fields like artificial intelligence and data analytics, can significantly bolster the leverage of employees.
When there's a limited supply of workers with in-demand skills, employers must compete more fiercely to attract and keep them. This competition often translates into higher salary demands and more attractive benefit packages. For instance, in 2024, the demand for cybersecurity professionals in the financial sector outstripped supply, leading to average salary increases of 15-20% for experienced individuals in this niche.
Berkshire Bank, like many financial institutions, relies heavily on external data and information providers for critical functions such as credit assessment, market analysis, and ensuring regulatory compliance. These suppliers, offering financial data, market intelligence, and credit reporting services, possess a moderate level of bargaining power. The essential nature and often specialized content of this data make these providers significant partners, though the existence of multiple potential suppliers can temper their individual leverage.
Professional and Consulting Services
Berkshire Bank relies on a range of professional services, such as legal counsel, accounting expertise, and management consulting. The leverage these suppliers hold is directly tied to their standing, unique skills, and the intricacy of the tasks they undertake.
For highly specialized legal advice or complex accounting audits, these service providers can wield considerable influence. For instance, in 2024, the average hourly rate for specialized legal services in the financial sector saw an increase, reflecting the demand for niche expertise.
- Reputation and Specialization: Top-tier law firms or accounting practices with proven track records in financial services command higher rates and can dictate terms more effectively.
- Switching Costs: The effort and potential disruption involved in onboarding new legal or accounting partners can make it costly for Berkshire Bank to switch suppliers, increasing supplier power.
- Market Concentration: If only a few firms possess the specific expertise Berkshire Bank needs, their bargaining power is amplified. For example, regulatory compliance consulting for banking often involves a limited pool of highly sought-after experts.
- Importance of Service: Critical services, like those related to regulatory compliance or major litigation, give suppliers greater leverage due to the high stakes involved for Berkshire Bank.
Infrastructure and Real Estate Providers
Berkshire Bank's reliance on physical branches in the Northeast means infrastructure and real estate providers hold some sway. Landlords for prime branch locations and providers of essential maintenance and utility services can influence operational expenses, particularly for long-term lease agreements.
- Lease Commitments: As of year-end 2023, Berkshire Bank reported significant lease obligations for its real estate portfolio, indicating ongoing commitments to landlords.
- Location Dependency: The bargaining power of real estate providers is amplified in areas with high demand for commercial space, potentially increasing rental costs for new or renewed leases.
- Service Contracts: Specialized maintenance and IT infrastructure providers critical to branch operations can also exert influence through service contract terms and pricing.
The bargaining power of suppliers to Berkshire Bank is a significant factor, particularly for specialized technology and data providers. High switching costs associated with core banking systems, estimated in the tens to hundreds of millions of dollars for financial institutions in 2024, grant these vendors considerable leverage. Similarly, the scarcity of skilled professionals in areas like AI and data analytics, leading to average salary increases of 15-20% for experienced cybersecurity professionals in 2024, empowers employees and specialized service providers.
Berkshire Bank's dependence on external data providers for credit assessment and market intelligence also contributes to supplier power. While multiple providers exist, the critical nature of the data can still give these suppliers a moderate level of influence. Furthermore, specialized legal and accounting firms can command higher rates and dictate terms, especially when their expertise is unique or crucial for regulatory compliance. This is evident in the rising average hourly rates for specialized financial sector legal services observed in 2024.
