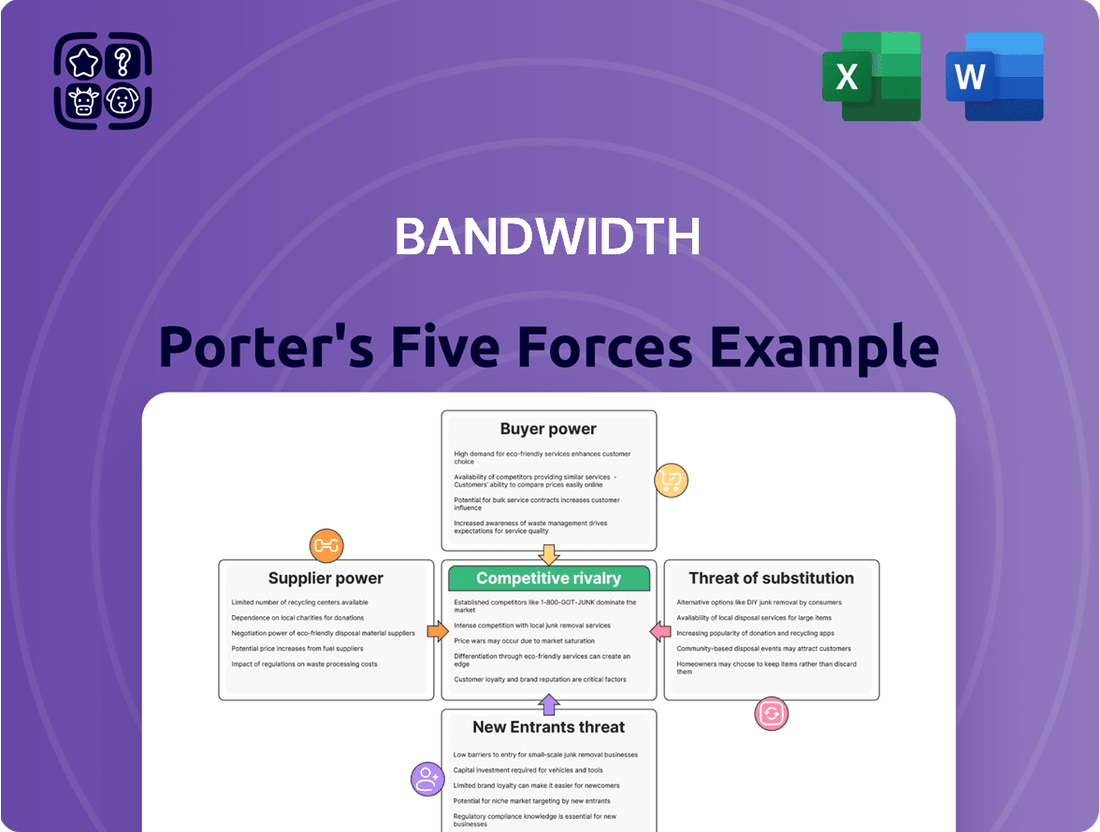
Bandwidth Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Bandwidth Bundle
Bandwidth's competitive landscape is shaped by powerful forces, from the intense rivalry among existing players to the constant threat of new entrants disrupting the market. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for any stakeholder looking to navigate this evolving industry.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Bandwidth’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Bandwidth Inc.'s reliance on a global network means it must secure access to local network infrastructure, data center space, and peering agreements. When these critical suppliers are concentrated in particular regions or hold dominant market positions, they gain considerable leverage over Bandwidth, influencing pricing and service conditions. The distinctiveness of specific routing capabilities or the extent of geographic reach can further amplify supplier power.
Bandwidth's ability to switch between network providers, data center operators, and software/hardware vendors significantly influences supplier power. If numerous high-quality, competitively priced alternatives exist, Bandwidth gains leverage. For instance, in 2024, the telecommunications infrastructure market continued to see robust competition, with several Tier 1 carriers offering comparable services, reducing the individual power of any single supplier.
Switching bandwidth suppliers often comes with substantial costs for businesses. These can include the expense and time involved in integrating new technical systems, fulfilling existing contractual commitments, and the risk of service interruptions during the transition period. For instance, a company might face significant upfront fees for new equipment or software licenses when changing providers.
These high switching costs directly empower bandwidth suppliers. When it's difficult and costly for Bandwidth to change providers, existing suppliers gain leverage, as they know their customer is less likely to seek alternatives. This is especially true for critical infrastructure components where deep integration is already in place.