Real estate and infrastructure providers also hold some sway, particularly for prime branch locations. Long-term lease commitments, as reported by Berkshire Bank at year-end 2023, can tie the bank to specific landlords, and high demand for commercial space can escalate rental costs. Specialized maintenance and IT infrastructure providers also influence operational expenses through service contract terms.
| Supplier Category | Estimated Bargaining Power | Key Factors Influencing Power | Relevant 2024 Data/Trends |
|---|---|---|---|
| Core Banking Technology Providers | Moderate to High | Proprietary technology, high switching costs | Switching costs: $10M - $100M+ |
| Specialized Talent (e.g., AI, Cybersecurity) | Moderate to High | Scarcity of skilled professionals, high demand | Cybersecurity salary increases: 15-20% |
| Data & Information Providers | Moderate | Essential nature of data, specialized content | N/A (Industry-wide reliance) |
| Specialized Professional Services (Legal, Accounting) | Moderate to High | Reputation, specialization, switching costs | Increased hourly rates for specialized legal services |
| Real Estate & Infrastructure Providers | Low to Moderate | Location dependency, lease commitments | Significant lease obligations reported by banks |
What is included in the product
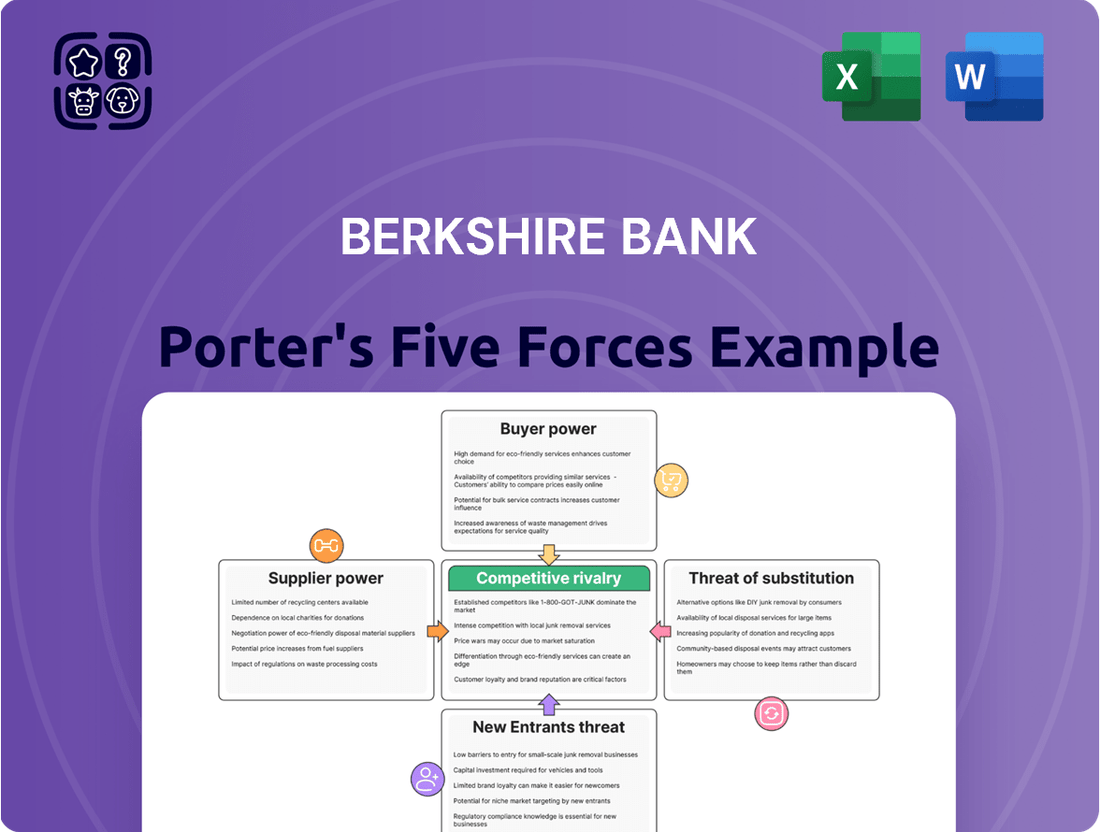
Berkshire Bank's Porter's Five Forces analysis reveals the competitive intensity, buyer power, supplier leverage, threat of new entrants, and availability of substitutes impacting its strategic positioning.
Understand competitive intensity with a visual breakdown of each force, making strategic adjustments effortless.
Customers Bargaining Power
For basic checking and savings accounts, customers at institutions like Berkshire Bank often face minimal hurdles when switching providers. This is particularly true with the proliferation of user-friendly digital banking platforms, making it simpler than ever to move funds and services. In 2024, reports indicated that the average customer might consider switching banks if offered a mere 0.25% higher interest rate on savings, highlighting the sensitivity to even small financial incentives.
This ease of movement directly translates into significant bargaining power for retail customers. They can readily explore and migrate to competitors offering more attractive interest rates, reduced or eliminated fees, or a superior digital banking experience. Berkshire Bank's strategic initiative in developing robust digital deposit programs is a direct response to this dynamic, aiming to retain customers by offering competitive digital tools and services.
Customers today have an unprecedented selection of financial products and services at their fingertips. The rise of digital banks and innovative fintech firms means that consumers are no longer solely reliant on traditional institutions like Berkshire Bank. This wider market access significantly boosts their bargaining power.
Berkshire Bank, which offers a diverse portfolio including retail and commercial banking, wealth management, and insurance, must actively compete to retain its customer base. With numerous alternatives available, customers can easily switch to providers offering better rates, lower fees, or more convenient digital experiences, putting pressure on Berkshire Bank to maintain competitive offerings.
Customers in the banking sector, especially for loans and deposits, are very attuned to interest rates and fees. They readily compare options from various banks, forcing institutions like Berkshire Bank to keep their pricing competitive. This dynamic is further intensified by the anticipated decrease in interest rates by 2025, which will compel banks to explore alternative avenues for profit generation.
Digital Sophistication and Expectation of Seamless Experience
Modern customers, particularly millennials and Gen Z, increasingly demand intuitive and frictionless digital banking experiences. This expectation spans everything from account opening to managing finances, pushing banks like Berkshire Bank to prioritize robust digital platforms. Failure to meet these evolving digital standards risks customer attrition to more agile, tech-savvy institutions.
Berkshire Bank's strategic investments in digital transformation are paramount to retaining its customer base and attracting new clients. By offering features like AI-powered financial insights and automated customer service, the bank aims to align with user expectations for convenience and efficiency. For instance, by mid-2024, a significant portion of new account openings at many traditional banks were being initiated online, highlighting the demand for digital onboarding.
- Digital Onboarding Growth: By Q2 2024, digital channels accounted for over 60% of new account applications for many regional banks, a trend Berkshire Bank must actively address.
- Customer Retention through Tech: A 2024 Accenture report indicated that banks with superior digital customer experience saw a 15% higher customer retention rate compared to those with lagging digital offerings.
- AI in Banking Services: Early 2024 data suggests that banks leveraging AI for customer queries experienced a 20% reduction in call center volume, freeing up resources and improving response times.
Consolidation and Financial Literacy of Commercial Clients
Commercial clients, especially those with significant financial acumen, can wield considerable bargaining power. Their sophistication allows them to demand highly customized financial solutions and specialized lending arrangements, putting pressure on Berkshire Bank to offer competitive and tailored services.
In 2024, the increasing financial literacy among commercial clients means they are better equipped to negotiate terms, seeking value-added services and favorable pricing. This trend is evident across the banking sector, where clients can readily compare offerings and switch providers if their needs aren't met.
- Sophisticated Demands: Large commercial clients often require bespoke lending, treasury management, and investment banking services.
- Negotiation Leverage: Their financial expertise enables them to scrutinize terms and conditions, seeking the most advantageous deals.
- Competitive Pressure: The ability of these clients to compare and switch providers intensifies competition for banks like Berkshire.
- Value-Added Services: Banks must differentiate themselves by offering specialized advice and integrated solutions to retain these powerful clients.