Uniqueness of Supplier Inputs
Suppliers offering highly specialized or proprietary technology, unique network routes, or critical regulatory access, such as for emergency services, significantly enhance their bargaining power. When these inputs are fundamental to Bandwidth's core services and lack readily available substitutes, suppliers can exert greater influence over pricing and contract terms, increasing Bandwidth's reliance on them.
For instance, in 2024, the telecommunications infrastructure sector continued to see consolidation, meaning fewer providers for certain specialized network components. This scarcity can empower those remaining suppliers. Bandwidth's reliance on specific undersea cable routes or unique fiber optic deployments, if not easily replicated by competitors, further strengthens supplier leverage.
- Specialized Technology: Suppliers with patented network switching technology or unique software for service provisioning can command higher prices.
- Network Infrastructure: Access to critical, hard-to-replicate network backhaul or international fiber routes gives suppliers significant power.
- Regulatory Access: Providers of essential regulatory compliance services or access to specific telecommunication licenses are difficult to replace.
- Proprietary Inputs: Unique hardware components or software algorithms that are integral to Bandwidth's platform create supplier dependence.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of forward integration by Bandwidth's suppliers significantly amplifies their bargaining power. If suppliers can directly offer cloud communication services to enterprises, they essentially become competitors, creating a more challenging environment for Bandwidth. This potential shift underscores the importance of robust supplier relationships and strategic diversification to counter this leverage.
For instance, a key component supplier with advanced software capabilities might consider offering its own platform, bypassing Bandwidth. This move would directly challenge Bandwidth's core business model. In 2024, the increasing commoditization of certain network infrastructure components could incentivize such forward integration by suppliers seeking higher margins.
- Supplier Capability: Suppliers with integrated software and hardware solutions are better positioned for forward integration.
- Market Opportunity: The growing demand for unified communications as a service (UCaaS) presents a lucrative opportunity for suppliers to enter Bandwidth's market.
- Mitigation Strategy: Bandwidth must foster strong partnerships and explore alternative sourcing to reduce reliance on any single supplier with integration ambitions.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Bandwidth Inc. is a significant factor within Porter's Five Forces. When suppliers offer specialized infrastructure, unique routing capabilities, or possess dominant regional market positions, their leverage increases. This is particularly true if Bandwidth faces high switching costs, such as the expense and complexity of integrating new technical systems or fulfilling existing contracts. For example, in 2024, the telecommunications infrastructure market continued to experience consolidation, which can empower remaining specialized providers.
| Supplier Characteristic | Impact on Bargaining Power | Example for Bandwidth (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Concentration & Market Dominance | High | Fewer providers for critical undersea cable routes or specific fiber optic deployments can dictate terms. |
| Switching Costs | High | Significant upfront fees for new hardware or software licenses when changing providers. |
| Uniqueness of Input | High | Proprietary network switching technology or unique software for service provisioning. |
| Threat of Forward Integration | High | Suppliers offering their own UCaaS platforms, directly competing with Bandwidth. |
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects the competitive forces impacting Bandwidth, including the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry.
Gain immediate clarity on competitive pressures with a visually intuitive five forces summary, eliminating the guesswork in strategic planning.
Customers Bargaining Power
Bandwidth's customer base includes major enterprises, tech firms, and service providers, many of whom are substantial revenue sources. When a small number of these large clients contribute a significant percentage of Bandwidth's income, their individual negotiating strength increases considerably. This allows them to push for lower prices, tailored functionalities, or more advantageous contract conditions.
The sheer volume of communication traffic generated by these key customers further bolsters their influence. For instance, if a few top clients represent over 10% of Bandwidth's total revenue, their ability to negotiate favorable terms is amplified, potentially impacting Bandwidth's profitability if not managed effectively.
Customer switching costs are a significant factor in Bandwidth's competitive landscape. While Bandwidth's platform is designed for straightforward integration, businesses looking to move their communication services to a competitor often encounter expenses. These can include the costs of migrating existing infrastructure, the technical effort involved in porting phone numbers, and the potential need to re-integrate application programming interfaces (APIs) with a new provider's system.
When these switching costs are high, customers find it less appealing to change providers. The effort and financial outlay required to switch can easily outweigh any perceived benefits, such as slightly lower pricing from a competitor. This dynamic effectively locks customers into Bandwidth's services, a phenomenon often referred to as customer stickiness.
For instance, in the telecommunications sector, the complexity of migrating thousands of phone numbers and ensuring seamless integration with existing CRM or ERP systems can represent a substantial project for a business. In 2024, many companies are investing heavily in unified communications platforms, making the disruption of switching even more impactful on operational efficiency.
Bandwidth's customer price sensitivity is a key factor in its market position. For instance, if a large enterprise relies heavily on Bandwidth's communication APIs for its core operations, its sensitivity to price might be lower than a smaller business where these services are less critical. This dynamic is further influenced by the availability and cost of comparable alternatives in the market.
In 2024, the telecommunications market remains highly competitive, compelling Bandwidth to maintain aggressive pricing strategies. Customers are actively comparing offerings, making it crucial for Bandwidth to not only compete on price but also to clearly articulate the superior value proposition of its global network infrastructure and its robust, developer-friendly APIs.
Availability of Alternative Communication Solutions
The bargaining power of customers in the communication solutions market is significantly influenced by the availability of alternative options. Customers can choose to develop their own in-house communication platforms, opt for competing Communications Platform as a Service (CPaaS) providers, or revert to traditional telecommunications carriers. This wide array of choices directly amplifies their leverage.
The ease with which customers can switch to or integrate these alternatives is a key determinant of their power. For instance, a business can evaluate the cost and complexity of building a custom solution versus subscribing to a CPaaS vendor. In 2024, the global CPaaS market was valued at approximately $25.8 billion, with projections indicating substantial growth, suggesting a competitive landscape where customer choice is paramount.
- Diverse Alternatives: Customers can build in-house systems, switch to other CPaaS providers, or use traditional telecom services.
- Ease of Switching: The simpler it is to access and integrate alternatives, the greater the customer's bargaining power.
- Value Proposition Focus: A rich ecosystem of choices allows customers to demand the best pricing and service features.
- Market Dynamics: The growing CPaaS market in 2024, valued around $25.8 billion, reflects intense competition that benefits customers.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
Large enterprise and technology companies, Bandwidth's key customers, possess the potential to develop their own communication infrastructure or API layers. This would allow them to bypass Bandwidth's offerings entirely. For instance, a major cloud provider might invest in building its own CPaaS (Communications Platform as a Service) capabilities, directly competing with Bandwidth.
While the significant capital expenditure and technical expertise required for such backward integration act as a deterrent, the mere threat amplifies customer bargaining power. This forces Bandwidth to continually prove its competitive edge.
- Customer Leverage: The potential for customers to develop in-house communication solutions grants them significant leverage in negotiations.
- Value Proposition: Bandwidth must consistently offer superior value, scalability, and cost-effectiveness to retain its customer base.
- Competitive Pressure: This threat necessitates ongoing innovation and service enhancement to preempt customers from building their own alternatives.
Bandwidth's customers, particularly large enterprises, wield considerable power due to the availability of numerous alternatives. These options range from building proprietary communication systems to switching to rival CPaaS providers or traditional telecom carriers, amplifying their negotiation leverage. The growing CPaaS market, valued at approximately $25.8 billion in 2024, underscores this competitive environment where customers can demand better pricing and features.
| Customer Bargaining Power Factors | Impact on Bandwidth | 2024 Market Context |
|---|---|---|
| Availability of Alternatives | High leverage for customers to switch or develop in-house solutions. | Growing CPaaS market ($25.8B in 2024) offers abundant choices. |
| Switching Costs | Moderate to high, depending on integration complexity, creating customer stickiness. | Businesses investing in unified communications in 2024 face significant disruption if switching. |
| Customer Concentration | Large clients representing significant revenue streams have increased negotiation power. | A few top clients exceeding 10% of revenue can dictate terms. |
| Price Sensitivity | Customers actively compare offerings, forcing competitive pricing. | Bandwidth must highlight its global network and developer-friendly APIs to justify costs. |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Bandwidth Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Bandwidth Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a thorough examination of competitive forces within the industry. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted file you will receive immediately upon purchase, ensuring no surprises. Gain immediate access to this comprehensive analysis, ready for your strategic planning and decision-making needs.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Communications Platform as a Service (CPaaS) and cloud communications sector is a bustling arena with numerous participants. Companies like Twilio, a leading player, operate alongside a wide array of smaller, niche providers and even established telecommunications giants venturing into these digital services.