Customers, both retail and commercial, possess significant bargaining power due to the ease of switching and the availability of numerous alternatives. This power is amplified by increasing financial literacy and the demand for superior digital experiences, forcing institutions like Berkshire Bank to offer competitive rates, lower fees, and personalized services to retain their business.
| Customer Segment | Key Bargaining Factors | Impact on Berkshire Bank |
|---|---|---|
| Retail Customers | Interest Rates, Fees, Digital Experience | Pressure to maintain competitive pricing and invest in digital platforms. |
| Commercial Clients | Customized Solutions, Value-Added Services, Favorable Pricing | Need to offer specialized services and tailored lending arrangements. |
What You See Is What You Get
Berkshire Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Berkshire Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering an in-depth examination of competitive forces within its industry. The document you see here is precisely the same professionally formatted analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, providing actionable insights without any alterations or placeholders.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The banking market in the Northeastern US, Berkshire Bank's core territory, is a dynamic landscape featuring a blend of national giants, strong regional institutions, and numerous community banks. This presents a highly competitive environment where differentiation and scale are crucial for success.
Consolidation is a major theme, with mergers and acquisitions reshaping the competitive forces. A prime example is Berkshire Bank's own pending merger with Brookline Bancorp, a move that underscores the industry's drive for greater scale and market presence. This union is set to create the fifth-largest bank in New England by asset size, highlighting the intensifying competition driven by increased scale.
Banks, including Berkshire Bank, face intense rivalry for both customer deposits, their core funding, and lending opportunities across all market segments. This constant competition often leads to pressure on net interest margins, compelling institutions to offer more appealing rates and terms to attract and retain business. For instance, in 2024, the average savings account interest rate hovered around 0.40%, a figure that can fluctuate significantly based on market conditions and a bank's specific strategy to attract deposits.
Berkshire Bank's extensive service portfolio, encompassing retail and commercial banking, wealth management, and insurance, creates a broad competitive landscape. This diversity means they face rivals not just from other banks but also from specialized financial service providers, agile fintech companies, and member-focused credit unions across each of these distinct areas.
The sheer variety of services offered by Berkshire Bank results in a wide array of direct and indirect competitors. For instance, in wealth management, they might contend with independent financial advisors and robo-advisors, while in commercial banking, they could be up against larger national banks or regional credit unions with specialized business lending divisions. This multifaceted competition underscores the complexity of Berkshire Bank's market positioning.
Geographic Concentration and Local Market Dynamics
Berkshire Bank's competitive rivalry is intensified by its geographic concentration in the Northeastern United States. This region features robust local competitors with deep-rooted community ties and significant market share. For instance, as of the first quarter of 2024, regional banks in the Northeast often reported strong deposit growth, indicating intense competition for customer funds.
To stand out, Berkshire Bank must leverage differentiators like a strong community focus, personalized customer service, and an accessible local branch network. These elements are crucial for building loyalty in markets where established relationships are paramount. The bank's pending merger is a strategic move designed to broaden its geographic footprint, thereby mitigating some of the pressures from intense local rivalry.
- Northeastern Focus: Berkshire Bank operates predominantly in the Northeastern US, facing established regional banks.
- Key Differentiators: Community engagement, personalized service, and branch networks are vital for competitive advantage.
- Merger Impact: The pending merger aims to improve geographic diversification and reduce reliance on concentrated markets.
Regulatory Landscape and Compliance Costs
The banking sector faces a constantly evolving regulatory landscape. New rules and heightened scrutiny are common, with compliance costs often hitting smaller or regional banks harder than their larger counterparts. This disparity can significantly influence competitive positioning.
Adapting to changes, such as those in the Community Reinvestment Act (CRA) or digital payment regulations, adds layers of complexity. For instance, in 2024, regulatory bodies continued to emphasize cybersecurity and data privacy, requiring significant investment in technology and compliance personnel across the industry.
- Increased Regulatory Scrutiny: Banks are under more pressure to adhere to evolving compliance standards.
- Disproportionate Impact on Smaller Banks: Compliance costs can represent a larger percentage of revenue for regional institutions.
- Digital Payment Regulation: New rules in this area necessitate ongoing investment and adaptation.
- Cybersecurity Focus: Enhanced requirements for data protection and resilience are a key driver of compliance spending in 2024.
Berkshire Bank operates in a highly competitive Northeastern US market, facing a mix of national banks, strong regional players, and community institutions. This intense rivalry is evident in the constant pursuit of deposits and loans, often leading to pressure on interest margins, as seen with average savings account rates around 0.40% in 2024. The bank's diverse offerings mean it competes across multiple financial service areas, from retail banking to wealth management, encountering specialized firms and fintechs. Its pending merger with Brookline Bancorp is a strategic response to this competitive pressure, aiming to bolster scale and geographic reach.
| Competitor Type | Key Characteristics | Impact on Berkshire Bank |
|---|---|---|
| National Banks | Extensive resources, broad product offerings, significant market share. | Force Berkshire to compete on scale, technology, and pricing. |
| Regional Banks | Strong local presence, established customer relationships, similar service portfolios. | Direct competition for deposits and loans in core markets; merger aims to counter this. |
| Community Banks | Deep local ties, personalized service, agility in niche markets. | Challenge Berkshire's community focus and can attract customers seeking highly localized relationships. |
| Fintech Companies | Digital-first approach, innovative solutions, often lower overhead. | Pressure Berkshire to enhance digital offerings and customer experience. |
| Credit Unions | Member-focused, often competitive rates, community orientation. | Compete for retail customers, particularly those valuing cooperative structures and local engagement. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Fintech companies and digital-only banks present a significant threat of substitutes for Berkshire Bank. These entities offer streamlined digital alternatives for core banking functions such as payments, lending, and savings, often at a lower cost and with a more user-friendly interface. For instance, by mid-2024, digital banks continued to gain traction, with some reporting triple-digit percentage growth in customer acquisition year-over-year, driven by their ability to bypass the overhead of physical branches.
The agility and technological prowess of these new entrants, utilizing advancements like artificial intelligence and sophisticated mobile applications, allow them to attract and retain a growing segment of the population, particularly younger, tech-savvy consumers. This directly challenges the traditional, branch-centric operating model of established institutions like Berkshire Bank, forcing them to innovate rapidly to remain competitive in the evolving financial landscape.
For wealth management, direct investment platforms and robo-advisors present a significant threat. These services allow individuals to manage their own portfolios or use automated, algorithm-driven advice, often at a lower cost than traditional human advisors. This trend is amplified by the rise of AI in wealth management, making sophisticated tools more accessible.
In 2024, the assets under management (AUM) for robo-advisors continued to grow, with many platforms offering services for as little as 0.25% of AUM, a stark contrast to the 1% or more charged by some traditional advisors. This cost-effectiveness, coupled with increasing user comfort with digital solutions, makes them a compelling substitute for Berkshire Bank's wealth management services.
Peer-to-peer lending and crowdfunding platforms present a significant threat by offering alternative funding avenues, especially for small businesses and individuals who might find traditional bank loans less accessible or slower. These platforms directly substitute commercial and retail loans, often with more agile processes and tailored terms, thereby challenging Berkshire Bank's traditional lending business.
The growth in this sector is notable; for instance, the global P2P lending market was valued at approximately $98.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach $434.4 billion by 2030, indicating a substantial shift in capital access. In 2023, crowdfunding platforms facilitated billions in funding for various projects and businesses, demonstrating their increasing role as a viable alternative to conventional financial institutions like Berkshire Bank.