This broad spectrum of competitors, differing in scale, specialization, and global presence, fuels intense competition. Each entity strives to capture a larger piece of the market, driving the need for constant innovation and unique value propositions to stand out.
For instance, in 2024, the global CPaaS market was projected to reach over $20 billion, highlighting the significant revenue potential and the attractiveness of this market to a diverse range of companies, from startups to multinational corporations.
The cloud communications market, where Bandwidth operates, is experiencing robust growth. However, this expansion doesn't negate the potential for heightened competitive rivalry, especially as specific market segments mature or overall growth rates begin to moderate. A rapidly expanding market can often absorb numerous participants, but as the landscape becomes more established, the battle for existing customers and emerging opportunities intensifies.
Bandwidth navigates this dynamic environment, characterized by ongoing growth, but also by significant and aggressive competition. For instance, the global Unified Communications as a Service (UCaaS) market, a key area for Bandwidth, was projected to reach approximately $109.7 billion by 2026, indicating substantial growth potential. Yet, this growth attracts numerous players, from established tech giants to specialized startups, all vying for market share.
As the cloud communications sector matures, the focus shifts from acquiring new customers to retaining existing ones and differentiating services. This often leads to price pressures and increased marketing expenditures. Bandwidth's strategy must account for this evolving competitive intensity, ensuring it maintains a strong value proposition in a market that, while growing, is far from uncontested.
Competitors in the Communications Platform as a Service (CPaaS) market vie for attention by offering distinct features, unwavering reliability, expansive global networks, flexible pricing, and niche services like emergency response or regulatory compliance. Bandwidth itself stands out with its robust global infrastructure and a strong emphasis on enterprise-grade solutions, setting it apart from smaller or more specialized providers.
The relentless pace of technological advancement in CPaaS necessitates continuous innovation. Companies must consistently upgrade their platforms and services to avoid their offerings becoming standard, or commoditized, which erodes pricing power. For instance, the ongoing development in AI-powered customer service and advanced analytics within CPaaS solutions are critical areas where differentiation is key. As of early 2024, the CPaaS market is projected to reach over $30 billion, highlighting the intense competition and the need for unique value propositions.
High Fixed Costs and Exit Barriers
The cloud communications sector demands substantial initial capital for network infrastructure, software innovation, and navigating complex regulations, resulting in elevated fixed costs. For instance, major players often invest billions in global network build-outs and research and development.
These substantial fixed costs, combined with assets that are highly specialized and deeply ingrained customer relationships, erect significant barriers to exiting the market. Companies find it financially prohibitive to simply walk away.
Consequently, businesses are strongly motivated to remain active and compete fiercely, even when market conditions are unfavorable, rather than cease operations. This dynamic inherently fuels a more intense competitive rivalry among existing players.
- High Capital Investment: Cloud communication providers often spend hundreds of millions, if not billions, on building out robust, global network infrastructure.
- Specialized Assets: Much of the infrastructure, like data centers and fiber optic networks, has limited alternative uses, increasing exit costs.
- Customer Lock-in: Long-term contracts and integration into core business processes for clients make switching providers costly and complex.
- Intensified Competition: The reluctance to exit due to high costs means companies must continuously innovate and compete on price and service to maintain market share.
Switching Costs for Customers Among Competitors
The ease with which customers can switch between Communications Platform as a Service (CPaaS) providers significantly shapes competitive rivalry. When switching costs are low, the market becomes more dynamic, with providers frequently employing aggressive pricing strategies and innovative feature rollouts to lure customers away from rivals. This can lead to intense price wars and a constant battle for market share.
Conversely, higher switching costs can foster greater customer retention for established CPaaS players. This doesn't eliminate competition, but it shifts the focus from price alone to other value drivers such as superior service quality, reliability, and the development of long-term, integrated solutions. Companies in such environments may compete more on building stronger customer relationships and demonstrating ongoing value.
- Low Switching Costs: In 2024, the CPaaS market saw continued innovation, with many platforms offering easy integration and flexible APIs, contributing to lower perceived switching costs for many businesses.
- Impact on Rivalry: This ease of transition means that pricing and feature differentiation are critical competitive levers, driving aggressive marketing and sales efforts among CPaaS providers.
- Customer Retention Strategies: Companies with higher switching costs, often due to deep integration into a client's existing systems or proprietary technologies, can focus on service excellence and long-term partnership building to maintain their customer base.