Alternative Payment Solutions
Alternative payment solutions present a significant threat to traditional banking services like those offered by Berkshire Bank. Digital payment platforms, mobile wallets, and the burgeoning cryptocurrency space provide convenient and often faster ways for consumers and businesses to transact, bypassing traditional checking accounts and payment processing. This shift is driven by a global trend towards digital adoption, with many consumers now preferring these newer methods for everyday purchases.
The increasing prevalence of these substitutes can erode a bank's transaction fee revenue and reduce customer reliance on core banking products. For instance, by the end of 2023, global digital payment transaction volume was projected to exceed $10 trillion, demonstrating the scale of this shift. This growing market share for non-bank payment providers directly challenges the established position of traditional financial institutions.
Berkshire Bank must consider how these evolving payment landscapes impact its business model. The threat is amplified by the ease with which new digital payment solutions can emerge and gain traction.
- Digital Payment Growth: Global digital payment transaction volume is expected to surpass $10 trillion by the end of 2023.
- Mobile Wallet Adoption: Mobile wallet usage continues to rise, with a significant percentage of consumers now regularly using them for purchases.
- Cryptocurrency Integration: While still evolving, cryptocurrency payment solutions offer an alternative to fiat currency transactions.
- Consumer Preference: Convenience and speed are key drivers for consumers adopting alternative payment methods over traditional banking services.
Credit Unions and Non-Bank Lenders
Credit unions present a significant threat as substitutes for Berkshire Bank, often leveraging their member-owned structure to offer competitive rates and personalized service. In 2024, credit union membership continued to grow, with over 130 million Americans belonging to a credit union, many of whom may opt for these institutions over traditional banks for their financial needs.
The rise of specialized non-bank lenders further intensifies this threat. These entities, focusing on specific financial products like mortgages or auto loans, can provide tailored solutions and potentially faster approval processes than a diversified bank like Berkshire. For instance, online mortgage lenders have captured a substantial portion of the mortgage market, offering a direct alternative for a key Berkshire Bank product.
- Credit Unions: Member-owned, often offer lower loan rates and higher deposit yields.
- Non-Bank Lenders: Specialize in specific loan types, providing focused competition.
- Market Share: Non-bank lenders have steadily increased their share in segments like mortgage origination.
- Customer Focus: Substitutes often excel at niche customer segments or specific product offerings.
The threat of substitutes for Berkshire Bank is multifaceted, encompassing digital-first financial technology companies, alternative lending platforms, and even credit unions. These substitutes often provide more streamlined, cost-effective, or niche-focused services that directly challenge traditional banking offerings.
Fintechs and digital banks, for instance, continue to attract customers with user-friendly interfaces and lower fees, while P2P lending platforms offer alternative funding sources that bypass conventional bank loans. By mid-2024, digital banks saw significant customer acquisition growth, underscoring their appeal.
In wealth management, robo-advisors are a growing substitute, managing billions in assets with significantly lower fees than traditional advisors. For example, in 2024, many robo-advisors charged around 0.25% of AUM, compared to 1% or more for some human advisors.
Alternative payment solutions, including mobile wallets and evolving cryptocurrency options, also chip away at traditional banking revenue streams by offering faster, more convenient transaction methods.
Entrants Threaten
The banking sector faces formidable regulatory barriers and substantial capital demands, significantly deterring new entrants. Institutions must adhere to stringent licensing procedures, complex compliance mandates like Basel III and Dodd-Frank, and maintain considerable capital reserves. For instance, in 2024, the average Tier 1 capital ratio for large U.S. banks remained robust, reflecting these ongoing requirements.
Established brand loyalty and trust represent a significant barrier to entry in the banking sector. Existing institutions like Berkshire Bank have cultivated decades of recognition and deep-seated customer relationships, making it difficult for newcomers to gain traction. For instance, in 2024, customer retention rates for established banks often exceed 90%, a testament to this loyalty.
New banks often struggle to attract a consistent and varied deposit base, a fundamental need for funding their lending operations. Established institutions benefit from long-standing customer relationships and widespread physical branch networks, which naturally facilitate deposit gathering.