The cloud communications sector, including CPaaS and UCaaS, is characterized by a high number of competitors, ranging from global tech giants to specialized startups. This crowded landscape means companies must constantly innovate and offer compelling value propositions to capture market share. In 2024, the global CPaaS market was projected to exceed $30 billion, underscoring the intense competition and the drive for differentiation.
Bandwidth's competitive rivalry is amplified by the substantial capital investment required for network infrastructure and R&D, creating high fixed costs. These costs, coupled with specialized assets and customer lock-in, make exiting the market financially prohibitive. Consequently, companies remain active and compete fiercely, even in less favorable conditions, to maintain their position.
The ease with which customers can switch between CPaaS providers also fuels rivalry. In 2024, many platforms offered flexible APIs and straightforward integrations, lowering switching costs. This necessitates aggressive pricing and feature innovation to attract and retain customers, making pricing and service differentiation crucial competitive tools.
| Key Competitor | Primary Offerings | Market Position |
| Twilio | CPaaS, APIs for SMS, Voice, Video | Market Leader |
| Vonage (Ericsson) | UCaaS, CPaaS, APIs | Major Player |
| RingCentral | UCaaS, Contact Center | Leading UCaaS Provider |
| Bandwidth | Voice, SMS, 911 APIs, UCaaS | Strong Enterprise Focus |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Enterprises can bypass cloud-based communication platforms like Bandwidth by opting for traditional fixed-line or mobile services directly from telecommunication carriers. These established services, while potentially less flexible, serve as a direct substitute for basic voice and messaging requirements.
The perceived value of traditional services often lies in their bundled nature and established infrastructure, contrasting with the programmability and agility offered by Communications Platform as a Service (CPaaS) solutions. For instance, in 2024, the global telecommunications market was valued at over $1.6 trillion, indicating a substantial existing customer base for these traditional offerings.
Large enterprises with substantial IT budgets and unique requirements may opt to develop their own communication infrastructure, effectively bypassing third-party providers. This internal development, while resource-intensive, can serve as a direct substitute for Bandwidth's core offerings.
For instance, a major financial institution might invest heavily in a private cloud-based communication system to ensure maximum control over data security and latency, especially crucial for high-frequency trading operations. Such a move directly challenges Bandwidth's market share by offering a tailored, albeit more costly, alternative.
Bandwidth must continually highlight its advantages in terms of cost efficiency, rapid scalability, and specialized technical expertise to counter the allure of in-house solutions. The company's ability to offer advanced features and integration capabilities that are difficult or prohibitively expensive to replicate internally is key to mitigating this threat.
The rise of robust open-source communication software, such as FreeSWITCH and Asterisk, presents a significant threat of substitutes for CPaaS providers. These platforms empower businesses to develop custom communication solutions, bypassing the need for commercial services. For instance, a business could leverage Asterisk to build its own PBX system, handling voice calls and messaging internally.
While these open-source alternatives demand considerable technical skill and ongoing maintenance, their cost-effectiveness is undeniable, especially for businesses with unique requirements or limited budgets. This accessibility means that even smaller enterprises can achieve a degree of self-sufficiency in their communication infrastructure, directly impacting the market share of traditional CPaaS vendors.
The global open-source software market was valued at approximately $36 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, indicating a strong and expanding ecosystem of alternatives. This growth underscores the increasing viability and adoption of open-source solutions across various business functions, including communication.
Direct Carrier Relationships for Specific Needs
For very high-volume or highly specialized communication needs, large enterprises may forge direct relationships with telecom carriers. This allows them to bypass CPaaS providers for specific services such as bulk SMS or international voice termination, creating a substitute channel.
Bandwidth's strategic advantage lies in its ability to aggregate multiple carriers and offer a unified, programmable interface. This integration simplifies complex carrier management for businesses, a key differentiator compared to the often fragmented and technical nature of direct carrier relationships.
While direct carrier relationships can offer cost savings for highly specific, large-scale needs, they demand significant in-house expertise for management and integration. This complexity can outweigh the benefits for many businesses.
For instance, in 2024, the global CPaaS market was valued at approximately $25 billion, with significant growth driven by enterprises seeking simplified access to communication APIs. This highlights the value proposition of providers like Bandwidth in abstracting the complexities of direct carrier engagement.
Unified Communications as a Service (UCaaS) Platforms
Unified Communications as a Service (UCaaS) platforms like Microsoft Teams Phone, Zoom Phone, and RingCentral offer comprehensive integrated communication solutions. These platforms bundle voice, video, and messaging, potentially serving as direct alternatives for some business communication needs, particularly for internal collaboration or simpler external calls.
While Bandwidth excels in providing the foundational APIs that power many UCaaS services, the end-user platforms themselves can act as substitutes for businesses that might otherwise rely on Bandwidth's direct API integrations for specific communication functionalities. This presents a competitive dynamic where the platform, rather than the underlying infrastructure, becomes the primary choice for many customers.
The market for UCaaS is robust, with significant growth projected. For instance, the global UCaaS market was valued at approximately $37.7 billion in 2023 and is anticipated to reach over $100 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of around 15% during this period. This expansion indicates a strong customer preference for integrated, feature-rich communication suites, which can divert demand from more specialized API-driven communication solutions.
- Market Dominance of UCaaS Providers: Key players in the UCaaS market are increasingly bundling advanced features, making them a one-stop shop for many businesses.
- Feature Overlap: UCaaS platforms offer features like direct calling, conferencing, and messaging, which can substitute for functionalities traditionally accessed through direct API integrations.
- Customer Preference for Simplicity: Many businesses prefer the convenience of a single, integrated platform over managing multiple communication APIs.
- Strategic Partnerships: While Bandwidth often partners with UCaaS providers, these partnerships also highlight the potential for UCaaS platforms to be viewed as the ultimate solution by end-users.
Unified Communications as a Service (UCaaS) platforms represent a significant threat of substitutes for Bandwidth. These integrated solutions, offering voice, video, and messaging, can fulfill many communication needs, particularly for internal collaboration and simpler external interactions.
The substantial growth of the UCaaS market, valued at approximately $37.7 billion in 2023 and projected to exceed $100 billion by 2030, underscores customer preference for comprehensive, user-friendly suites. This trend can divert demand from specialized API-driven communication services.
UCaaS providers often bundle advanced features, positioning themselves as all-in-one solutions and potentially reducing the perceived need for direct API integrations for specific functionalities.
While Bandwidth’s APIs underpin many UCaaS services, the end-user platforms themselves can become the primary choice, substituting for direct engagement with communication APIs.
| Substitute Type | Key Characteristics | Market Context (2023/2024 Data) | Implication for Bandwidth |
|---|---|---|---|
| UCaaS Platforms | Integrated voice, video, messaging; user-friendly interface | UCaaS market ~ $37.7 billion (2023), projected to grow ~15% CAGR | Can fulfill many communication needs, potentially reducing demand for direct API integration. |
| Open-Source Software | Customizable, cost-effective; requires technical expertise | Global open-source market ~ $36 billion (2023) | Enables self-sufficiency for businesses with unique needs or budget constraints. |
| Direct Carrier Relationships | High-volume, specialized services; requires in-house management | Global telecom market > $1.6 trillion (2024) | Can bypass CPaaS for specific tasks but involves significant complexity. |
Entrants Threaten
The capital requirements for establishing a global communications network are immense. Building out the necessary fiber optic cables, securing spectrum licenses, and developing resilient data centers demand billions of dollars. For instance, major telecommunications companies often report capital expenditures in the tens of billions annually to maintain and expand their infrastructure, a figure that new entrants must match or exceed to even consider competing.
Securing the necessary regulatory licenses across multiple jurisdictions also represents a significant financial and time investment. These licenses are often awarded through costly auctions or require substantial upfront fees and ongoing compliance costs. The complexity and expense involved create a substantial barrier, making it difficult for smaller, less-capitalized companies to gain a foothold.
New entrants must also contend with the existing, deeply entrenched infrastructure of established players like Bandwidth. Companies that have already invested heavily in their own network assets and operational efficiencies possess a significant cost advantage. This high barrier to entry, driven by the sheer scale of required investment, effectively deters many potential competitors from entering the bandwidth market.
The telecommunications sector faces substantial regulatory hurdles, particularly in areas like emergency service provision (911/E911), number portability, and evolving data privacy laws across various jurisdictions. New companies entering this space must contend with intricate and often differing global regulatory landscapes, creating a significant barrier to entry.
Bandwidth's existing proficiency in navigating these complex compliance requirements provides a distinct competitive advantage. For instance, in 2023, Bandwidth reported that its compliance and regulatory teams successfully managed adherence to over 100 different regulatory frameworks globally, a testament to their established expertise.