While digital banking solutions offer a pathway for new entrants, replicating the scale and trust associated with incumbent banks’ deposit-gathering infrastructure remains a significant hurdle. For instance, in 2023, the average cost of deposits for smaller, newer banks could be higher compared to established players with deeper, more stable funding pools.
Technological Investment and Infrastructure Costs
The threat of new entrants in banking is significantly shaped by the substantial technological investment and infrastructure costs required. While fintech startups can be nimble, establishing a robust, secure, and scalable banking operation, encompassing digital platforms, advanced cybersecurity measures, and sophisticated data analytics, demands considerable capital outlay. For instance, in 2024, major banks continued to allocate billions to digital transformation and cybersecurity, highlighting the immense barrier to entry. New players must either undertake these massive upfront investments or depend on costly third-party solutions, both of which present significant financial hurdles.
These high initial costs act as a powerful deterrent. Consider the expenses associated with building out a secure core banking system, developing user-friendly mobile applications, and ensuring compliance with stringent financial regulations. These are not trivial undertakings.
- High Capital Requirements: Building a comprehensive banking infrastructure, including digital channels and cybersecurity, requires billions in investment.
- Technological Complexity: New entrants must navigate complex systems integration and data management, adding to costs and time-to-market.
- Regulatory Compliance: Meeting rigorous financial regulations necessitates significant investment in compliance technology and personnel.
- Scalability Challenges: Ensuring infrastructure can scale with customer growth requires ongoing, substantial technological investment.
Competition from Existing Players and Aggressive Responses
New entrants into the banking sector, particularly in regions where Berkshire Bank operates, are likely to encounter a highly competitive environment. The existing landscape is marked by significant consolidation; for instance, the US banking industry saw 143 bank mergers and acquisitions in 2023, indicating strong incumbents actively seeking to expand their reach and market share.
These established players, including Berkshire Bank, possess considerable advantages such as extensive customer networks, broad product portfolios, and significant capital reserves. Such strengths enable them to mount aggressive defenses against newcomers, potentially through price wars or enhanced service offerings, making it challenging for new entrants to capture market share. For example, in 2023, large regional banks continued to report robust profitability, with many showing double-digit percentage increases in net interest income, providing them the financial muscle to counter competitive threats.
- Intense Rivalry: Established banks leverage scale and customer loyalty to deter new entrants.
- Consolidation Trends: Ongoing M&A activity strengthens incumbent positions.
- Aggressive Defense: Incumbents can deploy financial resources to protect market share.
The threat of new entrants for Berkshire Bank is considerably low due to immense capital requirements and stringent regulatory hurdles. New banks must navigate complex licensing, compliance with regulations like Basel III, and maintain substantial capital reserves. For instance, in 2024, the average Tier 1 capital ratio for large U.S. banks remained high, underscoring these ongoing demands.
Established brand loyalty and trust are significant barriers, with incumbent banks like Berkshire Bank benefiting from decades of recognition and deep customer relationships. In 2024, customer retention rates for established banks often surpassed 90%, a clear indicator of this loyalty.
New entrants face challenges in building a stable deposit base, crucial for funding lending operations, as established players leverage existing networks and physical branches. For example, in 2023, the cost of deposits for smaller, newer banks was often higher than for established institutions with deeper funding pools.
| Factor | Impact on New Entrants | Example Data (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Very High | Billions required for technology, compliance, and operations. |
| Regulatory Barriers | Very High | Complex licensing and compliance mandates (e.g., Basel III). |
| Brand Loyalty & Trust | High | Customer retention rates exceeding 90% for incumbents. |
| Deposit Gathering | Challenging | Higher deposit costs for new entrants compared to established banks. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Berkshire Bank leverages insights from their annual reports, investor presentations, and SEC filings. We also incorporate data from industry-specific publications and market research reports to understand the broader competitive landscape.