Bandwidth, as an established player in the communications platform as a service (CPaaS) market, leverages significant economies of scale. This allows them to achieve lower per-unit costs in network operations and customer acquisition compared to potential new entrants. For example, in 2023, Bandwidth reported a gross profit margin of 47.4%, indicating efficient cost management facilitated by their scale.
Network effects also act as a substantial barrier. The more developers and businesses integrate with Bandwidth's platform, the more valuable it becomes for everyone. This growing ecosystem makes it challenging for newcomers to offer a comparable level of functionality and reach, as demonstrated by Bandwidth’s over 3,000 active customers in 2023.
Technical Expertise and Intellectual Property
The technical expertise and intellectual property held by existing cloud communications providers represent a significant barrier to entry. Developing and maintaining a sophisticated, scalable, and secure platform demands deep knowledge in VoIP, messaging protocols, API integration, and robust cybersecurity measures. For instance, companies like Twilio have invested heavily in their proprietary technology stack and developer ecosystem, which is not easily replicated.
Established players benefit from years of research and development, accumulating valuable intellectual property and operational know-how. This accumulated knowledge base makes it challenging for newcomers to match the performance, reliability, and feature sets of incumbents without substantial upfront investment in R&D. In 2024, the global cloud communications market was valued at approximately $125 billion, with a significant portion attributed to the value of these established technological assets.
- Specialized Expertise Required: Deep knowledge in VoIP, messaging protocols, API development, and cybersecurity is crucial for building competitive cloud communication platforms.
- Intellectual Property Advantage: Incumbents possess proprietary technology and accumulated operational knowledge, creating a high barrier for new entrants.
- R&D Investment: Replicating the capabilities of established providers necessitates substantial and ongoing investment in research and development.
- Market Value of Technology: The significant value of the global cloud communications market in 2024 underscores the substantial investment in underlying technology and IP.
Brand Reputation, Customer Trust, and Existing Relationships
In enterprise communications, brand reputation, customer trust, and existing relationships are paramount. Bandwidth has cultivated a strong reputation among large enterprises and technology companies through years of reliable service delivery. New entrants face a significant hurdle in replicating this established trust and the deep-seated relationships Bandwidth enjoys with its clients.
Businesses are inherently risk-averse when it comes to critical communication infrastructure, often hesitating to switch providers without demonstrable proof of reliability and robust support. This makes it challenging for new players to gain traction quickly. For instance, in 2024, the enterprise communication market continued to see consolidation, with established players like Bandwidth benefiting from their long-standing customer commitments. The cost and time required for a new entrant to build comparable brand recognition and a loyal customer base are substantial barriers.
- Brand Loyalty: Established providers like Bandwidth benefit from high customer loyalty, making it difficult for new entrants to poach clients.
- Switching Costs: The effort and potential disruption involved in migrating core communication systems deter many businesses from switching providers.
- Reputational Risk: Enterprises are wary of entrusting their vital communication needs to unproven entities, favoring established and trusted brands.
- Relationship Equity: Bandwidth's long-term relationships with key enterprise clients provide a significant competitive advantage that is hard for newcomers to overcome.
The threat of new entrants in the bandwidth market is significantly mitigated by the substantial capital required to build and maintain global communication networks. These high upfront costs, coupled with the need for specialized technical expertise and intellectual property, create formidable barriers. Furthermore, established players like Bandwidth benefit from strong brand loyalty, customer relationships, and economies of scale, making it exceedingly difficult for newcomers to compete effectively.
| Barrier Type | Description | Example/Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Immense investment needed for infrastructure and licenses. | Major telcos report annual capex in the tens of billions. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex and costly licensing and compliance across jurisdictions. | Bandwidth managed over 100 global regulatory frameworks in 2023. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs due to large operational size. | Bandwidth achieved a 47.4% gross profit margin in 2023. |
| Technical Expertise & IP | Proprietary technology and accumulated R&D knowledge. | Global cloud communications market valued at ~$125 billion in 2024, reflecting tech asset value. |
| Brand Reputation & Relationships | Established trust and existing client commitments. | Bandwidth had over 3,000 active customers in 2023. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our bandwidth Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of robust data, including financial reports from major telecommunications providers, market research from firms specializing in the telecom sector, and regulatory filings from government bodies overseeing communication infrastructure.
